Figure 4.
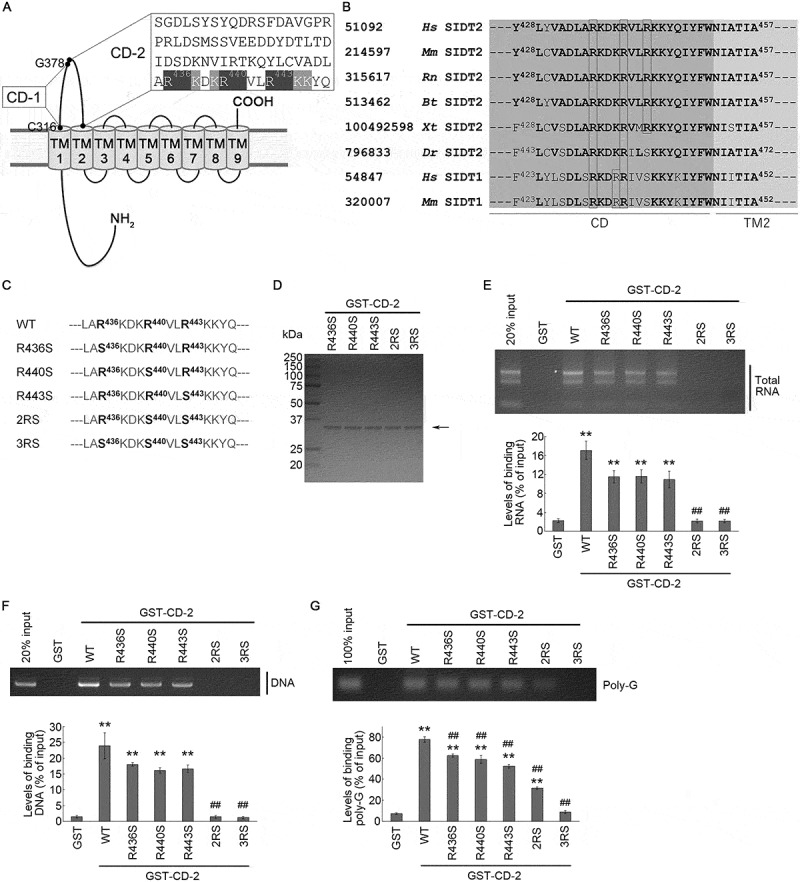
Requirement of arginine residues for interaction of the CD-2 of SIDT2 with RNA and DNA. (A) Amino acid sequence of SIDT2 CD-2. (B) Amino acid sequences in the proximity of transmembrane domain 2 of SIDT2 and SIDT1 from various species. On the outer left are the NCBI gene identification numbers, then the species names, followed by the common names of the proteins. Hs, Homo sapiens; Mm, Mus musculus; Rn, Rattus norvegicus; Bt, Bos taurus; Xt, Xenopus tropicalis; Dr, Danio rerio. Amino acids conserved among species are shown in bold letters. Arginine residues are boxed in black. TM2 stands for transmembrane domain 2. (C) Partial amino acid sequence of WT SIDT2 and mutants used in this study. (D) Purified GST-fused proteins expressed in Rosetta 2 competent cells were stained with CBB. (E, F) Affinity-isolation assays were performed using GST or GST-fused proteins and 1 μg of purified total RNA (E) or (F) 1 μg of plasmid DNA. After elution, levels of affinity-isolated RNA/DNA were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis, followed by EtBr staining. Intensities of nucleic acids signals were quantified. (G) Affinity-isolation assays were performed using 1 pmol of poly-G and GST-fused proteins. Intensities of nucleic acids signals were quantified. **, P < 0.01 vs GST; ##, P < 0.01 vs WT (n = 3)
