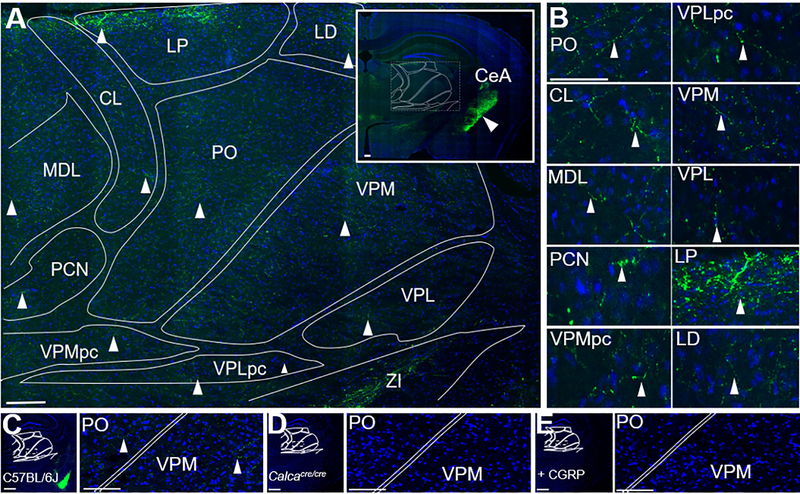
Figure 2. CGRP fibers are present in multiple nuclei of the posterior thalamus.
A. CGRP (green) staining of a C57BL/6J mouse coronal brain section counterstained with DAPI (blue). B. Magnified images of nuclei shown in panel A, with arrowheads highlighting CGRP-containing fibers. C. CGRP (green) staining of a C57BL/6J mouse coronal brain section counterstained with DAPI (blue) for comparison with controls in panels D and E. The bright amygdala signal can be seen in the lower right quadrant. Right panel is a magnified view of box in the left panel, CGRP-containing fibers indicated with arrowheads. D. CGRP staining of a Calcacre/cre mouse (which does not express αCGRP) coronal brain section, showing absence of staining. Right panel is a magnified view of box in left panel. E. CGRP staining C57BL/6J mouse coronal brain section after the primary antibody was pre-incubated with CGRP (20 μM), showing absence of staining. Right panel is magnified view of box in left panel. Abbreviations are: CL = central lateral nucleus of the thalamus, LD = lateral dorsal nucleus of the thalamus, LP = lateral posterior nucleus of the thalamus, PO = posterior thalamus, VPMpc = ventral posteromedial nucleus of the thalamus, parvicellular part, VPLpc = ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus, parvicellular part, VPM = ventral posteromedial nucleus of the thalamus, VPL = ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus. MDL = medial dorsal nucleus of the thalamus, PCN = paracentral nucleus, ZI = zona incerta. Scale bar = 100 μm for all images.