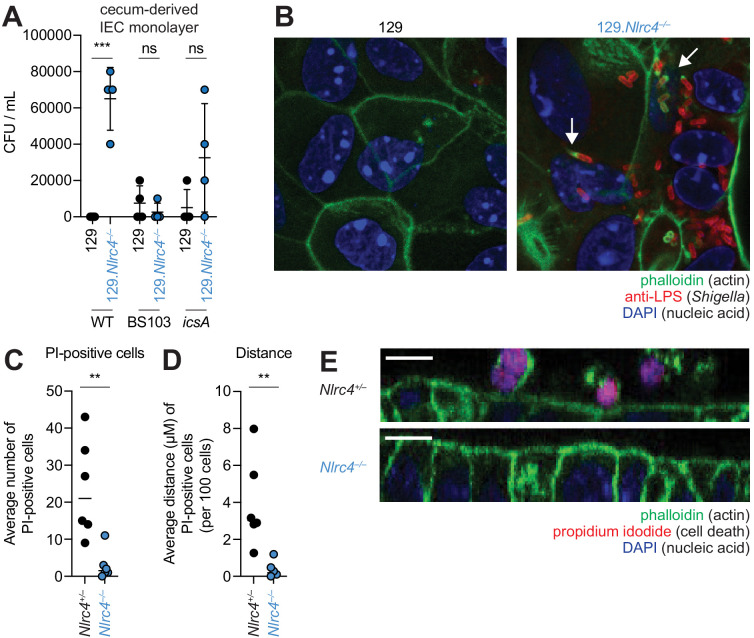
Figure 6. NLRC4 prevents Shigella colonization and cell expulsion in IEC monolayer cultures.
(A) Shigella (WT, BS103, or icsA) CFU from transwell culture of WT or 129.Nlrc4–/– cecum-derived IEC monolayers. CFU was determined 8 hr p.i. Each symbol represents one infected monolayer. (B) Immunofluorescent staining of WT Shigella-infected transwell cultures of WT or 129.Nlrc4–/– cecum-derived IEC monolayers: green, fluorescent phalloidin (actin); red, anti-Shigella LPS, blue, DAPI (nucleic acid). (C,D) Quantification of the number and position of propidium iodide (PI)-positive cells in Shigella-infected 129.Nlrc4+/– or 129.Nlrc4–/– cecum-derived IEC monolayers. In (C), each symbol represents the average number of PI-positive cells within an imaged field. In (D), each symbol represents the average distance of PI-positive cells from the lower boundary of the z-stack, per 100 cells. Two fields were counted for three independent slides. (E) A representative XZ-projection of Shigella-infected transwell cultures of 129.Nlrc4+/– or 129.Nlrc4–/– cecum-derived IEC monolayers showing expulsed PI+ cells above the monolayer. Green, fluorescent phalloidin (actin); red, PI (cell death); blue, DAPI (nucleic acid). Mann-Whitney test, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns = not significant (p > 0.05).