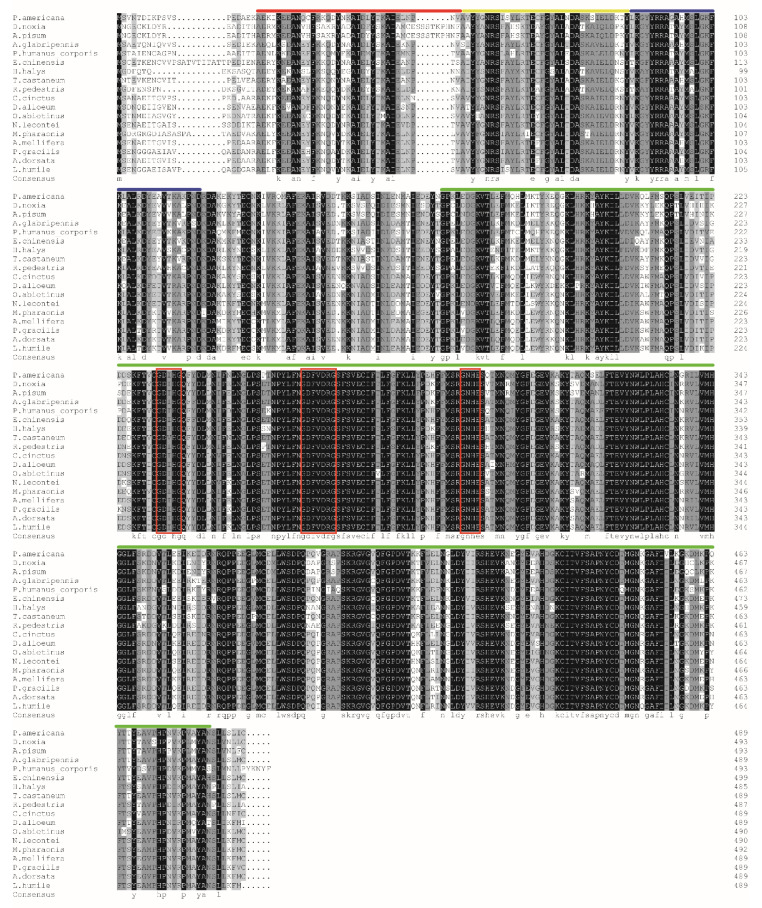
Figure 2.
Multiple alignments of the deduced amino acid sequences of PP5 from P. americana and with other insect species ((D. noxia, GenBank: XP_015379688.1; A. pisum, GenBank: XP_008181438.1; A. glabripennis, XP_018576896.1; P. humanus corporis, XP_002425763.1; E. chinensis, AHF45878.1, H. halys XP_014290865.1, T. castaneum XP_971407.1, R. pedestris BAN20786.1; C. cinctus, XP_015610020.1; D. alloeum, XP_015119779.1; O. abietinus, XP_012286908.1; N. lecontei, XP_015517121.1; M. pharaonic, XP_012542571.1; A. mellifera, XP_006567817.1; P. gracilis, XP_020284073.1; A. dorsata, XP_006613765.1; L. humile, XP_012231410.1). The TPR domains are shown in red, yellow, and blue lines. The predicted catalytic domain of PaPP5 (PP5c) is indicated by a green line. The three conserved motifs (-GDXHG-, -GDXVDRG-, and -GNHE-) are presented in a red horizontal rectangle.