Summary
This protocol describes a highly standardized pipeline for transcription factor-mediated forward programming of human pluripotent stem cells into highly enriched glutamatergic or GABAergic neurons followed by a cryopreservation step that enables the generation of large quality-controlled batches. This approach is particularly useful for reducing interexperimental variability in the context of collaborative studies across different locations and time points.
For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Meijer et al. (2019) and Rhee et al. (2019).
Graphical Abstract

Highlights
-
•
Clonal hPSC lines with inducible transcription factor construct in the AAVS1 locus
-
•
Virus- and glia-free programming of hPSCs into glutamatergic or GABAergic neurons
-
•
Quality-controlled batches of cryopreserved neurons
This protocol describes a highly standardized pipeline for transcription factor-mediated forward programming of human pluripotent stem cells into highly enriched glutamatergic or GABAergic neurons followed by a cryopreservation step that enables the generation of large quality-controlled batches. This approach is particularly useful for reducing interexperimental variability in the context of collaborative studies across different locations and time points.
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Integration of Transgene Cassettes into the AAVS1 Locus
-
1.
80% confluent hPSC culture
-
2.
Geltrex-coated 10 cm dishes and 96-well plates (one of each per nucleofection round)
-
3.
Nucleofection mix (Amaxa nucleofection kit V): 82 μl of Nucleofector solution V plus 18 μl of Supplement 1 per reaction (prepare fresh before use)
-
4.
StemMACS iPS Brew supplemented with 10 μM ROCK inhibitor (RI) and 5 μM L755507 (StemMACS iPS Brew can be stored at 4°C for up to one month, RI and L755507 have to be added shortly before use)
-
5.
DPBS supplemented with 50 mM EDTA (store at 4°C)
-
6.
Plasmids (1–2 μg/μl) in nuclease-free water or elution buffer
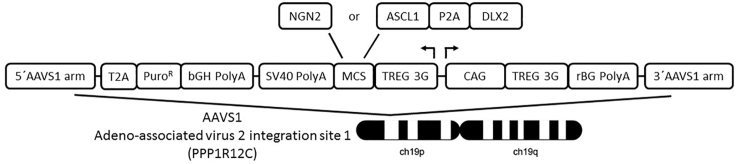
Note: We used the AAVS1-GFP vector and plasmids encoding a corresponding TALEN pair that were kindly provided by Dr. Su-Chun Zhang (University of Wisconsin). To establish AAVS1-NGN2 and AAVS1-ASCL1/DLX2 targeting constructs (Figure 1), the GFP coding sequence was removed from the AAVS1-GFP plasmid and replaced with an NGN2 or an ASCL1-P2A-DLX2 (APD) insert, respectively, both synthesized by GeneArt based on codon-optimized human coding sequences (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Schematic Representation of the AAVS1 Targeting Vector for Doxcycline-Inducible Gene Expression
The multiple cloning site (MCS) allows the insertion of candidate transcription factors.
Forward Programming of hPSCs into Neuron Preparations
-
7.
80% confluent hPSC culture
-
8.
6-well plates, coated with Geltrex and T175 flasks, coated with polyornithine (PO)/laminin (prepared freshly before use)
Cryopreservation of Neuron Preparations
-
9.
DPBS
-
10.
Prewarmed Accutase supplemented with freshly added 10 μM RI
-
11.
Plain NBB27 medium to dilute Accutase
-
12.
50 mL Falcon tubes and 500 mL bottles
-
13.
1.5 mL tubes, trypan blue and a counting chamber
-
14.
Labeled cryovials, stored at −20°C until use
Optional: tube cooling module
Thawing Neuron Preparations
-
15.
Neuronal medium, pre-warmed to 37°C
-
16.
Cell culture plates of desired format coated with PO/laminin
-
17.
Water bath pre-warmed to 37°C
Prepare Coated Cell Culture Plates
-
18.
PO/Laminin coating
-
a.
Apply 15 mg/mL polyornithine (diluted in ddH2O and then sterile-filtered) and incubate for 16–24 h at 37°C.
-
b.
Remove polyornithine and wash three times with PBS.
-
c.
Apply laminin (diluted in DPBS 1:100) and incubate overnight for 16–24 h at 4°C.
Note: We found it sufficient to use 20 mL of 1:100 laminin solution per T175 flask. We also found that it is preferable to use plates immediately instead of storing them at 4°C.
-
19.
Geltrex coating
-
a.
Apply ice-cold Geltrex solution (1 mL per well for a 6-well plate) and incubate for 1 h at 20°C–25°C.
Note: Geltrex concentration depends on the length of plate usage.
-
b.
Coat 10 cm dishes used for nucleofection and 96-well plates used for clone expansion with 0.48 g/l Geltrex solution.
-
c.
6-well plates for forward programming should be coated with 0.16 g/l Geltrex solution.
Note: Coated plates can be stored at 4°C for up to one week.
KEY RESOURCES TABLE
| REAGENT OR RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| Alexa Fluor 488 Goat anti-Mouse | ThermoFisher | Cat#A11001 |
| Alexa Fluor 488 Goat anti-Rabbit | ThermoFisher | Cat#A11008 |
| Alexa Fluor 555 Goat anti-Mouse | ThermoFisher | Cat#A21429 |
| Alexa Fluor 555 Goat anti-Rabbit | ThermoFisher | Cat#A21424 |
| Anti-FOXG1, rabbit | Abcam | Cat#18259 |
| Anti-GABA, rabbit | Sigma | Cat#A-2052 |
| Anti-TUBB3, mouse | Biolegend | Cat#801202 |
| Anti-TUBB3, rabbit | Biolegend | Cat#802001 |
| Chemicals, Peptides, and Recombinant Proteins | ||
| Accutase | Gibco | Cat#A11105-01 |
| Ara-C | Merck | Cat#C1768 |
| B-27 supplement (50x) | Gibco | Cat#12587-010 |
| DAPT | Sigma | Cat#D5942-5MG |
| DMEM/F-12 | Gibco | Cat#11320-074 |
| DMSO | Sigma | Cat#D4540 |
| Doxycycline | Sigma | Cat#D9891-1G, |
| dTTP | VWR Life Science | Cat#20-1041 |
| dCTP | VWR Life Science | Cat#20-1020-88 |
| dATP | VWR Life Science | Cat #20-1011 |
| dGTP | VWR Life Science | Cat #20-1030-88 |
| EDTA | Sigma | Cat#E6635 |
| Geltrex | Gibco | Cat#A14132-02 |
| GlutaMAX (100x) | Gibco | Cat#35050-38 |
| KnockOut Serum Replacement | Gibco | Cat#10828-028 |
| Laminin | Sigma | Cat#L2020 |
| L755507 | Sigma Aldrich | Cat#SML 1362 |
| N2 Supplement (100x) | GE Healthcare | Cat#T11292005 |
| Neurobasal | Gibco | Cat#21103-049 |
| DPBS (1x) | Gibco | Cat#14190-094 |
| Poly-L-ornithine hydrobromide | Sigma Aldrich | Cat#P3655 |
| Recombinant human BDNF | Cell GS | Cat#GFH1 |
| ROCK Inhibitor | Cellagen Technology LLC | Cat#C9127-2 |
| StemMACS iPS-Brew 50x supplement | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat#130-107-086 |
| StemMACS iPS-Brew | Miltenyi Biotec | Cat#130-107-087 |
| Trehalose | Sigma | Cat#T9531 |
| Q5 Buffer | New England BioLabs | Cat#B90275 |
| Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase | New England BioLabs | Cat#M0492L |
| Critical Commercial Assays | ||
| Amaxa nucleofection kit V | Lonza | Cat#VVSA-1003 |
| Experimental Models: Cell Lines | ||
| C-14 m-s11 NGN2 iPSCs (for generation of iGlutNs) |
Rhee et al., 2019 Meijer et al., 2019 |
n/a |
| C-133bm-s4 ADP#8 iPSCs (for generation of iGABANs) |
Rhee et al., 2019 Meijer et al., 2019 |
n/a |
| Oligonucleotides | ||
| AAVS1 insertion validation primer fwd: ACCAACGCCGACGGTATCAG |
Integrated DNA Technologies | n/a |
| AAVS1 insertion primer rv: CAGACCCTTGCCCTGGTGGT |
Integrated DNA Technologies | n/a |
| AAVS1 wt site sequence primer rv: CACCAGGATCAGTGAAACGC |
Integrated DNA Technologies | n/a |
| AAVS1 fwd 3′ primer TACCACCGATTCTATGCCCC |
Integrated DNA Technologies | n/a |
| AAVS1 rv 3′ primer AGGATGCAGGACGAGAAACA |
Integrated DNA Technologies | n/a |
| Recombinant DNA | ||
| AAVS1-ASCL1-P2A-DLX2 | Rhee et al., 2019 | n/a |
| AAVS1-NGN2 |
Rhee et al., 2019 Meijer et al., 2019 |
n/a |
| AAVS1-TALEN-L | Dr. Su-Chun Zhang (University of Wisconsin) Qian et al., 2014 | n/a |
| AAVS1-TALEN-R | Dr. Su-Chun Zhang (University of Wisconsin) Qian et al., 2014 | n/a |
| Other | ||
| 40 μm Cell Strainer | Falcon | Cat#352340 |
| Trypan Blue Stain (0.4%) | Gibco | Cat#15250-061 |
| 50 mL polypropylene conical tube | Falcon | Cat#352070 |
| Cryotube 1.8 mL | Thermo Scientific | Cat#377267 |
| Counting chamber Fuchs-Rosenthal |
Optik Labor | Cat#270000 |
MATERIALS AND EQUIPMENT
hPSC Medium
| StemMACS iPS-Brew | 500 mL |
| StemMACS iPS-Brew 50x supplement | 10 mL |
Can be stored at 4°C for up to one month.
Neuronal Induction Medium
| DMEM/F-12 | 500 mL |
| N2 supplement | 5 mL |
| Doxycycline | 2 μg/mL (final concentration) |
DMEM/F-12 supplemented with N2 can be stored at 4°C for up to one month.
CRITICAL: Doxycycline is added shortly before use.
Neuronal Medium (NBB27)
| Neurobasal medium | 500 mL |
| B-27 supplement (50x) | 10 mL |
| GlutaMAX (100x) | 5 mL |
| Doxycycline | 2 μg/mL (final concentration) |
| BDNF | 10 ng/mL (final concentration) |
| Laminin | 1:500 dilution (according to the manufacturer the stock solution concentration varies between 1–2 mg/mL) |
Neurobasal medium supplemented with B-27 and GlutaMAX can be stored at 4°C for up to one month.
CRITICAL: Doxycycline, BDNF and laminin are added shortly before use.
Freezing Medium
| KnockOut Serum Replacement | 70% |
| 1M trehalose | 20% |
| DMSO | 10% |
Prepare freshly before use and store on ice.
Solutions for Genotyping PCR
Primer Mix
-
1.
AAVS1 insertion validation primer fw: ACCAACGCCGACGGTATCAG
-
2.
AAVS1 insertion validation primer rv: CAGACCCTTGCCCTGGTGGT
-
3.
AAVS1 wt site sequence primer rv: CACCAGGATCAGTGAAACGC
-
4.
AAVS1 fwd 3′ primer: TACCACCGATTCTATGCCCC
-
5.
AAVS1 rv 3′ primer: AGGATGCAGGACGAGAAACA
For PCR 1: mix primers 1, 2 and 3 with the ratio 2:1:1 (10μM:5μM:5μM)
For PCR 2: mix primers 4 and 5 with the ratio 1:1 (5μM:5μM)
PCR Mix (including 10% Extra)
| Reagent | Final Concentration | Volume (μL) |
|---|---|---|
| H2O | n/a | 11.3 μl |
| 5x Q5 buffer | n/a | 5.5 μl |
| 5x GC-Enhancer | n/a | 5.5 μl |
| dNTPs | 10 mM each | 2.8 μl |
| PrimerMix (see above) | PCR 1: 0.4 μM:0.2μM:0.2μM; PCR 2: 0.2μM:0.2μM | 1.1 μl |
| Template | 100 ng/μl | 1 μl |
| Polymerase | 5.5 units | 0.3 μl |
STEP-BY-STEP METHOD DETAILS
Stable Integration of Transgene Cassettes into the AAVS1 Locus
Timing: 4–6 weeks
These steps describe the targeting of a doxycycline-inducible vector coding for NGN2 or ASCL1-P2A-DLX2 into the AAVS1 locus of hPSCs.
-
1.
Preincubate 80% confluent hPSCs in StemMACS iPS-Brew supplemented with 10 μM RI for 1 h.
-
2.
Incubate cells with PBS supplemented with 50 mM EDTA for 10 min.
-
3.
Add 3 mL StemMACS iPS-Brew per well and pipette up and down 4–7 times with a 1000 μl pipette to dissociate the cells.
-
4.
Count cells before centrifugation.
-
5.
Pellet 3–4 million cells per nucleofection round at 1200 rcf for 3 min.
-
6.
Aspirate medium as completely as possible, wait for 10 seconds and remove remaining traces of medium without disturbing the cell pellet.
CRITICAL: From this point, complete steps 7 to 11 within 5 min or less.
-
7.
Add to each cell pellet a total of 5 μg plasmid DNA (0.5 μg TALEN left, 0.5 μG TALEN right, 4 μg AAVS1-APD or AAVS1-NGN2). Do not exceed 10 μl total volume of added DNA solution.
-
8.
Add 100 μl nucleofection mix per condition and mix by pipetting up and down one time with a pipette provided with the nucleofection kit.
-
9.
Transfer to a cuvette with the same pipette. We use the Nucleofector™ II (Amaxa Biosystems) that comes with a uniform cuvette size.
-
10.
Nucleofect using Program B-023.
-
11.
Remove cells from the cuvette using a pipette included in the nucleofection kit and transfer into Geltrex-coated 10 cm dishes containing 10 mL StemMACS iPS-Brew supplemented with 10 μM RI and 5 μM L755507.
-
12.
After 24 h, replace medium with fresh StemMACS iPS-Brew supplemented with 10 μM RI.
-
13.
From this point on, replace medium every other day. Leave RI in the medium until cells start forming colonies.
-
14.
Wait for small colonies to form that consist of 5–10 cells each. This is usually the case on day 2–3 post nucleofection.
-
15.
At this stage, start to select for transgene integration by adding 0.3 μg/mL puromycin for 96 h. Change medium daily, puromycin has to be added freshly to StemMACS iPS-Brew before the medium change.
Expected result: 10–50 puromycin-resistant colonies per 10 cm dish 2 weeks after nucleofection.
-
16.
Pick colonies under sterile conditions using a 10 μl pipette tip. Scratch off a single colony and transfer it into a well of 96-well plate coated with Geltrex and containing 300 μl StemMACS iPS-Brew.
-
17.
Cultivate candidate clones until colonies are large but still growing in a monolayer (4–7 days). Then dissociate cultures and plate them into fresh dishes. Save dissociated cells from each clone for DNA extraction and subsequent genotyping.
-
a.
For genotyping of isolated clones perform two different PCRs:
-
i.
PCR 1 tests for the proper integration of the 5′ homology arm of the targeting vector and is performed with primers 1, 2 and 3. The expected outcome of PCR 1 is as follows:
-
-
single 2 kb product: bi-allelic insertion
-
-
one 1.8 and 2 kb product: mono-allelic insertion
-
-
single 1.8 kb product: no insertion
-
ii.
PCR 2 tests for the integration of the 3′ homology arm and is performed with primers 4 and 5. Expected outcome for PCR 2:
-
-
single 2.4 kb product: on-target insertion
-
-
no product: no insertion of 3′ homology arm or off-target insertion
-
b.
For both PCRs, use the following program:
| 1 | 98°C | 4 min |
| 2 | 98°C | 30 s |
| 3 | 68°C | 30 s (−1°C per cycle) |
| 4 | 72°C | 6 min, back to step 2 (5x) |
| 5 | 98°C | 30 s |
| 6 | 63°C | 30 s |
| 7 | 72°C | 6 min, back to step 5 (40x) |
| 8 | 72°C | 5 min |
-
18.
Select clones with validated genotype and expand them to obtain three 6-well plates with 80% confluency. Cryopreserve one well per cryovial to establish a master cell bank of 18 cryovials.
Pause Point: Cryopreserved stable hPSC lines can be stored for several years at a temperature of −150°C or below.
Forward Programming of hPSCs into Neurons
Timing: 11–12 days
This section covers the derivation of glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons from AAVS1-transgenic hPSC lines that were generated in the previous steps.
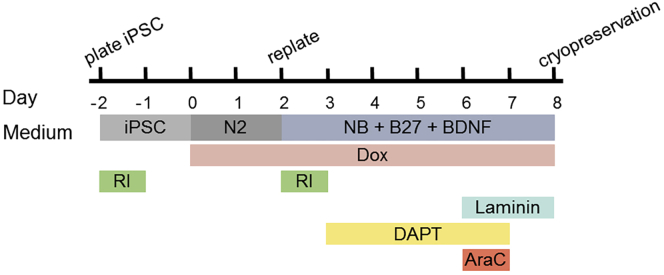
Note: The forward programming protocols for induced glutamatergic (iGlutNs) and induced GABAergic (iGABANs) neurons are very similar (Figure 2) with only minor differences as specified in the following steps.
Figure 2.
Schematic Representation of the Forward Programming Protocol
-
19.
Day −2: Dissociate 80% confluent NGN2- or APD-transgenic hPSCs with Accutase and seed them on Geltrex-coated 6-well plates at a density of 200,000 cells/well in StemMACS iPS-Brew supplemented with 10 μM RI (2 mL/well).
Alternatives: Cells can be seeded on day −1 at a density of 600,000 cells/well.
CRITICAL: After thawing hPSCs and before the dissociation step on day −2 it is essential to keep them in culture for at least two passages to ensure that they are highly proliferative and free of differentiated cells.
Note: To start bulk differentiation, at least 3x6-well plates per line are required. This should result in the generation of 25–40 x 106 neurons by day 8.
-
20.
Day −1: Change medium to StemMACS iPS-Brew (2 mL/well) without RI.
-
21.
Day 0: Change medium to neuronal induction medium (4 mL/well) supplemented with 2 μg/mL doxycycline (dox) to induce transgene expression. Dox remains in the medium from now on until cryopreservation on day 8 (Figure 3A).
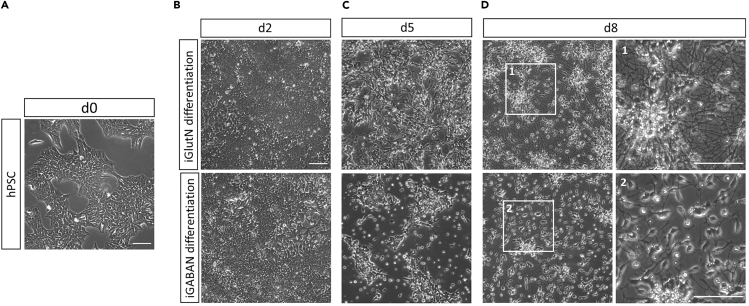
Figure 3.
Phase Contrast Pictures Showing Cultured Cells at Different Stages of the Forward Programming Protocol
(A) hPSC culture before dox induction. Colonies should show no signs of differentiation.
(B) Dox-induced cells at day 2. At this point cultures should have a confluency of 90%–100% and only consist of small cells with epithelial morphology.
(C) Day 5 of dox-induction. iGlutN progenitors start showing neuronal morphology. iGABAN progenitors mostly remain arranged in colonies, and cultures show a noticeable decrease in cell density in comparison to day 2.
(D) iGlutNs and iGABANs right before cryopreservation. At this stage, cultures exclusively contain neurite-bearing cells. Scale bar: 100 μm.
-
22.
Day 2: Dissociate cells with Accutase for 10 min at 37°C. Plate cells on PO/laminin-coated T175 flasks at a density of i) 10–15 x 106 cells/flask for the generation of glutamatergic neurons or ii) 20–25 x 106 cells/flask for iGABAN programming. At this point, change to neuronal medium supplemented with 2 μg/mL dox and 10 μM RI (30 mL/flask) (Figure 3B).
Note: Optimally, three T175 flasks per cell line should be seeded to obtain 25–40 x 106 neurons. Handling of more than 9 flasks in parallel is challenging and might impair batch quality.
Note: During the conversion process iGlutNs typically show a higher survival rate compared to iGABAN cultures.
-
23.
Day 3: Medium change (dox-supplemented neuronal medium containing 10 μM DAPT; DAPT remains in the medium from day 3 until day 7).
CRITICAL: During medium change, cells should not dry out. Thus, always leave about 5 mL medium of the old medium in the flask. When performing a medium change, tilt the plate slowly so that the medium is accumulated at the corner of the flask, then slowly aspirate the medium.
CRITICAL: Never touch the bottom of the plate with the pipette tip and keep cells exposed to air as short as possible.
Note: As neurons mature they become sensitive to mechanical stress and might start to detach. Thus, we suggest removing media with a pipette instead of a vacuum pump from day 5 onwards.
-
24.
Day 5: Medium change (dox-supplemented neuronal medium containing 10 μM DAPT) (Figure 3C).
Note: iGABAN conversion cultures might exhibit a significant fraction of dead cells between day 3 and day 5.
-
25.
Day 6: Medium change (dox-supplemented neuronal medium containing 10 μM DAPT, 5 μM Ara-C and 1:500 laminin). Ara-C will induce a growth arrest of remaining proliferative cells.
-
26.
Day 7: Medium change (dox-supplemented neuronal medium containing 1:500 laminin).
-
27.
Day 8: Culture dissociation and batch cryopreservation (Figure 3D).
Note: From our experience, for most hPSC lines one day of Ara-C treatment is enough to avoid the presence of proliferative cells. However, if at day 7 cultures still contain cells with non-neuronal morphology, an additional day of Ara-C treatment is recommended. In this case, cells can be cryopreserved on day 9.
Note: In general, we found that freezing of neurons at an earlier time point (day 8) is advantageous for cell survival. Longer culturing times result in cell clustering as well as formation of longer processes that form a more complex network. Such cultures are harder to dissociate which presumably leads to reduced culture viability before cryopreservation. iGABAN cultures do not show complex networks or cell clusters and tolerate dissociation at day 9 without impacting cell survival.
Cryopreservation of Post-Mitotic Neurons
Timing: 2–2.5 h per line
The following steps detail the cryopreservation of neurons that were derived as described in the previous section.
-
28.
Gently wash cells with 20 mL DPBS. If the culture is about to detach (e.g. the cell layer is already lifted at the edges), skip this step.
-
29.
Add pre-warmed Accutase supplemented with 10 μM RI (15 mL per T175 flask). Incubate for 60 min at 37°C, then check whether the cells are sufficiently dissociated. For doing so, gently tap the flask 3–4 times. If large clumps are still present, extend the incubation time to up to 90 min in total.
-
30.
Gently wash off the cells with 15 mL pre-warmed NBB27 medium, dissociate further by pipetting very gently 5–10 times up and down with a 25 mL pipette.
-
31.
Transfer cell suspension into a collection bottle.
-
32.
Wash the flask again with 15 mL of medium to harvest remaining cells and transfer to the collection bottle. Pool cell suspensions that belong to the same line in one bottle.
-
33.
Gently mix by swirling and distribute the cell suspension from the bottle into several 50 mL Falcon tubes. While transferring the suspension, pass through a 40 μm cell strainer to filter out clumps.
Note: You can extract genomic DNA from cell material retained in the cell strainer for quality control assays such as mycoplasma tests and SNP karyotyping.
-
34.
Determine total cell number in the flow-through fraction.
CRITICAL: Steps 35 and 36 should be performed as quickly as possible.
-
35.
Centrifuge Falcon tubes at 1200 rcf for 3 min, in the meantime count cell sample from step 34. Prepare required number of labeled cryovials. We recommend to freeze 1 x 106 cells per cryovial in 1 mL of freezing medium.
-
36.
After centrifugation remove supernatant, resuspend the pellet in the calculated amount of ice-cold freezing medium and aliquot quickly into cryovials. Cryovials should be stored at −20°C until this point and placed into a tube cooling module during the process of aliquoting.
-
37.
Transfer tubes into a freezing container and place them into a −80°C freezer without any delay. The cells should freeze with a rate of approximately −1°C per min.
-
38.
On the next day, transfer cryovials to a −150°C or liquid nitrogen freezer for long-term storage.
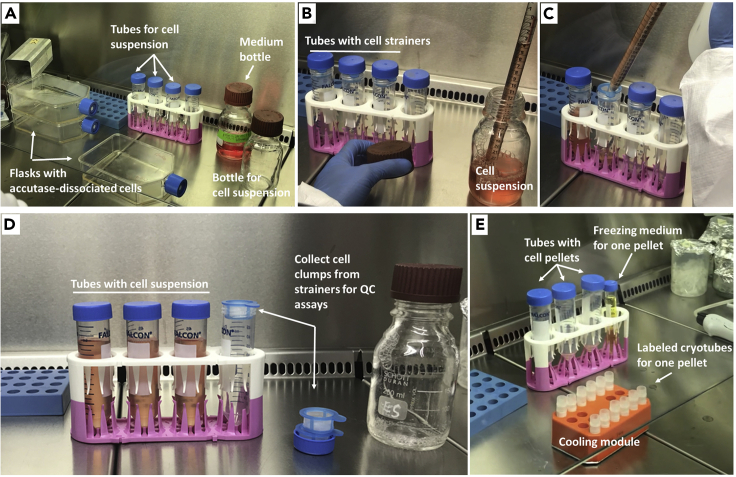
Note: We found it optimal to aliquot no more than 10–15 cryovials at once, so that freezing conditions are similar for all cryovials. In the following, we describe how to freeze 30 x 106 neurons. Before starting, we distribute cryovials into three plastic bags (ten cryovials per bag) and store them at −20°C. We also prepare 4 empty 50 mL Falcon tubes and an empty bottle for the cell suspension (Figure 4A). Once cells are collected into the bottle (steps 31 and 32), we distribute them equally into three 50 mL Falcon tubes (Figures 4B–4D) as detailed in step 33. During centrifugation, we determine cell number and prepare the first ten cryovials. For this, we place them into a tube cooling module and loosen the lids (Figure 4E). After centrifugation, we remove supernatant from all three tubes (see step 36). We start with one of the tubes to resuspend the pellet with freezing medium, quickly aliquot the cells into 10 cryovials and transfer them to −80°C (steps 36 and 37). Then we repeat the same procedure to process the remaining pellets.
Figure 4.
Suggested Cell Culture Hood Setup for the Cryopreservation of Neurons
Figures show the setup before step 30 (A), before step 33 (B), at step 33 (C), before step 34 (D), and before step 36 (E).
Pause Point: We stored cryopreserved neurons for up to one year at −150°C without any noticeable effect on cell quality.
Validation of the Batch: Thawing and Culturing Neurons
Timing: 9 days
This step describes how to thaw cryopreserved neurons and how to keep them in culture for batch quality control.
-
39.
Take a cryovial with neurons from the −150°C freezer and place it immediately in a water bath at 37°C for 2.5–3 min.
-
40.
Remove the cryovial from the water bath shortly before its content is completely thawed, wipe dry, and spray with 70% ethanol.
-
41.
Transfer the content of the cryovial with a 5 mL pipette into a 15 mL tube.
-
42.
Rinse the cryovial with 1 mL neuronal medium and add the medium dropwise to thawed cells in the 15 mL tube while carefully swirling to ensure gentle mixing.
Note: The dropwise transition from freezing medium to culture medium leads to an increased cell viability.
-
43.
Slowly fill up the tube to a volume of 10 mL and mix carefully by swirling the tube.
-
44.
Collect a sample to determine the number of viable cells.
-
45.
Spin cells down at 1200 rcf for 4 min and determine cell number during centrifugation. Based on our experience, about 60%–70% of the cells should be viable.
-
46.
Use a 1 mL pipette to gently resuspend the pellet in dox-supplemented neuronal medium containing 1:500 laminin and 10 μM RI, then fill up using a 5 mL pipette to obtain the desired cell concentration and mix gently.
-
47.
Seed cells on previously prepared PO/laminin coated plates.
Note: We found it convenient to use PO/laminin-coated ibidi 96-well plates. We recommend for these plates a neuronal cell density of 1 x 105 cells/well.
-
48.
Place dishes into a CO2 incubator at 37°C and make sure that cells are equally distributed.
-
49.
On the next day, change medium to neuronal medium pre-equilibrated in a CO2 incubator for 1–2 h, and supplemented with dox as well as 1:500 mL laminin (Figure 5A).
Figure 5.
Validation of Cryopreserved iGlutN and iGABAN Batches
(A) iGlutN and iGABAN cultures one day after thawing. Cultures should not contain cell clusters or non-neuronal cells.
(B) Validation staining of iGlutN and iGABAN cultures one week after thawing. The cells show prominent expression of TUBB3 and FOXG1. In iGABAN cultures most cells are GABA-positive while iGlutN cultures contain only occasional cells positive for GABA. Scale bar: 100 μm.
Note: To avoid the formation of non-neuronal cells, additional days of dox treatment are required after thawing. We found that glutamatergic neurons should be supplemented with dox for at least one day after thawing, while GABAergic neurons require dox supplementation for at least one week after thawing.
-
50.
Change half of the medium every other day, use medium pre-equilibrated in a CO2 incubator for 1–2 h.
-
51.
Before proceeding with immunofluorescence staining, keep cells in culture for at least one week (Figure 5B).
EXPECTED OUTCOMES
Our protocol yields an almost pure neuronal population with a minimum of 95% glutamatergic neurons or almost 90% of GABAergic neurons. In both cases typically about 90% of neurons are positive for FOXG1 (Figure 5B). This protocol allows the scalable production of neurons, and, based on our experience, the optimal final batch size is up to 30 x 106 neurons (starting with 3.6 x 106 hPSCs in three 6-well plates on day −2). Up to three batches can be easily differentiated in parallel by a single person.
LIMITATIONS
iGABAN populations derived with this protocol contain up to 10% GABA-negative cells. Populations of iGlutNs obtained with this protocol usually contain 1%–2% (rarely up to 5%) GABA-positive cells. Moreover, some iGlutNs show multiple axons (about 25%, whereas less than 10% of classical hPSC-derived GlutNs show multiple axons) and a corelease of glutamate and GABA (up to 10%). For details and discussion see Rhee et al. (2019). Please note that it can be challenging for a single operator to produce more than a total of 90 x 106 neurons in one round of forward programming.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Problem
Non-neuronal cell populations on or after day 7.
Potential Solution
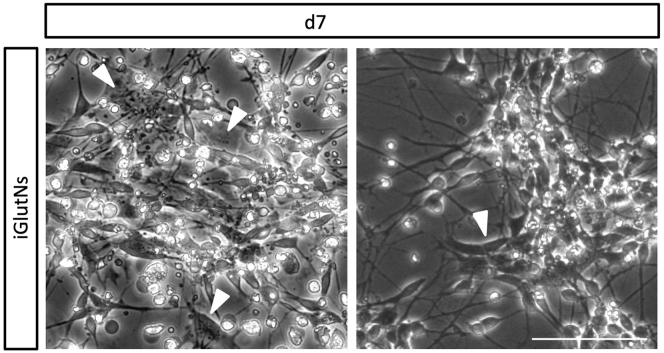
Typically, cultures should look very homogeneous through the whole process of differentiation, and there should be no cells with non-neuronal morphology by day 7. Otherwise, one additional day of Ara-C treatment is recommended. If non-neuronal cells survive the extended Ara-C treatment (Figure 6), this might indicate that the starting quality of hPSCs was not optimal. In this case make sure that hPSC lines are free of any differentiated cells.
Figure 6.
Phase Contrast Images of Exemplary Low-Quality iGlutN Preparations
Arrowheads indicate exemplar cells with non-neuronal morphology on day 7 of the forward programming protocol. Scale bar: 100 μm.
Problem
Cell detachment.
Potential Solution
-
•
Improve initial coating: Only use freshly prepared laminin-coated plates, and make sure that the coating does not dry before seeding cells.
-
•
Refresh coating: Supplement medium with laminin at a 1:500 dilution starting from day 6, or at a 1:100 dilution to thawed neurons that start to detach.
-
•
Reduce mechanical stress: Starting from day 5 of differentiation, carefully remove medium with a Pipetboy instead of a vacuum pump, never aspirate medium completely (only during washing steps before dissociation) and don’t touch the bottom of a plate with the pipette tip.
-
•
Equilibrate culture medium: before adding fresh medium to neuronal cultures put it into a CO2 incubator for 1–2 h in order to equilibrate pH and temperature.
Problem
Less than 60% viable cells after thawing.
Potential Solution
Mechanical stress induced by the dissociation process before freezing might result in pronounced cell death. To reduce this stress, follow these recommendations:
-
•
Make sure that the plates have a fresh and high quality coating to avoid formation of cell clusters that are hard to dissociate.
-
•
Freeze cells at day 8 instead of later time points. The longer neurons stay in culture, the more complex networks form which are harder to dissociate.
-
•
When washing cultures with DPBS before the application of Accutase it has to be avoided that the neurons detach in the form of a single layer: once the culture gets washed off as a whole, it forms a clump that is hard to dissociate.
-
•
If cells do not dissociate easily, it is more beneficial to extend incubation time of Accutase (up to 90 min) rather than performing intense mechanical dissociation steps.
Problem
Low cell survival after thawing.
Potential Solutions
Based on our experience, cell survival is affected by cell density upon freezing. We found it optimal to freeze 1 x 106 cells/vial. The lowest number that still led to acceptable viability in our hands was 0.5 x 106 cells/vial. Freezing more than 1 x 106 cells/vial did not affect cell survival, however, the highest cell number we tested was 2 x 106 cells/vial.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This protocol was developed as part of a project funded by COSYN (Comorbidity and Synapse Biology in Clinically Overlapping Psychiatric Disorders) (Horizon 2020 Program of the European Union under RIA grant agreement 667301). This protocol builds on previous work demonstrating that hPSCs can be rapidly differentiated into excitatory neurons by the forced expression of Ngn2 (Zhang et al., 2013) or into GABAergic neurons by co-expressing Ascl1 and Dlx2 (Yang et al., 2017). We advanced these approaches by eliminating heterogeneity in transgene expression as well as the requirement of astrocytes for neuronal induction, and by including a cryopreservation step.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
M.P. conceived the protocol together with T.K. T.K. wrote the text and prepared the figures under the supervision of M.P. and O.B.
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Contributor Information
Michael Peitz, Email: peitz@uni-bonn.de.
Oliver Brüstle, Email: brustle@uni-bonn.de.
References
- Meijer M., Rehbach K., Brunner J.W., Classen J.A., Lammertse H.C.A., van Linge L.A., Schut D., Krutenko T., Hebisch M., Cornelisse L.N. A Single-Cell Model for Synaptic Transmission and Plasticity in Human iPSC-Derived Neurons. Cell Rep. 2019;2:2199–2211. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian K., Huang C.T., Chen H., 4th, Blackbourn L.W., Chen Y., Cao J., Yao L., Sauvey C., Du Z., Zhang S.C. A simple and efficient system for regulating gene expression in human pluripotent stem cells and derivatives. Stem Cells. 2014;32:1230–1238. doi: 10.1002/stem.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee H.J., Shaib A.H., Rehbach K., Lee C., Seif P., Thomas C., Gideon S.E., Guenther A., Krutenko T., Hebisch M. An Autaptic Culture System for Standardized Analyses of iPSC-Derived Human Neurons. Cell Rep. 2019;27:2212–2228. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang N., Chanda S., Marro S., Ng Y.H., Janas J.A., Haag D., Ang C.E., Tang Y., Flores Q., Mall M. Generation of pure GABAergic neurons by transcription factor programming. Nat. Methods. 2017;14:621–628. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Pak C., Han Y., Ahlenius H., Zhang Z., Chanda S., Marro S., Patzke C., Acuna C., Covy J. Rapid single-step induction of functional neurons from human pluripotent stem cells. Neuron. 2013;78:785–798. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.05.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]