Abstract
Background & Aims
Notch signaling maintains intestinal stem cells (ISCs). When ISCs exit the niche, Notch signaling among early progenitor cells at position +4/5 regulates their specification toward secretory vs enterocyte lineages (binary fate). The transcription factor ATOH1 is repressed by Notch in ISCs; its de-repression, when Notch is inactivated, drives progenitor cells to differentiate along the secretory lineage. However, it is not clear what promotes transition of ISCs to progenitors and how this fate decision is established.
Methods
We sorted cells from Lgr5-GFP knockin intestines from mice and characterized gene expression patterns. We analyzed Notch regulation by examining expression profiles (by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and RNAscope) of small intestinal organoids incubated with the Notch inhibitor DAPT, intestine tissues from mice given injections of the γ-secretase inhibitor dibenzazepine, and mice with intestine-specific disruption of Rbpj. We analyzed intestine tissues from mice with disruption of the RUNX1 translocation partner 1 gene (Runx1t1, also called Mtg8) or CBFA2/RUNX1 partner transcriptional co-repressor 3 (Cbfa2t3, also called Mtg16), and derived their organoids, by histology, immunohistochemistry, and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq). We performed chromatin immunoprecipitation and sequencing analyses of intestinal crypts to identify genes regulated by MTG16.
Results
The transcription co-repressors MTG8 and MTG16 were highly expressed by +4/5 early progenitors, compared with other cells along crypt-villus axis. Expression of MTG8 and MTG16 were repressed by Notch signaling via ATOH1 in organoids and intestine tissues from mice. MTG8- and MTG16-knockout intestines had increased crypt hyperproliferation and expansion of ISCs, but enterocyte differentiation was impaired, based on loss of enterocyte markers and functions. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and sequencing analyses showed that MTG16 bound to promoters of genes that are specifically expressed by stem cells (such as Lgr5 and Ascl2) and repressed their transcription. MTG16 also bound to previously reported enhancer regions of genes regulated by ATOH1, including genes that encode Delta-like canonical Notch ligand and other secretory-specific transcription factors.
Conclusions
In intestine tissues of mice and human intestinal organoids, MTG8 and MTG16 repress transcription in the earliest progenitor cells to promote exit of ISCs from their niche (niche exit) and control the binary fate decision (secretory vs enterocyte lineage) by repressing genes regulated by ATOH1.
Keywords: Niche Exit, Lineage Specification, Chromatin Remodeling, Lateral Inhibition
Abbreviations used in this paper: ChIP-seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled-deep sequencing; DBZ, dibenzazepine; DHS, DNase I hypersensitivity; DKO, double knockout; Dll, Delta like; GFP, green fluorescent protein; ISC, intestinal stem cell; MTG, myeloid translocating gene; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction; RNA-seq, RNA sequencing; RSPO, R-spondin; WT, wild type
Graphical abstract
What You Need to Know.
Background and Context
Notch signaling maintains intestinal stem cells (ISCs) and determines whether early progenitor cells develop along the secretory or enterocyte lineage. The transcription factor ATOH1 is repressed by Notch in ISCs; its de-repression causes precursor cells to differentiate along the secretory lineage.
New Findings
In the intestine, MTG8 and MTG16 are repressed by Notch signaling indirectly, via ATOH1; this promotes exit of ISCs from their niche and regulates progenitor lineage specification, by repressing ATOH1-target genes.
Limitations
MTG8 null mice died at birth. Studies of mice with intestine-specific knockout of MTG8 are needed to determine phenotypes of adult intestine.
Impact
MTG8 and MTG16 are chromatin modulators that regulate differentiation of ISCs into secretory vs enterocyte lineages.
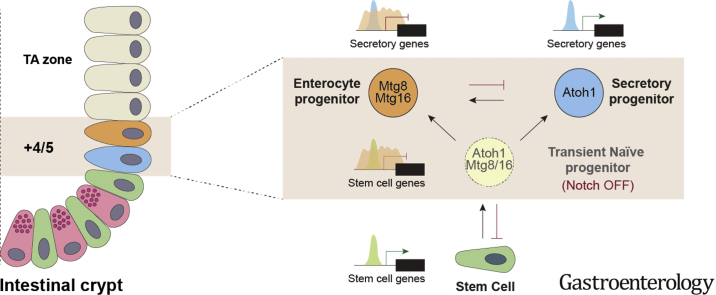
The intestinal epithelium renews every 5 days, a process that is driven by the intestinal stem cells (ISCs) located at the crypt base. ISCs divide and give rise to early progenitor populations at the +4/5 cell position, where lineage specifications take place (Extended Data Supplementary Figure 1).1,2 Notch signaling plays a key role in lineage commitment and plasticity. Activation of Notch drives enterocyte differentiation, while Notch inactivation de-represses the transcription factor ATOH1, a master regulator of all secretory lineages: Paneth, goblet, and enteroendocrine cells.3, 4, 5, 6 This binary fate decision is believed to be driven by the emerging expression of the Notch ligand Delta-like (Dll) family on early secretory progenitors, which activates Notch in surrounding progenitor cells. This instructs these “naïve” neighbors to take the opposite (enterocyte) fate. This process is termed “lateral inhibition” and is proposed to be under ATOH1 regulation.7, 8, 9, 10 Dll1+ secretory progenitors exert plasticity, that is, they can revert to stem cells on stem cell loss.11 Although the signaling pathways regulating ISC fate are well-defined, the underlying mechanism of how stem cells commit to differentiation and undergo the subsequent binary fate decision remains largely uncharacterized. Importantly, transcriptional control and molecular markers of enterocyte progenitors remain largely undefined. Very recent studies propose that chromatin accessibility plays a crucial role in fate decisions and plasticity at the early progenitor stage.8,12,13
To delineate the early stem cell–daughter cell transition, we studied transcriptional control directly at the earliest progenitor cell at the +4/5 position on niche exit. In this study, we identified 2 transcriptional co-repressor homologues, MTG8 and MTG16, that are expressed in these early progenitors. MTG8 and MTG16 were repressed by Notch signaling both in ex vivo organoids and in vivo. We further showed that the 2 co-repressors play central roles in early fate decision of ISCs by repressing the stem cell gene expression program and Dll expression for lateral inhibition. Previous studies have demonstrated that MTG8 and MTG16 recruit chromatin-modifying enzymes for transcriptional regulation.14 Together, our findings indicate a critical role for MTG8 and MTG16 in niche exit and in early fate decision of ISCs by regulating chromatin accessibility of the target genes.
Materials and Methods
Please refer to the online Supplementary Materials for detailed additional Methods.
Animals and Drug Administration
All animal regulated procedures were carried out according to Project License constraints (PEF3478B3) and Home Office guidelines and regulations. Lgr5-EGFP-IRES-CreERT215 mice were used for FACS sorting experiments. Rbpjfl/fl mice16 were crossed with VillinCreER17 mice for inducible intestinal-specific deletion. Mtg16−/−, Mtg8−/−; and Mtgr1−/− mice were kind gift from Scott W. Hiebert. Lgr5DTR-EGFP mice (kind gift from Genentech, hereafter named as Lgr5-GFP mice because only the green fluorescent protein [GFP] reporter element was used in this study) were crossed with Mtg16−/− mice to generate Mtg16−/−; Lgr5-GFP animals. VillinCreER; Rbpjfl/fl or VillinCreER animals were injected with tamoxifen (T5648, Sigma-Aldrich) intraperitoneally at 1.6 mg per 10g of mice and collected at the indicated time points. For proliferation analysis, animals were injected intraperitoneally (IP) with 30 mg/kg EdU (E10187, Molecular Probes) 2 hours before tissue collection. EdU treatment in newborn pups was performed the same as in adults except that the pups were culled 20 minutes after injection. Dibenzazepine (4489 DBZ; Tocris, Bristol, UK) was administered to wild-type (WT) animals as described previously.8 Briefly, mice were injected IP twice the same day, 6 hours apart, with a dose of 100 μmol/kg DBZ suspended in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxypropylmethyl-cellulose (94378, Methocel E4M; Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO) and 0.1% (wt/vol) Tween 80 (P1754; Sigma-Aldrich) in water or only the vehicle as a control. Mice were collected at the indicated time points after the first injection.
Statistical Analysis
Results are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001). Statistical significance of mean values was assessed using unpaired Student t-test or analysis of variance, 1- or 2-way, followed by Tukey’s or Sidak’s Multiple Comparison Post-test respectively. The corresponding number of N and experiments are indicated in the figure legends. Statistics were performed using GraphPad Prism 7 software (La Jolla, CA).
Results
Expression of Mtg8 and Mtg16 in a Subpopulation of +4/5 Cells of Intestinal Crypt
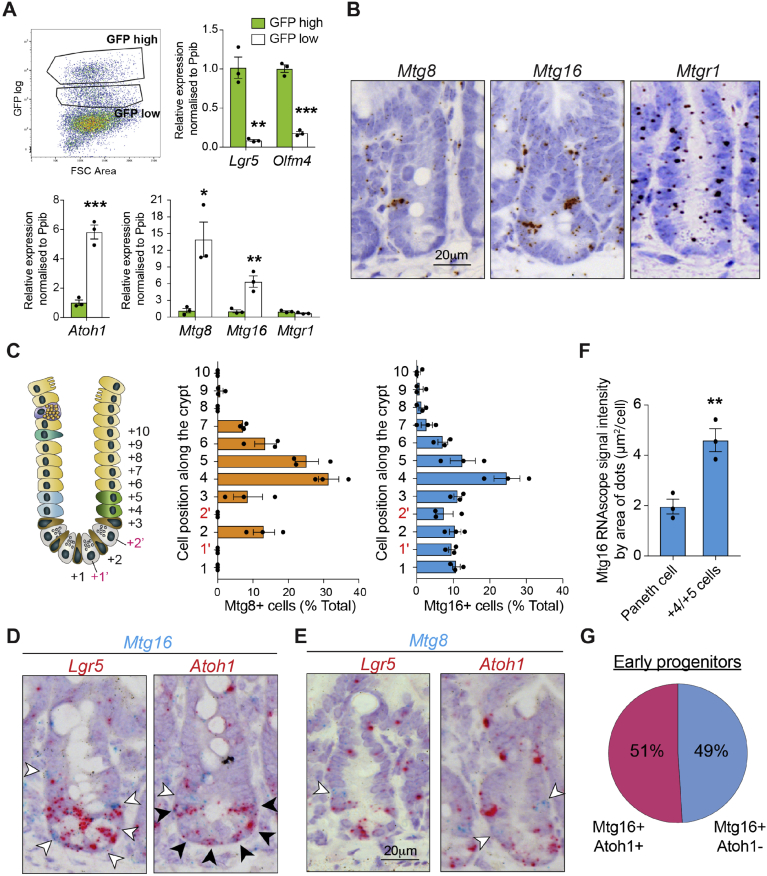
To investigate the transcriptional regulation of stem cell fate and early lineage commitment at the +4/5 progenitor stage, we analyzed the expression profile of sorted LGR5-GFP cells (GSE36497).18 Rather than focusing on the GFP-high (LGR5-GFP 5+) stem cell population, we examined the GFP-low (LGR5-GFP 2+, 3+, and 4+) fractions that represent immediate daughter cells. This allowed us to identify +4/5 cell-enriched genes in the absence of a specific molecular marker. Hierarchical clustering analysis revealed 525 genes that were enriched in GFP-low populations (Supplementary Figure 1B and Supplementary Table 1). These included Atoh1, Dll1, and Dll4 that have previously been reported to be expressed in the early secretory progenitors.8,11,19 Among the 525 genes, we further screened for transcription factors that were enriched in LGR5-GFP-low and absent in LGR5-GFP-high stem cell populations. This resulted in the identification of the 2 related transcriptional regulators Mtg8 and Mtg16.
MTG8, MTG16, and MTGR1 (also known as RUNX1T1, CBFA2T3, and CBFA2T2, respectively) are transcriptional co-repressors that comprise the myeloid translocating gene (MTG) family.14,20 Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) confirmed the enriched expression of Mtg8 and Mtg16 in LGR5-GFP-low early progenitors in the crypts, similar to Atoh1 (Figure 1A and Supplementary Figure 1C). RNAscope analysis further demonstrated enriched expression of Mtg8 and Mtg16 at +4/5 cell positions directly above the LGR5+ ISC compartment (Figure 1B–D), whereas Mtgr1 was expressed throughout the crypt (Figure 1A and B). Quantification of the RNAscope signal confirmed that most Mtg8+ cells were present at positions 4 and 5 (31.5% and 25.3%, respectively), whereas Mtg16+ cells were distributed throughout the lower crypt with a peak frequency at positions 4 and 5 (24.7% and 12.6%, respectively) (Figure 1C). RNAscope co-staining further revealed that expression of Mtg16 was mostly exclusive with Lgr5 but colocalized with Atoh1 at the crypt bottom, indicating that Mtg16 is also expressed by Paneth cells (Figure 1D). It is worth noting that the RNAscope signal of Mtg16 was significantly stronger at positions 4 and 5 than in Paneth cells (Figure 1F, Supplementary Figure 1D), indicating that Mtg16 is indeed enriched in early crypt progenitors. Expression of Mtg8 was mostly exclusive from Atoh1 (Figure 1E), whereas Mtg16 was expressed in both Atoh1+ and Atoh1− populations in the early progenitors in roughly equal proportions (Figure 1D and G). Mtg8 was also found to colocalize with Mtg16 (Supplementary Figure 1E). In addition, co-staining of Mtg16 and Muc2 showed that Mtg16 was also expressed in a small subset of goblet cells that were mainly localized at the crypt-villus junction (red arrows in Supplementary Figure 1F). We also observed stromal expression of Mtg16 in the intestine (Figure 1B, white arrows in Supplementary Figure 1F). Because MTG16 is required for hematopoietic progenitor cell fate decision,21 it is highly likely that the mesenchymal expression of Mtg16 is localized to hematopoietic cells. Taken together, our data suggest that a subpopulation of +4/5 cells express Mtg8/16 and are negative for Atoh1. Of note, Mtg8 transcript levels were very low in abundance throughout the intestinal tissue, suggesting that its expression might be transient and dynamic under strict regulation at the +4/5 cells.
Figure 1.
Expression of Mtg8 and Mtg16 in the +4/5 early progenitor cells. (A) FACS isolation of GFP-high and GFP-low cells from the Lgr5-EGFP-IRES-CreERT2 intestinal crypts. qRT-PCR analysis of the indicated genes in the 2 populations. Data represent mean ± SEM from biologically independent animals (n = 3). ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, 2-sided t-test. (B) RNAscope brown staining of Mtg8, Mtg16 and Mtgr1 in intestinal crypts from WT mice. (C) Quantification of Mtg8 and Mtg16 RNAscope staining in (B) along the crypt. Data represent mean ± SEM from biologically independent animals (n = 3). (D, E) RNAscope duplex staining of Mtg16 (D) or Mtg8 (E) (blue) with Atoh1 or Lgr5 (red) in WT intestinal crypts. Empty arrows indicate exclusive staining, black arrows indicate colocalized staining. (F) Quantification of Mtg16 RNAscope signal (area of dots) in Paneth cells and progenitor cells. Data represent mean ± SEM from biologically independent animals (n = 3). ∗∗P < .01, 2-sided t-test. (G) Quantification of Mtg16+Atoh1+ and Mtg16+Atoh1− cell populations in early progenitors (+3–5 positions) from the RNAscope staining in (D). Scale bars, 20 μm.
Mtg8 and Mtg16 Are Negatively Regulated by Notch Signaling
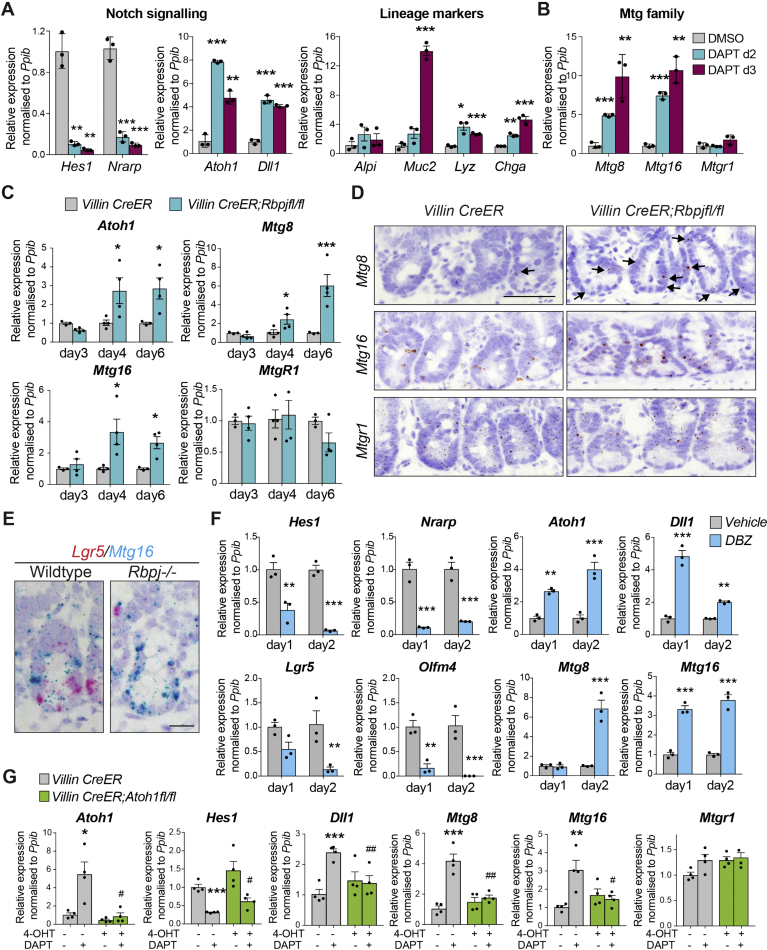
Because Mtg16 expression partially overlaps with Atoh1 expression in +4/5 cells, we asked whether the co-repressors are regulated by Notch signaling. Mouse small intestinal organoids were treated with the Notch inhibitor DAPT followed by qRT-PCR analysis. As expected, DAPT-treated organoids showed significant suppression of Notch signaling and de-repression of Atoh1 and Dll1, while secretory lineage markers were upregulated (Figure 2A). Remarkably, both Mtg8 and Mtg16, but not Mtgr1, were significantly upregulated upon DAPT treatment (Figure 2B). We observed similarly upregulated expression of MTG8 and MTG16 in DAPT-treated human intestinal organoids, indicating that the Notch-controlled expression of the 2 genes is conserved in human (Supplementary Figure 2A).
Figure 2.
Mtg8 and Mtg16 are regulated by Notch signaling. (A, B) qRT-PCR analysis of WT mouse intestinal organoids treated with Notch inhibitor DAPT for 2 and 3 days. Data represent mean ± SEM from biologically independent small intestinal organoid isolations (n = 3). The experiment was performed twice. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, 2-sided t-test. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of intestinal epithelium from Villin CreER and Villin CreER;Rbpjfl/fl mice collected at indicated days after tamoxifen induction. Data represent mean ± SEM from biologically independent animals (n = 4 per group). Three independent experiments were performed. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). (D) RNAscope brown staining of Mtg8, Mtg16, and Mtgr1 in intestinal tissue obtained from Villin CreER and Villin CreER;Rbpjfl/fl mice collected at day 4 post-tamoxifen induction. Arrows indicate Mtg8+ cells. Scale bars, 50 μm. (E) RNAscope duplex staining of Mtg16 (blue) and Lgr5 (red) in intestinal tissues of the indicated genotypes at day 6 post-tamoxifen induction. (F) qRT-PCR analysis of intestinal epithelium from WT mice collected at the indicated days after DBZ or vehicle treatment. Data represent mean ± SEM from biologically independent animals (n = 3 per group). ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, 2-way ANOVA. (G) qRT-PCR analysis of DAPT-treated Villin CreER and Villin CreER;Atoh1fl/fl organoids induced with 4-OHT. Data represent mean ± SEM. The experiment was performed 4 times. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, compared with untreated control group; #P < .05, ##P < .01, compared with DAPT-treated control group, 2-sided t-test.
To confirm the Notch regulation in vivo, we depleted the Notch downstream transcription factor Rbpj for 3 to 6 days. Loss of Rbpj resulted in a progressive drift of differentiation toward the secretory lineage, concurrent with increased Atoh1 expression (Figure 2C; Supplementary Figure 2B and C). Consistent with the organoid data, qRT-PCR analysis showed robust upregulation of Mtg8 and Mtg16 in the intestinal crypts upon Rbpj loss in vivo, while Mtgr1 expression was unchanged (Figure 2C). Interestingly, expression of Mtg8 and Mtg16 was also significantly increased at day 4 post-Rbpj deletion in vivo, when most of the differentiation markers remained unchanged (Figure 2C and Supplementary Figure 2C and D). RNAscope staining confirmed upregulation of Mtg8 and Mtg16, and loss of the ISC marker Lgr5 upon Rbpj deletion (Figure 2D and E). We further validated the findings by treating WT animals with the γ-secretase inhibitor, DBZ, as an alternative Notch inactivation model, which again resulted in a progressive shift toward the secretory lineage (Supplementary Figure 2E). Similar to the Rbpj deletion data, expression of Atoh1, Mtg8, and Mtg16 was significantly upregulated immediately after treatment (1–2 days) (Figure 2F and Supplementary Figure 2F), confirming that MTG8 and 16 are repressed by Notch signaling. Previous data have suggested regional differences in Notch signaling in the intestine, where proximal duodenum shows higher Notch signaling than distal parts of ileum.22 In agreement, higher expression of Atoh1 and Mtg16 was observed in the distal ileum (Supplementary Figure 2G).
Because the secretory progenitor marker ATOH1 is also repressed by Notch signaling in +4/5 cells, we asked whether the Notch-regulated Mtg8 and Mtg16 expression is dependent on ATOH1 using Atoh1 floxed organoids. Indeed, the DAPT-induced expression of Mtg8 and Mtg16 was abrogated on Atoh1 deletion, indicating that Mtg8 and Mtg16 expression is mediated by Atoh1 (Figure 2G). Furthermore, ectopic expression of ATOH1 in HEK293T cells was able to induce MTG8 and MTG16 expression (Supplementary Figure 2H), indicating that the Atoh1-mediated MTG expression is independent of change of cell fate. To verify the hierarchical regulation of ATOH1 and MTG8/16, we further examined their expression dynamics in a short time-course DAPT treatment of organoids. The results demonstrated that Atoh1 was significantly upregulated 12 hours after DAPT induction, whereas Mtg16 was only upregulated 15 hours after induction (Supplementary Figure 2I). Mtg8 remained unchanged during the first 16 hours of DAPT treatment. The data suggest that the expression of Mtg8 and Mtg16 is likely to be driven by Atoh1 at different dynamics. We conclude that MTG8 and MTG16, but not MTGR1, are repressed by Notch signaling indirectly via ATOH1 in the intestine.
Loss of Mtg8 and Mtg16 Induces Hyperproliferation and Expansion of ISCs
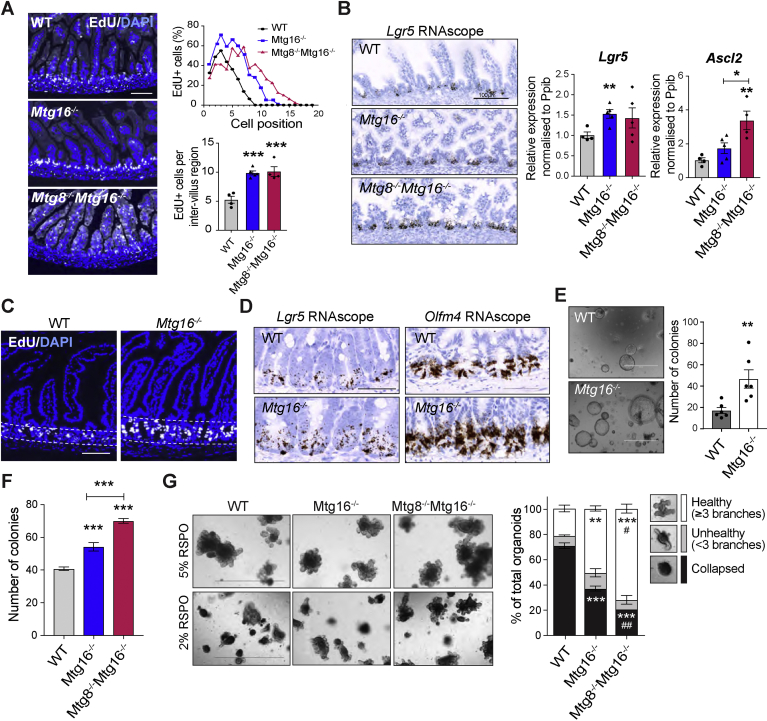
The Notch-regulated expression of Mtg8 and Mtg16 in +4/5 cells led us to investigate whether the co-repressors play a role in ISC fate decision. We analyzed the Mtg8−/− and Mtg16−/− animals. Mtg16−/− mice were healthy and viable, whereas Mtg8−/− and double knockout (DKO) animals died shortly after birth, in accordance with previous findings.21,23 We then proceeded to analyze Mtg16−/− and DKO newborn pups. The intestine obtained from DKO pups was significantly shorter than from WT, which was consistent with the Mtg8-null phenotype (Supplementary Figure 3A).23 Both Mtg16−/− and DKO animals showed significantly increased proliferation in the inter-villus regions that would later give rise to crypts (Figure 3A and Supplementary Figure 3B). Notably, EdU+ cells were also detected in the villi of the DKO intestine, indicating that epithelial cell proliferation was extended beyond inter-villus regions to the villi. Next, we analyzed whether the increase in the inter-villus epithelial cell proliferation is accompanied by upregulated ISC gene expression. RNAscope and qRT-PCR demonstrated that the ISC marker Lgr5 and its transcriptional activator Ascl2 were both significantly upregulated in the mutants (Figure 3B). Similarly, significant increases in crypt proliferation and ISC markers (Lgr5 and Olfm4) were also observed in Mtg16−/− adult intestine (Figure 3C and D; Supplementary Figure 3 C and D). Co-staining of Lgr5 and Atoh1 confirmed significantly increased Lgr5 expression in the trans-amplifying region above the Atoh1+ progenitors in the mutant intestines (Supplementary Figure 3E). We further generated Mtg16−/−;Lgr5-GFP mice to label the endogenous LGR5+ ISCs. In agreement with the RNAscope observations, an increased number of GFP+ ISCs were detected in the Mtg16−/− adult intestine, confirming the ISC expansion phenotype (Supplementary Figure 3F).
Figure 3.
Loss of Mtg8 and Mtg16 increases ISC numbers and proliferation. Intestinal tissues were collected from newborn (P0) (n = 4–5 for each genotype) (A, B) or adult mice (n = 3–6 mice per group) (C–E) for analysis. (A) EdU staining showing increased proliferation in Mtg16−/− and Mtg8−/− Mtg16−/− animals compared with WT. Graphs showing EdU+ cells distribution along the crypt and quantitation of EdU+ cells per inter-villus region in WT, Mtg16−/− and Mtg8−/−Mtg16−/− intestine. Data represent mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. At least 10 representative crypts per animal have been analyzed. (B) Lgr5 RNAscope staining and qRT-PCR showing increased ISC gene expression in newborn Mtg16−/− and Mtg8−/−Mtg16−/− tissues. Data represent mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments (n = 4 per group). ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). (C) EdU staining in WT and Mtg16−/− adult intestine. (D) Lgr5 and Olfm4 RNAscope brown staining in small intestinal tissue from WT and Mtg16−/− adult mice. (E) Colony formation assay of small intestine organoids isolated from WT and Mtg16−/− adult mice. Data represent mean ± SEM of 2 independent experiments (n = 6 mice per group). ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, 2-sided t-test. Scale bars, 100 μm (B–D), 1000 μm (E). (F) Colony formation assay of small intestine organoids derived from WT, Mtg16−/− and Mtg16−/−Mtg8−/− newborn pups. Data represent mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments (n = 2–4 mice per group). ∗∗∗P < .001, 1-way ANOVA. (G) Representative images showing newborn organoids of the indicated genotypes cultured in 5% or 2% RSPO conditions for 3 to 4 days. Scale bar, 1000 μm. Right, quantification of the organoid health status maintained in 2% of RSPO condition. Data represent mean ± SEM of 2 independent experiments (n = 2–4 mice per group). ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with WT, 1-way ANOVA. #P < .05, ##P < .01 compared to Mtg16−/−, 1-way ANOVA.
To test whether the stem cell–repressive role of MTG16 is cell-intrinsic, we further examined the colony formation capacity of WT and mutant organoids ex vivo in the absence of any stromal niche. We confirmed that Mtg16−/− organoids grew faster than the WT controls, suggesting that the stem cell–repressive role of MTG16 is indeed cell-intrinsic (Figure 3E). Similarly, organoids derived from Mtg16−/− and DKO newborn intestine also grew significantly faster than the WT counterparts (Figure 3F and Supplementary Figure 3G). We further challenged the organoids by reducing the Wnt agonist R-spondin (RSPO) concentration. Neither WT nor MTG mutant organoids survived in the absence of RSPO. However, Mtg16−/− and DKO organoids grew significantly better in the low-RSPO (2%) condition with fewer collapsed organoids and more healthy branching organoids compared with WT (Figure 3G). The results suggest that MTG KO organoids have a growth advantage in the low-RSPO condition but are still dependent on exogenous Wnt signaling for ISC survival. Because MTG16 is expressed in Paneth cells, we asked whether the increase in crypt proliferation and stem cell markers in Mtg16−/− intestine is caused by dedifferentiation of Paneth cells, which has recently been reported to occur on injury.24 However, immunostaining of WT and Mtg16−/− tissue did not show any colocalization of Paneth cell marker lysozyme and proliferation marker Ki67 (Supplementary Figure 3H), indicating that the increase in stem cell gene expression on MTG16 loss is caused by stem cell de-repression in the early progenitors rather than Paneth cell plasticity. Together, we tentatively conclude that MTG8 and MTG16 regulate niche exit at the +4/5 cells by repressing the ISC fate and proliferation.
Mtg8 and Mtg16 Deletion Impairs Intestinal Lineage Specification
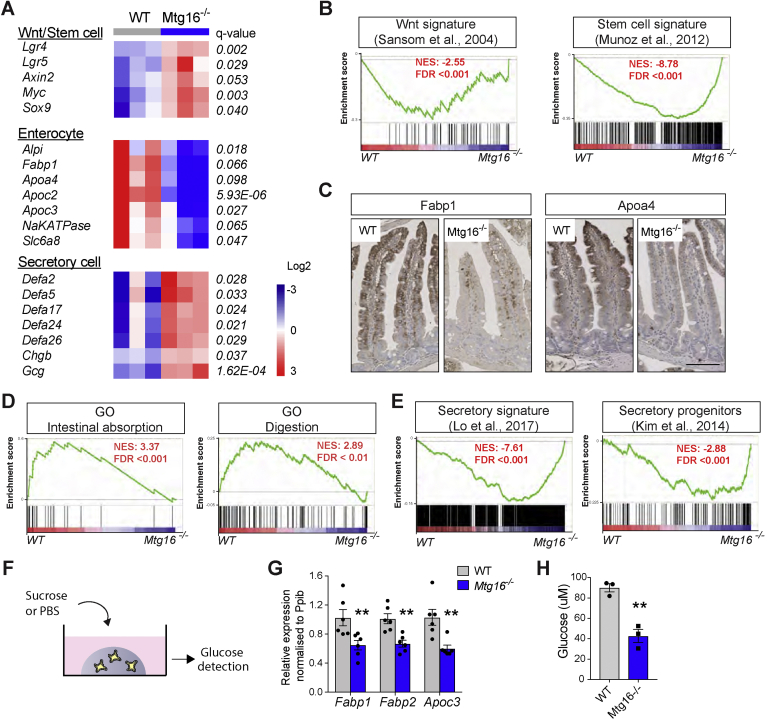
MTGR1 has previously been shown to be required for intestinal secretory cell differentiation in adult tissue.25 We therefore asked whether loss of MTG8/16 would alter lineage selection in the intestine. Because intestinal differentiation is incomplete in newborn animals, we decided to focus on analyzing Mtg16−/− adult intestine. Reduced goblet cell numbers (AB-PAS) were observed in Mtg16−/− adult intestine (Supplementary Figure 4A and B). This is in concordance with the previously reported phenotype of Mtg16 null animals.26 Similarly, there was a tendency toward reduction of enterocyte markers (villin and alkaline phosphatase) in the mutant intestines (Supplementary Figure 4A). We believe that the moderate alteration of terminal differentiation might be due to the redundant role of Mtg8. To provide a global, unbiased picture of gene expression changes in the mutant animals, we further performed transcriptional profiling on the WT and Mtg16−/− intestine. RNA-seq analysis revealed 478 genes that were differentially expressed upon Mtg16 deletion (Supplementary Figure 4C and D; Supplementary Table 2). Consistent with the increased crypt proliferation observed in Figure 3, Wnt and stem cell signatures18,27 were both significantly upregulated upon loss of MTG16 (Figure 4B). Interestingly, we further observed significant reduction of enterocyte markers and upregulation of secretory markers such as Paneth cells and enteroendocrine cells in the Mtg16 mutant intestine (Figure 4A). Of note, RNA-seq data did not reveal significant alteration of goblet cell markers. Comparison of various enterocyte markers with the previously published single-cell RNA-seq data (GSE92332) revealed differential expression of the markers between mature and immature enterocytes.28 In particular, Alpi expression did not distinguish between mature and immature enterocytes, while other markers such as Apoa4, Fabp1 and Fabp2 were preferentially expressed in mature enterocytes (Supplementary Figure 4E). Our RNA-seq data suggested that deletion of Mtg16 results in a loss of mature enterocyte markers. Indeed, a clear reduction of FABP1 and APOA4 proteins was observed in the Mtg16−/− intestine, indicating that loss of MTG16 inhibits enterocyte differentiation and maturation (Figure 4C). Gene set enrichment analysis further confirmed the loss of absorptive signatures (Figure 4D) and enrichment of secretory signatures8,29 (Figure 4E) in the Mtg16−/− intestine. To further demonstrate the functional defect of the MTG mutant intestine, we examined the disaccharidase (brush border enzyme) activity in the WT and Mtg16−/− organoids (Figure 4F). Downregulated expression of mature enterocyte markers was confirmed in Mtg16−/− organoids (Figure 4G). Consistent with our observation of impaired enterocyte differentiation in vivo, the disaccharidase activity of the adult Mtg16−/− organoid was significantly reduced when compared to WT control organoids (Figure 4H).
Figure 4.
Mtg8 and Mtg16 deletion impairs intestinal lineage specification. Intestinal tissues were collected from newborn (P0) (n = 4–5 for each genotype) (A) Heatmap showing genes differentially expressed in WT and Mtg16−/− intestine. (B, D, E) Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) probing (B) Wnt/Stem cell signature genes, (D) intestinal absorption and digestion, and (E) secretory signature genes. (C) FAPB1 and APOA4 immunostaining in adult WT and Mtg16−/− intestinal tissue. (F) Scheme showing the disaccharidase assay performed in organoids. (G) qRT-PCR of mature enterocyte markers in adult WT and Mtg16−/− organoids. (H) Glucose levels detected in the supernatant of intestinal organoids of the indicated genotypes after 1-hour sucrose incubation. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, 2-sided t-test.
Taken together, our data support the notion that MTG16 represses stem cell proliferation and promotes enterocyte over secretory lineage differentiation. Interestingly, we also noted enrichment of chromatin remodeling and epigenetic regulatory genes in the Mtg16 mutant intestine (Supplementary Figure 4F), suggesting that the co-repressor MTG16 may regulate gene expression by chromatin remodeling.
Mtg16 Binds to ISC Signature Genes and Atoh1-targets for Niche Exit and Fate Decision
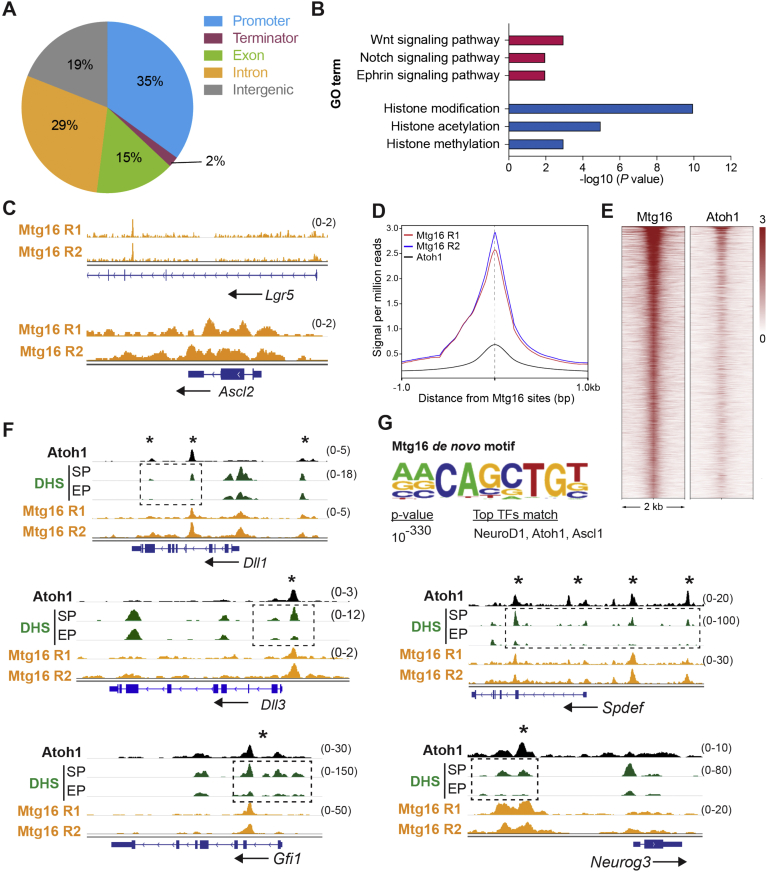
To investigate how the co-repressors regulate ISC gene expression program and lineage selection, we then performed chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled-deep sequencing (ChIP-seq) to identify the MTG targetome. To capture the physiological binding targets in vivo, intestinal crypts were isolated 4 days after Rbpj-depletion to enhance endogenous MTG16 expression, while most of the differentiation markers remained unaltered (Figure 2C and D and Supplementary Figure 2C and D). MTG16 ChIP-seq identified 7843 reproducible binding sites (Figure 5A, Supplementary Figure 5A and Supplementary Table 3). Gene ontology analysis of MTG16 targets revealed enrichment of genes associated with Wnt and Notch signaling, as well as histone-modifying genes (Figure 5B and Supplementary Table 4). Comparison between the ChIP-seq and RNA-seq data showed that 35% of the genes differentially expressed upon Mtg16 deletion harbored MTG16-binding sites within 5kb of the transcription start site (Supplementary Figure 5B), where the odds of genes being differential were observed to be increased by a factor of 2.4 (P < 2e-16, hypergeometric test). In particular, we observed clear MTG16-binding signals over the key ISC genes Lgr5 and Ascl2 (Figure 5C). These sites coincided with the previously reported regulatory regions in these genes.30,31 MTG16 also bound to the promoter regions of other Wnt targets such as Axin2, Myc, and Sox9, suggesting that MTG16 represses ISC signature genes and Wnt targets through direct binding to their regulatory sequences (Supplementary Figure 5C). This result was consistent with our observation that Lgr5 and Ascl2 are upregulated on MTG8 and MTG16 loss (Figure 3B and D).
Figure 5.
MTG16 binds to ISC- and secretory lineage-signature gene loci. (A) Genome-wide distribution of 7843 MTG16-binding sites. (B) Gene ontology analysis identified ontology terms associated significantly with MTG16 targetome, including Wnt, Notch, and Ephrin pathways, as well as in histone-modifying genes. (C) ChIP-seq data showing MTG16 binding signal (per million reads) to ISC gene loci (Lgr5 and Ascl2). (D, E) Composite profile (D) and heatmap (E) showing striking overlap between ATOH1 and MTG16 binding sites (7843 sites). (F) ChIP-seq data showing MTG16 binding signal (per million reads) to previously reported ATOH1-enhancer regions12 (asterisk) of the indicated gene. Reduced levels of DHS in enterocyte progenitors (EP) versus secretory progenitors (SP) are indicated by dotted box. (G) MTG16 de novo motif matches with previously reported ATOH1 and ASCL1/2 motif.
Because MTG8 and MTG16 are repressed by Notch signaling in +4/5 cells, we asked whether they play a role in lineage selection, similar to ATOH1. We compared our MTG16 ChIP-seq data with the previously reported ATOH1 ChIP-seq and DNase I hypersensitivity (DHS, a measure of chromatin accessibility) data on secretory- or enterocyte progenitors.8 A striking overlap (84.08%) between MTG16 and ATOH1 binding sites was observed between the 2 datasets, suggesting that MTG16 may also be involved in fate decision (Figure 5D and E).
ATOH1 has previously been reported to drive lateral inhibition and to set the secretory fate by regulating expression of the Dll Notch ligands.8,29 We analyzed the ChIP-seq profiles of the Notch ligands Dll1 and Dll3. Remarkably, we found that MTG16 bound to the previously reported ATOH1-enhancer regions of both Dll1 and Dll3 (Figure 5F). Interestingly, loss of or reduced levels of DHS were observed in enterocyte progenitors compared with secretory progenitors at the regions where MTG16- and ATOH1-binding overlapped (Figure 5F). These results suggest that MTG16 binds to the ATOH1-bound loci to reduce chromatin accessibility of Dll genes in enterocyte progenitors for lateral inhibition and early fate decision. Similar to Dll ligands, MTG16 also occupied most of the reported ATOH1-binding sites in all secretory signature genes including Spdef, Gfi1, and Neurog3 with reduced DHS levels in enterocyte progenitors (Figure 5F). Given that MTG proteins repress gene transcription by recruiting various chromatin-modifying enzymes (eg, histone deacetylases),14 we propose that MTG8/16 regulate lateral inhibition and binary fate decisions of +4/5 progenitors by repressing ATOH1-mediated Dll ligands and secretory signature gene transcription. Indeed, de novo motif analysis identified an MTG16 consensus motif that was matched to the reported ATOH1 motif, suggesting that MTG16 occupies ATOH1-bound enhancers to regulate lineage specification (Figure 5G and Supplementary Table 5). Co-immunoprecipitation analysis further confirmed the physical binding of ATOH1 with both MTG8 and MTG16 (Supplementary Figure 5D). Consistently, ATOH1-mediated DLL1 expression was significantly downregulated by MTG8 or MTG16 expression (Supplementary Figure 5E). In addition to ATOH1, MTG family members have previously been shown to interact with TCF4 for transcriptional suppression.32 Together, our findings support the notion that the MTG co-repressors bind to the transcription factors TCF4/β-catenin and ATOH1 to repress the stem cell program and Dll expression for lateral inhibition. We further noted that MTG16 bound strongly to its own locus as well as to the promoter regions of Mtgr1 and Atoh1 (Supplementary Figure 5F), whereas MTG16 has recently been reported as an ATOH1 target.29 The data imply that ATOH1 and the MTG family together contribute to a “cross-over” feedback loop in +4/5 cells to regulate rapid, dynamic fate decisions.
Discussion
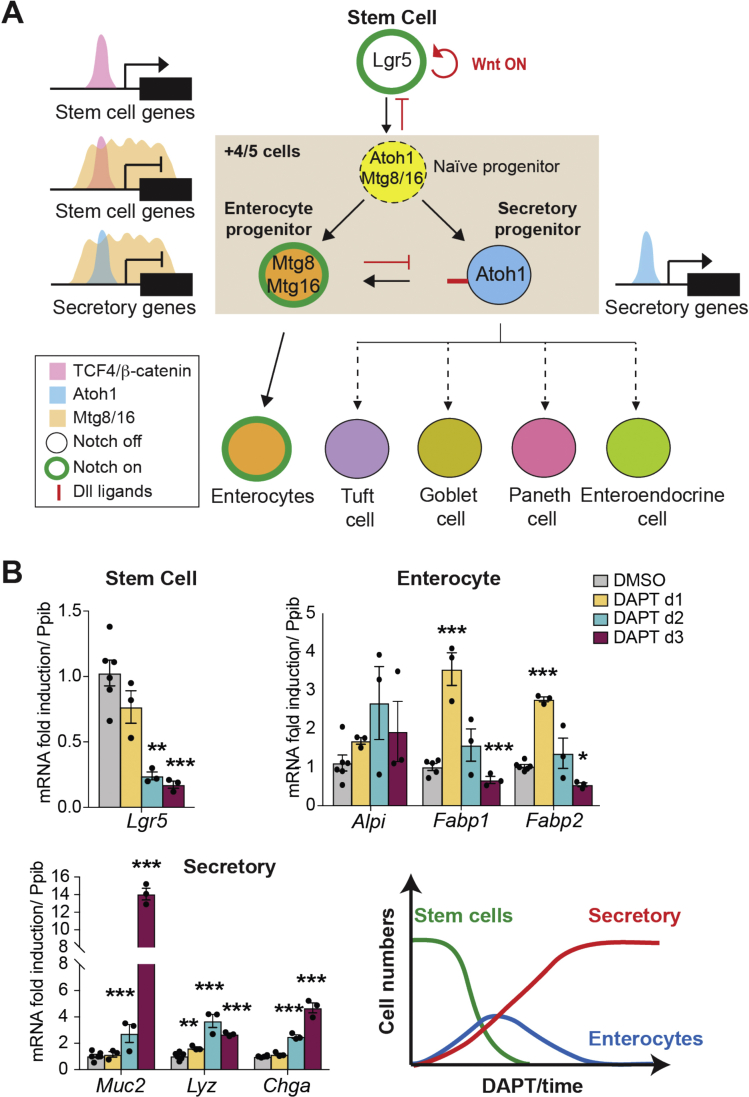
Extensive studies in the past have focused on characterizing the signaling pathways regulating ISCs, yet it has remained elusive how the tightly regulated ISC fate remains restricted to a fixed number of proliferative cells at the crypt base. Paneth cells have been shown to constitute the essential niche to define ISC identity,9,33, 34, 35 yet functional ISCs can be maintained upon Paneth cell ablation.36,37 Therefore, it remains unclear how Paneth cells contribute to ISC homeostasis. The undifferentiated cells immediately above the ISC compartment (+4/5 progenitors) are heterogeneous in terms of marker gene expression. ATOH1 marks a subpopulation of +4/5 cells that have entered the secretory lineage differentiation and mediate lateral inhibition,3,8 while molecular markers of the remaining +4/5 progenitors entering the absorptive enterocyte differentiation have not yet been identified. Here we report that the Notch-repressed transcriptional co-repressors MTG8 and MTG16 are expressed in +4/5 progenitors to switch off the stem cell expression program. Our current findings provide insights into the underlying mechanism of ISC fate decisions (Figure 6A). Our data support the notion that the “Notch-off” state is the first “priming” step to drive ISC-daughter cell transition by committing to transient bi-potent progenitors, which is consistent with the recently proposed “multi-lineage progenitor” population as the earliest progeny of LGR5+ stem cells.38 When an ISC occupies the +4/5 cell position and loses its contact with Dll-expressing Paneth cells (niche exit), Notch is switched off as a consequence, thereby de-repressing ATOH1, MTG8 and MTG16. The co-repressors then drive differentiation by switching off the Wnt-mediated ISC gene expression program in the immediate progenitors, leading to transient activation of the whole differentiation program. This is consistent with the data obtained from our time-course DAPT-treated organoids, where downregulation of ISC markers was accompanied by transient upregulation of both absorptive and secretory lineage markers upon early Notch inhibition (Figure 6B). Subsequently, ATOH1 and MTG8/16 work together in these naïve bi-potent progenitors to control lateral inhibition and binary fate decision (Figure 6A). Our findings uncover a novel role of MTG8/16 in promoting enterocyte differentiation by direct repression of ATOH1-mediated secretory differentiation and Dll ligands expression. The differential expression dynamics of Atoh1, Mtg8, and Mtg16 and their potential negative feedback network may perhaps explain the heterogeneity within the early progenitor population. MTG16 is initially co-expressed with ATOH1 immediately after niche exit and Notch inhibition. Subsequently, MTG8 and MTG16 expression starts to dominate and repress ATOH1 expression, resulting in MTG8/16+ATOH1− cells. It is conceivable that the fate decision at these progenitors is dependent on the expression dynamics of ATOH1 and MTG. Interestingly, 2 recent studies showed direct binding of HES1 to the promoter of Mtg16,39,40 suggesting that MTG8/16 may also be actively repressed by Notch directly via HES1 at the ISCs. It is also worth noting that all Dll ligands are transcriptional targets of ATOH1 and MTG16, including Dll3 that has previously been reported to function exclusively as cis-inhibition rather than trans-activation of Notch signaling.41 This may imply a previously underappreciated role of DLL3 in the dynamic lateral inhibition and fate decision in the early progenitors, where DLL1/4 trans-activate Notch in the neighboring cells and DLL3 inhibits Notch cell-autonomously.
Figure 6.
Proposed model for intestinal stem cell hierarchy. (A) Updated ISC fate model. See text for details. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of the indicated genes after 1, 2, or 3 days of DAPT treatment. On the right, illustration of expression kinetics of the stem cell, secretory and enterocyte markers upon time-course Notch inhibition. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, 2-sided t-test.
Previous studies have shown that MTG16 is required for injury-induced epithelial cell survival and regeneration in the intestine.26,42 Interestingly, increased proliferation of Mtg16-depleted intestine has been demonstrated, although the underlying mechanism remained uncharacterized.26 More recently, increased ß-CATENIN staining has also been observed in MTG16-deleted colitis-associated tumors,43 suggesting a potential Wnt inhibitory role of MTG16. In the current study, we focused on characterizing the mechanistic role of MTG in normal intestinal stem cell homeostasis. Beyond the increase in crypt proliferation as previously reported, we further observed a significant increase in stem cell number in the MTG mutants. Global genomic and transcriptomic analysis further revealed that MTG16 binds to the gene loci of stem cell and Wnt signature genes for transcriptional repression. Our data on the Notch-regulated MTG expression at +4/5 progenitor cells provide mechanistic insight into how MTG regulates stem cells and the Wnt transcriptional program under normal stem cell homeostasis, which will help understand the tumor suppressive role of MTG in colorectal cancer.44
Regulation of chromatin accessibility has recently been reported in these highly dynamic progenitors for fate decision and plasticity.8,12,13 It is believed that dynamic reorganization of chromatin remodeling controls the rapid, dynamic lineage specifications of early progenitors, as well as permitting dedifferentiation of progenitors into stem cells on damage. However, the underlying mechanism of how chromatin remodeling is regulated remains unknown. The discovery of the co-repressors Mtg8/16 in the +4/5 cells offers a compelling explanation for this epigenetic regulation by recruiting various chromatin-modifying enzymes to stem cell- and lineage-specific genes for dynamic fate decisions. Controlling the expression of MTG8 and MTG16, via Notch signaling upon damage could allow the early progenitors to reacquire multipotency by de-repressing the ISC gene expression program. It is interesting to note that MTGR1 is not regulated by Notch signaling despite the previously reported role in secretory lineage differentiation.25 Because our ChIP-seq data revealed that MTGR1 is a transcriptional target of MTG16, it is conceivable that the MTG family function together with ATOH1 to drive fate decision via transcription activator-repressor network and chromatin remodeling. Our findings provide a direct link between Notch signaling and chromatin remodeling for ISC fate decision. Further characterization of MTG8, MTG16 and MTGR1 targetomes will help understand their transcriptional regulation of ISC fate as homodimer or heterodimer.
Acknowledgments
We thank S.W. Hiebert and C.S. Williams for providing the Mtg8−/− and Mtg16−/− mice; L. Meran for establishing human intestinal organoid culture; H.F. Farin for providing VillinCreER;Atoh1fl/fl organoids; the Francis Crick Institute’s Experimental Histopathology, Advanced Sequencing, Bioinformatics, Flow Cytometry and Biological Research Facilities. This work was supported by the Francis Crick Institute, which receives its core funding from Cancer Research UK (FC001105), the UK Medical Research Council (FC001105), and the Wellcome Trust (FC001105). Work in the V.S.W.L laboratory was also supported by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (668294).
Raw and processed data for the ChIP-seq and RNA-seq experiments can be accessed from GEO with identifier GSE124186.
CRediT Authorship Contributions
Anna Baulies, PhD (Data curation: Lead; Formal analysis: Lead; Investigation: Lead; Methodology: Lead; Project administration: Lead; Resources: Lead; Software: Lead; Validation: Lead; Visualization: Lead; Writing – original draft: Lead; Writing – review & editing: Lead). Nikolaos Angelis, BSc (Data curation: Supporting; Formal analysis: Supporting; Investigation: Supporting; Methodology: Supporting; Validation: Supporting; Writing – original draft: Supporting; Writing – review & editing: Supporting). Valentina Foglizzo, PhD (Formal analysis: Supporting; Investigation: Supporting; Methodology: Supporting). E. Thomas Danielsen, PhD (Methodology: Supporting; Resources: Supporting). Harshil Patel, PhD (Data curation: Supporting; Formal analysis: Supporting; Software: Supporting). Laura Novellasdemunt, PhD (Investigation: Supporting; Methodology: Supporting). Anna Kucharska, BSc (Methodology: Supporting; Resources: Supporting). Joana Carvalho, PhD (Methodology: Supporting). Emma Nye, PhD (Methodology: Supporting; Resources: Supporting; Supervision: Supporting). Paolo De Coppi, MD, PhD (Resources: Supporting). Vivian S.W. Li, PhD (Conceptualization: Lead; Data curation: Lead; Formal analysis: Lead; Funding acquisition: Lead; Investigation: Lead; Methodology: Lead; Project administration: Lead; Resources: Lead; Supervision: Lead; Validation: Lead; Visualization: Lead; Writing – original draft: Lead; Writing – review & editing: Lead).
Footnotes
Conflict of interest The authors disclose no conflicts.
Funding This work was supported by the Francis Crick Institute, which receives its core funding from Cancer Research UK (FC001105), the UK Medical Research Council (FC001105), and the Wellcome Trust (FC001105). Work in the V.S.W.L laboratory was also supported by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (668294).
Author names in bold designate shared co-first authorship.
Note: To access the supplementary material accompanying this article, visit the online version of Gastroenterology at www.gastrojournal.org, and at https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.012.
Supplementary Methods
Expression Analysis of LGR5-GFP Sorted Cells
Transcriptomic data of LGR5-GFP sorted cells was extracted from GSE36497 (Agilent array 4x44K).1 LGR5-GFP high (5+) represents stem cell population, while LGR5-GFP-low (4+ to 2+) represents immediate daughter cells. Given the dynamic and heterogeneous nature of the +4/5 early progenitor cells, we decided to include LGR5-GFP 2+, 3+, and 4+ cell fractions together as GFP-low progenitors for hypothesis-free unsupervised clustering analysis. Of note, the GFP-negative population that consists of differentiated cells in the villi as well as non–GFP-expressing crypt cells was not included in the analysis. We further selected genes with >2-fold difference in at least 3 arrays and performed hierarchical clustering. This resulted in 525 genes that were enriched in GFP-low populations (Supplementary Figure 1B and Supplementary Table 1).
Crypts Isolation and Mouse Organoids Culture
Organoids were established from freshly isolated adult WT and Mtg16−/− small intestine, or P0 WT, Mtg16−/− and Mtg8−/−Mtg16−/− intestine. Tissues were incubated in cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 2 mM EDTA for isolating epithelial crypts and cultured in Cultrex BME, Type 2 RGF PathClear (Amsbio, Abington, UK; 3533-010-02) as previously described.2 All freshly isolated organoids were initially cultured in IntestiCult Organoid Growth Medium (Stem Cell technologies, Vancouver, BC, Canada; #06005). For P0 intestine, organoids were cultured for at least 4 weeks before any experiments to allow maturation. The Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (Sigma, Y0503) was added to the culture during first week of crypt isolation and single cell dissociation. For R-spondin (RSPO) depletion experiments, organoids were switched to basal media containing epidermal growth factor (EGF) (Invitrogen; PMG8043), Noggin, and RSPO (ENR) as previously described.2 For Notch inhibition, organoids were treated with 10 μM DAPT (Sigma; D5942) for the indicated times. Villin-CreERT2;Atoh1fl/fl organoids were kind gift from Dr. Henner Farin. For complete gene deletion, Villin-CreERT2;Atoh1fl/fl organoids were treated with 1 μM 4-hydrotamoxifen (4-OHT) for 24 hours, followed by 48 hours of 10 μM DAPT treatment for Notch inhibition. For the RSPO-low challenge experiments, organoids were plated in ENR containing 5% or 2% RSPO.
Organoid Colony Formation Assay
Organoids were dissociated using ACCUMAX (Merck, Kenilworth, NJ; SCR006) and counted. A total of 2000 single cells were seeded in BME (Cultrex, Minneapolis, MN) per well in a 48-well plate and placed in a 37°C incubator to polymerize for 30 minutes; 300 μL of small intestinal organoid growth media (see previously) plus Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (Sigma-Aldrich; Y0503) was added and cultured for the indicated times. Number of spheres formed in each well was counted as plating efficiency.
Human Organoids Culture
Samples have been harvested during surgeries at the Great Ormond Street Hospital, London, in accordance with ethical approval, REC Ref: 11/LO/1522. Written informed consent was obtained. Intestinal samples were obtained from patients with various intestinal diseases. Crypts were isolated from human intestinal tissue by incubating for 1 hour with chelation buffer (5.6 mM Na2HPO4, 8 mM KH2PO4, 96 mM NaCl, 1.6 mM KCl, 44 mM sucrose, 54.8 mM D-sorbitol, 0.5 M EDTA, and 1M DTT) at 4°C, and plated in drops of BME. After polymerization, culture media was added. Human intestinal organoid media contains advanced Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM)/F12 medium (Invitrogen; 12634010) including B27 (Invitrogen; 17504044), nicotinamide (Sigma-Aldrich; N3376), N-acetylcysteine (Sigma-Aldrich; A7250), EGF (Invitrogen; PMG8043), transforming growth factor-β type I receptor inhibitor A83-01 (Tocris, Bristol, UK; 2939), P38 inhibitor SB202190 (Sigma-Aldrich; S7067), gastrin I (Sigma-Aldrich; G9145), Wnt3a conditioned media (50% produced using stably transfected L cells), Noggin, and RSPO conditioned media.
Disaccharidase Activity Assay
Organoids were washed twice with PBS and incubated with a 56 mM solution of sucrose for 1 hour. Supernatants were collected and frozen until the assay was performed. To detect glucose content, Amplex Red Glucose/Glucose Oxidase Assay Kit (Invitrogen; A22189) was used. Samples were diluted when necessary and incubated with the reaction buffer containing Amplex Red, horseradish peroxidase, and glucose oxidase. Fluorescence was measured in a microplate reader with an excitation wavelength of 540 nm and fluorescence emission detection at 590 nm. Glucose concentration was assessed using a glucose standard curve from 0 to 200 μM.
FACS Sorting
Crypts were harvested from the proximal jejunum (∼10 cm) by 30-minute incubation in ice-cold 5 mM EDTA/PBS and filtered through a 70-μm strainer. Crypts were dissociated by incubating with Collagenase/Dispase (Roche, Basel, Switzerland; 11097113001) for 20 minutes at 37oC, followed by 20-minute incubation with TrypLE (Gibco, Waltham, MA; 12604013) for 20 minutes at 37oC. TrypLE was stopped by adding Advanced DMEM (Gibco; 12491015) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco; 10270106) and dissociated cells were passed through a 20-μm strainer. Cells were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) and resuspended in PBS-0.5% BSA-2 mM EDTA. Cells were separated and re-collected in Advanced DMEM plus 10% FBS based on GFP intensity. Cell sorting was performed on a BD FACSAria II System.
Cell Culture
HEK293T and LS174T cells were maintained in DMEM GlutaMAX (Gibco; 10566-01) supplemented with 5% FBS (Gibco; 10270106) and 100 units/mL penicillin (Gibco; 15140122) and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Gibco). Cells were incubated in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 at 37°C. For transient overexpression, plasmids were transfected with polyethylenimine (PEI; Polysciences, Warrington, PA; 23966) according to manufacturer’s instructions. For immunoprecipitation (IP) experiments, cells were seeded 24 hours before transfection in a 10-cm plate, using 2 plates per condition and 8 μg of indicated plasmids. For qRT-PCR experiments, cells were seeded 24 hours before transfection in 6-well plates using 1 μg of indicated plasmids.
Quantitative RT-PCR
RNA was extracted according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen RNAeasy). Complementary DNA (cDNA) was prepared using High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA; #4368813). Quantitative PCR detection was performed using PowerUp SYBR Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems; A25742). Assays for each sample were run in triplicate and were normalized to housekeeping genes Ppib or β-actin, where data was expressed as mean ± SEM. Primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Table 6.
Immunoprecipitation and Immunoblotting
HEK293T cells were treated with doxycycline (Sigma-Aldrich; D9891) 1 μg/mL to induce Flag-MTGs expression for 7 hours before lysate collection. Cells were washed and collected with cold PBS and lysed in cold lysis buffer containing 150 mM NaCl, 30 mM Tris (pH7.5), 1 mM EDTA, 1% Triton X-100, 10% Glycerol, 0.5 mM DTT, protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (Thermo Scientific; 78446). After clarification by centrifugation (18800 g for 30 minutes at 4°C), the cellular lysates were precleared with IgG-agarose beads (Millipore, Bedford, MA; 16-266 for 1 hour at 4°C). Immunoprecipitation of Flag complexes was performed by incubating the cellular lysates with anti-Flag-M2 affinity beads (Sigma; A2220) at 4°C overnight. Immunocomplexes were washed with cold lysis buffer 5 times, resuspended in lysis buffer containing sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sample buffer, and subjected to SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and western blot analysis.
Immunohistochemistry
For analysis of small intestine by immunohistochemistry, tissues were fixed in 10% formalin and embedded in paraffin. Sections were deparaffinized with xylene and rehydrated in a graded series of ethanol. Antigen-retrieval was performed for 20 minutes at high temperature in citrate or tris-EDTA buffer. Slides were then blocked and incubated overnight with anti-Chromogranin A antibody (ab15160, Abcam, Cambridge, UK), anti-lysozyme (A0099; Dako, Glostrup, Denmark), anti-DCAMKL1 (ab37994; Abcam, Cambridge, UK), anti-VILLIN (sc-58897; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX), anti-MUC2 (sc-15334; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), anti-FABP1 (328607, Thermo Fisher), anti-APOA4 (AF8125, R&D, Minneapolis, MN), anti-RBPJ (RBPSUH [D10A4], Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA; 5313T), anti-GFP (ab6673, Abcam) or negative control at 4°C. Finally, slides were incubated with the secondary antibody for 1 hour, washed 3 times with PBS, incubated with peroxidase substrate, and mounted. For immunofluorescence, slides were incubated with Alexa 488 and Cy5 secondary antibody for 1 hour, washed 3 times with PBS, incubated with DAPI for 15 minutes to visualize nuclear DNA, and mounted with ProLong Gold Antifade Mountant (ThermoFisher; P36934). When indicated, sections were stained for hematoxylin-eosin, alkaline phosphatase and Alcian Blue–Periodic Acid–Schiff staining. EdU was detected according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Click-iT Plus EdU Alexa Fluor 555 imaging kit C 10638, Thermo Fisher Scientific) to evaluate proliferating cell number. Edu+ cells were quantified in at least 10 crypts per mouse (n = 3 mice per group per condition).
RNAscope
Single-molecule in situ hybridization was performed on mouse intestine as recommended by the manufacturer (ACD; https://acdbio.com, user manual doc. 322310-QKG or 322500 for duplex detection). The probes used were against MTG8/Runx1t1 (REF 434601), MTG16/ Cbfa2t3 (REF 474921), Mtgr1/Cbfa2t2 (REF 491601), Atoh1 (REF 408791_C2), Lgr5 (312171), Olfm4 (REF 311831). Briefly, guts were fixed in formalin O/N, paraffin-embedded and cut into 4-μm-thick slices. Target retrieval was performed for 15 minutes, followed by RNAScope Protease Plus incubation for 24 minutes on the formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded Sample Preparation. The counterstaining and mounting of the slides was performed on a Tissue-Tek Prisma staining machine. RNAscope staining quantifications were performed using ZEN blue software in images acquired at ×40 with a Zeiss Axio Scan.Z1 Slide Scanner. RNAscope score of 1 was assigned to the cells with 1 to 3 dots of staining. Score 2 was for cells with bigger number of dots and/or cluster of dots bigger than 3 μm2.
For combined RNAscope and immunofluorescence of Mtg16 and Muc2, samples were first stained for Mtg16 using the red channel of duplex RNAscope kit, followed by anti-Muc2 immunostaining as described previously.
ChIP-seq
Isolated mouse crypts were dual cross-linked first in 2 mM Di(N-succinimidyl) glutarate (DSG; Sigma-Aldrich; 80424) for 45 minutes at room temperature followed by incubation in 1% formaldehyde for 10 minutes as previous described.3 The fixation was terminated by quenching with glycine (Sigma-Aldrich; 50046) for 5 minutes at room temperature. The samples were washed twice in PBS and resuspended in commercial lysis buffer containing protease inhibitors from the MAGnify Chromatin Immunoprecipitation System kit (Thermo Scientific; 492024). The chromatin was sheared using the Covaris S2 sonicator (Covaris, Woburn, MA) at 4°C for 10 minutes with the following settings; duty cycle 5%, intensity: 2, cycles per burst: 200, cycle time: 60 seconds. The sonicated chromatin was incubated for one hour at 4°C with Dynabeads protein A/G beads from the kit coupled to 10 μL of anti-MTG16 antibody (Abcam; ab33072) per IP; 10% of the chromatin was used for the Inputs control. The beads were washed with buffers supplied with the kit and samples were de-crosslinked in buffer containing Proteinase K at 55°C for 15 minutes according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The DNA was purified using the DNA Purification Magnetic Beads supplied with the kit and the eluted DNA was verified using the Agilent Bioanalyzer. The DNA library for sequencing was prepared using 20 ng of ChIP’ed DNA for the Kapa Hyper Prep kit with 16 cycles of PCR amplification. The quality of the final DNA library was confirmed on the Agilent Tapestation before the samples were submitted to sequencing on the HiSeq 4000 (Illumina, San Diego, CA).
ChIP-seq Analysis
ChIP sequencing typically generated ∼27 million 101 base pair paired-end reads per sample. Adapter trimming was performed with cutadapt (version 1.9.1)4 and the resulting reads were mapped to the mouse mm10 genome using BWA (version 0.6.2).5 Reads that were properly paired, uniquely mapped, and had an insert size ≤2 kb were kept for further analysis.
Genome-wide peak calling was performed with MACS2 callpeak (version 2.1.1.20160309).6 Peaks common to both Mtg16 replicates were carried forward for further analysis. Motif discovery was carried out with the HOMER findMotifsGenome.pl program (version 4.8)7 using its in-built mm10 annotation with a peak size of ±50 base pairs around the peak summit. The ChIP-Enrich package (version 1.10.0)8 was used for gene set enrichment analysis relative to Gene Ontology (GO) biological process. Heatmaps and metaprofiles were generated with deepTools (version 2.5.3).9 A scatterplot was generated to show the correlation between the union set of peaks from both Mtg16 ChIP-seq replicates. Read counting was performed with featureCounts,10 and normalization was performed with the normalize.quantiles function in R.
Atoh1 and DNase I hypersensitive data were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus database (GSE51464),11 and reanalyzed in line with the methods described previously.
RNA-seq and Bioinformatics Analysis
RNA was extracted from isolated mouse crypts of full-length small intestine of 3 WT and 3 Mtg16 −/− mice according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen RNAeasy). RNA integrity was examined using Bioanalyzer 2100 RNA 6000 Nano kit from Agilent. Libraries were generated according to manufacturer’s instructions (KAPA RNA HyperPrep with RiboErase (HMR) - KK8561) and 200 ng RNA input.
RNA sequencing was carried out on the Illumina HiSeq 2500 platform and typically generated ∼20 million 76 base pair strand-specific single-end reads per sample. Adapter trimming was performed with cutadapt (version 1.9.1)4 with parameters “--minimum-length=25 --quality-cutoff=20 -a AGATCGGAAGAGC”. The RSEM package (version 1.3.0)12 in conjunction with the STAR alignment algorithm (version 2.5.2a)13 was used for the mapping and subsequent gene-level counting of the sequenced reads with respect to mm10 RefSeq genes downloaded from the UCSC Table Browser14 on December 11, 2017. The parameters used were “--star-output-genome-bam --forward-prob 0”. Differential expression analysis was performed with the DESeq2 package (version 1.12.3)15 within the R programming environment (version 3.3.1). An adjusted P value (FDR, false discovery rate) of ≤0.1 was used as the significance threshold for the identification of differentially expressed genes.
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) (version 2.2.3)16 pre-ranked analysis was performed using the Wald statistic with respect to MSigDB (version 6.1) C2 canonical pathways, C5 GO biological process, and custom signatures obtained from the literature. All parameters were kept as default except for enrichment statistic (classic), min size (5), and max size (50,000).
Author names in bold designate shared co-first authorship.
References
- 1.Bjerknes M., Cheng H. The stem-cell zone of the small intestinal epithelium. V. Evidence for controls over orientation of boundaries between the stem-cell zone, proliferative zone, and the maturation zone. Am J Anat. 1981;160:105–112. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001600109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tetteh P.W., Farin H.F., Clevers H. Plasticity within stem cell hierarchies in mammalian epithelia. Trends Cell Biol. 2015;25:100–108. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yang Q., Bermingham N.A., Finegold M.J. Requirement of Math1 for secretory cell lineage commitment in the mouse intestine. Science. 2001;294:2155–2158. doi: 10.1126/science.1065718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.van Es J.H., van Gijn M.E., Riccio O. Notch/gamma-secretase inhibition turns proliferative cells in intestinal crypts and adenomas into goblet cells. Nature. 2005;435:959–963. doi: 10.1038/nature03659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.VanDussen K.L., Samuelson L.C. Mouse atonal homolog 1 directs intestinal progenitors to secretory cell rather than absorptive cell fate. Dev Biol. 2010;346:215–223. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.07.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Noah T.K., Donahue B., Shroyer N.F. Intestinal development and differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 2011;317:2702–2710. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Stamataki D., Holder M., Hodgetts C. Delta1 expression, cell cycle exit, and commitment to a specific secretory fate coincide within a few hours in the mouse intestinal stem cell system. PLoS One. 2011;6 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kim T.H., Li F., Ferreiro-Neira I. Broadly permissive intestinal chromatin underlies lateral inhibition and cell plasticity. Nature. 2014;506:511–515. doi: 10.1038/nature12903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Philpott A., Winton D.J. Lineage selection and plasticity in the intestinal crypt. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2014;31:39–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2014.07.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Rand M.D., Lake R.J. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999;284:770–776. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5415.770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.van Es J.H., Sato T., van de Wetering M. Dll1+ secretory progenitor cells revert to stem cells upon crypt damage. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14:1099–1104. doi: 10.1038/ncb2581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jadhav U., Nalapareddy K., Saxena M. Acquired tissue-specific promoter bivalency is a basis for PRC2 necessity in adult cells. Cell. 2016;165:1389–1400. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jadhav U., Saxena M., O’Neill N.K. Dynamic reorganization of chromatin accessibility signatures during dedifferentiation of secretory precursors into Lgr5+ intestinal stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;21:65–77.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rossetti S., Hoogeveen A.T., Sacchi N. The MTG proteins: chromatin repression players with a passion for networking. Genomics. 2004;84:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2004.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Barker N., van Es J.H., Kuipers J. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 2007;449:1003–1007. doi: 10.1038/nature06196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Han H., Tanigaki K., Yamamoto N. Inducible gene knockout of transcription factor recombination signal binding protein-J reveals its essential role in T versus B lineage decision. Int Immunol. 2002;14:637–645. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxf030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.el Marjou F., Janssen K.P., Chang B.H. Tissue-specific and inducible Cre-mediated recombination in the gut epithelium. Genesis. 2004;39:186–193. doi: 10.1002/gene.20042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Munoz J., Stange D.E., Schepers A.G. The Lgr5 intestinal stem cell signature: robust expression of proposed quiescent ‘+4’ cell markers. EMBO J. 2012;31:3079–3091. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shimizu H., Okamoto R., Ito G. Distinct expression patterns of Notch ligands, Dll1 and Dll4, in normal and inflamed mice intestine. PeerJ. 2014;2:e370. doi: 10.7717/peerj.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Davis J.N., McGhee L., Meyers S. The ETO (MTG8) gene family. Gene. 2003;303:1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(02)01172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chyla B.J., Moreno-Miralles I., Steapleton M.A. Deletion of Mtg16, a target of t(16;21), alters hematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation and lineage allocation. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:6234–6247. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00404-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Fre S., Hannezo E., Sale S. Notch lineages and activity in intestinal stem cells determined by a new set of knock-in mice. PLoS One. 2011;6 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Calabi F., Pannell R., Pavloska G. Gene targeting reveals a crucial role for MTG8 in the gut. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:5658–5666. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.16.5658-5666.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yu S., Tong K., Zhao Y. Paneth cell multipotency induced by Notch activation following injury. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;23:46–59.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Amann J.M., Chyla B.J., Ellis T.C. Mtgr1 is a transcriptional corepressor that is required for maintenance of the secretory cell lineage in the small intestine. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:9576–9585. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.21.9576-9585.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Poindexter S.V., Reddy V.K., Mittal M.K. Transcriptional corepressor MTG16 regulates small intestinal crypt proliferation and crypt regeneration after radiation-induced injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015;308:G562–G571. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00253.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sansom O.J., Reed K.R., Hayes A.J. Loss of Apc in vivo immediately perturbs Wnt signaling, differentiation, and migration. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1385–1390. doi: 10.1101/gad.287404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Haber A.L., Biton M., Rogel N. A single-cell survey of the small intestinal epithelium. Nature. 2017;551:333–339. doi: 10.1038/nature24489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lo Y.H., Chung E., Li Z. Transcriptional regulation by ATOH1 and its target SPDEF in the intestine. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;3:51–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2016.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Qi Z., Li Y., Zhao B. BMP restricts stemness of intestinal Lgr5(+) stem cells by directly suppressing their signature genes. Nat Commun. 2017;8:13824. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schuijers J., Junker J.P., Mokry M. Ascl2 acts as an R-spondin/Wnt-responsive switch to control stemness in intestinal crypts. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16:158–170. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Moore A.C., Amann J.M., Williams C.S. Myeloid translocation gene family members associate with T-cell factors (TCFs) and influence TCF-dependent transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:977–987. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01242-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bjerknes M., Cheng H. The stem-cell zone of the small intestinal epithelium. I. Evidence from Paneth cells in the adult mouse. Am J Anat. 1981;160:51–63. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001600105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sato T., van Es J.H., Snippert H.J. Paneth cells constitute the niche for Lgr5 stem cells in intestinal crypts. Nature. 2011;469:415–418. doi: 10.1038/nature09637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fukuda M., Mizutani T., Mochizuki W. Small intestinal stem cell identity is maintained with functional Paneth cells in heterotopically grafted epithelium onto the colon. Genes Dev. 2014;28:1752–1757. doi: 10.1101/gad.245233.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kim T.H., Escudero S., Shivdasani R.A. Intact function of Lgr5 receptor-expressing intestinal stem cells in the absence of Paneth cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:3932–3937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1113890109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Durand A., Donahue B., Peignon G. Functional intestinal stem cells after Paneth cell ablation induced by the loss of transcription factor Math1 (Atoh1) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:8965–8970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201652109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kim T.H., Saadatpour A., Guo G. Single-cell transcript profiles reveal multilineage priming in early progenitors derived from Lgr5(+) intestinal stem cells. Cell Rep. 2016;16:2053–2060. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.07.056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.de Lichtenberg KH, Seymour PA, Jørgensen MC, et al. Notch controls multiple pancreatic cell fate regulators through direct Hes1-mediated repression. 2018. Available at: 10.1101/336305. Accessed September 4, 2020. [DOI]
- 40.Doyen CM, Depierre D, Yatim A, et al. NOTCH assembles a transcriptional repressive complex containing NuRD and PRC1 to repress genes involved in cell proliferation and differentiation. 2019. Available at: 10.1101/513549. Accessed September 4, 2020. [DOI]
- 41.Ladi E., Nichols J.T., Ge W. The divergent DSL ligand Dll3 does not activate Notch signaling but cell autonomously attenuates signaling induced by other DSL ligands. J Cell Biol. 2005;170:983–992. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200503113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Williams C.S., Bradley A.M., Chaturvedi R. MTG16 contributes to colonic epithelial integrity in experimental colitis. Gut. 2013;62:1446–1455. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.McDonough E.M., Barrett C.W., Parang B. MTG16 is a tumor suppressor in colitis-associated carcinoma. JCI Insight. 2017;2 doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.78210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Parang B., Bradley A.M., Mittal M.K. Myeloid translocation genes differentially regulate colorectal cancer programs. Oncogene. 2016;35:6341–6349. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Supplementary References
- 1.Munoz J., Stange D.E., Schepers A.G. The Lgr5 intestinal stem cell signature: robust expression of proposed quiescent ‘+4’ cell markers. EMBO J. 2012;31:3079–3091. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Novellasdemunt L., Foglizzo V., Cuadrado L. USP7 Is a Tumor-Specific WNT Activator for APC-Mutated Colorectal Cancer by Mediating beta-Catenin Deubiquitination. Cell Rep. 2017;21:612–627. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.09.072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tian B., Yang J., Brasier A.R. Two-step cross-linking for analysis of protein-chromatin interactions. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;809:105–120. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-376-9_7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Martin M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. 2011 2011;17:3.
- 5.Li H., Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1754–1760. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhang Y., Liu T., Meyer C.A. Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS) Genome Biol. 2008;9:R137. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-9-r137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Heinz S., Benner C., Spann N. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol Cell. 2010;38:576–589. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Welch R.P., Lee C., Imbriano P.M. ChIP-Enrich: gene set enrichment testing for ChIP-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:e105. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ramirez F., Ryan D.P., Gruning B. deepTools2: a next generation web server for deep-sequencing data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:W160–W165. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liao Y., Smyth G.K., Shi W. featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:923–930. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kim T.H., Li F., Ferreiro-Neira I. Broadly permissive intestinal chromatin underlies lateral inhibition and cell plasticity. Nature. 2014;506:511–515. doi: 10.1038/nature12903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Li B., Dewey C.N. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:323. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dobin A., Davis C.A., Schlesinger F. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 2013;29:15–21. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Karolchik D., Hinrichs A.S., Furey T.S. The UCSC Table Browser data retrieval tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:D493–D496. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Love M.I., Huber W., Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15:550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Subramanian A., Tamayo P., Mootha V.K. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:15545–15550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.