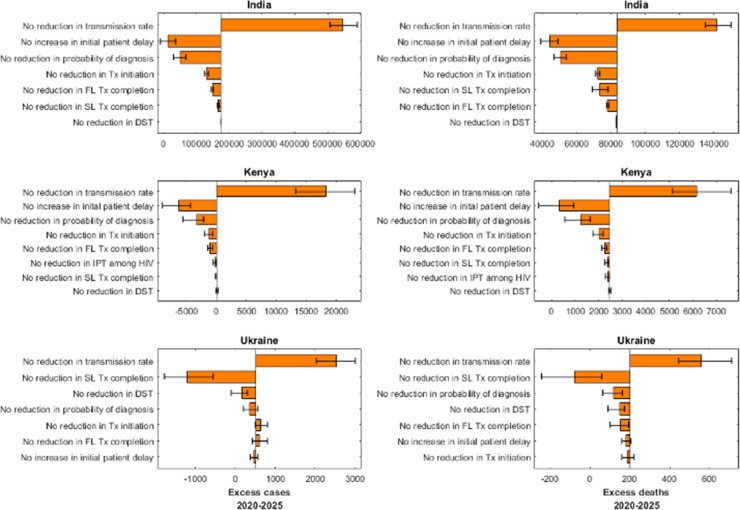
Fig. 3.
Sensitivity analysis: influence of specific components of a lockdown on excess TB cases and deaths. Shown here is a ‘leave-one-out’ analysis, where we simulate a scenario with all disruptions in Table 1 in effect, with the exception of one (given by the label to the left). Bars in the figures show the excess TB burden between 2020 and 2025 arising from this scenario, relative to the scenario where all disruptions are in effect. Vertical lines mark median excess TB cases and deaths in the ‘full-impact’ scenario. The largest bars therefore indicate those types of disruption that are most influential, for excess TB burden. Left-hand panels show results in terms of excess TB incidence, and right-hand panels show excess TB deaths. Error bars show 95% credible intervals, calculated by iterating this process over 250 posterior samples for each country. Abbreviations: DST: drug susceptibility test, FL: first-line, HIV: human immunodeficiency virus, IPT: isoniazid preventive therapy, SL: second-line, Tx: treatment.