Figure 4.
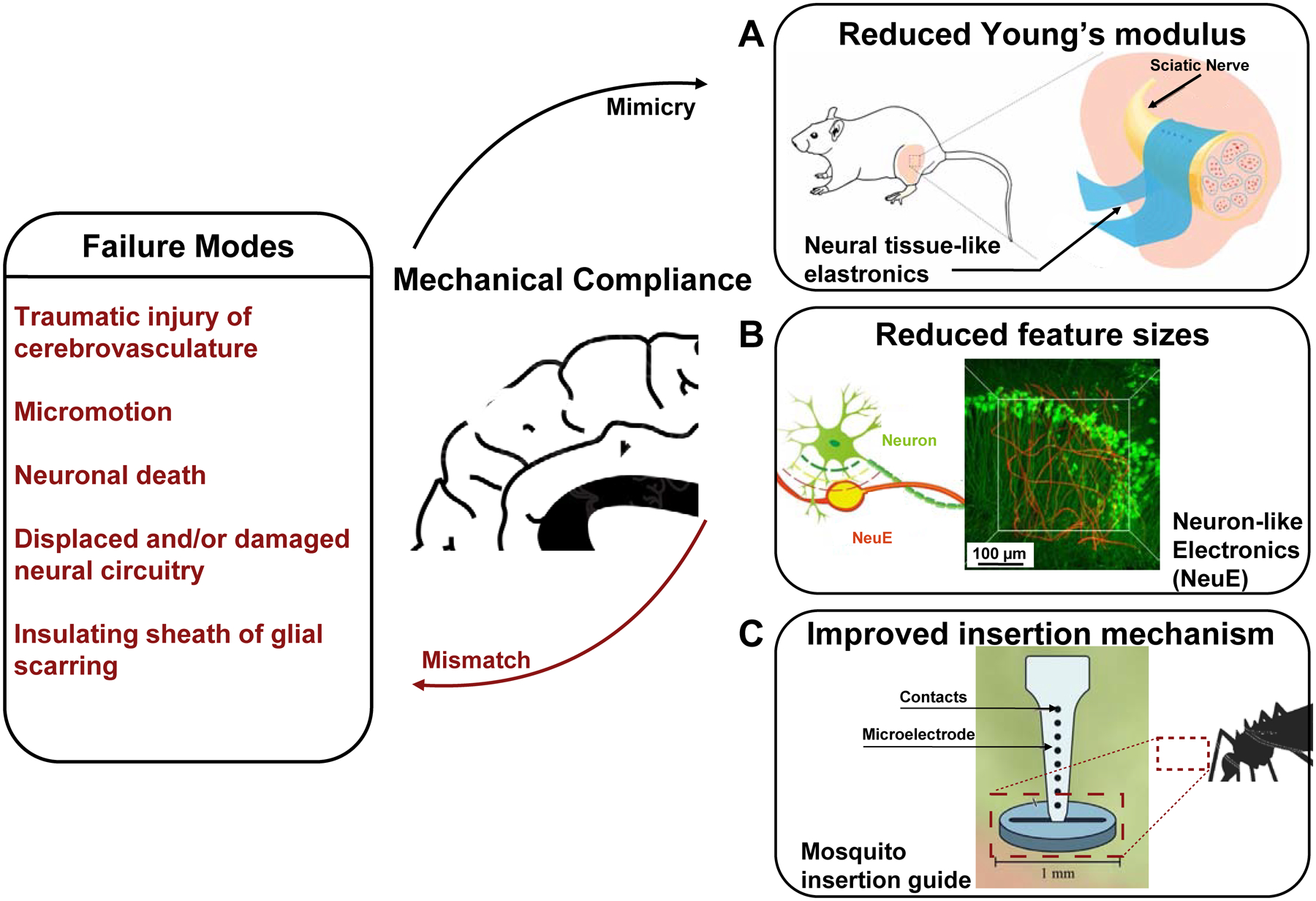
Bioelectronic neural interfaces inspired by the mechanical properties of neural tissue. Bioinspired mechanical compliance may result from the reduction of (A) the material’s Young’s modulus, through engineering thin-film hydrogel elastronics with Young’s moduli on the order of kPa, or (B) feature sizes, with neuron-like electronics (NeuE). A schematic of the intertwined neuron-NeuE interface is shown on the left, and a reconstructed 3D image of neurons (green) interpenetrating the electronic network of NeuE (red) in shown on the right. Finally, improved insertion mechanisms of flexible neural interfaces may be realized through a variety of bioinspired strategies, such as the fascicles of female mosquitos, thereby reducing buckling during implantation (C). Reproduced with permission from Refs. 63, 110, 112.
