Abstract
Objectives
Adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART) leads to viral suppression for people living with HIV (PLHIV) and is critical for both individual health and reducing onward HIV transmission. HIV stigma is a risk factor that can undermine adherence. We explored the association between HIV stigma and self‐reported ART adherence among PLHIV in 21 communities in the HPTN 071 (PopART) trial in Zambia and the Western Cape of South Africa.
Methods
We conducted a cross‐sectional analysis of baseline data collected between 2013 and 2015, before the roll‐out of trial interventions. Questionnaires were conducted, and consenting participants provided a blood sample for HIV testing. Poor adherence was defined as self‐report of not currently taking ART, missing pills over the previous 7 days or stopping treatment in the previous 12 months. Stigma was categorised into three domains: community, health setting and internalised stigma. Multivariable logistic regression was used for analysis.
Results
Among 2020 PLHIV self‐reporting ever taking ART, 1888 (93%) were included in multivariable analysis. Poor ART adherence was reported by 15.8% (n = 320) of participants, and 25.7% (n = 519) reported experiencing community stigma, 21.5% (n = 434) internalised stigma, and 5.7% (n = 152) health setting stigma. PLHIV who self‐reported previous experiences of community and internalised stigma more commonly reported poor ART adherence than those who did not (aOR 1.63, 95% CI 1.21 −2.19, P = 0.001 and aOR 1.31, 95% CI 0.96–1.79, P = 0.09).
Conclusions
HIV stigma was associated with poor ART adherence. Roll‐out of universal treatment will see an increasingly high proportion of PLHIV initiated on ART. Addressing HIV stigma could make an important contribution to supporting lifelong ART adherence.
Keywords: human immunodeficiency virus, antiretroviral therapy, treatment adherence, stigma, South Africa, Zambia
Abstract
Objectifs
L'adhésion à la thérapie antirétrovirale (ART) conduit à la suppression virale pour les personnes vivant avec le VIH (PVVIH) et est essentielle à la fois pour la santé individuelle et pour réduire la transmission du VIH. La stigmatisation du VIH est un facteur de risque qui peut compromettre l’adhésion. Nous avons exploré l'association entre la stigmatisation du VIH et l'adhésion autodéclarée à l’ART chez les PVVIH dans 21 communautés dans l'essai HPTN 071 (PopART) en Zambie et dans le Western Cape en Afrique du Sud.
Méthodes
Nous avons effectué une analyse transversale des données de base collectées entre 2013‐2015, avant le déploiement des interventions d'essai. Des questionnaires ont été réalisés et les participants consentants ont fourni un échantillon de sang pour le dépistage du VIH. Une mauvaise adhésion a été définie comme l'autodéclaration de ne pas prendre actuellement l’ART, d'omettre des comprimés au cours des 7 jours précédents ou d'arrêter le traitement au cours des 12 mois précédents. La stigmatisation a été classée en trois domaines: communautaire, en milieu de santé et stigmatisation intériorisée. Une régression logistique multivariée a été utilisée pour l'analyse.
Résultats
Parmi les 2.020 PVVIH autodéclarant avoir déjà pris un ART, 1.888 (93%) ont été inclus dans l'analyse multivariée. Une mauvaise adhésion à l’ART a été signalée par 15,8% (n = 320) des participants, 25,7% (n = 519) ont déclaré avoir subi une stigmatisation communautaire, 21,5% (n = 434) une stigmatisation internalisée et 5,7% (n = 152) une stigmatisation en milieu de santé. Les PVVIH qui ont auto‐déclaré des expériences antérieures de stigmatisation communautaire et intériorisée ont plus souvent rapporté une mauvaise adhésion à l’ART que ceux qui ne l'ont pas fait (aOR 1,63 ; IC95%: 1,21–2,19 ; P = 0,001 et aOR 1,31 ; IC95%: 0,96–1,79 ; P = 0,09).
Conclusions
La stigmatisation du VIH était associée à une mauvaise adhésion à l’ART. Le déploiement du traitement universel verra une proportion de plus en plus élevée de PVVIH initiées à l’ART. Lutter contre la stigmatisation du VIH pourrait apporter une contribution importante au soutien de l'adhésion à l’ART au cours de la vie.
Numéro d'essai clinique
Mots‐clés: virus de l'immunodéficience humaine, thérapie antirétrovirale, adhésion au traitement, stigmatisation, Afrique du Sud, Zambie
Introduction
For people living with HIV (PLHIV), adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART) is crucial for viral suppression [1, 2, 3] and reducing HIV‐related morbidity and mortality [4], onward transmission [5, 6, 7] and drug resistance [8]. UNAIDS 90‐90‐90 targets captured the importance of achieving high levels of HIV testing and ART coverage, with the ‘third 90’ target being that by 2020 90% of those on ART were virally suppressed [9]. In 2016, an estimated 89% of PLHIV in Zambia who reported current ART use [10] and 85% of those registered in HIV care and taking ART in South Africa [11] were virally suppressed. Understanding the factors that influence adherence to ART is crucial if high levels of viral suppression are to be sustained and increased.
HIV stigma can undermine ART adherence [12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17] and is a frequently reported barrier to adherence in sub‐Saharan Africa [13]. HIV stigma is common in both Zambia and South Africa, with over 35% of PLHIV reporting some type of stigma [18]. Whilst ART adherence is consistently found to be worse among individuals experiencing stigma than among those who do not [19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25], a 2013 review concluded that all but one study was at risk of bias, and most had not used validated exposure or outcome measures [19]. Currently, data come mostly from facility‐based or purposively sampled populations, and there is heterogeneity in the measurement of both ART adherence and HIV stigma.
We analysed baseline data from the HPTN 071 (PopART) trial [26, 27] to explore the association between HIV stigma and ART adherence for adults with HIV in a random population sample from 21 urban and peri‐urban communities in Zambia and the Western Cape of South Africa. Data were collected between 2013 and 2015, after more than 10 years of scale‐up of HIV treatment services and ART in both countries. We explored these associations among individuals who started ART prior to the implementation of the PopART universal test and treat (UTT) interventions.
Methods
HPTN071 (PopART) was a cluster‐randomised trial conducted in Zambia and South Africa to assess the impact of a combination of HIV prevention interventions, including household‐based HIV testing and an offer of universal ART initiation regardless of CD4 count or clinical stage for those testing HIV‐positive, on HIV infection rates. Twenty‐one urban communities were purposively selected for inclusion in the trial if they had a heath facility offering HIV and TB services, high HIV prevalence and a population of >20 000. In each country, study communities were matched in triplets based on HIV prevalence and geographic proximity and then randomised to one of three trial arms [26, 27].
Between November 2013 and March 2015, approximately 2000 individuals were enrolled in each study community as a ‘population cohort’ to assess the effect of trial interventions on primary and secondary outcomes. From a simple random sample of households, household members were enumerated and one adult (18–44 years) per household randomly selected for inclusion in the cohort. Selected adults were asked for consent to enrol in the study and participate in a baseline survey and three follow‐up surveys. For those giving consent, a venous blood sample was taken and analysed in‐country using a single fourth‐generation serologic assay. A second fourth‐generation assay was used to confirm HIV‐positive results, and any discrepancies tested with additional assays to confirm HIV status. The baseline survey was conducted using face‐to‐face interviewer administered questionnaires, with data collected on electronic devices. Participants were asked about their HIV status and, if they were happy to do so, share the results of their last HIV test. All participants were offered an on‐the‐spot rapid HIV test.
Our analysis was restricted to individuals who self‐reported living with HIV, with confirmation from the laboratory HIV testing. Among this group, individuals were included if they reported ever starting ART before the 1 January 2014. We excluded participants if they had no information on the year of starting ART or reported starting ART for the prevention of mother to child transmission of HIV (PMTCT) but were no longer taking it, as this may have been due to earlier initiation guidelines and not reflect non‐adherence. We excluded respondents if they had incomplete outcome data or missing data on all stigma questions.
We created a primary outcome variable from three survey questions on ART adherence. We defined poor adherence as ‘respondents self‐reporting that they had ever started ART but were not currently taking ART, or currently taking ART but had either stopped in the past 12 months, or missed pills in the past seven days’. To explore whether our findings were sensitive to our primary definition of adherence, we looked at a secondary outcome, restricting our definition to those reporting they were currently taking ART but had missed taking pills in the previous seven days. Both outcome variables were binary.
We used 11 survey questions on HIV stigma to generate composite ‘yes/no’ binary variables for experienced community stigma, experienced health setting stigma and current internalised stigma. Composite variables were only generated for participants responding to all stigma questions contributing to that variable. Reponses on internalised stigma were given on a 4‐point Likert scale (0 = strongly disagree, 1 = disagree, 2 = agree and 3 = strongly agree) and later aggregated for each question (0/1 = disagree. 2/3 = agree). Questions on community and health setting stigma used pre‐coded response categories capturing the frequency of experiences during the last year (0 = never, 1 = once, 2 = a few times, 3 = often and 4 = not applicable because no one knows my status (‘never disclosed’)). Those responding ‘never’ or ‘never disclosed’ were categorised as ‘never experiencing either community or health setting stigma’. To create the three variables, respondents who disagreed or never experienced stigma on all the questions related to that variable were grouped as ‘never experiencing’ that type of stigma. Those agreeing or experiencing stigma on ≥1 question were categorised as ‘ever experiencing’ that type of stigma [18]. Our stigma measures were aligned with standardised measures that were approved by the UNAIDS’ monitoring and evaluation reference group (MERG) in 2014 [18, 28, 29].
A priori knowledge on risk factors for ART adherence informed decisions on other explanatory variables to explore for inclusion in analysis. We considered demographic variables (country, community/ study triplet, gender, age and marital status), socio‐economic factors (education, wealth, employment status and food security), mobility factors (nights spent away from home), behavioural factors (alcohol and drug use) and HIV‐specific factors (year of HIV diagnosis, time on ART, hiding pills (responding to the question ‘Have you ever hidden your ART pills so that others couldn’t see them’), HIV status disclosure and reason for starting ART). For alcohol use, we categorised respondents using scores from the WHO Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT), [30] and for wealth, we used quintiles derived using principal component analysis. The group identified at lowest risk of the outcome was used as the reference category. Where this was unclear, we used the group with the largest numbers.
We developed a conceptual framework (Figure 1) to structure our analysis using a hierarchical approach [31] based on previous work conceptualising HIV stigma [32] and associations between stigma and ART adherence [19]. We conducted analyses for the study population and then separately for each country.
Figure 1.
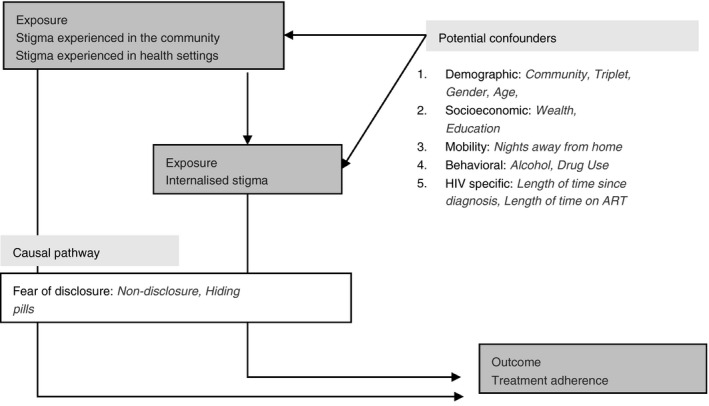
Conceptual framework.
We first described our study participants. Second, we described the distribution of ART adherence, HIV stigma and other explanatory variables. Third, we used logistic regression to estimate unadjusted associations between HIV stigma and ART adherence. We also estimated unadjusted associations between the other covariates and ART adherence and did the same for HIV stigma to understand potential confounding factors and identify variables to consider further in multivariable models. We conducted an analysis of the association between HIV stigma and ART adherence, stratified on the other explanatory variables that were considered a priori confounders and also those showing evidence of associations (P < 0.05) with adherence from our earlier unadjusted analysis.
Last, we conducted an adjusted analysis using multivariable logistic regression. We included groups of variables in our models in the stages identified in our conceptual framework, in order of their proximity to the outcome. Variables were included if they were considered potential confounders, either a priori and/or those showing an unadjusted association (P < 0.05) with the outcome. We excluded variables from our model if they were perceived to be on the causal pathway between stigma and ART adherence. To control for confounding by community‐level factors, we adjusted for study community (in Zambia) and study triplet (in South Africa) in all multivariable analysis. Study triplet was used instead of community in South Africa due to small numbers in the study population for several communities. The same series of models were built for each of the three stigma variables. We considered internalised stigma proximal to ART adherence and community and health setting stigma distal, adjusting a final set of models for each of the experienced stigmas (health setting and community) to account for this. We ran our models again with our restricted outcome definition (only those reporting they were currently taking ART but had missed taking pills in the previous seven days).
Written informed consent was obtained for all respondents enrolled in the population cohort. Ethics approval was obtained for the HPTN 071 (PopART) trial from the University of Zambia, Stellenbosch University, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.
Results
Our analysis initially included 2020 PLHIV (Zambia n = 1099; South Africa n = 921) (Figure 2). The number of individuals per community ranged from three to 250, with a higher proportion of women (88.6%) than men (11.4%). 76.6% of the study population were over the age of 30, and 6.3% aged 18–24 years. Approximately half the population (49%) were married or living as married, but with a higher proportion in Zambia (62.3%) than in South Africa (33.1%). Upper secondary school or University education was reached by 45.5% of respondents, although this proportion was notably higher in South Africa (70.1%) than Zambia (24.8%). Similar proportions of the study population were diagnosed with HIV each year, from before 2007 up until 2012. Only 6.4% of respondents were initiated on ART prior to 2005, with >60% starting ART after 2010 in both countries. Disclosure of HIV status (to friends, a religious leader, a health worker, family or a partner) was common, at 96.4% in Zambia and 97.7% in South Africa. 28% of the study population reported hiding their ART pills, with a higher proportion in Zambia (40.7%) than South Africa (12.9%). Missing data on all variables were minimal, ranging from 0 to 2.5% in Zambia and 0 to 2.7% in South Africa (Table 1).
Figure 2.
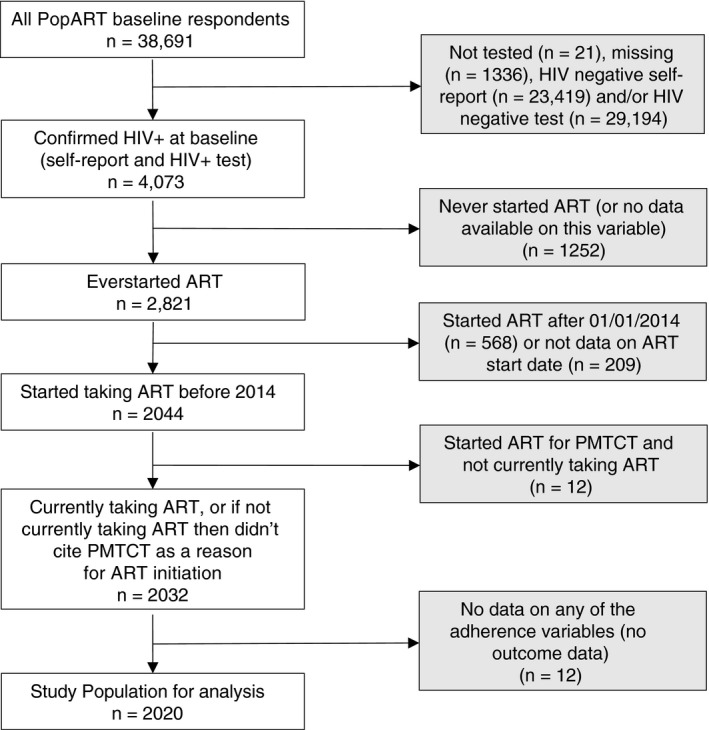
Study population
Table 1.
Study population characteristics
| Total study population | Zambia | South Africa | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | n/2020% | n | n/1099% | n | n/921% | |||
| Demographic characteristics | ||||||||
| Gender | ||||||||
| Female | 1790 | 88.6% | 950 | 86.4% | 840 | 91.2% | ||
| Male | 230 | 11.4% | 149 | 13.6% | 81 | 8.8% | ||
| Age | ||||||||
| 18–24 | 128 | 6.3% | 76 | 6.9% | 52 | 5.6% | ||
| 25–29 | 344 | 17.0% | 165 | 15.0% | 179 | 19.4% | ||
| 30–34 | 521 | 25.8% | 272 | 24.7% | 249 | 27.0% | ||
| 35–39 | 567 | 28.1% | 310 | 28.2% | 257 | 27.9% | ||
| >40 | 459 | 22.7% | 275 | 25.0% | 184 | 20.0% | ||
| Missing | 1 | 0.0% | 1 | 0.1% | 0.0% | |||
| Study Triplet | ||||||||
| – | – | 258 | 23.5% | 529 | 57.4% | |||
| – | – | 278 | 25.3% | 292 | 31.7% | |||
| – | – | 291 | 26.5% | 100 | 10.9% | |||
| – | – | 272 | 24.7% | |||||
| Marital status | ||||||||
| Married | 990 | 49.0% | 685 | 62.3% | 305 | 33.1% | ||
| Divorced/Separated | 246 | 12.2% | 214 | 19.5% | 32 | 3.5% | ||
| Widowed | 146 | 7.2% | 127 | 11.6% | 19 | 2.1% | ||
| Never married | 636 | 31.5% | 73 | 6.6% | 563 | 61.1% | ||
| Missing | 2 | 0.1% | 0 | 0.0% | 2 | 0.2% | ||
| Socio‐economic characteristics | ||||||||
| Wealth quintile | ||||||||
| 1 – Lowest | 536 | 26.5% | 295 | 26.8% | 241 | 26.2% | ||
| 2 | 426 | 21.1% | 173 | 15.7% | 253 | 27.5% | ||
| 3 | 422 | 20.9% | 219 | 19.9% | 203 | 22.0% | ||
| 4 | 408 | 20.2% | 249 | 22.7% | 159 | 17.3% | ||
| 5 – Highest | 223 | 11.0% | 163 | 14.8% | 60 | 6.5% | ||
| Missing | 5 | 0.2% | 0 | 0.0% | 5 | 0.5% | ||
| Education | ||||||||
| None/Primary | 558 | 27.6% | 468 | 42.6% | 90 | 9.8% | ||
| Lower Secondary | 527 | 26.1% | 354 | 32.2% | 173 | 18.8% | ||
| Upper Secondary/University | 919 | 45.5% | 273 | 24.8% | 646 | 70.1% | ||
| Missing | 16 | 0.8% | 4 | 0.4% | 12 | 1.3% | ||
| Currently working | ||||||||
| No | 1494 | 74.0% | 802 | 73.0% | 692 | 75.1% | ||
| Yes | 526 | 26.0% | 297 | 27.0% | 229 | 24.9% | ||
| Food security | ||||||||
| No | 1225 | 60.6% | 605 | 55.1% | 432 | 46.9% | ||
| Yes | 793 | 39.3% | 489 | 44.5% | 487 | 52.9% | ||
| Missing | 2 | 0.1% | 5 | 0.5% | 2 | 0.2% | ||
| Mobility characteristics | ||||||||
| Nights away from home† | ||||||||
| No | 1685 | 83.4% | 876 | 79.7% | 809 | 87.8% | ||
| Yes | 322 | 15.9% | 216 | 19.7% | 106 | 11.5% | ||
| Missing | 13 | 0.6% | 7 | 0.6% | 6 | 0.7% | ||
| Behavioural characteristics | ||||||||
| Alcohol Audit score | ||||||||
| Score 0–7 | 1771 | 87.7% | 967 | 88.0% | 804 | 87.3% | ||
| Score 8–15 | 155 | 7.7% | 85 | 7.7% | 70 | 7.6% | ||
| Score 16+ | 42 | 2.1% | 20 | 1.8% | 22 | 2.4% | ||
| Missing | 52 | 2.6% | 27 | 2.5% | 25 | 2.7% | ||
| Drug use (past 12 months) | ||||||||
| No | 1988 | 98.4% | 1076 | 97.9% | 912 | 99.0% | ||
| Yes | 22 | 1.1% | 16 | 1.5% | 6 | 0.7% | ||
| Missing | 10 | 0.5% | 7 | 0.6% | 3 | 0.3% | ||
| HIV‐specific characteristics | ||||||||
| Year of HIV diagnosis | ||||||||
| Before 2009 | 421 | 20.8% | 170 | 15.5% | 251 | 27.3% | ||
| 2007–2008 | 334 | 16.5% | 176 | 16.0% | 158 | 17.2% | ||
| 2009–2010 | 438 | 21.7% | 260 | 23.7% | 178 | 19.3% | ||
| 2011–2012 | 436 | 21.6% | 261 | 23.8% | 175 | 19.0% | ||
| 2013–2014 | 275 | 13.6% | 165 | 15.0% | 110 | 11.9% | ||
| Missing | 116 | 5.7% | 67 | 6.1% | 49 | 5.3% | ||
| First started ART | ||||||||
| 1996–2005 | 130 | 6.4% | 69 | 6.3% | 61 | 6.6% | ||
| 2006–2009 | 593 | 29.4% | 323 | 29.4% | 270 | 29.3% | ||
| 2010–2011 | 500 | 24.8% | 283 | 25.8% | 217 | 23.6% | ||
| 2012–2013 | 797 | 39.5% | 424 | 38.6% | 373 | 40.5% | ||
| Hiding pills | ||||||||
| No | 1445 | 71.5% | 645 | 58.7% | 800 | 86.9% | ||
| Yes | 566 | 28.0% | 447 | 40.7% | 119 | 12.9% | ||
| Missing | 9 | 0.4% | 7 | 0.6% | 2 | 0.2% | ||
| HIV status disclosure | ||||||||
| Disclosed to anyone | ||||||||
| No | 61 | 3.0% | 40 | 3.6% | 21 | 2.3% | ||
| Yes | 1959 | 97.0% | 1059 | 96.4% | 900 | 97.7% | ||
| Disclosed to friends | ||||||||
| No | 1711 | 84.7% | 980 | 89.2% | 731 | 79.4% | ||
| Yes | 309 | 15.3% | 119 | 10.8% | 190 | 20.6% | ||
| Disclosed to religious leader | ||||||||
| No | 1969 | 97.5% | 1064 | 96.8% | 905 | 98.3% | ||
| Yes | 51 | 2.5% | 35 | 3.2% | 16 | 1.7% | ||
| Disclosed to health care worker | ||||||||
| No | 1892 | 93.7% | 1020 | 92.8% | 872 | 94.7% | ||
| Yes | 128 | 6.3% | 79 | 7.2% | 49 | 5.3% | ||
| Disclosed to family | ||||||||
| No | 406 | 20.1% | 235 | 21.4% | 171 | 18.6% | ||
| Yes | 1614 | 79.9% | 864 | 78.6% | 750 | 81.4% | ||
| Disclosed to partner | ||||||||
| No | 1024 | 50.7% | 505 | 46.0% | 519 | 56.4% | ||
| Yes | 996 | 49.3% | 594 | 54.0% | 402 | 43.6% | ||
| Primary reason for starting ART | ||||||||
| Started for PMTCT | ||||||||
| No | 1760 | 87.1% | 958 | 87.2% | 802 | 87.1% | ||
| Yes | 260 | 12.9% | 141 | 12.8% | 119 | 12.9% | ||
| Recommend by health worker | ||||||||
| No | 1330 | 65.8% | 616 | 56.1% | 714 | 77.5% | ||
| Yes | 690 | 34.2% | 483 | 43.9% | 207 | 22.5% | ||
| Started to protect partner | ||||||||
| No | 1828 | 90.5% | 973 | 88.5% | 855 | 92.8% | ||
| Yes | 192 | 9.5% | 126 | 11.5% | 66 | 7.2% | ||
| Started for own health | ||||||||
| No | 938 | 46.4% | 473 | 43.0% | 465 | 50.5% | ||
| Yes | 1082 | 53.6% | 626 | 57.0% | 456 | 49.5% | ||
>1 in the past 3 months.
Poor adherence to ART was reported by 320 (15.8%) respondents, with similar country‐specific findings (Zambia n = 186, 16.9%; SA n = 134, 14.5%). Most of those categorised as poor adherers reported ‘missing pills in the past seven days’ (n = 244). Thirty‐two respondents reported that they were not currently taking ART, and 80 respondents reported stopping in the previous 12 months. Poor adherence was slightly higher for men (18.7%) than women (15.5%), with similar distributions in each country (Table 2).
Table 2.
Distribution of ART adherence and HIV stigma
| ART Adherence | Total study population | Zambia | South Africa | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | n/2020% | n | n/1099% | n | n/921% | ||
| Currently taking ART | Yes | 1988 | 98.4% | 1092 | 99.4% | 896 | 97.3% |
| No | 32 | 1.6% | 7 | 0.6% | 25 | 2.7% | |
| Stopped ART in the past 12 months | Yes | 80 | 4.0% | 36 | 3.3% | 44 | 4.8% |
| No | 1908 | 94.5% | 1056 | 96.1% | 852 | 92.5% | |
| Missing | 32 | 1.6% | 7 | 0.6% | 25 | 2.7% | |
| Missed pills in the past 7 days | Yes | 244 | 12.1% | 153 | 13.9% | 91 | 9.9% |
| No | 1744 | 86.3% | 939 | 85.4% | 805 | 87.4% | |
| Missing | 32 | 1.6% | 7 | 0.6% | 25 | 2.7% | |
| ART adherence | Yes | 1700 | 84.2% | 913 | 83.1% | 787 | 85.5% |
| No | 320 | 15.8% | 186 | 16.9% | 134 | 14.5% | |
| HIV Stigma | |||||||
| I have lost respect or standing in the community because of my HIV status | Disagree | 1732 | 85.7% | 919 | 83.6% | 813 | 88.3% |
| Agree | 258 | 12.8% | 161 | 14.6% | 97 | 10.5% | |
| Missing | 30 | 1.5% | 19 | 1.7% | 11 | 1.2% | |
| I think less of myself | Disagree | 1763 | 87.3% | 952 | 86.6% | 811 | 88.1% |
| Agree | 240 | 11.9% | 137 | 12.5% | 103 | 11.2% | |
| Missing | 17 | 0.8% | 10 | 0.9% | 7 | 0.8% | |
| I have felt ashamed because of my HIV status | Disagree | 1758 | 87.0% | 945 | 86.0% | 813 | 88.3% |
| Agree | 242 | 12.0% | 141 | 12.8% | 101 | 11.0% | |
| Missing | 20 | 1.0% | 13 | 1.2% | 7 | 0.8% | |
| Internalised Stigma | No | 1552 | 76.8% | 819 | 74.5% | 733 | 79.6% |
| Yes | 434 | 21.5% | 257 | 23.4% | 177 | 19.2% | |
| Missing | 34 | 1.7% | 23 | 2.1% | 11 | 1.2% | |
| People have talked badly about me because of my HIV status | None | 1617 | 80.0% | 846 | 77.0% | 771 | 83.7% |
| Some | 382 | 18.9% | 238 | 21.7% | 144 | 15.6% | |
| Missing | 21 | 1.0% | 15 | 1.4% | 6 | 0.7% | |
| I have been verbally insulted, harassed and/or threatened because of my HIV status | None | 1803 | 89.3% | 972 | 88.4% | 831 | 90.2% |
| Some | 200 | 9.9% | 116 | 10.6% | 84 | 9.1% | |
| Missing | 17 | 0.8% | 11 | 1.0% | 6 | 0.7% | |
| I have been physically assaulted because of my HIV status | None | 1899 | 94.0% | 1046 | 95.2% | 853 | 92.6% |
| Some | 106 | 5.2% | 43 | 3.9% | 63 | 6.8% | |
| Missing | 15 | 0.7% | 10 | 0.9% | 5 | 0.5% | |
| Someone else disclosed my HIV status without my permission | None | 1682 | 83.3% | 904 | 82.3% | 778 | 84.5% |
| Some | 314 | 15.5% | 184 | 16.7% | 130 | 14.1% | |
| Missing | 24 | 1.2% | 11 | 1.0% | 13 | 1.4% | |
| I have felt that people have not wanted to sit next to me because of my HIV status | None | 1915 | 94.8% | 1060 | 96.5% | 855 | 92.8% |
| Some | 89 | 4.4% | 31 | 2.8% | 58 | 6.3% | |
| Missing | 16 | 0.8% | 8 | 0.7% | 8 | 0.9% | |
| Experienced stigma in the community | No | 1468 | 72.7% | 764 | 69.5% | 704 | 76.4% |
| Yes | 519 | 25.7% | 317 | 28.8% | 202 | 21.9% | |
| Missing | 33 | 1.6% | 18 | 1.6% | 15 | 1.6% | |
| Healthcare workers talked badly about me because of my HIV status | Disagree | 1905 | 94.3% | 1050 | 95.5% | 855 | 92.8% |
| Agree | 99 | 4.9% | 39 | 3.5% | 60 | 6.5% | |
| Missing | 16 | 0.8% | 10 | 0.9% | 6 | 0.7% | |
| A health worker disclosed my HIV status without my permission | Disagree | 1909 | 94.5% | 1054 | 95.9% | 855 | 92.8% |
| Agree | 91 | 4.5% | 35 | 3.2% | 56 | 6.1% | |
| Missing | 20 | 1.0% | 10 | 0.9% | 10 | 1.1% | |
| I have been denied health services because of my HIV status | Disagree | 1939 | 96.0% | 1081 | 98.4% | 858 | 93.2% |
| Agree | 65 | 3.2% | 10 | 0.9% | 55 | 6.0% | |
| Missing | 16 | 0.8% | 8 | 0.7% | 8 | 0.9% | |
| Experienced stigma in health settings | Disagree | 1844 | 91.3% | 1020 | 92.8% | 824 | 89.5% |
| Agree | 152 | 7.5% | 66 | 6.0% | 86 | 9.3% | |
| Missing | 24 | 1.2% | 13 | 1.2% | 11 | 1.2% | |
Stigma experienced in the community was most frequently reported (overall 25.7%; Zambia 28.8%; SA 21.9%), then internalised stigma (overall 21.5%; Zambia 23.4%; SA 19.2%). Stigma experienced in health care settings was less frequently reported (overall 7.5%; Zambia 6%; SA 9.3%) (Table 2).
Among the total study population, those reporting stigma experienced in the community or internalised stigma were more likely to be non‐adherent than those who did not, with unadjusted ORs of 1.68 (95% CI 1.29–2.18, P < 0.001) and 1.52 (95% CI 1.15–2.01, P = 0.003), respectively. Those experiencing health setting stigma were only slightly more likely to be non‐adherent to ART than those who did not (OR 1.19, 95% CI 0.76–1.85, P = 0.45). Country‐specific estimates were similar. In Zambia, those experiencing community stigma had 1.89 (95% CI 1.35–2.65, P < 0.001) the odds of poor adherence, and those reporting internalised stigma 1.62 (95% CI 1.13–2.3, P = 0.008) the odds of poor adherence. In South Africa, the association between each of community and internalised stigma and poor adherence gave ORs of 1.32 (95% CI 0.85–2.05, P = 0.22) and 1.34 (95% CI 0.85–2.11, P = 0.21), respectively (Table 4).
Table 4.
Univariable and multivariable logistic regression estimates of odds ratios for each stigma variable and ART adherence
| ART adherence | Unadjusted models | Adjusted models§ | Adjusted models¶ | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n/N † | % | OR | 95% CI | Pw | aOR | 95% CI | Pw | aOR | 95% CI | Pw | |
| Total Study Population | N = 2020 | Analysis restricted to n = 1888‡ | |||||||||
| Experienced stigma in the community | |||||||||||
| No | 201/1468 | 13.7% | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Yes | 110/519 | 21.2% | 1.68 | (1.29–2.19) | <0.001 | 1.65 | (1.25–2.18) | <0.001 | 1.63 | (1.21–2.19) | 0.001 |
| Experienced stigma in health settings | |||||||||||
| No | 290/1844 | 15.7% | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Yes | 27/152 | 17.8% | 1.19 | (0.76–1.86) | 0.44 | 1.38 | (0.87–2.20) | 0.17 | 1.05 | (0.64–1.72) | 0.86 |
| Internalised Stigma | |||||||||||
| No | 228/1552 | 14.7% | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Yes | 87/434 | 20.0% | 1.51 | (1.15–2.00) | 0.004 | 1.50 | (1.12–2.01) | 0.007 | 1.31 | (0.96–1.79) | 0.09 |
| Zambia | N = 1099 | Analysis restricted to n = 1034‡ | |||||||||
| Experienced stigma in the community | |||||||||||
| No | 106/764 | 13.9% | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Yes | 75/317 | 23.7% | 1.89 | (1.35–2.65) | <0.001 | 1.98 | (1.38–2.83) | <0.001 | 2.03 | (1.40–2.94) | <0.001 |
| Experienced stigma in health settings | |||||||||||
| No | 174/1020 | 17.1% | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Yes | 11/66 | 16.7% | 0.99 | (0.51–1.94) | 0.98 | 1.10 | (0.55–2.22) | 0.79 | 0.80 | (0.39–1.65) | 0.54 |
| Internalised Stigma | |||||||||||
| No | 125/819 | 15.3% | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Yes | 58/257 | 22.6% | 1.62 | (1.13–2.31) | 0.008 | 1.67 | (1.15–2.44) | 0.007 | 1.44 | (0.97–2.14) | 0.07 |
| South Africa | N = 921 | Analysis restricted to n = 854‡ | |||||||||
| Experienced stigma in the community | |||||||||||
| No | 95/704 | 13.5% | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Yes | 35/202 | 17.3% | 1.32 | (0.85–2.05) | 0.22 | 1.21 | (0.76–1.93) | 0.43 | 1.01 | (0.58–1.74) | 0.98 |
| Experienced stigma in health settings | |||||||||||
| No | 116/824 | 14.1% | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Yes | 16/86 | 18.6% | 1.45 | (0.80–2.64) | 0.22 | 1.67 | (0.89–3.13) | 0.11 | 1.66 | (0.79–3.47) | 0.18 |
| Internalised Stigma | |||||||||||
| No | 103/733 | 14.1% | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Yes | 29/177 | 16.4% | 1.34 | (0.85–2.11) | 0.21 | 1.41 | (0.87–2.27) | 0.16 | 1.31 | (0.78–2.21) | 0.30 |
n = non‐adherent; N = total individuals reporting ever starting ART.
Analysis restricted to respondents with complete data on community/triplet, gender, age, education, wealth, mobility, alcohol and all stigma variables.
Adjusted for community/triplet, gender, age, education, wealth, mobility, alcohol.
Adjusted for community/triplet, gender, age, education, wealth, mobility, alcohol and experienced stigma (internalised stigma adjusted for community and health setting stigma; health setting stigma adjusted for community stigma; community stigma adjusted for health setting stigma.
In the total study population, poor ART adherence was associated with explanatory variables including community/triplet (P < 0.001), higher alcohol consumption (P < 0.001), lower educational attainment (P = 0.04), increased mobility (P < 0.001) and hiding pills (P = 0.03). Of these, community/triplet showed strong evidence of an association with all three stigma variables (all P < 0.001). Higher alcohol consumption was associated with internalised stigma (P < 0.001), and hiding pills was associated with both internalised and health setting stigma (P < 0.001 and P = 0.02, respectively), but there was no evidence of an association with experienced community stigma (P = 0.73). These associations differed slightly in each country, for example, there was evidence that education was associated with poor adherence in South Africa but not Zambia and mobility in Zambia but not South Africa (Table 3).
Table 3.
Univariable logistic regression estimates of odds ratios for each variable with ART adherence
| Study Population (N = 2020) | Non‐adherence (n = 320) | % | OR | 95% CI | P‐value† | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | ||||||
| Gender | ||||||
| Female | 1790 | 277 | 15.5% | 1 | 0.22 | |
| Male | 230 | 43 | 18.7% | 1.26 | (0.88–1.79) | |
| Age | ||||||
| 18–24 | 128 | 19 | 14.8% | 0.97 | (0.56–1.68) | 0.50 |
| 25–29 | 344 | 66 | 19.2% | 1.32 | (0.91–1.91) | |
| 30–34 | 521 | 79 | 15.2% | 0.99 | (0.70–1.41) | |
| 35–39 | 567 | 86 | 15.2% | 0.99 | (0.71–1.40) | |
| >40 | 459 | 70 | 15.3% | 1 | ||
| Study Triplet | ||||||
| Zambia – 1 | 258 | 53 | 20.5% | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Zambia – 2 | 278 | 46 | 16.5% | 0.77 | (0.50–1.19) | |
| Zambia – 3 | 291 | 63 | 21.6% | 1.07 | (0.71–1.61) | |
| Zambia – 4 | 272 | 24 | 8.8% | 0.37 | (0.22–0.63) | |
| SA – 5 | 529 | 65 | 12.3% | 0.54 | (0.36–0.81) | |
| SA – 6 | 292 | 49 | 16.8% | 0.78 | (0.51–1.20) | |
| SA – 7 | 100 | 20 | 20.0% | 0.97 | (0.54–1.72) | |
| Socio‐economic | ||||||
| Wealth quintile | ||||||
| 1 – Lowest | 536 | 83 | 15.5% | 1 | 0.06 | |
| 2 | 426 | 70 | 16.4% | 1.07 | (0.76–1.52) | |
| 3 | 422 | 50 | 11.8% | 0.73 | (0.50–1.07) | |
| 4 | 408 | 73 | 17.9% | 1.19 | (0.84–1.68) | |
| 5 – Highest | 223 | 44 | 19.7% | 1.34 | (0.90–2.01) | |
| Missing | 5 | 5 | ||||
| Education | ||||||
| None/Primary | 558 | 84 | 15.1% | 1 | 0.04 | |
| Lower Secondary | 527 | 103 | 19.5% | 1.37 | (1.00–1.88) | |
| Upper Secondary/University | 919 | 133 | 14.5% | 0.95 | (0.71–1.28) | |
| Mobility | ||||||
| Nights away | ||||||
| No | 1685 | 249 | 14.8% | 1 | 0.002 | |
| Yes | 322 | 71 | 22.0% | 1.63 | (1.21–2.19) | |
| Behavioural | ||||||
| Alcohol Audit score‡ | ||||||
| Score 0–7 | 1771 | 253 | 14.3% | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Score 8–15 | 155 | 40 | 25.8% | 2.09 | (1.42–3.06) | |
| Score 16+ | 42 | 14 | 33.3% | 3.00 | (1.56–5.78) | |
| Drug use (past 12 months) | ||||||
| No | 1988 | 308 | 15.5% | 1 | 0.06 | |
| Yes | 22 | 7 | 31.8% | 2.55 | (1.03–6.29) | |
| HIV‐specific | ||||||
| Hiding pills | ||||||
| No | 1445 | 212 | 14.7% | 1 | 0.03 | |
| Yes | 566 | 105 | 18.6% | 1.32 | (1.02–1.71) | |
| HIV status disclosure | ||||||
| No | 61 | 12 | 19.7% | 1 | 0.42 | |
| Yes | 1959 | 308 | 15.7% | 0.76 | (0.40–1.45) | |
| Year of HIV diagnosis | ||||||
| Before 2007 | 421 | 64 | 15.2% | 1 | 0.43 | |
| 2007–2008 | 334 | 45 | 13.5% | 0.87 | (0.58–1.31) | |
| 2009–2010 | 438 | 70 | 16.0% | 1.06 | (0.73–1.53) | |
| 2011–2012 | 436 | 80 | 18.3% | 1.25 | (0.87–1.80) | |
| 2013–2014 | 275 | 47 | 17.1% | 1.15 | (0.76–1.74) | |
| First started ART | ||||||
| 1996–2005 | 130 | 20 | 15.4% | 0.87 | (0.52–1.45) | 0.46 |
| 2006–2009 | 593 | 84 | 14.2% | 0.79 | (0.59–1.06) | |
| 2010–2011 | 500 | 78 | 15.6% | 0.88 | (0.65–1.20) | |
| 2012–2013 | 797 | 138 | 17.3% | 1 | ||
LRT for the overall association of the variable with ART adherence.
Low dependence 0–7, medium dependence 8–15, high dependence 16+.
Stigma experienced in the community was more likely to be reported by those who had disclosed their HIV status to their family (OR 1.42 95% CI 1.08–1.87, P = 0.01) or friends (OR 1.38 95% CI 1.05–1.81, P = 0.02). There was little evidence that food security was associated with ART adherence (OR 1.03 95% CI 0.75–1.42, P = 0.83), but strong evidence that those experiencing HIV stigma were more likely to be food insecure than those who did not (community, OR 1.88, 95% CI 1.53–2.32, P < 0.001, internalised, OR 1.72 95% CI 1.38–2.14, P < 0.001 and health setting, OR 95% CI, P = 0.02).
Multivariable analysis was restricted to individuals with complete data on all variables (Total n = 1888; Zambia n = 1034, South Africa n = 854). After adjusting for the potential confounding effects of demographic, socio‐economic, mobility and behavioural factors and for the other domains of stigma in line with our conceptual framework, there remained strong evidence of an association between experienced community stigma and ART adherence (aOR 1.63, 95% CI 1.21−2.19, P = 0.001) but not internalised stigma and ART adherence (aOR 1.31, 95% CI 0.96–1.79, P = 0.09) or health setting stigma and ART adherence (aOR 1.05; 95% CI 0.64–1.72; P = 0.86) (Table 4).
In Zambia, there was strong evidence of an association between stigma experienced in the community poor adherence (aOR 2.03, 95% CI 1.40–2.94, P < 0.001), weak evidence of an association between internalised stigma and poor adherence (aOR 1.44; 95% CI 0.97–2.14; P = 0.09) and no evidence of an association between health setting stigma and poor adherence (aOR 0.80; 95% CI 0.39–1.65; P = 0.54) (Table 4).
In South Africa, there was a stronger association between health setting stigma and ART adherence than in Zambia, although the evidence for this association was weak (aOR 1.66 95% CI 079–3.47, P = 0.18). For community and internalised stigma, odds ratios were close to 1, and there was no evidence of associations with either (Table 4).
Although the odds of poor adherence for those reporting stigma experienced in the community were different in each country (aOR 2.03 in Zambia vs aOR 1.01 in South Africa), there was only weak evidence that these associations were different (P = 0.08). There was no evidence that the associations for health setting stigma and ART adherence (P = 0.38) and internalised stigma and ART adherence (P = 0.57) differed in Zambia and South Africa.
We conducted further analysis, restricting our outcome to individuals reporting they were currently on ART (n = 1861) and defining non‐adherence as missing pills in the previous 7 days. Findings from our adjusted models for the whole study population were similar to our primary definition of ART adherence (community stigma aOR 1.60 95% CI 1.15–2.22 P = 0.005, internalised stigma aOR 1.28 95% CI 0.90–1.81, P = 0.17; health setting stigma aOR 0.86 96% CI 0.48–1.53 P = 0.60) (Table S1).
Discussion
Among a large population sample of PLHIV reporting ever taking ART in the 21 communities included in the HPTN 071 (PopART) study in Zambia and South Africa, 16% reported one or more of missing pills in the previous seven days (12%), currently taking ART but having stopped during the previous 12 months (4%), or no longer taking ART (2%). Approximately 25% reported ever experiencing community stigma, 20% internalised stigma and 8% health setting stigma. PLHIV reporting stigma experienced in the community were more than 1.5 times more likely to report poor ART adherence than those who did not.
In Zambia, participants reporting experiences of community stigma were twice as likely to report poor adherence as those who did not, but we saw no such association in South Africa. Although there was only weak evidence that these associations were different in each country, it is also possible that they represent the different contexts. HIV stigma and poor adherence were both more common in Zambian than South African study communities. In the South Africa, a strong history of community led HIV treatment advocacy and awareness could have mitigated HIV stigma and its effect on ART adherence.
Health setting stigma was less frequently reported and may play a less important role in adherence because people generally take their pills away from a health facility. In both countries, the association between internalised stigma and ART adherence was partly explained after adjustments were made for experienced stigma in community or health settings. We hypothesised that stigma experienced in the community may itself cause internalised stigma.
Our findings are similar to previous cross‐sectional studies looking at stigma and ART adherence [19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25], yet direct comparisons are challenging due to variation in the specific measures used to look at these concepts. Variation also exists in the statistical adjustments made when investigating these associations. We made our own theoretical assumptions on factors to include in our multivariable models. Alcohol was considered a potential confounder, as it has been in other studies exploring these associations [19, 22, 33]. Some studies have, however, identified alcohol as a means of coping with HIV status [19], compromising ability to adhere to treatment. Similarly, wealth was treated as a confounding factor in our analysis, but the relationship between economic security and HIV‐related stigma is likely to be more complicated and potentially ‘mutually reinforcing’ [19]. We did not treat hiding pills and HIV status disclosure as confounders in our multivariable models as we suggest these variables lie on the causal pathway between experience of stigma and ART adherence. Including either of these variables in our models made little difference to the associations we saw between stigma and ART adherence. Hiding pills has been frequently reported in Zambia and South Africa [34] and, with strong unadjusted associations seen in this study, would be useful to explore in further work on stigma related to HIV treatment.
Ours was a large study, and we used validated measures of HIV stigma [29] and measured a large number of characteristics providing the opportunity for a thorough assessment of potential confounding. We looked at the association between three stigma ‘domains’ on adherence to ART, giving an opportunity to identify the specific areas of stigma that had the strongest associations with ART adherence. We interpreted our findings based on a conceptual framework that considered some of the latest thinking on HIV stigma, enabling wider comparison and contributing to existing work in this field. A composite measure of ART adherence was used to ensure inclusion of poor adherence over a year, in line with our stigma measures. In a systematic review of self‐report measures, seven‐day recall was most commonly used and considered effective due to the inclusion of a shorter time period, whilst covering a weekend (where adherence is often lower), but longer recall also considered important for allowing greater variability in adherence [35]. We acknowledge that our composite adherence outcome could measure slightly different concepts, but tested this using a restricted outcome in our analysis and found similar results. There were relatively few missing data.
There were also limitations. Our study communities were purposively sampled, and although we consider our findings generalisable to socio‐economically disadvantaged, peri‐urban communities with high HIV prevalence in Zambia and the Western Cape of South Africa [27, 36], the generalisability of our findings to other sub‐Saharan African settings may be limited. The greater proportion of women in our study population was reflective of the overall population cohort and the higher HIV prevalence among women (26%) than men (12%) [27], rather than a selection bias among individuals who had ever taken ART. Yet, this disparity limits the generalisability of our findings to men, who in previous research have shown worse ART adherence than women [15, 37]. Our analysis excluded individuals who were not aware of or not willing to report their HIV status and those who reported no date for starting ART. Experiences of stigma may have been different among those not willing to disclose their HIV status to our research team and may have led to an underestimation of HIV stigma and of its association with ART adherence. Underreporting of poor ART adherence was possible due to it being contrary to clinical guidance. However, the extent of underreporting to our research team was unlikely to differ according to an individual's experience of stigma, and so, it is unlikely to have introduced bias to our findings. Our findings of approximately 84% adherence are compatible with viral suppression data on a random subsample of individuals who were HIV‐positive at the time of the baseline survey; these data indicated that approximately 90% of HIV‐positive individuals who were taking ART were virally suppressed [27]. Other factors also relied on self‐report and were potentially prone to either under or over‐reporting (e.g. alcohol consumption and wealth). Stigma questions specifically relating to HIV treatment [38] may have given a more specific indication of mechanisms for non‐adherence and would be useful for consideration in future work.
Conclusions
Our analysis has provided additional evidence that HIV‐related stigma is associated with poor ART adherence and has identified the relative importance of the different types and components of stigma among a large sample of PLHIV across 21 communities in Zambia and South Africa. If we are to reach viral suppression among 90% of people on ART by 2020 and 95% by 2030, it will be important to learn whether interventions that reduce HIV stigma could also improve lifelong adherence to ART.
Supporting information
Table S1. Univariable and multivariable logistic regression estimates of odds ratios for each stigma variable and missing ART pills in the previous 7 days.
Acknowledgements
HPTN 071 (PopART) was sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) under Cooperative Agreements UM1‐AI068619, UM1‐AI068617 and UM1‐AI068613, with funding from the U.S. President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR). Additional funding was provided by the International Initiative for Impact Evaluation (3ie) with support from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, as well as by NIAID, the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) and the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), all part of the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Richard Hayes and Sian Floyd are jointly funded by the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) and the UK Department for International Development (DFID) under the MRC/DFID Concordat agreement, which is also part of the EDCTP2 programme supported by the European Union. Grant Ref: MR/R010161/1. Sarah Fidler acknowledges funding from the Imperial College National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre. The stigma ancillary study was funded by NIMH. James Hargreaves, Anne Stangl and Triantafyllos Pliakas are members of the STRIVE consortium, which produces research on the structural drivers of HIV, including stigma. The STRIVE consortium is funded by UKaid from the Department for International Development (http://strive.lshtm.ac.uk/). However, the views expressed do not necessarily reflect the department's official policies. The authors acknowledge all members of the HPTN 071 (PopART) study team.
No funding bodies had any role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIAID, NIMH, NIDA, PEPFAR, 3ie or the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Clinical Trial Number: NCT01900977
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): SDG 3 (good health and well‐being), SDG 10 (reduced inequalities), SDG 17 (partnerships for the goals)
References
- 1. Maggiolo F, Airoldi M, Kleinloog HD et al Effect of adherence to HAART on virologic outcome and on the selection of resistance‐conferring mutations in NNRTI‐ or PI‐treated patients. HIV Clin Trials 2007: 8: 282–292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Bangsberg DR. Less than 95% adherence to nonnucleoside reverse‐transcriptase inhibitor therapy can lead to viral suppression. Clin Infect Dis 2006: 43: 939–941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Gardner EM, McLees MP, Steiner JF, Del Rio C, Burman WJ. The spectrum of engagement in HIV care and its relevance to test‐and‐treat strategies for prevention of HIV infection. Clin Infect Dis 2011: 52: 793–800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. De Cock KM, Crowley SP, Lo YR, Granich RM, Williams BG. Preventing HIV transmission with antiretrovirals. Bull World Health Organ 2009: 87: 488–488A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Attia S, Egger M, Muller M, Zwahlen M, Low N. Sexual transmission of HIV according to viral load and antiretroviral therapy: systematic review and meta‐analysis. AIDS 2009: 23: 1397–1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Baggaley RF, White RG, Hollingsworth TD, Boily MC. Heterosexual HIV‐1 infectiousness and antiretroviral use systematic review of prospective studies of discordant couples. Epidemiology 2013: 24: 110–121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Cohen MS, Chen YQ, McCauley M et al Prevention of HIV‐1 infection with early antiretroviral therapy. N Engl J Med 2011: 365: 493–505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. WHO . HIV Drug Resistance Report 2017. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 9. UNAIDS . Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. 90‐90‐90 An ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS: Geneva; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Ministry of Health Zambia . Zambia Population‐Based HIV Impact Assessment (ZAMPHIA) 2016: Final Report. Ministry of Health: Lusaka, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 11. Joseph Davey D, Abrahams Z, Feinberg M et al Factors associated with recent unsuppressed viral load in HIV‐1‐infected patients in care on first‐line antiretroviral therapy in South Africa. Int J Std AIDS 2018: 29: 603–610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Shubber Z, Mills EJ, Nachega JB et al Patient‐reported barriers to adherence to antiretroviral therapy: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. PLoS Medicine 2016: 13: e1002183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Croome N, Ahluwalia M, Hughes LD, Abas M. Patient‐reported barriers and facilitators to antiretroviral adherence in sub‐Saharan Africa. AIDS 2017: 31: 995–1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Mills EJ, Nachega JB, Bangsberg DR et al Adherence to HAART: a systematic review of developed and developing nation patient‐reported barriers and facilitators. PLoS Medicine 2006: 3: e438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Heestermans T, Browne JL, Aitken SC, Vervoort SC, Klipstein‐Grobusch K. Determinants of adherence to antiretroviral therapy among HIV‐positive adults in sub‐Saharan Africa: a systematic review. Bmj Glob Health 2016: 1: e000125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Mackworth‐Young CR, Bond V, Wringe A et al "My mother told me that I should not": a qualitative study exploring the restrictions placed on adolescent girls living with HIV in Zambia. J Int AIDS Soc 2017; 20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Langebeek N, Gisolf EH, Reiss P et al Predictors and correlates of adherence to combination antiretroviral therapy (ART) for chronic HIV infection: a meta‐analysis. BMC Med 2014: 12: 142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Hargreaves JR, Krishnaratne S, Mathema H et al Individual and community‐level risk factors for HIV stigma in 21 Zambian and South African communities: analysis of data from the HPTN071 (PopART) study. AIDS 2018: 32: 783–793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Katz IT, Ryu AE, Onuegbu AG et al Impact of HIV‐related stigma on treatment adherence: systematic review and meta‐synthesis. J Int AIDS Soc 2013: 16(3 Suppl 2): 18640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Sweeney SM, Vanable PA. The association of HIV‐related stigma to HIV medication adherence: a systematic review and synthesis of the literature. AIDS Behav 2016: 20: 29–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Diiorio C, McCarty F, Depadilla L et al Adherence to antiretroviral medication regimens: a test of a psychosocial model. AIDS Behav 2009: 13: 10–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Boyer S, Clerc I, Bonono CR, Marcellin F, Bile PC, Ventelou B. Non‐adherence to antiretroviral treatment and unplanned treatment interruption among people living with HIV/AIDS in Cameroon: Individual and healthcare supply‐related factors. Soc Sci Med 2011: 72: 1383–1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Rao D, Feldman BJ, Fredericksen RJ et al A structural equation model of HIV‐related stigma, depressive symptoms, and medication adherence. AIDS Behav 2012: 16: 711–716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Nachega JB, Stein DM, Lehman DA et al Adherence to antiretroviral therapy in HIV‐infected adults in Soweto, South Africa. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 2004: 20: 1053–1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Morojele NK, Kekwaletswe CT, Nkosi S. Associations between alcohol use, other psychosocial factors, structural factors and antiretroviral therapy (ART) adherence among South African ART recipients. AIDS Behav 2014: 18: 519–524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Hayes R, Ayles H, Beyers N et al HPTN 071 (PopART): rationale and design of a cluster‐randomised trial of the population impact of an HIV combination prevention intervention including universal testing and treatment – a study protocol for a cluster randomised trial. Trials 2014: 15: 57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Hayes RJ, Donnell D, Floyd S et al Effect of universal testing and treatment on HIV incidence – HPTN 071 (PopART). N Engl J Med 2019: 381: 207–218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Hargreaves JR, Stangl A, Bond V et al HIV‐related stigma and universal testing and treatment for HIV prevention and care: design of an implementation science evaluation nested in the HPTN 071 (PopART) cluster‐randomized trial in Zambia and South Africa. Health Policy Plan 2016: 31: 1342–1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Stangl AL, Sievwright K, Bell‐Mandla N et al Development of parallel measures to assess HIV stigma and discrimination among people living with HIV, community members and health workers in the HPTN 071 (PopART) trial in Zambia and South Africa. J Int AIDS Soc 2019: 22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Babor JC, Higgins‐Biddle JB, Saunders MG, Monteiro TF. The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test Guidelines for Use in Primary Care. World Health Organization: Geneva, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 31. Victora CG, Huttly SR, Fuchs SC, Olinto MT. The role of conceptual frameworks in epidemiological analysis: a hierarchical approach. Int J Epidemiol 1997: 26: 224–227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Stangl A, Brady L, Fritz K. STRIVE Technical Brief: Measuring HIV stigma and discrimination. International Center for Research on Women: Washington DC, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 33. Do NT, Phiri K, Bussmann H, Gaolathe T, Marlink RG, Wester CW. Psychosocial factors affecting medication adherence among HIV‐1 infected adults receiving combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) in Botswana. Aids Res Hum Retrov 2010: 26: 685–691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Bond V, Nomsenge S, Mwamba M et al “Being seen” at the clinic: Zambian and South African health worker reflections on the relationship between health facility spatial organisation and items and HIV stigma in 21 health facilities, the HPTN 071 (PopART) study. Health Place 2019: 2018: 87–99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Simoni JM, Kurth AE, Pearson CR, Pantalone DW, Merrill JO, Frick PA. Self‐report measures of antiretroviral therapy adherence: A review with recommendations for HIV research and clinical management. AIDS Behav 2006: 10: 227–245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Perriat D, Balzer L, Hayes R et al Comparative assessment of five trials of universal HIV testing and treatment in sub‐Saharan Africa. J Int AIDS Soc 2018: 21: e25048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Maqutu D, Zewotir T. Optimal HAART adherence over time and time interval between successive visits: their association and determinants. Aids Care 2011: 23: 1417–1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Cama E, Brener L, Slavin S, de Wit J. The impact of HIV treatment‐related stigma on uptake of antiretroviral therapy. Aids Care 2015: 27: 739–742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1. Univariable and multivariable logistic regression estimates of odds ratios for each stigma variable and missing ART pills in the previous 7 days.


