Abstract
Specific gene expression in granulosa cells is key for the function of ovary, but the molecular mechanism of transcriptional activation is not well studied. Here we investigated the regulatory mechanism of the mouse stearoyl-CoA desaturase 2 (Scd2) gene encoding an enzyme for lipid metabolism. Northern blot and in situ hybridization indicated that the mouse Scd2 mRNA was highly expressed in ovarian granulosa cells. We found four conserved noncoding sequences (CNSs) and two long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) transcribed from regions upstream of the Scd2 gene as candidates of regulatory elements/factors. These lncRNAs were predominantly transcribed in the opposite direction to Scd2 and localized in nuclei and showed the correlation with Scd2 expression, raising the possibility of their transcriptional regulatory roles. Indeed, knockdown of both lncRNAs, lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2, significantly decreased the Scd2 mRNA level in primary granulosa cells. Then, we investigated the histone modification pattern at this locus by a chromatin immunoprecipitation assay, and two CNSs, CNS1 and CNS2, were found to be marked with high levels of histone H3K9/K27 acetylation in primary granulosa cells. By a reporter gene assay, both CNS1 and CNS2 interdependently exhibited enhancer activity for the Scd2 promoter in primary granulosa cells. These data suggest that the mouse Scd2 gene is activated by two lncRNAs and interdependent enhancers in ovarian granulosa cells, which provides a new insight into transcriptional activation in granulosa cells.
Keywords: Granulosa cell, Histone acetylation, Interdependent enhancer, Long noncoding RNA, Ovary, Stearoyl-CoA desaturase
Tissue or cell characteristics are determined by specific patterns of gene expression, which is strictly controlled by mechanisms involving cis-regulatory elements (e.g. promoters, enhancers, and dual promoter‒enhancers) and trans-regulatory factors (e.g. transcription factors) [1,2,3,4]. The cis-regulatory elements are epigenetically controlled in ways that several types of histone modifications loosen the chromatin encompassing the element, which allows transcription factors to bind and activate gene transcription [5]. In addition, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) often bind to the chromatin at cis-regulatory elements and function in transcriptional regulation [6,7,8]. How these elements/factors coordinate to regulate gene transcription is different depending on tissues or cell types or different between genes in one cell type. Thus, a detailed understanding of transcriptional activation of each gene in each tissue or cell type is of great importance, but only a small number of studies reported the mechanism in some tissues such as granulosa cells in the ovary.
The ovary is an organ to generate oocytes, and granulosa cells surround an oocyte in a follicle. Various genes are specifically expressed in granulosa cells and play essential roles in the progression of meiosis, oocyte maturation, follicular development, and ovulation [9,10,11], indicating the importance of gene regulation in this cell type. Nonetheless, the mechanism of transcriptional activation, especially the involvement of enhancers and lncRNAs, is not well understood in granulosa cells. We previously reported mechanisms of two genes that are functionally unrelated but highly expressed in mouse granulosa cells. The prolyl oligopeptidase (Prep) gene is ubiquitously expressed at different levels and the highest expression is observed in granulosa cells [12]. This robust transcription partly attributes to a potential enhancer overlapping with a CpG island and lncRNA transcribed downstream of the Prep gene [12, 13]. The anti-Müllerian hormone type II receptor (Amhr2) gene is specifically expressed in ovarian granulosa cells and testicular Sertoli and Leydig cells. An lncRNA, lncRNA-Amhr2, is transcribed upstream of the Amhr2 gene and participates in its activation by enhancing promoter activity in granulosa cells [14]. These suggest that transcriptional activation in granulosa cells requires enhancers and/or lncRNAs, irrespective of the tissue specificity and function of genes.
To gain more insights into the gene activation in granulosa cells, here we focused on stearoyl-CoA desaturase 2 (Scd2) gene. The Scd2 gene was identified as a gene which was upregulated during adipocyte differentiation [15]. It encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the desaturation of fatty acid and is required for lipid synthesis during skin and liver development in embryo [16]. In the ovary, saturated free fatty acids have negative effects on oocyte maturation and follicular development, and the SCD enzymes alleviate the toxicity by metabolizing them [17, 18]. Because the Scd2 gene is expressed at high levels in rat granulosa cells, it is considered to play a major role in weakening the toxicity of saturated free fatty acids during oogenesis [19]. The transcriptional regulation was reported in mouse adipocytes and brain; SREBP1a and EGR2 bind to the Scd2 promoter and enhance its activity [20, 21]. However, the regulatory mechanism in granulosa cells is unclear.
In this study, we attempted to identify cis-regulatory elements and lncRNAs that were responsible for Scd2 gene activation in granulosa cells and found interdependent enhancers and two lncRNAs that possibly functioned in activation of this gene.
Materials and Methods
Animals
Mice (C57B/6 or BDF1) were kept at 25°C with a photoperiod 14 h light and 10 h dark, and food and water were freely accessed. Experimental procedures used in this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Use and Care Committee at Hokkaido University.
Northern blot analysis
Northern blot was performed as previously described [12]. Briefly, total RNAs were isolated from each tissue using ISOGEN (Nippongene, Tokyo, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Twenty micrograms of the RNA were electrophoresed on an agarose gel containing formaldehyde and transferred to a nylon membrane. The membrane was hybridized with radio-labelled probes and detected by autoradiography.
Probes were prepared as follows. Scd2 and Actb sequences were amplified by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) with total RNA from the testis using primers shown in Table 1. The products were subcloned into a pBluescript II KS+ vector (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA) and checked by DNA sequencing. The fragments were cut out from the vector by digestion with SmaI/SalI for Scd2 and EcoRI/HindIII for Actb and purified with a Geneclean kit. Due to high sequence homology, the Actb probe also hybridized with Actg1 and Actg2 mRNAs.
Table 1. Oligo DNAs used in this study.
| Designation | Forward | Reverse | |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Probe for Northern blot] | |||
| Scd2 | GGTGGCAACTGAGGAACTTCG | TTGTGGGCACGACCATCATC | |
| Actb | ACATCCGTAAAGACCTCTATG | TAAAACGCAGCTCAGTAACAGT | |
| [RT-PCR] | |||
| lncRNA-sc2 | TGTGGAGCCTCTGTATTCCTGC | TCCACCTGCTGCTGATACAAGT | |
| lncRNA-sc1 | AGCTGCAAGATGCCATTCCT | CCATCCCTTGAGCTCACAAC | |
| -6kb | CTTTCTGCTCAGAAACATTTG | GTTTTTGCTTGTCAATCCAA | |
| CNS1 | GGAGATACAGTAATGGGGTGACC | TTGCCCATTCACACTGGTCTGG | |
| CNS3 | CACGTGCACATACAAAGATGGA | CCCACTTGGTCTGGATTTATCC | |
| Scd2 | GACATTAATACCCCACTGCCA | GCTCCCCAGTGGTGAGAACTCT | |
| Gapdh | CATGACCACAGTCCATGCCATC | TAGCCCAAGATGCCCTTCAGTG | |
| [Strand-specific RT] | |||
| RT for lncRNA-sc2 | CAAAAGCTCTGCAAGCTGACA | TGGCAGGTCCTTGTAAGAGAAATC | |
| RT for lncRNA-sc1 | AACCAGGCAAGACTAGAC | CCATCCCTTGAGCTCACAAC | |
| [qRT-PCR] | |||
| lncRNA-sc1 | AGCTGCAAGATGCCATTCCT | AGGCCAGCCTGGTCTACATCAT | |
| lncRNA-sc2 | TGACACAGGCTGGAGTTATC | TCCACCTGCTGCTGATACAAGT | |
| Scd2 | ACCCTTTGTCGCTGAGGTCTGAAG | GATTGTGGTGGTGGCTGAGTAAGC | |
| Prep | GGAATCGATGCTGCTGATTA | CCATCCAGCTTTATGCCTTT | |
| Gapdh | CATGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTA | CCTGCTTCACCACCTTCTTGA | |
| [shRNA construct] | |||
| shlncRNAsc1 | GATCCGAACAAAGTCCACTAGAAACCGTGTGCT GTCCGGTTTCTAGTGGACTTTGTTCTTTTTTA | AGCTTAAAAAAGAACAAAGTCCACTAGAAACCG GACAGCACACGGTTTCTAGTGGACTTTGTTCG | |
| [ChIP] | |||
| Aip promoter | GGGCTTCAGCACAGAATCCA | TGAAAAATCCTGAGAGCCTCATT | |
| lncRNA-sc2 | CAAAAGCTCTGCAAGCTGACA | GGGATCTCCTCAGCGAGTCTT | |
| lncRNA-sc1 | AGCTGCAAGATGCCATTCCT | GGCCCATCACAGGCTGTTTA | |
| CNS1 | GTGAGCCAGGCCTGCAAT | GCATTTCCTGAGACCAAACCA | |
| Scd2 promoter | GTGAGAAGCCAGGAGCAGAAA | TCGTCCTGCTGCTCTCATTG | |
| CNS2 | GTGATGCAGGGCTCTGGTTAC | TCCCAACTCCCGTACCTCCTA | |
| CNS3 | CACGTGCACATACAAAGATGGA | CCCACTTGGTCTGGATTTATCC | |
| [Reporter construct] | |||
| Scd2 promoter | ATGGTCTCCCACCTTTTCTTCC | TGCAGACACCAACACCGCATT | |
| CNS2 | TCCTGTAGGAGGTACGGGAGTT | CTGACACCCTCCCCCTATTTGC | |
| CNS1 mutation | GCCATTTGCTGAGGACACCTGGCCTGG CATCTCTCTTCTTG | CAAGAAGAGAGATGCCAGGCCAGGTGT CCTCAGCAAATGGC | |
Scd2, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 2; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; qRT-PCR, quantitative RT-PCR; CNS, conserved noncoding sequence.
In situ hybridization
Four-week-old female mice were administrated with pregnant mare serum gonadotropin, and 48 h later, with human chorionic gonadotropin. Ovaries were collected 6 h after the injection of human chorionic gonadotropin, embedded in TissueTek, and frozen. Ten-micrometer sections were prepared, and in situ hybridization was performed as previously described [12]. We labeled the same Scd2 sequence as used in Northern blot with digoxigenin by in vitro transcription in both directions and used as sense and antisense probes.
Cell culture
Primary granulosa cells were obtained and cultured as previously described [12, 14]. Briefly, ovaries were collected from immature female mice administrated with hormones as above 5 h after human chorionic gonadotropin injection, and preantral follicles were punctured with a 26G needle. The granulosa cells were spread onto 24-well plates or 35-mm dishes that were coated with fibronectin, and cultured in Dulbecco modified Eagles medium/F12 containing 10% fetal bovine serum.
Hepa1-6 cells (RCB1638; Riken Bioresource Center, Tsukuba, Japan) derived from mouse hepatic tumor were cultured in Dulbecco modified Eagles medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum.
RT-PCR
Total RNAs from cells and tissues were purified as above. Nuclear and cytoplasmic RNAs were isolated by a method using NP-40 lysis buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, 10 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.5% NP-40, pH 7.5) for cell lysis as previously described [13]. RNA isolation, DNase I treatment, RT-PCR, and quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) were performed as previously described [12, 13, 22, 23]. The transcriptional direction was determined by qRT-PCR using gene-specific primers for reverse transcription. Primers are listed in Table 1.
Knockdown of lncRNA-sc1 by shRNA
Short hairpin RNA (shRNA) constructs were generated by annealing oligonucleotides (Table 1) and inserting them into a pBAsi-mU6 Neo DNA vector (Takara, Kusatsu, Japan) that was digested with BamHI and HindIII. The constructs were transfected into primary granulosa cells using GeneJuice transfection reagent (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Twenty-four hours later, 1 mg/ml G418 was added to the medium and cultured for 4 days, changing the medium every day. Total RNAs were isolated using ISOGEN II (Nippongene) according to the manufacture’s protocol.
Knockdown of lncRNA-sc2 by antisense oligonucleotide
Because shRNAs did not reduce the lncRNA-sc2 expression, this lncRNA was knocked down by the 2’4’-bridged nucleic acid (2’,4’-BNA) gapmer type of antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) with fully phosphorothioated linkage, which was generated by Hokkaido System Science (Sapporo, Japan). The ASO sequences were 5’-ATGTGATCGCGCTTCT-3’ for the control (complementary to EGFP sequence) and 5’-GGATATCAGTCGTTCC-3’ for the knockdown, and two nucleotides at each end were 2’,4’-BNA. Each ASO was transfected into primary granulosa cells using LipoTrust Ex Oligo (Hokkaido System Science) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Two days later, the cells were collected with ISOGEN II (Nippongene) and total RNAs were purified.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay
ChIP assay for histone acetylation was performed as previously described [12]. The antibody against acetylated histone H3 lysine 9 and lysine 27 (H3K9/K27ac) was kindly gifted by Dr Hiroshi Kimura at Tokyo Institute of Technology [24]. Primer sequences for quantitative PCR (qPCR) are listed in Table 1.
Reporter constructs
2.4kPr: The transcriptional start site (TSS) of mouse Scd2 gene was reported in the DBTSS database (https://dbtss.hgc.jp/). A 2377-bp Scd2 promoter sequence was obtained by PCR with genome DNA and KOD FX (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan) using a primer pair shown in Table 1, and subcloned into a pBluescript II KS + vector. After we confirmed the sequence by DNA sequencing, the promoter was cut out by digestion with EcoRI and HindIII, blunted by T4 DNA polymerase (Takara), and inserted into pGL3-Basic (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) at the SmaI site.
0.6kPr: 2.4kPr was digested with SacI and self-ligated.
1.3kPr: 2.4kPr was digested with MluI and BstXI, blunted and self-ligated. The BstXI site was located in the 147-bp CNS1 sequence, and the 1.3-kb promoter contained a 57-bp sequence of CNS1.
1.3kPr-CNS2: The CNS2 sequence was amplified by genomic PCR with the primer pair shown in Table 1, and inserted into 1.3kPr at the blunted BamHI site. The sequence was checked by DNA sequencing.
2.4kPr-CNS2: The CNS2 sequence was amplified as above and inserted into 2.4kPr at the blunted BamHI site. The sequence was checked by DNA sequencing.
2.4kΔCNS1Pr: The first PCR reactions were done with a sense primer of Scd2 Promoter and an antisense primer of CNS1 mutation and with a sense primer of CNS1 mutation and an antisense primer of Scd2 Promoter (Table 1). The products were purified, mixed and subjected to 2 cycles of PCR without additional primers, followed by 30 cycles of PCR with sense and antisense primers of Scd2 Promoter. The product was inserted into pGL3-Basic at the SmaI site and checked by DNA sequencing.
2.4kΔCNS1Pr-CNS2: The CNS2 sequence was amplified as above and inserted into 2.4kΔCNS1Pr at the blunted BamHI site. The sequence was checked by DNA sequencing.
Reporter gene assay
Luciferase activity assay was performed as previously described [12]. Briefly, each construct was transfected into primary granulosa cells or Hepa1-6 cells using Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) together with the pRL-CMV vector (Promega) according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Two days later, luciferase activity was measured using a Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay system (Promega).
Statistical analysis
The data are presented as means ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical significance was assessed by Student t test or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey-Kramer test. The P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Mouse ovarian granulosa cells express Scd2 mRNA at a high level
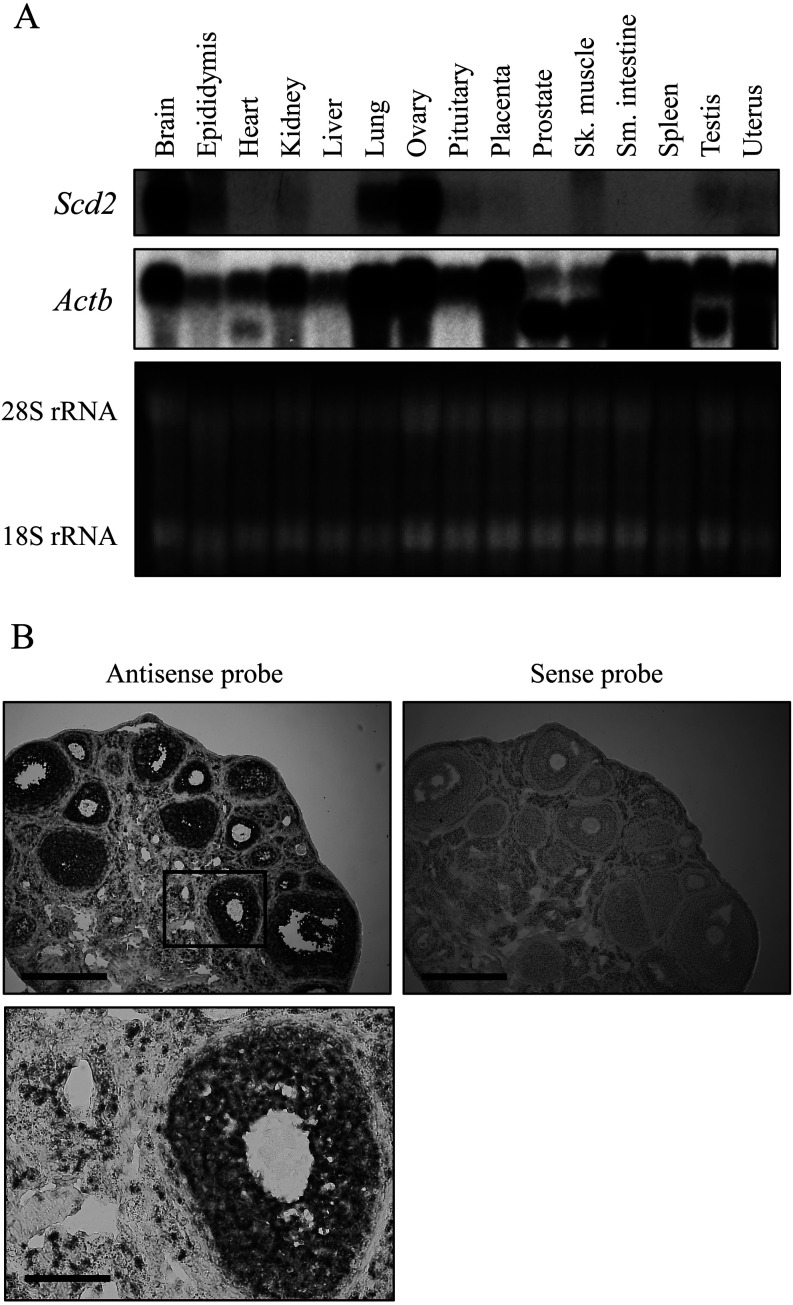
We first investigated the expression pattern of mouse Scd2 mRNA to confirm the tissue specificity of this gene. Northern blot analysis, using 15 tissues from adult mice, showed strong signals in brain and ovary and detected fainter bands in several tissues (Fig. 1A), which was consistent with a previous result in rats [19]. Then, we checked the localization of Scd2 mRNA in the ovary by in situ hybridization with superovulated mouse ovaries. The signal was observed specifically in granulosa cells with the antisense probe whereas the sense probe did not hybridize with any cells in the section (Fig. 1B). These data indicate that the mouse Scd2 gene is highly expressed in ovarian granulosa cells.
Fig. 1.
Mouse stearoyl-CoA desaturase 2 (Scd2) mRNA expression. (A) Northern blot analysis of Scd2 in various mouse tissues. Twenty micrograms of total RNAs from 15 tissues were electrophoresed on a denaturing agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide (bottom). The gel was blotted to a nylon membrane and hybridized with a 32P-labeled Scd2 or Actb probe. The signals were detected by autoradiography (top and middle). The probe for Actb cross-hybridized to Actg1 and Actg2 due to high sequence homology, and the upper band is the signal of Actb and Actg1 and the lower band is that of Actg2. Intense Scd2 signal was observed in brain and ovary. (B) In situ hybridization analysis of Scd2 in the mouse ovary. Frozen sections (10 µm) from an ovary of a superovulated mouse were hybridized with a digoxigenin-labeled antisense or sense cRNA probe. A region marked in a box in the upper panel is shown at higher magnification at the bottom. The scale bar represents 400 µm in upper panels and 100 µm in a lower panel.
Identification of conserved noncoding sequences at the Scd2 gene locus
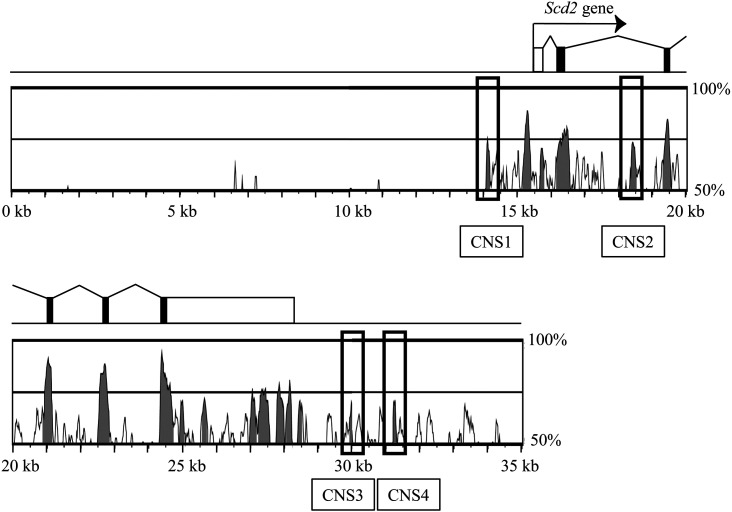
To identify cis-regulatory elements for Scd2 gene activation, we searched for conserved noncoding sequences (CNSs) that are evolutionarily conserved between species and often overlap with transcriptional regulatory elements. We compared the genome sequence at the mouse Scd2 locus with that at the human SCD1 locus, given that only the SCD1 gene is present in human in contrast to four paralogous Scd genes in rodents [25]. The mVista program (http://genome.lbl.gov/vista/index.shtml) identified four non-exonic sequences conserved in a 35-kb mouse genome encompassing 15-kb upstream and 7-kb downstream of Scd2 gene. To identify cis-regulatory sequences outside the promoter, a conserved region just upstream of the Scd2 gene was excluded. We designated the four conserved sequences as CNS1-CNS4 (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Conserved noncoding sequences (CNSs) at the stearoyl-CoA desaturase 2 (Scd2) locus. A 35-kb sequence of the mouse Scd2 locus was compared with the corresponding region of the human SCD1 locus. The mouse Scd2 locus is depicted by rectangles indicating exons. White rectangles are 5’ and 3’ untranslated regions, and black shows the coding region. Below the gene structure, the sequence homology is shown. Highly conserved regions are painted with grey, and the grey regions not overlapping with Scd2 promoter or exons are CNSs. Four CNSs were found at this locus and named CNS1-CNS4 as indicated.
Noncoding transcription at the Scd2 gene locus
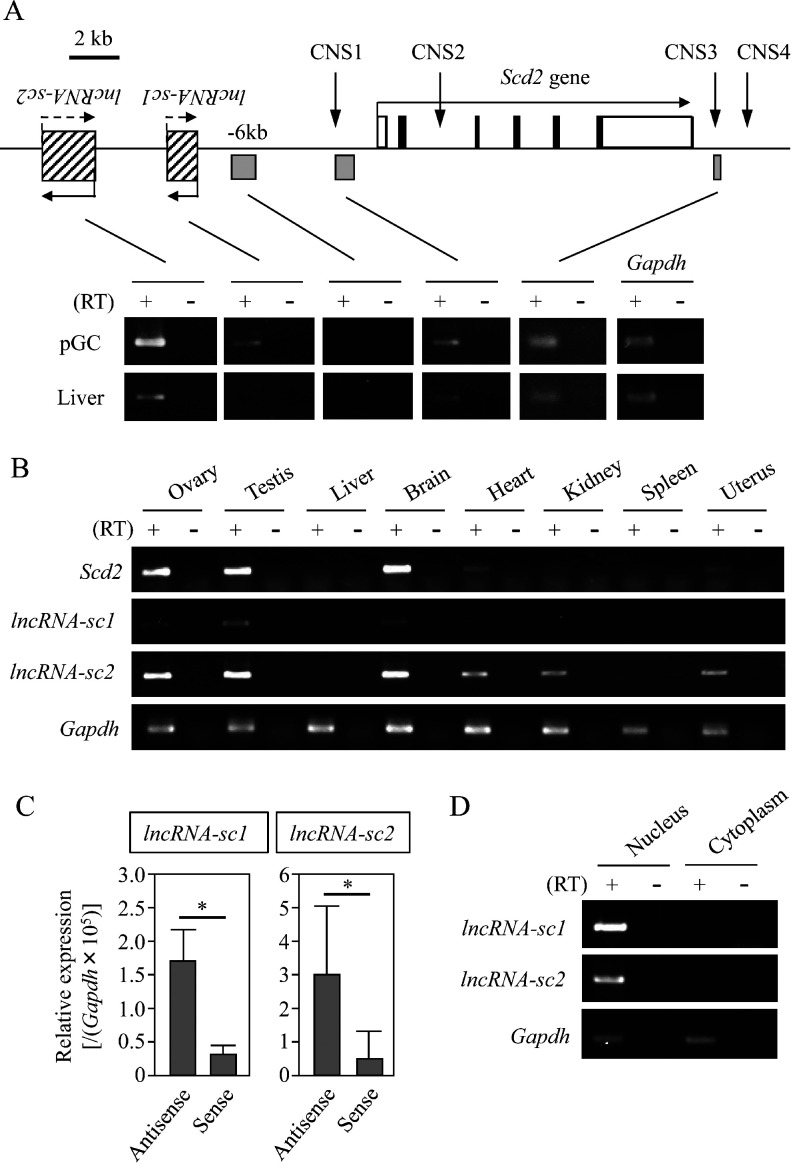
We next examined whether any regions upstream or downstream of the mouse Scd2 gene were transcribed by RT-PCR with total RNAs from liver and primary granulosa cells. Based on the Long-RNA-seq database from ENCODE/Cold Spring Harbor Lab (GEO accession number: GSM900195 and GSM900183), a 15-kb upstream region of the Scd2 gene was explored together with CNS1 and CNS3. CNS2 was not examined because it is so difficult to distinguish whether CNS2 is transcribed by itself or as a part of Scd2 gene expression. CNS4 was not examined, either, because the entire region overlapped with repeat sequences. Intriguingly, noncoding transcripts were detected in both tissues for CNS1 and CNS3, while two upstream regions were exclusively or predominantly transcribed in granulosa cells (Fig. 3A). We named these transcripts lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 and further characterized them.
Fig. 3.
Noncoding transcription at the stearoyl-CoA desaturase 2 (Scd2) locus. (A) The structure of the mouse Scd2 locus is depicted. The Scd2 gene is drawn as in Fig. 2. At upstream of the Scd2 gene, two lncRNAs are shown by striped rectangles, and the other amplified regions are indicated with grey rectangles below the genome structure. RT-PCR was performed with the oligo(dT) primer and total RNAs from primary granulosa cells (pGC) and the liver. The products were separated on an agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide. The cycle number was 35 for both tissues. Gapdh was amplified as an internal control and the cycle number for this gene was 30. Two lncRNAs are predominantly or specifically expressed in pGC. (B) Tissue specificity of lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 was investigated by RT-PCR with the oligo(dT) primer and total RNAs isolated from 8 mouse tissues. Scd2 and Gapdh genes were also detected for comparison and as a control, respectively. The cycle numbers were 35 for two lncRNAs, 25 for Scd2, and 22 for Gapdh. (C) The transcriptional direction of lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 was investigated by strand-specific qRT-PCR. cDNAs were synthesized with a sense or antisense primer specific to each lncRNA sequence, and qPCR was performed to measure the levels of antisense and sense transcripts of these lncRNAs. Antisense transcripts were detected at significantly higher levels for both lncRNAs. The data are presented as mean ± SD from three or four independent experiments, and the statistical significance was analyzed by Student’s t test. * P < 0.05. (D) Subcellular localization of lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2. Primary granulosa cells were fractionated into nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, and total RNAs were purified from both samples. RT-PCR was performed using the oligo(dT) primer for reverse transcription. Gapdh was amplified as a control to amplify a sequence within exon 6. The cycle numbers were 40 for two lncRNAs and 22 for Gapdh. Both lncRNAs were detected in the nuclear fraction.
The tissue specificity of lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 was examined by RT-PCR with 8 mouse tissues, and the signals of both lncRNAs were detected in ovary, testis, and brain, similarly to Scd2 mRNA (Fig. 3B). The transcriptional direction was determined by qRT-PCR using strand-specific primers for reverse transcription. The result indicated that both lncRNAs were transcribed in both directions, but more RNAs were in the antisense direction (Fig. 3C). The transcription level of antisense strand was 5.2-fold and 4.9-fold higher than that of sense for lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 respectively. The subcellular localization was also investigated by performing RT-PCR with total RNAs from nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of granulosa cells. Both lncRNAs were present only in the nucleus, and no cytoplasmic signal was observed (Fig. 3D). Collectively, lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 transcription were correlated with Scd2 expression, and both of them were localized in the nucleus of granulosa cells. This raised the possibility that these lncRNAs were involved in the Scd2 gene activation in the ovary.
Both lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 contributes to Scd2 gene activation
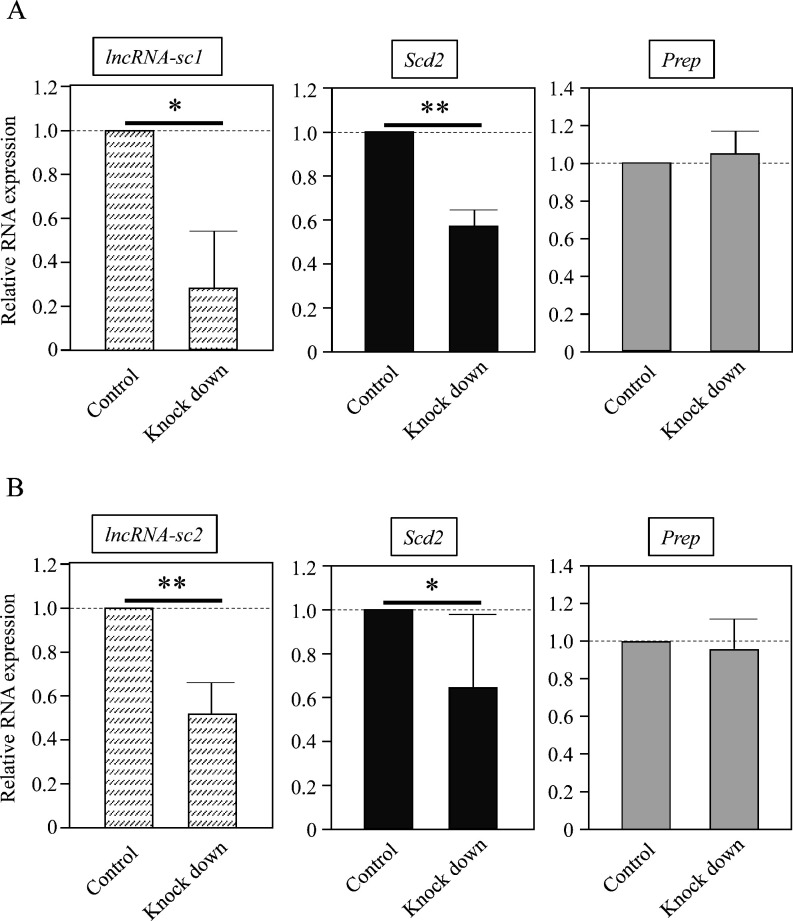
To see whether the two lncRNAs were involved in the regulation of the Scd2 gene, we attempted to knock them down. The knockdown with shRNA was only successful for lncRNA-sc1, and we used the 2’,4’BNA gapmer type of ASO for lncRNA-sc2. By transfection with shRNA or ASO into primary granulosa cells, the level of lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 was decreased by 70% and 47%, respectively (Fig. 4). These knockdowns caused 45% and 36% significant reductions in the Scd2 mRNA level compared to the control, while off-target knockdown of Prep mRNA was not observed by shRNA or ASO, suggesting the successful knockdown of specific lncRNAs (Fig. 4). These results raise the possibility that both lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 contribute to Scd2 gene activation in mouse granulosa cells.
Fig. 4.
Knockdown of lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 in primary granulosa cells. (A) Primary granulosa cells were transfected with a vector containing shRNA for lncRNA-sc1 (Knock down) or a control vector (Control). After selection with G418, total RNAs were purified and the expression of lncRNA-sc1, Scd2, and Prep was investigated by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR). The level was normalized to Gapdh, and the value in the control sample was set to 1.0. Successful knockdown of lncRNA-sc1 significantly decreased stearoyl-CoA desaturase 2 (Scd2) expression. The data are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments, and the statistical significance was analyzed by Student’s t test. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01. (B) Primary granulosa cells were transfected with the 2’,4’BNA gapmer type of ASO for lncRNA-sc2 (Knock down) or EGFP (Control), and total RNAs were isolated two days later. The expression of lncRNA-sc2, Scd2, and Prep was investigated and presented as in (A). The knockdown of lncRNA-sc2 significantly reduced Scd2 expression. The data are presented as mean ± SD from six independent experiments, and the statistical significance was analyzed by Student’s t test. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01.
Histone acetylation pattern at the Scd2 locus
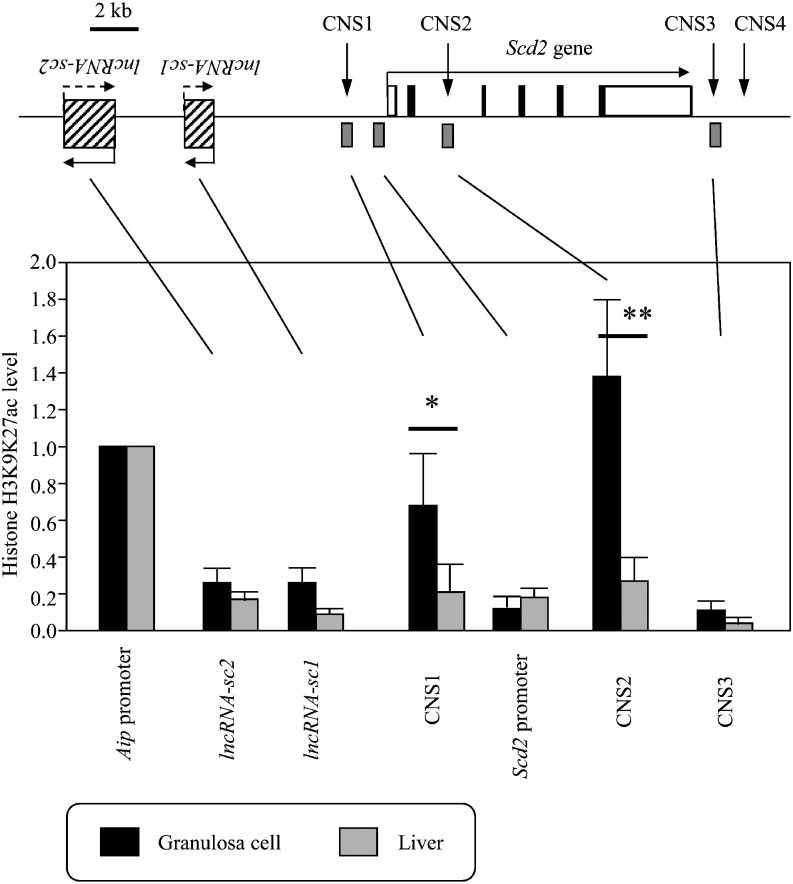
In contrast to lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2, the transcription at CNSs was not correlated with Scd2, but they might function as enhancers. Because the chromatin at active cis-regulatory elements are often acetylated, we next investigated histone H3K9/K27ac patterns at the Scd2 locus. We performed the ChIP-qPCR analysis with nuclei from primary granulosa cells and liver and measured the histone acetylation level in each CNS, each lncRNA sequence, and the Scd2 promoter. The acetylation level was normalized to that at the Aip promoter because this gene is recognized as one of the best control genes for expression analysis and is positively marked with H3K9/K27ac in both tissues [12, 26]. In the liver, H3K9/K27ac levels at all regions were lower than the Aip promoter, while in granulosa cells, CNS1 and CNS2 showed a comparable level to and a higher level than the Aip promoter, respectively (Fig. 5). The levels at CNS1 and CNS2 were significantly higher in granulosa cells than in the liver (Fig. 5). The two lncRNA sequences showed slightly higher H3K9/K27ac levels in granulosa cells than in the liver, but the difference was not statistically significant. These results raised the possibility that CNS1 and CNS2, rather than their transcripts, were cis-regulatory elements for Scd2 gene activation in granulosa cells.
Fig. 5.
Histone acetylation patterns at the mouse stearoyl-CoA desaturase 2 (Scd2) locus. ChIP was performed with nuclei from primary granulosa cells and liver using anti-histone H3K9/K27ac antibody. DNAs were purified from the chromatin precipitated with the antibody (bound) and before immunoprecipitation (input), and subjected to qPCR for the indicated regions. The acetylation level was calculated as the bound to input ratio, and further normalized to the level at the housekeeping Aip gene promoter, which was set to 1.0. The levels in granulosa cells and liver are shown by black and light gray bars, respectively. The data are presented as mean ± SD from four independent experiments with two sets of cell/tissue samples, and the statistical significance was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer test. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01.
CNS1 and CNS2 exhibit interdependent enhancer activity for the Scd2 promoter
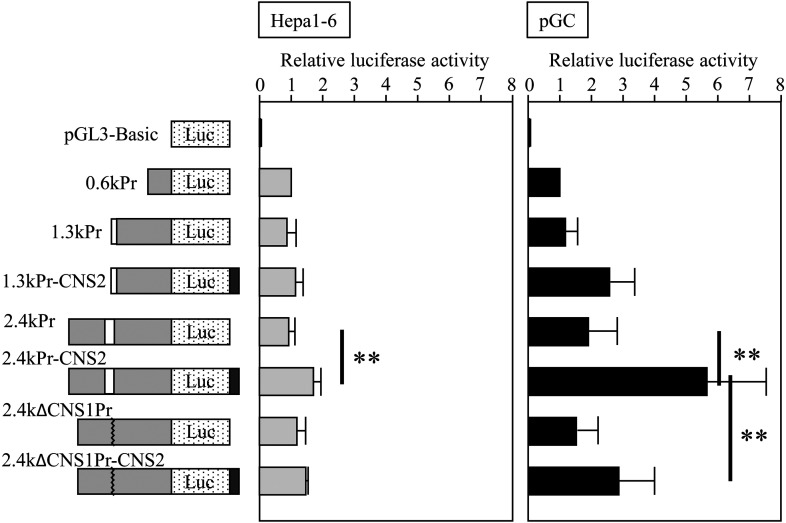
Finally, we assessed the enhancer activity of CNS1 and CNS2 by a transient reporter gene assay. We obtained a 2.4-kb Scd2 promoter sequence, which contained CNS1, by PCR, and connected it to the luciferase gene. 0.6-kb and 1.3-kb promoter sequences that contained no and partial CNS1, respectively, were obtained by restriction digestion of the 2.4-kb promoter. The 2.4-kb promoter, in which the CNS1 sequence was deleted, was also generated, and then CNS2 was connected to each construct. These constructs were transfected into primary granulosa cells or mouse hepatic Hepa1-6 cells, and luciferase activity was measured two days later.
In both granulosa and hepatic cells, CNS2 showed enhancer activity only when CNS1 was present because luciferase activity was significantly higher in 2.4kPr-CNS2 than 2.4kPr while no difference was observed between 1.3kPr and 1.3kPr-CNS2 or between 2.4kΔCNS1Pr and 2.4kΔCNS1Pr-CNS2 (Fig. 6). However, the fold increase in luciferase activity of 2.4kPr-CNS2 to 2.4kPr was higher in granulosa cells (3.0) than in hepatic cells (1.8), suggesting the physiological significance of CNS2 in granulosa cells. By contrast, CNS1 showed enhancer activity only in granulosa cells, because a significant difference was detected between 2.4kPr-CNS2 and 2.4kΔCNS1Pr-CNS2 in granulosa cells but not in hepatic cells (Fig. 6). The enhancer activity was also dependent on the presence of CNS2, since luciferase activity was not significantly different between 1.3kPr and 2.4kPr or between 2.4kPr and 2.4kΔCNS1Pr in granulosa cells (Fig. 6). These raised the possibility that both CNS1 and CNS2 possessed enhancer activity for the Scd2 promoter to function predominantly and specifically in granulosa cells and they were interdependent.
Fig. 6.
Reporter gene assay in mouse hepatic and primary granulosa cells. The indicated constructs were transfected into Hepa1-6 cells or primary granulosa cells (pGC), and luciferase activity was measured two days later. White and black rectangle indicated CNS1 and CNS2, respectively in the illustration of the constructs. The activity was normalized to that of 0.6kPr, which was set to 1.0. Light gray and black bars in the graph show the data in mouse hepatic Hepa1-6 cells and pGC, respectively. The data are presented as mean ± SD from five to eleven independent experiments, and the statistical significance was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer test. ** P < 0.01.
Discussion
Here we report a possible mechanism of mouse Scd2 gene activation in ovarian granulosa cells by two enhancers and two lncRNAs. The potential enhancers are CNSs identified by comparison of the mouse Scd2 locus with the human SCD1 locus, but these two genes show different tissue distribution: mouse Scd2 in ovary and brain and human SCD1 in liver and brain [27]. Transcriptional regulation of human SCD1 gene has been well studied, and several transcription factors contribute to the gene activation by binding to a promoter region mostly within 1 kb from TSS [28]. On the other hand, sequences more than 1 kb distant from TSS are shown to have little effect on the transcription [29]. CNS1 is located further upstream of the 1-kb promoter region, so it is unlikely to be involved in human SCD1 regulation, and the function of CNS2 has never been assessed in any species. These CNSs may have unknown functions in human.
It is interesting that CNS1 and CNS3 are transcribed in both granulosa cells and liver, even if the Scd2 gene is not expressed in the adult liver. These noncoding transcripts may have some common functions to both tissues such as the construction of subnuclear or subcellular structures and the regulation of RNA stability [6, 30]. Alternatively, the transcripts may contribute to the repression of a neighboring gene in both tissues. Indeed, mouse genome contains four Scd genes consisting of a gene cluster, and Scd3 and Scd4 genes are expressed at undetectable levels in liver and ovary according to the Mouse ENCODE transcriptome data [31] and some literatures [32, 33]. In contrast to these noncoding RNAs from CNSs, lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 are transcribed from non-conserved sequences.
Both lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 transcripts are longer than 200 bases and have little coding potential, and therefore, they are highly likely to function as lncRNAs. They were detected by RT-PCR with the oligo(dT) primer, which suggests that they are polyadenylated. However, we cannot conclude it because the identification of 5’- and 3’-ends of these lncRNAs was not successful by the methods that were successful for other lncRNAs [13, 14, 22, 23, 34]. lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 may have multiple transcriptional start and termination sites, as is the case for some lncRNAs [35,36,37]. These lncRNAs were localized to nuclei of granulosa cells, which encouraged us to examine their contribution to transcriptional regulation. Using shRNA and ASO, we successfully knocked down these lncRNAs and observed significant decreases in Scd2 expression. This and the correlation of both lncRNAs with Scd2 in tissue distribution support that they are regulatory factors of Scd2 gene activation in mouse granulosa cells. However, the mechanism by which these lncRNAs contribute to Scd2 gene activation remains unknown, and they may directly interact with the Scd2 gene or be involved in the regulation indirectly.
Besides lncRNAs, we found CNS1 and CNS2 to be potential enhancers for Scd2 gene in granulosa cells. CNS2 significantly increased promoter activity in hepatic cells, but the fold increase was small and only a low level of histone acetylation was associated with CNS2 in the liver. This suggests that CNS2 does not physiologically function as an enhancer in the liver even if it showed significant activity by an in vitro reporter gene assay. In contrast, both CNS1 and CNS2 clearly increased Scd2 promoter activity and the chromatin at these regions were highly acetylated at H3K9/K27 in granulosa cells. H3K9ac is widely distributed in active chromatin and actively transcribed regions [38], and H3K27ac is known to be an enhancer mark in some cell types [39, 40]. Therefore, the high levels of H3K9/K27ac at CNS1 and CNS2 regions raises the possibility that they are located at active chromatin in granulosa cells and function as granulosa cell-specific enhancers for Scd2 gene.
Notably, our data show that CNS1 and CNS2 enhance Scd2 promoter activity in an interdependent manner. A pair of interdependent enhancers was shown by some studies demonstrating that they increase promoter activity of their target genes only when both are present [41]. The mechanism is largely unclear, but at the human CIITA locus, distal enhancers interact with each other via chromatin looping and cooperate together for gene activation [42]. In this case, a chromatin-remodeling enzyme BRG1 is necessary for the cooperation. It is reported that two transcription factors, SREBP1a and EGR2, bind to the Scd2 promoter for the transcriptional activation in other tissues [20, 21], and these factors are expressed in mouse granulosa cells [43, 44]. In addition, their binding motifs are found in both CNS1 and CNS2 by searching at TFBIND (http://tfbind.hgc.jp/). These raise the possibility that these or other transcription factors mediate the chromatin opening and facilitate the genomic interaction between CNSs and the Scd2 promoter in granulosa cells, leading to enhancing the gene expression. More studies will be required for detailed mechanisms.
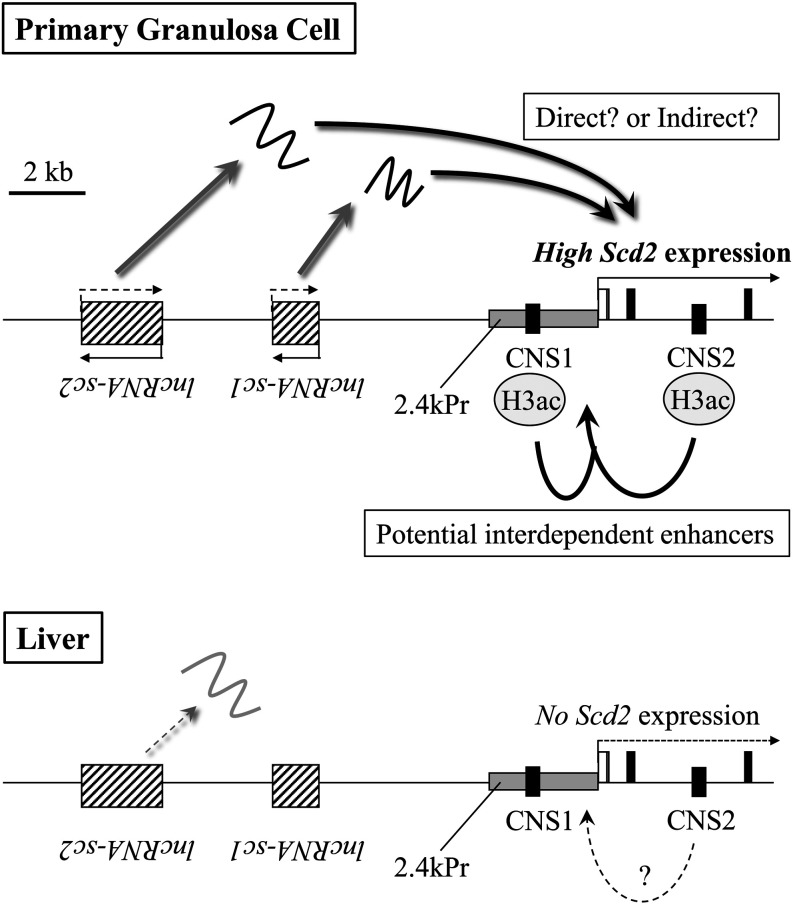
From these data, we propose a possible model of mouse Scd2 gene activation in granulosa cells (Fig. 7). In this model, transcription of mouse Scd2 gene in granulosa cells is activated by two enhancers and two lncRNAs. lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 that are not expressed or expressed at a low level in the liver are transcribed approximately 7 kb and 12 kb upstream of the Scd2 gene, respectively, and contribute to the gene activation by a direct or indirect mechanism in granulosa cells. CNS1 located 1.2 kb upstream of the Scd2 gene and CNS2 in intron 2 are acetylated at histone H3K9/K27, which may allow these CNSs to interact with each other and enhance Scd2 gene transcription in granulosa cells. CNSs with low levels of histone acetylation in the liver may not be competent for enhancing or even transcribing the Scd2 gene. Although the causal relationship between lncRNAs and CNSs is not clear, it may be possible that the noncoding transcription recruits a histone acetyltransferase for acetylation of CNSs, or vice versa.
Fig. 7.
A proposed model of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 2 (Scd2) gene activation in mouse granulosa cells and liver. Two lncRNAs are transcribed at the upstream of Scd2 gene, and both lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2 play roles in Scd2 gene activation in granulosa cells. In the liver, lncRNA-sc2 may be expressed at a low level but lncRNA-sc1 is not expressed. CNS1 and CNS2 are predominantly marked with acetylated histone H3 in granulosa cells and possibly function as granulosa cell-specific enhancers in an interdependent manner. In the liver, CNS2 showed low enhancer activity in vitro, which may not be physiologically significant. Two CNSs and two lncRNAs may thus function in the mouse Scd2 gene activation in granulosa cells. Details are described in the text. The genome regions transcribed into lncRNAs are depicted with striped rectangles, and CNS1 and CNS2 are black rectangles marked with each name. The 2.4-kb Scd2 promoter in our reporter gene assay is indicated as a grey rectangle pointed with ‘2.4kPr’.
Specific gene expression in granulosa cells plays central roles in control of oogenesis, and the regulatory mechanism of transcriptional activation has been studied for several genes such as Cyp11a1, Cyp19a1, Star, and Adamts-1 [45,46,47,48]. Most of them focused on their promoters and upstream enhancers and a few investigated the significance of epigenetic regulation. As a result, it was found that the chromatin at their promoters and enhancers are highly acetylated at histone H3 and thereby transcription factors bind to the regulatory sequences to activate transcription. However, the knowledge of cis-regulatory elements and epigenetic regulation in granulosa cells is still limited and little is known about the function of lncRNAs. The current study, together with our previous data [12,13,14], extends our understanding of cis-elements and epigenetics and suggests the existence of another gene whose expression is regulated by lncRNAs for gene activation in granulosa cells. These predict a complex mechanism of gene regulation in granulosa cells.
In conclusion, we identified two potential enhancers and two lncRNAs (lncRNA-sc1 and lncRNA-sc2) possibly involved in mouse Scd2 gene activation in granulosa cells. The potential enhancers (CNS1 and CNS2) are marked with high levels of H3K9/K27ac and can function in an interdependent manner. This is an interesting model of granulosa cell-specific gene activation and provides significant insights into the regulation of the function of granulosa cells.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Acknowledgments
We express our sincere thanks to Dr Hiroshi Kimura for kindly gifting us an antibody for H3K9/K27ac. This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Young Scientists 19770048 and 21770068 from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
References
- 1.Heinz S, Romanoski CE, Benner C, Glass CK. The selection and function of cell type-specific enhancers. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2015; 16: 144–154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kurihara M, Kimura AP. Characterization of the human TCAM1P pseudogene and its activation by a potential dual promoter-enhancer: comparison with a protein-coding mouse orthologue. FEBS Lett 2015; 589: 540–547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zabidi MA, Stark A. Regulatory enhancer-core-promoter communication via transcription factors and cofactors. Trends Genet 2016; 32: 801–814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rickels R, Shilatifard A. Enhancer logic and mechanics in development and disease. Trends Cell Biol 2018; 28: 608–630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lawrence M, Daujat S, Schneider R. Lateral thinking: how histone modifications regulate gene expression. Trends Genet 2016; 32: 42–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kopp F, Mendell JT. Functional Classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018; 172: 393–407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ransohoff JD, Wei Y, Khavari PA. The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2018; 19: 143–157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sun Q, Hao Q, Prasanth KV. Nuclear long noncoding RNAs: key regulators of gene expression. Trends Genet 2018; 34: 142–157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Khan DR, Fournier É, Dufort I, Richard FJ, Singh J, Sirard MA. Meta-analysis of gene expression profiles in granulosa cells during folliculogenesis. Reproduction 2016; 151: R103–R110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jaffe LA, Egbert JR. Regulation of mammalian oocyte meiosis by intercellular communication within the ovarian follicle. Annu Rev Physiol 2017; 79: 237–260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Richards JS, Ascoli M. Endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine signaling pathways that regulate ovulation. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2018; 29: 313–325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Matsubara S, Takahashi T, Kimura AP. Epigenetic patterns at the mouse prolyl oligopeptidase gene locus suggest the CpG island in the gene body to be a novel regulator for gene expression. Gene 2010; 465: 17–29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Matsubara S, Kurihara M, Kimura AP. A long non-coding RNA transcribed from conserved non-coding sequences contributes to the mouse prolyl oligopeptidase gene activation. J Biochem 2014; 155: 243–256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kimura AP, Yoneda R, Kurihara M, Mayama S, Matsubara S. A long noncoding RNA, lncRNA-Amhr2, plays a role in Amhr2 gene activation in mouse ovarian granulosa cells. Endocrinology 2017; 158: 4105–4121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kaestner KH, Ntambi JM, Kelly TJ, Jr, Lane MD. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. A second differentially expressed gene encoding stearoyl-CoA desaturase. J Biol Chem 1989; 264: 14755–14761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Miyazaki M, Dobrzyn A, Elias PM, Ntambi JM. Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-2 gene expression is required for lipid synthesis during early skin and liver development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 12501–12506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mu YM, Yanase T, Nishi Y, Tanaka A, Saito M, Jin CH, Mukasa C, Okabe T, Nomura M, Goto K, Nawata H. Saturated FFAs, palmitic acid and stearic acid, induce apoptosis in human granulosa cells. Endocrinology 2001; 142: 3590–3597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Aardema H, van Tol HTA, Wubbolts RW, Brouwers JFHM, Gadella BM, Roelen BAJ. Stearoyl-CoA desaturase activity in bovine cumulus cells protects the oocyte against saturated fatty acid stress. Biol Reprod 2017; 96: 982–992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Moreau C, Froment P, Tosca L, Moreau V, Dupont J. Expression and regulation of the SCD2 desaturase in the rat ovary. Biol Reprod 2006; 74: 75–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tabor DE, Kim JB, Spiegelman BM, Edwards PA. Transcriptional activation of the stearoyl-CoA desaturase 2 gene by sterol regulatory element-binding protein/adipocyte determination and differentiation factor 1. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 22052–22058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Leblanc SE, Srinivasan R, Ferri C, Mager GM, Gillian-Daniel AL, Wrabetz L, Svaren J. Regulation of cholesterol/lipid biosynthetic genes by Egr2/Krox20 during peripheral nerve myelination. J Neurochem 2005; 93: 737–748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kurihara M, Shiraishi A, Satake H, Kimura AP. A conserved noncoding sequence can function as a spermatocyte-specific enhancer and a bidirectional promoter for a ubiquitously expressed gene and a testis-specific long noncoding RNA. J Mol Biol 2014; 426: 3069–3093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yoneda R, Satoh Y, Yoshida I, Kawamura S, Kotani T, Kimura AP. A genomic region transcribed into a long noncoding RNA interacts with the Prss42/Tessp-2 promoter in spermatocytes during mouse spermatogenesis, and its flanking sequences can function as enhancers. Mol Reprod Dev 2016; 83: 541–557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kimura H, Hayashi-Takanaka Y, Goto Y, Takizawa N, Nozaki N. The organization of histone H3 modifications as revealed by a panel of specific monoclonal antibodies. Cell Struct Funct 2008; 33: 61–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Castro LF, Wilson JM, Gonçalves O, Galante-Oliveira S, Rocha E, Cunha I. The evolutionary history of the stearoyl-CoA desaturase gene family in vertebrates. BMC Evol Biol 2011; 11: 132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Frericks M, Esser C. A toolbox of novel murine house-keeping genes identified by meta-analysis of large scale gene expression profiles. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008; 1779: 830–837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhang L, Ge L, Parimoo S, Stenn K, Prouty SM. Human stearoyl-CoA desaturase: alternative transcripts generated from a single gene by usage of tandem polyadenylation sites. Biochem J 1999; 340: 255–264. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mauvoisin D, Mounier C. Hormonal and nutritional regulation of SCD1 gene expression. Biochimie 2011; 93: 78–86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhang L, Ge L, Tran T, Stenn K, Prouty SM. Isolation and characterization of the human stearoyl-CoA desaturase gene promoter: requirement of a conserved CCAAT cis-element. Biochem J 2001; 357: 183–193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hirose T, Mishima Y, Tomari Y. Elements and machinery of non-coding RNAs: toward their taxonomy. EMBO Rep 2014; 15: 489–507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yue F, Cheng Y, Breschi A, Vierstra J, Wu W, Ryba T, Sandstrom R, Ma Z, Davis C, Pope BD, Shen Y, Pervouchine DD, Djebali S, Thurman RE, Kaul R, Rynes E, Kirilusha A, Marinov GK, Williams BA, Trout D, Amrhein H, Fisher-Aylor K, Antoshechkin I, DeSalvo G, See LH, Fastuca M, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Dobin A, Prieto P, Lagarde J, Bussotti G, Tanzer A, Denas O, Li K, Bender MA, Zhang M, Byron R, Groudine MT, McCleary D, Pham L, Ye Z, Kuan S, Edsall L, Wu YC, Rasmussen MD, Bansal MS, Kellis M, Keller CA, Morrissey CS, Mishra T, Jain D, Dogan N, Harris RS, Cayting P, Kawli T, Boyle AP, Euskirchen G, Kundaje A, Lin S, Lin Y, Jansen C, Malladi VS, Cline MS, Erickson DT, Kirkup VM, Learned K, Sloan CA, Rosenbloom KR, Lacerda de Sousa B, Beal K, Pignatelli M, Flicek P, Lian J, Kahveci T, Lee D, Kent WJ, Ramalho Santos M, Herrero J, Notredame C, Johnson A, Vong S, Lee K, Bates D, Neri F, Diegel M, Canfield T, Sabo PJ, Wilken MS, Reh TA, Giste E, Shafer A, Kutyavin T, Haugen E, Dunn D, Reynolds AP, Neph S, Humbert R, Hansen RS, De Bruijn M, Selleri L, Rudensky A, Josefowicz S, Samstein R, Eichler EE, Orkin SH, Levasseur D, Papayannopoulou T, Chang KH, Skoultchi A, Gosh S, Disteche C, Treuting P, Wang Y, Weiss MJ, Blobel GA, Cao X, Zhong S, Wang T, Good PJ, Lowdon RF, Adams LB, Zhou XQ, Pazin MJ, Feingold EA, Wold B, Taylor J, Mortazavi A, Weissman SM, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Snyder MP, Guigo R, Gingeras TR, Gilbert DM, Hardison RC, Beer MA, Ren B. Mouse ENCODE Consortium.A comparative encyclopedia of DNA elements in the mouse genome. Nature 2014; 515: 355–364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zheng Y, Prouty SM, Harmon A, Sundberg JP, Stenn KS, Parimoo S. Scd3—a novel gene of the stearoyl-CoA desaturase family with restricted expression in skin. Genomics 2001; 71: 182–191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Miyazaki M, Jacobson MJ, Man WC, Cohen P, Asilmaz E, Friedman JM, Ntambi JM. Identification and characterization of murine SCD4, a novel heart-specific stearoyl-CoA desaturase isoform regulated by leptin and dietary factors. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 33904–33911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Satoh Y, Takei N, Kawamura S, Takahashi N, Kotani T, Kimura AP. A novel testis-specific long noncoding RNA, Tesra, activates the Prss42/Tessp-2 gene during mouse spermatogenesis. Biol Reprod 2019; 100: 833–848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lessard L, Liu M, Marzese DM, Wang H, Chong K, Kawas N, Donovan NC, Kiyohara E, Hsu S, Nelson N, Izraely S, Sagi-Assif O, Witz IP, Ma XJ, Luo Y, Hoon DSB. The CASC15 long intergenic noncoding RNA locus is involved in melanoma progression and phenotype switching. J Invest Dermatol 2015; 135: 2464–2474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yunusov D, Anderson L, DaSilva LF, Wysocka J, Ezashi T, Roberts RM, Verjovski-Almeida S. HIPSTR and thousands of lncRNAs are heterogeneously expressed in human embryos, primordial germ cells and stable cell lines. Sci Rep 2016; 6: 32753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liu S, Wang Z, Chen D, Zhang B, Tian RR, Wu J, Zhang Y, Xu K, Yang LM, Cheng C, Ma J, Lv L, Zheng YT, Hu X, Zhang Y, Wang X, Li J. Annotation and cluster analysis of spatiotemporal- and sex-related lncRNA expression in rhesus macaque brain. Genome Res 2017; 27: 1608–1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rahhal R, Seto E. Emerging roles of histone modifications and HDACs in RNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res 2019; 47: 4911–4926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zentner GE, Scacheri PC. The chromatin fingerprint of gene enhancer elements. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 30888–30896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kim TK, Shiekhattar R. Architectural and functional commonalities between enhancers and promoters. Cell 2015; 162: 948–959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Shimotsuma M, Okamura E, Matsuzaki H, Fukamizu A, Tanimoto K. DNase I hypersensitivity and epsilon-globin transcriptional enhancement are separable in locus control region (LCR) HS1 mutant human beta-globin YAC transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 14495–14503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ni Z, Abou El Hassan M, Xu Z, Yu T, Bremner R. The chromatin-remodeling enzyme BRG1 coordinates CIITA induction through many interdependent distal enhancers. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 785–793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Liu Z, Rudd MD, Hernandez-Gonzalez I, Gonzalez-Robayna I, Fan HY, Zeleznik AJ, Richards JS. FSH and FOXO1 regulate genes in the sterol/steroid and lipid biosynthetic pathways in granulosa cells. Mol Endocrinol 2009; 23: 649–661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Carletti MZ, Christenson LK. Rapid effects of LH on gene expression in the mural granulosa cells of mouse periovulatory follicles. Reproduction 2009; 137: 843–855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Doyle KM, Russell DL, Sriraman V, Richards JS. Coordinate transcription of the ADAMTS-1 gene by luteinizing hormone and progesterone receptor. Mol Endocrinol 2004; 18: 2463–2478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hiroi H, Christenson LK, Chang L, Sammel MD, Berger SL, Strauss JF., 3rd. Temporal and spatial changes in transcription factor binding and histone modifications at the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (stAR) locus associated with stAR transcription. Mol Endocrinol 2004; 18: 791–806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mizutani T, Ju Y, Imamichi Y, Osaki T, Yazawa T, Kawabe S, Ishikane S, Matsumura T, Kanno M, Kamiki Y, Kimura K, Minamino N, Miyamoto K. C/EBPβ (CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β) mediates progesterone production through transcriptional regulation in co-operation with SF-1 (steroidogenic factor-1). Biochem J 2014; 460: 459–471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Okada M, Lee L, Maekawa R, Sato S, Kajimura T, Shinagawa M, Tamura I, Taketani T, Asada H, Tamura H, Sugino N. Epigenetic changes of the Cyp11a1 promoter region in granulosa cells undergoing luteinization during ovulation in female rats. Endocrinology 2016; 157: 3344–3354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]