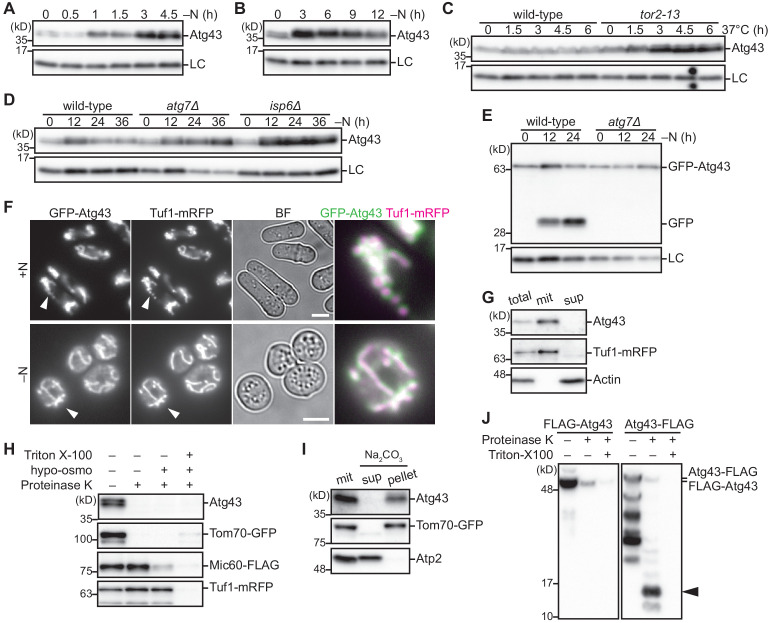
Figure 2. Atg43 is a transmembrane protein localized to the MOM.
(A, B) Wild-type cells were grown in EMM and shifted to EMM–N for nitrogen starvation. Cells were collected at the indicated time points after shifting to nitrogen starvation medium and were then subjected to immunoblotting. (C) The indicated strains were grown in EMM at 26°C. The temperature was then shifted to 37°C to inactivate TORC1. Cells were collected at the indicated time points after the temperature shift and were used for immunoblotting. (D, E) The indicated strains were collected at the indicated time points after shifting to nitrogen starvation medium and were used for immunoblotting. (F) Cells expressing GFP-Atg43 and Tuf1-mRFP were grown in EMM (+N) or cultured in EMM–N for 12 hr (–N) for microscopy. A magnified view of the indicated area is shown in the right panel. Scale bars represent 5 µm. BF, bright-field image. (G) Fractionation was conducted using cells expressing Tuf1-mRFP. The total cell homogenate (total) was fractionated by centrifugation to obtain a mitochondria-enriched pellet (mit) and supernatant (sup). Tuf1-mRFP and actin were detected as markers of the mitochondria and cytosol, respectively. (H) A mitochondrial fraction was prepared from cells expressing Tom70-GFP, Mic60-FLAG, and Tuf1-mRFP, treated with (+) or without (–) proteinase K, under different conditions. Hypo-osmotic swelling resulted in rupture of the MOM and the detergent Triton X-100 lysed mitochondria. Tom70-GFP, Mic60-FLAG, and Tuf1-mRFP were detected as markers of the mitochondrial outer membrane, inner membrane, and matrix, respectively. (I) The mitochondrial fraction (mit) was prepared from cells expressing Tom70-GFP, treated with sodium carbonate, and separated into the soluble supernatant (sup) and membrane pellet (pellet) by centrifugation. Tom70-GFP and Atp2 were detected as markers for integral and peripheral membrane proteins, respectively. (J) The mitochondrial fraction was prepared from cells expressing N-terminal or C-terminal FLAG-tagged Atg43 (FLAG-Atg43 or Atg43-FLAG, respectively), followed by treatment with (+) or without (–) proteinase K. The Triton X-100 detergent lysed mitochondria. The proteinase-resistant band is indicated by the arrowhead. Histone H3 was used as a loading control (LC) for immunoblotting.