Abstract
Respiratory infections, like the current COVID‐19 pandemic, target epithelial cells in the respiratory tract. Alveolar macrophages (AMs) are tissue‐resident macrophages located within the lung. They play a key role in the early phases of an immune response to respiratory viruses. AMs are likely the first immune cells to encounter SARS‐CoV‐2 during an infection, and their reaction to the virus will have a profound impact on the outcome of the infection. Interferons (IFNs) are antiviral cytokines and among the first cytokines produced upon viral infection. In this study, AMs from non‐infectious donors are challenged with SARS‐CoV‐2. We demonstrate that challenged AMs are incapable of sensing SARS‐CoV‐2 and of producing an IFN response in contrast to other respiratory viruses, like influenza A virus and Sendai virus, which trigger a robust IFN response. The absence of IFN production in AMs upon challenge with SARS‐CoV‐2 could explain the initial asymptotic phase observed during COVID‐19 and argues against AMs being the sources of pro‐inflammatory cytokines later during infection.
Keywords: alveolar macrophages, COVID‐19, interferon, interferon lambda, SARS‐CoV‐2
Subject Categories: Development & Differentiation, RNA Biology
Alveolar macrophages produce interferons and activate interferon stimulated genes when challenged with influenza A virus or Sendai virus, but not when challenged with SARS‐CoV‐2, suggesting that its genomic RNA is undetectable for innate immune sensors.

Introduction
The apical side of the airway epithelia is populated by a specialised subset of macrophages known as alveolar macrophages (AMs). AMs are a specific type of tissue‐resident macrophages that originate from the yolk sac during early embryogenesis (Guilliams et al, 2013). These cells have the capacity to self‐replenish (Hashimoto et al, 2013). However, bone marrow‐derived monocytes have also been shown to be recruited to the lung to repopulate this organ following specific conditions such as radiation (Brunstetter et al, 1971) and infection (Divangahi et al, 2015). AMs work closely together with the epithelial cell layer to maintain a healthy lung by clearing apoptotic cells and cellular debris, as well as maintaining surfactant homeostasis (Hussell & Bell, 2014). In addition, they are likely to be a major determinant of early responses to respiratory virus infections due to their abundant numbers and their physical location in the lung. Thus, AMs are probably the first type of immune cells that respiratory viruses encounter (Pribul et al, 2008). In line with this, others have reported that AMs are one of the main producers of type I interferons (IFNs) during infection with respiratory viruses, like influenza virus (Kumagai et al, 2007; Wang et al, 2012; Hussell & Bell, 2014; Divangahi et al., 2015) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) (Goritzka et al, 2015). A key feature of innate immune cells like macrophages and dendritic cells is the expression of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), both on their cell surface and within endosomes and phagosomes. PRRs enable the recognition of pathogens by AMs in their immediate environment even when they are not productively infected (Lee & Barton, 2014; Tatematsu et al, 2018).
IFNs are classical antiviral cytokines which constitute a critical first line of defence against viral infections by activating the transcription of numerous antiviral factors (Schoggins et al, 2011). IFNs are divided into three groups (type I, II and III IFNs) based on their receptor usage (Pestka et al, 2004). However, only type I and type III IFNs are true antiviral IFNs, whereas type II IFNs mainly induce immunomodulatory activities (Young & Bream, 2007). The induction of type I and type III IFNs is mediated by PRRs in response to the invading virus (Onoguchi et al, 2007). Both production of IFN and a cellular response to IFN are critical steps for the restriction of viral dissemination.
In December 2019, a new series of respiratory symptoms of a novel aetiology emerged in Wuhan, Hubei province, China (Wang et al, 2020; Zhou et al, 2020). The disease was named coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) and is caused by a novel coronavirus designated as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) (Zhou et al., 2020; Zhu et al, 2020). SARS‐CoV‐2 belongs to the genus Betacoronavirus and is an enveloped virus with a positive‐sense, single‐stranded RNA genome of approx. 30 kilobases. Previously, other members of the Betacoronavirus genus have caused high mortality outbreaks: SARS‐CoV‐1 in 2002 and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)‐CoV in 2012. SARS‐CoV‐2 is closely related to SARS‐CoV‐1 and more distantly to MERS‐CoV and displays 79 and 50% nucleotide identity with SARS‐CoV‐1 and MERS‐CoV, respectively (Lu et al, 2020). The COVID‐19 outbreak spread rapidly, and quickly became a global pandemic. This new pandemic has challenged healthcare systems worldwide, causing severe economic and social distress. Many aspects of COVID‐19 are still unknown, and further research is needed in order to understand the disease mechanism.
As described above, AMs are likely to be the first immune cells encountering SARS‐CoV‐2 in the beginning of the infection. Using a model where lung biopsies were infected in vitro, a recent study detected SARS‐CoV‐2 RNA in AMs (Chu et al, 2020). Furthermore, AMs are known to be some of the best producers of IFNs during infection with other pulmonary viruses as described above. Thus, AMs are thought to be major producers of pro‐inflammatory cytokines and, in particular, IFNs during SARS‐CoV‐2 infection. However, recent reports show that SARS‐CoV‐2 only induces a weak expression of IFNs in infected human lung tissue (Blanco‐Melo et al, 2020; Chu et al, 2020). In line with those studies, a recent set of publications identified a series of SARS‐CoV‐2 encoded genes restricting IFN production (Lei et al, 2020). Together, these studies suggest that SARS‐CoV‐2 evades IFN production in lung epithelial cells. However, we suspected that AMs, being immune cells, would have the potential to recognise SARS‐CoV‐2 without allowing viral replication, and thus prevent the virus from synthetising its IFN agonist. To test our hypothesis, AMs obtained from bronchoalveolar lavages (BAL) from donors diagnosed for non‐infectious lung disorders were challenged with SARS‐CoV‐2. We demonstrate that this specific cellular subset of macrophages does not sense SARS‐CoV‐2 and, therefore, also does not produce IFN in response to SARS‐CoV‐2. This observation contrasts with the strong IFN production observed in response to other respiratory viruses, such as influenza A virus (IAV) or Sendai virus (SeV).
Results and Discussion
AMs are efficient producers of IFNs upon viral challenge
AMs from nine different donors were purified from BAL fluid by allowing them to attach to the culture dish for 2 h. At this point, we selected a sample for RNA purification (labelled c for control in Fig 1). The purpose of this sample was to determine the endogenous expression of IFNs and IFN‐stimulated genes (ISGs) as well as to test how the culturing method affected IFN and ISG expression. The donor‐to‐donor variation was acceptable within one log unit, but with a trend towards lower ISG expressing after culturing (comparing c with untreated mock).
Figure 1. Alveolar macrophages are highly responsive to IFN‐λ and good producers of IFNs.
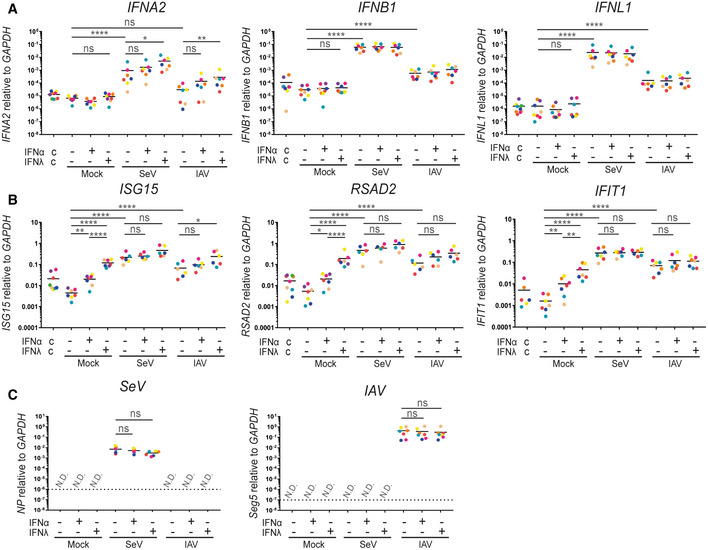
-
A–C(A) Total RNA was harvested and subjected to qPCR for quantification of the IFN response measured by IFNA2, IFNB1 and IFNL1. (B) ISG response measured by ISG15 and RSAD2. (C) Quantification of the presence of SeV or IAV. (A–C) Each colour corresponds to a donor; 9 different donors were analysed. The dashed line represents the detection limit. An ordinary one‐way ANOVA test was used for the statistical analysis: ns, not significant; *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001.
Alveolar macrophages from different donors were purified from BAL fluid by allowing them to attach to the culture dish for 2 h. Subsequently, they were pre‐treated overnight with either type I or type III IFNs (1 ng/ml IFN‐λ1 and 10 U/ml IFN‐α2, respectively) before infection with Sendai virus (SeV) and influenza A virus (IAV, strain PR8) for 6 h as indicated. The column labelled c shows control samples collected directly after purification.
Source data are available online for this figure. Source data are available online for this figure.
Pre‐exposure of immune cells to low concentrations of IFNs increases their capacity to produce IFN‐αs upon subsequent viral infection, a phenomenon known as priming (Stark et al, 1998). In order to verify this phenomenon in AMs and to maximise their IFN‐ability, we treated the remaining cells with either type I (IFN‐α) or type III (IFN‐λ) IFNs overnight before infection with SeV or IAV for 6 h (Fig 1). IAV is a natural human pathogen of the airways that encodes the NS1 protein reported as a potent inhibitor of IFN production; hence, IAV induces moderate IFN production (Kochs et al, 2009). In sharp contrast, the SeV Cantell strain used in this study, which causes respiratory infections in rodents, contains a large number of defective viral particles known to potently stimulate IFN responses (Cantell et al, 1981; Baum et al, 2010).
Both IFNB1 and IFNL1 were significantly induced upon SeV and IAV challenge of AMs, but the expression of those IFNs was not influenced by priming (Fig 1A). Furthermore, SeV resulted in a significant induction of IFNA2 without IFN priming. In comparison, IAV challenge resulted in a trend towards increased IFNA2 expression but this was not significant probably due to donor‐to‐donor variation. Priming with type I IFN showed a trend towards increased IFNA2 expression for both viruses, but in neither case was this significant. In contrast, priming with type III IFN led to a significant enhancement of IFNA2 expression with both viruses, suggesting that priming of AMs is necessary for proper induction of IFNA2 but not IFNB1 or IFNL1 (Fig 1A). While AMs are clearly very responsive to IFN‐λ, there is no international unit definition for IFN‐λ; thus, we compare somewhat arbitrary concentrations of the two types of IFNs.
ISG expression in AMs was also measured (Fig 1B). AMs responded well to pre‐treatment with both type I and type III IFNs. The pre‐treatment effect was diminished when comparing the infected AMs to the uninfected. This is most likely due to viral‐induced IFN production, since the viral infection increased ISG expression on its own. However, in uninfected cells, ISG expression was stronger upon treatment with type III IFN compared to type I IFN, agreeing with our observations in Fig 1A. Furthermore, we observed a slight tendency towards increased ISG expression in the type III pre‐treated, virus‐challenged cells.
In order to examine whether viral loads were comparable for both viruses and if pre‐treatment with IFNs influenced viral load, we measured the amount of viral RNA present within AMs (Fig 1C). For SeV, the gene encoding the nucleoprotein was assessed and no significant difference between no treatment and pre‐treatment with either of the two IFNs was observed. A similar trend was detected for IAV, when the amount of IAV segment 5 encoding the nucleoprotein was quantified. However, we measured more viral RNA for IAV compared to SeV. This could in part be due to the defective viral particles of SeV described above.
Our data are consistent with previous studies (Kumagai et al, 2007; Wang et al, 2012; Hussell & Bell, 2014; Divangahi et al, 2015), demonstrating that AMs are efficient producers of type I IFNs (Fig 1A). Furthermore, we demonstrated that AMs are both highly responsive to and good producers of type III IFNs. We also show that priming of AMs is necessary for the induction of IFNA2 but not IFNB1 or IFNL1. The high responsiveness of AMs to type III IFNs as well as their ability to produce type III IFNs is in accordance with the hypothesis that type III IFNs are critical for the mucosal immune response to viral infections and the concurrent assumption that AMs play a critical role in the response to respiratory viruses (Wack et al, 2015).
AMs do not produce IFNs upon SARS‐CoV‐2 challenge
As we have just shown, AMs are efficient producers of IFNs in response to IAV and SeV (Fig 1). Therefore, we wanted to investigate the production of IFNs upon challenge with SARS‐CoV‐2. Following pre‐treatment with type III IFN, AMs from six different donors were challenged with SARS‐CoV‐2 (Fig 2). Since AMs showed an increased responsiveness to IAV and SeV following type III IFN priming, we opted for the use of type III IFN in two different doses in our SARS‐CoV‐2 experimental setup. Poly(I:C) was used as a surrogate for viral infection and positive control in our experiments with SARS‐CoV‐2, since local regulations in Denmark prevented us from working with other viruses concurrent with working with SARS‐CoV‐2 virus. Poly(I:C) was delivered directly to the culture medium; hence, AMs had to respond to it either through cellular surface receptors or by endocytosis. Only Poly(I:C) treatment was capable of inducing the measured IFNs, whereas no significant IFN induction was observed upon SARS‐CoV‐2 challenge (Fig 2A). Pre‐treated with type III IFN also failed to induce a significant increase in IFN production upon SARS‐CoV‐2 challenge. Furthermore, SARS‐CoV‐2 challenge did not promote ISG expression compared to uninfected and untreated cells (Fig 2B). As expected, both Poly(I:C) treatment and IFN pre‐treatment induced ISG expression, but no significant changes were observed when challenging the pre‐treated cells with SARS‐CoV‐2. The amount of viral RNA, measured by the nucleoprotein gene N, was furthermore unaffected by pre‐treatment with either dose of IFN (Fig 2C). Thus, much to our surprise, challenge of AMs with SARS‐CoV‐2 did not result in any measurable IFN induction.
Figure 2. Alveolar macrophages do not produce an IFN response upon SARS‐CoV‐2 challenge.
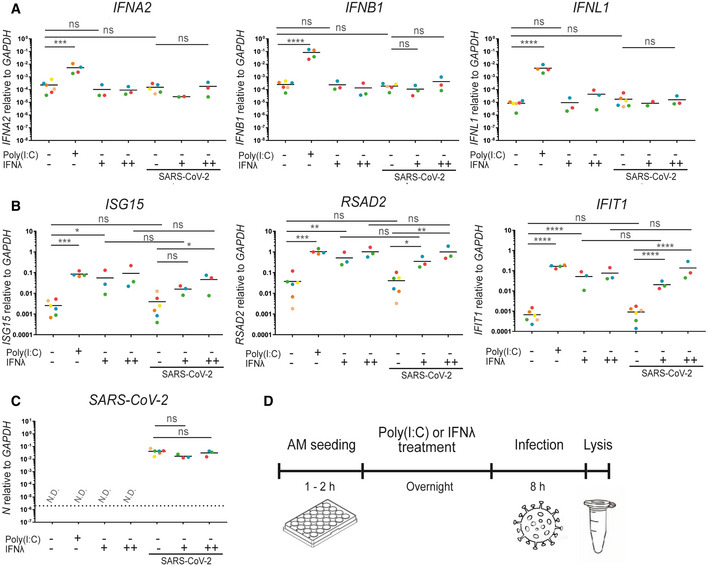
-
A–DAlveolar macrophages from different donors were purified from BAL fluid and pre‐treated with either Poly(I:C) or IFN‐λ1 (+; 1 ng/ml, or ++; 10 ng/ml) before infection with SARS‐CoV‐2. (A) Total RNA was harvested and subjected to qPCR for quantification of the IFN response measured by IFNA2, IFNB1 and IFNL1 (Donors marked in orange and blue were not quantifiable in all test conditions). (B) ISG response measured by ISG15, RSAD2 and IFIT1. (C) Quantification of the presence of SARS‐CoV‐2. (D) An overview of the timeline of the experiment. (A–C) Each colour corresponds to a donor; 6 different donors were analysed. The dashed line represents the detection limit. An ordinary one‐way ANOVA test was used for statistical analysis: ns, not significant; *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001.
Source data are available online for this figure. Source data are available online for this figure.
SARS‐CoV‐2 does not display any interaction with the IFN system in AMs
We altered the experimental setup from pre‐treatment with type III IFN before SARS‐CoV‐2 challenge (Fig 2D) to SARS‐CoV‐2 challenge prior to type III IFN or Poly(I:C) treatment (Fig 3A). In this setup, the challenge with SARS‐CoV‐2 was allowed to proceed for 8 h before we treated with either IFN‐λ or Poly(I:C). Thus, the cells were exposed to SARS‐CoV‐2 for 20 h. Regardless of the exposure time of the AMs to SARS‐CoV‐2 (8 h in Fig 2 and 20 h in Fig 3), no IFN production was observed (Fig 3B). Furthermore, SARS‐CoV‐2 challenge by itself did not alter ISG expression (Fig 3C). In contrast, Poly(I:C) treatment was capable of inducing IFN production both in unchallenged cells and in cells challenged with SARS‐CoV‐2 prior to treatment (Fig 3B). Furthermore, there was no significant difference in Poly(I:C)‐induced IFN production (true for all three IFNs tested) between unchallenged and SARS‐CoV‐2 challenged cells. Both Poly(I:C) and IFN‐treated cells did, as expected, induce expression of ISGs. Furthermore, the amount of viral RNA did not change upon treatment with either Poly(I:C) or IFN (Fig 3D). We also tested both SARS‐CoV‐2‐challenged and SARS‐CoV‐2‐unchallenged cells from two donors for the expression of IFIT1, and RSAD2 by Western blot (Fig 3E). Both donors showed induction of the two ISGs (IFIT1 and RSAD2) at the protein level upon Poly(I:C) and IFN treatment, but SARS‐CoV‐2 challenge did not induce their expression by itself, thus confirming the qPCR results.
Figure 3. SARS‐CoV‐2 challenge does not affect the IFN response in alveolar macrophages.

-
A–E(A) Timeline of the experiment. (B) Total RNA was harvested and subjected to qPCR for quantification of the IFN response measured by IFNA2, IFNB1 and IFNL1. (C) ISG response measured by ISG15, RSAD2 and IFIT1 (Donors marked in green and red were not quantifiable in all test conditions). (D) Quantification of the presence of SARS‐CoV‐2. (E) Western blots were performed using samples from two donors. (B–D) Each colour corresponds to a donor; 5 different donors were analysed. The dashed line represents the detection limit. An ordinary one‐way ANOVA test was used for statistical analysis: ns, not significant; *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001.
Alveolar macrophages from different donors were purified from BAL fluid and infected with SARS‐CoV‐2 before treatment with either Poly(I:C) or IFN‐λ1 (1 ng/ml).
Source data are available online for this figure. Source data are available online for this figure.
The lack of a functional interactions between SARS‐CoV‐2 and the IFN system suggests that AMs are not productively infected. Therefore, we used a mass spectrometry‐based approach to test for SARS‐CoV‐2‐related proteins. We collected samples 2 and 24 h postchallenge and could detect the nucleocapsid protein in all samples challenged with SARS‐CoV‐2; importantly, those samples were separated from the untreated control by at least two orders of magnitude (Fig 4A). However, the amount of nucleocapsid protein detected declined over time (Fig 4B). We were furthermore not able to detect viral proteins, which are synthesised upon viral infection such as the replicase R1AB. Both observations support the conclusion that the SARS‐CoV‐2 challenge did not lead to the release of free SARS‐CoV‐2 RNA to the cytoplasm. We also tested the expression of the ACE2 receptor on AMs and were not able to reliably detect expression of ACE2 mRNA in AMs, whereas we did reproducibly detect ACE2 mRNA in primary human airway epithelial cells (Fig 5A).
Figure 4. SARS‐CoV‐2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein decreases over time.
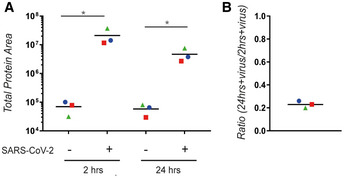
- The amount of SARS‐CoV‐2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein was quantified using LC‐MS/MS.
- After subtraction of the background (unchallenged AMs), the ratio between the amount of SARS‐CoV‐2 nucleocapsid phosphoprotein at 24 and 2 h was calculated. (A–B) Each colour corresponds to a donor; 3 different donors were analysed. An ordinary one‐way ANOVA test was used for statistical analysis: ns, not significant; *P ≤ 0.05.
Alveolar macrophages from different donors were purified from BAL and treated with SARS‐CoV‐2 for either 2 or 24 h.
Source data are available online for this figure. Source data are available online for this figure.
Figure 5. Determination of viral infection effectivity.
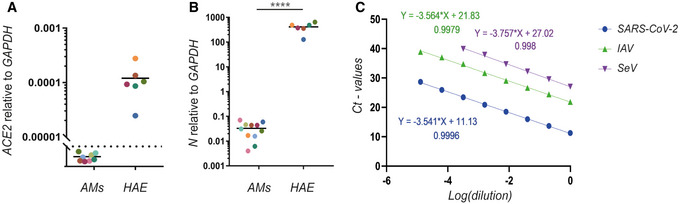
- Total RNA was harvested from AMs and primary human airway epithelial cells (HAE) and subjected to qPCR for quantification of the ACE2 receptor. Each colour corresponds to a donor. The dashed line represents the detection limit.
- The presence of nucleoprotein mRNA of SARS‐CoV‐2 in AMs and primary HAE was also quantified after SARS‐CoV‐2 treatment. (A–B) Each colour corresponds to a donor. An unpaired t‐test test was used for statistical analysis: ****P ≤ 0.0001.
- Primer efficiency was tested using serial dilutions of positive samples using qPCR. The C t values were plotted on a logarithmic scale along with the corresponding dilutions before performing a linear regression in order to calculate the slope of the trend line through the data points. This analysis revealed an amplification factor of 1.92, 1.91 and 1.85 for the SARS‐CoV‐2, IAV and SeV primer set, respectively. The different colours correspond to different primer sets.
Source data are available online for this figure. Source data are available online for this figure.
The absence of IFN induction in AMs suggests that SARS‐CoV‐2 genomic RNA is undetectable for innate immune sensors
Although we observed no IFN production upon SARS‐CoV‐2 challenge, we detected viral RNA in AMs (Fig 3D). The amount of viral RNA was comparable to the levels of viral RNA in both SeV and IAV infections (Figs 1C and 2C) both of which led to a robust IFN induction. While the levels of SARS‐CoV‐2 RNA we measured within AMs are approximately 10,000‐fold lower than what we would measure in infected human airway epithelial cells (Fig 5B), we were unable to detect viral RNA in the non‐challenged cells. The level of RNA that we detect from SARS‐CoV‐2 is lower than the one of IAV but above the one of SeV, which both give a robust IFN response, suggesting that the levels of SARS‐CoV‐2 RNA present within AMs are in principle sufficient to initiate an IFN response. All primers were designed to measure the nucleoprotein encoding RNA of the respective viruses (SARS‐CoV‐2; N, IAV; segment 5, SeV; NP). As part of the primer validation, the primer efficiency was tested by serial dilutions of the target genes in order to make sure that the amplification efficiency was similar for the three viruses and within the optimal range for qPCR performance (Fig 5C). We estimated an amplification factor of 1.92, 1.91 and 1.85 for the SARS‐CoV‐2, IAV and SeV primer sets, respectively. Thus, there is no obvious technical bias by comparing the viral RNA despite using different primer sets. Using those parameters, we measured an average level of 0.37, 0.005 and 0.03 relative to GADPH mRNA for IAV, SeV and SARS‐CoV‐2, respectively. Therefore, our data indicate that SARS‐CoV‐2 RNA is difficult to detect for the innate immune sensors present within AMs.
As we do not observe any production of SARS‐CoV‐2‐related proteins after challenge with the virus (Fig 4), it is unlikely that the virus actively suppresses IFN induction. Therefore, our data suggest that SARS‐CoV‐2 avoids triggering the IFN induction pathway by somehow masking its viral RNA and thereby evading recognition by the PRRs. The family of Coronoviridae is known to contain a cap structure on the viral genome resembling the 5ʹ‐cap of eukaryotic mRNAs (Chen & Guo, 2016). This structure prevents the viral RNA from activating the host innate immune response through the RIG‐I/MAVS pathway, which recognises single‐stranded RNAs without a cap structure (Pichlmair et al, 2006). This pathway is known to recognise both the SeV and the IAV (Baum et al, 2010; Sakabe et al, 2011; Yu et al, 2011). However, whether this capability of producing a 5ʹ‐cap‐like structure is also preserved for SARS‐CoV‐2 will require further investigation. Finally, both TLR3 and TLR7 can also recognise virus‐derived RNA and both pathways are assumed to be operational in AMs, but they also appear incapable of recognising SARS‐CoV‐2.
Our findings have important implications for understanding the mechanism behind SARS‐CoV‐2 infection. Here, we show that AMs do not recognise the SARS‐CoV‐2, and upon viral challenge fail to produce an IFN‐mediated response. This implies that the immune system is not activated appropriately in the initial phase of infection and allows the virus to replicate until further damage is inflicted upon the lung tissue. The early phase of COVID‐19 infection is characterised by a low level of symptoms that allows establishment of viraemia in infected individuals and causes immense problems with virus spreading in the community. The failure of AMs to recognise SARS‐CoV‐2 may be linked to this low‐symptom phase of the disease.
Our research also shows that AMs are capable of both producing and responding to IFNs during a SARS‐CoV‐2 infection, which implies that the use of exogenous IFN or other immunostimulatory drugs to boost antiviral immunity might be an effective strategy for an early treatment of SARS‐CoV‐2 infections. We have not, however, directly addressed how SARS‐CoV‐2 evades the innate immune response and suppresses endogenous IFN production. Further research on this topic is hence crucial in order to fully understand the disease mechanism behind COVID‐19.
Materials and Methods
Ethics
The project was performed in accordance with local and national Danish laws and regulations. The project has been approved by the Health Research Ethics Committee of Region Midtjylland, Denmark (Journal nr. 1‐10‐72‐103‐20).
Alveolar macrophages
BAL fluids were obtained from 20 donors without symptoms of acute infection that were investigated for cancer and processed within 6 h. For isolation of the alveolar macrophages, the BAL was centrifuged, and cells were resuspended in 10 ml cold Hank’s balanced salt solution (HBSS, Sigma‐Aldrich). The cells were washed twice in cold HBSS before they were seeded at a density of 1 × 106 cells/ml in RPMI 1640 medium (Sigma‐Aldrich) supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin and streptomycin. The cells were incubated at 37°C for 2 h before non‐adherent cells were removed and fresh media with or without stimulating agents was added.
Primary Human Airway Epithelial cells
Primary nasal cells were isolated and cultured in monolayer culture using tissue culture flask coated with 0.1 mg/ml Bovine type I collagen solution (Sigma‐Aldrich). Cells were seeded and submerged in 2× P/S (200 U/ml Pen/Strep) DMEM‐low glucose (Sigma‐Aldrich) mixed 1:1 with 2× Monolayer medium (Airway Epithelium Cell Basal Medium (PromoCell), supplemented with two packs of Airway Epithelial Cell Growth Medium Supplement (PromoCell) without triiodothyronine +1 ml of 1.5 mg/ml BSA). When cultures reached full confluency Air‐liquid interface (ALI) was introduced and medium was changed to ALI medium (PneumaCult ALI medium kit (StemCell) with ALI medium supplement (StemCell) and 100 U/ml Pen/strep) supplemented with 24 µg of hydrocortisone (StemCell) and 0.2 mg heparin (StemCell). Membranes were allowed at least 21 days of differentiation, verified by extensive cilia beating and mucus covering.
Infection and stimulation
AMs were infected with either 5 HAU/ml SeV (Cantell strain) or 0.1 EID50/cell IAV (PR8 strain) for 6 h or 1 MOI SARS‐CoV‐2 (291.3 FR‐4286, a kind gift from Professor Georg Koch, Freiburg) for 8 h. The primary Human Airway Epithelial cells were infected with 0.05 MOI SARS‐CoV‐2 for 24 h. The SARS‐CoV‐2 virus was amplified using primary Human Airway Epithelial cells then tittered on Vero cells. SARS‐CoV‐2 was verified as the infectious substance by PCR. Stimulation was performed either pre‐ or post‐infection with either 10 U/ml IFN‐α2 (Millipore) or 1 or 10 ng/ml IFN‐λ1 from (Mohlenberg et al, 2019) overnight.
qPCR
Total RNA was extracted with the E.Z.N.A. Total RNA Kit I (Omega BioTek) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The cDNA synthesis was performed using RevertAid Reverse Transcriptase and random hexamer primer according to the manufacturer's instructions (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The cDNA was quantified by qPCR using SYBR Green I (Roche) and a LightCycler 480 Instrument II (Roche). The following primers were used as follows:
GAPDH: Forward 5ʹ‐GCTCCTCCTGTTCGACAGTCA, Reverse 5ʹ‐ACCTTCCCCATGGTGTCTGA.
IFNA2: Forward 5ʹ‐AAATACAGCCCTTGTGCCTGG, Reverse 5ʹ‐GGTGAGCTGGCATACGAATCA.
IFNB1: Forward 5ʹ‐TGGGAGGATTCTGCATTACC, Reverse 5ʹ‐AAGCAATTGTCCAGTCCCAG.
IFNL1: Forward 5ʹ‐TTCCAAGCCCACCACAACTG, Reverse 5ʹ‐GTGACTCTTCCAAGGCGTCC.
ISG15: Forward 5ʹ‐TCCTGCTGGTGGTGGACAA, Reverse 5ʹ‐TTGTTATTCCTCACCAGGATGCT.
RSAD2: Forward 5ʹ‐CTTTGTGCTGCCCCTTGAG, Reverse 5ʹ‐TCCATACCAGCTTCCTTAAGCAA.
IFIT1: Forward 5ʹ‐CCTCCTTGGGTTCGTCTACA, Reverse 5ʹ‐GGCTGATATCTGGGTGCCTA.
ACE2: Forward 5ʹ‐GGAGTTGTGATGGGAGTGAT, Reverse 5ʹ‐GATGGAGGCATAAGGATTTT.
SeV ‐ NP: Forward 5ʹ‐ATGCAGCAGTACGTCACAGG, Reverse 5ʹ‐AGGCACTGCTGATCTTCGAT.
IAV ‐ seq5: Forward 5ʹ‐CTAGCACGGTCTGCACTCAT, Reverse 5ʹ‐TCAAAGTCGTACCCACTGGC.
SARS‐CoV‐2 ‐ N: Forward 5ʹ‐AAATTTTGGGGACCAGGAAC, Reverse 5ʹ‐TGGCACCTGTGTAGGTCAAC.
The cycling parameters were 95°C for 10 min followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 10 s, 60°C for 5 s and 72°C for 4 s. The crossing points of the amplification curves were determined using the second derivative method on the LightCycler 480 Instrument II software 1.5 (Roche). Ct values higher than 50 cycles were determined as non‐detectable. The level of mRNA was normalised against internal GAPDH mRNA content, which was used as a reference gene. Relative mRNA levels of each target gene were calculated using the following formula: 2(−(Ct (target)−Ct (reference))).
Western blot
AMs were lysed using 60 µl of lysis buffer consisting of Pierce RIPA lysis buffer (Thermo) supplemented with 5 IU/ml benzonase (Sigma), 10 mM NaF and 1× complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche). A BCA protein assay kit (Thermo) was used to determine protein concentration, and lysis buffer was used to equalise samples. Before loading, samples containing 1× XT Sample Buffer were denatured for 2 min at 98°C (Bio‐Rad) and 1× XT Reducing Agent (Bio‐Rad). For separation by SDS–PAGE, 8–18 µg of reduced samples was loaded on a 4–20% Criterion TGX precast gradient gels (Bio‐Rad). Each gel was run at 70 V for 20 min followed by approx. 45–60 min at 110 V. Protein transfer onto PVDF membranes (Bio‐Rad) was done using a Trans‐Blot Turbo Transfer for 7 min. Blocking was done in PBS (BIOWEST) with 0.05% Tween‐20 (Sigma‐Aldrich) (PBST) supplemented with 5% skim‐milk powder (Sigma‐Aldrich) for 1.5 h at room temperature. Following blocking, membranes were cut and incubated with one of the following specific primary antibodies diluted in PBST: anti‐Spike (GeneTex, #GTX632604), anti‐IFIT1 (Cell Signalling, #14769, 1:1,000), anti‐RSAD2 (Cell Signalling, #13996, 1:1,000) and anti‐Vinculin (Cell Signalling, #18799, 1:1,000). Anti‐Vinculin was used as a loading control. Following incubation with primary antibodies, membranes were washed three times using PBST. Following the washed, secondary antibodies, peroxidase‐conjugated F(ab)2 donkey anti‐mouse IgG (Jackson, #715‐036‐150, 1:10,000) or peroxidase‐conjugated F(ab)2 donkey anti‐rabbit IgG (Jackson, #711‐036‐152, 1:10,000), were added to the membranes in PBST + 1% milk powder. Incubation with secondary antibodies was done for 1.5 h at room temperature. Lastly, membranes were washed thrice with PBST before being exposed using either SuperSignal West Pico PLUS chemiluminescent substrate (Thermo) or the SuperSignal West Femto maximum sensitivity substrate (Thermo). Imaging was done using an Image Quant LAS4000 mini imager (GE Healthcare).
Mass spectrometry
Sample preparation—cells were lysed in 6 M urea, 20 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.4. Protein concentration was estimated using the 2D Quant Kit (GE Healthcare). Fifty micrograms of each sample was reduced in 10 mM DTT for 30 min at room temperature, followed by alkylation using 25 mM IAA incubated for another 30 min, while kept dark. Samples were transferred to 10 kDa cut‐off spin filters (Millipore) and spun for 30 min at 14,000 g to remove urea. The filters were washed once in 50 µl 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate before digested at 37°C overnight with 75 µl 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate added 1 µg MS grade trypsin (Sigma). The next day, peptides were recovered by centrifugation and acidified using 10 µl 5% formic acid. Peptide samples were micropurified prior to MS analysis. Samples amounts used for the MS analysis were normalised based on A280 using a NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Scientific).
LC‐PRM‐MS—The liquid chromatography‐parallel reaction monitoring‐mass spectrometry (LC‐PRM‐MS) analysis was performed on an Orbitrap Eclipse mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific) equipped with an in‐line Easy nLC‐1200 (Thermo Scientific). Samples were injected and trapped on an in‐house packed trap column (2 cm × 100 μm I.D) using RP ReproSil‐Pur C18‐AQ 3 μm resin (Dr. Maisch GmbH). Peptides were separated on a 15 cm analytical column (75 μm i.d.) pulled and packed in‐house with RP ReproSil‐Pur C18‐AQ 3 μm resin (Dr. Maisch GmbH) and sprayed directly into the mass spectrometer. Peptides were eluted at a flow rate of 250 nl/min using a 110 min gradient from 5 to 44% solvent B (A solvent: 0.1% formic acid; B solvent: 80% acetonitrile/0.1% formic acid). The PRM analysis consisted of an MS1 scan recorded in the Orbitrap at 120,000 resolution and using the default setting. The targeted MS2 (tMS2) scans were recorded at 60,000 resolution in the Orbitrap using a precursor isolation width of 1.6 m/z, HCD fragmentation of 30% (plus/minus of 3) collision energy, injection time (IT) of 118 ms and an AGC target set to 800%. The inclusion list monitored 11 of the SARS‐CoV‐2 proteins represented by 55 peptides compiled by own experimental data supplemented with viral peptides reported in PeptideAtlas (Desiere et al, 2006).
Post‐acquisition quantification—the MS raw files were converted to MGF files using the RawConverter (The Scripps Research Institute) and search against a combined SARS‐CoV‐2 (UP000464024; 14 sequences) and human (UP000005640; 20,600 sequences) references proteome using Mascot 2.5.1 (Matrix Science). Trypsin was selected as the digestion enzyme allowing one missed cleavage. The data were searched with a mass tolerance of the precursor and product ions of 10 ppm and 0.2 Da using ESI‐4SECTOR as the instrument setting. The significance threshold (p) was set at 0.05, and the ion score expect cut‐off at 30. Mascot DAT files were extracted and used to build a spectral library in Skyline v.20.1.0 (Desiere et al, 2006). The Skyline PRM analysis was performed using Orbitrap settings. Only peptides represented with identification from the Mascot search were used for post‐acquisition label‐free quantification at the MS2 level, which included the following peptides derived from the SARS‐CoV‐2 Nucleocapsid phosphoprotein; ITFGGPSDSTGSNQNGER, GQGVPINTNSSPDDQIGYYR, DGIIWVATEGALNTPK and NPANNAAIVLQLPQGTTLPK. Each peptide was represented by 5 fragment ions.
Statistical analysis
One‐way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Turkey´s multiple comparison testing on log‐transformed data or an unpaired t‐test was used to test for statistical significance. Only P values of 0.05 or lower were considered statistically significant (P > 0.05 [ns, not significant], P ≤ 0.05; [*], P ≤ 0.01; [**], P ≤ 0.001; [***], P ≤ 0.0001; [****]. For all statistical analyses, the GraphPad Prism 7 software package was used (GraphPad Software).
Author contributions
LD conceived the study and performed experiment. MM conceived the study, performed experiments and wrote the paper. JT and JB‐C performed experiments. ETP performed experiments. BHF and SHS identified donors and collected BAL. LR and DO contributed critical reagents. HJH conceived the study. JJE supervised research. CKH conceived the study. RH conceived the study and wrote the paper. All authors read and commented upon the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Supporting information
Review Process File
Source Data for Figure 1
Source Data for Figure 2
Source Data for Figure 3
Source Data for Figure 4
Source Data for Figure 5
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Danish Council for Independent Research, Medical Research (grant 7016‐00331B). The authors are grateful to Anne‐Marie Toft and Hans Nymand Pedersen, Department of Respiratory Diseases and Allergy, Aarhus University Hospital, for their technical assistants with handling BAL, as well as to Dr. Hans Henrik Gad, Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Aarhus University, for reading and commenting the manuscript.
EMBO Reports (2020) 21: e51252.
Data availability
The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via PRIDE (Perez‐Riverol et al, 2019) partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD021685 and https://doi.org/10.6019/PXD021685 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD0216885#).
References
- Baum A, Sachidanandam R, García‐Sastre A (2010) Preference of RIG‐I for short viral RNA molecules in infected cells revealed by next‐generation sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 16303–16308 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco‐Melo D, Nilsson‐Payant BE, Liu WC, Uhl S, Hoagland D, Møller R, Jordan TX, Oishi K, Panis M, Sachs D et al (2020) Imbalanced host response to SARS‐CoV‐2 drives development of COVID‐19. Cell 181: 1036–1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunstetter M‐A, Hardie JA, Schiff R, Lewis JP, Cross CE (1971) The origin of pulmonary alveolar macrophages: studies of stem cells using the Es‐2 marker of mice. Arch Intern Med 127: 1064–1068 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantell K, Hirvonen S, Kauppinen HL, Myllylä G (1981) Production of interferon in human leukocytes from normal donors with the use of Sendai virus. Methods Enzymol 78: 29–38 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y, Guo D (2016) Molecular mechanisms of coronavirus RNA capping and methylation. Virologica Sinica 31: 3–11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu H, Chan JF, Wang Y, Yuen TT, Chai Y, Hou Y, Shuai H, Yang D, Hu B, Huang X et al (2020) Comparative replication and immune activation profiles of SARS‐CoV‐2 and SARS‐CoV in human lungs: an ex vivo study with implications for the pathogenesis of COVID‐19. Clin Infect Dis 71: 1400–1409 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desiere F, Deutsch EW, King NL, Nesvizhskii AI, Mallick P, Eng J, Chen S, Eddes J, Loevenich SN, Aebersold R (2006) The PeptideAtlas project. Nucleic Acids Res, 34, D655‐8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divangahi M, King IL, Pernet E (2015) Alveolar macrophages and type I IFN in airway homeostasis and immunity. Trends Immunol 36: 307–314 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goritzka M, Makris S, Kausar F, Durant LR, Pereira C, Kumagai Y, Culley FJ, Mack M, Akira S, Johansson C (2015) Alveolar macrophage‐derived type I interferons orchestrate innate immunity to RSV through recruitment of antiviral monocytes. J Exp Med 212: 699–714 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilliams M, De Kleer I, Henri S, Post S, Vanhoutte L, De Prijck S, Deswarte K, Malissen B, Hammad H, Lambrecht BN (2013) Alveolar macrophages develop from fetal monocytes that differentiate into long‐lived cells in the first week of life via GM‐CSF. J Exp Med 210: 1977–1992 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto D, Chow A, Noizat C, Teo P, Beasley MB, Leboeuf M, Becker CD, See P, Price J, Lucas D et al (2013) Tissue‐resident macrophages self‐maintain locally throughout adult life with minimal contribution from circulating monocytes. Immunity 38: 792–804 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussell T, Bell TJ (2014) Alveolar macrophages: plasticity in a tissue‐specific context. Nat Rev Immunol 14: 81–93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochs G, Martinez‐Sobrido L, Lienenklaus S, Weiss S, Garcia‐Sastre A, Staeheli P (2009) Strong interferon‐inducing capacity of a highly virulent variant of influenza A virus strain PR8 with deletions in the NS1 gene. J Gen Virol 90: 2990–2994 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai Y, Takeuchi O, Kato H, Kumar H, Matsui K, Morii E, Aozasa K, Kawai T, Akira S (2007) Alveolar macrophages are the primary interferon‐alpha producer in pulmonary infection with RNA viruses. Immunity 27: 240–252 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee BL, Barton GM (2014) Trafficking of endosomal Toll‐like receptors. Trends Cell Biol 24, 360–369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei X, Dong X, Ma R, Wang W, Xiao X, Tian Z, Wang C, Wang Y, Li L, Ren L et al (2020) Activation and evasion of type I interferon responses by SARS‐CoV‐2. Nat Commun 11: 3810 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H, Wang W, Song H, Huang B, Zhu N et al (2020) Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 395: 565–574 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohlenberg M, Gad HH, Hartmann R (2019) The Influence of the rs30461 single nucleotide polymorphism on IFN‐lambda1 activity and secretion. J Interferon Cytokine Res 39: 661–667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onoguchi K, Yoneyama M, Takemura A, Akira S, Taniguchi T, Namiki H, Fujita T (2007) Viral infections activate types I and III interferon genes through a common mechanism. J Biol Chem 282: 7576–7581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez‐Riverol Y, Csordas A, Bai J, Bernal‐Llinares M, Hewapathirana S, Kundu DJ, Inuganti A, Griss J, Mayer G, Eisenacher M et al (2019) The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res 47: D442–D450 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S, Krause CD, Walter MR (2004) Interferons, interferon‐like cytokines, and their receptors. Immunol Rev 202: 8–32 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichlmair A, Schulz O, Tan CP, Näslund TI, Liljeström P, Weber F, Reis e Sousa C (2006) RIG‐I‐mediated antiviral responses to single‐stranded RNA bearing 5'‐phosphates. Science 314: 997–1001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribul PK, Harker J, Wang B, Wang H, Tregoning JS, Schwarze J, Openshaw PJM (2008) Alveolar macrophages are a major determinant of early responses to viral lung infection but do not influence subsequent disease development. J Virol 82: 4441–4448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakabe S, Iwatsuki‐Horimoto K, Takano R, Nidom CA, Le MTQ, Nagamura‐Inoue T, Horimoto T, Yamashita N, Kawaoka Y (2011) Cytokine production by primary human macrophages infected with highly pathogenic H5N1 or pandemic H1N1 2009 influenza viruses. J Gen Virol 92: 1428–1434 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoggins JW, Wilson SJ, Panis M, Murphy MY, Jones CT, Bieniasz P, Rice CM (2011) A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 472: 481–485 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BR, Silverman RH, Schreiber RD (1998) How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem 67: 227–264 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatematsu M, Funami K, Seya T, Matsumoto M (2018) Extracellular RNA sensing by pattern recognition receptors. J Innate Immun 10, 398–406 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wack A, Terczynska‐Dyla E, Hartmann R (2015) Guarding the frontiers: the biology of type III interferons. Nat Immunol 16: 802–809 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Nikrad MP, Travanty EA, Zhou B, Phang T, Gao B, Alford T, Ito Y, Nahreini P, Hartshorn K et al (2012) Innate immune response of human alveolar macrophages during influenza A infection. PLoS One 7: e29879 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG, Gao GF (2020) A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet 395: 470–473 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young HA, Bream JH (2007) IFN‐gamma: recent advances in understanding regulation of expression, biological functions, and clinical applications. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 316: 97–117 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu WC, Chan RW, Wang J, Travanty EA, Nicholls JM, Peiris JS, Mason RJ, Chan MC (2011) Viral replication and innate host responses in primary human alveolar epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages infected with influenza H5N1 and H1N1 viruses. J Virol 85: 6844–6855 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, Si HR, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang CL et al (2020) A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 579: 270–273 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R et al (2020) A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med 382: 727–733 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Review Process File
Source Data for Figure 1
Source Data for Figure 2
Source Data for Figure 3
Source Data for Figure 4
Source Data for Figure 5
Data Availability Statement
The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via PRIDE (Perez‐Riverol et al, 2019) partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD021685 and https://doi.org/10.6019/PXD021685 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD0216885#).


