We commend Ding and colleagues for their innovative work investigating how high-fat diet-induced changes to the gut microbiome can alter spermatogenesis.1 This link between the gut microbiome and testicular function had earlier been suggested by studies that reported the consumption of probiotic bacteria could improve spermatogenesis and testosterone production in both mice and men.2 3 Furthermore, we had earlier published the Gut Endotoxin Leading to a Decline IN Gonadal function (GELDING) theory that outlined the scientific evidence behind why obesity related change in the gut microbiome, and the associated increase in intestinal permeability with passage of gut bacterial endotoxin (metabolic endotoxaemia, ME) into the systemic circulation, may impair testicular function.4 Since that publication we have gone on to show that obesity related ME is associated with low-grade systemic inflammation, reduction in testosterone production and impaired sperm quality5 6—all consistent with the probiotic studies2 3 and the experimental findings of Ding et al. 1
While we agree that Ding’s murine faecal transplant study does confirm that alteration of the gut microbiome and associated ME can disturb spermatogenesis independent of adiposity, we do not agree that their transfer of bacteria by repeated gastric lavage is an appropriate model for what happens in the obese state. Obesity and its associated lifestyle (high fat diet, minimal exercise) primarily produce colonic dysbiosis, with bacterial numbers still remaining low in the small intestine due to the inhibitory action of gastric acid and bile.4 In the Ding paper1 the authors delivered large numbers of faecal bacteria direct to the small intestine by gastric lavage over a 15-week period. While this did modify the recipient’s faecal (colonic) microbiome, it also resulted in very significant small intestinal inflammation suggestive of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). As SIBO is seen in only a fraction of obese men,7 it is questionable whether these findings are relevant to all obese men. Instead, we believe that Ding’s experimental work, plus our own preliminary findings described below, support a link between SIBO and impaired spermatogenesis.
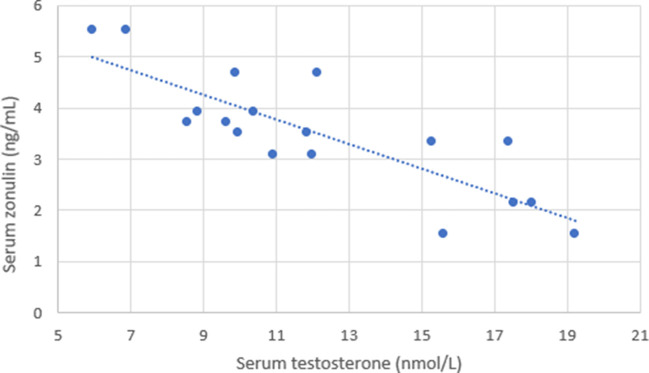
The small intestine is particularly susceptible to migration of bacteria into the systemic circulation (ME) as it must exhibit permeability to other macro-molecules (digested food), and unlike the colon is not protected by a thick mucus barrier. In the presence of bacteria, the small intestine produces zonulin which increases intestinal permeability by triggering disengagement of epithelial tight junctions, thereby flushing out bacteria and preventing colonisation. Pilot data from our group confirms a significant positive correlation between serum zonulin production and ME, while a negative correlation exist between these two markers of intestinal permeability and serum testosterone (figure 1, table 1). While neither zonulin nor ME are conclusive for the presence of SIBO, these observations in the context of Ding’s findings,1 certainly support the concept that bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine may trigger an increase in intestinal permeability and ME, which then impairs testicular function.5 6
Figure 1.
Serum samples were taken from nine male subjects after a period of overnight fasting on two occasions, separated by a week. Serum testosterone and zonulin were assessed as previously published.5 6 The recorded values in this figure represent duplicate sample results from all nine individuals.
Table 1.
Correlation matrix examining the relationship between subject BMI, metabolic endotoxaemia (LBP) and serum zonulin plus testosterone
| BMI (kg/m2) | Serum testosterone (nmol/L) | LBP (µg/mL) | |
| Serum zonulin (ng/mL) | 0.675** | −0.830** | 0.609** |
| BMI (kg/m2) | −0.827** | 0.470* | |
| Serum testosterone (nmol/L) | −0.586* |
Metabolic endotoxaemia was indirectly quantified by assessment of serum LBP levels, as previously described.4–6
*p<0.05, **p<0.01.
BMI, body mass index; LBP, lipopolysaccharide binding protein.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPI) are one of the most commonly prescribed medications, with PPI use being a significant risk factor for development of SIBO.8 Interestingly, PPI use has already been linked with impaired spermatogenesis and low serum testosterone in some studies.9 10 As such we call for more research and awareness of this possible link between the gut microbiome and testicular function, and we specifically caution gastroenterologists about this possible link between PPI use, SIBO and impaired male reproductive function.
Footnotes
Collaborators: Amy Hill.
Contributors: Both authors have read the Ding et al paper in Gut. KT wrote this letter to the editor response and KP reviewed it. Both authors were involved in the pilot research study contained in this letter.
Funding: The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent for publication: Not required.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
References
- 1. Ding N, Zhang X, Zhang XD, et al. Impairment of spermatogenesis and sperm motility by the high-fat diet-induced dysbiosis of gut microbes. Gut 2020;69:1608–19. 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Poutahidis T, Springer A, Levkovich T, et al. Probiotic microbes sustain youthful serum testosterone levels and testicular size in aging mice. PLoS One 2014;9:e84877 10.1371/journal.pone.0084877 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Maretti C, Cavallini G. The association of a probiotic with a prebiotic (Flortec, Bracco) to improve the quality/quantity of spermatozoa in infertile patients with idiopathic oligoasthenoteratospermia: a pilot study. Andrology 2017;5:439–44. 10.1111/andr.12336 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Tremellen K. Gut Endotoxin Leading to a Decline IN Gonadal function (GELDING) - a novel theory for the development of late onset hypogonadism in obese men. Basic Clin Androl 2016;26:7 10.1186/s12610-016-0034-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Tremellen K, McPhee N, Pearce K, et al. Endotoxin-initiated inflammation reduces testosterone production in men of reproductive age. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2018;314:E206–13. 10.1152/ajpendo.00279.2017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Pearce KL, Hill A, Tremellen KP. Obesity related metabolic endotoxemia is associated with oxidative stress and impaired sperm DNA integrity. Basic Clin Androl 2019;29:6 10.1186/s12610-019-0087-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Wijarnpreecha K, Werlang ME, Watthanasuntorn K, et al. Obesity and risk of small intestine bacterial overgrowth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci 2019;3 10.1007/s10620-019-05887-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Su T, Lai S, Lee A, et al. Meta-Analysis: proton pump inhibitors moderately increase the risk of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. J Gastroenterol 2018;53:27–36. 10.1007/s00535-017-1371-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Huijgen NA, de Ridder MAJ, Verhamme KM, et al. Are proton-pump inhibitors harmful for the semen quality of men in couples who are planning pregnancy? Fertil Steril 2016;106:1666–72. 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.09.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Maggio M, Lauretani F, Ceda GP, et al. Use of proton pump inhibitors is associated with lower trabecular bone density in older individuals. Bone 2013;57:437–42. 10.1016/j.bone.2013.09.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]