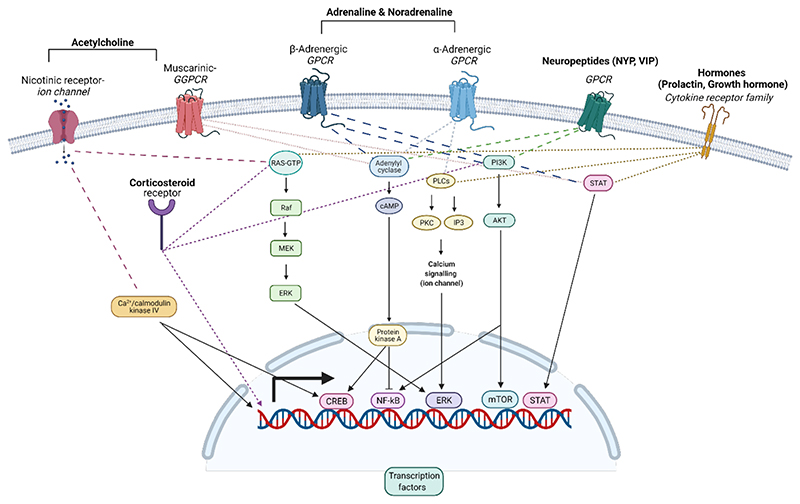
Figure 3. Intracellular immune cell-signaling by stress-induced mediators.
Representative examples of receptors and their corresponding pathways that can be activated by stress-induced mediators. Immune cells express nicotinic and muscarinic receptors for acetylcholine, α- and β-adrenergic receptors for both adrenaline and noradrenaline, and members of the cytokine receptor family for hormones. Receptors for neuropeptides include mainly GPCR (e.g NPY, VIP), although exceptions exist, and the receptor for substance P, for example, is a member of the cytokine receptor family. Downstream signaling of these receptors regulates gene expression via transcription factors such as NF-κB, CREB, ERK, STAT, mTOR etc. Most of the receptors are expressed on the cell membrane, while corticosteroid receptors reside mostly within the cytosol.
GPCR: G-protein-coupled receptor; cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PLC: Phospholipase C; PKC: Protein Kinase C; IP3: Inositol trisphosphate; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinases; Akt: protein kinase B; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cell; CREB: cAMP response element-binding protein; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinases; STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription; mTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin.