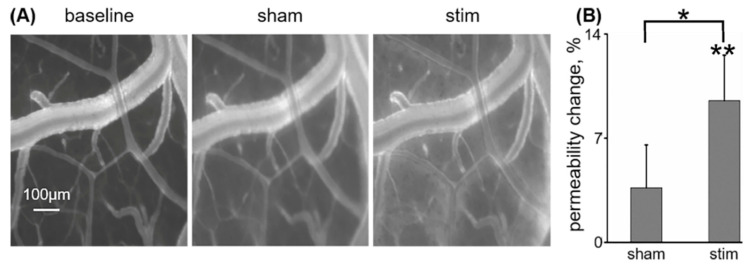
Figure 3.
Low-frequency rTMS increases neocortical vascular permeability to IGF-Trap: (A) Fluorescent angiography of the exposed anesthetized rat cortex, following intravenous administration of succinimidyl ester-conjugated IGF-Trap (20 mg/kg), at prestimulation (baseline, left), following sham rTMS (sham, center) and following real rTMS (stim, right) at 1 Hz, 130% of resting motor threshold. Extravasation of fluorescent IGF-Trap into extravascular space, following real stimulation, is apparent. (B) Mean ± SEM increase in permeability index (see Section 2) from baseline, for post-sham and post-real stimulation. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.