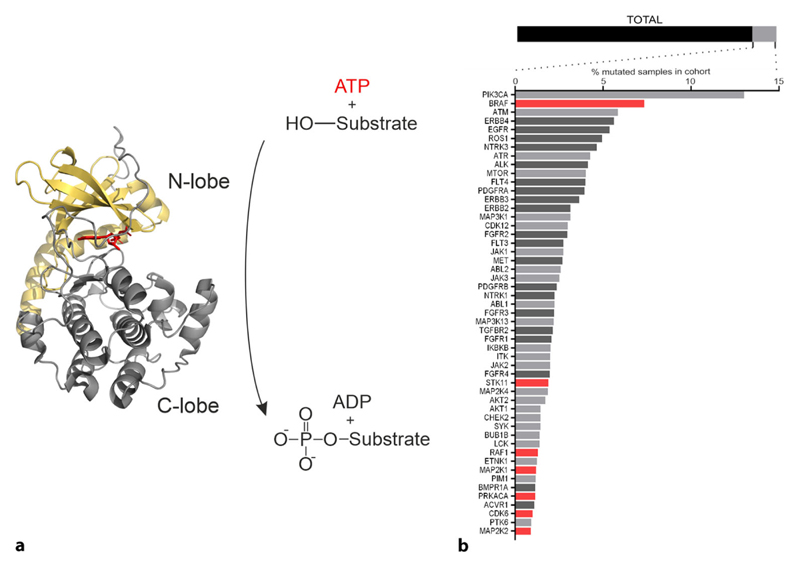
Fig. 1. Kinase domain function and kinase mutations.
a Exemplary a phosphotransferase reaction catalyzed by a kinase domain is illustrated. Conventionally, the respective kinase transfers the γ-phosphate of ATP to a hydroxyl group of either a serine, threonine or tyrosine residue of the substrate protein. We have illustrated the structure of the catalytic sub-unit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PRKACA, RCSB 4O21). The N-lobe is marked in beige, the C-lobe in grey, and the bound ATP in red. The image was created using PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.1.1 Schrödinger, LLC, New York City, NY, USA. b Mutated genes (576) of a patient cohort consisting of 12,647 cases represented by the bar on top (TOTAL). Mutated kinases (52) are highlighted in light grey, the remaining mutated genes (524) are shown in black. Below the percentage of simple somatic mutations occurring for each kinase are shown. For the kinases highlighted in red Kin-Con biosensors are available. Kinases with transmembrane regions are highlighted in dark grey. Data were obtained at https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/