Abstract
HACE1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase with important roles in tumor biology and tissue homeostasis. Loss or mutation of HACE1 has been associated with the occurrence of a variety of neoplasms, but the underlying mechanisms have not been defined yet. Here we report that HACE1 is frequently mutated in human lung cancer. In mice, loss of Hace1 led to enhanced progression of KRasG12D-driven lung tumors. Additional ablation of the oncogenic GTPase Rac1 partially reduced progression of Hace1-/- lung tumors. RAC2, a novel ubiquitylation target of HACE1, could compensate for the absence of its homolog RAC1 in Hace1-deficient, but not in HACE1-sufficient tumors. Accordingly, ablation of both Rac1 and Rac2 fully averted the increased progression of KRasG12D-driven lung tumors in Hace1-/- mice. In lung cancer patients, increased expression of HACE1 correlated with reduced levels of RAC1 and RAC2 and prolonged survival, while elevated expression of RAC1 and RAC2 was associated with poor prognosis. This work defines HACE1 as a crucial regulator of the oncogenic activity of RAC-family GTPases in lung cancer development.
Introduction
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in developed countries (1). The prognosis of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) patients remains poor despite therapeutic advances due to late diagnosis, limited efficacy of available treatments and development of drug resistance (2–4). Lung cancer initiation and progression are the result of genetic alterations and deregulation of several critical signaling pathways that prevent DNA damage and control critical cellular processes, such as proliferation, DNA repair and apoptosis (2,5). Unraveling the complex molecular mechanisms of lung cancer development is therefore crucial to enable the identification of novel therapeutic targets.
HACE1 (HECT-domain and ankyrin-repeat containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1) was identified in the context of Wilms’ tumor (6). We previously showed that genetic inactivation of Hace1 renders mice more susceptible to spontaneous and induced tumors, highlighting the function of HACE1 as a tumor suppressor (7). Since then, several independent studies have shown that HACE1 is mutated or functionally inactivated in different types of human cancer, including osteosarcoma (8), B-cell lymphoma (9), colon carcinoma (10), gastric carcinoma (11) and breast carcinoma (12). In addition, low HACE1 expression has been linked to a poor overall survival of patients with osteosarcoma (8), hepatocellular carcinoma (13) and neuroblastoma (14). We recently reported that Hace1-deficient mice show increased susceptibility to inflammation-driven colon cancer due to deregulated tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1) signaling and exaggerated induction of RIPK3-dependent necroptosis (15). However, dependent on the type of tumor and based on in vitro experiments, other mechanisms have been suggested to mediate tumorigenesis in the absence of HACE1, including impaired autophagic uptake of oxidatively damaged proteins (16) or deregulation of RAC1 activity (17–19).
RAC1 is a small GTPase that regulates cell proliferation, motility, stress responses, or production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (20). RAC1 belongs to a RAS superfamily of small GTP-binding proteins that also includes RAC2 and RAC3. These three proteins are 90% identical in their amino acid sequence but have different tissue-specific expression profiles. While RAC1 is widely expressed, RAC2 expression is mainly confined to hematopoietic cells; RAC3, though more broadly expressed than RAC2, is most abundant in the brain (21,22). Active GTP-bound RAC1 (GTP-RAC1) initiates cellular ROS production by plasma membrane and endosomal nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase complexes (17). Similarly to RAC1, RAC2 has also been implicated in NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS production (23). Although the ability of RAC3 to activate the NADPH oxidase complex was proposed, a role for RAC3 in ROS production has not yet been formally established (24).
Deletion of Rac1 was shown to impede tumorigenesis in animal models of skin cancer (25,26), pancreatic cancer (27) and KRasG12D-driven lung cancer (28). Conversely, hyperactivation of RAC1 and RAC2 can promote tumorigenesis in various cancer types (29,30), such as breast cancer (12) and melanoma (31,32). Importantly, HACE1 was shown to preferentially ubiquitylate and drive proteasomal degradation of GTP-RAC1 when it is bound to the NADPH oxidase complex (17–19,33). As a consequence, Hace1-deficient cells show deregulated activation of RAC1 and increased levels of genotoxic cellular ROS, leading to genomic instability, DNA damage and cyclin D1-mediated hyperproliferation (17). Additionally, HACE1 can mediate the activation of NRF2 (34), reinforcing the function of HACE1 in the control of cellular oxidative stress.
We previously reported an increased susceptibility of Hace1–/– mice to urethane-driven lung tumor (7). However, the molecular mechanisms by which HACE1 controls lung cancer formation remained unknown. Here, we investigated the role of HACE1 in KRasG12D-driven lung tumors and uncovered a key role of deregulated activation of RAC1 and, surprisingly, also RAC2 in the pathogenesis of lung tumors in the absence of HACE1. We also report that in lung cancer patients, increased expression of HACE1 is associated with prolonged survival, while elevated expression of RAC1 and RAC2 correlate with a poor prognosis, highlighting HACE1 and RAC-family GTPases as key drivers and potential targets for the treatment of lung cancer.
Materials and Methods
Mice
Hace1−/− mice were generated in our laboratory as described previously (7) and crossed to LSL-KRasG12D mice (35) to generate KRasG12D;Hace1−/− and control KRasG12D;Hace1+/+ animals. To analyze the role of RAC1 and RAC2 in KRasG12D-driven lung cancer in the absence of HACE1, Rac1fl/flRac2−/− mice on a C57BL/6J background (generated by David A Williams, Boston Children’s Hospital) were crossed to KRasG12D;Hace1−/− mice, generating KRasG12D;Hace1+/–Rac1fl/+Rac2+/– mice. These triple-heterozygous mice were then interbred to yield KRasG12D;Hace1−/−, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl, KRasG12D;Hace1−/−Rac1fl/fl, KRasG12D;Rac2−/−, KRasG12D;Hace1−/−Rac2−/−, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/flRac2−/− and KRasG12D;Hace1−/−Rac1fl/flRac2−/− as well as control KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+Rac2+/+ mice. The generation of Ripk3–/– animals has been previously described (36). Ripk3–/– and KRasG12D;Hace1−/− mice were bred to generate KRasG12D;Hace1−/−Ripk3–/– mice. Animals were genotyped by PCR analysis of genomic DNA. If not stated otherwise, 8–12-week-old, sex- and age-matched mice were used for experiments. All animal experiments were carried out complying with the current Austrian and European legislation and have been approved by the Austrian Federal Ministry of Science, Research and Economy (GZ) BMWFW-66.015/0008-WF/II/3b/2014 and (GZ) BMBWF-66.015/0030-V/3b/2019.
Induction of lung cancer in LSL-KRasG12D mice
Inhalation of 8–12-week-old mice with Cre-expressing adeno-virus was performed as previously reported (35,37,38). Briefly, mice were anesthetized with Ketasol/Xylasol and placed on a heated pad. An Adeno-Cre-CaCl2 precipitate was produced by mixing 60 μl MEM, 2.5 μl Adeno-Cre (1010 pfu/ml; University of Iowa, Gene Transfer Vector Core Iowa, USA) and 0.6 μl CaCl2 (1 M) for each mouse and incubated for 20 min at room temperature (21–22 °C). Adeno-Cre was delivered by intratracheal administration to induce KRasG12D expression and Rac1 deletion in pneumocytes in vivo. In vivo treatment with N-acetylcystein (NAC) was performed starting at day 9 post lung tumor induction by supplementing NAC (Sigma, A9165) in drinking water (1 g/L).
Histology and immunohistochemistry
For histopathology analysis of lung tumors, lungs were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) overnight at 4°C and embedded in paraffin after dehydration in ascending concentrations of ethanol. For each lung, sections were prepared at a thickness of 2 μm at three different levels and stained using haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) with an automated stainer (HMS 740, Microm). Sections were imaged and digitized by the 3D Histech Pannoramic Flash II whole slide scanner. Tumor burden was automatically evaluated by an algorithm programmed and executed using the Definiens Developer software suite. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed using an automatic staining system (Leica Bond III). After dehydration and heat-induced antigen retrieval using a 10 mM citrate solution (pH 6.0), sections were incubated with rabbit monoclonal anti-γH2AX (Cell Signaling, 9718, 1:200 dilution) or rabbit monoclonal anti-Ki67 (Abcam, ab16667, 1:200 dilution). γH2AX- and Ki67-positive tumor cells were manually counted by a pathologist using a Zeiss Axioskop 2 MOT microscope. Positive tumor cell nuclei were counted in 10 representative 40x objective fields per tumor section. Representative H&E and IHC images were acquired by the Pannoramic Viewer software and a SPOT Insight color camera (SPOT Imaging, Diagnostic Instruments, Inc.). Data were validated by a certified pathologist.
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis
mRNA was enriched using the NEBNext Ultra RNA Library Prep Kit and sequenced using single‐end sequencing with 50‐bp reads on an Illumnia HiSeq2500. RNA-seq reads were trimmed using trim_galore v0.3.7 and reads mapping to known mitochondrial and ribosomal sequences were removed using bowtie2 v2.1.0. Thereafter, reads were aligned to the Mus musculus genome mm10 (iGenomes) using star v2.5.0a and reads in genes were counted with featureCounts from subread v1.4.6. Gene expression measurements in fragments per kilobase per million reads (FPKM) and transcripts per million (TPM) were calculated using RSEM v1.2.25. The RNA-seq dataset produced in this study is available at NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, accession number GSE149137 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE149137).
Cell culture and reagents
All cell lines were cultured in DMEM (Dulbecco) supplemented with 10% FCS, non-essential amino acids and penicillin–streptomycin. Wild-type (+/+) and Hace1 knockout (−/−) MEFs were derived from Hace1+/+ and Hace1−/− littermates bred on a C57BL/6J background and allowed to spontaneously immortalize (17). HEK293 cells were purchased from ATCC (CRL-1573) and authenticated by the provider. UACC melanoma cell lines were obtained from TGen and were started using fresh patient material at the University of Arizona and originally banked at The University of Arizona Cancer Center. The HACE1 mutations in the UACC lines were initially discovered using exome sequencing and authenticated with Sanger sequencing. UACC lines used for experiments were of low passage number. All cell lines were tested negative for Mycoplasma before experiments. MSCV-HA and MSCV-HA-Hace1 vectors were cloned as described in (7). Transfections of siRNAs were performed with 25 nM siRNA using Lipofectamine RNAiMax (Invitrogen). The following siRNAs were used in the study: Control siRNA (C): (5′–3′) AUAUCGGCUAGGUCUAACA; HACE1-1 (H1): Hs_HACE1_1 (FlexiTube, Qiagen); HACE1-2 (H2): Hs_HACE1_4 (FlexiTube, Qiagen). Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and 2-acetylphenothiazine (ML171) were purchased from Sigma. Piperlongumine (PL) was purchased from RD Chemicals.
Detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS)
Dihydroethidium (DHE; Sigma) was used to measure superoxide levels, as previously described (17). In brief, 20 μm-thick sections of frozen tumors were incubated with 10 μM DHE dissolved in methanol in the dark for 30 min at room temperature (RT). Then, sections were adhered onto covered slips and mounted with fluorescent mounting medium (Vectorshield mounting medium for fluorescence with DAPI, Cedarlane) and immediately imaged using an epifluorescent microscope (Axio Observer Z1; Carl Zeiss; Excitation 540nm and emission 605nm) using a 20X objective lens. All images were captured using identical exposure times and signal intensities were analyzed using ImageJ software.
Isolation and culture of lung tumor cells
Primary lung tumor cells from Adeno-Cre treated LSL-KRasG12D-carrying mice were purified as described (38,39). In brief, lungs were dissected from 8–12-week-old mice, infused with IMDM containing 5000 U/mL dispase (BD) and 200 U/mL DNase (Worthington), followed by an incubation for 1 h at 37°C. After the isolation, cells were maintained in Ham’s F-12 media supplemented with 15 mM HEPES, 0.8 mM CaCl2, 0.25% BSA, ITS (Sigma) and 2% FCS, at 37°C and 5% CO2 conditions.
RAC1 activation assay
The GST-tagged p21-binding domain (PBD) of PAK1 (GST–PBD) was used to specifically precipitate active GTP-RAC1 from lysates of primary lung tumor cells (40), according to the company’s protocol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 16118).
In vitro ubiquitylation assay
His-tagged recombinant human RAC1 (Cytoskeleton, RC01) and RAC2 (Cytoskeleton, RC02) were preloaded with GTP or GDP as described (41). Briefly, 300 ng of RAC1 and RAC2 were loaded with GTP (5mM) or GDP (5mM) by incubation 30 min at 30°C in a buffer containing 20mM TRIS-HCl, 0.1mM DTT, 2.5mM NaCl, 4 mM EDTA (pH7.5). Subsequently, GTP- and GDP-loaded RAC1 or RAC2 (300ng) were incubated for 3 h at 37°C with recombinant human HACE1 (wildtype or catalytic dead C876S mutant, 2μg), Ube1 (E1, 250ng), Ubch7 (E2, 500ng), ubiquitin (Sigma-Aldrich U6253, 10 μg) and ATP (Roche, 1051997900, 2mM) in a reaction buffer consisting of 50mM HEPES, 150nM NaCl, 20mM MgCl2 (pH7.5), at 37 °C for 3 h. Reactions were terminated by adding 2xSDS sample buffer and incubating at 96 °C for 1 min. Samples were then subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies.
Protein purification
Purification of E1 and E2 was performed as described in (42).The codon-optimized sequence of human wildtype HACE1 or the catalytic dead C876S HACE1 mutant was cloned into pETM33_ccdB (Genewiz). The expression constructs were transformed into E. coli Bl21(DE3) and cultivated overnight at 37°C in LB medium with kanamycin. 3 L of LB were inoculated overnight (15 ml/L) and grown at 37°C until an OD600 of 0.5 was reached. Cultures were shifted to a shaker with pre‐set temperature of 20°C. After 15 min (OD600 = 1) expression was induced with 1mM IPTG. After 6 h, culture was harvested and stored at –80°C overnight. The pellet from the 3 L of expression culture was thawed and resuspended in 75 ml buffer A (50 mM Tris pH 7, 500 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM TCEP, 4°C). Cells were lysed via sonication. Cleared lysate was loaded onto a 5 ml GSTrap column equilibrated with buffer A. After a wash with 30 column volumes of buffer A, bound protein was eluted with buffer B (50 mM Tris pH 7, 500 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM TCEP, 10 mM reduced GSH, 4°C). The elution fraction was concentrated using Vivaspin (MWCO 50 kDa).
Immunoblotting
Immunoblotting was performed following standard protocols. Blots were blocked for 1 h with 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in TBST (1X Tris-buffered saline (TBS) and 0.1% Tween-20) and then incubated overnight at 4°C with the indicated primary antibodies diluted in 5% BSA in TBST. After washing three times in TBST for 15 min, blots were probed with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies (anti-mouse: Promega, W402B, 1:2,500 dilution; anti-rabbit: GE Healthcare, NA9340V, 1:2,500 dilution) for 1 h at room temperature. Proteins were detected by enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL Plus, Pierce, 1896327). The following primary antibodies were used: anti-HACE1 (Abcam, ab133637, 1:500 dilution), anti-RAC1 (Cytoskeleton, ARC03, 1:500 dilution), anti-β-Actin (Sigma, A5316, 1:10,000 dilution), anti-His (ThermoFisher Scientific, MA1-21315, 1:1,000), anti-ubiquitin (P4D1) (Santa Cruz, sc-8017, 1:1000), anti-HA (Covance, MMS-101P, 1:1,000 dilution), anti-p53 (Cell Signaling, 2524, 1:1,000 dilution), anti-phosphoS15-p53 (Cell Signaling, 9284, 1:1,000 dilution), anti-Cyclin D1 (Cell Signaling, 2922, 1:1,000 dilution), and anti-GAPDH (Cell Signaling, 2118, 1:2,000 dilution).
Human database analyses
The mutational data of HACE1 in human cancers were obtained from published and publically available datasets on cBioPortal (www.cbioportal.org), including The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) datasets and TGen datasets. For mRNA expression analyses, z-Scores (RNA Seq V2 RSEM) for the LUAD TCGA cohort were obtained from cBioPortal. The cohort was stratified based on HACE1 (high z-score>0, low z-score<0), RAC1 and RAC2 (high z-score>1.5, low z-score<1.5) mRNA expression. Only groups with 10 or more patients were included in the analysis. Survival analysis was performed with R package survminer (43), p-values were computed with log-rank test and adjusted by the Benjamini and Hochberg procedure (44). For construction of the correlation heatmap and correlation matrix, only samples with an absolute z-score higher than 2 in any of the 4 mRNA expression profiles were included. Correlation matrices were plotted with R package corrplot (45). GISTIC copy number alterations and mutation data were retrieved from a 507 patient Lung Adenocarcinoma (TCGA, PanCancer) cBioPortal cohort.
Statistical analyses
All values are given as means ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M.). Student’s t-test was used to compare two groups. Multiple comparisons were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc tests for multiple comparisons. Details of the statistical tests used are indicated in the respective figure legends. For the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, a log rank test was performed. In all tests, P <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA).
Results
HACE1 is mutated in multiple human cancers
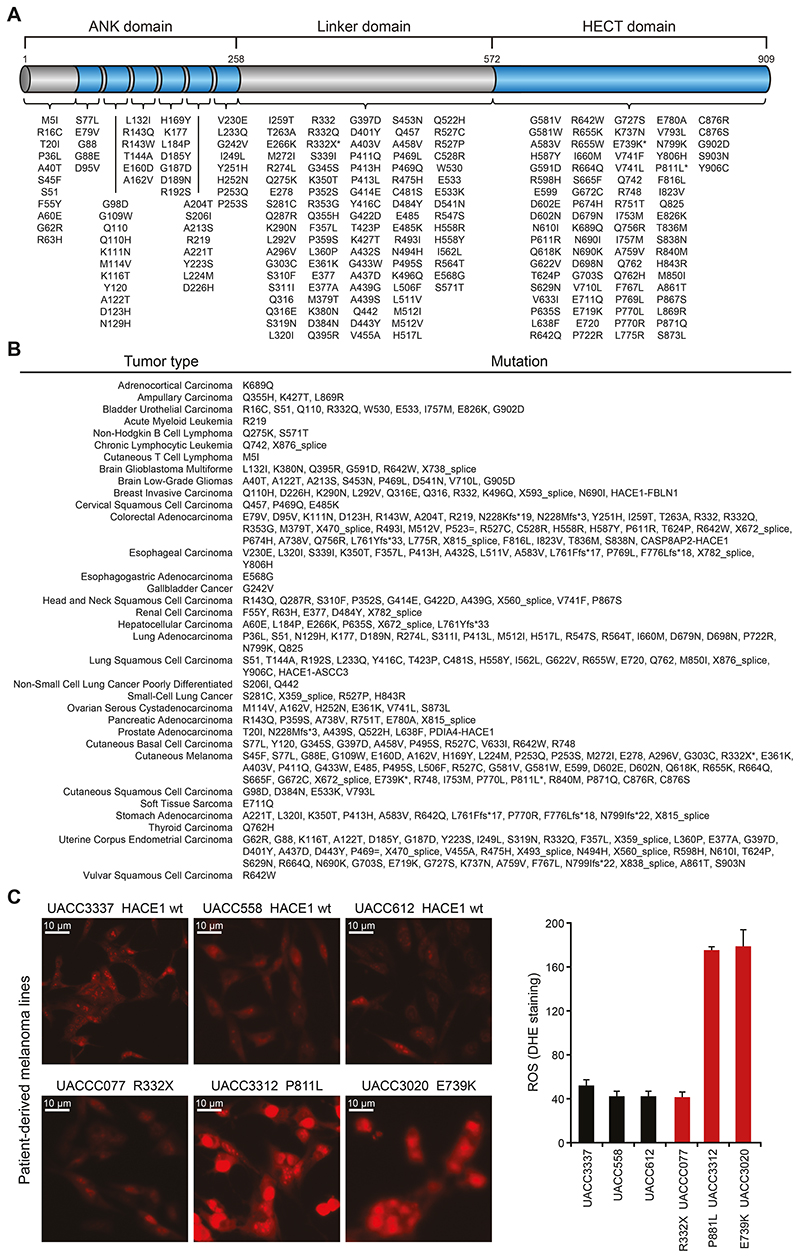
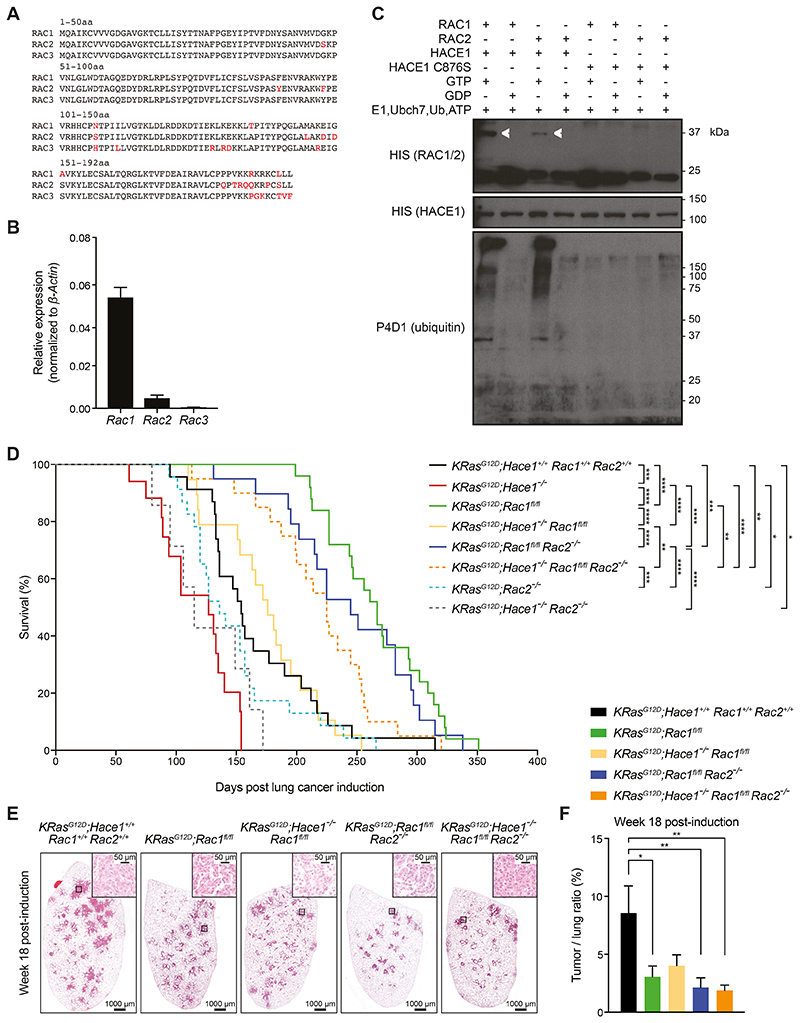
To explore the tumor suppressor function of HACE1 in cancer patients, we performed a meta-analysis of somatic mutations of HACE1 in several human tumors using published and publically available datasets from cBioPortal and TGen (46,47). HACE1 consists of a catalytic HECT domain (amino-acids 572–909), the linker domain (amino-acids 258–571) and ankyrin-repeats (ANK; amino-acids 1–257). While the HECT domain is responsible for the ubiquitin ligase activity of HACE1, the highly conserved ANK domain, especially ANK 4–7, mediates the interaction of HACE1 with its targets. Mutations in the HECT as well as in the ANK domains have been implicated to play a critical role in the tumor suppressor function of HACE1 (17–19,33). We identified numerous mutations in the catalytic HECT domain as well as in the non-catalytic ANK and linker domains of HACE1 in cancer patients (Fig. 1A, Supplementary Table S1). Furthermore, these somatic mutations occurred in multiple cancer types. Fortyone (41) of the total 292 HACE1 mutations we identified in the databanks occurred in lung cancer patients (lung adenocarcinomas, lung squamous cell carcinomas and small-cell carcinomas) (Fig. 1B, Supplementary Table S1).
Figure 1. The HACE1 mutation landscape of human cancer.
(A) Intra-protein location of HACE1 mutations identified in human cancers as available from datasets on cBioPortal and TGen datasets. The asterisks highlight HACE1 mutations present in patient-derived melanoma cell lines used in (C). The different HACE1 domains are indicated. (B) HACE1 mutation profile in individual cancer types as available from the cBioPortal and TGen datasets. (C) Patient-derived human melanoma cell lines expressing endogenous wildtype HACE1 (wt) or mutated (R332X, P811L, E739K) HACE1, were analyzed for superoxide content by dihydroethidium (DHE) staining. Representative pictures of DHE-stained patient-derived melanoma cells (left) and the quantitative analysis of DHE fluorescence intensity in 200 cells/cell line (right) (Student’s two-tailed t-test, n=3) are shown. Red staining indicates the presence of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Scale bars, 20μm. Data in (C) are presented as mean values SEM.
Previous studies reported that deletion/downregulation of HACE1 results in increased levels of ROS (17). Therefore, we used dihydroethidium (DHE) to evaluate ROS production in patient-derived melanoma cells harboring HACE1 mutations (Fig. 1C). Tumor cells from patients carrying the mutations P811L and E739K in the HECT domain, showed significantly higher ROS levels compared to tumor cells from patients with either wild type HACE1 (wt) or a HACE1 mutation R332X in the linker domain, though the sample size is too small to also exclude a role of the linker region in ROS production. Thus, HACE1 is frequently mutated in different cancer types including lung cancer and somatic mutations in the HECT domain of HACE1 in cancer cells derived from melanoma patients can lead to elevated levels of cellular ROS.
Hace1 deficiency in mice results in increased lung tumorigenesis
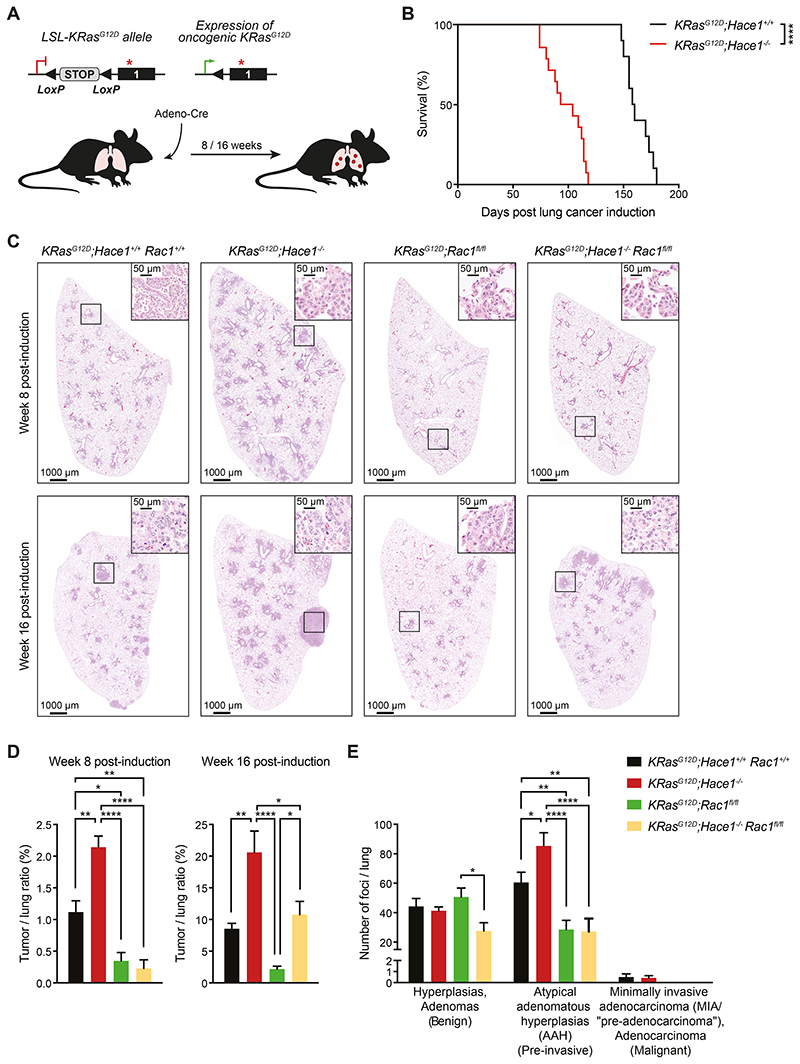
As we have previously reported, aged Hace1–/– mice have a higher incidence of spontaneous lung tumors, which is significantly increased upon urethane-treatment compared to Hace1+/+ littermate controls (7). Therefore, we speculated that HACE1 might also control tumorigenesis in KRasG12D-driven lung tumors (35). In this model, mice bearing the Lox-Stop-Lox (LSL)-KRasG12D allele can be induced to express oncogenic mutated KRasG12D in lung epithelial cells after the removal of the Stop cassette following intratracheal administration of Cre recombinase-expressing adenovirus (Adeno-Cre), which leads to the development of epithelial hyperplasia and progression to benign adenomas and malignant adenocarcinomas (35) (Fig. 2A). Therefore, we crossed Hace1-deficient (Hace1–/–) animals to LSL-KRasG12D conditional mice, generating KRasG12D;Hace1+/+ and KRasG12D;Hace1–/– animals. Indeed, KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice showed significantly reduced survival in the KRasG12D-driven lung tumor model compared to littermate controls following lung tumor induction (Fig. 2B). These data show that loss of Hace1 markedly enhances the development of KRasG12D-driven lung tumors.
Figure 2. Genetic deletion of Rac1 reduces the increased lung tumorigenesis of Hace1–/– mice.
(A) Illustration of the KRasG12D-driven lung adenocarcinoma mouse model. Mice carrying the conditional Lox-Stop-Lox (LSL)-KRasG12D allele develop lung adenocarcinomas upon intratracheal instillation of Adeno-Cre which excises the Stop cassette allowing the constitutive expression of oncogenic KRasG12D. (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of KRasG12D;Hace1+/+ (n=10) and littermate KRasG12D;Hace1–/– (n=14) mice injected with Adeno-Cre on day 0. **** P<0.0001 (log-rank test). (C) Representative pictures of haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained-lung sections and (D) tumor-to-lung ratios at week 8 and 16 post lung cancer induction for KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+, KRasG12D;Hace1–/–, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl, and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice. Scale bars, 1 mm for 10x images and 50μm for 40x images of lung sections. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, **** P<0.0001 (One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc test, n 5 mice per cohort). (E) Numbers of benign (hyperplasias and adenomas), pre-invasive (atypical adenomatous hyperplasias) and malignant (minimally invasive adenocarcinomas (MIA / “pre-adenocarcinoma”), adenocarcinoma) tumor foci at week 8 post lung cancer induction for KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+, KRasG12D;Hace1–/–, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, **** P<0.0001 (Two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc test, n≥4 mice per cohort). Data in (D) and (E) are presented as mean values ± SEM.
Concomitant inactivation of Rac1 reduces lung tumorigenesis in Hace1–/– mice
We have recently shown that HACE1 is involved TNFR1-RIP3 kinase signaling and plays a role in inflammation-driven colon cancer (15). We therefore first determined if deregulation of TNFR1-mediated RIP3 kinase signaling contributes to the increased tumorigenesis in KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice crossing KRasG12D;Hace1 mutant mice to Rip3k knockout animals and induced lung tumors following Adeno-Cre administration (28). However, in KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Ripk3–/– mice we failed to observe a rescue of the enhanced lung tumor phenotype in KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice (Supplementary Fig. S1A). Thus, loss of Hace1 increases the susceptibility to KRasG12D-driven lung tumors independently of pro-necroptotic RIP3 kinase.
HACE1 was previously shown to ubiquitylate and mediate degradation of the small GTPase RAC1, predominantly in its active, GTP-bound form (17,33). Deregulation of RAC1 has previously been associated with tumor development (29). To examine if increased tumorigenesis in the absence of HACE1 could be explained by deregulation of RAC1, we crossed KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice to Rac1fl/fl mice (48) to generate KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice, in which deletion of Rac1 and expression of oncogenic KRasG12D can be simultaneously induced by Adeno-Cre administration (28). Rac1 inactivation in lung tumor cells but not in adjacent tissue and lung macrophages was confirmed by IHC, Western blot and transcript analysis (Supplementary Fig. S2A-D). In line with the survival data in Fig. 2B, deletion of Hace1 resulted in a significantly higher tumor burden at weeks 8 and 16 post lung tumor induction compared to KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+ control mice. Genetic inactivation of Rac1 alone led to significantly reduced tumor burden compared to KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+ control animals (Fig. 2C,D), confirming previous data (28). Eight weeks post lung tumor induction, KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice, similar to KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl mice, had strongly reduced tumor growth as compared to both KRasG12D;Hace1–/– and KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+ control mice. After 16 weeks KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice still had a significant reduction in tumor burden compared to KRasG12D;Hace1–/– animals, but this reduction was not as pronounced as in the KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl mice (Fig. 2C,D).
We further assessed tumor initiation and progression using established pathology criteria (49–50). At week 8 post lung tumor induction, we observed foci of hyperplasia and adenomas (benign lesions), irrespective of the genotype (Fig. 2E). Foci of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (pre-neoplastic / pre-invasive lesions) were more prominent in KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice. Borderline minimally invasive adenocarcinomas (malignant lesions) were also more evident in KRasG12D;Hace1–/– and KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+ control mice. Mice lacking RAC1 either in the presence or absence of HACE1 showed notably reduced numbers of pre-invasive and malignant lesions. Genetic inactivation of Hace1 resulted in a higher number of tumor foci (Fig. 2E), supporting the notion that Hace1 loss leads to more malignant and aggressive type of lung tumors. Together, these data support a role for RAC1 in the progression of Hace1-deficient KRasG12D-driven lung tumors.
Rac1 deficiency affects lung tumor progression in Hace1–/– mice
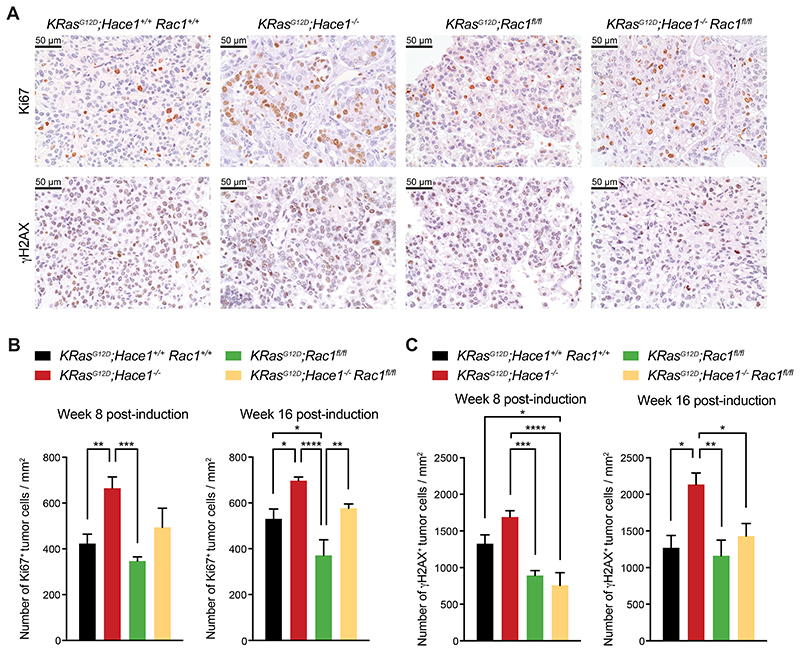
To further characterize tumor progression, we assessed the proliferation index of the lung tumors at weeks 8 and 16 post lung tumor induction by Ki67 immunostaining. In line with tumor growth, proliferation of lung tumor cells in KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice was elevated compared to the other groups while, consistently, Rac1 deletion led to reduced tumor cell proliferation (Fig. 3A, upper panels, and Fig. 3B). In KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice the number of Ki67+ lung tumor cells was lower than in KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice and comparable to those in KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+ control animals. Furthermore, we assessed DNA damage in lung tumor cells by γH2AX immunostaining. Consistent with accelerated tumorigenesis, we observed increased DNA damage in tumor foci of KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice at weeks 8 and 16 post lung tumor induction, while this was reduced in KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl tumors to levels detected in KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl and KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+ control mice (Fig. 3A, bottom panels, and Fig. 3C). These data show that the enhanced proliferation as well as increased DNA damage observed in Hace1–/– lung tumors are reduced upon additional inactivation of Rac1.
Figure 3. Elevated proliferation and DNA damage of tumor cells in Hace1–/– mice is reduced upon loss of Rac1.
(A) Representative pictures of Ki67 and γH2AX immunostaining of lungs at week 16 post lung cancer induction for KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+, KRasG12D;Hace1–/–, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice. Scale bars, 50μm. (B) Quantification of Ki67+ and (C) γH2AX+ tumor cells at week 8 (left panels) and 16 (right) post lung cancer induction for KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+, KRasG12D;Hace1–/–, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, **** P<0.0001 (One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc test, n 3 mice per cohort). Data in (B) and (C) are presented as mean values SEM.
HACE1 controls ROS accumulation in tumor cells
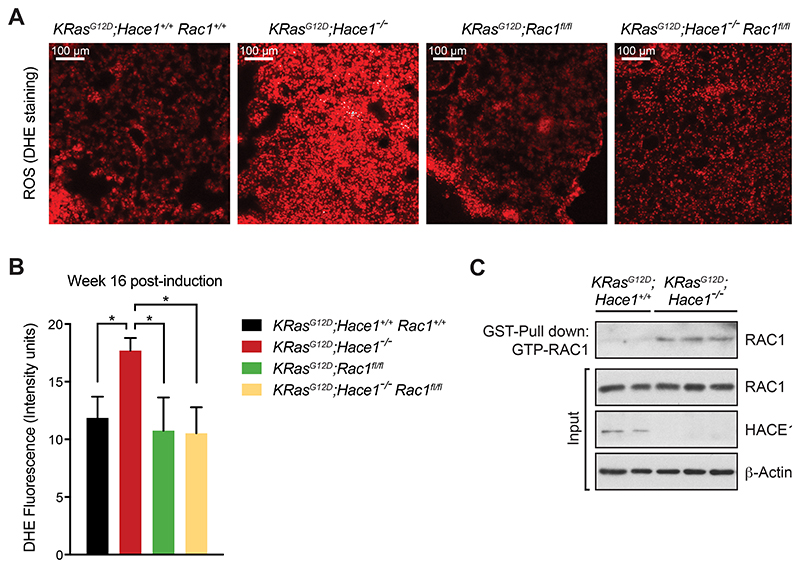
Previous in vitro findings have shown that deregulated activation of RAC1 in the absence of HACE1 is responsible for increased production of ROS by the NADPH-oxidase pathway (17). Given the important impact of ROS in driving cellular damage and cancer development (51), we performed DHE staining to evaluate ROS generation in lung tumor cells. We indeed observed elevated ROS levels in KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice compared to the other groups (Fig. 4A,B). These findings were supported by staining with additional oxidative stress markers, NRF2 and 4‐hydroxynonenal (4HNE) (Supplementary Fig. S2E,F) (52). To test whether absence of HACE1 would lead to the accumulation of active GTP-RAC1, we isolated primary lung tumor cells from KRasG12D;Hace1–/– and KRasG12D;Hace1+/+ control mice at week 12 post lung tumor induction and measured activation of RAC1 by Western blot after affinity-precipitation using the GST-tagged GTP-RAC1 binding motif of PAK (40). The fraction of active GTP-bound RAC1 was markedly increased in KRasG12D;Hace1–/– tumor cells compared to tumor cells from KRasG12D;Hace1+/+ control mice (Fig. 4C). These results indicate that lung tumors of KRasG12D;Hace1–/– have increased levels of active RAC1 and exhibit enhanced ROS production.
Figure 4. Genetic inactivation of Hace1 results in increased levels of ROS and active GTP-RAC1.
(A) Representative images of DHE-stained lung sections and (B) quantification of the DHE fluorescence intensity at week 16 post lung cancer induction for KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+, KRasG12D;Hace1–/–, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice (Student’s two-tailed t-test, n≥5 mice per cohort). Red staining indicates the presence of ROS. Scale bars, 100μm. Data in (B) are presented as mean values SEM. (C) Detection of active RAC1 in Hace1 mutant lung tumor cells. Tumor cells, isolated from KRasG12D;Hace1+/+ (n=2) and KRasG12D;Hace1–/– (n=3) mice at week 12 post lung cancer induction, were treated with EGF (50ng/ml) for 5 minutes, followed by GST-PAK pull-down of active GTP-RAC1 and immunoblotting for total RAC1 and HACE1. β-Actin is shown as loading control.
RAC2 can partially compensate for RAC1 loss in Hace1–/– lung tumors
Although KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice displayed a reduced lung tumor burden as compared to KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice, this reduction was not as pronounced as in KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl mice (Fig. 2C,D), indicating that, in addition to RAC1, another factor must be involved in the increased tumorigenesis of Hace1-deficient animals. The RAC-family of GTPases encompasses three very closely related structural and functional homologues: RAC1, RAC2, and RAC3 (Fig. 5A). Rac2 mRNA was also expressed in lung tumor cells, albeit at lower levels compared to Rac1, while Rac3 was expressed at low levels (Fig. 5B, and Supplementary Fig. S2C,D). Given the expression pattern and homology, we hypothesized that RAC2 might compensate for the loss of RAC1 and thereby drive tumor formation in KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice. Importantly, we confirmed that HACE1 ubiquitylates GTP-bound but not GDP-bound RAC2 (Fig. 5C), indicating that HACE1 might directly contribute to the regulation of the activation state of RAC2, similar to RAC1. Subsequently, we investigated the involvement of RAC2 in KRasG12D-driven lung tumorigenesis in vivo.
Figure 5. Simultaneous loss of Rac1 and Rac2 improves the survival of Hace1–/– mice.
(A) Amino acid (aa) sequence alignments of murine RAC1, RAC2, and RAC3. Amino acids highlighted in red indicate differences among the family members. The amino acid positions are indicted. (B) Relative mRNA expression of Rac1, Rac2 and Rac3 normalized to β-Actin expression in primary lung tumor cells, isolated from KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+Rac2+/+ mice (n=5) at week 7 post lung cancer induction, followed by RT-qPCR analysis. (C) In vitro ubiquitylation assay. Recombinant GST-HACE1 was incubated with GTP- or GDP-preloaded His-tagged RAC1 or RAC2 in the presence of E1, E2 (Ubch7), ubiquitin and ATP. As a control, catalytic dead HACE1C876S was used. Blots show RAC1 and RAC2 (detected via the His-tag), HACE1 and ubiquitin after 3 h incubation. Ubiquitylated RAC1 and RAC2 are indicated (white arrows). (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+Rac2+/+ (n=23), KRasG12D;Hace1–/– (n=15), KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl (n=25), KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl (n=19), KRasG12D;Rac2–/– (n=23) and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac2–/– (n=7), KRasG12D;Rac1fl/flRac2–/– (n=19) and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/flRac2–/– (n=20) mice. Mice were intratracheally instilled with Adeno-Cre virus on the indicated day 0. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, **** P<0.0001 (log-rank test). (E) Representative H&E stained-lung sections and (F) tumor-to-lung ratios at week 18 post lung cancer induction for KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+Rac2+/+, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl, KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/flRac2–/– and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/flRac2–/– mice. Scale bars, 1 mm for 10x images and 50μm for 40x images of lung sections. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01 (One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-hoc test, n≥5 mice per cohort). Data in (B) and (F) are presented as mean values ± SEM.
To examine the role of RAC2, we crossed Rac2–/– as well as Rac1fl/fl mice onto the KRasG12D;Hace1–/– background to generate Hace1, Rac1 and Rac2 triple mutants, plus all relevant genetic cohort controls. The survival of lung tumor-bearing KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice with a mean survival time of 176 days was enhanced compared to KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice with a mean survival time of 127 days (p<0.0001, log-rank test) and similar to KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+Rac2+/+ control animals with a mean survival time of 154 days (p=0.7122, log-rank test), but still less compared to KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl animals with a mean survival time of 267 days (p<0.0001, log-rank test) (Fig. 5D), corroborating the tumor burden analysis shown in Fig. 2C,D. KRasG12D;Rac2–/– mice (mean survival time 136 days) showed no significant survival advantage compared to KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+Rac2+/+ control animals (p=0.2422, log-rank test) after induction of lung tumors (Fig. 5D). KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac2–/–mice (mean survival time 115 days) also did not show any difference in survival compared to KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice (p=0.2698, log-rank test). The survival of KRasG12D;Rac1fl/flRac2–/– mice (mean survival time 245 days) was comparable to KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl mice (p=0.3037, log-rank test). These data indicated that RAC2 has no important role in the progression of KRasG12D-driven lung tumor and that, in these genetic scenarios, it cannot compensate for the absence of RAC1. However, the genetic inactivation of Rac2 intriguingly did lead to markedly prolonged survival when both Rac1 and Hace1 were knocked-out: KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/flRac2–/– triple knock-out mice (mean survival time 225 days) survived much longer compared to KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice (p=0.0017, log-rank test) and almost reached the survival of KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl mice (p=0.0019, log-rank test) (Fig. 5D). In line with the enhanced survival, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl, KRasG12D;Rac1fl/flRac2–/– and KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/flRac2–/– mice exhibited a significant reduction in tumor burden compared to KRasG12D;Hace1+/+Rac1+/+Rac2+/+ control animals (Fig. 5E,F). We also observed decreased tumor burden in KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice, albeit this was statistically not significant (Fig. 5E,F), in line with the survival curves of this genetic cohort (Fig. 5D). Expression of Ki67 by tumor cells did not significantly differ among the different groups (Supplementary Fig. S3A). Similarly, infiltration of tumors by different immune cells was largely unaffected across the various genotypes (Supplementary Fig. S3B-E). Of note, KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice were not included in this tumor burden analysis because at the time point of analysis half of these mice had already died. Taken together, these data show that concurrent loss of Rac2 reduces the tumor growth of KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice. Thus, RAC2 appears – at least in part – to compensate for the loss of RAC1 in driving lung cancer development in KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice.
HACE1/RAC expression correlate with survival in human lung adenocarcinoma patients
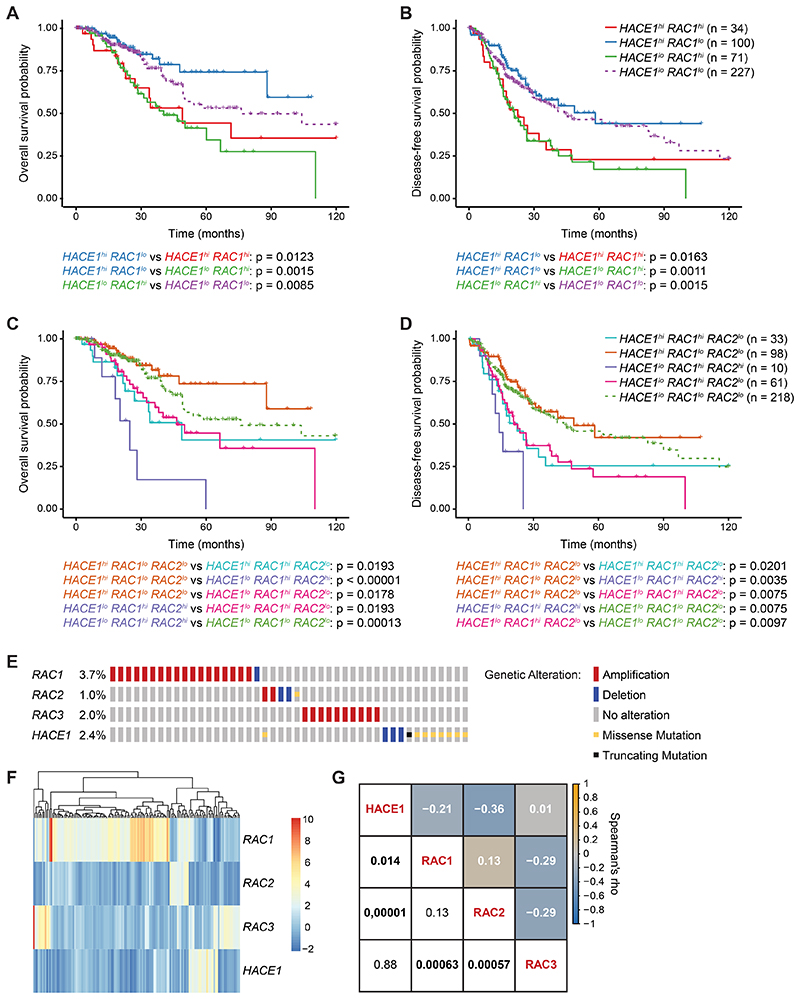
To further investigate the role of HACE1, RAC1 and RAC2 in human lung cancer, we stratified lung adenocarcinoma patients according to the mRNA expression of HACE1, RAC1 and RAC2 using TCGA RNAseq data sets (53). These data revealed that lung adenocarcinoma patients showing high expression of HACE1 and low expression of RAC1 had a significantly better disease-free as well as a better overall survival prognosis than patients with high expression of RAC1 and low expression of HACE1 (Fig. 6A,B). High expression of both RAC1 and RAC2 significantly correlated with even poorer survival as compared to high expression of RAC1 alone (Fig. 6C,D). Thus, deregulated expression of the HACE1/RAC pathway is associated with the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma patients.
Figure 6. HACE1/RAC are deregulated in lung adenocarcinoma patients.
(A) Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival and (B) disease-free survival for lung adenocarcinoma patients, based on HACE1 and RAC1 mRNA expression. (C) Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival and (D) disease-free survival for lung adenocarcinoma patients, based on HACE1, RAC1 and RAC2 mRNA expression. (E) Schematic representation of genetic alterations in HACE1, RAC1, RAC2 and RAC3 in lung adenocarcinoma patients from the TCGA (PanCancer Atlas) data set for 507 cases. Color coding indicates mutation types: red, amplification; blue, homozygous deletion; yellow, missense mutation; black, truncating mutation. Percentages (%) of cases with alteration in HACE1, RAC1, RAC2 and RAC3 are indicated. Only altered cases are shown. (F) Heatmap of gene expression profiles of HACE1, RAC1, RAC2 and RAC3 in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Each row represents the expression of either HACE1, RAC1, RAC2 or RAC3. Each line corresponds to one lung cancer patient. Z-score (RNA Seq V2 RSEM) is shown from 10 (red, highest expression) to -2 (blue, lowest expression). The mRNA expression level in a single sample is depicted according to the color scale. (G) Correlation matrix showing Spearman’s rank correlation of HACE1, RAC1, RAC2 and RAC3 mRNA expression profiles. Correlation coefficients are shown in white and the associated p-values in black (statistically significant values with P<0.05 in bold). Orange and blue colors indicate positive and negative correlations, respectively, beige indicates no correlation.
We next analyzed the mutation frequency of HACE1 and RAC-family members in 507 cases of human lung adenocarcinoma (Fig. 6E). We observed in 9.1% of the adenocarcinoma cases genetic alterations in the RAC and HACE1 genes (Fig. 6E). The most abundant HACE1 alterations detected in lung adenocarcinoma patients were deletions, missense mutations and truncations. Conversely, the predominant genetic alterations for RAC1, RAC2 or RAC3 were amplifications (Fig. 6E). In addition, the mRNA expression level of HACE1 showed a significant negative correlation to that of RAC1 or RAC2 in lung cancer patients, while it did not correlate with RAC3 expression, i.e. high HACE1 mRNA expression correlates with reduced expression of RAC1/2 and vice versa (Fig. 6F,G). Thus, HACE1 is mutated in a subset of lung adenocarcinoma patients. High mRNA expression of HACE1 has positive prognostic value while RAC1 and RAC2 high mRNA expression are associated with a poor disease-free and overall survival in lung cancer patients.
Discussion
Here we report that the HECT-family E3 ligase HACE1 is mutated in multiple types of cancers, including lung tumors. Importantly, we provide direct genetic evidence that HACE1 regulates KRasG12D-dependent lung tumor formation via RAC-family GTPases.
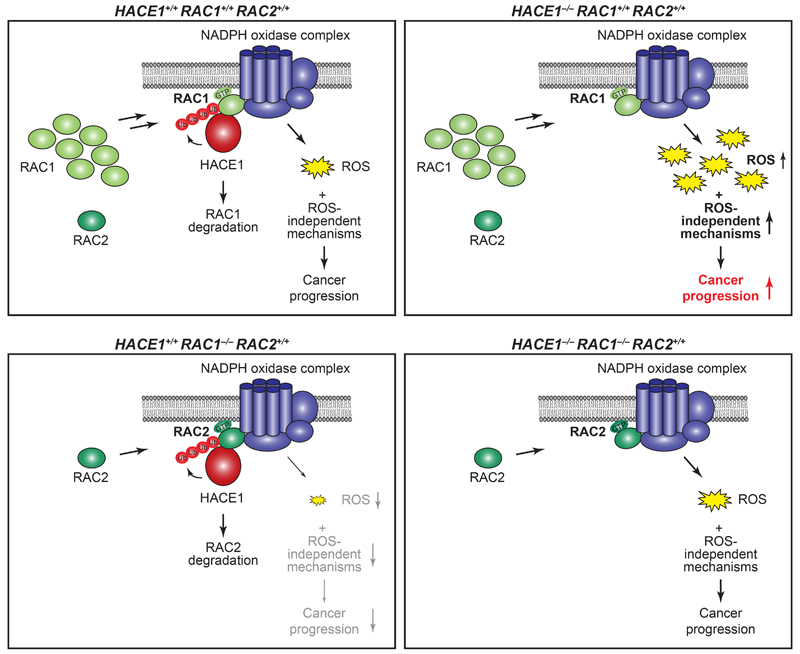
Our in vivo and in vitro data demonstrate that lung tumorigenesis in Hace1-deficient mice is associated with elevated RAC1 activity and enhanced ROS levels. We did not observe any significant effect of RAC2 on lung tumorigenesis while RAC1 was still expressed. However, we found that RAC2 promotes lung tumorigenesis in a scenario where both Rac1 and Hace1 were ablated. These data indicate that RAC2 normally only plays a marginal role in driving pneumocyte transformation and tumorigenesis, probably due to much lower expression levels compared to RAC1. In a context in which the more abundant homologue Rac1 is ablated, RAC2 can drive lung tumor development. However, this compensation only occurs if HACE1 is also absent, indicating that HACE1 can effectively also dampen the potential oncogenic function of RAC2. Indeed, we found that GTP-bound RAC2, similar to RAC1, is ubiquitylated by HACE1, implying an important function of HACE1 as a general “molecular brake” of RAC GTPase activity. Interestingly, the presence of RAC2 did not appear to impact the early stages of tumor growth in KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/fl mice, and these animals only showed increased tumor burdens compared to KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl mice at later time points. This might be indicative of a role of RAC2 in the promotion of tumor growth rather than tumorigenesis in these animals. Although RAC1 and RAC2 seem to be the main drivers of lung tumorigenesis in Hace1-deficient mice, KRasG12D;Hace1–/–Rac1fl/flRac2–/– triple knock-out mice displayed a slightly reduced survival compared to KRasG12D;Rac1fl/fl mice. Therefore, we hypothesize that additional factors (possibly the third homolog RAC3) could also participate in lung tumorigenesis in the absence of HACE1, RAC1 and RAC2. Whether HACE1 also regulates RAC3, needs to be determined in future experiments.
Loss of Hace1 results in lung tumor formation which is associated with enhanced oxidase-dependent ROS generation. Human melanoma cells harboring mutations of HACE1 also displayed increased ROS levels. Maintenance of redox balance is crucial for the survival and functionality of cells, and intracellular ROS are crucial for maintaining a variety of homeostatic processes, such as proliferation, survival, metabolism and differentiation (54). The accumulation of ROS also results in oxidative stress, causing genomic instability, mutagenesis and cell transformation. Active GTP-RAC1 as well as active RAC2 can directly promote ROS generation through NADPH oxidase (24). HACE1 has been previously shown in in vitro experiments to dampen NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS generation by inducing proteasomal degradation of GTP-RAC1 (17). In the present study, we show that, besides RAC1, HACE1 also interacts with and inhibits the oncogenic function of RAC2. Therefore, we postulate that a key function of HACE1 in oncogenesis is to control RAC-family GTPases and consequently NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS generation (Fig. 7). However, our data does not exclude the possibility that generation of ROS might be controlled by RAC1 via NADPH oxidase-independent mechanisms. Importantly, in line with enhanced ROS we also observed increased DNA damage as determined by γH2AX immunostaining.
Figure 7. Schematic representation of HACE1 and RAC-family GTPases driving lung cancer development.
HACE1 ubiquitylates GTP-RAC1 when bound to the NADPH oxidase complex, leading to RAC1 degradation and thereby controlling ROS production (top, left). HACE1 deficiency results in an accumulation of GTP-bound RAC1, increased NADPH oxidase activity and enhanced levels of genotoxic cellular ROS, promoting cancer progression (top, right). Additionally, deregulated RAC1 could promote tumor development by ROS-independent mechanisms. In the absence of the more abundant RAC1, the activity of GTP-RAC2 when bound to the NADPH oxidase complex is controlled by HACE1, leading to decreased cellular ROS levels (bottom, left). When HACE1 and RAC1 are both ablated, active GTP-RAC2 can compensate and promote cancer progression (bottom, right).
To assess whether increased oxidative stress might sustain tumor development in the absence of HACE1, we induced lung cancer in KRasG12D;Hace1–/– and control KRasG12D;Hace1+/+ mice and treated them with ROS scavenger N-acetylcysteine (NAC). Strikingly, NAC-treated KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice showed significantly reduced tumor burdens compared to untreated KRasG12D;Hace1–/– animals (Supplementary Fig. S4A,B). Interestingly, treatment of NAC was previously suggested to accelerate the development of lung tumors (55), whereas our control KRasG12D;Hace1+/+ mice were unaffected by NAC treatment. While we are unsure about the reason for this discrepancy, differences in the genetic background of the animals (the previous study used mixed Sv129/C57BL/6, whereas our mice were on C57BL/6 background) might affect the absorption and metabolization of NAC, leading to different amounts of available NAC and accordingly a different impact on the redox balance of tumor cells. Our data indicates that elevated ROS levels contribute to increased tumorigenesis in Hace1-deficient animals, although we cannot exclude that ROS-independent functions of deregulated RAC1 might also promote tumor development in KRasG12D;Hace1–/– mice.
While increased amounts of ROS might sustain tumorigenesis by promoting genomic instability, excessive amounts of intracellular ROS are highly cytotoxic and induce apoptosis (56). Elevated ROS levels in the absence of HACE1 coupled with the impaired capacity of Hace1-deficent cells to activate crucial anti-oxidant mediator NRF2 (34), open the possibility for therapeutic opportunities. We therefore hypothesized that treatment with ROS-inducing agents might specifically induce apoptosis in Hace1-deficient cells by further increasing intracellular ROS to cytotoxic levels. In Hace1–/– mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), treatment with the ROS-inducer piperlongumine (PL) (57) indeed increased cell death, p53 phosphorylation and cyclin D1 expression compared to control cells and untreated cultures (Supplementary Fig. S4C,D). This effect was reversed upon re-expression of HACE1 in Hace1–/– MEFs. Treatment with 2-Acetylphenothiazine (ML171) which specifically inhibits NOX1-containing NADPH oxidase complexes (58), prevented cell death in PL-treated Hace1–/– MEFs. Furthermore, H2O2 challenge reduced the clonogenic survival of Hace1–/– MEFs in a concentration-dependent manner compared to untreated and control MEFs (Supplementary Fig. S4E). We also observed enhanced cell death in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells upon knock-down of HACE1 expression when treated with either PL or H2O2 (Supplementary Fig. S4F). Thus, further induction of oxidative stress upon treatment with ROS-inducers destabilized Hace1-deficient cells to trigger cell cycle-arrest and apoptosis, suggesting that ROS-inducing agents could be employed to therapeutically enhance cellular ROS and preferentially eliminate Hace1-mutated cancer cells while sparing healthy cells.
Our findings complement and highlight the role of HACE1 as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer. Mechanistically, it appears that HACE1 ubiquitylates active RAC proteins leading to their proteasomal degradation and the subsequent impaired activation of the NADPH oxidase complex. Hence, by inhibiting ROS generation, HACE1 prevents DNA damage and tumor development. Importantly, our data also position the HACE1-RAC axes as a key driver of human lung cancer pathogenesis associated with patient survival.
Supplementary Material
Statement of significance.
Findings reveal that mutation of the tumor suppressor HACE1 disrupts its role as a regulator of the oncogenic activity of RAC-family GTPases in human and murine lung cancer.
Acknowledgements
We thank all members of our laboratories for constructive discussions and expert advice. We also thank A. Kavirayani, M. Zeba, T. Engelmaier, J. Klughofer, A. Mancebo Gimenez and A. Piszczek for histology services, and the members of the IMP-IMBA Biooptics facility, especially G. Schmauss and T. Lendl, for assistance in image quantification. We thank Lilian M. Fennell for the help with the ubiquitylation assay. L.T. is supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation [Grant#: PBEZP3_145993]. S.M. is supported by funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement [Grant#: 841319]. I.U. is supported by an EMBO Long‐term Fellowship and a Marie Curie Fellowship from the European Commission. J.M.P. is supported by grants from IMBA, the Austrian Ministry of Sciences, the Austrian Science Fund (Grant#: Z 271-B19), the Austrian Academy of Sciences, a European Research Council (ERC) Advanced Grant, an Era of Hope Innovator award, and a Canada 150 Grant. M.D. is supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) [Grant#: 377771]. P.H.S. is supported by CIHR Foundation [Grant#: FDN-143280], and by the British Columbia Cancer Foundation through generous donations from Team Finn and other riders in the Ride to Conquer Cancer.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: David A. Williams received funding from Bluebird Bio and Novartis. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
References
- 1.Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. American Cancer Society. 2018;68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. Nature. Vol. 553. Nature Publishing Group; 2018. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer; pp. 446–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cronin KA, Lake AJ, Scott S, Sherman RL, Noone A-M, Howlader N, et al. Cancer. 3rd. Vol. 124. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2018. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, part I: National cancer statistics; pp. 2785–800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Walters S, Maringe C, Coleman MP, Peake MD, Butler J, Young N, et al. Lung cancer survival and stage at diagnosis in Australia, Canada, Denmark, Norway, Sweden and the UK: a population-based study, 2004-2007. Thorax. (7) 2013;68:551–64. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2012-202297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Network TCGAR. Nature. Vol. 511. Nature Publishing Group; 2014. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma; pp. 1–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Anglesio MS, Evdokimova V, Melnyk N, Zhang L, Fernandez CV, Grundy PE, et al. Differential expression of a novel ankyrin containing E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, Hace1, in sporadic Wilms’ tumor versus normal kidney. Human Molecular Genetics. 2004;13:2061–74. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhang L, Anglesio MS, O’Sullivan M, Zhang F, Yang G, Sarao R, et al. Nature Medicine. Vol. 13. Nature Publishing Group; 2007. The E3 ligase HACE1 is a critical chromosome 6q21 tumor suppressor involved in multiple cancers; pp. 1060–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.El-Naggar AM, Clarkson PW, Negri GL, Turgu B, Zhang F, Anglesio MS, et al. Cell Death Dis. Vol. 10. Nature Publishing Group; 2019. HACE1 is a potential tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma; p. 21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bouzelfen A, Kora H, Alcantara M, Bertrand P, Latouche J-B, Jardin F. Heterogeneous epigenetic regulation of HACE1 in Burkitt- Lymphoma-derived cells. Leuk Res. 2017;60:53–7. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2017.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hibi K, Sakata M, Sakuraba K, Shirahata A, Goto T, Mizukami H, et al. Aberrant methylation of the HACE1 gene is frequently detected in advanced colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2008;28:1581–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sakata M, Kitamura Y-H, Sakuraba K, Goto T, Mizukami H, Saito M, et al. Methylation of HACE1 in gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:2231–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Goka ET, Lippman ME. Oncogene. Vol. 34. Nature Publishing Group; 2015. Loss of the E3 ubiquitin ligase HACE1 results in enhanced Rac1 signaling contributing to breast cancer progression; pp. 5395–405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gao Z-F, Wu Y-N, Bai Z-T, Zhang L, Zhou Q, Li X. Oncol Rep. Vol. 36. Spandidos Publications; 2016. Tumor-suppressive role of HACE1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical significance; pp. 3427–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Diskin SJ, Capasso M, Schnepp RW, Cole KA, Attiyeh EF, Hou C, et al. Nat Genet. Vol. 44. Nature Publishing Group; 2012. Common variation at 6q16 within HACE1 and LIN28B influences susceptibility to neuroblastoma; pp. 1126–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tortola L, Nitsch R, Bertrand MJM, Kogler M, Redouane Y, Kozieradzki I, et al. The Tumor Suppressor Hace1 Is a Critical Regulator of TNFR1-Mediated Cell Fate. CellReports. 2016;15:1481–92. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.04.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Liu Z, Chen P, Gao H, Gu Y, Yang J, Peng H, et al. Ubiquitylation of autophagy receptor Optineurin by HACE1 activates selective autophagy for tumor suppression. Cancer Cell. 2014;26:106–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.05.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Daugaard M, Nitsch R, Razaghi B, McDonald L, Jarrar A, Torrino S, et al. Nature Communications. Vol. 4. Nature Publishing Group; 2013. Hace1 controls ROS generation of vertebrate Rac1-dependent NADPH oxidase complexes; p. 2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Castillo-Lluva S, Tan C-T, Daugaard M, Sorensen PHB, Malliri A. Oncogene. Vol. 32. Nature Publishing Group; 2013. The tumour suppressor HACE1 controls cell migration by regulating Rac1 degradation; pp. 1735–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Torrino S, Visvikis O, Doye A, Boyer L, Stefani C, Munro P, et al. The E3 ubiquitin-ligase HACE1 catalyzes the ubiquitylation of active Rac1. Dev Cell. 2011;21:959–65. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Parri M, Chiarugi P. Cell Commun Signal. Vol. 8. BioMed Central; 2010. Rac and Rho GTPases in cancer cell motility control; p. 23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Haataja L, Groffen J, Heisterkamp N. Characterization of RAC3, a novel member of the Rho family. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997;272:20384–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.33.20384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Didsbury J, Weber RF, Bokoch GM, Evans T, Snyderman R. rac, a novel ras-related family of proteins that are botulinum toxin substrates. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1989;264:16378–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Knaus UG, Heyworth PG, Evans T, Curnutte JT, Bokoch GM. Science. Vol. 254. American Association for the Advancement of Science; 1991. Regulation of phagocyte oxygen radical production by the GTP-binding protein Rac 2; pp. 1512–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Debidda M, Williams DA, Zheng Y. Journal of Biological Chemistry. Vol. 281. American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology; 2006. Rac1 GTPase regulates cell genomic stability and senescence; pp. 38519–28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Deshmukh J, Pofahl R, Pfister H, Haase I. Oncotarget. Vol. 7. Impact Journals; 2016. Deletion of epidermal Rac1 inhibits HPV-8 induced skin papilloma formation and facilitates HPV-8- and UV-light induced skin carcinogenesis; pp. 57841–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wang Z, Pedersen E, Basse A, Lefever T, Peyrollier K, Kapoor S, et al. Oncogene. Vol. 29. Nature Publishing Group; 2010. Rac1 is crucial for Ras-dependent skin tumor formation by controlling Pak1-Mek-Erk hyperactivation and hyperproliferation in vivo; pp. 3362–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Heid I, Lubeseder-Martellato C, Sipos B, Mazur PK, Lesina M, Schmid RM, et al. Early requirement of Rac1 in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:e1–7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.04.043. 719–30–730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kissil JL, Walmsley MJ, Hanlon L, Haigis KM, Bender Kim CF, Sweet-Cordero A, et al. Requirement for Rac1 in a K-ras induced lung cancer in the mouse. Cancer Research. 2007;67:8089–94. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kawazu M, Ueno T, Kontani K, Ogita Y, Ando M, Fukumura K, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. Vol. 110. National Academy of Sciences; 2013. Transforming mutations of RAC guanosine triphosphatases in human cancers; pp. 3029–34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Davis MJ, Ha BH, Holman EC, Halaban R, Schlessinger J, Boggon TJ. RAC1P29S is a spontaneously activating cancer-associated GTPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:912–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1220895110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Krauthammer M, Kong Y, Ha BH, Evans P, Bacchiocchi A, McCusker JP, et al. Nat Genet. Vol. 44. Nature Publishing Group; 2012. Exome sequencing identifies recurrent somatic RAC1 mutations in melanoma; pp. 1006–14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hodis E, Watson IR, Kryukov GV, Arold ST, Imielinski M, Theurillat J-P, et al. A landscape of driver mutations in melanoma. Cell. 2012;150:251–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Andrio E, Lotte R, Hamaoui D, Cherfils J, Doye A, Daugaard M, et al. Sci Rep. Vol. 7. Nature Publishing Group; 2017. Identification of cancer-associated missense mutations in hace1 that impair cell growth control and Rac1 ubiquitylation; 44779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rotblat B, Southwell AL, Ehrnhoefer DE, Skotte NH, Metzler M, Franciosi S, et al. HACE1 reduces oxidative stress and mutant Huntingtin toxicity by promoting the NRF2 response. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences; 2014. pp. 3032–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jackson EL, Willis N, Mercer K, Bronson RT, Crowley D, Montoya R, et al. Analysis of lung tumor initiation and progression using conditional expression of oncogenic K-ras. Genes & Development. 2001;15:3243–8. doi: 10.1101/gad.943001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Newton K, Sun X, Dixit VM. Kinase RIP3 is dispensable for normal NF-kappa Bs, signaling by the B-cell and T-cell receptors, tumor necrosis factor receptor 1, and Toll-like receptors 2 and 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:1464–9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.4.1464-1469.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.DuPage M, Dooley AL, Jacks T. Conditional mouse lung cancer models using adenoviral or lentiviral delivery of Cre recombinase. Nat Protoc. 2009;4:1064–72. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2009.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Schramek D, Kotsinas A, Meixner A, Wada T, Elling U, Pospisilik JA, et al. Nat Genet. Vol. 43. Nature Publishing Group; 2011. The stress kinase MKK7 couples oncogenic stress to p53 stability and tumor suppression; pp. 212–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rao S, Sigl V, Wimmer RA, Novatchkova M, Jais A, Wagner G, et al. Genes & Development. Vol. 31. Cold Spring Harbor Lab; 2017. RANK rewires energy homeostasis in lung cancer cells and drives primary lung cancer; pp. 2099–112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Benard V, Bohl BP, Bokoch GM. Characterization of rac and cdc42 activation in chemoattractant-stimulated human neutrophils using a novel assay for active GTPases. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1999;274:13198–204. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.19.13198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Self AJ, Hall A. Measurement of intrinsic nucleotide exchange and GTP hydrolysis rates Meth Enzymol. Vol. 256. Elsevier; 1995. pp. 67–76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Asaoka T, Almagro J, Ehrhardt C, Tsai I, Schleiffer A, Deszcz L, et al. Linear ubiquitination by LUBEL has a role in Drosophila heat stress response. EMBO Rep. 2016;17:1624–40. doi: 10.15252/embr.201642378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kassambara A, Kosinski M, Biecek P, Fabian S. Package ‘Survminer’: Drawing Survival Curves Using ‘Ggplot2’. 2018:1–62. R Package Version 0.4.3. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological) Vol. 57. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 1995. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing; pp. 289–300. (10.1111) [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wei T, Simko V, Levy M, Xie Y, Jin Y, Zemla J. Package “corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix (Version 0.84) 2017:1–18. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Weinstein JN, Collisson EA, Mills GB, Shaw KRM, Ozenberger BA, et al. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Nat Genet. Vol. 45. Nature Publishing Group; 2013. The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-Cancer analysis project; pp. 1113–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tate JG, Bamford S, Jubb HC, Sondka Z, Beare DM, Bindal N, et al. COSMIC: the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:D941–7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Glogauer M, Marchal CC, Zhu F, Worku A, Clausen BE, Foerster I, et al. Rac1 Deletion in Mouse Neutrophils Has Selective Effects on Neutrophil Functions. The Journal of Immunology. 2003;170:5652–7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.11.5652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG, Yatabe Y, Austin JHM, Beasley MB, et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10:1243–60. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Renne R, Brix A, Harkema J, Herbert R, Kittel B, Lewis D, et al. Toxicol Pathol. Vol. 37. SAGE PublicationsSage CA: Los Angeles, CA; 2009. Proliferative and nonproliferative lesions of the rat and mouse respiratory tract; pp. 5S–73S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gorrini C, Harris IS, Mak TW. Nat Rev Drug Discov. Vol. 12. Nature Publishing Group; 2013. Modulation of oxidative stress as an anticancer strategy; pp. 931–47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.El-Naggar AM, Somasekharan SP, Wang Y, Cheng H, Negri GL, Pan M, et al. Class I HDAC inhibitors enhance YB-1 acetylation and oxidative stress to block sarcoma metastasis. EMBO Rep. 2019;20:e48375. doi: 10.15252/embr.201948375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Campbell JD, Alexandrov A, Kim J, Wala J, Berger AH, Pedamallu CS, et al. Nat Genet. Vol. 48. Nature Publishing Group; 2016. Distinct patterns of somatic genome alterations in lung adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas; pp. 607–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Schieber M, Chandel NS. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 2014;24:R453–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sayin VI, Ibrahim MX, Larsson E, Nilsson JA, Lindahl P, Bergo MO. Science Translational Medicine. Vol. 6. American Association for the Advancement of Science; 2014. Antioxidants accelerate lung cancer progression in mice; pp. 15–5.221ra. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Redza-Dutordoir M, Averill-Bates DA. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1863:2977–92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Karki K, Hedrick E, Kasiappan R, Jin U-H, Safe S. Piperlongumine Induces Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Dependent Downregulation of Specificity Protein Transcription Factors. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2017;10:467–77. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-17-0053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Gianni D, Taulet N, Zhang H, DerMardirossian C, Kister J, Martinez L, et al. A novel and specific NADPH oxidase-1 (Nox1) small-molecule inhibitor blocks the formation of functional invadopodia in human colon cancer cells. ACS Chem Biol. 2010;5:981–93. doi: 10.1021/cb100219n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.