Abstract
Simple Summary
The low pathogenic avian influenza H9N2 virus has been associated with severe economic losses in broiler chicken flocks. Problems associated with its control strategy are potential early infection and level of immune response that may be high in one-day-old chicks due to maternally derived antibodies. Herein, two vaccination regimes were evaluated in commercial broilers kept under either field or laboratory conditions. Two different vaccine types and concentrations were used, and the results highlighted a significantly higher protection against early infection when a homologous vaccine of high antigenic mass was applied at 7 days of life. Shedding was significantly reduced in this regime.
Abstract
Low pathogenic avian influenza virus is one of the major threats that has been affecting the poultry industry in the Middle East region for decades. Attempts to eradicate this disease have failed. Currently, there are commercial vaccines that are either imported or produced locally from recently circulating isolates of H9N2 in Egypt and Middle Eastern countries. This present work focused on comparing the effectiveness of two vaccines belonging to these categories in Egypt. Two commercial broiler flocks (Cobb-500 Broiler) with maternally derived immunity (MDA) against H9N2 virus were employed and placed under normal commercial field conditions or laboratory conditions. Immunity was evaluated on the basis of detectable humoral antibodies against influenza H9N2 virus, and challenge was conducted at 28 days of life using a recent wild H9N2 virus. The results showed that vaccination on the 7th day of life provided significantly higher immune response in both vaccine types, with significantly lower virus shedding compared to vaccination at day 1 of life, regardless of field or laboratory conditions. In addition, the vaccine produced from a recent local H9N2 isolate (MEFLUVAC-H9-16) provided a significantly higher humoral immune response under both field and laboratory conditions, as measured by serology and virus shedding (number of shedders and amount of shedding virus), being significantly lower following challenge on the 28th day of life, contrary to the imported H9 vaccine. In conclusion, use of H9N2 vaccine at 7 days of life provided a significantly higher protection than vaccination at day 1 of life in birds with MDA, suggesting vaccination regimes between 5–8-days of life for broiler chicks with MDA. Moreover, use of a vaccine prepared from a recently circulating H9N2 virus showed significantly higher protection and was more suitable for birds in the Middle East.
Keywords: avian influenza, homologous vaccine, heterologous vaccine, broiler, early infection
1. Introduction
The poultry industry has been suffering from several pathogens in Egypt during recent decades, including avian influenza viruses (AIV) that may be either highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAIV; H5N1, H5N2, H5N8) or low-pathogenic avian influenza (LPAIV; H9N2) viruses, velogenic Newcastle disease virus (vNDV), infectious bronchitis virus (IBV; variant 1, variant 2, and classic wild virus), infectious bursal disease (either variant or virulent virus), multidrug-resistant bacteria (MDR; Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Pasteurella, etc.), in addition to coccidia species. All these pathogens have caused severe economic losses and have badly affected the veterinary care strategies [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Avian influenza (AI) is a contagious viral disease, belonging to the Orthomyxoviridae family, and is a segmented, single-stranded, negative sense RNA virus [11,12]. Avian influenza viruses (AIV) belong to type-A and are divided into subtypes on the basis of antigenic relationships of the surface glycoproteins (hemagglutinin and neuraminidase) into 18 hemagglutinins (HA) and 11 neuraminidases (NA), with variable combinations. These glycoproteins are considered the main antigenic components of the virus and act as immune modulators for pattern recognition receptors of the immune system. Structural variations within these pathogen surface glycoproteins were shown to affect the different host responses, whether they be avian, fish, or mammalian [13,14,15,16]. On the basis of the pathogenicity of the avian virus, it is further classified into two types known as a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus “H5/H7” (HPAIV) and a low pathogenic avian influenza virus (LPAIV) [12,17,18]. The H9N2 avian influenza virus is associated with one of the major viral problems affecting the poultry industry in Egypt since it was officially reported for the first time in 2011 until now [19]. Virus infection leads to high economic losses in both layers and for breeders due to a drop in egg production. Broilers may also show severe losses during co-infection with other pathogens, especially Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV),Newcastle disease virus (NDV), bacteria such as E. coli and Mycoplasma, or even live virus vaccines [5,9,20,21]. Recently several reports have highlighted the immunosuppressive effect associated with LPAI-H9N2 in poultry flocks either by altering the differentiation of lymphocytes or inflammatory cytokines or the depletion and apoptosis of some immune cells [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. Moreover, some reports have discussed the effect of H9N2 on the alteration of blood biochemical and hematological parameters [30]. Regarding the potency and efficacy of the H9N2 inactivated vaccine in Egypt, there is a paucity of knowledge addressing this issue.
This work focuses on evaluating the value of applying the H9N2 vaccine at 1 day or 7 days of life on the developed immune response under both farm commercial conditions and laboratory standard conditions in broiler chicks with maternally derived immunity (MDA). Two commercially available vaccines were compared: one imported that is based on an old Middle East isolate (1998) and another produced in Egypt from a recent Middle East isolate (2016). Protection following challenge was assessed against live H9N2 virus in birds kept under standard laboratory conditions only.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
Animal studies were approved by the Animal Welfare and Research Ethics Committee of Suez Canal University and all procedures were conducted strictly in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Every effort was made to minimize animal suffering.
2.2. Birds and Vaccines
A total of 108,120 one-day-old commercial Cobb-500 broilers from vaccinated broiler breeders with H9N2 vaccine was used in this experiment. All birds were given vaccines for infectious bursal disease (IBD), AIV-H5, and Newcastle disease (ND) as is routine for commercial broilers in Egypt. Two commercial inactivated H9N2 vaccines were used in this trial (vaccines A and B). Vaccine A (MEFLUVAC-H9ND-16) is produced by MEVAC Co. Egypt and prepared from the A/ck/Egypt/ME/543V/2016(H9N2) virus. Vaccine B (Gallimune 208 H9ND) is produced by Merial Incorporation, France, and was brought from a local agency in Egypt. Vaccine B is prepared from A/chicken/Iran/Av1221/1998. Both were used according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
2.3. Experiment Design
2.3.1. Laboratory Groups
A total of 120 one-day-old commercial Cobb-500 broiler chicks with maternally derived antibodies for H9N2 virus (MDA) were divided into 6 different experimental groups: group 1 was vaccinated with MEFLUVAC-H9ND-16 (vaccine A) and group-2 received an imported H9ND vaccine (vaccine B)—both were administered at day 1 of life. Group 3 took vaccine A and group 4 took vaccine B, but at the 7th day of life. Group 5 served as a positive control (non-vaccinated, challenged group) and group 6 served as a negative control (non-vaccinated, non-challenged group). All vaccines were provided as per the manufacturer’s recommendations, as shown in Table 1. Challenge was conducted in G1-5 (10 birds from each group) at the 28th day of life using a previously identified AIV-H9N2 virus [31].
Table 1.
Experimental design for different groups (G-1-10).
| Group No. | Bird No. | Vaccine Regime | Challenge at 28 Day of Age | Assessment of Protection | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccine Type | Age/Days | Dose/mL | |||||
| Experiment 1 lab experiment |
G-1 | 20 | A | 1 | 0.3 | +++ | Follow up of immune response of vaccinated birds at weeks post vaccination to H9, H5, ND, IBD, and IB vaccines using HI and ELISA tests. Viral shedding detected by real-time PCR. |
| G-2 | 20 | B | 1 | 0.3 | +++ | ||
| G-3 | 20 | A | 7 | 0.3 | +++ | ||
| G-4 | 20 | B | 7 | 0.3 | +++ | ||
| G-5 | 20 | - | ------ | ---- | +++ | ||
| G-6 | 20 | - | ------ | --- | ----- | ||
| Experiment 2 field group |
G-7 | 27K | A | 1 | 0.3 | - | Follow up of immune response of vaccinated birds on weekly basis. Measure of performance parameters and field exposure. Natural exposure monitoring by RT-PCR. |
| G-8 | 27K | B | 1 | 0.3 | - | ||
| G-9 | 27K | A | 6 | 0.3 | - | ||
| G-10 | 27K | B | 6 | 0.3 | - | ||
2.3.2. Field-monitored Groups
A total of 108,000 broiler chickens (Cobb-500) produced from vaccinated broiler breeders with H9N2 vaccine and showing maternally derived antibodies for H9N2 virus (MDA) were placed equally in 4 pens, each with 27,000 birds (G-7-10). Group 7 took a commercial local H9ND vaccine (A), while group 8 took a commercial imported H9ND vaccine (B); both products were administered at the 1st day of life by subcutaneous (S/C) injection using the manufacturer’s recommended dose. Group 9 took vaccine A while group 10 took vaccine B at the 7th day of life. Birds in groups 7–10 were brought from the same broiler breeder flock and the same hatchery and kept under commercial field conditions with proper biosecurity measures and took the same ratio and management standers.
2.4. Hemagglutination Inhibition (HI) Test
The HI test was used to monitor post-vaccination humoral immune response for each vaccine using avian influenza H9N2 antigens (one representative of the circulating virus in Egypt and another imported antigen). Chicken sera were examined for HA-specific antibodies against H9N2 virus by HI test according to the Office International des Epizooties (OIE) manual (OIE, 2015). Serial twofold serum dilutions in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) were subsequently mixed with equal volumes (25 μL) of the virus containing 4 hemagglutinating units (HAU), then 25 μL of washed chicken red blood cells were added. After we incubated the HI titers for 40 min at room temperature, we determined them as reciprocals of highest serum dilutions in which inhibition of hemagglutination was observed.
2.5. Challenge Virus
Vaccinated birds grown in isolated rooms were challenged at 4 weeks of age by intranasal inoculation of 6 log10 embryo infective dose50 (EID50) of the previously isolated wild type AI-H9N2 virus [31].
2.6. qRT-PCR for Virus Shedding
Tracheal swabs were collected from the challenged birds for detection of virus shedding by RT-PCR at 3 and 7 days post challenge, as per the OIE manual [32], using specific primers and probes, as previously described [31]. qRT-PCR titers were converted into log10 EID50/mL, as described previously [33]. Briefly, a triplicate of 6 10-fold dilutions of challenge AIV-H9N2 (AIV-H9N2; 106 EID50/mL) were used to generate a standard curve using stock virus dilutions from 10−1 to 10−6. Since Ct is defined as the point at which the curve crosses the horizontal threshold line, we plotted virus log10 titers of a specimen against the Ct value, and the best fit line was constructed. The linear range of the assay ranged from 1 to 106 EID50/mL, with a correlation coefficient of 0.99. System detection limit was 0.5 EID50/mL, as has been standardized and described previously [31]. AIV-H9N2 quantity in unknown samples were derived by plotting the Ct of an unknown against the standard curve and were expressed in log10 EID50/mL equivalents.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Where necessary, data were analyzed by Student’s t-test or by ANOVA followed by application of Duncan’s new multiple range test to determine the significance of differences between individual treatments and corresponding control [34].
3. Results
3.1. Different AIV-H9N2 Virus Hemagglutinin Segment Amino Acid Identity Degrees
The hemagglutination segment (HA) amino acids identity degree showed higher similarities with vaccine A seed, ranging from 93.8 to 98.8% with different isolated viruses from Middle Eastern countries while with vaccine B, the degree of similarity was lower as it ranged from 89.5 to 92.8%, as shown in Table 2.
Table 2.
Different avian influenza (AIV)-H9N2 virus hemagglutinin segment amino acid identity degrees.
| Items | Alg. 2017 |
Egypt 2018 |
Iraq 2017 |
KSA 2018 |
Leb. 2017 |
Libya 2015 |
Mor. 2018 |
Pak. 2018 |
Tun. 2015 |
UEA 2017 |
Vaccine A |
Vaccine B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alg./2017 | 94.59 | 94.78 | 96.39 | 94.59 | 96.39 | 99.28 | 91.88 | 91.76 | 98.10 | 93.68 | 92.24 | |
| Egypt/2018 | 94.59 | 94.79 | 93.68 | 94.64 | 95.54 | 94.64 | 92.54 | 94.58 | 96.46 | 98.86 | 91.79 | |
| Iraq/2017 | 94.78 | 94.79 | 94.34 | 93.32 | 93.93 | 93.21 | 94.46 | 93.11 | 93.04 | 94.43 | 90.71 | |
| KSA/2018 | 96.39 | 93.68 | 91.34 | 94.22 | 95.49 | 96.57 | 90.43 | 92.31 | 96.39 | 94.78 | 91.88 | |
| Leb./2017 | 94.59 | 94.64 | 92.32 | 94.22 | 96.79 | 94.82 | 90.89 | 93.41 | 94.64 | 94.75 | 92.86 | |
| Libya/2015 | 96.39 | 95.54 | 93.93 | 95.49 | 96.79 | 96.25 | 92.86 | 95.33 | 96.07 | 94.64 | 93.93 | |
| Mor./2018 | 99.28 | 94.64 | 93.21 | 96.57 | 94.82 | 96.25 | 91.96 | 92.31 | 99.82 | 94.75 | 92.14 | |
| Pak./2018 | 91.88 | 90.54 | 94.46 | 90.43 | 90.89 | 92.86 | 91.96 | 89.84 | 91.79 | 94.18 | 89.11 | |
| Tun./2015 | 91.76 | 92.58 | 90.11 | 92.31 | 93.41 | 95.33 | 92.31 | 89.84 | 92.31 | 95.48 | 89.56 | |
| UEA/2017 | 98.10 | 94.46 | 93.04 | 96.39 | 94.64 | 96.07 | 99.82 | 91.79 | 92.31 | 96.57 | 91.96 | |
| Vaccine A | 94.68 | 98.86 | 94.43 | 94.78 | 93.75 | 94.64 | 94.75 | 94.18 | 95.48 | 96.57 | 90.61 | |
| Vaccine B | 92.24 | 91.79 | 90.71 | 91.88 | 92.86 | 93.93 | 92.14 | 89.11 | 89.56 | 91.96 | 91.61 |
Alg.: Algeria; Leb.: Lebanon; Mor.: Morocco; Pak.: Pakitsan.
3.2. Immune Response to Other Vaccines at 28th Day of Life
Birds in all groups showed immune responses for vaccinations with infectious bursal disease vaccine, avian Influenza-H5 vaccine, and Newcastle disease vaccines. No significant differences were found among the different groups, as is shown in Table 3.
Table 3.
Serological response of broiler chickens to infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV), Newcastle disease (ND), and avian influenza-H5N1 (AI-H5) vaccines at 28 days of age.
| Group No. |
Bird No. |
Vaccine Regime | ELISA Mean Titers | HI Titer Log2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccine Type | Age/days | Dose/mL | IBD | AI-H5 | ND | ||
| 28 Days | 28 Days | 28 Days | |||||
| G-1 | 20 | A | 1 | 0.3 | 17,553 ± 1105 | 3.7 ± 0.51 | 4.8 ± 0.72 |
| G-2 | 20 | B | 1 | 0.3 | 17,703 ± 1120 | 3.8 ± 0.61 | 4.9 ± 0.61 |
| G-3 | 20 | A | 7 | 0.3 | 17,612 ± 1090 | 3.6 ± 0.42 | 4.7 ± 0.66 |
| G-4 | 20 | B | 7 | 0.3 | 16,217 ± 1220 | 3.6 ± 0.52 | 4.8 ± 0.62 |
| G-5 | 20 | - | - | - | 17,533 ± 1140 | 3.7 ± 0.65 | 4.9 ± 0.56 |
| G-6 | 20 | - | - | - | 17,533 ± 1170 | 3.7 ± 0.72 | 4.8 ± 0.81 |
ELISA = enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HI = hemagglutination inhibition test; IBDV = infectious bursal disease virus; ND = Newcastle disease virus; AI-H5 = avian influenza-H5N1.
3.3. Immune Response in Groups Kept under Laboratory Conditions
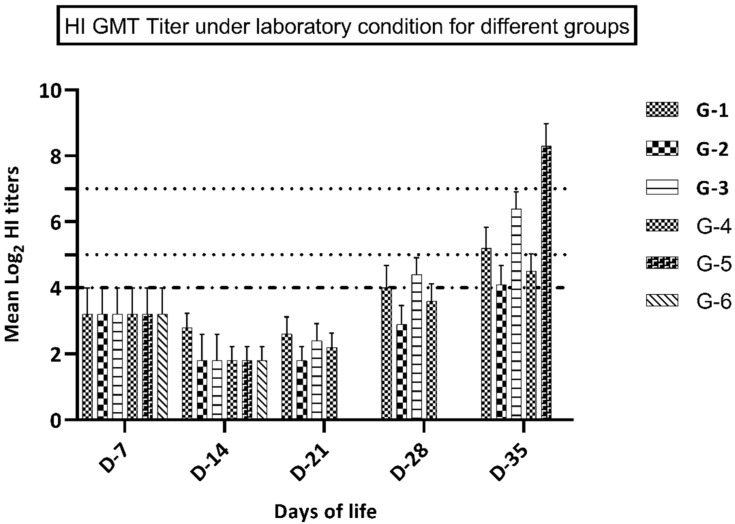
HI assay using antigen A (representing recently circulating H9N2 virus in the Middle East), not H9N2 virus challenge, revealed that birds in groups 3–4 (vaccinated at 7 days of life) had significantly higher (p ≤ 0.05) immune responses at 28 and 35 days of life, compared to groups 1 and 2 that were vaccinated at day 1 of life. Moreover, group 1 (vaccine A) showed a significantly higher immune response (p ≤ 0.05) at 21, 28, and 35 days of life compared to birds in group 2 (vaccine B). At 7 and 14 days of life, birds in group 1 showed a higher but not significantly different (p value ≥ 0.05) immune response compared to group 2, as shown in Figure 1 and Table 3. Birds in group 3 (vaccine A at D-7) showed a significantly higher immune response (p ≤ 0.05) at 28 and 35 days of life in comparison with birds in group 4 (vaccine B). Yet, at 7, 14, and 21 days of life, birds in group 3 showed a higher but non-significant difference in the immune response (p ≥ 0.05) compared to group 4, as shown in Figure 1 and Table 3. Birds in groups 5 and 6 showed non-detectable (nt) HI titer at 21 and 28 days of life, which reflected complete weaning from the maternally derived antibodies at 21 days of age. Birds in group 6 showed an undetectable immune response at 35 days of life, which ensured a negative control condition. Birds in group 6 developed seroconversion at 35 days of life (7 days post-challenge), which reflected the positive effect of the challenge virus. Performing HI assay using antigen B (representing the imported vaccine, not the recently circulating virus in the Middle East) without challenge showed that birds in groups 3–4 (vaccinated at the 7th day of life) developed a significantly higher (p ≤ 0.05) immune response at 28 and 35 days of life versus groups 1-2 that were vaccinated at day 1 of life. There was no significant difference between the HI titers of the different groups vaccinated at the same age. Birds in group 5 showed significantly lower HI titers using antigen B as compared with antigen A at 7 days post-challenge, as shown in Table 4.
Figure 1.
GMT of HI titers in groups 1-6 (kept under laboratory conditions).
Table 4.
Hemagglutination inhibition (HI) test results in bird groups (G-1-6) using two-antigens.
| Days of Life | Antigen Type | Experimental Groups | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-1 | G-2 | G-3 | G-4 | G-5 | G-6 | ||
| D-7 | Antigen A | 3.2 ± 0.79 | 3.2 ± 0.79 | 3.2 ± 0.79 | 3.2 ± 0.79 | 3.2 ± 0.79 | 3.2 ± 0.79 |
| Antigen B | 2.6 ± 0.69 | 2.6 ± 0.69 | 2.6 ± 0.69 | 2.6 ± 0.69 | 2.6 ± 0.69 | 2.6 ± 0.69 | |
| D-14 | Antigen A | 2.8 ± 0.54 | 1.8 ± 0.42 | 1.8 ± 0.49 | 1.8 ± 0.56 | 1.8 ± 0.48 | 1.8 ± 0.32 |
| Antigen B | 2.1 ± 0.44 | 2.2 ± 0.54 | 1.6 ± 0.74 | 1.6 ± 0.64 | 1.6 ± 0.74 | 1.6 ± 0.64 | |
| D-21 | Antigen A | 2.6 ± 0.55 | 1.8 ± 0.67 | 2.4 ± 0.52 | 2.2 ± 0.42 | nd | nd |
| Antigen B | 2.2 ± 0.54 | 2.3 ± 0.64 | 2.1 ± 0.54 | 2.1 ± 0.54 | nd | nd | |
| D-28 | Antigen A | 4.1 ± 0.71 | 2.9 ± 0.59 | 4.4 ± 0.57 | 3.6 ± 0.46 | nd | nd |
| Antigen B | 3.1 ± 0.44 | 3.1 ± 0.54 | 3.4 ± 0.64 | 3.2 ± 0.64 | nd | nd | |
| D-35 | Antigen A | 5.4 ± 0.61 | 4.0 ± 0.57 | 6.4 ± 0.52 | 4.5 ± 0.67 | 8.3 ± 0.65 | nd |
| Antigen B | 4.2 ± 0.54 | 4.1 ± 0.48 | 5.1 ± 0.45 | 4.9 ± 0.64 | 7.4 ± 0.82 | nd | |
Antigen A: antigen prepared from recently circulating H9N2 virus similar to vaccine A seed virus; antigen B: imported antigen representing vaccine B seed virus; D-7: 7 days of life; D-14: 14 days of life; D-21: 21 days of life; D-28: 28 days of life; D-35: 35 days of life; nd: non-detectable level; G-1: vaccine A at D-1; G-2: vaccine B at D-1; G-3: vaccine A at D-7; G-4: vaccine B at D-7; G-5: non-vaccinated, challenged (positive control); G-6: non-vaccinated, non-challenged (negative control).
3.4. Protection Following Challenge with a Wild Type H9N2 at the 28th Day of Life
3.4.1. Seroconversion 7-DPC with Recent Middle Eastern H9N2
At 7-DPC (days post-challenge), birds in group 5 (non-vaccinated, challenged) showed seroconversion with an average Geometric mean titer (GMT) HI titer of 8.3 ± 0.65 using antigen representing the recently circulating H9N2 virus in Egypt. At the same time, the titer was 7.4 ± 0.82 using the standard imported H9N2 antigen. Birds in group 2 and group 4 showed a significant increase in immune response (HI titer) at 7-DPC in comparison with birds of the same group and age, but unchallenged. Birds in group 1 and group 3 at 7-DPC demonstrated a declined immune response compared to those unchallenged in the same group and age, as shown in Table 5.
Table 5.
The seroconversion at 7-DPC (days post-challenge) with recent Middle East H9N2 virus with two types of AIV-H9 antigen.
| Group No. | Bird No. | Vaccine Regime | GMT Log2 HI Titer (n = 10) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccine Type | Age/days | Dose/mL | 7 Days Post-Challenge | |||
| Local Antigen | Imported Antigen | |||||
| 1 | 10 | A | 1 | 0.3 | 4.1 ± 1.2 * | 3.2 ± 1.21 * |
| 2 | 10 | B | 1 | 0.3 | 7.0 ± 2.57 * | 5.9 ± 2.57 * |
| 3 | 10 | A | 7 | 0.3 | 5.1 ± 0.92 * | 4.8 ± 0.89 * |
| 4 | 10 | B | 7 | 0.3 | 6.5 ± 1.67 * | 5.5 ± 1.87 * |
| 5 | 10 | - | - | - | 8.3 ± 0.65 * | 7.4 ± 0.82 * |
| 6 | 10 | - | - | - | - | - |
*: mean there is a significant difference between means when p > 0.05.
3.4.2. Virus Shedding Following Challenge with H9N2 at 28 Days of Life
Birds in groups 3 and 4 (vaccinated at 7 days of life) showed a significantly lower number of shedders at 3-DPC in comparison with groups 1 and 2 (vaccinated at day 1 of life). Of groups vaccinated on the first day of life, group 1 (vaccine A) showed a significant reduction in virus shedding; number of shedders and amount of shed virus at 3/7-DPC compared to group 2 (vaccine B) (Table 6). Birds in group 3 (vaccine A at D-7) showed a significant reduction in virus shedding in terms of number of shedders and amount of shed virus at 3/7-DPC compared to group 2 (vaccine B), as shown in Table 6. Birds in group 2 (vaccine B) showed a reduction in the number of shedders compared to birds in group 5 (non-vaccinated, challenged), while there was no significant difference in the amount of virus shedding via the cloacal route at 3-DPC between birds in group 2 (vaccine B at day 1 of life) and group 5 (non-vaccinated, challenged). Moreover, birds in both groups (group 2 and group 5) showed the same virus shedding amount via tracheal route at 7-DPC, while birds in group 6 showed non-detectable (nd) virus shedding at 3- and 7-DPC in both tracheal and cloacal swaps.
Table 6.
Virus shedding at 3- and 7-days post-challenge.
| Group No. | Vaccinal Regime | Assessment of Protection | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccine Type | Vaccine Age | 3-DPC | 7-DPC | |||||||
| Tracheal Swabs | Cloacal Swabs | Tracheal Swabs | Cloacal Swabs | |||||||
| No./EID50 | % | No./EID50 | % | No./EID50 | % | No./EID50 | % | |||
| G-1 | A | 1 | 4/10 (2.1 ± 0.9) b | 40% | 3/10 (1.5 ± 0.3) c | 30% | 3/10 (1.8 ± 0.7) b | 30% | 3/10 (1.8 ± 0.8) b | 30% |
| G-2 | B | 1 | 6/10 (2.8 ± 0.8) c | 60% | 4/10 (2.1 ± 0.4) c | 40% | 3/10 (2.3 ± 1.1) c | 30% | 4/10 (2.5 ± 0.8) c | 40% |
| G-3 | A | 7 | 2/10 (1.6 ± 0.6) a | 20% | 2/10 (1.1 ± 0.3) a | 20% | 1/10 (1.3 ± 0.0) a | 10% | 2/10 (1.8 ± 0.5) a | 20% |
| G-4 | B | 7 | 4/10 (2.4 ± 0.7) c | 40% | 3/10 (1.9 ± 0.3) c | 30% | 2/10 (1.9 ± 0.7) c | 20% | 3/10 (2.1 ± 0.6) c | 30% |
| G-5 | - | - | 10/10 (3.1 ± 0.9) d | 100% | 6/10 (2.1 ± 0.3) c | 60% | 7/10 (2.3 ± 1.9) c | 70% | 10/10 (3.1 ± 1.8) d | 100% |
| G-6 | - | - | nd | - | nd | - | nd | - | nd | - |
abcd means different superscripts differ significantly (p ≤ 0.05); DPC: days post-challenge; EID50: egg infectious dose50; nd: non-detectable level; G-1: vaccine A at day 1; G-2: vaccine B at day 1; G-3: vaccine A at day 7; G-4: vaccine B at day 7; G-5: non-vaccinated, challenged (+ control); G-6: non-vaccinated, non-challenged (control).
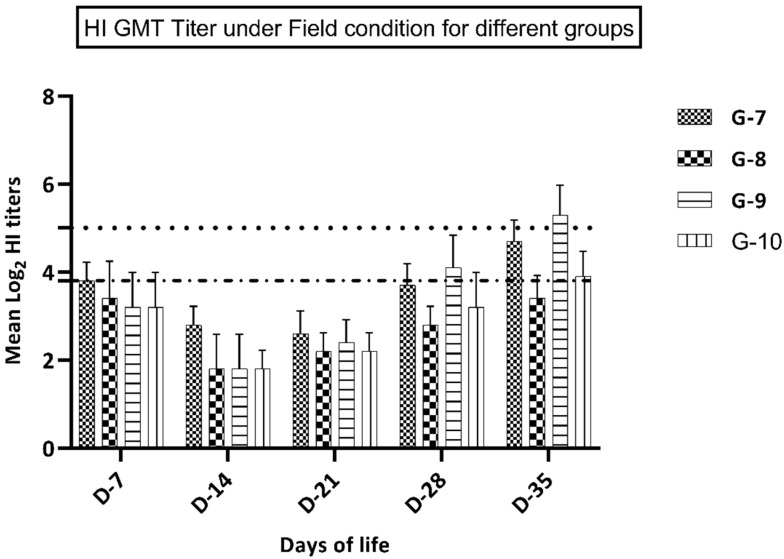
3.5. Immune Response in Groups Kept under Field Condition
Birds in groups 9–10 (vaccinated at 7 days of life) showed a significantly higher immune response at 28 and 35 days of life in comparison with groups 7 and 8 that were vaccinated at day 1 of life. In groups vaccinated at the first day of life, group 7 (vaccine A) showed a significantly higher immune response (p ≤ 0.05) at 28 and 35 days of life compared to birds in group 8 (vaccine B), while at 7, 14, and 21 days of life, birds in this group showed a non-significant increase (p ≥ 0.05) in the immune response versus group 8 (Figure 2). Birds in group 9 (vaccine A at 7 days of life) showed a significantly higher immune response (p ≤ 0.05) at 28 and 35 days of life in comparison with birds in group 10 (vaccine B), while at 14 and 21 days of life, birds in group 9 showed a non-significant increase (p ≥ 0.05) in the immune response compared to group 10 (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
GMT HI titer in groups 7–10 (kept under field conditions).
4. Discussion
Broiler chicks in Egypt and the Middle East almost always arise from broiler-breeders’ flocks vaccinated against H9N2. Accordingly, the vast majority of one-day-old broiler chicks produced in the region carry MDA against H9N2, which compromises the use of the inactivated H9N2 vaccines [29,31]. However, the immune response to other applied vaccines (IBD, NDV, H5) among all bird groups showed detectable antibody levels, with no significant differences after receiving one of the two vaccines employed either at day 1 of life or 7 days of life, or among non-vaccinated controls, which agrees with the previous reports of Kilany et al., Sultan et al., and Khalil et al., who claimed that applying vaccines does not interfere with the immune response of other different vaccines [30,35,36].
Commercial broilers with MDA against AIV-H9N2 face difficulties in developing an immune response following vaccination with inactivated H9N2 vaccines at day 1 of life due to interference. However, the most common regime for H9N2 vaccination in Egypt is to administer a single-dose between days 1–5 of life in broiler sectors, resulting in frequent vaccine failure. Results from the present study show that commercial broilers with MDA against H9N2 develop significantly higher immune response when applied at 7 days of life rather than day 1 of life, regardless the vaccine type used (either A or B). This result explains in part the repeated H9N2 vaccination failure in commercial boiler flocks with MDA (vaccinated at day 1 of life). Interference of the vaccine with the high titer of MDA against H9N2 (average = 6–8 log2) leads to this failure, as previously reported [37,38,39]. Under standard laboratory conditions, birds receiving vaccine A developed significantly higher immune response compared to vaccine B when administered at the same age (day 1 of life and 7 days of life). This may be referred to the amount of antigen in each vaccine, with vaccine A containing a higher amount of antigen (350 HAU unit/dose), while vaccine B contained around 200 HAU unit/dose [38]. As previously reported by Kilany et al. (2016), increasing the dose from 200 to 250 or 350 HAU can improve the immune response and protection against H9N2 [6].
Virus shedding is an important factor in the epidemiology of avian influenza; the lower the amount of virus shedding (amount of virus shedding and number of shedders’ birds), the better we can control avian influenza. Results from the current study showed that use of the inactivated H9N2 vaccine at 7 days of life significantly reduced the virus shedding at 3- and 7-DPC compared to the inoculation at day 1 of life. Birds receiving vaccine A at day 1 of life significantly showed lower virus shedding in amount and number of shedders compared to those receiving vaccine B at the same age. However, birds receiving vaccine B at day 1 of life showed a significant reduction in virus shedding compared to the non-vaccinated challenge group, with tracheal shedding at 3-DPC and cloacal shedding at 7-DPC. No significant virus shedding was observed in the tracheal and cloacal swabs at 7-DPC between group 5 (non-vaccinated challenged) and group 2 (vaccine B at day 1 of life), which may have been due to the lower antigenic mass in the vaccine dose and higher level of MDA at day 1 of life. This negatively impacts the development of immune response, in agreement with the previous reports by Kilany et al. (2016), who demonstrated that lower antigenic masses (less than 128–200 HAU/dose) do not significantly reduce virus shedding compared to non-vaccinated challenged birds [40].
Applying vaccine-A at 7 days of life showed a significant reduction in virus shedding at 3- and 7-DPC compared to administering it at day 1 of life. This is contrary to the findings from vaccine B at 1 or 7 days of life, which may be explained by the higher antigenic mass in vaccine A along with the decline of MDA at 7 days of life, consent with Sun et al. (2012) and Khalil et al. (2015), who reported a significantly higher protection in chickens with H9N2 vaccines containing a higher antigenic mass than 250 HAU/dose. Moreover, Elfeil et al. (2019) reported a significant reduction in virus shedding in turkey following vaccination with H9N2 vaccine (350 HAU/dose) [36,40,41].
Commercial farm conditions always differ from laboratory conditions. In this study, birds kept under farm conditions and vaccinated at 7 days of life showed a significantly higher immune response than those vaccinated at day 1 of life. This matches with the results of laboratory groups and confirms the observation that vaccination at 7 days of life provides a significantly higher immune response and expected protection [36,42]. In addition, groups kept under farm commercial conditions of mass production (25,000 birds/pen) showed 1–3 log2 lower HI titers than those kept under laboratory conditions, indicating that there is around 7–25% difference in expected immune response between farm and laboratory conditions. This finding highlights the need to perform more research trials under commercial farm conditions, including virus challenge under Biosafety level-3 (BSL-3) isolators, bearing in mind that the negative pressure inside the isolators may affect virus spreading, as mentioned previously in the case of AIV-H9N2 in turkey poults, as well as in Newcastle disease virus and infectious bronchitis virus in chicken [40,41,42,43,44].
5. Conclusions
Application of AIV-H9N2 inactivated vaccine at 7 days of life provides a significantly higher protection on the basis of antibody level and reduction of virus shedding, number of shedders, and amount of virus shed per bird versus vaccines given at day 1 of life. Use of a homologous vaccine with high antigenic mass could also help in the reduction virus shedding and provide a significantly higher immunity and protection. Application of such a regime could help the control strategies of AIV-H9N2 in commercial broiler flocks in endemic areas and reduce the epidemiological load of AIV-H9N2 virus in the environment.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to extend their sincere appreciation to Professor Hesham Sultan, Sadat City University, Egypt, for technical support and advice. The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP-2020/96), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.T., W.K.E.; methodology, S.T., W.K.E.; software, S.T., R.R.A., W.K.E.; validation, S.T., R.R.A., W.K.E.; formal analysis, S.T., R.R.A., W.K.E.; investigation, S.T., R.R.A., R.A., M.M.A.-D.,W.K.E.; resources, S.T., R.R.A., R.A., M.M.A.-D., W.K.E.; data curation, S.T., R.R.A., R.A., M.M.A.-D., W.K.E.; writing—original draft preparation, S.T., R.R.A., R.A., M.M.A.-D., W.K.E.; writing—review and editing, S.T., R.R.A., R.A., M.M.A.-D., W.K.E.; visualization S.T., R.R.A., W.K.E.; supervision S.T., R.R.A., W.K.E.; project administration, S.T., R.R.A., W.K.E.; funding acquisition, S.T., R.R.A., R.A., M.M.A.-D., W.K.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP-2020/96), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest and the funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Dia M.S., Hafez M.S.A.E., Ashry M.A., Elfeil W.K. Occurrence of avian influenza h5n1 among chicken, duck farms and human in Egypt. Am. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2019;14:26–32. doi: 10.3844/ajavsp.2019.26.32. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Eid H.M., Algammal A.M., Elfeil W.K., Youssef F.M., Harb S.M., Abd-Allah E.M. Prevalence, molecular typing, and antimicrobial resistance of bacterial pathogens isolated from ducks. Vet. World. 2019;12:677–683. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2019.677-683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sedeik M.E., Awad A.M., Rashed H., Elfeil W.K. Variations in Pathogenicity and Molecular Characterization of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV) in Egypt. Am. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2018;13:76–86. doi: 10.3844/ajavsp.2018.76.86. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Eid H.I., Algammal A.M., Nasef S.A., Elfeil W.K., Mansour G.H. Genetic variation among avian pathogenic E. coli strains isolated from broiler chickens. Asian J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2016;11:350–356. doi: 10.3923/ajava.2016.350.356. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ayoub M.A., Elfeil W.K., El Boraey D., Hammam H., Nossair M.A. Evaluation of some vaccination programs in protection of experimentally challenged broiler chicken against newcastle disease virus. Am. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2019;14:197–206. doi: 10.3844/ajavsp.2019.197.206. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sultan H.A., Talaat S., Elfeil W.K., Selim K., Kutkat M.A., Amer S.A., Choi K.S. Protective efficacy of the Newcastle disease virus genotype VII–matched vaccine in commercial layers. Poult. Sci. 2020;99:1275–1286. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2019.10.063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Elfeil W.K., Ezzat M.E., Fathi A., Alkilany M.-A.A., Abouelmaatti R.R. Prevalence and Genotypic Analysis and Antibiotic Resistance of Salmonella Species Isolated from Imported and Freshly Slaughtered Chicken. Am. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2020;15:134–144. doi: 10.3844/ajavsp.2020.134.144. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fawzy M., Ali R., Elfeil W., Saleh A., Eltarabilli M. Efficacy of inactivated velogenic Newcastle disease virus genotype VII vaccine in broiler chickens. Vet. Res. Forum. 2020;11:113–120. doi: 10.30466/vrf.2019.95311.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sultan H.A., Ali A., El Feil W.K., Bazid A.H.I., Zain El-Abideen M.A., Kilany W.H. Protective Efficacy of Different Live Attenuated Infectious Bronchitis Virus Vaccination Regimes against Challenge with IBV Variant-2 Circulating in the Middle East. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019;6:341. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rady M., Ezz-El-Din N., Mohamed K.F., Nasef S., Samir A., Elfeil W.K. Correlation between ESβL Salmonella Serovars Isolated from Broilers and their Virulence Genes. J. Hell. Vet. Med Soc. 2020;71:2163–2170. doi: 10.12681/jhvms.23645. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Capua I. Avian Influenza and Newcastle Disease: A Field and Laboratory Manual. Springer; Milan, Italy: 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Swayne D.E., Glisson J.R. Diseases of Poultry. Wiley-Blackwell; Ames, Iowa: 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Abouelmaatti R.R., Algammal A.M., Li X., Ma J., Abdelnaby E.A., Elfeil W.M.K. Cloning and analysis of Nile tilapia Toll-like receptors type-3 mRNA. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013;38:277–282. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2013.37740. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Elfeil W.K., Abouelmaatti R.R., Sun C., Han W., Li X., Ma J., Lei L., Liu S., Yang Y., Wang Y., et al. Identification, cloning, expression of a novel functional anasplatyrhynchos mRNA TLR4. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2012;11:1727–1733. doi: 10.3923/javaa.2012.1727.1733. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Elfeil W.M.K., Algammal A.M., Abouelmaatti R.R., Gerdouh A., Abdel-Daim M.M. Molecular characterization and analysis of TLR-1 in rabbit tissues. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016;41:236–242. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2016.63121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Abouelmaatti R.R., Algammal A.M., Elfeil W.M.K., Elshaffy N.M., Li X., Ma J., Fawzy M., Wahdan A., El-Tarabili R., Shabana I.I. Genetic characterization, cloning, and expression of Toll-like Receptor 1 mRNA Oreochromis niloticus. Vet. Arh. 2020;90:193–204. doi: 10.24099/vet.arhiv.0563. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Capua I., Alexander D.J. Avian influenza: Recent developments. Avian Pathol. 2004;33:393–404. doi: 10.1080/03079450410001724085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Spackman E. Avian Influenza Virus. Volume 436 Humana Press; Totowa, NJ, USA: 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 19.El-Zoghby E.F., Arafa A.S., Hassan M.K., Aly M.M., Selim A., Kilany W.H., Selim U., Nasef S., Aggor M.G., Abdelwhab E.M., et al. Isolation of H9N2 avian influenza virus from bobwhite quail (Colinus virginianus) in Egypt. Arch. Virol. 2012;157:1167–1172. doi: 10.1007/s00705-012-1269-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Monne I., Hussein H.A., Fusaro A., Valastro V., Hamoud M.M., Khalefa R.A., Dardir S.N., Radwan M.I., Capua I., Cattoli G. H9N2 influenza A virus circulates in H5N1 endemically infected poultry population in Egypt. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses. 2013;7:240–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-2659.2012.00399.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.El Sayed M., Alyousef Y., Al Sayed A., Elfeil W. Evaluation of the antibody response of two local Saudi lines and commercial chickens vaccinated against newcastle diseases virus and infectious bursal disease virus. Sci. J. King Faisal Univ. 2019;20:105–113. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gharaibeh S. Pathogenicity of an Avian Influenza Virus Serotype H9N2 in Chickens. Avian Dis. 2008;52:106–110. doi: 10.1637/8108-090907-Reg. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hsu S.M., Chen T.H.H., Wang C.H. Efficacy of Avian Influenza Vaccine in Poultry: A Meta-analysis. Avian Dis. 2010;54:1197–1209. doi: 10.1637/9305-031710-Reg.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ahad A., Thornton R.N., Rabbani M., Yaqub T., Younus M., Muhammad K., Mahmood A., Shabbir M.Z., Kashem M.A., Islam M.Z. Risk factors for H7 and H9 infection in commercial poultry farm workers in provinces within Pakistan. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014;117:610–614. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2014.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Qiang F., Youxiang D. The effects of H9N2 influenza A on the immune system of broiler chickens in the Shandong Province. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2011;58:145–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1865-1682.2010.01192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Farzin H., Toroghi R., Haghparast A. Up-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokine production in avian influenza H9N2 virus-infected human lung epithelial cell line (A549) Immunol. Investig. 2016;45:116–129. doi: 10.3109/08820139.2015.1099663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Arafat N., Eladl A.H., Marghani B.H., Saif M.A., El-shafei R.A. Enhanced infection of avian influenza virus H9N2 with infectious laryngeotracheitis vaccination in chickens. Vet. Microbiol. 2018;219:8–16. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bonfante F., Cattoli G., Leardini S., Salomoni A., Mazzetto E., Davidson I., Haddas R., Terregino C. Synergy or interference of a H9N2 avian influenza virus with a velogenic Newcastle disease virus in chickens is dose dependent. Avian Pathol. 2017;46:488–496. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2017.1319904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nagy A., Mettenleiter T.C., Abdelwhab E.M. A brief summary of the epidemiology and genetic relatedness of avian influenza H9N2 virus in birds and mammals in the Middle East and North Africa. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017;145:3320–3333. doi: 10.1017/S0950268817002576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sultan A.H., Abd El-Razik G.A., Allam S.T., El-Deeb A.H. Inactivated oil emulsion H9N2 vaccine in broiler chickens: Pathogenesis and Clinicopathological studies. Am. J. Res. Commun. 2015;3:38–53. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Elfeil W., Abouelmaatti R., Diab M., Mandour M., Rady M. Experimental Infection of Chickens by Avian Influenza H9N2 Virus: Monitoring of Tissue Tropism and Pathogenicity. J. Egypt. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2018;78:369–383. [Google Scholar]
- 32.OIE . OIE Terrestrial Manual 2015. OIE; Rome, Italy: 2015. Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals-Avian Influenza. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nolan T., Hands R.E., Bustin S.A. Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nat. Protoc. 2006;1:1559. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Steel R.G.D., Torrie J.H. Principles and Procedures of Statics. Mcgraw Hill Book Comp. Inc.; London, UK: 1960. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kilany W., Bazid A.-H., Ali A., El-Deeb A., Zain El Abideen M., Sayed M., El-Kady M. Comparative Effectiveness of Two Oil Adjuvant–Inactivated Avian Influenza H9N2 Vaccines. Avian Dis. 2016;60:226–231. doi: 10.1637/11145-050815-Reg. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Khalil A., Hussein H., Tolba S., El-Sanousi A. Preparation and Evaluation of H9n2 Vaccine Adjuvated with Montanide ISA71 VG. Glob. Vet. 2015;15:670–674. doi: 10.5829/idosi.gv.2015.14.05.94190. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Elfeil W.K., Abouelmaatti R.R., Ibrahim H.H., Ali A., Kilany W.H., Rady A., El-Sayed M. Comparison of the effectiveness of two local and imported inactivated combined H9N2-ND vaccines in broiler flocks in Egypt; Proceedings of the IX International Veterinary Conference: One World, One Health; Sharm El Sheikh City, Egypt. 9–13 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 38.El-Deeb A.H., Kilany W., Hanafie A., Echeverry F., El-Kady M. Comparative Field Evaluation of Protective Efficacy of Commercially Available H9N2 Vaccines in Breeders in Egypt; Proceedings of the 19th World Veterinary Poultry Association Congress; Cape Town, South Africa. 7–11 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Elfeil W., Hanfie A., Rady M., Kilany W., Ibrahim H., Elkady M., Elsayed M. Evaluation of Different H9N2 vaccination regime in commercial Broiler breeders flocks; Proceedings of the XX World Veterinary Poultry Association Congress, Edinburgh International Conference Centre (EICC); Edinburgh, UK. 2 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kilany W., Ali A., Bazid A.-H., El-Deeb A., Zain El Abideen M., Sayed M., El-Kady M. A Dose-Response Study of Inactivated Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza H9N2 Virus in Specific-Pathogen-Free and Commercial Broiler Chickens. Avian Dis. 2016;60:256–261. doi: 10.1637/11143-050815-Reg. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Elfeil W., Yousef H., Fawzy M., Ali A., Kilany W., Ibrahim H., Elsayed M. Protective efficacy of MEFLUVAC H9 in turkey poults in both lab and Field condition; Proceedings of the XXIst World Veterinary Poultry Association Congress; Angkok International Trade and Exhibition Centre, Bangkok, Thailand. 16–20 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sun Y., Pu J., Fan L., Sun H., Wang J., Zhang Y., Liu L., Liu J. Evaluation of the protective efficacy of a commercial vaccine against different antigenic groups of H9N2 influenza viruses in chickens. Vet. Microbiol. 2012;156:193–199. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Shahar E., Haddas R., Goldenberg D., Lublin A., Bloch I., Bachner Hinenzon N., Pitcovski J. Newcastle disease virus: Is an updated attenuated vaccine needed? Avian Pathol. 2018;47:467–478. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2018.1488240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Elhady M.A., Ali A., Kilany W.H., Elfeil W.K., Ibrahim H., Nabil A., Samir A., El Sayed M. Field Efficacy of an Attenuated Infectious Bronchitis Variant 2 Virus Vaccine in Commercial Broiler Chickens. Vet. Sci. 2018;5:49. doi: 10.3390/vetsci5020049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]