5-Hydroxy-3,6,7,8-tetramethoxyflavone was isolated from a butanol extract of the herb Scutellaria nepetoides M. Pop. and its structure has been established by X-ray crystallographic analysis.
Keywords: crystal structure, flavones, Hirshfeld surface analysis, hydrogen bonding
Abstract
The title compound (systematic name: 5-hydroxy-3,6,7,8-tetramethoxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one), C19H18O7, is a flavone that was isolated from a butanol extract of the herb Scutellaria nepetoides M. Pop. The flavone molecule is almost planar, with a dihedral angle between the planes of the benzopyran-4-one group and the attached phenyl ring of 6.4 (4)°. The 5-hydroxy group forms a strong intramolecular hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group, resulting in a six-membered hydrogen-bonded ring. The crystal structure has triclinic (P
 ) symmetry. In the crystal, the molecules are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds into a two dimensional network parallel to the ab plane. The Hirshfeld surface analysis indicates that the most important contributions to the crystal packing are from H⋯H (53.9%) and H⋯O/O⋯H (20.9%) interactions.
) symmetry. In the crystal, the molecules are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds into a two dimensional network parallel to the ab plane. The Hirshfeld surface analysis indicates that the most important contributions to the crystal packing are from H⋯H (53.9%) and H⋯O/O⋯H (20.9%) interactions.
Chemical context
Flavonoids are the most numerous class of natural phenolic compounds, which are characterized by structural diversity, high and versatile activity and low toxicity. Plants of the genus Scutellaria L. are widespread in Europe, North America, East Asia and are extensively used in traditional Chinese medicine (Shang et al., 2010 ▸). Flavonoids isolated from plants of the genus Scutellaria L. exhibit antitumor (Yu et al., 2007 ▸), hepatoprotective (Jang et al., 2003 ▸), antioxidant (Sauvage et al., 2010 ▸), anti-inflammatory (Dai et al., 2013 ▸), anticonvulsant (Park et al., 2007 ▸), antimicrobial (Arituluk et al., 2019 ▸) and antiviral activity (Leonova et al., 2020 ▸). The creation of drugs based on flavonoids is based on the establishment of the ‘chemical structure–pharmacological properties’ relationship, and the determination of the structure of a new flavonoid may become a key starting point.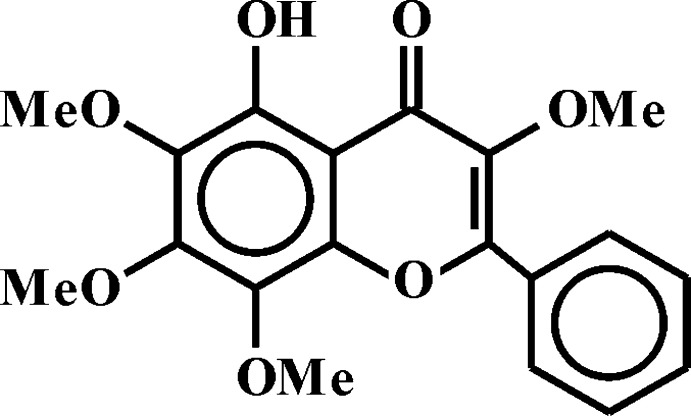
Structural commentary
The molecular structure of the title compound is presented in Fig. 1 ▸. The benzopyran moieties are practically planar, with r.m.s. deviations of 0.01 Å. The molecular conformation is restricted by the relative positions of the benzopyran unit and the phenyl ring, the dihedral angle between them being 6.4 (4)°. Atoms C3, C6, C7 and C8 of the methoxy substituent have an out-of-plane conformation with the methoxy groups at atoms C3 and C6 pointing in the same direction [C16—O2—C3—C2 = 109.3 (2) and C17—O5—C6—C5 = 66. 7(4)°], while the methoxy groups at atoms C7 and C8 point in opposite direction [C18—O6—C7—C6 = −56.3 (3) and C19—O7—C8—C7 = −91.4 (3)°]. The conformation of the molecule is fixed because of the intramolecular O4—H4⋯O3 hydrogen bond [2.599 (2) Å, 147°], which closes a six-membered ring with graph-set notation S(6) (Etter, 1990 ▸).
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, the molecules are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds into a two dimensional network parallel to the ab plane. A perspective view of the crystal packing in the unit cell is depicted in Fig. 2 ▸ and numerical details of the hydrogen bonds are presented in Table 1 ▸.
Figure 2.
Crystal structure of the title compound in projection on the ac plane. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O4—H4⋯O3 | 0.82 | 1.87 | 2.599 (2) | 147 |
| C16—H16A⋯O3 | 0.96 | 2.51 | 3.079 (3) | 118 |
| C16—H16B⋯O3i | 0.96 | 2.39 | 3.258 (3) | 150 |
| C18—H18B⋯O5 | 0.96 | 2.28 | 2.897 (4) | 121 |
| C18—H18C⋯O7ii | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.278 (4) | 135 |
| C17—H17C⋯O4 | 0.96 | 2.52 | 3.010 (4) | 111 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Hirshfeld surface analysis
In order to visualize the intermolecular interactions in the crystals of the title compound, a Hirshfeld surface analysis was carried out using Crystal Explorer 17.5 (Turner et al., 2017 ▸). The Hirshfeld surface mapped over d norm (Fig. 3 ▸) shows the expected bright-red spots near atoms O3, O7, H16B, which are involved in the C—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding interactions. Fingerprint plots (Fig. 4 ▸) reveal that H⋯H and H⋯O/O⋯H interactions make the greatest contributions to the surface contacts, while H⋯C/C⋯H, O⋯C/C⋯O, C⋯C and O⋯O contacts are less significant.
Figure 3.
The Hirshfeld surface analysis indicates that the most important contributions to the crystal packing are from H⋯H (53.9%) and H⋯O/O⋯H (20.9%) interactions.
Figure 4.
Full two-dimensional fingerprint plots for the title compound, showing all interactions (a), and delineated into (b) H⋯H, (c) H⋯O/O⋯H, (d) H⋯C/C⋯H, (e) O⋯C/C⋯O, (f) C⋯C and (g) O⋯O interactions. The d i and d e values are the closest internal and external distances (in Å) from a given point on the Hirshfeld surface.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD Version 5.41, update of November 2019; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) found 311 hits for the term ‘flavones’. Among these, nine are tetramethoxyflavones: 3,4′,6,7 (DAVREN; Geng et al., 2011 ▸), 6,2′3′,4′- (JEMGIN; Wallet et al., 1990a ▸) and 2′,4′,5,7- (KEPLEW; Wallet et al., 1990b ▸), 3,4′,6,7- (MENSII; Meng et al., 2006 ▸), 3′,4′,5,7- (PIQPEK; Shoja, 1997 ▸), 3,4′5,7- (PUGKEI; Aree et al., 2009 ▸), 3′,5,5′,6- (TMOFLV10; Ting et al., 1972 ▸), 3,7,4′,5′- (YASCIF; Etti et al., 2005 ▸). The compound FATZOR (Vijayalakshmi et al., 1986 ▸) is also a 3,6,7,8 tetramethylflavone, but with two hydroxy substituents at the 5,4′-positions.
Synthesis and crystallization
Air-dried whole plants (1.1 kg) of Scutellaria nepetoides M. Pop. were extracted three times (each 3 h) with butanol (5 l) at 353 K. The butanol filtrates were collected and concentrated under reduced pressure to provide 10.2 g of butanol extract. The butanol extract (1 g) was subjected to silica gel (60–100 mesh) column (gradient of butanol:water = 0:1, 2:8, 1:1, 8:2, 1:0) as eluent, and five fractions were collected according to TLC analysis. All fractions were concentrated under reduced pressure. A crystallization procedure with different solvents at high temperature was used to obtain the pure compounds. Fraction 5 (0.23 g) was eluted with butanol (100%) at 353 K and with ethanol (95%) at 343 K. The obtained polycrystals were removed from the butanol solution by filtration. Yellow prismatic single crystals were prepared by slow evaporation of butanol solution at room temperature.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The C-bound H atoms were positioned geometrically and were included in the refinement in the riding-model approximation, with C—H = 0.96 Å (CH3), 0.93 Å (aryl H) and O—H = 0.82 Å and with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C) (aryl H) and 1.5U eq(C-methyl, O).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C19H18O7 |
| M r | 358.33 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P

|
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 5.0789 (4), 8.0801 (6), 20.8682 (19) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 92.481 (7), 91.984 (7), 94.253 (6) |
| V (Å3) | 852.62 (12) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.90 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.03 × 0.02 × 0.01 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Agilent Xcalibur, Ruby |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.818, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 6484, 3458, 2408 |
| R int | 0.023 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.630 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.056, 0.174, 1.03 |
| No. of reflections | 3458 |
| No. of parameters | 240 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.22, −0.18 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020013596/zn2001sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020013596/zn2001Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020013596/zn2001Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2036551
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We are especially grateful to Jamshid Ashurov DSc for help in discussing the results.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C19H18O7 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 358.33 | F(000) = 376 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.396 Mg m−3 |
| a = 5.0789 (4) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| b = 8.0801 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 1498 reflections |
| c = 20.8682 (19) Å | θ = 5.5–75.0° |
| α = 92.481 (7)° | µ = 0.90 mm−1 |
| β = 91.984 (7)° | T = 293 K |
| γ = 94.253 (6)° | Prism, yellow |
| V = 852.62 (12) Å3 | 0.03 × 0.02 × 0.01 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur, Ruby diffractometer | Rint = 0.023 |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Cu) X-ray Source | θmax = 76.1°, θmin = 4.2° |
| /ω scans | h = −6→4 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlisPro; Agilent, 2014) | k = −10→9 |
| Tmin = 0.818, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −25→25 |
| 6484 measured reflections | 3 standard reflections every 100 reflections |
| 3458 independent reflections | intensity decay: 2.6% |
| 2408 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.056 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.174 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0902P)2 + 0.0534P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3458 reflections | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 240 parameters | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.4105 (3) | 0.28804 (17) | 0.27044 (7) | 0.0575 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.3672 (3) | 0.59876 (19) | 0.39973 (8) | 0.0659 (4) | |
| O7 | 0.3450 (3) | 0.10219 (19) | 0.16067 (8) | 0.0685 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.0122 (3) | 0.69625 (19) | 0.30889 (9) | 0.0714 (5) | |
| O4 | −0.2527 (4) | 0.6406 (2) | 0.20033 (9) | 0.0740 (5) | |
| H4 | −0.209283 | 0.687910 | 0.235051 | 0.111* | |
| O6 | 0.0019 (3) | 0.1855 (2) | 0.06667 (8) | 0.0725 (5) | |
| O5 | −0.3071 (4) | 0.4564 (2) | 0.08488 (9) | 0.0792 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.2302 (4) | 0.3341 (2) | 0.22626 (10) | 0.0532 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.4615 (4) | 0.3764 (2) | 0.32748 (10) | 0.0531 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.6627 (4) | 0.3000 (2) | 0.36663 (10) | 0.0547 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.3289 (4) | 0.5145 (2) | 0.34102 (10) | 0.0559 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.0862 (4) | 0.4721 (2) | 0.23720 (11) | 0.0549 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.1951 (4) | 0.2349 (3) | 0.17031 (11) | 0.0570 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.1327 (4) | 0.5696 (3) | 0.29666 (11) | 0.0576 (5) | |
| C5 | −0.1022 (4) | 0.5106 (3) | 0.19027 (12) | 0.0598 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.0153 (4) | 0.2777 (3) | 0.12324 (11) | 0.0591 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.7909 (5) | 0.1680 (3) | 0.33913 (12) | 0.0621 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.747162 | 0.131003 | 0.297010 | 0.074* | |
| C6 | −0.1322 (4) | 0.4180 (3) | 0.13258 (12) | 0.0620 (5) | |
| C13 | 1.0487 (5) | 0.1457 (3) | 0.43582 (13) | 0.0693 (6) | |
| H13 | 1.178385 | 0.095483 | 0.458888 | 0.083* | |
| C12 | 0.9801 (5) | 0.0925 (3) | 0.37353 (13) | 0.0690 (6) | |
| H12 | 1.062501 | 0.004788 | 0.354580 | 0.083* | |
| C15 | 0.7318 (5) | 0.3509 (3) | 0.42988 (11) | 0.0676 (6) | |
| H15 | 0.648243 | 0.437172 | 0.449493 | 0.081* | |
| C14 | 0.9221 (5) | 0.2750 (3) | 0.46366 (13) | 0.0735 (7) | |
| H14 | 0.966483 | 0.310908 | 0.505855 | 0.088* | |
| C16 | 0.5102 (5) | 0.7581 (3) | 0.39759 (14) | 0.0755 (7) | |
| H16A | 0.429300 | 0.821692 | 0.365563 | 0.113* | |
| H16B | 0.689782 | 0.743522 | 0.387050 | 0.113* | |
| H16C | 0.507312 | 0.815778 | 0.438727 | 0.113* | |
| C18 | −0.2471 (6) | 0.1157 (4) | 0.04230 (15) | 0.0884 (9) | |
| H18A | −0.223724 | 0.046870 | 0.004568 | 0.133* | |
| H18B | −0.356737 | 0.203034 | 0.031583 | 0.133* | |
| H18C | −0.329956 | 0.049683 | 0.074221 | 0.133* | |
| C19 | 0.2318 (8) | −0.0502 (3) | 0.1815 (2) | 0.1081 (11) | |
| H19A | 0.058829 | −0.073200 | 0.161721 | 0.162* | |
| H19B | 0.218626 | −0.043294 | 0.227342 | 0.162* | |
| H19C | 0.341133 | −0.137746 | 0.169734 | 0.162* | |
| C17 | −0.2436 (9) | 0.6092 (4) | 0.05619 (19) | 0.1199 (14) | |
| H17A | −0.331407 | 0.608230 | 0.014676 | 0.180* | |
| H17B | −0.056050 | 0.624212 | 0.051646 | 0.180* | |
| H17C | −0.300412 | 0.698631 | 0.082812 | 0.180* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0628 (8) | 0.0517 (7) | 0.0575 (8) | 0.0094 (6) | −0.0003 (7) | −0.0097 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0782 (10) | 0.0584 (8) | 0.0601 (9) | 0.0080 (7) | 0.0036 (8) | −0.0145 (7) |
| O7 | 0.0779 (10) | 0.0586 (9) | 0.0692 (10) | 0.0145 (7) | 0.0065 (8) | −0.0124 (7) |
| O3 | 0.0744 (10) | 0.0578 (9) | 0.0823 (11) | 0.0181 (7) | 0.0011 (8) | −0.0153 (8) |
| O4 | 0.0755 (10) | 0.0626 (9) | 0.0847 (12) | 0.0200 (8) | −0.0046 (9) | −0.0056 (8) |
| O6 | 0.0745 (10) | 0.0820 (11) | 0.0589 (9) | 0.0029 (8) | 0.0009 (8) | −0.0155 (8) |
| O5 | 0.0868 (11) | 0.0719 (10) | 0.0773 (12) | 0.0038 (9) | −0.0178 (9) | 0.0043 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0550 (10) | 0.0496 (10) | 0.0547 (11) | 0.0038 (8) | 0.0037 (9) | −0.0023 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0550 (10) | 0.0492 (10) | 0.0541 (11) | 0.0013 (8) | 0.0058 (9) | −0.0070 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0545 (10) | 0.0497 (10) | 0.0591 (12) | 0.0011 (8) | 0.0036 (9) | −0.0022 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0616 (11) | 0.0486 (10) | 0.0565 (12) | 0.0016 (9) | 0.0064 (9) | −0.0079 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0585 (11) | 0.0474 (10) | 0.0583 (12) | 0.0025 (8) | 0.0050 (9) | −0.0016 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0612 (11) | 0.0510 (10) | 0.0585 (12) | 0.0047 (9) | 0.0063 (9) | −0.0053 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0595 (11) | 0.0472 (10) | 0.0657 (13) | 0.0040 (9) | 0.0096 (10) | −0.0058 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0591 (11) | 0.0503 (11) | 0.0702 (14) | 0.0062 (9) | 0.0036 (10) | −0.0006 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0628 (12) | 0.0570 (11) | 0.0560 (12) | −0.0022 (9) | 0.0039 (10) | −0.0046 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0675 (12) | 0.0539 (11) | 0.0639 (13) | 0.0065 (10) | −0.0025 (10) | −0.0081 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0617 (12) | 0.0585 (12) | 0.0651 (13) | 0.0012 (10) | −0.0036 (10) | 0.0039 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0669 (13) | 0.0645 (13) | 0.0766 (16) | 0.0085 (11) | −0.0065 (12) | 0.0067 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0695 (13) | 0.0565 (12) | 0.0816 (16) | 0.0148 (10) | −0.0023 (12) | −0.0039 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0737 (14) | 0.0685 (13) | 0.0608 (13) | 0.0133 (11) | 0.0015 (11) | −0.0085 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0782 (15) | 0.0806 (16) | 0.0610 (14) | 0.0112 (13) | −0.0066 (12) | −0.0056 (12) |
| C16 | 0.0753 (15) | 0.0613 (13) | 0.0871 (17) | 0.0041 (11) | −0.0025 (13) | −0.0212 (12) |
| C18 | 0.0800 (16) | 0.0908 (19) | 0.090 (2) | −0.0031 (14) | −0.0024 (14) | −0.0297 (15) |
| C19 | 0.129 (3) | 0.0560 (15) | 0.142 (3) | 0.0176 (16) | 0.020 (2) | 0.0052 (17) |
| C17 | 0.164 (4) | 0.085 (2) | 0.107 (3) | −0.005 (2) | −0.047 (3) | 0.0312 (19) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C9 | 1.360 (3) | C5—C6 | 1.387 (3) |
| O1—C2 | 1.368 (2) | C7—C6 | 1.414 (3) |
| O2—C3 | 1.376 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.374 (3) |
| O2—C16 | 1.434 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| O7—C8 | 1.373 (3) | C13—C12 | 1.376 (4) |
| O7—C19 | 1.413 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.384 (4) |
| O3—C4 | 1.252 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| O4—C5 | 1.357 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| O4—H4 | 0.8200 | C15—C14 | 1.373 (4) |
| O6—C7 | 1.365 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| O6—C18 | 1.415 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| O5—C6 | 1.372 (3) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| O5—C17 | 1.416 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C9—C8 | 1.386 (3) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.393 (3) | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.370 (3) | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| C2—C1 | 1.474 (3) | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C15 | 1.391 (3) | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| C1—C11 | 1.403 (3) | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.444 (3) | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C10—C5 | 1.406 (3) | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C10—C4 | 1.443 (3) | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C8—C7 | 1.390 (3) | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C9—O1—C2 | 121.52 (16) | C5—C6—C7 | 119.4 (2) |
| C3—O2—C16 | 114.26 (18) | C12—C13—C14 | 119.1 (2) |
| C8—O7—C19 | 114.8 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.4 |
| C5—O4—H4 | 109.5 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.4 |
| C7—O6—C18 | 119.0 (2) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.5 (2) |
| C6—O5—C17 | 115.0 (2) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| O1—C9—C8 | 116.32 (18) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| O1—C9—C10 | 121.69 (19) | C14—C15—C1 | 120.7 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 122.0 (2) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.7 |
| O1—C2—C3 | 119.82 (19) | C1—C15—H15 | 119.7 |
| O1—C2—C1 | 110.68 (17) | C15—C14—C13 | 120.9 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 129.50 (19) | C15—C14—H14 | 119.5 |
| C15—C1—C11 | 117.9 (2) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.5 |
| C15—C1—C2 | 123.54 (19) | O2—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C11—C1—C2 | 118.60 (19) | O2—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—O2 | 120.3 (2) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.67 (19) | O2—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O2—C3—C4 | 117.84 (18) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—C5 | 118.9 (2) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—C4 | 119.0 (2) | O6—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C5—C10—C4 | 122.2 (2) | O6—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O7—C8—C9 | 120.3 (2) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O7—C8—C7 | 121.05 (19) | O6—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 118.6 (2) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O3—C4—C10 | 121.9 (2) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O3—C4—C3 | 121.7 (2) | O7—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C10—C4—C3 | 116.34 (18) | O7—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| O4—C5—C6 | 119.3 (2) | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| O4—C5—C10 | 120.4 (2) | O7—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C10 | 120.2 (2) | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| O6—C7—C8 | 117.0 (2) | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| O6—C7—C6 | 122.1 (2) | O5—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 120.8 (2) | O5—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—C1 | 120.9 (2) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.5 | O5—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C1—C11—H11 | 119.5 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O5—C6—C5 | 121.6 (2) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O5—C6—C7 | 119.0 (2) | ||
| C2—O1—C9—C8 | −179.93 (18) | C2—C3—C4—C10 | −0.5 (3) |
| C2—O1—C9—C10 | −0.8 (3) | O2—C3—C4—C10 | −176.28 (18) |
| C9—O1—C2—C3 | 0.1 (3) | C9—C10—C5—O4 | 177.6 (2) |
| C9—O1—C2—C1 | 179.66 (17) | C4—C10—C5—O4 | −1.6 (3) |
| O1—C2—C1—C15 | −172.2 (2) | C9—C10—C5—C6 | −3.7 (3) |
| C3—C2—C1—C15 | 7.3 (4) | C4—C10—C5—C6 | 177.1 (2) |
| O1—C2—C1—C11 | 7.3 (3) | C18—O6—C7—C8 | 128.1 (3) |
| C3—C2—C1—C11 | −173.2 (2) | C18—O6—C7—C6 | −56.3 (3) |
| O1—C2—C3—O2 | 176.21 (17) | O7—C8—C7—O6 | −2.2 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—O2 | −3.2 (3) | C9—C8—C7—O6 | 174.70 (19) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.6 (3) | O7—C8—C7—C6 | −177.85 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −178.9 (2) | C9—C8—C7—C6 | −1.0 (3) |
| C16—O2—C3—C2 | 109.3 (2) | C15—C1—C11—C12 | −0.5 (3) |
| C16—O2—C3—C4 | −74.9 (2) | C2—C1—C11—C12 | 180.0 (2) |
| O1—C9—C10—C5 | −178.38 (18) | C17—O5—C6—C5 | 66.7 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C5 | 0.7 (3) | C17—O5—C6—C7 | −115.1 (3) |
| O1—C9—C10—C4 | 0.8 (3) | O4—C5—C6—O5 | 1.2 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C4 | 179.88 (19) | C10—C5—C6—O5 | −177.50 (19) |
| C19—O7—C8—C9 | 91.8 (3) | O4—C5—C6—C7 | −177.0 (2) |
| C19—O7—C8—C7 | −91.4 (3) | C10—C5—C6—C7 | 4.4 (3) |
| O1—C9—C8—O7 | −2.4 (3) | O6—C7—C6—O5 | 4.3 (3) |
| C10—C9—C8—O7 | 178.53 (19) | C8—C7—C6—O5 | 179.8 (2) |
| O1—C9—C8—C7 | −179.25 (18) | O6—C7—C6—C5 | −177.5 (2) |
| C10—C9—C8—C7 | 1.7 (3) | C8—C7—C6—C5 | −2.0 (3) |
| C9—C10—C4—O3 | 179.0 (2) | C1—C11—C12—C13 | −0.3 (4) |
| C5—C10—C4—O3 | −1.8 (3) | C14—C13—C12—C11 | 0.8 (4) |
| C9—C10—C4—C3 | −0.2 (3) | C11—C1—C15—C14 | 0.8 (4) |
| C5—C10—C4—C3 | 179.03 (19) | C2—C1—C15—C14 | −179.7 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—O3 | −179.7 (2) | C1—C15—C14—C13 | −0.3 (4) |
| O2—C3—C4—O3 | 4.6 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.5 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O4—H4···O3 | 0.82 | 1.87 | 2.599 (2) | 147 |
| C16—H16A···O3 | 0.96 | 2.51 | 3.079 (3) | 118 |
| C16—H16B···O3i | 0.96 | 2.39 | 3.258 (3) | 150 |
| C18—H18B···O5 | 0.96 | 2.28 | 2.897 (4) | 121 |
| C18—H18C···O7ii | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.278 (4) | 135 |
| C17—H17C···O4 | 0.96 | 2.52 | 3.010 (4) | 111 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z; (ii) x−1, y, z.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by Chinese Academy of Sciences Center of Drag Discovery and Development Center of Central Asia grant CAM 201907.
References
- Agilent (2014). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Aree, T. & Sawasdee, P. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o2706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Arituluk, Z., Kocak, C., Renda, G., Ekizoglu, M. & Ezer, N. (2019). J Res Pharm. Pract. 23(3), 552–558.
- Dai, Z. J., Lu, W. F., Gao, J., Kang, H. F., Ma, Y. G., Zhang, S. Q., Diao, Y., Lin, S., Wang, X. J. & Wu, W. Y. (2013). BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 13, 240–248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Etter, M. C. (1990). Acc. Chem. Res. 23, 120–126.
- Etti, S., Shanmugam, G., Ponnuswamy, M. N., Balakrishna, K. & Vasanth, S. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o846–o848.
- Geng, H.-W., Wang, G.-C., Li, G.-Q., Jiang, R.-W. & Li, Y.-L. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Jang, S. I., Kim, H. J., Hwang, K. M., Jekal, S. J., Pae, H. O., Choi, B. M., Yun, Y. G., Kwon, T. O., Chung, H. T. & Kim, Y. C. (2003). Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 25, 585–594. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Leonova, G. N., Shutikova, A. L., Lubova, V. A. & Maistrovskaya, O. S. (2020). Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 168, 665–668. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.-L., Qi, Y.-Y., Liu, R.-M., Sun, A.-L. & Wang, D.-Q. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o3831–o3832.
- Park, H. G., Yoon, S. Y., Choi, J. Y., Lee, G. S., Choi, J. H., Shin, C. Y., Son, K. H., Lee, Y. S., Kim, W. K., Ryu, J. H., Ko, K. H. & Cheong, J. H. (2007). Eur. J. Pharmacol. 574, 112–119. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sauvage, S., Granger, M., Samson, E., Majumdar, A., Nigam, P. & Nahar, L. (2010). Oriental Pharmacy Experimental Medicine. 10, 304–309.
- Shang, X. F., He, X. R., He, X. Y., Li, M. X., Zhang, R. X., Fan, P. P., Zhang, Q. L. & Jia, Z. P. (2010). J. Ethnopharmacol. 128, 279–313. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Shoja, M. (1997). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 212, 385–386.
- Siemens (1994). XP. Siemens Analytical X-Ray Instruments Inc.,Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Ting, H.-Y., Watson, W. H. & Domínguez, X. A. (1972). Acta Cryst. B28, 1046–1051.
- Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). CrystalExplorer17.5. University of Western Australia. http://hirshfeldsuface.net
- Vijayalakshmi, J., Rajan, S. S., Srinivasan, R. & Ramachandran Nair, A. G. (1986). Acta Cryst. C42, 1752–1754.
- Wallet, J.-C., Gaydou, E., Tinant, B., Declercq, J.-P., Baldy, A. & Bonifassi, P. (1990a). Acta Cryst. C46, 1131–1133.
- Wallet, J.-C., Gaydou, E. M., Jaud, J. & Baldy, A. (1990b). Acta Cryst. C46, 1536–1540.
- Yu, J., Liu, H., Lei, J., Tan, W., Hu, X. & Zou, G. (2007). Phytother. Res. 21, 817–822. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020013596/zn2001sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020013596/zn2001Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989020013596/zn2001Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2036551
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report






