Figure 3. Comparison of network model predictions to recorded data.
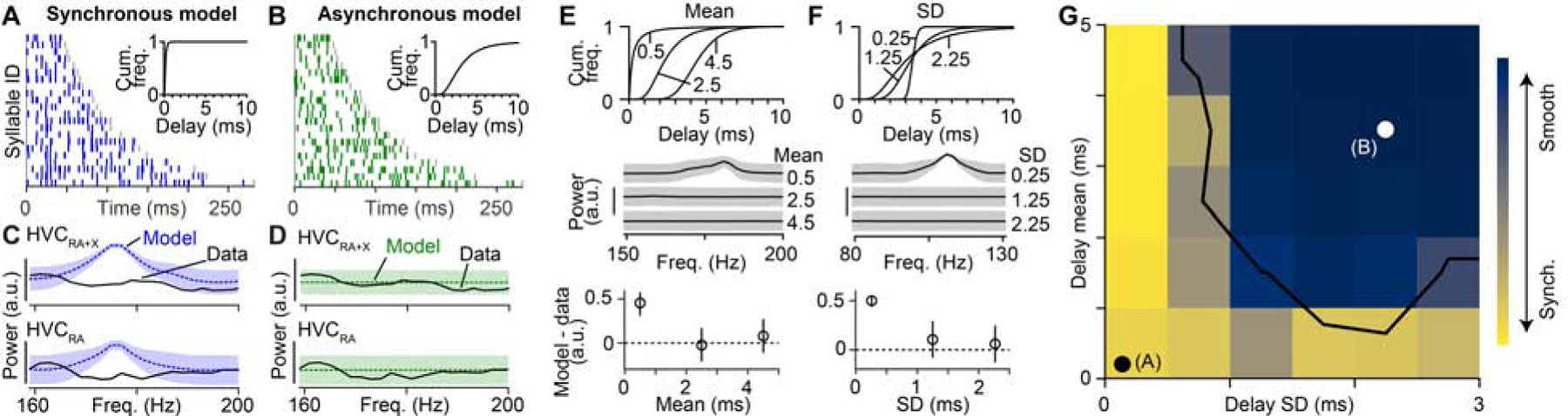
(A, B) Simulated burst onset times for the synchronous (A) and asynchronous (B) models. Insets indicate the distributions of delays used. (C, D) Power spectra used to measure the presence of periodic activity patterns in synchronous (C) and asynchronous (D) models and in the experimental data (from Figure 2G). Shaded area: ± 3 SD. (E, F) Top: Three distributions of delays when varying the mean delay (SD fixed at 1.25 ms) (E) or the delay SD (mean fixed at 3.5 ms) (F). Center: Power spectra of burst onset times for network models with above delay distributions. Bottom: Difference in peak power in the frequency band from 75–200 Hz for the models based on the delay distributions and the observed HVC(RA) burst times (dashed line). Error bars: 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles. (G) Two-dimensional parameter grid of network synchrony with different mean and SD values for delay distributions. Each grid point is colored according to the peak power of the burst onset times (i.e., smooth sequences in dark blue; synchronous sequences in yellow). White/black dots: Locations of the two models in (A, B). Black line: Models to the left and below this line display sequences with synchronously active groups of neurons that are inconsistent with song-related activity of HVC(RA) neurons (p < 0.05, bootstrap, see Methods). See also Figures S2, S3 and S4.
