This prespecified analysis of a randomized clinical trial investigates the effect of cerebral microbleeds on patients with embolic stroke of undetermined source taking either daily rivaroxaban or aspirin.
Key Points
Question
Does the presence of cerebral microbleeds (CMBs) modify the effect of rivaroxaban, 15 mg, compared with aspirin, 100 mg, daily in patients with embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS)?
Findings
In this analysis of a randomized clinical trial that included 3699 patients with ESUS, those with CMBs had higher rates of recurrent stroke, ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, and mortality during 11 months of follow-up. There was, however, no treatment effect modification observed with CMBs for these outcomes.
Meaning
In this study, CMBs marked an increased risk of adverse clinical outcomes in ESUS but did not appear to influence the effects of rivaroxaban.
Abstract
Importance
The reported associations of cerebral microbleeds with recurrent stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage have raised concerns regarding antithrombotic treatment in patients with a history of stroke and microbleeds on magnetic resonance imaging.
Objective
To characterize microbleeds in embolic strokes of undetermined source (ESUS) and report interactions between microbleeds and the effects of random assignment to anticoagulant vs antiplatelet therapy.
Design, Setting, and Participants
Subgroup analyses of the New Approach Rivaroxaban Inhibition of Factor Xa in a Global Trial vs Aspirin to Prevent Embolism in ESUS (NAVIGATE ESUS) international, double-blind, randomized, event-driven phase 3 clinical trial. Participants were enrolled between December 2014 and September 2017 and followed up for a median of 11 months. The study setting included 459 stroke recruitment centers in 31 countries. Patients aged 50 years or older who had neuroimaging-confirmed ESUS between 7 days and 6 months before screening were eligible. Of these 7213 NAVIGATE ESUS participants, 3699 (51%) had information on cerebral microbleeds reported on their baseline clinical magnetic resonance imaging and were eligible for these analyses. Patients with a prior history of symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage were excluded from the NAVIGATE ESUS trial.
Interventions
Rivaroxaban, 15 mg, compared with aspirin, 100 mg, daily.
Main Outcomes and Measures
The primary outcome was recurrent stroke. Secondary outcomes were ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, and all-cause mortality.
Results
Microbleeds were present in 395 of 3699 participants (11%). Of patients with cerebral microbleeds, mean (SD) age was 69.5 (9.4) years, 241 were men (61%), and 201 were White (51%). Advancing age (odds ratio [OR] per year, 1.03; 95% CI, 1.01-1.04), East Asian race/ethnicity (OR, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.04-2.37), hypertension (OR, 2.20; 95% CI, 1.54-3.15), multiterritorial infarcts (OR, 1.95; 95% CI, 1.42-2.67), chronic infarcts (OR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.42-2.23), and occult intracerebral hemorrhage (OR, 5.23; 95% CI, 2.76-9.90) were independently associated with microbleeds. The presence of microbleeds was associated with a 1.5-fold increased risk of recurrent stroke (hazard ratio [HR], 1.5; 95% CI, 1.0-2.3), a 4-fold risk of intracerebral hemorrhage (HR, 4.2; 95% CI, 1.3-13.9), a 2-fold risk of all-cause mortality (HR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.1-4.3), and strictly lobar microbleeds with an approximately 2.5-fold risk of ischemic stroke (HR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.3-4.3). There were no interactions between microbleeds and treatment assignments for recurrent stroke, ischemic stroke, or all-cause mortality. The HR of intracerebral hemorrhage on rivaroxaban was similar between persons with microbleeds (HR, 3.1; 95% CI, 0.3-30.0) and persons without microbleeds (HR, 3.0; 95% CI, 0.6-14.7; interaction P = .97).
Conclusions and Relevance
Microbleeds mark an increased risk of recurrent stroke, ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, and mortality in ESUS but do not appear to influence effects of rivaroxaban on clinical outcomes.
Trial Registration
Introduction
Cerebral microbleeds (CMBs) are radiologic markers of cerebral small vessel disease and present in one-third of patients with ischemic stroke.1 They are associated with increased risks of recurrent ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), and death.2 In patients with ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), the relative and absolute risks of ICH increased more steeply with greater CMB burden than the risks of ischemic stroke; however, absolute ischemic stroke rates continue to exceed those of ICH even in patients with severe CMB burden.3,4,5 These observations have raised questions about the safety of anticoagulant therapy in patients with stroke and CMBs. The observational design of relevant studies to date limits the examination of the interaction between CMBs and anticoagulation for recurrent stroke and ICH.
The prevalence and determinants of CMBs remain to be established in embolic strokes of undetermined source (ESUS; also called cryptogenic stroke), and it is uncertain whether the previously reported prognostic implications of CMBs persist in this prevalent stroke subtype. Accordingly, we aimed to characterize CMBs in a well-defined population of ESUS by examining participants in the New Approach Rivaroxaban Inhibition of Factor Xa in a Global Trial vs Aspirin to Prevent Embolism in ESUS (NAVIGATE ESUS) trial and to assess the relationship between CMBs and recurrent stroke, ICH, and mortality. Notably, we report interactions between CMBs and the effects of random assignment to anticoagulant therapy. We hypothesized that CMBs would be associated with an increased risk of recurrent stroke, ICH, and mortality in ESUS but that patients with ESUS and CMBs will respond to treatment assignment similarly to those without CMBs.
Methods
Study Design
The rationale, design, and main results of the NAVIGATE ESUS trial have been reported elsewhere.6,7 The protocol was approved by appropriate health authorities and institutional review boards at all study sites, and all patients provided written informed consent before participation. In brief, NAVIGATE ESUS was an international, double-blind, randomized, event-driven phase 3 clinical trial conducted at 459 centers in 31 countries (trial protocol in Supplement 1) comparing rivaroxaban, 15 mg, vs aspirin, 100 mg, daily for the primary outcome of recurrent stroke and systemic embolism in patients with recent ESUS. We present exploratory subgroup analyses of CMBs in trial participants who underwent T2*-weighted sequences at baseline magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Study Participants
Patients aged 50 years or older who had neuroimaging-confirmed ischemic stroke between 7 days and 6 months before screening were eligible if the stroke fulfilled proposed criteria for ESUS: the infarct was not lacunar, was not associated with extracranial vessel atherosclerosis causing more than 50% luminal stenosis in arteries supplying the area of ischemia, was not associated with identified high-risk cardioembolic sources (atrial fibrillation or flutter, left ventricular thrombus, mechanical prosthetic cardiac valve, or severe mitral stenosis), and no other cause of stroke could be found (the protocol in Supplement 1 includes a complete list of exclusion criteria).7 NAVIGATE ESUS participants were eligible for the present subgroup analyses if they had CMBs reported on T2* sequences (gradient recalled echo [GRE] or susceptibility-weighted image [SWI]) as part of their baseline MRI before randomization. Patients were followed up until trial termination on October 5, 2017. The NAVIGATE ESUS trial was terminated early at the recommendation of the data monitoring committee because of the absence of efficacy for stroke prevention coupled with an increase in major bleeding associated with rivaroxaban.7 This study followed the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) reporting guideline.
Intervention
Eligible participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to rivaroxaban, 15 mg, daily plus placebo or aspirin, 100 mg, daily plus placebo. In each group, the 2 tablets (active drug and placebo) were taken orally once daily with food.
Data Collection
Demographic information, vascular risk factors, and neuroimaging findings were prospectively recorded at the time of study enrollment.6,7,8 Race/ethnicity was self-reported.
Imaging Acquisition and Analysis
Participants underwent structural brain MRI before study entry as part of their clinical management without a prespecified protocol for data acquisition. Presence, location, and number of CMBs were determined by local radiologists at the clinical sites (stroke centers) based on T2* sequences (GRE or SWI). A proportion of these MRIs were submitted for central adjudication as part of the NAVIGATE MIND substudy.
CMBs were categorized as present or absent, and if present, strictly lobar (with or without cerebellar CMBs), strictly deep (deep/brainstem, cerebellar CMBs, or both) or mixed (concurrent lobar and deep/brainstem CMBs). Additionally, their severity was categorized as absent (0 CMBs), mild (1-2 CMBs), moderate (3-10 CMBs), or severe (>10 CMBs).9,10
Interrater agreement between local rating and central adjudication of research MRIs in the subset of patients participating in the NAVIGATE MIND substudy was 509 of 697 (73%) for CMB presence (Cohen κ, 0.23), indicating fair reliability. Reliability for total CMB number (intraclass correlation, 0.63; n = 682) was moderate. The majority of disagreements (88%) were due to classification of participants as CMB negative at clinical sites. Compared with the core laboratory rating of research MRIs, the positive predictive value of CMB presence on clinical MRIs indicated by the site was 70% and the negative predictive value was 74%. Local rating of CMBs was used for analyses in all participants.
Occult ICH was defined as an asymptomatic macrohemorrhage (>10 mm in diameter) that was identified incidentally on baseline neuroimaging. Patients with a prior history of symptomatic ICH were excluded from the NAVIGATE ESUS trial.
Outcomes
The primary efficacy outcome was recurrent stroke. Secondary outcomes were ischemic stroke, ICH, and all-cause mortality. These outcomes have been defined previously.6,7
Statistical Analysis
Patient demographic and clinical characteristics were compared between groups in cross-sectional analyses using a χ2 test or Fisher exact test for categorical variables and a t test or Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables. Variables associated with CMB presence (P < .05) in univariate analyses were inserted into multivariable logistic regression analyses to identify variables independently associated with CMBs. Multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression models, adjusting for treatment assignment and the independent variables identified previously, were then used to estimate the contribution of CMBs to risk of recurrent stroke, ischemic stroke, ICH, and all-cause mortality. Satisfaction of Cox proportional hazards regression assumptions was confirmed using the Assess statement. Treatment interactions were assessed. Analyses followed the intent-to-treat paradigm, were 2-sided, and statistical significance was accepted at the .05 level. Statistical analyses of data were performed from April 10, 2018, to July 7, 2020.
Role of Funding Source
The study sponsors participated in the design of the parent NAVIGATE ESUS trial along with the investigators. Two of the coauthors (H.M. and S.D.B.) are employed by the sponsors. The sponsors were not otherwise involved in the design, analysis, or interpretation of this subgroup analysis. The sponsors had the opportunity to review the manuscript and to provide optional suggestions, but sponsor approval was not required. The sponsors had no other role in the writing of this report nor in the decision to submit for publication. The corresponding author had full access to all the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Results
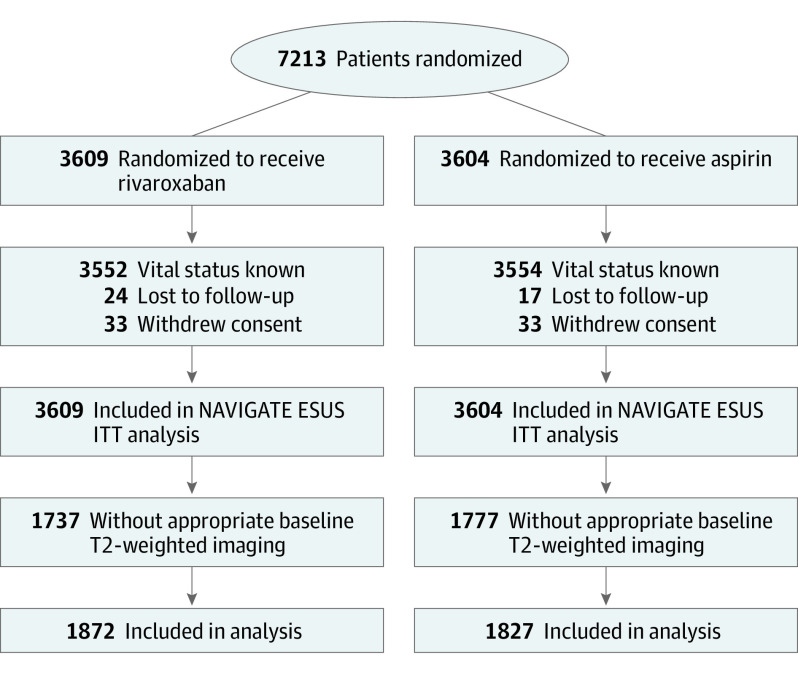
Overall, 3699 of 7213 (51%) enrolled participants between December 2014 and September 2017 had information on CMBs reported on their baseline MRI and were eligible for these analyses. Included participants were relatively similar to participants excluded from this analysis; however, statistically significant differences in race/ethnicity, past medical history (hypertension, previous stroke or TIA, and gastrointestinal bleeding), and baseline function were identified (Figure 1; eTable 1 in Supplement 2).
Figure 1. CONSORT Flow Diagram.
Three hundred ninety-five of 3699 participants (11%) had at least 1 CMB. Of patients with CMBs, mean (SD) age was 69.5 (9.4) years, 241 were men (61%), and 201 were White (51%). Global regional variation existed, with overrepresentation of East Asian participants (150; 38%) and underrepresentation of European and Latin American (32; 8%) countries of origin in participants with CMBs. Associations with CMBs in univariate analyses are listed in Table 1. Advancing age (odds ratio [OR] per year, 1.03; 95% CI, 1.01-1.04), East Asian race/ethnicity (OR, 1.57; 95% CI, 1.04-2.37), hypertension (OR, 2.20; 95% CI, 1.54-3.15), multiterritorial ESUS (OR, 1.95; 95% CI, 1.42-2.67), chronic infarcts (OR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.42-2.23), and occult ICH (OR, 5.23; 95% CI, 2.76-9.90) remained independently associated with CMBs in multivariable regression analysis (Table 2).
Table 1. Baseline Characteristics and MRI Findings by Cerebral Microbleed Status.
| Characteristic | No. (%)a | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMB positive (n = 395) | CMB negative (n = 3304) | ||
| Age, y | |||
| Mean (SD) | 69.5 (9.4) | 66.7 (9.8) | <.001 |
| <60 | 65 (16) | 800 (24) | <.001 |
| Male | 240 (61) | 2076 (63) | .42 |
| Race/ethnicity | |||
| White only | 202 (51) | 2218 (67) | <.001 |
| Black only | 11 (3) | 48 (1) | .05 |
| East Asian only | 151 (38) | 757 (23) | <.001 |
| Otherc (includes not reported and multiracial) | 31 (8) | 281 (9) | .66 |
| Global region | |||
| United States and Canada | 65 (16) | 544 (16) | >.99 |
| Latin America | 14 (4) | 246 (7) | .004 |
| Western Europe | 151 (38) | 1499 (45) | .007 |
| Eastern Europe | 20 (5) | 286 (9) | .014 |
| East Asia | 145 (37) | 729 (22) | <.001 |
| Medical history | |||
| Hypertension | 338 (86) | 2460 (74) | <.001 |
| Diabetes | 104 (26) | 813 (25) | .45 |
| Current tobacco use | 79 (20) | 686 (21) | .72 |
| Coronary artery disease | 29 (7) | 197 (6) | .28 |
| Heart failure | 10 (3) | 69 (2) | .56 |
| Cancer | 38 (10) | 328 (10) | .85 |
| Prior stroke or TIA | 89 (23) | 613 (19) | .06 |
| Renal dysfunction | 15 (4) | 114 (3) | .72 |
| Liver disease | 7 (2) | 56 (2) | .91 |
| History of GI bleeding | 9 (2) | 61 (2) | .55 |
| CHADS2, median (IQR) | 3.0 (3.0-4.0) | 3.0 (3.0-4.0) | <.001 |
| CHA2DS2-VASc, median (IQR) | 5.0 (4.0-6.0) | 4.0 (3.0-5.0) | <.001 |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 26.0 (4.8) | 27.0 (4.9) | <.001 |
| Blood pressure, mean (SD), mm Hg | |||
| Systolic | 135.3 (17.7) | 134.7 (16.7) | .51 |
| Diastolic | 78.7 (12.1) | 78.9 (11.1) | .75 |
| eGFR, mL/min per 1.73 m2 | 74.6 (20.3) | 78.2 (20.2) | <.001 |
| Qualifying ESUS | |||
| One cerebral hemisphere with cortical involvement | 185 (47) | 1810 (55) | .00 |
| One cerebral hemisphere, subcortical only | 74 (19) | 642 (19) | .74 |
| Brainstem only | 16 (4) | 167 (5) | .38 |
| Cerebellum only | 26 (7) | 277 (8) | .22 |
| Multiple locations | 94 (24) | 404 (12) | <.001 |
| Chronic infarct on imaging (in addition to index stroke) | 207 (53) | 1157 (35) | <.001 |
| Hemorrhagic transformation | 43 (11) | 268 (8) | .06 |
| Evidence of old macrohemorrhage | 21 (5) | 30 (1) | <.0001 |
| Oral antithrombotic therapy use before qualifying stroke | 0 | 0 | .55 |
| Statin use prior to randomization | 233 (59) | 2031 (61) | .34 |
| Treated with intravenous tPA for qualifying stroke | 47 (12) | 526 (16) | .04 |
| Treated with endovascular intervention | 18 (5) | 129 (4) | .53 |
| Function measures at randomization | |||
| EQ-5D, median (IQR) | 75.0 (60.0-90.0) | 80.0 (65.0-90.0) | .02 |
| MoCA, median (IQR) | 24.0 (21.0-27.0) | 25.0 (21.0-27.0) | .004 |
| NIHSS score at randomization, median (IQR) | 1.0 (0.0-2.0) | 1.0 (0.0-2.0) | >.99 |
| mRS at randomization, median (IQR) | 1.0 (0.0-2.0) | 1.0 (0.0-2.0) | .02 |
| LV ejection fraction | 63.4 (8.4) | 62.5 (7.9) | .07 |
| LV hypertrophy | 112 (28) | 794 (24) | .06 |
| Functional outcomes at 12 mo, median (IQR) | |||
| EQ-5D | 80.0 (70.0-90.0) | 80.0 (70.0-90.0) | .50 |
| MoCA | 25.0 (21.0-27.0) | 26.0 (22.0-28.0) | .005 |
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared); CHADS2, congestive heart failure, hypertension, age, diabetes, and stroke or transient ischemic attack; CHA2DS2-VASc, congestive heart failure, hypertension, age, diabetes, previous stroke or transient ischemic attack, and vascular disease; CMB, cerebral microbleed; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; EQ-5D, Euro-QoL 5D; and ESUS, embolic stroke of undetermined source; GI, gastrointestinal; IQR, interquartile range; LV, left ventricular; MoCA, Montreal Cognitive Assessment; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; mRS, modified Rankin Scale; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; TIA, transient ischemic attack; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator.
Values are listed as No. (%) unless otherwise specified.
Table 2. Multivariable Model of Patient Characteristics Independently Associated With Cerebral Microbleedsa.
| Characteristic | Odds ratio (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.03 (1.01-1.04) | .00 |
| Race | ||
| White only | 0.71 (0.49-1.04) | .08 |
| East Asian only | 1.57 (1.04-2.37) | .03 |
| Hypertension | 2.20 (1.54-3.15) | <.001 |
| CHA2DS2-VASc | 0.96 (0.83-1.11) | .57 |
| BMI | 0.98 (0.95-1.01) | .12 |
| eGFR | 1.00 (0.99-1.00) | .13 |
| ESUS involving cortex confined to one cerebral hemisphere | 1.02 (0.78-1.33) | .87 |
| Multiterritorial ESUS | 1.95 (1.42-2.67) | <.001 |
| Chronic infarct on imaging (in addition to index stroke) | 1.78 (1.42-2.23) | <.001 |
| Evidence of old macrohemorrhage | 5.23 (2.76-9.90) | <.001 |
| Treated with intravenous tPA for qualifying stroke | 0.87 (0.62-1.23) | .44 |
| EQ-5D | 0.99 (0.99-1.00) | .12 |
| MoCA | 1.01 (0.99-1.03) | .44 |
| mRS at randomization | 1.03 (0.91-1.17) | .65 |
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; CHA2DS2-VASc, congestive heart failure, hypertension, age, diabetes, previous stroke or transient ischemic attack, and vascular disease; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; EQ-5D, Euro-QoL 5D; ESUS, embolic stroke of undetermined source; MoCA, Montreal Cognitive Assessment; mRS, modified Rankin Scale; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator.
Multiple logistic regression in which dependent variable equals cerebral microbleed presence, and independent variables are listed in the output tables.
Information on CMB burden was available in 3624 participants. Of those with CMBs, burden of disease (CMB count burden) was mild in 218 participants (68%), moderate in 85 (27%), and severe in 17 (5%; eTable 2 in Supplement 2). Patients with more severe CMB burden were more often East Asian and hypertensive. Patients with more CMB burden also had overrepresentation of multiterritorial ESUS, chronic infarcts on imaging, and left ventricular hypertrophy. A qualifying ESUS involving the cortex was less frequent with greater CMB burden (eTable 2 in Supplement 2).
Information on CMB topography was available for 3692 participants. Location of CMBs was strictly deep in 213 participants (55%), strictly lobar in 102 (26%), and mixed in 73 (19%). Participants with strictly lobar ICH were more often White and from the US or Canada and more likely to have a qualifying ESUS involving the cortex (eTable 3 in Supplement 2). Participants with deep and mixed CMBs were more often East Asian. Participants with mixed CMBs had the greatest rates of chronic infarct, left ventricular hypertrophy, and cognitive decline at baseline (eTable 3 in Supplement 2).
Outcomes
During a median follow-up of 11 months, 190 of the 3699 participants had recurrent stroke of any type, 161 (5.0 per 100 person-years) of which occurred in the 3304 participants without CMBs, whereas 29 (7.7 per 100 person-years) occurred in the 395 participants with CMBs (Table 3 and Figure 2A and 2B). Participants with CMBs were at increased risk of recurrent stroke (hazard ratio [HR], 1.51; 95% CI, 1.02-2.25). Risk of recurrent stroke increased with greater CMB burden (none, 5.0 per 100 person-years; mild, 5.6; and moderate-severe, 8.5) and was greatest in patients with strictly lobar CMBs (12.1 per 100 person-years) who had an approximately 2.5-fold increased risk of recurrent stroke (HR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.34-4.34) (Table 3 and eFigure in Supplement 2). The association between recurrent stroke and strictly lobar CMBs persisted in adjusted analyses.
Table 3. Risk of Recurrent Stroke, Intracerebral Hemorrhage, and Death by Cerebral Microbleed Status.
| Characteristic | Recurrent stroke | Ischemic stroke | Intracerebral hemorrhage | All-cause mortality | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of events (rate)a | HR (95% CI) | aHRb (95% CI) | No. of events (rate)a | HR (95% CI) | aHR (95% CI) | No. of events (rate)a | HR (95% CI) | aHR (95% CI) | No. of events (rate)a | HR (95% CI) | aHR (95% CI) | |
| CMB presence | ||||||||||||
| None | 161 (5.0) | NA | NA | 153 (4.8) | NA | NA | 8 (0.2) | NA | NA | 39 (1.2) | NA | NA |
| CMB | 29 (7.7) | 1.51 (1.02-2.25) | 1.31 (0.87-1.98) | 26 (6.9) | 1.43 (0.94-2.16) | 1.26 (0.82-1.95) | 4 (1.0) | 4.18 (1.26-13.90) | 2.97 (0.85-10.43) | 10 (2.5) | 2.13 (1.06-4.26) | 1.87 (0.90-3.85) |
| CMB burden | ||||||||||||
| None | 161 (5.0) | NA | NA | 153 (4.8) | NA | NA | 8 (0.2) | NA | NA | 39 (1.2) | NA | NA |
| 1-2 | 12 (5.6) | 1.11 (0.62-2.00) | 0.95 (0.52-1.73) | 11 (5.2) | 1.07 (0.58-1.98) | 0.92 (0.49-1.72) | 1 (0.5) | 1.88 (0.23-14.99) | 1.59 (0.19-13.13) | 8 (3.6) | 3.05 (1.42-6.53) | 2.69 (1.23-5.91) |
| 3 or more | 8 (8.5) | 1.66 (0.82-3.38) | 1.29 (0.62-2.68) | 6 (6.4) | 1.31 (0.58-2.96) | 1.07 (0.46-2.48) | 3 (3.0) | 12.52 (3.32-47.22) | 6.08 (1.44-25.67) | 0 (0.0) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| CMB topography | ||||||||||||
| None | 161 (5.0) | NA | NA | 153 (4.8) | NA | NA | 8 (0.2) | NA | NA | 39 (1.2) | NA | NA |
| Strictly deep/mixed | 17 (6.2) | 1.22 (0.74-2.01) | 1.01 (0.60-1.70) | 15 (5.5) | 1.13 (0.67-1.93) | 0.96 (0.56-1.67) | 3 (1.1) | 4.37 (1.16-16.48) | 2.79 (0.70-11.17) | 6 (2.1) | 1.77 (0.75-4.19) | 1.50 (0.61-3.67) |
| Strictly lobar | 12 (12.1) | 2.42 (1.34-4.34) | 2.30 (1.28-4.16) | 11 (11.1) | 2.33 (1.26-4.30) | 2.22 (1.20-4.11) | 1 (1.0) | 3.95 (0.49-31.61) | 3.93 (0.48-32.12) | 4 (3.8) | 3.22 (1.15-9.01) | 3.01 (1.07-8.50) |
Abbreviations: aHR, adjusted hazard ratio; CMB, cerebral microbleed; HR, hazard ratio; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; NA, not applicable.
aEvent rates reported in 100 person-years.
bAdjusted hazard ratios for all outcomes adjusting for age, East Asian race/ethnicity, hypertension, chronic infarcts, and macrohemorrhages on MRI, and treatment assignment.
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier Curves for Outcomes Stratified by Cerebral Microbleed (CMB) Status.
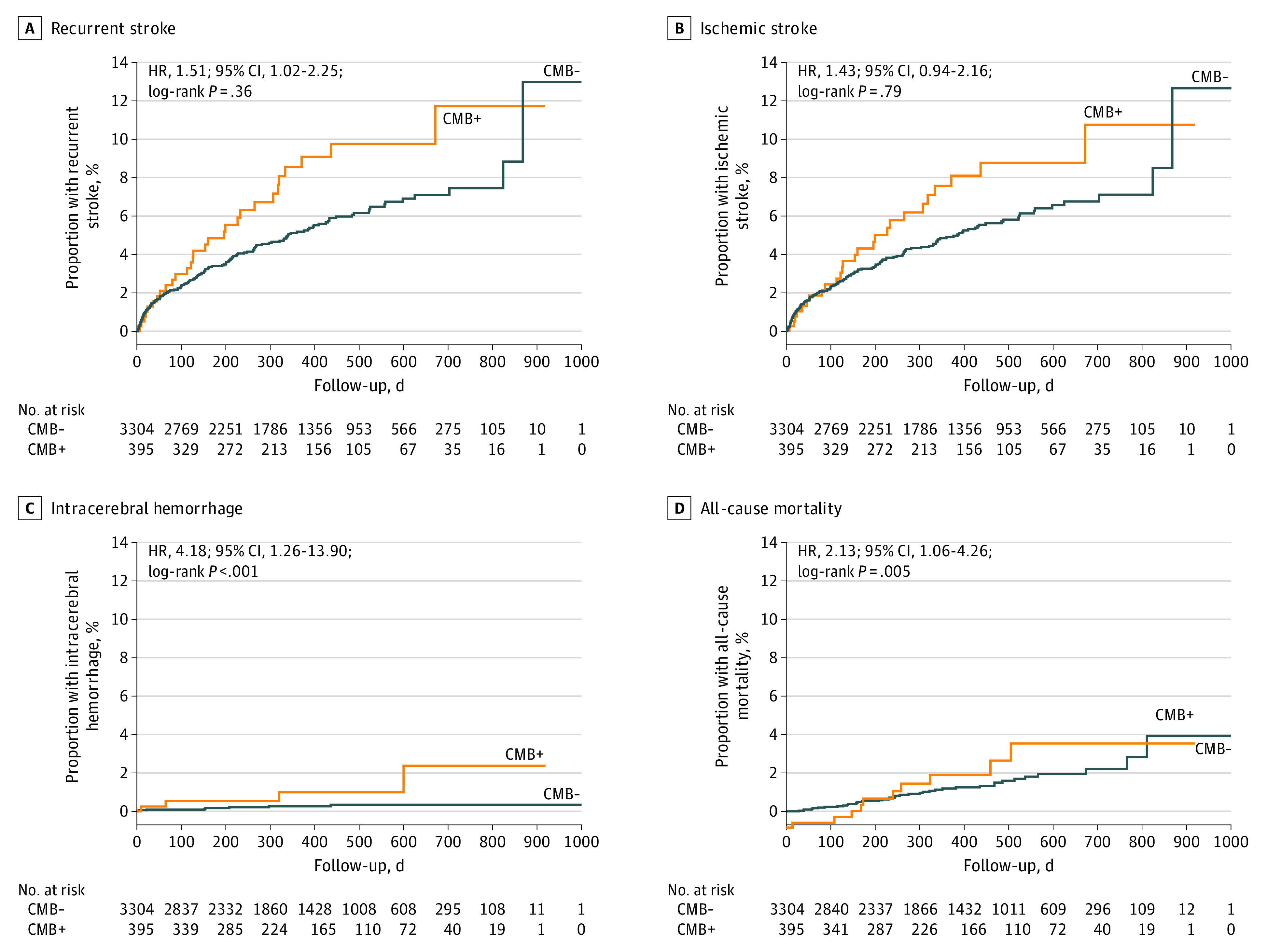
From a total of 7213 randomized participants, 395 CMBs were reported. CMB status included 190 recurrent stroke (A), 179 ischemic stroke (B), 12 intracerebral hemorrhage (C), and 49 all-cause mortality (D). HR indicates hazard ratio.
Similarly, strictly lobar CMBs were associated with an approximately 2.5-fold increased risk (11.1 per 100 person-years; HR, 2.33; 95% CI, 1.26-4.30) of ischemic stroke, and numerical trends for greater rates of ischemic stroke were observed with greater CMB burden (Table 3 and eFigure in Supplement 2). Recurrent ischemic stroke subtypes were similar between patients with and without CMBs (eTable 4 in Supplement 2). The association between ischemic stroke and strictly lobar CMBs persisted in adjusted analyses.
ICH occurred in 8 of 3304 (0.2 per 100 person-years) participants without CMBs and 4 of 395 (1.0 per 100 person-years) with CMBs (Table 3 and Figure 2C). Participants with CMBs had a 4-fold increased risk of ICH (HR, 4.18; 95% CI, 1.26-13.90). Risk of ICH increased with greater CMB burden (none, 0.2 per 100 person-years; mild, 0.5; and moderate-severe, 3.0) but was similar between participants with strictly lobar and deep/mixed CMBs (Table 3 and eFigure in Supplement 2). The association persisted with moderate-severe CMB burden in adjusted analyses.
Death of any cause occurred in 39 (1.2 per 100 person-years) participants without CMBs and in 10 (2.5 per 100 person-years) with CMBs (Table 3 and Figure 2D). Patients with CMBs had a 2-fold increased risk of death (HR, 2.13; 95% CI, 1.06-4.26). There was no detectable relationship between mortality and increasing CMB burden (Table 3 and eFigure in Supplement 2). Patients with strictly lobar CMBs had the greatest all-cause mortality (3.8 per 100 person-years; HR, 3.22; 95% CI, 1.15-9.01). The association with CMBs and strictly lobar CMBs persisted in adjusted analyses.
Effect of Treatment Assignment
Risk of recurrent stroke for those randomized to rivaroxaban vs aspirin among patients with CMBs (10 per 100 person-years vs 5.6, respectively; HR, 1.68; 95% CI, 0.79-3.56) and those without CMBs (5 vs 5.1, respectively; HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.73-1.35) did not differ significantly, and no significant interaction was observed (P = .33 for interaction; eTable 5 in Supplement 2). This outcome was consistent in analyses assessing CMB burden and topography categories.
There was no effect modification observed with CMBs for the secondary outcomes of ischemic stroke, ICH, or all-cause mortality (eTables 6, 7, and 8 in Supplement 2). Particularly, there was no notable trend for greater risk of ICH with rivaroxaban in patients with CMBs (1.6 per 100 person-years vs 0.5, respectively; HR, 3.12; 95% CI, 0.32-30.01) compared with those without CMBs (0.4 vs 0.1, respectively; HR, 2.96; 95% CI, 0.60-14.66) (P = .97 for interaction; eTable 8 in Supplement 2). There was no effect modification for secondary outcomes by prespecified CMB burden or topography categories.
Discussion
In this well-characterized cohort of patients with recent ESUS, CMBs were prevalent and associated with advancing age, East Asian race/ethnicity, hypertension, multiterritorial ESUS, and chronic stroke (both infarcts and occult ICH) on imaging. We observed greater rates of recurrent stroke, ischemic stroke, ICH, and all-cause mortality in NAVIGATE ESUS participants with CMBs, but there was no apparent treatment effect modification on these outcomes, albeit with limited power. In particular, CMBs did not appear to influence effects of rivaroxaban on the outcome of ICH.
We observed an independent association between multiterritorial qualifying ESUS and CMBs, an association that increased with increasing CMB burden. These observations raise the intriguing possibility of a mechanistic link between the qualifying multiterritorial ischemic lesions in such cases and cerebral small vessel disease. Patients with multiple, concurrent, small (<1.5 cm) cortical or subcortical infarcts were eligible for enrollment into NAVIGATE ESUS. A similar pattern of ischemic lesions has been reported on diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with acute ICH and is hypothesized to result from underlying active cerebral small vessel disease in this context.11 The possibility of a similar process occurring in acute ischemic strokes has received limited attention, as such findings are often clinically assumed to result from multiple emboli. However, a recent study in patients with ischemic stroke observed a strong association between microinfarcts (diffusion-weighted imaging hyperintensities ≤5 mm in diameter) outside the territory of the primary infarct and MRI markers of small vessel disease but not with presence of a proximal embolic source.12 The association between multiterritorial ESUS and CMBs will be explored further in the NAVIGATE MIND neuroimaging substudy.
The increased risk of recurrent stroke, ICH, and all-cause mortality in patients with ESUS and CMBs is consistent with previously reported findings from broader populations with stroke.1 However, reported associations between CMBs and all-cause mortality are likely confounded by underlying cerebral small vessel disease, as they have not been replicated in patients with ICH or lacunar stroke.9,10 Of note, all recurrent ischemic stroke subtypes, apart from large artery atherosclerotic disease, were numerically increased in participants with CMBs. This finding suggests that the association between CMBs and ischemic events is not solely due to an increased risk of lacunar stroke from cerebral small vessel disease, but rather patients with CMBs have higher overall risk of vascular events, probably due to their greater age and often multiple vascular risk factors. Interestingly, similar to observations in patients with lacunar stroke in the Secondary Prevention of Small Subcortical Strokes (SPS3) trial, patients with strictly lobar CMBs had the greatest risk of recurrent ischemic stroke, particularly recurrent ESUS.9
To our knowledge, our reported findings are the first to assess interactions between CMBs and the effects of randomized anticoagulant therapy for clinical outcomes. In contrast to questions raised from meta-analyses of observational studies,13 we found no indication of interaction between the effects of rivaroxaban and CMBs, including multiple or strictly lobar CMBs, for the outcome of ICH. Although our analysis lacks the power to confidently exclude such an effect, there were no suggestive numerical trends identified. The underlying cerebral small vessel diseases for which CMBs are a marker are prevalent in populations with stroke of all causes; hence, our reported lack of effect modification may be generalizable to other stroke subtypes beyond the ESUS population reported here. There were no interactions observed between the effect of dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel and CMBs in patients with lacunar stroke participating in the SPS3 trial, nor was there an interaction between CMBs and randomized assignment to antiplatelet therapy compared with no antithrombotic therapy in survivors of ICH participating in the Restart or Stop Antithrombotics Randomised Trial (RESTART).9,14 Up to one-third of participants in atrial fibrillation randomized trials could have had CMBs at study entry,15,16,17 and there have been no unfavorable treatment interactions reported in subgroups that would be enriched with CMBs, such as the elderly, patients with hypertension, or patients of East Asian race/ethnicity.18,19,20,21,22,23,24 Furthermore, an MRI substudy embedded within the Apixaban vs Acetylsalicylic Acid to Prevent Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation Patients Who Have Failed or Are Unsuitable for Vitamin K Antagonist Treatment (AVERROES) trial reported similar CMB accrual during follow-up in patients with atrial fibrillation who were treated with apixaban compared with aspirin.25 As patients with CMBs in NAVIGATE ESUS were at increased risk of ICH at baseline, the absolute increased risk of ICH with rivaroxaban compared with aspirin was numerically higher in this subgroup, resulting in an absolute increase in ICH of approximately 1%, apart from participants with strictly lobar CMBs in which the ICH increased by approximately 2%. Should these observations be generalizable to the use of rivaroxaban in atrial fibrillation, in light of at least an estimated 50% relative risk reduction in ischemic stroke with factor Xa inhibitors (anticoagulation) relative to aspirin,26,27 an individual would require roughly a 2% to 4% annualized rate of ischemic stroke to benefit from net stroke prevention. This result would translate to a CHADS2 (for congestive heart failure, hypertension, age, diabetes, and stroke or TIA) score greater than or equal to 1 for most patients with CMBs and greater than or equal to 2 for patients with strictly lobar CMBs. These estimates suggest that any patient with a prior history of ischemic stroke or TIA (resulting in at least 2 points on the CHADS2 score) would have net stroke prevention from rivaroxaban relative to aspirin, irrespective of their CMB profile, in the setting of atrial fibrillation. In addition, these CHADS2 score cutoffs may very well be conservative given that CMBs also mark an increased risk for ischemic events.2,6 Overall, our results and the existing literature from randomized trials and recent meta-analyses3 do not support the clinical concern regarding antithrombotic therapy in patients with ischemic stroke and CMBs.
Limitations
Our results were limited by trial eligibility criteria, the potential for clinical selection bias during recruitment, and the unavailability of MRI sequences to allow for CMB assessment in all participants of NAVIGATE ESUS, which could limit the generalizability of our findings. Indeed, there were differences in demographics noted between participants who had requisite baseline MRI sequences for a CMB rating to be included in these analyses and those who did not. The nonstandardization of GRE or SWI sequence acquisition parameters and the unavailability of data on these parameters, which were never captured, may have resulted in heterogeneous CMB detection rates across the various recruitment centers and confounded our results. Reliability of CMB reporting at recruitment sites for presence and burden were fair (73% agreement; Cohen κ, 0.23) and moderate (intraclass correlation, 0.63), respectively, in comparison to central research MRI core lab adjudication. However, Cohen κ may not be a reliable measure of overall agreement for outcomes with low prevalence.28 Moreover, we believe that the local site interpretation of CMBs on clinical MRIs is more generalizable to clinical practice than central adjudication of research MRIs, and the heterogeneity in imaging parameters is most reflective of real-world practice. Moreover, the vast majority of disagreements were due to misclassification of a participant with CMBs as being without CMBs. Although this misclassification contributed to a lower prevalence of CMBs than previously reported in ischemic stroke or TIA cohorts, as participants without CMBs were most prevalent (3304 of 3699; 89%), it is unlikely that miscategorization of a relatively smaller number of participants with CMBs into this larger group would have significantly affected our results. We are further reassured by our observed associations between CMBs and baseline demographic factors, as well as the effect sizes of CMBs for ischemic stroke and ICH outcomes, which are consistent with the available literature.15 A final limitation is that our sample was underpowered to assess effect modification by CMB burden or topography and that estimates of risk for outcome events by CMB burden or location are imprecise.
Conclusions
CMBs are prevalent in ESUS and vary with race/ethnicity. CMBs mark an increased risk of recurrent ischemic stroke, ICH, and mortality in ESUS. The rate of ICH in participants with CMBs was not different among those assigned to rivaroxaban vs aspirin, but small numbers resulted in wide CIs around risk estimates.
Trial Protocol
eFigure. Kaplan-Meier Curves for Outcomes Stratified by CMB Burden
eTable 1. Baseline Characteristics and MRI Findings Between Included and Excluded Cohorts
eTable 2. Baseline Characteristics and MRI According to Number of Cerebral Microbleed Burden
eTable 3. Baseline Characteristics and MRI Findings by Cerebral Microbleed Topography
eTable 4. Recurrent Stroke Subtypes by Cerebral Microbleed Status
eTable 5. Efficacy in CMB Subgroups–Recurrent Stroke
eTable 6. Efficacy in CMB Subgroups–Ischemic Stroke
eTable 7. Efficacy in CMB Subgroups–All-Cause Mortality
eTable 8. Efficacy in CMB Subgroups–Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Data Sharing Statement
References
- 1.Charidimou A, Shams S, Romero JR, et al. ; International META-MICROBLEEDS Initiative. Clinical significance of cerebral microbleeds on MRI: a comprehensive meta-analysis of risk of intracerebral hemorrhage, ischemic stroke, mortality, and dementia in cohort studies (v1). Int J Stroke . 2018;. 13(5):454-468. doi: 10.1177/1747493017751931 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Romero JR, Preis SR, Beiser A, et al. Cerebral microbleeds as predictors of mortality: the Framingham Heart Study. Stroke. 2017;48(3):781-783. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.015354 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wilson D, Ambler G, Lee KJ, et al; Microbleeds International Collaborative Network. Cerebral microbleeds and stroke risk after ischaemic stroke or transient ischaemic attack: a pooled analysis of individual patient data from cohort studies. Lancet Neurol . 2019;. 18(7):653-665. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30197-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wilson D, Ambler G, Shakeshaft C, et al. ; CROMIS-2 Collaborators . Cerebral microbleeds and intracranial haemorrhage risk in patients anticoagulated for atrial fibrillation after acute ischaemic stroke or transient ischaemic attack (CROMIS-2): a multicentre observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(6):539-547. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30145-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shoamanesh A, Charidimou A, Sharma M, Hart RG. Should patients with ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack with atrial fibrillation and microbleeds be anticoagulated? Stroke. 2017;48(12):3408-3412. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.018467 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hart RGSM, Sharma M, Mundl H, et al. Rivaroxaban for secondary stroke prevention in patients with embolic strokes of undetermined source: design of the NAVIGATE ESUS randomized trial. Eur Stroke J. 2016;1(3):146-154. doi: 10.1177/2396987316663049 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hart RG, Sharma M, Mundl H, et al. ; NAVIGATE ESUS Investigators . Rivaroxaban for stroke prevention after embolic stroke of undetermined source. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(23):2191-2201. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1802686 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kasner SE, Lavados P, Sharma M, et al. ; NAVIGATE ESUS Steering Committee and Investigators . Characterization of patients with embolic strokes of undetermined source in the NAVIGATE ESUS randomized trial. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018;27(6):1673-1682. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.01.027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shoamanesh A, Pearce LA, Bazan C, et al. ; SPS3 Trial Investigators . Microbleeds in the Secondary Prevention Of Small Subcortical Strokes trial: stroke, mortality, and treatment interactions. Ann Neurol. 2017;82(2):196-207. doi: 10.1002/ana.24988 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shoamanesh A, Morotti A, Romero JM, et al; Antihypertensive Treatment of Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage 2 (ATACH-2) and the Neurological Emergencies Treatment Trials (NETT) Network Investigators. Cerebral microbleeds and the effect of intensive blood pressure reduction on hematoma expansion and functional outcomes: a secondary analysis of the ATACH-2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018;75(7):850-859. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.0454 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kidwell CS, Rosand J, Norato G, et al. Ischemic lesions, blood pressure dysregulation, and poor outcomes in intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology. 2017;88(8)782-788. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003630 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Oliveira-Filho J, Ay H, Shoamanesh A, et al. Incidence and etiology of microinfarcts in patients with ischemic stroke. J Neuroimaging . 2018;28(4):406-411. doi: 10.1111/jon.12512 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wilson D, Charidimou A, Ambler G, et al. Recurrent stroke risk and cerebral microbleed burden in ischemic stroke and TIA: a meta-analysis. Neurology. 2016;87(14):1501-1510. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003183 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Al-Shahi Salman R, Minks DP, Mitra D, et al. ; RESTART Collaboration . Effects of antiplatelet therapy on stroke risk by brain imaging features of intracerebral haemorrhage and cerebral small vessel diseases: subgroup analyses of the RESTART randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(7):643-652. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30184-X [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Haji S, Planchard R, Zubair A, et al. The clinical relevance of cerebral microbleeds in patients with cerebral ischemia and atrial fibrillation. J Neurol. 2016;263(2):238-244. doi: 10.1007/s00415-015-7966-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Charidimou A, Inamura S, Nomura T, Kanno A, Kim SN, Imaizumi T. Cerebral microbleeds and white matter hyperintensities in cardioembolic stroke patients due to atrial fibrillation: single-centre longitudinal study. J Neurol Sci. 2016;369:263-267. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2016.08.050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Song TJ, Kim J, Song D, et al. Association of cerebral microbleeds with mortality in stroke patients having atrial fibrillation. Neurology. 2014;83(15):1308-1315. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000862 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Eikelboom JW, Wallentin L, Connolly SJ, et al. Risk of bleeding with 2 doses of dabigatran compared with warfarin in older and younger patients with atrial fibrillation: an analysis of the randomized evaluation of long-term anticoagulant therapy (RE-LY) trial. Circulation. 2011;123(21):2363-2372. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.004747 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ruff CT, Giugliano RP, Braunwald E, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2014;383(9921):955-962. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62343-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, et al. ; RE-LY Steering Committee and Investigators . Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(12):1139-1151. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0905561 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJ, et al. ; ARISTOTLE Committees and Investigators . Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(11):981-992. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1107039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Patel MR, Mahaffey KW, Garg J, et al. ; ROCKET AF Investigators . Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(10):883-891. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1009638 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Giugliano RP, Ruff CT, Braunwald E, et al. ; ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 Investigators . Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(22):2093-2104. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1310907 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hori M, Matsumoto M, Tanahashi N, et al; J-ROCKET AF Study Investigators. Rivaroxaban vs. warfarin in Japanese patients with atrial fibrillation - the J-ROCKET AF study. Circ J . 2012;76(9):2104-2111. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-12-0454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.O’Donnell MJ, Eikelboom JW, Yusuf S, et al. Effect of apixaban on brain infarction and microbleeds: AVERROES-MRI assessment study. Am Heart J. 2016;178:145-150. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2016.03.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hart RG, Pearce LA, Aguilar MI. Meta-analysis: antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146(12):857-867. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-146-12-200706190-00007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Connolly SJ, Eikelboom J, Joyner C, et al. ; AVERROES Steering Committee and Investigators . Apixaban in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(9):806-817. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1007432 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Viera AJ, Garrett JM. Understanding interobserver agreement: the kappa statistic. Fam Med. 2005;37(5):360-363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Trial Protocol
eFigure. Kaplan-Meier Curves for Outcomes Stratified by CMB Burden
eTable 1. Baseline Characteristics and MRI Findings Between Included and Excluded Cohorts
eTable 2. Baseline Characteristics and MRI According to Number of Cerebral Microbleed Burden
eTable 3. Baseline Characteristics and MRI Findings by Cerebral Microbleed Topography
eTable 4. Recurrent Stroke Subtypes by Cerebral Microbleed Status
eTable 5. Efficacy in CMB Subgroups–Recurrent Stroke
eTable 6. Efficacy in CMB Subgroups–Ischemic Stroke
eTable 7. Efficacy in CMB Subgroups–All-Cause Mortality
eTable 8. Efficacy in CMB Subgroups–Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Data Sharing Statement