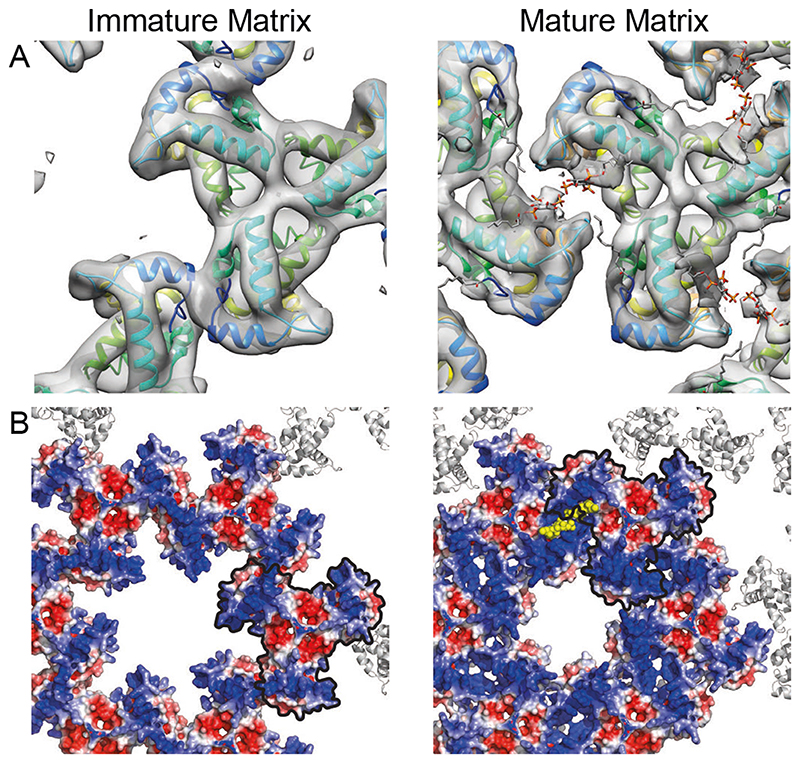
Fig. 4. Comparison of the immature and mature HIV-1 MA lattices.
(A) Immature and mature MA lattices are shown with one trimer aligned. In the immature lattice, contact with neighbouring trimers is mediated by N-terminal regions and the PI(4,5)P2 binding site is empty. In the mature lattice, contact with neighbouring trimers is mediated by the region surrounding the occupied PI(4,5)P2 binding site. (B) Electrostatic surface potential maps of the hexameric lattice of immature and mature MA trimers. The red (-5 kT/e) and blue (+5 kT/e) colours represent negatively and positively charged electric potentials. PI(4,5)P2 is shown in yellow. The negatively-charged lipid headgroups are surrounded by positively-charged residues. One MA trimer aligned as in (A) is outlined in black. The potential of the surface of MA facing the holes at the hexamer positions in the lattice changes from positive to neutral/negative during maturation. The hole becomes smaller.