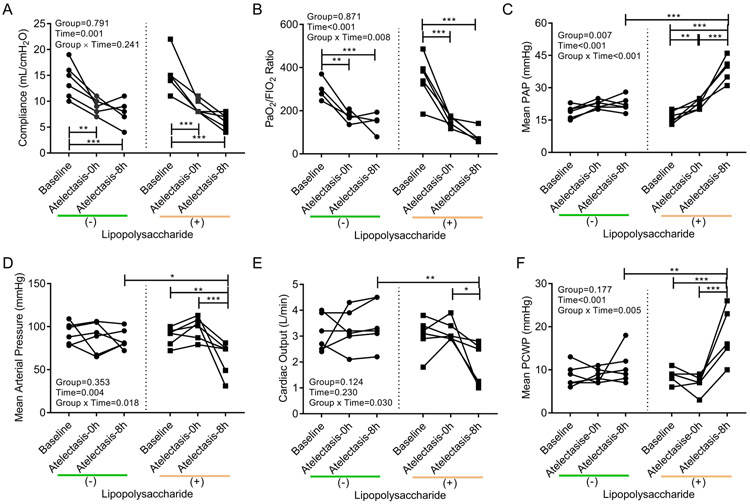
Figure 2. Compromised cardiopulmonary function along 8 hours of one-lung atelectasis and systemic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) exposure.
Atelectasis and systemic LPS significantly affected respiratory system compliance (A), ratio of arterial oxygen tension (PaO2) and inspired oxygen fraction (FIO2) (B), mean pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) (C), mean arterial pressure (D), cardiac output (E), and mean pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) (F). Lines connect data from each animal in the group exposed (+) or not (−) to LPS. P-values corresponding to analyzed effects (LPS exposure (Group), time point (Time), and their interaction (Group × Time)) are indicated. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001.