Figure 3 -. Biomolecular Ultrasound.
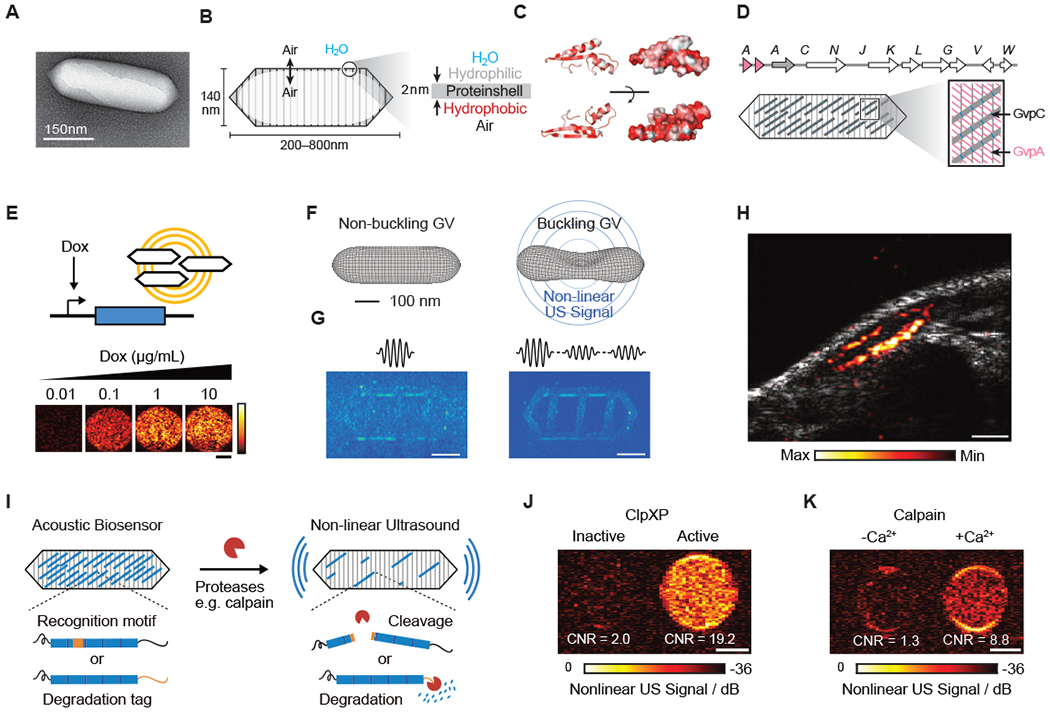
(A) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of a gas vesicle (GV). (B) Diagram of a GV, showing the ability of gas to cross the shell, and the exclusion of water (left); physiochemical properties of the GV shell, namely the hydrophilic exterior that helps to solubilize the GV in the aqueous environment of the cell and the hydrophobic interior that prevents water from forming a liquid phase inside the GV (right). (C) Structural models of GvpA, the primary structural protein of the GV. Hydrophilic residues are colored white and hydrophobic residues red. The former can be seen to cluster on the convex side and the latter on the concave side. (D) (Top) Gene cluster from Anabaena flos-aquae encoding the formation of GVs, with each Gvp gene labeled. (Bottom) Diagram of a GV showing the relative contributions of the two main structural proteins to the structure of the GV (A-D from Maresca et al., 2018a). (E) Ultrasound images of human HEK293T cells in agarose gel expressing GVs under the control of a doxycycline (Dox)-inducible promoter. Scale bar, 1 mm (adapted from Farhadi et al., 2019). (F) Diagram showing the linear and nonlinear responses of GVs to ultrasound. (G) (Left) Ultrasound pulse sequence and corresponding image for a sample in the linear imaging mode. Tissue-mimicking linearly scattering particles and GVs are indistinguishable. (Right) The same sample imaged in nonlinear mode is shown, which detects nonlinearly scattering GVs, but not linearly scattering particles (F and G adapted with permission from Maresca et al., 2017) . (H) Ultrasound image of a GV-expressing tumor growing directly underneath the skin of a mouse. Scale bar, 1 mm (adapted from Farhadi et al., 2019). (I) Diagram of GV-based acoustic biosensor of protease activitiy (J) Representative ultrasound images of agarose phantoms containing acoustic biosensors sensing ClpXP activity. (K) Representative ultrasound images of agarose phantoms containing acoustic biosensor of calpain incubated with calpain and Ca2+ or calpain without Ca2+. (I-K adapted with permission from Lakshmanan et al., 2020). Scale bars for (J) and (K), 1 mm.
