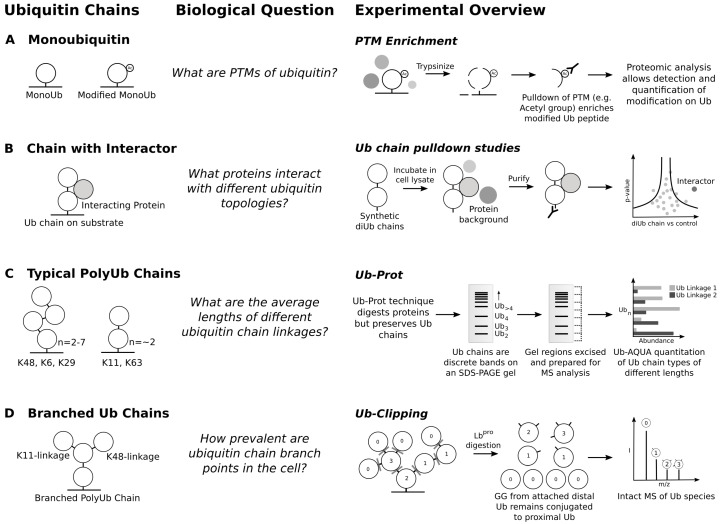
Figure 3.
MS advances in deciphering ubiquitin chain topology and the ubiquitin code. (A) Ubiquitin itself can be modified by a plethora of PTMs which are amenable to detection by MS-methods. (B) Novel interactors of ubiquitin chains have been identified through incubation of synthetic diUb chains with cell lysate. Pulldown of these short chains followed by proteomic analysis in the eluate enables detection of novel interactors for different ubiquitin chain types. (C) Typical ubiquitin chain structures have been suggested by Ub-Prot, a technique allowing analysis of the length of different ubiquitin chain types. (D) Quantitation of ubiquitin chain branch points has been enabled by Ub-Clipping. Lb cleaves ubiquitin between the 74th and 75th amino acid. For ubiquitin monomers in a chain, this cleavage leaves the characteristic GG remnant from a distal ubiquitin (furthest from substrate) conjugated to a proximal ubiquitin. The number of GG remnants can be detected by intact MS suggesting the degree of branching.