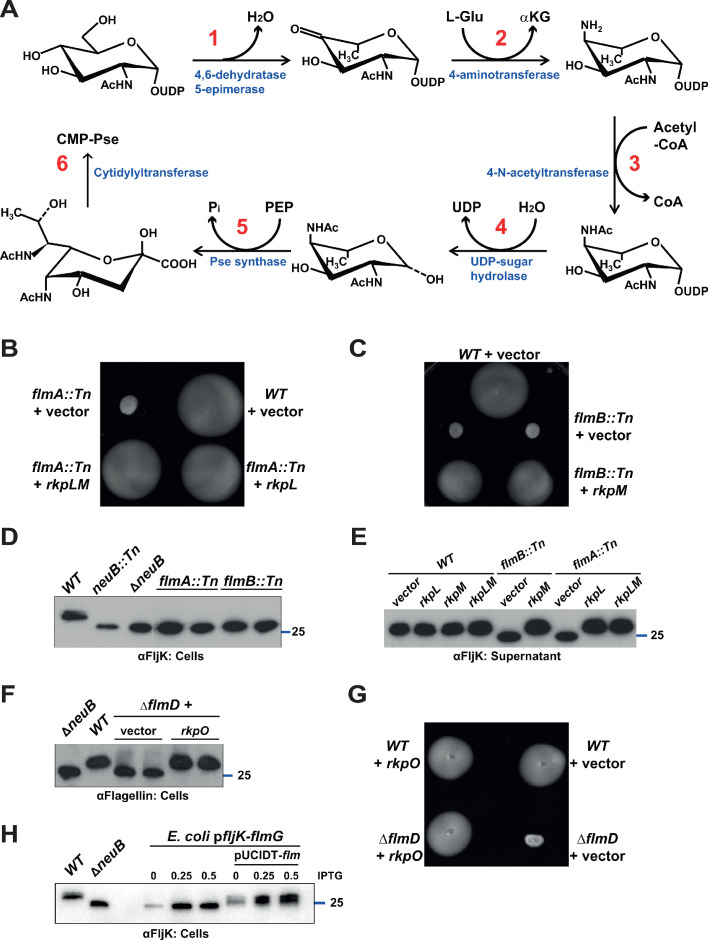
Figure 5. Pseudaminic acid biosynthetic pathway in C. crescentus.
(A) Schematic of the pseudaminic acid biosynthetic pathway as it has been described in C. jejuni and H. pylori (reviewed in Salah Ud-Din and Roujeinikova, 2018). The different steps are catalyzed by PseB (1), PseC (2), PseH (3), PseG (4), PseI (5), and PseF (6). (B) Motility assay of WT and flmA::Tn cells expressing S. fredii NGR234 rkpL and rkpM from Pvan ona plasmid. (C) Motility assay of WT and flmB::Tn cells expressing S. fredii NGR234 rkpM from Pvan on a plasmid. (D) Immunoblots of extracts from WT and mutant cells probed with polyclonal anti-FljK antibodies on whole cell lysates. Flagellins produced by flmA::Tn and flmB::Tn cells show the same migration profile as in ΔneuB mutant cells. The blue line indicates the migration of the molecular size standard, with the corresponding size in kDa. (E) Immunoblots of supernatants from WT, flmA::Tn and flmB::Tn cells probed with polyclonal anti-FljK antibodies. The expression of the S. fredii homologs RkpL and RkpM from Pvan on a plasmid restores the migration profile and secretion of flagellin in flmA::Tn and flmB::Tn cells, respectively. The blue line indicates the migration of the molecular size standard, with the corresponding size in kDa. (F) Immunoblot of extracts from WT and ΔflmD cells. Mutation of flmD impairs post-translational flagellin modification, and the defect is complemented by the expression of the S. fredii NGR234 homologue RkpO from a plasmid. The blue line indicates the migration of the molecular size standard, with the corresponding size in kDa. Note that antibodies used in this blot were raised against flagellins purified from C. crescentus (αFlagellins; Hahnenberger and Shapiro, 1987). (G) Motility assay of WT and ΔflmD cells expressing S. fredii NGR234 RkpO from Pvan on a plasmid. (H) Immunoblot with anti-FljK antibodies on whole cell lysates from E. coli expressing fljK and flmG from Plac on a plasmid, in the presence or absence of a compatible plasmid carrying the complete set of Caulobacter genes for the pseudaminic acid biosynthetic pathway (pUCIDT-flm, see Materials and methods and Supplementary file 1 Table S3). In the absence of pUCIDT-flm, FljK shows the same migration profile as in Caulobacter ΔneuB cells, whereas in the presence of pUCITD-flm FljK migration is shifted toward higher molecular mass, as in Caulobacter WT cells. The values above the panel indicate the concentration of the inducer for Plac-fljK-flmG (mM IPTG). The blue line indicates the migration of the molecular size standard, with the corresponding size in kDa.