Abstract
The ancient insect order Odonata is divided into three suborders: Anisoptera and Zygoptera with approximately 3000 species worldwide each, and Anisozygoptera with only four extant species in the relict family Epiophlebiidae. An updated list of Odonata species studied regarding chromosome number, sex chromosome mechanism and the occurrence of m-chromosomes (= microchromosomes) is given. Karyotypes of 607 species (198 genera, 23 families), covering approximately 10% of described species, are reported: 423 species (125 genera, 8 families) of the Anisoptera, 184 species (72 genera, 14 families) of the Zygoptera, and one species of the Anisozygoptera. Among the Odonata, sex determination mechanisms in males can be of X(0), XY and X1X2Y types, and diploid chromosome numbers can vary from 6 to 41, with a clear mode at 2n = 25(60%) and two more local modes at 2n = 27(21%) and 2n = 23(13%). The karyotype 2n = 25(24A + X) is found in each of the three suborders and is the most typical (modal) in many families, including the best-covered Libellulidae, Corduliidae (Anisoptera), Lestidae, Calopterygidae, and Platycnemididae (Zygoptera). This chromosome set is considered ancestral for the Odonata in general. Chromosome rearrangements, among which fusions and fissions most likely predominated, led to independent origins of similar karyotypes within different phylogenetic lineages of the order. The karyotype 2n = 27(26A + X) prevails in Aeshnidae and Coenagrionidae, whereas the karyotype 2n = 23(22A + X) is modal in Gomphidae and Chlorocyphidae, in both pairs of families one being from the Anisoptera while the other from the Zygoptera.
Keywords: Chromosome numbers, damseldragons, damselflies, dragonflies, m-chromosomes, sex chromosome mechanisms
Introduction
The order Odonata, which comprises slightly more than 6,000 described species worldwide, is one of the most ancient among winged insects (Pterygota), dating from the Permian (Grimaldi and Engel 2005). Extant Odonata include two main suborders with approximately 3,000 species each, the Zygoptera or damselflies with about 308 genera and the Anisoptera or true dragonflies with about 344 genera. Within these suborders, up to 21 and 11 families (and sometimes more), respectively, are currently recognized. The third suborder, the Anisozygoptera or damseldragons, includes only one genus Epiophlebia Calvert, 1903 with four extant species in the relict family Epiophlebiidae. A substantial body of evidence indicates that Anisoptera and Zygoptera are each monophyletic, and Zygoptera are sister to Epiophlebia plus Anisoptera (Rehn 2003; Kalkman et al. 2008; Dijkstra et al. 2013, 2014; Schorr and Paulson 2020).
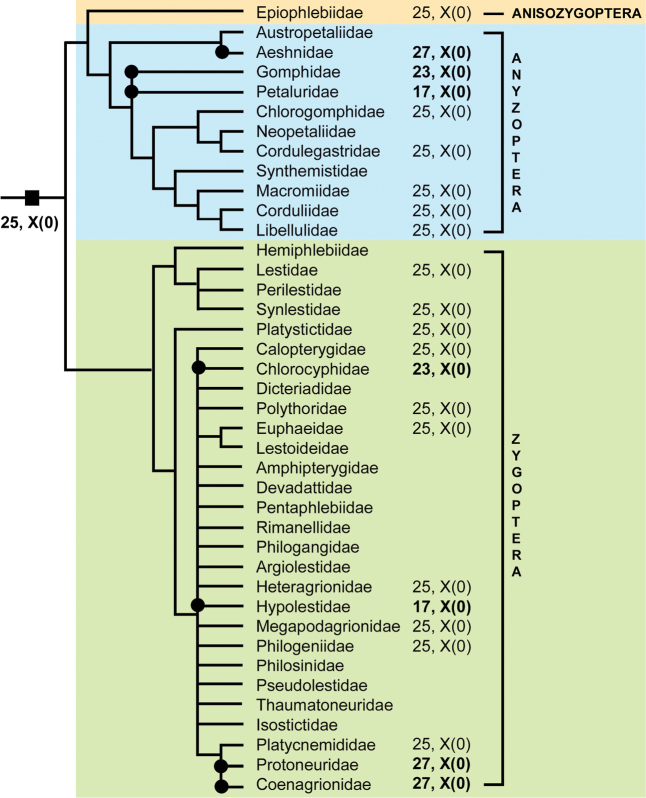
The field of Odonata cytogenetics was heavily influenced by Bastiaan Kiauta, who has published dozens of papers and analyzed karyotypes of about 260 species and subspecies of this group (see References and Table 1). During the years that have passed since the publication of chromosome number checklist of Odonata (Kiauta 1972c), approximately 90 chromosome papers have been published. The number of examined species has since increased by more than 2.3 times, and now it seems appropriate to publish an updated list. In this review article, all data available today are presented in two tables and one figure. Table 1 includes all species studied so far cytogenetically and compiles data on their chromosome numbers, sex chromosome mechanisms and the occurrence of the so-called m-chromosomes (= microchromosomes). Table 2 summarizes data presented in Table 1 and shows the family-level variability of the above-mentioned traits (except m-chromosomes, since data on their presence or absence in specific species are often questionable) together with the most characteristic (modal) karyotypes for each of the families explored. On the Fig. 1, the modal karyotypes are mapped onto phylogenetic tree of Odonata families taken from Bybee et al. (2016) who in turn redrawn and synthesized it from Dijkstra et al. (2014) and Carle et al. (2015). In the final section of the review, the main characteristics of Odonata karyotypes are briefly discussed and prospects for future research are outlined.
Table 1.
Cytogenetically analyzed species of Odonata and their main karyotype characteristics (chromosome numbers, sex chromosomes, m-chromosomes).
| Taxon | Karyotype formula 2n ♂ | m-chromo somes | Country | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anisozygoptera | |||||
| Epiophlebioidea | |||||
| Epiophlebiidae | |||||
| 1. | Epiophlebiasuperstes Selys, 1889 | 25(24A+X) | – | Japan | Oguma 1951 |
| Anisoptera | |||||
| Aeshnoidea | |||||
| Aeshnidae | |||||
| 2. | Aeshnacaerulea (Ström, 1783) | 24(22A+neo-XY) | – | Finland | Oksala 1943 |
| 3. | A. canadiensis Walker, 1908 | 27(26A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 4. | A. clepsydra Say, 1839 | 27(26A+X) | + | USA | Hung 1971 |
| 5. | A. crenata Hagen, 1856 | 27(26A+X) | + | Finland | Oksala 1939a, 1943, 1944, 1952 |
| – » – | – | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2002 | ||
| 6. | A. cyanea (Müller, 1764) | 27(26A+X) | + | Finland | Oksala 1943 |
| – » – | + | Netherlands | Kiauta 1969a | ||
| 7. | A. grandis (Linnaeus, 1758) | 27(26A+X) | + | Former USSR | Fuchsówna and Sawczyńska 1928 |
| 25(24A+X) | + | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 | ||
| 26(24A+neo-XY) | + | Finland | Oksala 1939a, 1943, 1944, 1945 | ||
| – » – | + | Netherlands | Kiauta 1967a–d,1968a, b, 1969a | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2002 | ||
| 25(24A+X) | – | Finland | Nokkala et al. 2002 | ||
| 8. | A. isoceles (Müller, 1767) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Kiauta 1978 as Anaciaeschna isosceles (Müller, 1767) |
| 25(24A + X) | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2020b | ||
| 9. | A. juncea (Linnaeus, 1758) | 26(24A+neo-XY) | + | Finland | Oksala 1939a, 1943, 1944 |
| – » – | + | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 | ||
| 27(26A+X) | + | Italy | Kiauta 1971a | ||
| 26(24A+neo-XY) | + | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2002 | ||
| 10. | A. mixta Latreille, 1805 | 27(26A+X) | + | Netherlands | Kiauta 1969a |
| 25(24A+X) | + | India | Sandhu and Malhotra 1994a | ||
| – » – | + | India | Sharma and Durani 1995 | ||
| 27(26A+X) | + | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b | ||
| 11. | A. nigroflava Martin, 1909 | 27(26A+X) | + | Japan | Katatani 1987 |
| – » – | – | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2002 | ||
| 12. | A. palmata Hagen, 1856 | 27(26A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 13. | A. serrata Hagen, 1856 | 26(24A+neo-XY) | + | Finland | Oksala 1943 as A. osiliensis Mierzejewski, 1913 and A. s. fennica Valle, 1938 |
| 14. | A. subarctica Walker, 1908 | 27(26A+X) | + | USA | Oksala 1939a, 1943, 1952 as A. s. elisabethae Djakonov, 1922 |
| – » – | + | Switzerland | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980a as A. s. elisabethae | ||
| 15. | A. umbrosa Walker, 1908 | 27(26A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 as A. u. occidentalis Walker, 1908 and A. u. umbrosa Walker, 1908 |
| 16. | A. verticalis Hagen, 1861 | 27(26A+X) | + | USA | Hung 1971 |
| 17. | A. viridis Eversmann, 1836 | 26(24A+neo-XY) | + | Finland | Oksala 1943 |
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov et al. 1998 | ||
| 18. | A. walkeri Kennedy, 1917 | 27(26A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 19. | Anaciaeschnajaspidea (Burmeister, 1839) | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Walia and Sandhu 1999 |
| 20. | Anaxamazili (Burmeister, 1839) | 27(26A+X) | – | Argentina | Capitulo et al. 1991 |
| – » – | + | Argentina | Mola et al. 1999 | ||
| 21. | A. concolor Brauer, 1865 | 27(26A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 22. | A. ephippiger (Burmeister, 1839) | 13(12A+X) | + | India | Seshachar and Bagga 1962 as Hemianax ephippiger (Burmeister, 1839) |
| 14(12A+neo-XY) | + | India | Kiauta 1969a as H. ephippiger | ||
| 23. | A. guttatus (Burmeister, 1839) | 15(14A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 |
| 24. | A. immaculiformis Rambur, 1842 | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Sangal and Tyagi 1982 |
| – » – | + | India | Walia et al. 2018 | ||
| 25. | A. imperator Leach, 1815 | 27(26A+X) | + | France | Kiauta 1965, 1969a |
| – » – | – | Kenya | Wasschner 1985 | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2002 | ||
| 26. | A. junius (Drury, 1773) | 27(26A+X) | + | USA | McGill 1904, 1907 |
| – » – | + | USA | Lefevre and McGill 1908 | ||
| – » – | – | Japan | Kichijo 1942a | ||
| – » – | + | USA | Cruden 1968 | ||
| – » – | – | ||||
| 27. | A. longipes Hagen, 1861 | 27(26A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 28. | A. nigrofasciatus Oguma, 1915 | 27(26A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 (A. n. nigrolineatus Fraser, 1935) |
| 25(24A+X) | + | India | Sandhu and Malhotra 1994a (A. n. nigrolineatus) | ||
| 27(26A+X) | + | India | Walia and Sandhu 1999 (A. n. nigrolineatus) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Walia et al. 2018 (A. n. nigrolineatus) | ||
| 29. | A. papuensis (Burmeister, 1839) | 27(26A+X) | + | Australia | Kiauta 1968c, 1969a as Hemianax papuensis (Burmeister, 1839) |
| 30. | A. parthenope (Selys, 1839) | 27(26A+X) | + | Japan | Omura 1957 as A. parthenope julius Brauer, 1865 |
| – » – | + | India | Thomas and Prasad 1986 | ||
| – » – | + | China | Zhu and Wu 1986 as A. p. julius | ||
| 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Suzuki and Saitoh 1990 as A. p. julius | ||
| 27(26A+X) | + | India | Sandhu and Malhotra 1994a | ||
| 31. | Andaeschnaunicolor (Martin, 1908) | 27(26A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 as Aeshna cf. unicolor Martin, 1908 |
| 32. | Austroaeschnaanacantha Tillyard, 1908 | 27(26A+X) | + | Australia | Kiauta 1968c as Acanthaeschna anacantha (Tillyard, 1908) |
| 33. | A. multipunctata (Martin, 1901) | 27(26A+X) | + | Australia | Kiauta 1968c as Acanthaeschna multipunctata (Martin, 1901) |
| 34. | Basiaeschnajanata (Say, 1939) | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 35. | Boyeriamaclachlani (Selys, 1883) | 27(26A+X) | + | Japan | Omura 1957 |
| 36. | B. vinosa (Say, 1839) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 37. | Caliaeschnamicrostigma (Schneider, 1845) | 16(14A+neo-XY) | + | Greece | Kiauta 1972a |
| 38. | Castoraeschnacastor (Brauer, 1865) | 27(26A+X) | + | Brazil | Kiauta 1972b |
| 39. | Cephalaeschnaorbifrons Selys, 1883 | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 |
| 40. | Cephalaeschna sp. | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Sandhu and Malhotra 1994a |
| 41. | Coryphaeschnaadnexa (Hagen, 1961) | 27(26A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 42. | C. perrensi (McLachlan, 1887) | 25(24A+X) | – | Argentina | Capitulo et al. 1991 |
| 27(26A+X) | + | Argentina | Mola et al. 1999 | ||
| – » – | + | Argentina | De Gennaro et al. 2008 | ||
| 43. | C. viriditas Calvert, 1952 | 23(22A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 44. | Gynacanthabayadera Selys, 1891 | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Walia 2007 as G. milliardi Fraser, 1936 |
| 27(26A+X) | + | ||||
| 45. | G. hyalina Selys, 1882 | 28(26A+XX)* | + | India | Tyagi 1978a, b |
| 46. | G. interioris Williamson, 1923 | 26(24A+neo-XY) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 47. | G. japonica Bartenev, 1909 | 27(26A+X) | + | Japan | Omura 1957 |
| 48. | Gynacanthaeschnasikkima (Karsch, 1891) | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Walia et al. 2016 |
| 49. | Oplonaeschnaarmata (Hagen, 1861) | 27(26A+X) | + | Mexico | Kiauta 1970a |
| 50. | Planaeschnamilnei (Selys, 1883) | 27(26A+X) | + | Japan | Kiauta 1968c, 1969a |
| 51. | Remartinialuteipennis (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a as Coryphaeschna l. luteipennis Burmeister, 1839 |
| 27(26A+X) | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 as C. l. luteipennis | ||
| 52. | Rhionaeschnabonariensis (Rambur, 1842) | 26(24A+neo-XY) | + | Argentina, Uruguay | Mola and Papeschi 1994 as Aeschna bonariensis Rambur, 1842 |
| 52. | Rhionaeschnabonariensis (Rambur, 1842) | – » – | + | Argentina, Uruguay | Mola 1995 as A. bonariensis |
| 53. | Rh. californica (Calvert, 1895) | 27(26A+X) | + | Canada | Kiauta 1973a as Aeshna californica Calvert, 1895 |
| 54. | Rh. confusa (Rambur, 1842) | 27(26A+X) | + | Argentina, Uruguay | Mola and Papeschi 1994 as Aeshna confuse Rambur, 1842 |
| – » – | + | Argentina, Uruguay | Mola 1995 as A. confuse | ||
| 55. | Rh. diffinis (Rambur, 1842) | 21(20A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 as Aeshna d. diffinis Rambur, 1842 |
| 56. | Rh. intricata (Martin, 1908) | 19(18A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 as Aeshna intricata Martin, 1908 |
| 57. | Rh. peralta (Ris, 1918) | 27(26A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 as Aeshna peralta Ris, 1918 |
| 58. | Rh. planaltica (Calvert, 1845) | 16(14A+neo-XY) | + | Argentina | Mola and Papeschi 1994 as Aeschna cornigera planaltica Calvert, 1952 |
| – » – | + | Argentina | Mola 1995 as A. c. planaltica | ||
| 59. | Staurophlebiareticulata (Burmeister, 1839) | 27(26A+X) | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 (S. r. reticulata (Burmeister, 1839)) |
| Petaluroidea | |||||
| Petaluridae | |||||
| 60. | Tachopteryxthoreyi (Hagen, 1857) | 19(18A+X) | + | USA | Cumming 1964 |
| 61. | Tanypteryxhageni (Selys, 1879) | 17(16A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 62. | T. pryeri (Selys, 1889) | 17(16A+X) | + | Japan | Kichijo 1939, 1942a |
| 63. | Uropetalacarovei (White, 1846) | 17(16A+X)** | + | New Zealand | Wolfe 1953 |
| 25(24A+X) | + | New Zealand | Jensen and Mahanty 1978 | ||
| – » – | + | New Zealand | Jensen 1980 | ||
| Gomphoidea | |||||
| Gomphidae | |||||
| 64. | Anisogomphusbivittatus (Selys, 1854) | 23(22A+X) | + | India | Das 1956 |
| – » – | + | India | Walia and Chahal 2020 | ||
| 65. | A. occipitalis (Selys, 1854) | 23(22A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| 66. | Aphyllaedentata Selys, 1869 | 23(22A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 67. | A. producta Selys, 1854 | 23(22A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 68. | A. theodorina (Navas, 1933) | 23(22A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 69. | A. williamsoni (Gloyd, 1936) | 23(22A+X) | + | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 |
| 70. | Aphylla sp. | 23(22A+X) | + | Argentina | Mola 2007 |
| 71. | Arigomphuslentulus (Needham, 1902) | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 as Gomphus lentulus Needham, 1902 |
| 72. | A. pallidus (Rambur, 1842) | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cumming 1964 as Gomphus pallidus Rambur, 1842 |
| 73. | A. submedianus (Williamson, 1914) | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 as Gomphus submedianus Williamson, 1914 |
| 74. | Asiagomphusmelaenops (Selys, 1854) | 23(22A+X) | + | Japan | Toyoshima and Hirai 1953 as Gomphus melaenops Selys, 1854 |
| – » – | + | Japan | Hirai 1956 as G. melaenops | ||
| – » – | + | USA | Cruden 1968 as G. melaenops | ||
| 75. | Burmagomphuspyramidalis Laidlaw, 1922 | 23(22A+X) | + | India | Tyagi 1977 |
| 76. | Davidiusnanus (Selys, 1869) | 23(22A+X) | – | Japan | Kichijo 1939, 1942a |
| 77. | Dromogomphusspinosus (Selys, 1854) | 23(22A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 78. | D. spoliatus (Hagen, 1857) | 23(22A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 79. | Epigomphusllama Calvert, 1903 | 23(22A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 80. | Erpetogomphusdesignatus Hagen, 1857 | 23(22A+X) | + | USA | Cumming 1964 |
| 81. | E. diadophis Calvert, 1905 | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cumming 1964 |
| 82. | E. ophibolus Calvert, 1905 | 23(22A+X) | + | Mexico | Kiauta 1970a |
| 83. | Gomphoides sp. | 23(22A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 84. | Gomphusconfraternus Selys, 1873 | 23(22A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 85. | G. exilis Selys, 1854 | 23(22A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| – » – | + | Canada | Kiauta 1969a | ||
| 86. | G. graslini Rambur, 1842 | 12(10A+neo-neo-XY) | + | France | Kiauta 1968d, 1969a |
| 87. | G. pulchellus Selys, 1840 | 23(22A+X) | + | France | Kiauta 1973b |
| 88. | G. vulgatissimus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 23(22A+X) | – | Russia | Perepelov et al. 2001 |
| 89. | Ictinogomphusrapax (Rambur, 1942) | 23(22A+X) | + | India | Asana and Makino 1935 |
| – » – | + | India | Makino 1935 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Kichijo 1942a | ||
| – » – | + | India | Omura 1949, 1952, 1953 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 | ||
| 90. | Nepogomphusmodestus (Selys, 1878) | 23(22A+X) | – | India | Walia et al. 2006 |
| – » – | – | India | Walia and Chahal 2014 | ||
| 91. | Nihonogomphusruptus (Selys, 1858) | 23(22A+X) | – | Russia | Perepelov et al. 2001 |
| 92. | N. viridis Oguma, 1926 | 23(22A+X) | + | Japan | Omura 1957 |
| 93. | Nychogomphusduaricus (Fraser, 1924) | 22(20A+neo-XY) | + | India | Tyagi 1977 |
| 94. | Octogomphusspecularis (Hagen, 1859) | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 95. | Onychogomphusforcipatus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 25(24A+X) | – | Finland | Oksala 1945 |
| 22(20A+neo-XY) | – | Austria | Kiauta 1969a | ||
| 25(24A+X) | – | ||||
| 96. | O. saundersii Selys, 1854 | 22(20A+neo-XY) | + | India | Tyagi 1977 (O. s. duaricus Fraser, 1924) |
| 97. | Ophiogomphusbison Selys, 1873 | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 25(24A+X) | – | ||||
| 98. | O. cecilia (Fourcroy, 1785) | 24(22A+XX)* | – | Finland | Oksala 1945 |
| 23(22A+X) | – | Russia | Perepelov et al. 1998 | ||
| – » – | – | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001a | ||
| 99. | O. colubrinus Selys, 1854 | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 100. | O. obscurus Bartenev, 1909 | 23(22A+X) | – | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b |
| 101. | O. occidentalis Hagen, 1882 | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 102. | O. rupinsulensis (Walsh, 1862) | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 103. | Phanogomphuslividus (Selys, 1854) | 23(22A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 as Gomphus lividus Selys, 1854 |
| 104. | Ph. militaris (Hagen, 1858) | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 as Gomphus militaris Hagen, 1858 |
| 105. | Ph. spicatus (Selys, 1854) | 23(22A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 as Gomphus spicatus Selys, 1854 |
| 106. | Paragomphuslineatus (Selys, 1850) | 23(22A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| – » – | – | India | Walia and Chahal 2014 | ||
| 107. | P. capricornis (Förster, 1914) | 23(22A+X) | – | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 |
| 108. | Phyllocyclapropinqua Belle, 1972 | 21(20A+X) | – | Argentina | De Gennaro 2004 |
| 109. | Phyllocycla sp. | 23(22A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 110. | Phyllocycla sp. 1 | 23(22A+X) | + | Argentina | Mola 2007 |
| 111. | Phyllocycla sp. 2 | 23(22A+X) | – | Argentina | Mola 2007 |
| 112. | Phyllogomphoidesundulatus (Needham, 1944) | 23(22A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 113. | Progomphusborealis McLachlan, 1873 | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 114. | P. intricatus (Hagen, 1857) | 23(22A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 115. | P. obscurus (Rambur, 1842) | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 116. | P. phyllochromus Ris, 1918 | 23(22A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 117. | Scalmogomphusbistrigatus (Hagen, 1854) | 23(22A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 as Onychogomphus bistrigatus (Hagen, 1854) |
| 118. | Shaogomphuspostocularis (Selys, 1869) | 23(22A+X) | + | Japan | Omura 1957 as Gomphus postocularis Selys, 1869 |
| – » – | – | Russia | Perepelov et al. 2001 as Gomphus epophtalmus Selys, 1872 | ||
| 119. | Sieboldiusalbardae Selys, 1886 | 23(22A+X) | + | Japan | Omura 1957 |
| 120. | Stylogomphussuzukii (Matsumura, 1926) | 23(22A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1930 |
| – » – | + | Japan | Kichijo 1942a | ||
| 121. | Stylurusflavipes (Charpentier, 1825) | 23(22A+X) | + | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b |
| 122. | S. plagiatus (Selys, 1854) | 23(22A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 as Gomphus plagiatus Selys, 1854 |
| 123. | S. scudderi (Selys, 1873) | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 as Gomphus scudderi Selys, 1873 |
| 124. | S. townesi Gloyd, 1936 | 22(20A+neo-XY) | – | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 as Gomphus townesi Gloyd, 1936 |
| 125. | Temnogomphusbivittatus (Selys, 1854) | 23(22A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 |
| 126. | Trigomphuscitimus (Needham, 1931) | 21(20A+X) | + | Japan | Toyoshima and Hirai 1953 (T. c. tabei Asahina, 1949) |
| – » – | + | Japan | Hirai 1956 (T. c. tabei) | ||
| 127. | T. interruptus (Selys, 1854) | 19(18A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1930 |
| – » – | + | Japan | Toyoshima and Hirai 1953 | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Hirai 1956 | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Omura 1957 | ||
| 128. | T. melampus (Selys, 1869) | 21(20A+X) | – | Japan | Oguma 1930, 1942 as T. unifasciatus (Oguma 1926) |
| 129. | Zonophoracallipus Selys, 1869 | 23(22A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| Libelluloidea | |||||
| Macromiidae | |||||
| 130. | Didymopstransversa (Say, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 131. | Epophthalmiafrontalis (Selys, 1871) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 (E. f. frontalis (Selys, 1871)) |
| 132. | Macromiadaimoji Okumura, 1949 | 25(24A+X) | – | Japan | Katatani 1987 |
| 133. | M. amphigenia Selys, 1871 | 25(24A+X) | – | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b (M. a. fraenata Martin, 1906) |
| 134. | M. magnifica (McLachlan, 1874) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| – » – | – | ||||
| 135. | M. moorei Selys, 1874 | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1977 |
| – » – | + | India | Walia and Chahal 2018 | ||
| Corduliidae | |||||
| 136. | Corduliaaenea (Linnaeus, 1758) | 25(24A+X) | – | Finland | Oksala 1939a |
| – » – | – | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 | ||
| – » – | – | Netherlands | Kiauta 1968b, 1969a | ||
| – » – | – | Russia | Perepelov et al. 1998 | ||
| – » – | – | Bulgaria | Grozeva and Marinov 2007 | ||
| – » – | – | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2018 | ||
| 137. | C. shurtleffi Scudder, 1866 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| – » – | + | Canada | Kiauta 1973a | ||
| 138. | Dorocordulialibera (Selys, 1871) | 11(10A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 13(12A+X) | – | ||||
| 14(12A+neo-XY) | – | USA | Kiauta 1969a | ||
| 13(12A+X) | – | ||||
| 139. | Epicorduliaprinceps (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Hung 1971 |
| 140. | Epithecabimaculata (Charpentier, 1825) | 25(24A+X) | – | Russia | Perepelov 2003 |
| – » – | – | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2018 | ||
| 141. | E. canis McLachlan, 1886 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 142. | E. cynosura (Say, 1839) | 19(18A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 21(20A+X) | – | ||||
| 143. | E. petechialis (Muttkowski, 1911) | 21(20A+X) | – | USA | Cumming 1964 as Tetragoneuria petechialis Muttkowski, 1911 |
| 144. | E. semiaquea (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 145. | E. spinigera (Selys, 1871) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Hung 1971 as Tetragoneuria spinigera (Selys, 1871) | ||
| 146. | Procorduliagrayi (Selys, 1871) | 25(24A+X) | + | New Zealand | Jensen 1980 |
| 147. | P. smithii (White, 1846) | 25(24A+X) | + | New Zealand | Jensen 1980 |
| 148. | Riallavillosa Rambur, 1842 | 25(24A+X) | + | Argentina | De Gennaro 2004 |
| 149. | Somatochloraalpestris (Selys, 1840) | 25(24A+X) | – | Switzerland | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980a |
| 27(26A+X) | + | ||||
| 150. | S. arctica (Zetterstedt, 1840) | 25(24A+X) | + | Russia | Perepelov 2003 |
| 151. | S. borisi Marinov, 2001 | 20(18A+XY) | – | Bulgaria | Grozeva and Marinov 2007 |
| 152. | S. flavomaculata (Van der Linden, 1825) | 25(24A+X) | – | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 |
| – » – | – | Russia | Perepelov 2003 | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2020b | ||
| 153. | S. graeseri Selys, 1887 | 25(24A+X) | – | Russia | Perepelov et al. 2001 |
| 154. | S. meridionalis Nielsen, 1935 | 25(24A+X) | – | Slovenia | Kiauta and Kiauta 1995 |
| – » – | – | Bulgaria | Grozeva and Marinov 2007 | ||
| 155. | S. metallica (Van der Linden, 1825) | 26(24A+XX)* | – | Finland | Oksala 1945 |
| 25(24A+X) | – | Finland | Nokkala et al. 2002 | ||
| – » – | – | Finland | Grozeva and Marinov 2007 | ||
| – » – | – | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b | ||
| 156. | S. semicircularis (Selys, 1871) | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 157. | S. uchidai Fürster, 1909 | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1915, 1930 |
| – » – | + | Japan | Kichijo 1942b | ||
| 158. | S. viridiaenea (Uhler, 1858) | 25(24A+X) | – | Japan | Oguma 1915, 1930 |
| – » – | – | Japan | Kichijo 1942b | ||
| Libellulidae | |||||
| 159. | Acisomapanorpoides Rambur, 1842 | 25(24A+X) | + | Bangladesh, India | Dasgupta 1957 (A. p. panorpoides Rambur, 1842) |
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 (A. p. panorpoides) | ||
| – » – | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 (A. p. panorpoides) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| 160. | Aethriamantabrevipennis (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| 161. | Anatyaguttata (Erichson, 1848) | 25(24A+X) | – | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 162. | Atoconeurabiordinata Karsch, 1899 | 21(20A+X) | + | Sudan | Wasscher 1985 |
| 163. | Brachydiplaxchalybea Brauer, 1868 | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| – » – | + | India | Taygi 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 | ||
| 164. | B. farinosa Krueger, 1902 | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| – » – | + | India | Taygi 1982 | ||
| – » – | – | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 | ||
| 165. | B. sobrina (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Ray Chaudhuri and Dasgupta 1949 |
| – » – | + | India | Taygi 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 | ||
| 166. | Brachvmesiafurcata (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | + | Argentina | Agopian and Mola 1988 | ||
| – » – | – | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| – » – | – | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 | ||
| 167. | B. gravida (Calvert, 1890) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 as Cannacria gravida (Calvert, 1890) |
| 168. | B. herbida (Gundlach, 1889) | 25(24A+X) | + | Jamaica | Cumming 1964 as Cannacria herbida (Gundlach, 1889) |
| 169. | Brachythemiscontaminata (Fabricius, 1793) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Asana and Makino 1935 |
| – » – | + | India | Makino 1935 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Kichijo 1942b | ||
| – » – | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 | ||
| 170. | B. lacustris (Kirby, 1899) | 25(24A+X) | + | Sudan | Wasscher 1985 |
| 171. | Bradinopygacornuta Ris, 1911 | 25(24A+X) | + | Republic of South Africa | Boyes et al. 1980 |
| 172. | B. geminata (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| 173. | Brechmorhogamendax (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| – » – | – | ||||
| 174. | B. nubecula (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 175. | B. pertinax (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 (B. p. peruviana Ris, 1913) |
| 176. | Cannaphilavibex (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 177. | Celithemisamanda (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 |
| 178. | C. elisa (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 179. | C. fasciata Kirby, 1889 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 180. | C. ornata (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 |
| 181. | Crocothemiserythraea (Brulle, 1832) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| – » – | + | Kenya | Kiauta 1969b | ||
| – » – | + | Italy | Kiauta 1971a | ||
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 | ||
| – » – | + | Republic of South Africa | Boyes et al. 1980 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| 182. | C. sanguinolenta (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Kingdom of Eswatini (Former Swaziland) | Boyes et al. 1980 |
| 183. | C. servilia (Drury, 1773) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Asana and Makino 1935 |
| – » – | + | India | Makino 1935 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Kichijo 1942b | ||
| – » – | + | India | Ray Chaudhuri and Dasgupta 1949 | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 | ||
| – » – | + | Philippines | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980b | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Katatani 1987 | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Higashi and Kayano 1993 | ||
| – » – | + | Japan, Taiwan | Higashi et al. 2001 | ||
| 24(22A+neo-XY) | + | Japan | Omura 1955 (C. s. mariannae Kiauta, 983) | ||
| – » – | – | Japan | Kiauta 1983 (C. s. mariannae) | ||
| – » – | – | Japan | Katatani 1987 (C. s. mariannae) | ||
| – » – | – | Japan | Higashi et al. 2001 (C. s. mariannae) | ||
| 184. | Dasythemisesmeralda Ris, 1910 | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 185. | D. mincki (Karsch, 1890) | 25(24A+X) | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 |
| 186. | D. venosa (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Brazil | Kiauta and Boyes 1972 |
| 187. | Diastatopsintensa Montgomery, 1940 | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 188. | D. obscura (Fabricius, 1775) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 189. | D. pullata (Burmeister, 1839) | 23(22A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 190. | Diplacodesbipunctata (Brauer, 1865) | 25(24A+X) | + | Australia | Kiauta 1969b |
| 29(28A+X) | + | ||||
| 191. | D. haematodes (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Australia | Kiauta 1969b |
| 23(22A+X) | – | ||||
| 192. | D. lefebvrei (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | Madagascar | Kiauta 1968c, 1969b |
| 193. | D. nebulosa (Fabricius, 1793) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| – » – | + | India | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| 194. | D. trivialis (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Asana and Makino 1935 |
| – » – | + | India | Makino 1935 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 | ||
| – » – | + | Australia | Kiauta 1969c | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| 195. | Dythemisfugax Hagen, 1861 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 196. | D. multipunctata Kirby, 1894 | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 197. | D. rufinefris (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Jamaica | Cumming 1964 |
| 198. | D. velox Hagen, 1861 | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Peru | Kiauta and Boyes 1972 | ||
| 199. | Elasmothemiscannacrioides (Calvert, 1906) | 21(20A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 as Dythemis cannacrioides Calvert, 1906 |
| 23(22A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a as D. cannacrioides | ||
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 200. | E. williamsoni (Ris, 1919) | 22(20A+neo-XY) | – | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a as Dythemis williamsoni (Ris, 1919) |
| 25(24A+X) | – | ||||
| 201. | Erythemisattala (Selys, 1857) | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Argentina | Agopian and Mola 1988 | ||
| 202. | E. collocata (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 203. | E. credula (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 204. | E. haematogastra (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | – | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 205. | E. peruviana (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | – | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 206. | E. plebeja (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 207. | E. simplicicollis (Say, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 208. | E. vesiculosa (Fabricius, 1775) | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 as Lepthemis vesiculosa (Fabricius, 1775) |
| – » – | – | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a as L. vesiculosa | ||
| – » – | + | Brasil | Ferreira et al. 1979 as L. vesiculosa | ||
| 209. | Erythrodiplaxanomala (Brauer, 1865) | 25(24A+X) | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 |
| 210. | E. atroterminala Ris, 1911 | 25(24A+X) | + | Uruguay | Goni and Abenante 1982 |
| – » – | + | Argentina | Mola 1996 | ||
| 211. | E. attenuata (Kirby, 1889) | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | + | Brasil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 212. | E. basalis (Kirby, 1897) | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a (E. b. basalis (Kirby, 1897)) | ||
| – » – | + | Brasil | Ferreira et al. 1979 (E. b. basalis) | ||
| 213. | E. berenice (Drury, 1770) | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 27(26A+X) | + | USA | Hung 1971 | ||
| 25(24A+X) | + | ||||
| 214. | E. castanea (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 215. | E. chromoptera Borror, 1942 | 23(22A+X) | + | Uruguay | Goni and Abenante 1982 |
| 216. | E. cleopatra Ris, 1911 | 25(24A+X) | + | Peru | Kiauta and Boyes 1972 |
| 217. | E. connata (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Chile | Kiauta and Boyes 1972 (E. c. connata (Burmeister, 1839)) |
| – » – | + | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 (E. c. minuscula (Rambur, 1842)) | ||
| 218. | E. coralline (Brauer, 1865) | 25(24A+X) | + | Argentina | Mola 1996 |
| 219. | E. famula (Erichson, 1848) | 25(24A+X) | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 |
| 220. | E. fusca (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 as E. connata fusca (Rambur, 1842) |
| – » – | – | Guatemala | Cruden 1968 as E. c. fusca | ||
| – » – | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a as E. c. fusca | ||
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 as E. c. fusca | ||
| – » – | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | Argentina | Mola 1996 | ||
| 221. | E. fervida (Erichson, 1848) | 25(24A+X) | + | Jamaica | Cumming 1964 |
| 222. | E. justiniana (Selys, 1857) | 25(24A+X) | + | Jamaica | Cumming 1964 |
| 223. | E. juliana Ris, 1911 | 25(24A+X) | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 |
| 224. | E. latimaculata Ris, 1911 | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | + | Brasil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 225. | E. lygaea Ris, 1911 | 25(24A+X) | + | Argentina | Capitulo et al. 1991 |
| – » – | + | Argentina | Mola 1996 | ||
| 226. | E. media Borror, 1942 | 21(20A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 22(20A+XX)* | + | Brazil | Kiauta and Boyes 1972 | ||
| 21(20A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a | ||
| – » – | + | Brasil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 22(20A+neo-XY) | + | Argentina | Mola 1996 | ||
| 227. | E. melanorubra Borror, 1942 | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Venezuela | Kiauta and Boyes 1972 | ||
| – » – | + | Argentina | Capitulo et al. 1991 | ||
| – » – | + | Argentina | Mola 1996 | ||
| 228. | E. minuscula (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 |
| 22(20A+neo-XY) | + | Argentina | Mola and Agopian 1985 | ||
| 229. | E. nigricans (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | Uruguay | Goni and Abenante 1982 |
| 229. | E. nigricans (Rambur, 1842) | – » – | + | Argentina | Mola 1996 |
| – » – | – | Argentina | De Gennaro 2004 | ||
| – » – | + | Argentina | De Gennaro et al. 2008 | ||
| 230. | E. ochracea (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Argentina | Mola 1996 |
| 231. | E. paraguayensis (Foerster, 1904) | 23(22A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a | ||
| 232. | E. umbrata (Linnaeus, 1758) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Dominica | Cruden 1968 | ||
| – » – | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a | ||
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al 1979 | ||
| – » – | + | Argentina | Mola 1996 | ||
| 233. | E. unimaculata (DeGeer, 1773) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a | ||
| 234. | Hydrobasileuscroceus (Brauer, 1867) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 |
| 235. | Ladonajulia (Uhler, 1857) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 236. | Lathrecistaasiatica (Fabricius, 1798) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| 237. | Leucorrhiniaalbifrons (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 |
| 238. | L. dubia (Van der Linden, 1825) | 26(24A+XX)* | – | Finland | Oksala 1939a, 1945 |
| 25(24A+X) | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2020b | ||
| 239. | L. frigida Hagen, 1890 | 21(20A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 23(22A+X) | + | ||||
| 240. | L. glacialis Hagen, 1890 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 241. | L. hudsonica (Selys, 1850) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| – » – | – | ||||
| 242. | L. intacta (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| – » – | – | ||||
| 243. | L. pectoralis (Charpentier, 1825) | 26(24A+XX)* | – | Finland | Oksala 1945 |
| 244. | L. proxima Calvert, 1890 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 245. | L. rubicunda (Linnaeus, 1857) | 25(24A+X) | – | Finland | Oksala 1939a |
| – » – | – | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 | ||
| – » – | – | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2018 | ||
| 246. | Libellulaangelina Selys, 1883 | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1915, 1930 |
| – » – | + | Japan | Kichijo 1942a | ||
| 247. | L. auripennis Burmeister, 1839 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 |
| 248. | L. axilena Westwood, 1837 | 23(22A+X) | – | USA | Cumming 1964 |
| 249. | L. basalis (Say, 1840) | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Smith 1916 |
| 250. | L. composita (Hagen, 1873) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 251. | L. croceipennis Selys, 1868 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 252. | L. cyanea Fabricius, 1775 | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 253. | L. depressa Linnaeus, 1758 | 23(22A+X) | – | Belgium | Carnoy 1885 |
| – » – | – | England | Hogben 1921 | ||
| 25(24A+X) | + | Austria | Kiauta 1968c, 1969b | ||
| 23(22A+X) | – | ||||
| 25(24A+X) | + | France | Kiauta 1973b | ||
| – » – | + | Croatia | Francovič and Jurečic 1986, 1989 | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov et al. 1998 | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2018 | ||
| 254. | L. flavida Rambur, 1842 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 255. | L. forensis Hagen, 1861 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 256. | L. fulva Muller, 1764 | 25(24A+X) | + | Switzerland | Kiauta and Kiauta 1979 |
| 27(26A+X) | + | Croatia | Francovič and Jurečic 1986, 1989 | ||
| 257. | L. insecta Hagen, 1861 | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | – | USA | Cruden 1968 | ||
| 258. | L. luctuosa Burmeister, 1839 | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Smith 1916 |
| 259. | L. pulchella Drury, 1773 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| – » – | + | Canada | Kiauta 1969a | ||
| 260. | L. quadrimaculata Linnaeus, 1758 | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1915, 1930 (L. q. asahinai Schmidt, 1957) |
| 260. | L. quadrimaculata Linnaeus, 1758 | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Kichijo 1942d (L. q. asahinai) |
| – » – | + | Japan | Omura 1955 (L. q. asahinai) | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Kiauta 1968b, c (L. q. asahinai) | ||
| – » – | + | Former USSR | Fuchsówna and Sawczyńska 1928 (L. q. quadrimaculata Linnaeus, 1758) | ||
| – » – | + | Finland | Oksala 1939a, b, 1945 (L. q. quadrimaculata) | ||
| – » – | + | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 (L. q. quadrimaculata) | ||
| – » – | + | Netherlands | Kiauta 1968b, c (L. q. quadrimaculata) | ||
| – » – | + | USA | Cruden 1968 (L. q. quadrimaculata) | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov et al. 1998 (L. q. quadrimaculata) | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2018 (L. q. quadrimaculata) | ||
| 261. | L. saturata Uhler, 1857 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 262. | L. semifasciata Burmeister, 1839 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 263. | L. vibrans Fabricius, 1793 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 264. | Lyriothemispachygastra (Selys, 1878) | 25(24A+X) | – | Japan | Omura 1955 |
| 265. | Macrothemisdeclivata Calvert, 1909 | 23(22A+X) | + | Brazil | Kiauta and Boyes 1972 |
| 266. | M. hemichlora (Burmeister, 1839) | 6(4A+neo-XY) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 267. | M. imitans Karsch, 1890 | 25(24A+X) | + | Brazil | Kiauta and Boyes 1972 (M. i. imitans Karsch, 1890) |
| 268. | M. mortoni Ris, 1913 | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 269. | M. musiva Calvert, 1898 | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 270. | Macrothemis sp. | 25(24A+X) | + | Argentina | Mola 2007 |
| 271. | Miathyriaartemis (Selys, 1857) | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 272. | M. marcella (Selys, 1857) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a | ||
| – » – | + | Argentina | Mola and Agopian 1985 | ||
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 273. | Micrathyriaartemis Ris, 1911 | 25(24A+X) | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 |
| – » – | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 | ||
| 274. | M. atra (Martin, 1897) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 275. | M. catenata Calvert, 1909 | 25(24A+X) | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 |
| – » – | + | Argentina | Mola 2007 | ||
| 276. | M. didyma (Selys, 1857) | 25(24A+X) | + | Jamaica | Cumming 1964 |
| 277. | M. exima Kirby, 1897 | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 278. | M. hagenii Kirby, 1890 | 25(24A+X) | + | Jamaica | Cumming 1964 |
| 279. | M. hesperis Ris, 1911 | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| – » – | + | Argentina | Mola et al. 1999 | ||
| 280. | M. hypodydima Calvert 1906 | 23(22A+X) | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 |
| 25(24A+X) | + | Argentina | Agopian and Mola 1988 | ||
| 281. | M. iheringi Santos, 1946 | 23(22A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 282. | M. laevigata Calvert, 1909 | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Brazil | Kiauta and Boyes 1972 | ||
| 283. | M. longifasciata Calvert, 1909 | 24(22A+neo-XY) | – | Argentina | Agopian and Mola 1988 |
| 284. | M. ocellata (Martin, 1897) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 (M. o. dentiens Calvert, 1909) |
| 285. | M. spuria (Selys, 1900) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Argentina | Mola et al. 1999 | ||
| 286. | M. stawiarskii Santos, 1953 | 25(24A+X) | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 |
| 287. | M. ungulata Foerster, 1907 | 23(20A+X1X2Y) | – | Argentina | Mola et al. 1999 |
| 288. | M. cf. eximia Kirby, 1879 | 21(20A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 289. | M. sp. (ungulata Foerster, 1907-group) | 23(22A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 290. | Nannothemisbella (Uhler, 1857) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 291. | Nesciothemisfarinosa (Foerster, 1898) | 25(24A+X) | + | Kenya | Kiauta 1969c |
| – » – | + | Kenya | Wasscher 1985 | ||
| 292. | Nesogoniablackburni (McLachlan, 1883) | 25(24A+X) | + | Hawaii | Kiauta 1969d |
| 293. | Neurothemisfulvia (Drury, 1773) | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| 294. | N. intermedia (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 (N. i. intermedia (Rambur, 1842)) |
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 (N. i. degener (Sel, 1842)) | ||
| 295. | N. terminata Ris, 1911 | 25(24A+X) | + | Philippines | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980b |
| 296. | N. tullia (Drury, 1773) | 28(26A+neo-XY) | + | India | Ray Chaudhuri and Dasgupta 1949 |
| – » – | + | India | Kiauta 1969a (N. t. tullia (Drury, 1773)) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 (N. t. tullia) | ||
| 25(24A+X) | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 | ||
| 297. | Oligocladaamphinome Ris, 1919 | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 298. | O. laetitia Ris, 1911 | 23(22A+X) | + | Argentina | Mola and Agopian 1985 |
| 21(20A+X) | – | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 | ||
| 299. | O. monosticha Borror, 1931 | 23(22A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 300. | O. pachystigma Karsch, 1890 | 23(22A+X) | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 |
| 301. | Orthemisaequilibris Calvert, 1909 | 12(10A+neo-XY) | – | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 302. | O. ambinigra Calvert, 1909 | 12(10A+neo-XY) | – | Argentina | Agopian and Mola 1984 |
| 303. | O. biolleyi Calvert, 1906 | 23(22A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 304. | O. cultiformis Calvert, 1906 | 23(22A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a | ||
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 305. | O. discolor Burmeister, 1839 | 23(22A+X) | + | Argentina | Mola 2007 |
| 306. | O. ferruginea (Fabricius, 1775) | 10(8A+neo-XY)*** | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 23(22A+X) | – | USA | |||
| – » – | + | Guatemala, Dominica | Cruden 1968 | ||
| – » – | + | Peru | Kiauta 1969a, 1971c | ||
| – » – | + | Peru | Kiauta and Boyes 1972 | ||
| 23(22A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a | ||
| 25(24A+X) | + | ||||
| 23(22A+X) | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 23(22A+X) | – | Brazil, Argentina | Mola and Agopian 1985 | ||
| 24(22A+XX)* | + | ||||
| 307. | O. levis Calvert, 1906 | 6(4A+neo-XY)*** | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 8(6A+neo-XY)*** | – | ||||
| 308. | O. nodiplaga Karsch, 1891 | 41(40A+X) | – | Argentina | Agopian and Mola 1984 |
| 309. | Orthetrumabbotti Calvert, 1892 | 25(24A+X) | + | Kingdom of Eswatini (Former Swaziland) | Boyes et al. 1980 |
| 310. | O. albistylum (Selys, 1848) | 25(24A+X) | + | Italy | Kiauta 1971a (O. a. albistylum (Selys, 1848)) |
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov et al. 1998 | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Oguma 1915, 1917, 1930 (O. a. speciosum (Uhler, 1858)) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Kichijo 1942b (O. a. speciosum) | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Omura 1955 (O. a. speciosum) | ||
| 311. | O. azureum (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | Madagascar | Kiauta 1969b, c |
| 312. | O. brachiale (Beauvois, 1805) | 21(20A+X) | – | Kenya | Kiauta 1969b, c |
| 25(24A+X) | + | Burkina Faso (Former Voltiac Republic) | Kiauta and Ochssée 1979 (O. b. brachiale (Beauvois, 1805)) | ||
| 313. | O. brunneum (Fonscolombe, 1837) | 25(24A+X) | + | Italy | Kiauta 1971a |
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov et al. 1998 | ||
| 314. | O. cancellatum (Linnaeus, 1758) | 25(24A+X) | + | Finland | Oksala 1939a |
| – » – | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 | ||
| – » – | + | Netherlands | Kiauta 1969a, b | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2018 | ||
| 315. | O. chrysostigma (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Burkina Faso (Former Voltiac Republic) | Kiauta and Ochssée 1979 |
| – » – | + | Kingdom of Eswatini (Former Swaziland) | Boyes et al. 1980 | ||
| – » – | + | Kenya | Wasscher 1985 | ||
| 316. | O. coerulescens (Fabricius, 1798) | 25(24A+X) | + | Austria | Kiauta 1969c |
| 23(22A+X) | – | ||||
| 25(24A+X) | + | Italy | Kiauta 1971a | ||
| 27(26A+X) | + | ||||
| 317. | O. glaucum (Brauer, 1865) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1978a, b | ||
| – » – | + | India | Handa and Batra 1980 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Handa et al. 1984 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Walia and Sandhu 2002 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Kumari and Gautam 2017 | ||
| 318. | O. guineese (Ris, 1909) | 25(24A+X) | + | Burkina Faso (Former Voltiac Republic) | Kiauta and Ochssée 1979 |
| 319. | O. japonicum (Uhler, 1858) | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1917, 1930 (O. j. internum McLachlan, 1894) |
| – » – | + | Japan | Kichijo 1942b (O. j. internum) | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Omura 1955 (O. j. internum) | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 (O. j. internum) | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1976 (O. j. internum) | ||
| 320. | O. julia Kirby, 1900 | 25(24A+X) | + | Kingdom of Eswatini (Former Swaziland) | Boyes et al. 1980 (O. j. falsum (Longfeild, 1955)) |
| – » – | + | Kenya | Wasscher 1985 (O. j. falsum) | ||
| 321. | O. luzonicum (Brauer, 1868) | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 |
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Thomas and Prasad 1981 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 | ||
| 322. | O. melania (Selys, 1883) | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1917 |
| – » – | + | Japan | Omura 1955 | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov 2003 | ||
| 323. | O. monardi (Schmidt, 1951) | 25(24A+X) | + | Burkina Faso (Former Voltiac Republic) | Kiauta and Ochssée 1979 |
| 324. | O. poecilops (Ris, 1916) | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Suzuki et al. 1991 (O. p. miyajimaensis Yuki et Doi, 1938) |
| 325. | O. pruinosum (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 (O. p. neglectum (Rambur, 1842)) |
| – » – | + | Taiwan | Kiauta 1969a, c (O. p. neglectum) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 (O. p. neglectum) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 (O. p. neglectum) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1978a, b (O. p. neglectum) | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 (O. p. neglectum) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Walia and Sandhu 2002 (O. p. neglectum) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Kumari and Gautam 2017 (O. p. neglectum) | ||
| 326. | O. sabina (Drury, 1773) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Asana and Makino 1935 |
| – » – | + | India | Makino 1935 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Kichijo 1942b | ||
| – » – | + | India | Ray Chaudhuri and Dasgupta 1949 | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 | ||
| 326. | O. sabina (Drury, 1773) | – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 |
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Walia and Sandhu 2002 (O. s. sabina (Drury, 1773)) | ||
| 327. | O. taeniolatum (Schneider, 1845) | 25(24A+X) | + | Greece | Kiauta 1972a |
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1978a, b | ||
| – » – | + | India | Handa and Batra 1980 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Handa et al. 1984 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Thomas and Prasad 1986 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Walia and Sandhu 2002a | ||
| – » – | + | India | Walia et al. 2015 | ||
| 328. | O. testaceum (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 |
| 329. | O. triangulare (Selys, 1878) | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Omura 1955 (O. t. melania (Selys, 1883)) |
| – » – | + | Taiwan | Kiauta 1969a, b (O. t. triangulare (Selys, 1878)) | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 (O. t. triangulare) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1978a, b (O. t. triangulare) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Handa and Batra 1980 (O. t. triangulare) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 (O. t. triangulare) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Walia and Sandhu 2002 (O. t. triangulare) | ||
| 330. | Pachydiplaxlongipennis (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | USA | Cruden 1968 | ||
| – » – | + | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 | ||
| 331. | Palpopleurajucunda Rambur, 1842 | 25(24A+X) | + | Kingdom of Eswatini (Former Swaziland) | Boyes et al. 1980 |
| 332. | P. lucia (Drury, 1773) | 25(24A+X) | + | Burkina Faso (Former Voltiac Republic) | Kiauta and Ochssée 1979 (P. l. portia (Drury, 1773)) |
| – » – | + | Kenya | Wasscher 1985 (P. l. portia) | ||
| 333. | P. sexmaculata (Fabricius, 1787) | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 (P. s. sexmaculata (Fabricius, 1787)) | ||
| 334. | Pantalaflavescens (Fabricius, 1798) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Asana and Makino 1935 |
| – » – | + | India | Makino 1935 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Kichijo 1942b | ||
| – » – | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Seshachar and Bagga 1963 | ||
| – » – | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 | ||
| – » – | + | Madagascar | Kiauta 1969b | ||
| – » – | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a | ||
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| – » – | + | Kingdom of Eswatini (Former Swaziland) | Boyes et al. 1980 | ||
| – » – | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | Argentina | Agopian and Mola 1988 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b | ||
| 23(22A+X) | + | India | Walia et al. 2011 | ||
| 335. | P. hymenaea (Say, 1836) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | USA | Cruden 1968 | ||
| 336. | Perithemiscornelia Ris, 1910 | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 337. | P. domitia (Drury, 1773) | 25(24A+X) | + | Jamaica | Cumming 1964 |
| 338. | P. electra Ris, 1928 | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 339. | P. icteroptera (Selys in Sagra, 1857) | 25(24A+X) | + | Argentina | Mola and Agopian 1985 |
| 340. | P. lais (Petry, 1834) | 17(16A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | – | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a | ||
| – » – | – | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 341. | P. mooma Kirby, 1889 | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a | ||
| – » – | – | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| – » – | + | Argentina | Mola and Agopian 1985 | ||
| 342. | P. tenera (Say, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 |
| 343. | P. seminole Calvert, 1907 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cumming 1964 |
| 344. | Perithemis sp. | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 345. | Planiplaxerythropyga (Karsch, 1891) | 25(24A+X) | + | Argentina | Mola et al. 1999 |
| – » – | + | – » – | De Gennaro 2004 | ||
| 346. | P. sanguiniventris (Calvert, 1907) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 347. | Plathemislydia (Drury, 1773) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | McGill 1907 |
| – » – | + | USA | Cruden 1968 | ||
| 348. | Potamarchacongener (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Asana and Makino 1935 as P. obscura (Rambur, 1842) |
| – » – | + | India | Makino 1935 as P. obscura | ||
| – » – | + | India | Kichijo 1942b as P. obscura | ||
| – » – | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 as P. obscura | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 as P. obscura | ||
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Sandhu and Walia 1995 | ||
| 349. | Pseudothemiszonata (Burmeister, 1839) | 24(22A+neo-XY) | – | Japan | Omura 1955 |
| 350. | Pseudotrameaprateri Fraser, 1920 | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| 351. | Rhodopygiacardinalis (Erichson, 1848) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 352. | R. geijskesi Belle, 1964 | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 353. | Rhodothemisrufa (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 |
| 354. | Rhyothemisfuliginosa Selys, 1883 | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Toyoshima and Hirai 1953 |
| – » – | + | Japan | Omura 1955 | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Hirai 1956 | ||
| 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Kiauta 1969c | ||
| 23(22A+X) | + | ||||
| 355. | R. variegata (Linnaeus et Johansson, 1763) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Ray Chaudhuri and Dasgupta 1949 |
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 | ||
| 356. | Scapaneafrontalis (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Jamaica | Cumming 1964 |
| 357. | Sympetrumcommixtum (Selys, 1884) | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Tyagi 1978a, b, 1982 |
| 358. | S. corruptum (Hagen, 1861 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 as Tarnetrum corruptum (Hagen, 1861) |
| – » – | + | USA | Kiauta 1969a, c as T. corruptum | ||
| 359. | S. costiferum (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 360. | S. croceolum (Selys, 1840) | 25(24A+X) | + | Russia | Perepelov 2003 |
| 361. | S. danae (Sulzer, 1776) | 25(24A+X) | + | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 |
| – » – | + | Finland | Oksala 1945 | ||
| – » – | + | USA | Cruden 1968 | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov 2003 | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2018 | ||
| 362. | S. eroticum (Selys, 1883) | 21(20A+X) | – | Japan | Kichijo 1942b, c |
| – » – | – | Japan | Hirai 1956 | ||
| – » – | – | Japan | Kiauta 1969c | ||
| 363. | S. flaveolum (Linnaeus, 1758) | 25(24A+X) | + | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 |
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov 2003 | ||
| 364. | S. fonscolombii (Selys, 1840) | 25(24A+X) | + | Russia | Perepelov 2003 |
| 365. | S. frequens (Selys, 1883) | 23(22A+X) | – | Japan | Oguma 1917, 1930 |
| – » – | – | Japan | Kichijo 1942a, b | ||
| – » – | – | Japan | Kiauta 1969c | ||
| 366. | S. infuscatum (Selys, 1883) | 25(24A+X) | + | Russia | Perepelov 2003 |
| 367. | S. internum Montgomery, 1943 | 27(26A+X) | + | Canada | Kiauta 1973a |
| 368. | S. madidum (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 368. | S. madidum (Hagen, 1861) | – » – | + | Canada | Kiauta 1973a |
| 369. | S. meridionale (Selys, 1841) | 25(24A+X) | + | Switzerland | Kiauta 1966 |
| 370. | S. obtrusum (Hagen, 1867) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 371. | S. parvulum Bartenev, 1912 | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Kiauta 1968c |
| 372. | S. pedemontanum Müller in Allioni, 1766 | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1917, 1930 (S. p. elatum (Selys, 1872)) |
| – » – | + | Japan | Kichijo 1942b (S. p. elatum) | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Kiauta and Brink 1975 (S. p. elatum) | ||
| – » – | + | Switzerland | Kiauta and Brink 1975 (S. p. pedemontanum (Müller, 1766)) | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov et al. 1998 (S. p. pedemontanum) | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b | ||
| 373. | S. rubicundulum (Say, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 374. | S. sanguineum (Müller, 1764) | 25(24A+X) | + | Italy | Kiauta 1971a |
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b | ||
| 375. | S. semicinctum (Say, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Smith 1916 |
| – » – | + | USA | Cruden 1968 | ||
| 376. | S. striolatum (Charpentier, 1840) | 25(24A+X) | – | Luxembourg | Kiauta 1966 |
| 377. | S. vicinum (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 378. | S. vulgatum (Linnaeus, 1758) | 25(24A+X) | + | Netherland | Kiauta 1972c |
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov 2003 | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2018 | ||
| 379. | Tarnetrumillotum (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | + | Jamaica | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | USA | Cruden 1968 | ||
| 380. | Tauriphilaaustralis (Hagen, 1867) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 381. | T. azteca Calvert, 1906 | 25(24A+X) | + | Mexico | Cruden 1968 |
| 382. | T. risi Martin 1896 | 25(24A+X) | + | Argentina, Uruguay | Mola and Agopian 1985 |
| 383. | Tholymiscitrina Hagen, 1867 | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 384. | Th. tillagra (Fabricius, 1798) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 |
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 | ||
| 385. | Trameaabdominalis (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 386. | T. basilaris (Palisot de Beauvois, 1817) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Das 1956 (T. b. burmeisteri (Kirby, 1889)) |
| – » – | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 (T. b. burmeisteri) | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 (T. b. burmeisteri) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 (T. b. burmeisteri) | ||
| 387. | T. binotata (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | – | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 388. | T. carolina (Linnaeus, 1763) | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | – | USA | Cruden 1968 | ||
| 389. | T. cophysa (Hagen, 1867) | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 390. | T. lacerata (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 391. | T. limbata (Desjardins, 1832) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Asana and Makino 1935 |
| – » – | + | India | Makino 1935 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Kichijo 1942b | ||
| 392. | T. virginia (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Oguma and Asana 1932 |
| – » – | + | India | Kichijo 1942b | ||
| – » – | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 | ||
| 393. | Trithemisannulata (Palisot de Beauvois, 1805) | 25(24A+X) | – | Republic of South Africa | Boyes et al. 1980 |
| – » – | + | Kenya | Wasscher 1985 | ||
| 394. | T. arteriosa (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Kingdom of Eswatini (Former Swaziland) | Boyes et al. 1980 |
| 395. | T. atra Pinhey, 1961 | 25(24A+X) | + | Burkina Faso (Former Voltiac Republic) | Kiauta and Ochssée 1979 |
| 396. | T. aurora (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Oguma and Asana 1932 |
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| 397. | T. dorsalis (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | Kingdom of Eswatini (Former Swaziland) | Boyes et al. 1980 |
| 398. | T. festiva (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| – » – | + | India | Tyagi 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 | ||
| 399. | T. furva Karsch, 1899 | 25(24A+X) | + | Sudan | Wasscher 1985 |
| 400. | T. imiata Pinhey, 1961 | 25(24A+X) | – | Burkina Faso (Former Voltiac Republic) | Kiauta and Ochssée 1979 |
| 401. | T. kirbyi Selys, 1891 | 25(24A+X) | – | Burkina Faso (Former Voltiac Republic) | Kiauta and Ochssée 1979 (T. k. ardens Gerstaecker, 1891) |
| – » – | + | Kenya | Wasscher 1985 (T. k. ardens) | ||
| 402. | T. pallidinervis (Kirby, 1889) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Asana and Makino 1935 |
| – » – | + | India | Makino 1935 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Kichijo 1942b | ||
| – » – | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 | ||
| – » – | + | Philippines | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980b | ||
| 403. | T. werneri Ris, 1912 | 25(24A+X) | + | Kenya | Wasscher 1985 |
| 404. | Uracisimbuta (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 405. | U. ovipositrix Calvert, 1909 | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | – | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 406. | Urothemisedwardsi (Selys, 1849) | 25(24A+X) | + | Sudan | Wasscher 1985 |
| 407. | U. signata (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Das 1956 (U. s. signata (Rambur, 1842)) |
| – » – | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 (U. s. signata) | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 | ||
| 408. | Zenithopterafasciata (Linnaeus, 1758) | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| 409. | Z. lanei Santos, 1941 | 25(24A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 410. | Z. viola Ris, 1910 | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 411. | Zygonyxiris Kirby, 1900 | 23(22A+X) | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 (Z. i. malayanus (Laidlaw, 1902)) |
| 412. | Z. torrida (Kirby, 1889) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Tyagi 1978a, b |
| 413. | Zyxommapetiolatum (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 |
| Cordulegastroidea | |||||
| Chlorogomphidae | |||||
| 414. | Watanabeopetaliaatkinsoni (Selys, 1878) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Walia and Chahal 2019 |
| Cordulegastridae | |||||
| 415. | Anotogasterbasalis Selys, 1854 | 23(22A+X) | – | India | Sandhu and Malhotra 1994b |
| 416. | A. kuchenbeiseri (Förster, 1899) | 25(24A+X) | + | China | Zhu and Wu 1986 |
| 417. | A. sieboldii (Selis, 1854) | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1930 |
| – » – | + | Japan | Kichijo 1942a | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Kiauta 1969a | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov et al. 2001 | ||
| 418. | Cordulegasterboltoni (Donovan, 1807) | 25(24A+X) | + | Finland | Oksala 1939a, b |
| – » – | – | Austria | Kichijo 1942a | ||
| – » – | + | Sweden | Kiauta 1968d, e, 1969a | ||
| 419. | C. brevistigma Selys, 1854 | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Walia and Chahal 2019 |
| 420. | C. diastatops (Selys, 1854) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 421. | C. dorsalis Hagen, 1857 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 422. | C. maculata Selys, 1854 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 423. | Neallogasterhermionae (Fraser, 1927) | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1976 |
| Zygoptera | |||||
| Lestoidea | |||||
| Lestidae | |||||
| 424. | Austrolestescolensonis (White, 1846) | 25(24A+X) | + | New Zealand | Jensen 1980 |
| 425. | Chalcolestesviridis (Van der Linden, 1825) | 25(24A+X) | + | Netherlands | Kiauta 1969a |
| 426. | Indolestescyaneus (Selys, 1862) | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1976 as I. cyanea (Selys, 1862) |
| 427. | Lestesbarbarus (Fabricius, 1798) | 25(24A+X) | + | Former Yugoslavia | Kiauta 1972a |
| 428. | L. congener Hagen, 1861 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 429. | L. disjunctus Selys, 1862 | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 430. | L. dorothea Fraser, 1924 | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| 431. | L. dryas Kirby, 1890 | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b | ||
| 432. | L. forcipatus Rambur, 1842 | 21(20A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 433. | L. forficula Rambur, 1842 | 25(24A+X) | + | Jamaica | Cumming 1964 |
| 434. | L. paulistus Calvert, 1909 | 25(24A+X) | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 |
| 435. | L. rectangularis Say, 1839 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 436. | L. similatrix McLachlan, 1895 | 25(24A+X) | + | Madagascar | Kiauta 1969b |
| 437. | L. sponsa (Hansemann, 1823) | 25(24A+X) | – | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 |
| – » – | + | Japan | Kichijo 1941, 1942a, d, e | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b | ||
| 438. | L. stultus Hagen, 1861 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 439. | L. vidua Hagen, 1861 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cumming 1964 |
| 440. | L. vigilax Selys, 1862 | 19(18A+X) | – | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 |
| 441. | L. virens Charpentier, 1825 | 25(24A+X) | + | Netherlands | Kiauta 1969a (L. v. vestalis Rambur, 1842) |
| 442. | Sympecmafusca (Van der Linden, 1823) | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Kichijo 1941, 1942d, e |
| 443. | S. paedisca (Brauer, 1877) | 25(24A+X) | + | Netherlands | Kiauta and Kiauta-Brink 1975 (S. annulata braueri (Bianchi, 1904)) |
| – » – | + | Russia | Perepelov 2003 (S. a. braueri) | ||
| Synlestidae | |||||
| 444. | Megalestesmajor Selys, 1862 | 25(24A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| Platystictoidea | |||||
| Platystictidae | |||||
| 445. | Drepanosticta sp. | 25(24A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1976 |
| 446. | Drepanosticta sp. | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Tyagi 1978a, b |
| 447. | Palaemnemapaulina (Drury, 1773) | 25(24A+X) | + | Costa Rica | Cumming 1964 |
| 448. | Protosticta sp. | 25(24A+X) | – | Tailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 |
| Calopterygoidea | |||||
| Calopterygidae | |||||
| 449. | Atrocalopteryxatrata (Selys, 1853) | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1930 as Calopteryx atrata Selys, 1853 |
| – » – | + | Japan | Kichijo 1942d as C. atrata | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Omura 1957 as C. atrata | ||
| 450. | Calopteryxaequabilis Say, 1839 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 451. | C. cornelia (Selys, 1853) | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1930 as Anaciagrion cornelia (Selys, 1853) |
| – » – | + | Japan | Kichijo 1942a as A. cornelia | ||
| 452. | C. dimidiata Burmeister, 1839 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 |
| 453. | C. japonica Selys, 1869 | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Kichijo 1942a |
| – » – | + | Japan | Hirai 1956 | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Omura 1957 | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Kiauta 1968e, f | ||
| 454. | C. maculata (Beauvois, 1805) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cumming 1964a |
| – » – | + | USA | Cruden 1968 | ||
| 455. | C. splendens (Harris, 1780) | 25(24A+X) | + | Turkey | Kiauta 1972a (C. s. amasina Bartenev, 1912) |
| 455. | C. splendens (Harris, 1780) | – » – | + | Italy | Kiauta 1971a (C. s. caprai Conci, 1956) |
| – » – | – | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 (C. s. splendens (Harris, 1782)) | ||
| – » – | – | Finland | Oksala 1945 (C. s. splendens) | ||
| – » – | – | Germany | Kiauta 1969a, 1971b (C. s. splendens) | ||
| – » – | – | France | Kiauta 1973b (C. s. splendens) | ||
| – » – | – | Russia | Perepelov et al. 1998 (C. s. splendens) | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2020b | ||
| 456. | C. virgo (Linnaeus, 1758) | 25(24A+X) | + | Spain | Kiauta 1971b (C. v. meridionalis Selys, 1873) |
| 27(26A+X) | + | ||||
| 25(24A+X) | + | Slovenija | Kiauta 1967a, 1968b, c (C. v. padana Conci, 1956) | ||
| – » – | + | Austria | Kiauta 1967a, 1968b, c (C. v. padana) | ||
| – » – | – | Belgium | Carnoy 1885 (C. v. virgo (Linnaeus, 1758)) | ||
| – » – | + | Finland | Oksala 1939 (C. v. virgo) | ||
| – » – | + | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 (C. v. virgo) | ||
| – » – | + | Germany, Luxembourg | Kiauta 1968e, f (C. v. virgo) | ||
| – » – | + | Netherlands | Kiauta 1972c (C. v. virgo) | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2020b | ||
| 457. | Hetaerinaamericana (Fabricius, 1798) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | USA | Cruden 1968 | |||
| 458. | H. charca Calvert, 1909 | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 459. | H. longipes (Hagen in Selys, 1853) | 25(24A+X) | + | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 as H. carnifex Hagen in Selys, 1853 |
| – » – | + | Brazil | Agopian and Mola 1984 as H. carnifex | ||
| 460. | H. rosea Selys, 1853 | 27(26A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Bolivia | Kiauta 1969c | ||
| 25(24A+X) | – | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 27(26A+X) | + | ||||
| 461. | H. sanguinea Selys, 1853 | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 462. | H. titia (Drury, 1773) | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Cumming 1964 |
| – » – | + | Mexico | Kiauta 1970a as H. tricolor (Burmeister, 1839) | ||
| 463. | H. vulnerata (Selys, 1853) | 25(24A+X) | + | Mexico | Kiauta 1970a |
| 464. | Matronabasilaris Selys, 1853 | 25(24A+X) | – | Taiwan | Kiauta 1968c |
| 465. | Mnaiscostalis Selys, 1869 | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1930 |
| – » – | + | Japan | Kichijo 1942a | ||
| 466. | M. pruinosa Selys, 1853 | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Oguma 1930 as M. strigata Selys, 1853 |
| – » – | + | Japan | Kichijo 1942a as M. strigata | ||
| – » – | + | Japan | Omura 1957 as M. strigata | ||
| 467. | Neurobasischinensis (Linnaeus, 1758) | 23(22A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 (N. c. chinensis (Linnaeus, 1758)) |
| 25(24A+X) | – | ||||
| 23(22A+X) | – | India | Tyagi 1978b (N. c. chinensis) | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 (N. c. chinensis) | ||
| – » – | – | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 (N. c. chinensis) | ||
| – » – | + | India | Walia and Sandhu 2002 (N. c. chinensis) | ||
| – » – | – | India | Walia et al. 2016 (N. c. chinensis) | ||
| – » – | – | India | Walia and Katnoria 2018 (N. c. chinensis) | ||
| 468. | Phaoniridipennis (Burmeister, 1839) | 25(24A+X) | + | Republic of South Africa | Boyes et al. 1980 |
| Chlorocyphidae | |||||
| 469. | Aristocyphafenestrella Rambur, 1842 | 23(22A+X) | – | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 as Rhinocypha fenestrella Rambur, 1842 |
| 470. | A. quadrimaculata (Selys, 1853) | 23(22A+X) | + | India | Chatterjee and Kiauta 1973 as Rhinocypha quadrimaculata Selys, 1853 |
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 as Rh. quadrimaculata | ||
| 471. | A. trifasciata (Selys, 1853) | 23(22A+X) | – | India | Tyagi 1978a, b as Rhinocypha trifasciata Selys, 1853 |
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 as Rh. trifasciata | ||
| 472. | Heliocyphabiforata (Selys, 1859) | 23(22A+X) | – | India | Tyagi 1978a, b as Rhinocypha biforata beesoni Selys, 1859 |
| 473. | H. biseriata (Selys, 1859) | 23(22A+X) | – | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 as Rhinocypha b. biforata Selys, 1859 |
| 474. | Libellagolineata (Burmeister, 1839) | 23(22A+X) | – | India | Walia et al. 2018 (L. l. lineata (Burmeister, 1839)) |
| 25(24A+X) | – | ||||
| 475. | Paracyphaunimaculata (Selys, 1879) | 23(22A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 as Rhinocypha unimaculata Selys, 1879 |
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 as Rh. unimaculata | ||
| 476. | Rhinocyphacolorata Selys, 1869 | 23(22A+X) | – | Philippines | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980b |
| 25(24A+X) | – | ||||
| 477. | Vestalisgracilis (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 |
| Polythoridae | |||||
| 478. | Corairene Ris, 1918 | 23(22A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 479. | Polythoreboliviana (McLachlan, 1878) | 23(22A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| Euphaeidae | |||||
| 480. | Anisopleuracomes Hagen, 1880 | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1976, 1982 |
| 481. | Bayaderaindica (Selys, 1853) | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Chatterjee and Kiauta 1973 |
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 | ||
| 482. | Euphaeaguerini Rambur, 1842 | 25(24A+X) | – | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 |
| 483. | Epallagefatime (Charpentier, 1840) | 25(24A+X) | – | Greece | Kiauta 1970b |
| – » – | – | Greece | Chatterjee and Kiauta 1973 | ||
| Megapodagrionidae | |||||
| 484. | Allopodagrioncontortum (Selys, 1862) | 25(24A+X) | + | Brazil | Kiauta 1972b as Megapodagrion contortum (Selys, 1862) |
| 485. | Teinopodagrionmacropus (Selys, 1862) | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 as Megapodagrion macropus (Selys, 1862) |
| 486. | T. setigerum (Selys, 1886) | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 as Megapodagrion setigerum Selys, 1886 |
| Heteragrionidae | |||||
| 487. | Heteragrionflavidorsum Calvert, 1909 | 25(24A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 488. | H. inca Calvert, 1909 | 25(24A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| Philogeniidae | |||||
| 489. | Philogeniacarrillica Calvert, 1907 | 25(24A+X) | + | Costa Rica | Cumming 1964 |
| Hypolestidae | |||||
| 490. | Hypolestesclara (Calvert, 1891) | l7(16A+X) | – | Jamaica | Cumming 1964 |
| Coenagrionoidea | |||||
| Platycnemididae | |||||
| 491. | Calicnemiaminiata (Selys, 1886) | 25(24A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 |
| 492. | C. pulverulans (Selys, 1886) | 25(24A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 |
| 493. | Calicnemia sp. | 25(24A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1975 |
| 494. | Calicnemia sp. | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Tyagi 1978b |
| 495. | Coelicciachromothorax (Selys, 1891) | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Walia and Devi 2020b |
| 496. | C. bimaculata (Laidlaw, 1914) | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Walia and Devi 2020b |
| 497. | C. didyma (Selys, 1863) | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Walia and Devi 2020b |
| 498. | C. fraseri (Laidlaw, 1932) | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Walia and Devi 2020b |
| 499. | C. renifera (Selys, 1886) | 25(24A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| – » – | – | India | Walia and Devi 2020b | ||
| 500. | Coperaannulata (Selys, 1863) | 25(24A+X) | + | Japan | Kichijo 1941, 1942a, c |
| – » – | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 | ||
| – » – | – | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Walia and Devi 2018 | ||
| 501. | C. marginipes (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Tyagi 1978a, b |
| – » – | – | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Walia and Devi 2018 | ||
| 502. | C. vittata (Selys, 1863) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Walia and Devi 2018 |
| – » – | + | India | Walia and Devi 2018 (C. v. assamensis (Laidlaw, 1914)) | ||
| 503. | Disparoneuraquadrimaculata (Rambur, 1842) | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Walia and Devi 2020a |
| 504. | Esmecyaneovittata Fraser, 1922 | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Walia and Devi 2020a |
| 505. | E. longistyla Fraser, 1931 | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Walia and Devi 2020a |
| 506. | Onychargiaatrocyana (Selys, 1865) | 25(24A+X) | – | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 |
| 507. | Platycnemispennipes (Pallas, 1771) | 25(24A+X) | – | Finland | Oksala 1945 |
| – » – | – | Italy | Kiauta 1971a | ||
| – » – | – | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b | ||
| 508. | Prodasineuraautumnalis (Fraser, 1922) | 25(24A+X) | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 |
| 509. | P. nigra (Fraser, 1922) | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Walia and Devi 2020a |
| 510. | P. verticalis (Selys, 1860) | 25(24A+X) | – | India | Walia and Devi 2020a |
| 511. | Prodasineura sp.1 | 25(24A+X) | – | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 |
| 512. | Prodasineura sp.2 | 25(24A+X) | – | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 |
| Coenagrionidae | |||||
| 513. | Acanthagrionascendens Calvert, 1909 | 27(26A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 514. | A. chacoense Calvert, 1909 | 27(26A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 515. | A. gracile (Rambur, 1842) | 27(26A+X) | – | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a (A. g. minarum Selys, 1876) |
| – » – | – | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 (A. g. minarum Selys, 1876) | ||
| 516. | Aeolagrioninca Selys, 1876 | 27(26A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 as A. foliaceum (Sjöstedt, 1918) |
| 517. | Agriocnemisclauseni Fraser, 1922 | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Tyagi 1978a, b |
| 518. | A. femina (Brauer, 1868) | 27(26A+X) | – | Philippines | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980b |
| – » – | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 | ||
| 519. | A. pygmaea (Rambur, 1842) | 27(26A+X) | – | India | Tyagi 1978b |
| – » – | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 | ||
| 520. | Amphiagrionabbreviatum (Selys, 1876) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 521. | Amphiallagmaparvum (Selys, 1876) | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Handa and Kochhar 1985 as Enallagma parvum Selys, 1876 |
| 522. | Argiaapicalis (Say, 1839) | 37(36A+X) | – | USA | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980b |
| 523. | A. fumipennis (Burmeister, 1839) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980c (A. f. atra Gloyd, 1968) |
| – » – | – | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 (A. f. fumipennis (Burmeister, 1839)) | ||
| – » – | – | USA | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980c (A. f. fumipennis) | ||
| – » – | + | Canada | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980c (A. f. violacea (Hagen, 1861)) | ||
| 524. | A. funebris (Hagen, 1861) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Kiauta 1972b |
| 28(26A+XX)* | – | Mexico | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980c | ||
| 525. | A. immunda (Hagen, 1861) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980c |
| 526. | A. moesta (Hagen, 1861) | 25(24A+X) | – | Canada | Kiauta 1978 |
| – » – | – | USA | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980c | ||
| 527. | A. nahuana Calvert, 1902 | 25(24A+X) | – | USA | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980c |
| 528. | A. sedula (Hagen, 1861) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| – » – | – | USA | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980c | ||
| 529. | A. tibialis (Rambur, 1842) | 37(36A+X) | – | USA | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980c |
| 530. | A. translata Hagen, 1865 | 25(24A+X) | + | USA | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980c |
| 531. | A. violacea (Hagen, 1861) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 532. | A. vivida (Hagen, 1861) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 533. | Ceriagrionauranticum Fraser, 1922 | 27(26A+X) | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 as C. latericium Lieftinck, 1951 |
| 534. | C. azureum (Selys, 1891) | 27(26A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| 535. | C. cerinomelas Lieftinck, 1927 | 27(26A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| 536. | C. cerinorubellum (Brauer, 1866) | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 | ||
| 537. | C. coromandelianum (Fabricius, 1798) | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Ray Chaudhuri and Dasgupta 1949 |
| – » – | + | India | Srivastava and Das 1953 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Das 1956 | ||
| – » – | + | Nepal | Kiauta and Kiauta 1982 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 | ||
| 538. | C. fallax Ris, 1914 | 27(26A+X) | + | Republic of South Africa | Dasgupta 1957 |
| 539. | C. glabrum (Burmeister, 1839) | 27(26A+X) | – | Kingdom of Eswatini (Former Swaziland) | Boyes et al. 1980 |
| 540. | C. rubiae Laidlaw, 1916 | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Asana and Makino 1935 |
| – » – | + | India | Makino 1935 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Kichijo 1942a | ||
| 541. | C. tenellum (Villers, 1789) | 27(26A+X) | + | Italy | Kiauta 1971a (C. t. tenellum (Villers, 1789)) |
| 542. | Chromagrionconditum (Hagen, 1876) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 543. | Coenagrionarmatum (Charpentier, 1840) | 27(26A+X) | – | Finland | Oksala 1939a |
| – » – | – | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 | ||
| 544. | C. hastulatum (Charpentier, 1825) | 27(26A+X) | – | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 |
| – » – | – | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b | ||
| 545. | C. hylas (Trybom, 1889) | 27(26A+X) | – | Austria | Kiauta and Kiauta 1991 (C. h. freyi (Bilek, 1954)) |
| 546. | C. lunulatum (Charpentier, 1840) | 27(26A+X) | + | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b |
| 547. | C. pulchellum (Vander Linden, 1823) | 27(26A+X) | – | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 |
| – » – | – | Netherlands | Kiauta 1969c | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2020b | ||
| 548. | C. puella (Linnaeus, 1758) | 27(26A+X) | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2020b |
| 549. | C. resolutum (Hagen, 1876) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 550. | Coenagrion sp. | 27(26A+X) | + | Japan | Kichijo 1941, 1942d, e |
| 551. | Diceratobasismacrogaster (Selys, 1875) | 27(26A+X) | + | Jamaica | Cumming 1964 |
| 552. | Enallagmaaspersum (Hagen, 1861) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 553. | E. boreale Selys, 1875 | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 554. | E. carunculatum Morse, 1895 | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 555. | E. circulatum Selys, 1883 | 27(26A+X) | + | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b |
| 556. | E. civile (Hagen, 1861) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 557. | E. cyathigerum (Charpentier, 1840) | 27(26A+X) | – | Finland | Oksala 1939a, 1945 |
| – » – | – | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 | ||
| – » – | + | USA | Brink and Kiauta 1964 | ||
| 27(26A+X), | – | USA | Cruden 1968 | ||
| 29(28A+X) | – | ||||
| 27(26A+X) | + | Netherlands | Kiauta 1969a, c | ||
| 29(28A+X) | + | ||||
| 558. | E. ebrium (Hagen, 1861) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 559. | E. praevarum (Hagen, 1861) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 560. | Erythrommalindeni (Selys, 1840) | 27(26A+X) | + | Italy | Kiauta 1971a |
| 561. | E. najas (Hansemann, 1823) | 27(26A+X) | – | Finland | Oksala 1939a |
| – » – | – | Former USSR | Makalowskaja 1940 | ||
| – » – | – | Netherlands | Kiauta 1969a | ||
| – » – | – | Russia | Perepelov and Bugrov 2001b | ||
| – » – | + | Russia | Kuznetsova et al. 2020b | ||
| 562. | Homeourachelifera (Selys, 1876) | 27(26A+X) | + | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a as Enallagma cheliferum (Selys, 1876) |
| – » – | + | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 as E. cheliferum | ||
| 563. | Ischnuraaurora (Brauer, 1865) | 27(26A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| – » – | – | India | Handa and Kochhar 1985 | ||
| 564. | I. capreola (Hagen, 1861) | 27(26A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 as Ceratura capreola (Hagen, 1861) |
| 565. | I. cervula Selys, 1876 | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 566. | I. denticollis (Burmeister, 1839) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 567. | I. elegans (Van der Linden, 1823) | 27(26A+X) | – | Finland | Oksala 1939a, 1945 |
| – » – | – | Netherlands | Kiauta 1969a | ||
| – » – | – | Russia | Perepelov 2003 | ||
| 568. | I. fluviatilis Selys, 1876 | 27(26A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 569. | I. forcipata Morton, 1907 | 27(26A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| 570. | I. nursei (Morton, 1907) | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Tyagi 1978b as Rhodischnura nursei (Morton, 1907) |
| 571. | I. pumilio (Charpentier, 1825) | 27(26A+X) | + | Netherlands | Kiauta 1979b |
| 572. | I. perparva Selys, 1876 | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 573. | I. ramburii (Selys, 1850) | 27(26A+X) | + | USA | Kiauta and Brink 1978 |
| 574. | I. rufostigma Selys, 1876 | 27(26A+X) | – | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 (I. r. annandalei Laidlaw, 1919) |
| 575. | I. senegalensis (Rambur, 1842) | 27(26A+X) | + | Japan | Kichijo 1941, 1942d, e |
| – » – | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 | ||
| – » – | + | Ethiopia | Kiauta 1969b | ||
| – » – | + | Philippines | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980b | ||
| – » – | – | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 | ||
| – » – | + | India | Prasad and Thomas 1992 | ||
| 576. | I. verticalis (Say, 1839) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 577. | I. ultima Ris, 1908 | 27(26A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 578. | Leptagrionmacrurum (Burmeister, 1839) | 30(28A+neo-XY) | – | Brazil | Kiauta 1971c, 1972d |
| 579. | Mecistogaster. sp. 1 | 29(28A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 580. | Mecistogaster sp. 2 | 12(10A+neo-XY) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 581. | Megalagrionoahuense (Blackburn, 1884) | 27(26A+X) | + | Hawaii | Kiauta 1969b |
| 582. | Mortonagrionselenion (Ris, 1916) | 27(26A+X) | + | Japan | Kichijo 1941, 1942a, d, e |
| 583. | Nehalenniairene (Hagen, 1861) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| 584. | N. speciosa (Charpentier, 1840) | 28(26A+XX)* | – | Finland | Oksala 1945 |
| 585. | Oxyagrionhempeli Calvert, 1909 | 27(26A+X) | – | Brazil | Souza Bueno 1982 |
| 586. | O. terminale Selys, 1876 | 27(26A+X) | – | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | – | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 587. | Paracercionhieroglyphicum (Brauer, 1865) | 27(26A+X) | + | Japan | Kichijo 1941, 1942d, e as Coenagrion hieroglyphicum (Brauer, 1865) |
| 588. | P. malayanum (Selys, 1876) | 27(26A+X) | + | Nepal | Kiauta 1974, 1975 |
| 589. | Proischnurasubfurcata (Selys, 1876) | 27(26A+X) | – | Kenya | Wasscher 1985 as Enallagma subfurcatum Selys, 1876 |
| 590. | Pseudagrionacaciae Förster, 1906 | 27(26A+X) | + | Republic of South Africa | Boyes et al. 1980 |
| 591. | P. australasiae Selys, 1876 | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| 592. | P. decorum (Rambur, 1842) | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| 593. | P. kersteni (Gerstaker, 1869) | 27(26A+X) | – | Kingdom of Eswatini (Former Swaziland) | Boyes et al. 1980 |
| 594. | P. microcephalum (Rambur, 1842) | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| – » – | + | Philippines | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980b | ||
| 595. | P. pruinosum (Burmeister, 1839) | 27(26A+X) | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 |
| 596. | P. rubripes (Selys, 1876) | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| – » – | + | Philippines | Kiauta and Kiauta 1980b | ||
| – » – | + | Thailand | Kiauta and Kiauta 1983 | ||
| 597. | P. salisburyense Ris, 1921 | 27(26A+X) | + | Kingdom of Eswatini (Former Swaziland) | Boyes et al. 1980 |
| 598. | P. spencei Fraser, 1922 | 27(26A+X) | + | India | Dasgupta 1957 |
| 599. | P. whellani Pinhey, 1956 | 25(24A+X) | + | Burkina Faso (Former Voltiac Republic) | Kiauta and Ochssée 1979 |
| 600. | Pyrrhosomanymphula (Sutzer, 1776) | 28(26A+XX)* | – | Finland | Oksala 1945 |
| 601. | Telebasiscarmesina Calvert, 1909 | 27(26A+X) | – | Surinam | Kiauta 1979a |
| – » – | – | Brazil | Ferreira et al. 1979 | ||
| 602. | Tigriagrionaurantinigrum Calvert, 1909 | 27(26A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 603. | Xanthocnemiszealandica (McLachlan, 1873) | 27(26A+X) | – | New Zealand | Jensen 1980 as X. zelandica (McLachlan, 1873) |
| 604. | Zoniagrionexclamationis (Selys, 1876) | 27(26A+X) | – | USA | Cruden 1968 |
| Protoneuridae | |||||
| 605. | Caconeuraautumnalis Fraser, 1922 | 25(24A+X) | + | India | Tyagi 1978b |
| 606. | Epipleoneura sp. | 27(26A+X) | – | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 |
| 607. | Protoneurarubriventris (Selys, 1860) | 27(26A+X) | + | Bolivia | Cumming 1964 as Neoneura rubriventris Selys, 1860 |
* In the original publication, the female karyotype is given. ** Jensen (1980) considers these data as erroneous (but see section “Concluding remarks and future directions” in the present paper). *** Karyotype formula is extrapolated based on vague descriptions by Cumming (1964).
Table 2.
The diversity of chromosome numbers and sex chromosome mechanisms, and modal karyotypes in 23 families of Odonata: a summary.
| Taxa | N of species/ genera studied | Male karyotypes | Modal karyotype | N of species/genera with modal karyotype (occurrence in percent) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N of species/genera described*) | |||||
| Anisozygoptera | |||||
| Epiophlebioidea | Epiophlebiidae (4/1) | 1/1 | 25, X0 | 24A + X | 1 (100) / 1 (100) |
| Anisoptera | |||||
| Aeshnoidea | Aeshnidae (456/51) | 58/18 | 13, X0; 14, neo-XY; 15, X0; 16, neo-XY; 19, X0; 21, X0; 24, neo-XY; 25, X0; 26, neo-XY; 27, X0 | 26A + X | 44 (76) / 14 (78) |
| Petaluroidea | Petaluridae (10/5) | 4/3 | 17, X0; 19, X0; 25, X0 | 16A + X | 3 (75) / 2 (67) |
| Gomphoidea | Gomphidae (980/87) | 66/31 | 12, neo-neo-XY; 21, X0; 22, neo-XY; 23, X0; 24, neo-XY; 25, X0 | 22A + X | 57 (86) / 28 (90) |
| Libelluloidea | Macromiidae (125/4) | 6/3 | 25, X0 | 24A + X | 6 (100) / 3 (100) |
| Corduliidae (154/20) | 23/7 | 10, neo-XY; 11, X0; 13, X0; 14, neo-XY, 20, XY; 21, X0; 25, X0; 26, neo-XY; 27, X0 | 24A + X | 19 (83) / 6 (86) | |
| Libellulidae (1037/142) | 255/59 | 6, neo-XY; 6 neo-XY; 8, neo-XY; 10, neo-XY; 12, neo-XY; 17, X0; 21, X0; 22, neo-XY; 23, X0; 23, X1X2Y; 24, neo-XY; 25, X0; 27, X0; 28, neo-XY; 29, X0; 41, X0 | 24A + X | 227 (89) / 57 (97) | |
| Cordulegastroidea | Cordulegastridae (46/3) | 9/3 | 23, X0; 25, X0 | 24A + X | 8 (89) / 3 (100) |
| Chlorogomphidae (47/3) | 1/1 | 25, X0 | 24A + X | 1 (100) / 1 (100) | |
| Zygoptera | |||||
| Lestoidea | Lestidae (151/9) | 20/5 | 19, X0; 21, X0; 25, X0 | 24A + X | 18 (90) / 5 (100) |
| Synlestidae (39/9) | 1/1 | 25, X0 | 24A + X | 1 (100) / 1 (100) | |
| Platystictoidea | Platystictidae (224/6) | 4/3 | 25, X0 | 24A + X | 4 (100) / 3 (100) |
| Calopterygoidea | Calopterygidae (185/21) | 20/8 | 23, X0; 25, X0; 27, X0 | 24A + X | 20 (100) / 8 (100) |
| Chlorocyphidae (144/19) | 9/6 | 23, X0; 25, X0 | 22A + X | 8 (89) / 5 (84) | |
| Polythoridae (59/7) | 2/2 | 23, X0 | 22A + X | 2 (100) / 2 (100) | |
| Euphaeidae (68/12) | 4/4 | 25, X0 | 24A + X | 4 (100) / 4 (100) | |
| Megapodagrionidae (296/42) | 3/2 | 25, X0 | 24A + X | 3 (100) / 2 (100) | |
| Heteragrionidae (57/2) | 2/1 | 25, X0 | 24A + X | 2 (100) / 1 (100) | |
| Philogeniidae (40/2) | 1/1 | 25, X0 | 24A + X | 1 (100) / 1 (100) | |
| Hypolestidae (6/4) | 1/1 | 17, X0 | 16A + X | 1 (100) / 1 (100) | |
| Coenagrionoidea | Platycnemididae (404/40) | 22/8 | 25, X0 | 24A + X | 19 (100) / 7 (100) |
| Coenagrionidae (1267/114) | 92/28 | 12, neo-XY; 25, X0; 27, X0; 29, X0; 30, neo-XY; 37, X0 | 26A + X | 81 (89) / 26 (90) | |
| Protoneuridae (260 / 25) | 3/3 | 25, X0; 27, X0 | 26A + X | 2 (70) / 2 (70) | |
*Taken from Dijkstra et al. 2013
Figure 1.
Mapping of modal karyotypes onto phylogenetic tree of Odonata families. The phylogenetic tree is taken from Bybee et al. (2016) who synthesized it based on trees from Dijkstra et al. (2014) and Carle et al. (2015). Plesiomorphic karyotype state is indicated by a black solid square (■), apomorphic karyotype states are indicated by black solid circles (●).
Concluding remarks and future directions
In total, karyotypes of 607 species (198 genera, 23 families) of Odonata are studied up to now. Table 1, presented in our work, includes 423 species (125 genera, 8 families) of the Anisoptera, 184 species (72 genera, 14 families) of the Zygoptera, and one species of the Anisozygoptera. Thus, the presently available karyotype data cover about 10% of the world species diversity of the order in general.
Within Odonata, chromosome numbers in males vary over a relatively wide range, from 2n = 6 in Macrothemis hemichlora and Orthemis levis to 2n = 41 in O. nodiplaga. Both low chromosome number species are suggested to have an evolutionarily secondary neo-XY system (Cumming 1964; Kiauta 1972c) that could have arisen through an X-autosome fusion from an X(0) system. All three of the above species belong to the largest dragonfly family Libellulidae, in which nearly 89% of studied species (255 in total) have the karyotype 2n = 25(24A + X). The last one is the most common in Odonata in general: it occurs in each of the three suborders, Zygoptera, Anisoptera and Anisozygoptera, and in all families with the exception of two damselfly families, the Polythoridae with only two studied species sharing 2n = 23(22A + X) and a monotypic family Hypolestidae with 2n = 17(16A + X) in male Hypolestes clara. Besides Libellulidae, the karyotype 2n = 25(24A + X) is currently the presumed modal one in 14 other families, such being the case at least in six better covered (at species and/or generic level) families, i.e. the dragonfly families Corduliidae, Cordulegastridae, and Macromiidae, and the damselfly families Lestidae, Calopterygidae, and Platycnemididae (Table 2, Fig. 1). This chromosome set is suggested to be an ancestral one for the order Odonata in general (Oguma 1930; Kuznetsova et al. 2020b) although this suggestion remains questionable at this stage.
Chromosomal rearrangements, among which fission and fusions apparently predominated (Kiauta 1969c, 1972c), led to the appearance of divergent karyotypes in the evolution of Odonata. As a result, in many dragonfly and damselfly families, other karyotypes, when occurring, are of secondary origin as indicated by either a diverged number of autosomes or a secondary sex chromosome system of an XY-type or both (e.g. Cumming 1964; Kiauta 1969a, c; Agopian and Mola 1984, 1988; Mola et al. 1999; Perepelov and Bugrov 2002). Some interesting examples of this kind can be found in the family Libellulidae, in which 2n = 25(24A + X) is most likely an evolutionarily initial karyotype (e.g. Agopian and Mola 1988). These examples are as follows (see Table 1): Orthemis nodiplaga and O. ambinigra with 2n = 41(40A + X) and 2n = 12(10A + neo-XY), respectively; Erythrodiplax media and E. minuscula, both with 2n = 22(20A + neo-XY); Micrathyria longifasciata and M. ungulata with 2n = 24(22A + neo-XY) and 2n = 23(20A + X1X2Y), respectively. In some families, any of these presumably derived karyotypes not only occurs but also prevails and may be considered modal (see Table 2 and Fig. 1). Within Anisoptera, such families are Aeshnidae (2n = 26A + X) and Gomphidae (2n = 22A + X), whereas within Zygoptera, these are Chlorocyphidae (2n = 22A + X) and Coenagrionidae (2n = 26A + X). Thus, Odonata, despite the fact that they have holokinetic chromosomes (Nokkala et al. 2002), demonstrate rather high karyotypic stability, with most species showing 2n = 25 (found in 60% of studied species), 2n = 27(21%) and 2n = 23(13%) which may point to some selective constraints acting to stabilize chromosome number in their evolution (Kuznetsova et al. 2020b).
There are the species for which different authors give various karyotypes that are sometimes difficult to interpret (see Table 1). In some cases, this might be due to misidentifications of a particular species or an error in determining the karyotype. For example, Wolfe (1953) reported 2n = 17(16A + X) for males of Uropetala carovei (Petaluridae, Anisoptera) from New Zealand. However, according to later studies of this species in the same locality (Jensen and Mahanty 1978; Jensen 1980), it has 2n = 25(24A + X), and Jensen (1980) therefore considers the Wolfe data as erroneous. We cannot exclude, however, that the above authors studied different U. carovei subspecies, U. c. carovei White, 1846 and U. c. chiltoni Tillyard, 1921, that may indeed have different karyotypes. In other cases, the chromosome number difference between geographic populations might be indicative of the inter-population variation within the bounds of one taxonomic species or even the existence of a species complex with several morphologically cryptic species. For example, 4 of the 17 studied species of the dragonfly genus Aeshna Fabricius, 1775 were reported to have different karyotypes in different populations. These are: Aeshna grandis – 2n = 26A + X (former USSR), 2n = 24A + X (former USSR, Finland), and 2n = 24A + neo-XY (Netherlands, Finland); A. isoceles – 2n = 26A + X (USA) and 2n = 24A + X (Russia); A. juncea – 2n = 26A + X (Italy) and 2n = 24A + neo-XY (Finland, former USSR, Italy); A. mixta – 2n = 26A + X (Netherlands) and 2n = 24A + X (India) (Table 1). In all such cases, special studies involving a combined analysis of karyotypes, morphology, distribution patterns and molecular markers are needed.
Approximately 80% of Odonata species have a pair of very small chromosomes, i.e. microchromosomes or m-chromosomes (Mola 2007, Table 1). A number of speculations have been forwarded to explain the origin of these chromosomes in Odonata. Kiauta (1968e) suggested m-chromosomes to be fragments of “normal” chromosomes, whereas Oguma (1930) considered them the remnants of an autosome pair in the process of its elimination by progressive loss of chromatin. The size of the smaller chromosome pair was shown to be variable within different species (Kiauta 1968e; see Mola 2007 for other references) which is consistent with both hypotheses. Closely related species and different populations of the same species often differ from each other in the presence/absence of m-chromosomes (Table 1). This is most likely due to the lack of clear criteria for the identification of a small chromosome pair as m-chromosomes in a particular karyotype (Mola 2007; Kuznetsova et al. 2020b).
Most cytogenetic studies of Odonata have been made only to determine the chromosome number and sex chromosome mechanism for which the routine staining was used. Although a considerable amount of such data was obtained (Table 1, 2), standard karyotypes of many Odonata taxa remain totally unknown (Fig. 1). Lack of data on more “primitive” families of Zygoptera (e.g. Hemiphlebiidae) and Anisoptera (e.g. Austropetaliidae and Neopetaliidae) makes difficult understanding karyotype evolution of the order in general.
During the last decades, karyotypes of a few dozen Odonata species were studied using various techniques of differential staining of chromosomes such as C-banding, AgNOR-staining and DNA specific fluorochrome banding visualiszing constitutive heterochromatin, nucleolus organizing regions (NORs) and AT- and GC-rich chromosome segments, respectively. Such data can be found in the following publications: Thomas and Prasad (1986), Prasad and Thomas (1992), Perepelov et al. (1998), Perepelov and Bugrov (2001a, b, 2002), Grozeva and Marinov (2007), De Gennaro et al. (2008), Walia et al. (2011, 2018), Walia and Chahal (2014, 2018), Walia and Devi (2018), Walia and Katnoria (2018), Walia and Devi (2020a, b). Unfortunately, these data alone did not shed much light on the karyotypic evolution of Odonata.
Although the classical cytological techniques remain necessary starting points for cytogenetic studies of Odonata to get an overview of their genomes, the future of Odonata cytogenetics must be coupled with the application of new cytogenetic molecular techniques that enable the localization of specific DNA sequences in chromosomes and the identification of individual chromosomes in karyotypes. In the article by Frydrychová et al. (2004) and, on a larger scale, in two of our recent publications (Kuznetsova et al. 2018, 2020b), the fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) technique was used for the first time for analyzing Odonata karyotypes. Several species belonging to the Anisoptera (from the families Aeshnidae, Libellulidae, and Corduliidae) and the Zygoptera (from the families Coenagrionidae and Calopterygidae) were studied regarding the occurrence of the TTAGG telomeric repeats and the distribution of the 18S rRNA genes in their karyotypes. The TTAGG repeats proved to be the canonical motif of telomeres in the class Insecta in general, which, however, was repeatedly lost in the evolution of different phylogenetic lineages (Kuznetsova et al. 2020a). It was shown in the listed Odonata publications that the (TTAGG)n motif does not occur in all but one (Sympetrum vulgatum) species, and the 18S is located on one of the largest pairs of autosomes in all studied dragonfly species but on m-chromosomes in all studied damselfly species (Kuznetsova et al. 2020b).
The results obtained showed great promise of the combined use of FISH and classical and banding cytogenetics in order to identify new chromosomal markers, reveal differences between species, particularly when they share the same or very close karyotypes, and speculate about the mechanisms involved in the karyotype evolution of Odonata (Kuznetsova et al. 2020b). Another promising line of future research could be to test hypotheses (Mola and Papeschi 1994; Ardila-Garcia and Gregory 2009) about whether there is a relationship between karyotype evolution and genome size diversity in the Odonata or there is no such relationship.
Acknowledgements
The present study was performed within the research project no. AAAA-A19-119020790106-0. The authors deeply grateful to the late Evgeny A. Perepelov whose thesis “Karyotype evolution of Odonata (Insecta) of Northern Palearctics” (2003; Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk, Russia) served as a starting point for preparing Table 1 of our paper. We thank two reviewers, Dr. M. Marinov and Dr. S. Grozeva, for their useful remarks to a draft of this MS. Special thanks to Dr. M. Marinov for his nomenclatural and taxonomic corrections and updates.
Citation
Kuznetsova VG, Golub NV (2020) A checklist of chromosome numbers and a review of karyotype variation in Odonata of the world. CompCytogen 14(4): 501–540. https://doi.org/10.3897/compcytogen.v14.i4.57062
References
- Agopian SS, Mola LM. (1984) An exceptionally high chromosome number in Orthemis nodiplaga Kersch (Anisoptera, Libellulidae). Notulae Odonatologicae 2(3): 45. [Google Scholar]
- Agopian SS, Mola LM. (1988) Intra and interspecific karyotype variability in five species of Libellulidae (Odonata, Anisoptera). Caryologia 41(1): 69–78. 10.1080/00087114.1988.10797849 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ardila-Garcia AM, Gregory TR. (2009) An exploration of genome size diversity in dragonflies anddamselflies (Insecta: Odonata). Journal of Zoology 278: 163–173. 10.1111/j.1469-7998.2009.00557.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Asana JJ, Makino S. (1935) A comparative study of the chromosomes in the Indian dragonflies. Journal of the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University Series 6, Zoology 4(2): 67–86.
- Boyes JW, van Brink JM, Kiauta B. (1980) Sixteen dragonfly karyotypes from the republic of South Africa and Swaziland, with evidence on the possible hybrid nature of Orthetrum julia falsum Longfeild (Anisoptera: Libellulidae). Odonatologica 9: 131–145. [Google Scholar]
- Bybee S, Córdoba-Aguilar A, Duryea MC, Futahashi R, Hansson B, Lorenzo-Carballa MO, Schilder R, Stoks R, Suvorov A, Svensson EI, Swaegers J, Takahashi J, Watts PC, Wellenreuther M. (2016) Odonata (dragonflies and damselflies) as a bridge between ecology and evolutionary genomics. Frontiers in Zoology 13: e46. 10.1186/s12983-016-0176-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Capitulo RA, Mola LM, Agopian SS. (1991) Species catalogue and chromosomal data of Odonata from Argentina. Revista de la Sociedad Entomológica Argentina 49(1–4): 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Carle FL, Kjer KM, May ML. (2015) A molecular phylogeny and classification of Anisoptera (Odonata). Arthropod Systematics and Phylogeny 73(2): 281–301. https://entomology.rutgers.edu/news/docs/Carle-2015-Anisoptera-Phylogeny-Classification.pdf [Google Scholar]
- Carnoy BJ. (1885) La cytodierese chez les arthropodes. IV. Pseudo-Nevropteres. Cellule 1: 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee K, Kiauta B. (1973) Male germ cell chromosomes of two Calopterygoidea from the Darjeeling Himalaya (Zygoptera: Chlorocyphidae, Euphaeidae). Odonatologica 2(2): 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Cruden RW. (1968) Chromosome numbers of some North American dragonflies (Odonata). Canadian Journal of Genetics and Cytology 10: 200–214. 10.1139/g68-029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming RB. (1964) Cytogenetic studies in the order Odonata. PhD thesis, University of Texas, Austin, 93 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Das C. (1956) Studies on the association between non-homologous chromosomes during meiosis in four species of the Indian dragonflies (Odonata). Journal of the Zoological Society of India 8(2): 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta J. (1957) Cytological studies of some Indian dragonflies. II: A study of the chromosomes during meiosis in thirty species of Indian Odonata (Insecta). Proceedings of the Zoological Society of Calcutta 10: 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- De Gennaro D. (2004) Análisis meiótic y caracterización de la heterocromatina en species argentinas de Anizoptera (Odonata). Tesis de Licenciatura. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales de la Universidad de Buenos Aires. Buenos Aires, 66 pp.
- De Gennaro D, Rebagliati PJ, Mola LM. (2008) Fluorescent banding and meiotic behaviour in Erythrodiplax nigricans (Libellulidae) and Coryphaeschna perrensi (Aeschnidae) (Anisoptera, Odonata). Caryologia 61: 60–67. 10.1080/00087114.2008.10589610 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra K-DB, Bechly G, Bybee SM, Dow RA, Dumont HJ, Fleck G, Garrison RW, Hämäläinen M, Kalkman VJ, Karube H, May ML, Orr AG, Paulson DR, Rehn AC, Theischinger G, Trueman JWH, van Tol J, Ellenrieder N, Ware J. (2013) The classification and diversity of dragonflies and damselflies (Odonata). In: Zhang ZQ. (Ed.) Animal Biodiversity: An Outline of Higher-level Classification and Survey of Taxonomic Richness (Addenda 2013).Zootaxa 3703: 36–45. 10.11646/zootaxa.3703.1.9 [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra K-DB, Kalkman VJ, Dow RA, Stokvis FR, van Tol J. (2014) Redefining the damselfly families: a comprehensive molecular phylogeny of Zygoptera (Odonata). Systematic Entomology 39: 68–96. 10.1111/syen.12035 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A, Kiauta B, Zaha A. (1979) Male germ cell chromosomes of thirty-two Brazilian dragonflies. Odonatologica 8: 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Francovič M, Jurečic R. (1986) Prilog citogenetickim i citotaksonomskim istrazivanjima vrste Libellula depressa L. (Odonata, Libellulidae). Plenarni Referati VII Kongres Biologa Jugoslavije, Budva, 341 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Francovič M, Jurečic R. (1989) Comparative cytogenetic analysis of karyotype morphology and organization in males of species Libellula depressa L. and L. fulva Müll. (Insecta: Odonata). Periodicum Biologorum 91(1): 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Frydrychová R, Grossmann P, Trubač P, Vítková M, Marec F. (2004) Phylogenetic distribution of TTAGG telomeric repeats in insects. Genome 47: 163–178. 10.1139/g03-100 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchsówna J, Sawczyńska J. (1928) Zachowanie sie heterochromosomóv podczam spermatogenezy u wažek (Odonata). Cz. I. Aeschna grandis L. Libellula quadrimaculata L. Archiwum Towarzystwa naukowego we Lwowie (III) 4(9): 177–197. [In Polish] [Google Scholar]
- Goni B, de Abenante YP. (1982) Cytological notes on five dragonfly species from Uruguay. Odonatologica 11(4): 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi D, Engel MS. (2005) Evolution of the Insects. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 755 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Grozeva SM, Marinov MG. (2007) Cytogenetic study of Somatochlora borisi Marinov, 2001 (Odonata: Corduliidae), and three relative species. Acta Zoologica Bulgarica 59(1): 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Handa SM, Batra HN. (1980) Cytology of ten species of dragonflies (Anisoptera: Odonata). Proceedings of the 67th Indian Science Congress, Part III, Calcutta, 103 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Handa SM, Kochhar N. (1985) Chromosomal architecture in two species of damselflies from Chandigarh and its surrounding areas. National Seminar on Current Trends in Chromosome Dynamics, Chandigarh, 34 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Handa SM, Mittal OP, Batra HN. (1984) Chromosomes in ten species of dragonflies (Anisoptera: Odonata). Research Bulletin of the Panjab University (Science) 35: 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Higashi K, Kayano H. (1993) The distribution of distinct karyomorphs of Crocothemis servilia Drury (Anisoptera, Libellulidae) in Kyushu and the south-western islands of Japan. Japanese Journal of Entomology 61: 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Higashi K, Lee CE, Kayano H, Kayano A. (2001) Korea strait delimiting distribution of distinct karyomorphs of Crocothemis servilia (Drury) (Anisoptera: Libellulidae). Odonatologica 30(3): 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H. (1956) Chromosomes of six species of dragonflies. Zoological Magazine, Tokyo 65: 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Hogben L. (1921) Studies on synapsis, III. The nuclear organisation of the germ cells in Libellula depressa. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B 92: 60–80. 10.1098/rspb.1921.0006 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hung ACF. (1971) Cytological studies of five dragonflies (Odonata: Anisoptera). Entomological News 82: 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen AL. (1980) The karyotypes of five species of Odonata endemic to New Zealand. Odonatologica 9: 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen AL, Mahanty HK. (1978) A preliminary note on the chromosome number of Uropetala carovei (White) (Anisoptera: Petaluridae). Odonatologica 7: 385–386. [Google Scholar]
- Kalkman VJ, Clausnitzer V, Dijkstra K-DB, Orr AG, Paulson DR, van Tol J. (2008) Global diversity of dragonflies (Odonata) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 595: 351–363. 10.1007/s10750-007-9029-x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Katatani N. (1987) On the chromosomes of dragonflies, 1. Synopsis on the studies in some Japanese dragonflies. Aeschna 20: 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1965) The chromosome behaviour in spermatogenetic meiosis of Anax imperator Leach (Odonata: Aeshnidae). Tombo 7(3–4): 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1966) The chromosome behaviour in spermatogenetic meiosis of the dragonfly Sympetrum striolatum (Charp.) (Odonata: Libellulidae) from Luxembourg. Bulletin de la Société des Naturalistes Luxembourgeois 69: 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1967a) Evolution of the chromosome complement in Odonata. Genen en Phaenen 11(4): 56–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1967b) Abstract. Evolution of the chromosome complement in Odonata. Genetica 38(3): 403–404. 10.1007/BF01507474 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1967c) A new hypothesis on the evolution of the chromosome complement in Odonata. Tombo 10(1–4): 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1967d) Considerations on the evolution of the chromosome complement in Odonata. Genetica 38(4): 430–446. 10.1007/BF01507474 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1967e) Meiotic chromosome behaviour in the male damselfly, Calopteryx virgo (Linnaeus), with a discussion on the value of chromosome numbers and karyotype morphology in odonate systematics. Deutsche Entomologische Zeitschrift 14(3–4): 339–348. 10.1002/mmnd.19670140312 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1968a) Evolution of the chromosome complement in Odonata. Entomologische Berichten, Amsterdam 28(5): 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1968b) Morphology and kinetic behaviour of the odonate sex chromosomes, with a review of the distribution of sex determining mechanisms in the order. Genen en Phaenen 12(1): 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1968c) The chromosome numbers of eight Old World dragonflies (Odonata). Chromosome Information Service, Tokyo 9: 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1968d) The chromosomes of the male dragonfly Cordulegaster boltoni (Donovan, 1807) (Odonata: Cordulegasteridae). Biološki Vestnik: glasilo slovenskih biologov 16: 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1968e) Variation in size of the m-chromosome of the dragonfly, Calopteryx virgo (L.), and its significance for the chorogeography and taxonomy of the Calopteryx virgo superspecies. Genen en Phaenen 12(1): 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1968f) Variation in size of the dragonfly m-chromosome, with considerations on its significance for the chorogeography and taxonomy of the order Odonata, and notes on the validity of the rule of Reinig. Genetica 39(1): 64–74. 10.1007/BF02324456 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1969a) Sex chromosomes and sex determining mechanisms in Odonata, with a review of the cytological conditions in the family Gomphidae, and reference to the karyotypic evolution in the order. Genetica 40(2): 127–157. 10.1007/BF01787346 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1969b) The chromosomes of eight dragonfly species from continental Africa and Madagascar (Odonata). Arnoldia (Rhodesia) 4(15): 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1969c) Autosomal fragmentations and fusions in Odonata and their evolutionary implications. Genetica 40(2): 158–180. 10.1007/BF01787347 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1969d) The chromosomes of the Hawaiian endemic dragonflies, Megalagrion oahuense (Blackburn) (Coenagrionidae: Pseudagrioninae) and Nesogonia blackburni (McLachlan) (Libellulidae: Sympetrinae), with a note on the cytotaxonomic affinities between the genera Nesogonia Kirby and Sympetrum Newman (order Odonata). Proceedings of the Hawaiian Entomological Society 20(2): 429–433. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1970a) The chromosomes of four Neotropical dragonflies from Mexico. Chromosome Information Service, Tokyo 11: 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1970b) The karyotype of the damselfly, Epallage fatime (Charpentier, 1840) (Odonata, Zygoptera: Epallagidae), with a note on the cytotaxonomic affinities in the superfamily Calopterygoidea. Genetica 41: 390–397. 10.1007/BF00958931 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1971a) Studies on the germ cell chromosome cytology of some cytotaxonomically interesting or hitherto not studied Odonata from the autonomous region Friuli-Venezia Giulia (northern Italy). Atti del Museo civico di Storia naturale di Trieste 27: 65–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1971b) An unusual case of precocious segregation and chromosome fragmentation in the primary spermatocytes of the damselfly, Calopteryx virgo meridionalis (Selys, 1873), as evidence for a possible hybrid character of some populations of the Calopteryx-virgo-complex (Odonata, Zygoptera: Calopterygidae). Genen en Phaenen 14(2): 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1971c) Cytotaxonomic peculiarities in the neotropical odonate genera Leptagrion Selys, Orthemis Hagen and Macrothemis Hagen. Abstracts of papers read at the 1st European Symposium on Odonatology, Gent, 27–28.
- Kiauta B. (1972a) Notes on new or little known dragonfly karyotypes, 2. Male germ cell chromosomes of four East Mediterranean species: Lestes barbarus (Fabricius), Calopteryx splendens amasina Bartenev (Zygoptera: Lestidae, Calopterygidae), Caliaeschna microstigma (Schneider) and Orthetrum taeniolatum (Schneider) (Anisoptera: Aeshnidae, Libellulidae). Genen en Phaenen 15: 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1972b) Notes on new or little known dragonfly karyotypes, 1. The germ cell chromosomes of three Latin American species: Argia funebris (Hagen), Megapodagrion contortum (Selys) (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae, Megapodagrionidae) and Castoraeschna castor (Brauer) (Anisoptera: Aeshnidae). Genen en Phaenen 15: 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1972c) Synopsis on the main cytotaxonomic data in the order Odonata. Odonatologica 1(2): 73–102. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1972d) The karyotype of the damselfly, Leptagrion macrurum (Burmeister, 1839), and its possible origin, with a note on the cytotaxonomic affinities of the genus (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae). Odonatologica 1(1): 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1973a) Notes on new or little known dragonfly karyotypes. III. Spermatocyte chromosomes of four Nearctic anisopterans: Aeshna californica Calvert (Aeshnidae), Cordulia shurtleffi Scudder (Corduliidae), Sympetrum internum Montgomery, and S. madidum (Hagen) (Libellulidae). Genen en Phaenen 16(1): 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1973b) Notes on new or little known dragonfly karyotypes. IV. Spermatocyte chromosomes of Calopteryx splendens splendens Harris (Zygoptera: Calopterygidae), Gomphus pulchellus Selys, Libellula depressa Linnaeus (Anisoptera: Gomphidae, Libellulidae) from northern France. Genen en Phaenen 16(2): 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1974) Introduction to insect cytotaxonomy. Lectures delivered at the Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, Vol. 1. Nepal Research Center, Kathmandu, 81 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1975) Cytotaxonomy of dragonflies, with special reference to the Nepalese fauna. Lectures delivered at the Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, Vol. 2. Nepal Research Center, Kathmandu, 78 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1977) Notes on new or little known dragonfly karyotypes.V. The male germ cell chromosomes of Macromia moorei Selys from Nepal (Anisoptera: Corduliidae, Epophthalmiinae). Genen en Phaenen 19: 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1978) Two cytotaxonomically interesting cases of irreversible autosome fusion in dragonflies Agria modesta (Hagen) (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae) and Anaciaeschna isosceles (Müller) (Anizoptera: Aeshnidae). Notulae Odonatologicae 1(1): 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1979a) The karyotypes of some Anisoptera from Surinam. Odonatologica 2: 267–283. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1979b) The karyotype of Ischnura pumilio (Charp.) (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae). Notulae Odonatologicae 1(3): 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B. (1983) The status of the Japanese Crocothemis servilia (Drury) as revealed by karyotypic morphology (Anisoptera: Libellulidae). Odonatologica 12: 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Boyes JW. (1972) Cytology of ten South American Libellulidae, with cytophylogenetic consideration of the genera Orthemis Hagen and Erythrodipax Brauer (Odonata, Anisoptera). Genetica 43(3): 407–421. 10.1007/BF00156136 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Brink JM. (1975) Cytotaxonomic notes on the Sympetrum pedemontanum complex (Anisoptera: Libellulidae). Odonatologica 4(4): 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Brink JM. (1978) Male chromosome complements of some Florida dragonflies, United States. Odonatologica 7(1): 155–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Kiauta MAJE. (1976) The chromosomes of some dragonflies from the Langtang Valley, Central Nepal. Odonatologica 5(4): 347–354. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Kiauta MAJE. (1979) The karyotype of Libellula fulva Müll, from Switzerland (Anisoptera: Libellulidae). Notulae Odonatologicae 1(4): 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Kiauta MAJE. (1980a) The karyotypes of Aeshna subarctica elisabethae Djak. and Somatochlora alpestris (Sel.) from Switzerland (Anisoptera, Aeshnidae, Corduliidae). Notulae Odonatologicae 1(6): 104–105. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Kiauta MAJE. (1980b) On a small collection of dragonfly karyotypes from the Philippines. Odonatologica 9(3): 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Kiauta MAJE. (1980c) Introduction to the cytotaxonomy of the odonate genus Agria Rambur (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae). Odonatologica 9(1): 35–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Kiauta MAJE. (1982) The chromosome numbers of sixteen dragonfly species from the Arun Valley, Eastern Nepal. Notulae Odonatologicae 9(1): 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Kiauta MAJE. (1983) The chromosome numbers of some Odonata from Thailand. Notulae Odonatologicae 2(2): 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Kiauta MAJE. (1991) Biogeographic considerations on Coenagrion hylas freyi (Bilek, 1954), based mainly on the karyotype features of a population from North Tyrol, Austria (Zygoptera: Coenagrionidae). Odonatologica 20(4): 417–431. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Kiauta MAJE. (1995) The karyotypes of Somatochlora meridionalis Nielsen from Slovenia and S. metallica (Vander L.) from Switzerland, with a tentative note on the origin of Central European S. metallica (Odonata: Corduliidae). Opuscula zoologica fluminensia 137: 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Kiauta-Brink MAJE. (1975) Chromosomes of the dragonfly, Sympecma annulata braueri (Yakobson & Bianki, 1905) from the Netherlands, with a note on the classification of the family Lestidae (Odonata, Zygoptera). Genen en Phaenen 18(2–3): 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kiauta B, Ochssée BV. (1979) Some dragonfly karyotypes from the Voltiac Republic (Haute Volta), West Africa. Odonatologica 8: 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kichijo H. (1939) Chromosomes of Tachopteryx pryeri and Gomphus hakiensis (Odonata, Aeshnidae). Japanese Journal of Genetics 15: 287–289. 10.1266/jjg.15.287 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kichijo H. (1941) Chromosomes of seven species of insects belonging to the order of dragonflies, suborder of damselfies. Nagasaki Medical Journal 19(10): 2033–2041. [In Japanese] [Google Scholar]
- Kichijo H. (1942a) Insect chromosomes. IV. Order of dragonflies, Pt. 2. Nagasaki Medical Journal 20(10): 1639–1648. [In Japanese] [Google Scholar]
- Kichijo H. (1942b) Insect chromosomes. III. Order of dragonflies, Pt. 1. Nagasaki Medical Journal 20(7): 1084–1092. [In Japanese] [Google Scholar]
- Kichijo H. (1942c) Chromosomes of Sympetrum eroticum eroticum (Odonata). Japanese Journal of Genetics 18: 195–196. 10.1266/jjg.18.195 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kichijo H. (1942d) A comparative study of seven species of Zygoptera from Japan. Acta medica Nagasakiensi 3(2): 95–97. [Google Scholar]
- Kichijo H. (1942e) On the chromosomes of some species of the zygopterous dragonflies (Odonata, Zygoptera). Japanese Journal of Genetics 18: 273–276. 10.1266/jjg.18.273 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kumari U, Gautam DC. (2017) Karyotypic studies on two species of Orthetrum (Anisoptera: Odonata) from Himachal Pradesh. The Journal of Cytology and Genetics 18: 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova V, Grozeva S, Gokhman V. (2020a) Telomere structure in insects: A review. Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research 58: 127–158. 10.1111/jzs.12332 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova VG, Maryańska-Nadachowska A, Shapoval NA, Anokhin BA, Shapoval AP. (2018) Cytogenetic characterization of eight Odonata species originating from the Curonian Spit (the Baltic Sea, Russia) using C-banding and FISH with 18S rDNA and telomeric (TTAGG)n n probes. Cytogenetic and Genome Research 153: 147–157. 10.1159/000486088 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova VG, Maryańska-Nadachowska A, Anokhin BA, Shapoval NA, Shapoval AP. (2020b) Chromosomal analysis of eight species of dragonflies (Anisoptera) and damselflies (Zygoptera) using conventional cytogenetics and FISH: insights into the karyotype evolution of the ancient insect order Odonata Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research 58, 00: 1–13. 10.1111/jzs.12429 [in press] [DOI]
- Lefevre G, McGill C. (1908) The chromosomes of Anasa tristis and Anax junius. The American Journal of Anatomy 7(4): 469–487. 10.1002/aja.1000070404 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Makalowskaja WN. (1940) Comparative karyological studies of dragonflies (Odonata). Archives russes d’Anatomie, d’Histologie et d’Embryologie 25: 24–39. [Google Scholar]
- Makino S. (1935) A comparative study of the chromosomes in the Indian dragonflies. Japanese Journal of Genetics 11: 234–235. 10.1266/jjg.11.234 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- McGill C. (1904) The spermatogenesis of Anax junius. University of Missouri Studies 2: 236–250. [Google Scholar]
- McGill C. (1907) The behavior of the nucleoli during oogenesis of the dragonfly with special reference to synapsis. Zoologische Jahrbücher. Abteilung für Anatomie und Ontogenie der Tiere 23: 207–230. [Google Scholar]
- Mola LM. (1995) Post-reductional meiosis in Aeshna (Aeshnidae, Odonata). Hereditas 122: 47–55. 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1995.00047.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mola LM. (1996) Meiotic studies in nine species of Erythrodiplax (Libellulidae, Odonata). Neo-XY sex chromosome system in Erythrodiplax media. Cytologia 61: 349–357. 10.1508/cytologia.61.349 [DOI]
- Mola LM. (2007) Cytogenetics of American Odonata. In: Tyagi BK. (Ed.) Odonata: Biology of Dragonflies.Scientific Publishers, India, 153–173.
- Mola LM, Agopian SS. (1985) Observations on the chromosomes of four South American Libellulidae (Anisoptera). Odonatologica 14(2): 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Mola LM, Papeschi AG. (1994) Karyotype evolution in Aeshna (Aeshnidae: Odonata). Hereditas 121: 185–189. 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1994.00185.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mola LM, Papeschi AG, Carrillo ET. (1999) Cytogenetics of seven species of dragonflies. Hereditas 131: 147–153. 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1999.00147.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nokkala S, Laukkanen A, Nokkala C. (2002) Mitotic and meiotic chromosomes in Somatochlora metallica (Corduliidae, Odonata). The absence of localized centromeres and inverted meiosis. Hereditas 136: 7–12. 10.1034/j.1601-5223.2002.1360102.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguma K. (1915) A study of the chromosomes of dragonflies. Zoological Magazine 27: 241–250. [In Japanese] [Google Scholar]
- Oguma K. (1917) Entomology and cytology. In: Nagano K. (Ed.) A Collection of Essays for Mr.Yasushi Nawa, Written in Commemoration of His Sixtieth Birthday, October 8, 1917. Gifu, 105–114.
- Oguma K. (1930) A comparative study of the spermatocyte chromosome in allied species of the dragonfly. Journal of Faculty of Sciences, Hokkaido University VI: 1–32.
- Oguma K. (1942) Observationes de formis compositionibusque chromosomatum et dispositionibus eorum in tempore divisionis atque propositio aliquorum novorum terminorum. Japanese Journal of Genetics 18: 205–216. 10.1266/jjg.18.205 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Oguma K. (1951) The chromosomes of Epiophlebia superstes Selys (dragonfly). Iden-no-Sogo-Kenkyu 2: 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Oguma K, Asana JJ. (1932) Additional data to our knowledge on the dragonfly chromosome with a note on the occurrence of X-Ychromosome in the ant-lion (Neuroptera). Journal of Faculty of Sciences, Hokkaido University 1(4): 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Oksala T. (1939a) Über Tetraploidie der Binde- und Fettgewebe bei den Odonaten. Hereditas 25: 132–144. 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1939.tb02690.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Oksala T. (1939b) Über die somatische Polyploidie bei Insekten. Annales Entomologici Fennici 5(3): 208–218. [Google Scholar]
- Oksala T. (1943) Zytologische Studien an Odonaten I. Chromosomenverhältnisse bei der Gattung Aeschna mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der postreduktionellen Teilung der Bivalente. Annales Academiae Scientiarum Fennicae (A) IV, Biologica (4): 1–64.
- Oksala T. (1944) Zytologische Studien an Odonaten. II. Die Enstehung der Meiotischen Präkozität. Annales Academiae Scientiarum Fennicae (A) IV, Biologica (5): 1–33.
- Oksala T. (1945) Zytologische Studien an Odonaten. III. Die Ovogenese. Annales Academiae Scientiarum Fennicae (A) IV, Biologica (9): 1–132.
- Oksala T. (1952) Chiasma formation and chiasma interference in the Odonata. Hereditas 38: 449–480. 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1952.tb02937.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Omura T. (1949) On at-random connection of chromosomes in the aeschnid dragonfly, Ictinus rapax. Japanese Journal of Genetics 24: 162–165. 10.1266/jjg.24.162 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Omura T. (1952) The spermatogenesis of an Indian dragonfly, Ictinus rapax (Rambur) with special reference to the behaviour of the spermatozoa in the cyst. Biological Journal of Okayama University 1(1–2): 103–146. [Google Scholar]
- Omura T. (1953) On the abnormal spermatogenesis in an Indian dragonfly, Ictinus rapax (Rambur). Biological Journal of Okayama University 1(3): 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Omura T. (1955) A comparative study of the spermatogenesis in the Japanese dragonflies. I. Family Libellulidae. Biological Journal of Okayama University 2(2–3): 95–135. [Google Scholar]
- Omura T. (1957) A comparative study of the spermatogenesis in the Japanese dragonfly II: Family Aeschnidae, Gomphidae and Calopterygidae. Biological Journal of Okayama University 3: 1–86. [Google Scholar]
- Perepelov EA. (2003) Karyotype evolution of Odonata (Insecta) of Northern Palearctics. Ph.D. Dissertation, Novosibirsk, Russian Federation: Institute of Systematics and Ecology of Animals of Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences, 144 pp [In Russian] https://www.dissercat.com/ content/evolyutsiya-kariotipov-strekoz-insecta-odonata-severnoi-palearktiki [Google Scholar]
- Perepelov E, Bugrov AG. (2001a) C-heterochromatin in chromosomes of Ophiogomphus Cecilia cecilia (Four.) (Anisoptera: Gomphidae) with notes on the sex chromosome origin in the species. Caryologia 54(2): 169–172. 10.1080/00087114.2001.10589224 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Perepelov E, Bugrov AG. (2001b) The constituent geterochromatin in karyotypes of dragonflies. Belyshevia 1(1): 10–13. [In Russian] [Google Scholar]
- Perepelov E, Bugrov AG. (2002) Constitutive heterochromatin in chromosomes of some Aeshnidae, with notes on the formation of the neo-XY/neo-XX mode of sex determination in Aeshna (Anisoptera). Odonatologica 31(1): 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Perepelov EA, Bugrov AG, Warchałowska-Śliwa E. (1998) C banded karyotypes of some dragonfly species from Russia. Folia biologica (Kraków) 46: 137–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perepelov EA, Bugrov AG, Warchalowska-Sliwa E. (2001) C-banded karyotypes of some dragonfly species from Russia. II. The families Cordulegasteridae, Corduliidae and Gomphidae. Folia biologica (Kraków) 49(3–4): 175–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad K, Thomas KI. (1992) C-band pattern homogeneity in dragonflies (Odonata). Caryologia 45: 57–68. 10.1080/00087114.1992.10797211 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ray Chaudhuri SP, Dasgupta J. (1949) Cytological studies on the Indian dragonflies I. Structure and behaviour of chromosomes in six species of dragonflies (Odonata). Proceedings of the Zoological Society of Bengal 2: 81–93. [Google Scholar]
- Rehn AC. (2003) Phylogenetic analysis of higher-level relationships of Odonata. Systematic Entomology 28: 181–240. 10.1046/j.1365-3113.2003.00210.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu R, Malhotra I. (1994a) Karyological studies of four aeshnid dragonflies from the states of Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh (India). In: Srivastava VK (Ed.) Advances in Oriental Odonatology: Proceedings of IV South Asian Symposium of Odonatology, Allahabad, India October 10–12, 1992, Cherry publications, Allahabad, 111–115.
- Sandhu R, Malhotra I. (1994b) New chromosome count in male dragonfly, Anatogaster s. basalis. Bionature 14: 69–70. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu R, Walia GK. (1995) A note on the karyotype of Potamarcha congener (Anisoptera: Libellulidae). Chromosome Information Service 58: 24–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sangal SK, Tyagi BK. (1982) The spermatocyte chromosomes of Anax immaculifrons Rambur from India (Anisoptera: Aeshnidae). Notulae odonatologicae 1(9): 154–155. [Google Scholar]
- Schorr M, Paulson D. (2020) World Odonata List. https://www.pugetsound.edu/academics/academic-resources/slater-museum/biodiversity-resources/dragonflies/world-odonata-list2/
- Seshachar BR, Bagga S. (1962) Chromosome number and sex-determining mechanism in dragonfly Hemianax ephippiger (Burmeister). Cytologia 27: 443–449. 10.1508/cytologia.27.443 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Seshachar BR, Bagga S. (1963) A cytochemical study of oogenesis in the dragonfly Pantala flavescens (Fabricius). Growth 27: 225–246. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma OP, Durani S. (1995) A study on the chromosomes of three species of dragonflies (Odonata: Anisoptera). National Academy Science Letters 18(5–6): 97.
- Smith EA. (1916) Spermatogensis of the dragonfly Sympetrum semicinctum with remarks upon Libellula basalis. Biological Bulletin 31: 269–290. 10.2307/1536236 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Souza Bueno AM. (1982) Estudos cromossomicos na ordem Odonata. M. Sc. Thesis, Universidad Estatal Paulista, 140 pp. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava MDL, Das CC. (1953) Heteropycnosis in the autosome segments of Ceriagrion coromandelianum (Odonata). Nature 172: 765–766. 10.1038/172765b0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki KJ, Saitoh K. (1990) A revised chromosome study of Japanese Odonates (I). Chromosomes of 14 species belonging to nine families. The Science Reports of the Hirosaki University 37: 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki KJ, Saitoh K, Sawano J. (1991) Male germ-line chromosomes of Orthetrum poecilops miyajimaensis Yuki et Doi, 1938 (Libellulidae: Odonata). Tombo 34: 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima H, Hirai H. (1953) Studies on chromosomes of four dragonflies from Kagawa Prefecture. Kagawa Biology 1: 17–19. [In Japanese] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas KI, Prasad R. (1981) The chromosomes of five Indian dragonflies (Odonata). Perspectives in Cytology and Genetics 3: 629–632. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas KI, Prasad R. (1986) A study of the germinal chromosomes and C-band patterns in four Indian dragonflies (Odonata). Perspectives in Cytology and Genetics 5: 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi BK. (1977) A note on the karyotypes of Burmagomphus pytamidalis Laidlow and Onychogomphus saundersi duaricus Faser (Anizoptera; Gomphidae). Odonatologica 6(4): 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi BK. (1978a) The chromosome numbers and sex-determining mechanisms newly recorded in thirteen Indian dragonflies (Odonata). Chromosome Information Service, Tokyo 25: 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi BK. (1978b) Studies on the chromosomes of Odonata of Dun Valley (Dehradun, India). PhD thesis, University of Garhwal, Srinagar.
- Tyagi BK. (1982) Cytotaxonomy of Indian dragonflies. Indian Review of Life Sciences 2: 149–161. [Google Scholar]
- van Brink JM, Kiauta B. (1964) Notes on chromosome behaviour in the spermatogenesis of the damselfly Enallagma cyathigerum (Charp.) (Odonata: Coenagrionidae). Genetica 35: 171–174. 10.1007/BF01804885 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK. (2007) Cytomorphological studies on Gynacantha milliardi Fraser of the family Aeschnidae (Anisoptera: Odonata). Cytologia 72(1): 57–62. 10.1508/cytologia.72.57 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Chahal SS. (2014) Distribution of constitutive heterochromatin and nucleolar organizer regions in two species of family Gomphidae (Odonata: Anisoptera). Nucleus 57: 223–227. 10.1007/s13237-014-0122-z [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Chahal SS. (2018) Cytogenetic characterization of Macromia moorei Selys, 1874 of family Macromiidae (Odonata: Anisoptera) from India by C-banding, silver nitrate staining and sequence specific staining. International Journal of Life Sciences Research 6(2): 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Chahal SS. (2019) Cytogenetic report on Cordulegaster brevistigma and Watanabeopetalia atkinsoni (Odonata: Cordulegastridae, Chlorogomphidae). Odonatologica 48(1–2): 101–113. [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Chahal SS. (2020) Linear differentiation of chromosomes of Anisogomphus bivittatus Selys, 1854 from India (Odonata: Anisoptera: Gomphidae). International Journal of Entomology 5(2): 120–122. [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Chahal SS, Babu R. (2016) Cytogenetic report on Gynacanthaeschna sikkima from India (Odonata: Aeshnidae). Odonatologica 45: 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Chahal SS, Somal DS. (2018) Chromosome observations based on C-banding, Ag-NOR and sequence-specific staining in two Anax species from India (Odonata: Aeshnidae). Odonatologica 47(1–2) 2018: 145–160.
- Walia GK, Devi M. (2018) Distribution of constitutive heterochromatin in four species of genus Copera of family Platycnemididae (Odonata: Zygoptera) from India. International Journal of Life Sciences 6(2): 457–461. [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Devi M. (2020a) Cytogenetic characterization of five species of genus Coeliccia of family Platycnemididae (Odonata: Zygoptera) using C-banding, silver nitrate staining and sequence specific staining. Nucleus (2020). 10.1007/s13237-020-00314-3 [DOI]
- Walia GK, Devi M. (2020b) Cytogenetic data of subfamily Disparoneurinae (Odonata: Zygoptera: Platycnemididae) based on localization of C-heterochromatin, AgNOR’s and AT-GC regions. International Journal of Entomology Research 5(2): 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Katnoria N. (2018) Morphological variation in the chromosome complement of Neurobasis chinensis chinensis of family Calopterygidae (Odonata: Zygoptera). International Journal of Life Sciences Research 6(4): 260–266. [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Katnoria N, Gill JK. (2018) Chromosomes of Libellago lineata lineata (Chlorocyphidae: Odonata). Indian Journal of Entomology 80(3): 737–740. 10.5958/0974-8172.2018.00118.9 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Kaur H, Kaur J. (2011) Karyotypic variations in the chromosome complement of Pantala flavescens (Fabricius) of the family Libellulidae (Anisoptera: Odonata). Cytologia 76(3): 301–307. 10.1508/cytologia.76.301 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Kaur H, Kaur J. (2015) Karyomorphological variations in the chromosome complement of Orthetrum taeniolatum of family Libellulidae (Odonata: Anisoptera). Cytologia 80(1): 95–99. 10.1508/cytologia.80.95 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Sandhu R. (1999) Karyotypic study of two species of family Aeschnidae (Anisoptera: Odonata). Chromosome Science 3: 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Sandhu R. (2002) Chromosomal data on seven species of genus Orthetrum (Libellulidae: Anisoptera: Odonata). Bionature 22: 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Walia GK, Sandhu R, Goyal S. (2006) Cytogenetical analysis of Nepogomphus modestus from Palampur area of Himachal Pradesh, India (Gomphidae: Anisoptera). Chromosome Science 9(3): 99–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wasscher M. (1985) The karyotypes of some dragonflies from Kenya and Sudan. Notulae odonatologicae 2(6): 105–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe LS. (1953) A study of the genus Uropetala Selys (order Odonata) from New Zealand. Transactions and Proceedings of the Royal Society of New Zealand 80(3–4): 245–275. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu H, Wu J. (1986) Notes on the male germ cell karyotypes of some Odonata from the Shanxi Province, China. Notulae odonatologicae 2: 118–120. [Google Scholar]