Abstract
COVID-19 has now spread to all the continents of the world with the possible exception of Antarctica. However, Africa appears different when compared with all the other continents.
The absence of exponential growth and the low mortality rates contrary to that experienced in other continents, and contrary to the projections for Africa by various agencies, including the World Health Organization (WHO) has been a puzzle to many. Although Africa is the second most populous continent with an estimated 17.2% of the world's population, the continent accounts for only 5% of the total cases and 3% of the mortality. Mortality for the whole of Africa remains at a reported 19,726 as at August 01, 2020.
The onset of the pandemic was later, the rate of rise has been slower and the severity of illness and case fatality rates have been lower in comparison to other continents. In addition, contrary to what had been documented in other continents, the occurrence of the renal complications in these patients also appeared to be much lower.
This report documents the striking differences between the continents and within the continent of Africa itself and then attempts to explain the reasons for these differences.
It is hoped that information presented in this review will help policymakers in the fight to contain the pandemic, particularly within Africa with its resource-constrained health care systems.
Keywords: COVID-19, Africa, Acute kidney injury, Pandemic, APOL1, COVAN, SARS-COV-2 virus, Chronic kidney disease
Introduction
COVID-19, a novel disease caused by the SARS-COV-2 virus1 was declared by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a public health emergency of international concern on January 30, 2020 and as a global pandemic on the 11 March 2, 020.2 First noted in Wuhan in the Hubei province of China in December 2019, it has now spread to all the continents except Antarctica.3 Every country in the world, with the possible exception of North Korea and Turkmenistan, has documented confirmed cases with a spiraling increase in COVID-19 related mortality and an excess of overall mortality compared to previous years.4
Although COVID-19 manifests primarily as a respiratory tract infection, there have been many reports of renal involvement, more so in the severe forms of the disease.5 , 6 Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are amongst those at the highest risk for developing severe disease. This is over and above other recognized risk factors like hypertension, diabetes, chronic lung disease, and cancers, - which are common comorbidities and often coexist with CKD.
Patients on maintenance haemodialysis (HD) are at particular risk, given the need to come into dialysis centres for their treatment sessions. The enclosed spaces of most dialysis units with centralized, recycled air-conditioning and the length of time necessary for haemodialysis further compounds this risk. Patients with kidney transplants need to use immunosuppressive agents which increases their risk of acquiring the illness and of progression to severe disease.
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is one of the more common complications of severe COVID-19 and studies have reported an incidence as high as 46% amongst hospitalized patients, with it being one of the major reasons for mortality in these patients.6 Recent reports have also suggested a possible association between high-risk APOL1 genotype, common in peoples of African descent, and the increased risk of kidney disease in COVID-19.7 Reports of collapsing glomerulopathy associated with COVID-19 in patients of African ancestry who are carriers of APOL1 risk variants have also been described and the name COVID-19-associated nephropathy (COVAN) for the condition has been proposed.8
These challenges are superimposed on nephrology practice in a continent that has limited resources and capacities to deal with renal patients even preceding the ongoing pandemic. Africa is the world region with the lowest density of nephrologists at 3.6 per million population (pmp), and nine of the ten countries with the lowest nephrologist densities are from the Africa region. Many countries have no trained nephrologists and many that do, have very low numbers with few dialysis units often restricted to the urban centres. Peritoneal dialysis is not widely available as the fluids are not manufactured locally and the cost of importation puts this beyond the reach of most patients as costs are often borne out-of-pocket by the patients themselves.9, 10, 11, 12, 13
Against this background, the African Association of Nephrology (AFRAN), developed COVID-19 guidelines to guide nephrologists in the continent on measures to be taken by nephrology practitioners in the care of our regular patients during this pandemic and also in the management of patients developing the renal complications of COVID-19.14 During the discussions leading to the production of the guidelines, local experiences and insights were shared by members of the expert committee from the different countries represented on the committee. These discussions prompted AFRAN to conduct a more formal survey to document the experience of COVID-19 in different member countries. This report also summarizes the results of the survey and reflects on the reasons for some of the apparent differences in the pandemic between African countries and those in other parts of the world.
Methods
Two sets of data were collected for this study. The first included data to allow comparisons between Africa and other regions as well as comparisons within Africa itself. We also collected data on variables that could explain the apparent differences in COVID-19 case numbers, mortality, and tests in Africa, compared to other parts of the world. For all data sets, publicly available data was gathered up until August 01, 2020. Data on COVID-19 cases, mortality, and test was retrieved from the Worldometer website (http://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/), Worldometer is a trusted data aggregator site that retrieves timely data from official websites and social media accounts of ministries of health, government institutions, and official press briefings.15 The African data was augmented with information from the African Centres for Disease Control (http://africacdc.org/covid-19/) and official reports from the Disease Control Centres of various African countries.
Data on environmental variables i.e. humidity, temperature, and UV index was obtained from Weather online (https://www.weatheronline.co.uk/), a site that provides global meteorological data.16 This source has also been used in previous studies on temperature and coronavirus cases.17 , 18 The Human Development Index (HDI) data was retrieved from the United Nations Development Program (UNDP) 2019 Human development report. Flights data was accessed from the International Civil Aviation Organization, which publishes civil aviation statistics on air transport. Additionally, data on healthcare access and quality index (HAQI) was sourced from the Lancet Global Burden of Disease Study.19 Furthermore, data on population density and diabetes prevalence was accessed from Worldometer and the International Diabetes Federation (IDF).15 , 20
The second set of data was collected via a survey amongst physicians in various countries in Africa in the process of developing the AFRAN COVID-19 guidelines. An electronic (Google Forms) questionnaire was sent out on a WhatsApp forum populated by nephrologists from different countries in Africa. Questions focused on the availability of nephrology resources in the countries of the various respondents and on their experience with managing cases of COVID-19 with particular focus on the renal complications of the disease.
Case numbers, mortality, number of tests performed, and demographic data were summarized and compared by continents, regions, and countries within the continent of Africa. Also, we compared all African countries to the top 10 worst-hit COVID-19 countries. Scatter plots were used to visualize the data and correlation coefficients were calculated to identify the strengths of the relationships between variables. The data analysis tool on the Google Forms platform was used to summarize the survey responses.
Results
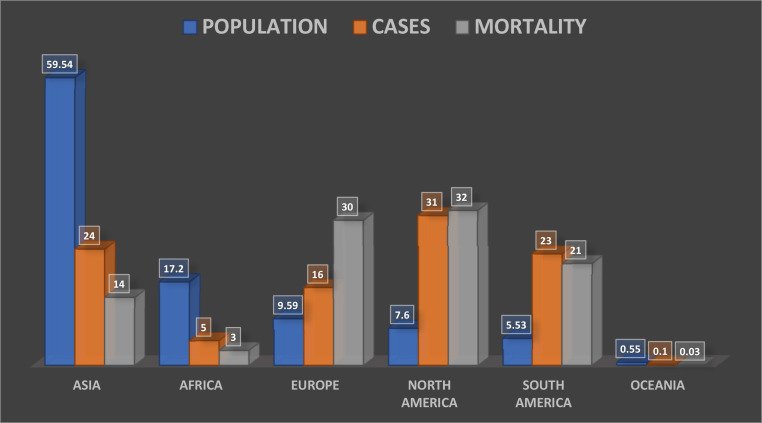
Africa accounts for 17.2% of the world's population, but only about 5% of the total COVID-19 cases diagnosed and 3% of the related mortality (Figure 1 ).
Figure 1.
Shows each continent's share of total global population, total COVID-19 cases and mortality in percentages.
Worldometer (Accessed: August 01, 2020).
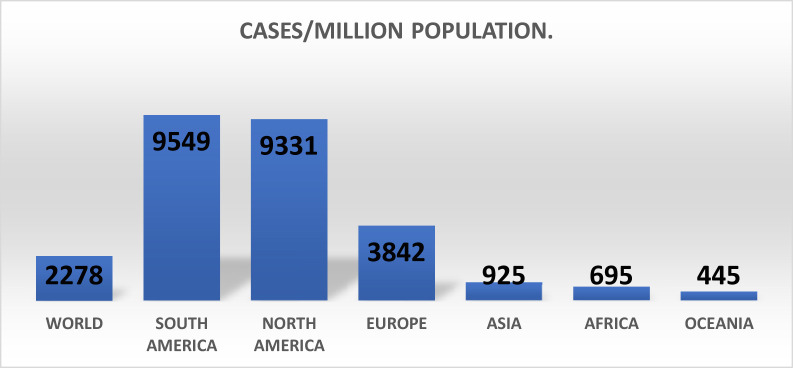
The number of cases per million population (pmp) globally is 2,278, with South America (9549 pmp), North America (9,331) and Europe (3,842) the most affected regions, while Africa has a lower rate of 695 pmp (Figure 2 ). The case fatality rates have been 3.9% worldwide, 7.1% in Europe, 4.0% in North America, 3.5% in South America and 2.1% in Africa.
Figure 2.
Comparing COVID-19 cases per million population for each continent.
Worldometer (Accessed: August 01, 2020).
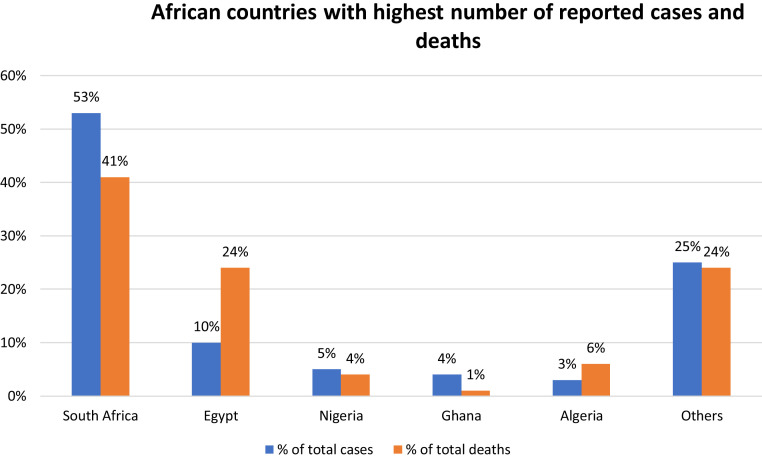
Furthermore, as shown in Figure 3 , the values also vary considerably within the various countries in the African continent, although this might be related to differences in the number of tests performed (Table 1 ).
Figure 3.
Only 5 countries account for 75% of all cases and 76% of all deaths reported in Africa.
Worldometer (Accessed: August 01, 2020).
Table 1.
Shows dataset of the top 10 most impacted COVID-19 countries and all African countries.
| Country | Tests pmp | Cases pmp | Total cases | Deaths pmp | Total deaths | Case fatality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 176,923 | 14,324 | 4,705,889 | 475 | 156,747 | 3.3 |
| Brazil | 61,575 | 12,580 | 2,666,298 | 436 | 92,568 | 3.5 |
| India | 13,636 | 1268 | 1,697,054 | 27 | 36,551 | 2.1 |
| Russia | 192,966 | 5793 | 839,981 | 96 | 13,963 | 1.7 |
| Mexico | 7628 | 3291 | 424,637 | 362 | 46,688 | 11 |
| Peru | 70,231 | 12,564 | 407,492 | 582 | 19,021 | 4.6 |
| Chile | 84,893 | 18,696 | 355,667 | 498 | 9457 | 2.7 |
| Spain | 142,834 | 7178 | 335,602 | 608 | 28,445 | 8.5 |
| Iran | 29,221 | 3648 | 304,204 | 202 | 16,766 | 5.5 |
| UK | 235,878 | 4475 | 303,181 | 680 | 46,119 | 15.2 |
| South Africa | 49,850 | 8307 | 493,183 | 135 | 19,726 | 1.6 |
| Egypt | 1317 | 918 | 94,078 | 47 | 8005 | 5.1 |
| Nigeria | 1321 | 209 | 43,151 | 4 | 879 | 2 |
| Ghana | 12,575 | 1141 | 35,501 | 6 | 182 | 0.5 |
| Algeria | NA | 705 | 30,394 | 28 | 1210 | 4 |
| Morocco | 33,897 | 677 | 24,322 | 10 | 353 | 1.5 |
| Kenya | 5541 | 397 | 20,636 | 6 | 341 | 1.7 |
| Ethiopia | 3667 | 156 | 17,530 | 0 | 274 | 1.6 |
| Cameroon | 5602 | 649 | 17,255 | 15 | 391 | 2.3 |
| Cote d'Ivoire | 3810 | 610 | 16,047 | 4 | 102 | 0.6 |
| Sudan | 9 | 267 | 11,644 | 17 | 746 | 6.4 |
| Madagascar | 1469 | 406 | 10,868 | 4 | 106 | 1 |
| Senegal | 6426 | 613 | 10,232 | 12 | 205 | 2 |
| DRC | NA | 101 | 9070 | 2 | 215 | 2.4 |
| Gabon | 33,736 | 3297 | 7352 | 22 | 49 | 0.7 |
| Guinea | 1095 | 555 | 7308 | 3 | 46 | 0.6 |
| Mauritania | 12,289 | 1354 | 6310 | 34 | 157 | 2.5 |
| Zambia | 4511 | 338 | 5963 | 8 | 151 | 2.5 |
| Djibouti | 57,343 | 5140 | 5084 | 59 | 58 | 1.1 |
| Equatorial Guinea | 31,542 | 3428 | 4821 | 59 | 83 | 1.7 |
| CAR | 6099 | 954 | 4608 | 12 | 59 | 1.3 |
| Malawi | 1544 | 213 | 4078 | 6 | 114 | 2.8 |
| Zimbabwe | 8806 | 213 | 3169 | 5 | 67 | 2.1 |
| Libya | 7274 | 526 | 3621 | 11 | 74 | 2 |
| Somalia | NA | 202 | 3212 | 6 | 93 | 2.9 |
| Congo | NA | 579 | 3200 | 10 | 54 | 1.7 |
| Eswatini | 17,889 | 2280 | 2648 | 35 | 41 | 1.5 |
| Mayotte | 47,565 | 10,838 | 2962 | 143 | 39 | 1.3 |
| Mali | 1118 | 125 | 2535 | 6 | 124 | 4.9 |
| Cabo Verde | 74,816 | 4457 | 2451 | 41 | 23 | 1 |
| South Sudan | 1075 | 207 | 2322 | 4 | 46 | 2 |
| Namibia | 10,321 | 874 | 2129 | 4 | 10 | 0.5 |
| Rwanda | 20,299 | 156 | 2022 | 0.4 | 5 | 0.2 |
| Guinea-Bissau | 761 | 1005 | 1981 | 13 | 26 | 1.3 |
| Mozambique | 1843 | 60 | 1864 | 0.4 | 11 | 0.6 |
| Sierra Leone | NA | 228 | 1823 | 8 | 67 | 3.7 |
| Benin | 7069 | 149 | 1805 | 3 | 36 | 2 |
| Tunisia | 8104 | 130 | 1535 | 4 | 50 | 3.3 |
| Liberia | NA | 235 | 1186 | 15 | 75 | 6.3 |
| Uganda | 5951 | 26 | 1154 | 0.07 | 3 | 0.3 |
| Angola | 1924 | 35 | 1148 | 2 | 52 | 4.5 |
| Burkina Faso | NA | 53 | 1106 | 3 | 53 | 4.8 |
| Niger | 373 | 47 | 1134 | 3 | 69 | 6.1 |
| Togo | 5126 | 113 | 941 | 2 | 19 | 2 |
| Chad | NA | 57 | 936 | 5 | 75 | 8 |
| Sao Tome & Principe | 13,295 | 3969 | 871 | 68 | 15 | 1.7 |
| Botswana | 29,051 | 341 | 804 | 0.8 | 2 | 0.2 |
| Lesotho | 3481 | 327 | 604 | 6 | 13 | 2.2 |
| Reunion | 39,537 | 741 | 660 | 4 | 4 | 0.6 |
| Tanzania | NA | 9 | 509 | 0.4 | 21 | 4.1 |
| Gambia | 2006 | 206 | 498 | 4 | 9 | 1.8 |
| Burundi | 1205 | 33 | 387 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.3 |
| Mauritius | 161,394 | 270 | 344 | 8 | 10 | 2.9 |
| Eritrea | NA | 79 | 279 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Comoros | NA | 443 | 378 | 8 | 7 | 1.9 |
| Seychelles | NA | 1159 | 114 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Western Sahara | NA | 17 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 10 |
Worldometer (Accessed: August 01, 2020).
South Africa and Egypt have reported the most cases. Importantly, these countries are amongst the countries at the top of tests done which is a critical factor in determining the number of confirmed cases. All the countries surveyed employed the rt-PCR method for diagnosis and many have experienced constraints with obtaining the necessary reagents. South Africa, Morocco, Ethiopia and Ghana however stand out prominently in terms of the number of tests done thus far. Ghana has used pooled samples for screening suspected cases with separate tests done for only the positive pooled samples.
The experience shared by African nephrologists has revealed that most of the cases have been completely asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic, with very few patients requiring intensive care. The first set of patients managed in Nigeria were mostly asymptomatic and none required intensive care.21
This has also reflected in the prevalence of the renal complications of COVID-19 and the need for renal replacement therapy (RRT). The responses from the survey have indicated a paucity of cases requiring RRT, with 61% of respondents having no cases in their country requiring RRT. Countries with more developed healthcare systems like Egypt and South Africa had a greater number of cases. Approximately 90% of respondents noted that haemodialysis was available as a means of RRT.
The survey also confirmed the poor state of nephrology care in the continent with many countries having limited numbers of nephrologists, few dialysis centres and very few dialysis machines. The median number of dialysis centres and nephrologists among the respondents were 25 and 28 respectively.
The public health response of several countries consisted of a containment policy involving the isolation of all positively diagnosed cases at isolation centres. Unfortunately, quite a number of these isolation centres lacked the capacity to perform dialysis as indicated by 28% of the survey respondents, with the consequences of avoidable mortality. Some centres with limited capacity had only a single dialysis unit.
There are regional differences within the continent as regards the severity of cases and the outcomes, with the countries in North Africa having the worst outcomes. The case fatality rate is 3.1% for North Africa, 1.4% for West Africa, 1.6% for South Africa, 1.3% for East Africa and 1.3% for Central Africa. South Africa and Egypt account for 63% of all African cases and for 65% of the mortality. These two countries along with Nigeria, the third ranked in terms of numbers, are also the three strongest economies on the continent. North Africa particularly appears to have the worst statistics in Africa, even though their numbers represent 17% of total cases, they constitute 34% of mortality.
Discussion
Several reasons have been adduced for this unexpected pattern of illness being seen in Africa.
Seeding effect
Given that COVID-19 reached countries in Africa by importation from Asia, Europe, and America, the onset of the disease in most countries was much later than was experienced in other continents. Of the 54 countries in Africa, 4 reported their first case in February, 42 in March, 7 in April, and 1 in May. This of course suggests that many of these countries are still experiencing the early stages of the pandemic.
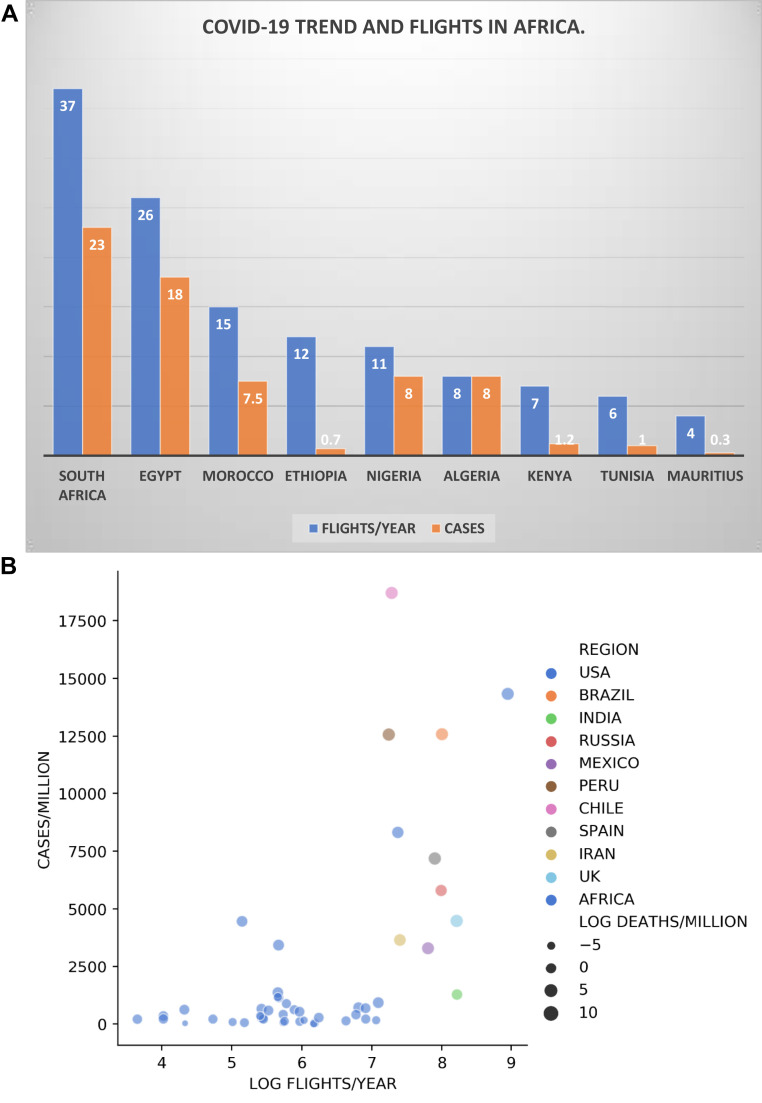
The number of cases in the early stages of the pandemic was directly proportional to the number of international flights into African countries. The busiest international airports in the continent are located in South Africa which also has the highest numbers on the continent, followed by Egypt which is also second in case numbers (Figure 4A). Countries with infrequent business and tourism contacts with other continents are those with the lowest numbers (Figure 4B). The few countries to buck this trend were countries like Kenya and Ethiopia whose airports serve as hubs for several countries on the continent and many international travelers pass through their airports and not actually into these countries.
Figure 4.
(A) Total flights per year in millions and Total COVID-19 cases in thousands in Africa. (B) Flights per year (log) charted against cases/million for all African countries and countries with top 10 highest cases.
Worldometer and International Civil Aviation Organization (Accessed: August 01, 2020).
Many African countries with previous experience of managing other epidemic infectious diseases like Ebola, Tuberculosis, and Lassa fever closed down their airports to international travels much earlier than had been done in other continents. Prior to the closure, many commenced disease surveillance activities and contact tracing at the airports, again much earlier than was done in many other countries outside the continent. All of these factors limited the number of cases “seeded” into African countries delaying the outset and the subsequent growth in numbers thereby “flattening the curve” in many of these countries.
Testing capacity
This is another major potential reason for the relatively lower numbers of cases on the continent. The number of positive cases reported is driven by the number of rt-PCR tests performed. The top five testing countries in the world (as of August 01, 2020) were China −90 million, the USA- 50 million, Russia- 26 million, India- 15 million, and the UK- 13 million. In contrast, the top four countries in Africa were South Africa with 2.9 million tests, Morocco with 1.2 million, Ethiopia with 422,000, and Ghana with 391,000 tests done as at the same date. Within the continent, the top testing countries were also the countries with the highest number of cases. Many countries have been limited by the costs of these tests and the non-availability of the necessary equipment, reagents, and trained personnel. Ghana notably has done many more tests per million of its population by pooling samples, thus testing more patients with each kit deployed. Antibody testing in several countries suggests that many cases might have been missed by the paucity of tests carried out in the continent. Many of these tests suggest that as much as 10%-20% of the population in some of these countries might have already contracted and recovered from the disease. In fact, preliminary results from a study from the Western Cape in South Africa revealed a seroprevalence of antibodies in 40% of antenatal screening specimens and routine monitoring blood tests done for HIV positive ante-natal clinic patients.21 It is also possible that many deaths attributed to other reasons in the absence of testing might have been due to COVID-19.
Population and population density
The population density in Africa is much lower than many of the countries in other continents. The disease spreads quicker and more easily in crowded, enclosed, and noisy spaces. Many communities on the continent are rural and widely dispersed, which slows the spread of the virus. The “hotspots” in most countries are the crowded major cities like Lagos in Nigeria (responsible for over 40% of cases), Johannesburg and Cape Town in South Africa, Nairobi in Kenya, and Cairo in Egypt. Within these cities, the greatest numbers are seen in crowded communities such as Kosofe and Alimosho in Lagos.
The institution of lockdown measures early in the pandemic has also served to limit the spread of the disease. Countries like Rwanda and Senegal which implemented strict and efficient measures were able to limit the spread even better than surrounding countries in their sub-regions. Many of these countries, following the economic distress caused by these lockdown measures, have had to relax some of these measures with the consequence of, in some cases, rising numbers.
Power of youth
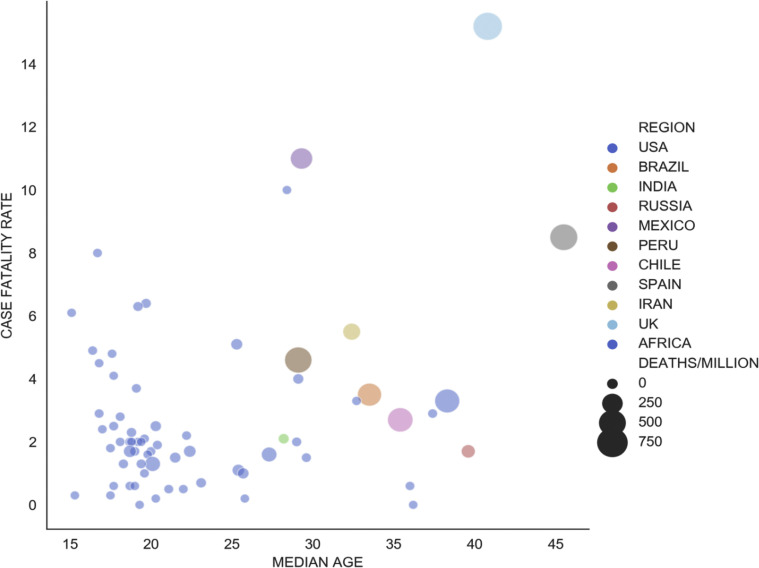
Africa is the youngest continent on the planet; the median age of the countries in Sub-Saharan Africa is 18 years. This is in comparison to Europe for instance where the median age is 37 years. Individuals in Europe over the age of 65 years constitute 20.8% of the population, whilst that of sub-Saharan Africa is 3%. Younger individuals are 4 times less likely to acquire the illness and when they do, they seldom develop severe symptoms or die from the illness. Within the continent as well, countries with slightly older populations like Egypt and South Africa are also the ones with the highest numbers and the greater case fatality rates (Figure 5 ).
Figure 5.
Median age and Deaths/million: Higher median age clearly correlates with more deaths per million population.
Worldometer and United Nations Population Division (Accessed: August 01, 2020).
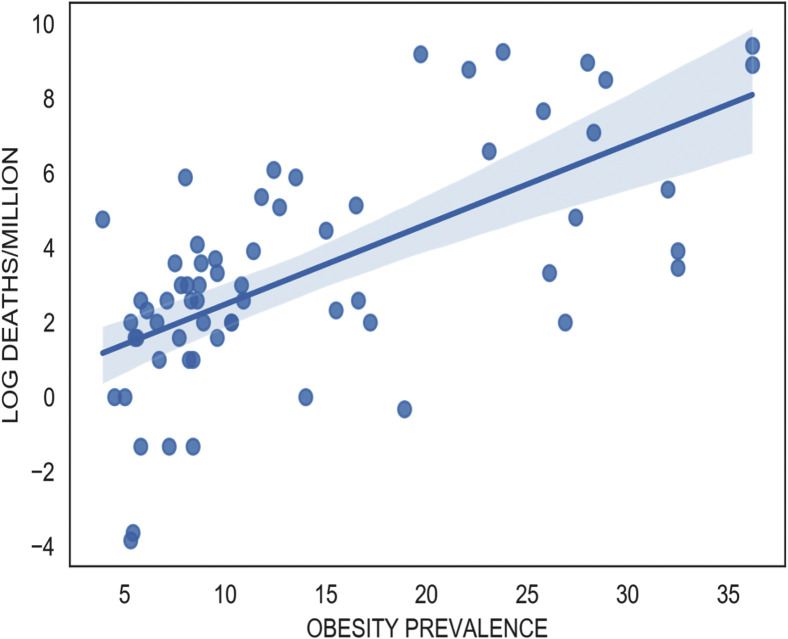
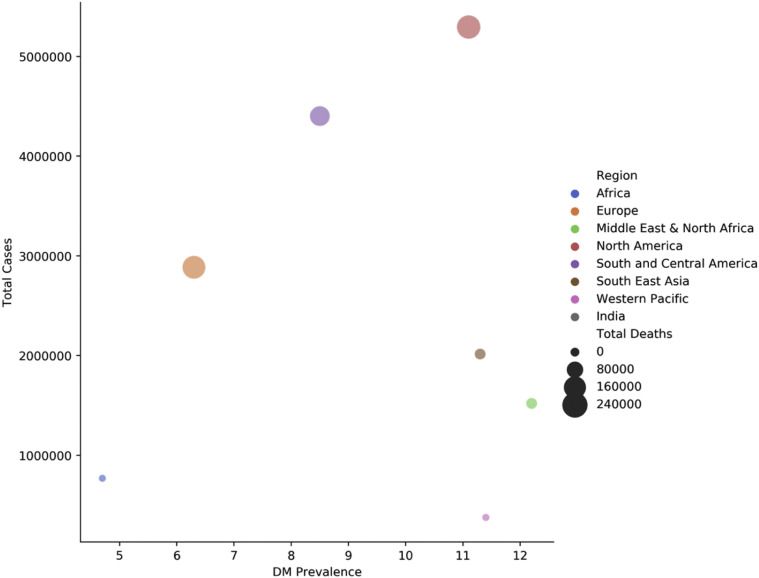
Older individuals are also the ones more likely to have the various co-morbidities that have been associated with severe disease and the risk of mortality. These include obesity, type 2 diabetes, and malignancies. The prevalence of these conditions is greatest in the countries of the Maghreb and South Africa all of which have the highest case numbers and the worst CFR on the continent (Figures 6 and 7 ). In Nigeria, 75% of patients admitted at the isolation centres had no comorbidities whilst in South Africa, 64% had at least one comorbidity. This could partly explain the larger numbers and higher mortality observed in South Africa.
Figure 6.
Obesity predicts worse COVID-19 outcomes.
Worldometer and WHO (Accessed: August 01, 2020).
Figure 7.
Correlation between Diabetes prevalence with total number of COVID-19 cases and deaths.
Worldometer and IDF (Accessed: August 01, 2020).
The cultural practice of caring for elderly relatives at home as opposed to using care facilities may also be a major factor. In Europe and the USA, these care homes were major centres for transmission of COVID-19 with the resultant heightened mortality.
Age might also be relevant in the Vitamin D related factor as younger individuals are more efficient in the production of Vitamin D from sunlight and are more likely to be ambulant and exposed to the sun for this to happen. People living near the equator get more UVB light from the sun and thus generally have higher serum Vitamin D levels than those living farther away. Healthy levels of Vitamin D give patients with COVID-19 a survival advantage by helping them avoid the cytokine storm. Some preliminary studies have demonstrated that Vitamin D status and sun exposure are important factors to consider for reducing the rates of transmission, infection, and severity of illness.22 , 23
Exposure to previous infections
There are speculations of the possible relative resistance to the virus with resultant milder presentation and much lower mortality being observed on the continent. There is a hypothesis that exposure to similar coronaviruses in the past may have conferred relative immunity to patients on the continent. Coronavirus cross-reactive antibodies may contribute to a low transmission rate and reduced severity of disease associated with SARS-COV-2 through cross-neutralization and rapid clearance.24
The heightened immunity obtained from exposure to previous infections like malaria and other ongoing endemic infections, like Tuberculosis and HIV, has been speculated as a possible reason for the milder presentation of the COVID-19 in Africa.
Ongoing vaccination for tuberculosis using the BCG vaccine has also been speculated to be a factor in protecting vaccinated individuals from acquiring the illness and when they do, from the severity of disease and mortality. Most countries in Africa continue to vaccinate their citizens against pulmonary tuberculosis with BCG, as the disease remains endemic in various countries on the continent. Countries in Europe with later discontinuation of BCG vaccination also all seem to have relatively fewer cases and milder illness than their surrounding neighbours. Although we could not find a correlation with BCG vaccination and the number of coronavirus cases, some studies have shown BCG to be protective against severe cases of the illness.25 , 26
Human development and healthcare quality
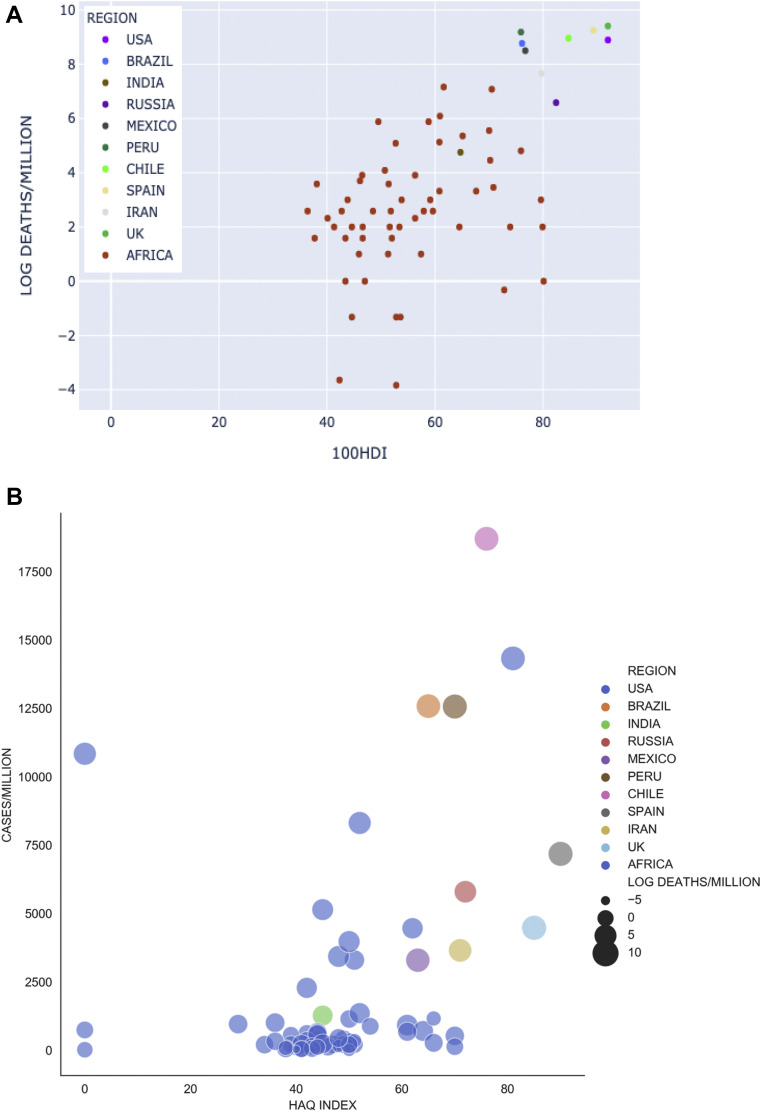
A correlation has been observed between the Human Development Index (HDI) and the numbers of cases and case fatality rate. Countries with higher HDI have higher numbers and worse outcomes (Figure 8A). Another surrogate of healthcare development, the Healthcare Access and Quality (HAQ) index showed quite a similar pattern (Figure 8B). The Pearson correlation coefficients for HDI and HAQ, against COVID-19 cases pmp were noted to be 0.69 and 0.51 respectively.
Figure 8.
(A) Human development index and deaths from COVID-19 per million population (Log scale). (B) HAQ index and cases of COVID-19 per million population.
Worldometer and UNDP (Accessed: August 01, 2020); Worldometer and Barber et al., 2017 (Accessed: August 01, 2020).
Sunlight, UV-light, heat and humidity
Some studies have suggested that temperatures in excess of 27 °C, ultra-violet rays associated with sunlight and humidity all tend to have negative effects on the survival of the virus.18 We could not demonstrate this for African countries. However, the rise in numbers in the southern part of the continent currently experiencing their winter season and the relatively lower numbers and mortality in countries closer to the equator with higher temperatures and higher intensity of UV-light might be in keeping with these speculations.
Conclusion
Despite weaker health care facilities and systems, the growth of cases in Africa has defied most predictions and has remained geometric and not exponential. Available data and statistics continue to reflect consistently lower numbers than those in other continents except for Oceania.
The severity of presentation has also remained relatively mild and the anticipated overwhelming of the health systems, including the renal services of the various countries on the continent has not been seen. Mortality and case fatality rates have been a fraction of what had been predicted.
This is however not a reason to be complacent as for many African countries, these are still early days in the pandemic and a change in the Pattern may yet occur as the numbers continue to rise. It has taken six months to reach the first 500,000 cases but less than two months to cross the million cases mark on the continent.
References
- 1.A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019 | NEJM [Internet] https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/nejmoa2001017 Available from: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 2.WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020 [Internet] https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 Available from:
- 3.WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Dashboard [Internet] https://covid19.who.int Available from:
- 4.Excess deaths associated with COVID-19 [Internet] 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/vsrr/covid19/excess_deaths.htm Available from:
- 5.Huang C., Wang Y., Li X. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cheng Y., Luo R., Wang K. Kidney disease is associated with in-hospital death of patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020;97(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Larsen C.P., Bourne T.D., Wilson J.D., Saqqa O., Sharshir M.A. Collapsing glomerulopathy in a patient with COVID-19. Kidney Int Rep. 2020;5(6):935–939. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2020.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Velez J.C.Q., Caza T., Larsen C.P. COVAN is the new HIVAN: the re-emergence of collapsing glomerulopathy with COVID-19. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020:1–3. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-0332-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ashuntantang G., Osafo C., Olowu W.A. Outcomes in adults and children with end-stage kidney disease requiring dialysis in Sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review. Lancet Glob Health. 2017;5(4):e408–e417. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Niang A., Lemrabott A.T. Global dialysis perspective: Senegal. Kidney360. 2020;1(6):538–540. doi: 10.34067/KID.0000882020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bello A., Levin A., Lunney M. International Society of Nephrology; 2019. ISN Global Kidney Health Atlas 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Osman M.A., Alrukhaimi M., Ashuntantang G.E. Global nephrology Opinion paper workforce: gaps and opportunities toward a sustainable kidney care system. Kidney Int Suppl. 2018;8(2):52–63. doi: 10.1016/j.kisu.2017.10.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bamgboye E. The challenges of ESRD care in developing economies: sub-Saharan African opportunities for significant improvement. Clin Nephrol. 2016;86(13):18–22. doi: 10.5414/CNP86S128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Elsayed H.M., Wadee S., Zaki M.S. Guidelines for the prevention, detection and management of the renal complications of COVID-19 in Africa. Afr J Nephrol. 2020;23(1):109–126. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Coronavirus update (live): 17,757,513 cases and 682,998 deaths from COVID-19 virus pandemic - worldometer [Internet] 2020. https://web.archive.org/web/20200801032838/https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/#c-all%22 Available from:
- 16.World weather | world weather online [Internet] https://www.worldweatheronline.com/country.aspx Available from:
- 17.Ibekwe P.U., Ukonu B.A. Impact of weather conditions on atopic dermatitis prevalence in abuja, Nigeria. J Natl Med Assoc. 2019;111(1):88–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jnma.2018.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gunthe S.S., Swain B., Patra S.S., Amte A. On the global trends and spread of the COVID-19 outbreak: preliminary assessment of the potential relation between location-specific temperature and UV index. J Public Health. 2020:1–10. doi: 10.1007/s10389-020-01279-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Barber R.M., Fullman N., Sorensen R.J.D. Healthcare Access and Quality Index based on mortality from causes amenable to personal health care in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2015: a novel analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2017;390(10091):231–266. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30818-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Global diabetes data report 2010 — 2045 [Internet] https://www.diabetesatlas.org/data/ Available from:
- 21.Spotlight A.B. Maverick citizen: spotlight: Covid-19: high prevalence found in Cape Town antibody study [Internet] Daily Maverick. 2020 https://www.dailymaverick.co.za/article/2020-09-04-covid-19-high-prevalence-found-in-cape-town-antibody-study/ Available from: [Google Scholar]
- 22.Daneshkhah A., Agrawal V., Eshein A., Subramanian H., Roy H.K., Backman V. The possible role of Vitamin D in suppressing cytokine storm and associated mortality in COVID-19 patients [Internet] Infectious Diseases. 2020 http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2020.04.08.20058578 Available from: [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lau F.H., Majumder R., Torabi R. Vitamin D insufficiency is prevalent in severe COVID-19 [Internet] Infectious Diseases. 2020 http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2020.04.24.20075838 Available from: [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sariol A., Perlman S. Lessons for COVID-19 immunity from other coronavirus infections. Immunity. 2020;53(2):248–263. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Escobar L.E., Molina-Cruz A., Barillas-Mury C. BCG vaccine protection from severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(30):17720–17726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008410117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gursel M., Gursel I. Is global BCG vaccination coverage relevant to the progression of SARS-CoV-2 pandemic? Med Hypotheses. 2020 doi: 10.1111/all.14345. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7136957/ Available from: [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]