Figure 2.
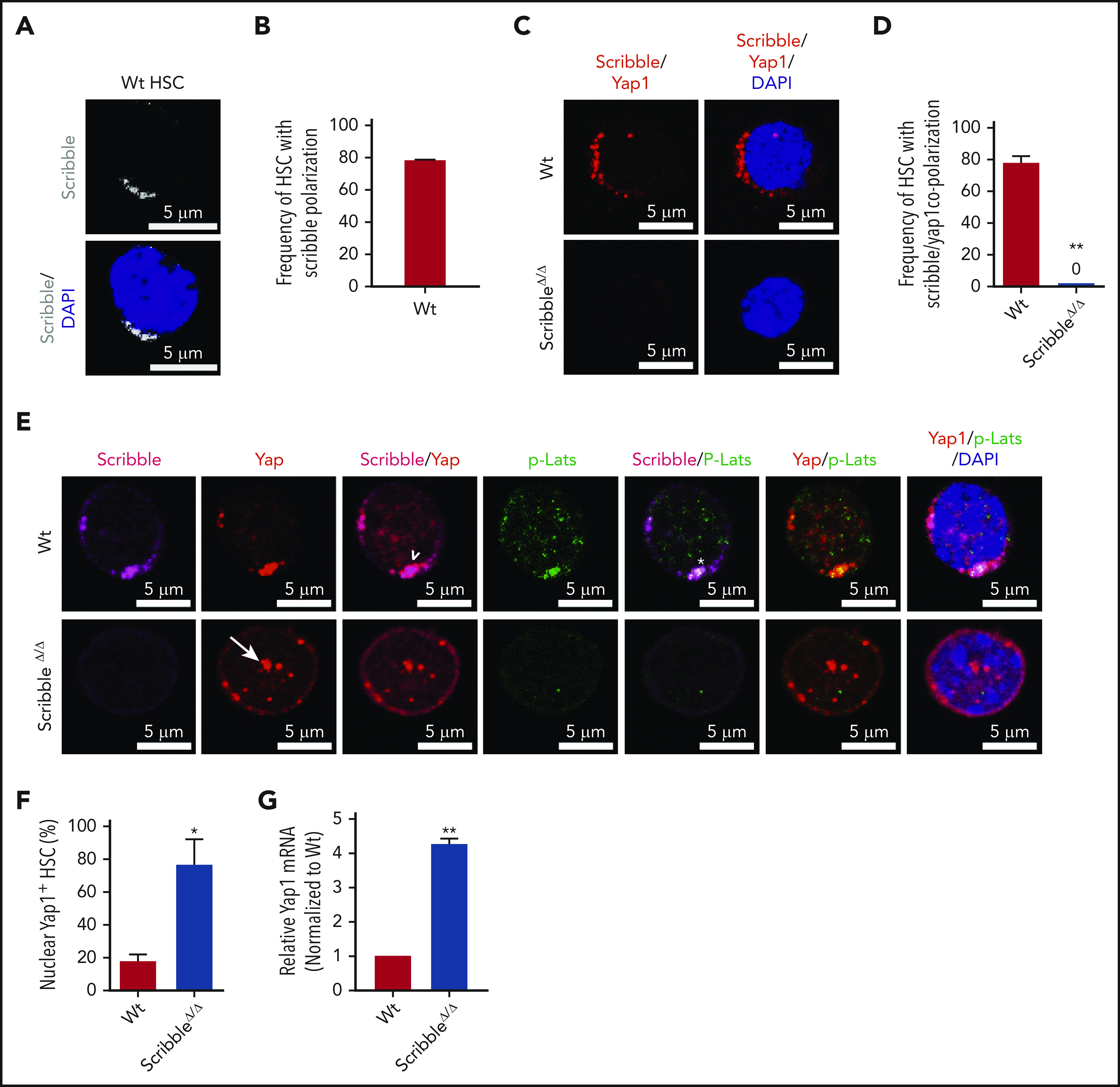
Scribble scaffolds components of the Hippo pathway in HSC and controls Yap1 cytoplasmic localization. (A) Immunofluorescence depicting Scribble protein localization in Wt HSC (immunophenotypically defined as LSK CD150+ CD48−) (white areas). Cells are counterstained with DAPI and merged images are shown in the bottom micrographs. Scale bar is 5 µm. (B) Quantification for the frequency of HSC with Scribble polarization. (C) Immunofluorescence depicting a proximity ligation assay (PLA) on Wt and ScribbleΔ/Δ HSC using anti-Scribble and anti-Yap1 primary antibodies subsequently targeted with corresponding probes for oligomerization. The detected dimers are pseudo-colored in red. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI and merged images are shown in the right micrographs. Scale bar is 5 µm. (D) Quantification of PLA signal. (E) Immunofluorescence showing Scribble polarization and Yap1 colocalization (white arrowheads) in HSC isolated from Wt mice. White asterisks indicate areas of colocalization between Scribble and the activated upstream inhibitory kinase of Yap1, phosphorylated Lats1/2. White arrows denote Yap1 nuclear translocation in ScribbleΔ/Δ HSC. Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI; merged images are shown in the right micrographs. Scale bar is 5 µm. (F) Quantification for the frequency of HSC with Yap1 nuclear foci. (G) Quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of Yap1 messenger RNA expression from HSC cultured for 40 hours; *P < .05; **P < .01.
