Abstract
Background
An association between the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and the presence of certain chronic conditions has been suggested. However, unlike influenza and other viruses, the disease burden of COVID-19 in patients with asthma has been less evident.
Objective
To understand the impact of COVID-19 in patients with asthma.
Methods
Using big-data analytics and artificial intelligence through the SAVANA Manager clinical platform, we analysed clinical data from patients with asthma from January 1 to May 10, 2020.
Results
Out of 71 182 patients with asthma, 1006 (1.41%) suffered from COVID-19. Compared to asthmatic individuals without COVID-19, patients with asthma and COVID-19 were significantly older (55 versus 42 years), predominantly female (66% versus 59%), smoked more frequently and had higher prevalence of hypertension, dyslipidaemias, diabetes and obesity. Allergy-related factors such as rhinitis and eczema were less common in asthmatic patients with COVID-19 (p<0.001). In addition, higher prevalence of these comorbidities was observed in patients with COVID-19 who required hospital admission. The use of inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) was lower in patients who required hospitalisation due to COVID-19, as compared to non-hospitalised patients (48.3% versus 61.5%; OR 0.58, 95% CI 0.44–0.77). Although patients treated with biologics (n=865; 1.21%) showed increased severity and more comorbidities at the ear, nose and throat level, COVID-19-related hospitalisations in these patients were relatively low (0.23%).
Conclusion
Patients with asthma and COVID-19 were older and at increased risk due to comorbidity-related factors. ICS and biologics are generally safe and may be associated with a protective effect against severe COVID-19 infection.
Short abstract
The increased risk of hospitalisation due to COVID-19 in patients with asthma is largely associated with age and related comorbidities. ICS and biologics may be associated with a protective effect against the most severe manifestations of COVID-19. https://bit.ly/37yhr5b
Introduction
Asthma remains a global major challenge for public health. Affecting ~272 million people of all ages (4.5% of adults aged 18–50 years), it is one of the most common chronic disorders worldwide [1, 2]. In the United States, it has been estimated that up to 12 million people experience an acute exacerbation of asthma every year; a quarter of these require hospitalisation [3]. In Europe, asthma ranks 14th in terms of duration and associated disability and leads to an estimated cost of EUR 25 billion per year [4]. Although 5% of adults and 10% of children have asthma in Spain, it has been estimated that up to 50% of patients remain undiagnosed. Indeed, 8.6% of adults (aged 18–70 years) and 14% of children show asthma-related symptoms, with the most frequent being dyspnoea and cough [4, 5]. Crucially, between 60% and 70% of patients with asthma in Spain are not properly controlled [6, 7]. This is critical since patients with uncontrolled asthma may generate direct and indirect costs 10-fold those of controlled patients [1], and both viral infections and virus-induced exacerbations (i.e. rhinovirus) influence asthma control [8].
Asthma severity and asthma control are two separate yet interlinked domains in all patients. Worsening symptoms and asthma exacerbations are associated with treatment-related variables (e.g. inappropriate treatment, lack of adherence, overtreatment, side-effects, etc.) or with the presence of underlying risk factors [6, 7, 9], most notably viral respiratory infection. Asthma exacerbations caused by respiratory infections or other conditions have a negative impact on the patient's health status and lead to worse prognosis [10].
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is the disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clinically, the severity of COVID-19 can vary from mild to very severe, causing mortality in some patients [11, 12]. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic certainly represents a major challenge for health systems globally. Since the beginning of the pandemic, an association between COVID-19 severity and chronic medical conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus and high blood pressure has been suggested. However, unlike influenza and other seasonal viruses, the impact of COVID-19 in patients with asthma has been less evident [13–16]. Conversely, the severity and mortality of COVID-19 has been strongly related to age. Although the virus can infect individuals of all ages, most severe cases to date have been described in adults aged ≤55 years, and in patients with the aforementioned comorbidities. In this age group, patients typically have more than one chronic condition, particularly endocrine–metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. With this background, it is imperative to characterise the clinical course of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with asthma and assess the impact of asthma and asthma-related comorbidities and treatment in COVID-19-related outcomes.
Emerging and rapidly evolving diseases such as COVID-19 are best understood using population-based registries containing real-world information [17]. In this context, combining real-world data with big-data analytics has the potential to increase our understanding of the effects of COVID-19 in patients with asthma and identify new strategies and management options for therapeutic intervention. A relevant data source with these characteristics is the clinical information contained in patients’ electronic health records (EHR).
Using the clinical information captured in the EHRs of patients with asthma and COVID-19, here we aimed to 1) describe the frequency and clinical characteristics of these patients and 2) understand the clinical impact of COVID-19 on the clinical course of patients with asthma. To achieve the study objectives, we used big-data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) through the SAVANA Manager clinical platform [18, 19].
Methods
This was a multicentre, non-interventional, retrospective study using free-text data captured in the EHRs of patients diagnosed with COVID-19. The study period was January 1, 2019 to May 10, 2020.
We followed the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) guidelines for reporting observational studies [20]. The study was conducted in accordance with legal and regulatory requirements and followed research practices described in the International Conference on Harmonisation guidelines for good clinical practice, the Declaration of Helsinki in its latest edition, the guidelines for good pharmacoepidemiology practice and local regulations. Given the retrospective and observational nature of the study, physicians’ prescribing habits and patient assignment to a specific therapeutic strategy were solely determined by the physician, team or hospital concerned. Likewise, a standard informed consent does not apply to this study. All actions towards data protection were taken in accordance with the European data protection authorities’ code of good practice regarding big-data projects and the European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This study was approved by the ethics and research committee of the University Hospital of Guadalajara (Guadalajara, Spain).
Clinical data from a total of 2 034 921 patients with available EHRs in the region of Castilla La-Mancha (Spain) were explored. Data were collected from all available services, including inpatient and outpatient departments, emergency room and primary care.
The information from EHRs was extracted using natural language processing (NLP) and AI techniques using SAVANA Manager, a powerful multilingual (natural language) engine for the analysis of free-text clinical information. This software can interpret any content included in EHRs, regardless of the electronic system in which it operates. Importantly, this tool can capture numerical values and clinical notes and transform them into accessible variables, thus allowing for the reuse of the information captured in large-scale collections of clinical records (i.e. big data). The data extraction process has four distinct phases aimed at transferring and aggregating the data into the study database, as follows. 1) Acquisition: data acquisition is the responsibility of the participating site, in close collaboration with SAVANA's information technology staff. In compliance with the European Union GDPR, data were anonymised and transferred to SAVANA during this phase; 2) integration: in this phase, data were integrated into the database; 3) NLP: SAVANA's EHRead technology applied NLP techniques to analyse and extract the unstructured free-text information written in large numbers of EHRs. The NLP output is a synthetic patient database, as the software creates a patient database from scratch. This process ensures that the information is not accessible and makes traceability to individual patients impossible; and 4) validation, consisting of a medical validation of the tool's output by doctors and researchers.
The terminology used by SAVANA is based on multiple sources such as SNOMED CT [21], which includes medical codes, concepts, synonyms and definitions regarding symptoms, diagnoses, body structures and substances commonly used in clinical documentation. Due to the novel methodological approach of this study, we complemented our clinical findings with the assessment of EHRead's performance. This evaluation was aimed at verifying the system's accuracy in identifying records that contain mentions of asthma and COVID-19 and its related variables. For a comprehensive description of the evaluation procedure, see Espinosa-Anke et al. [19]. Briefly, the annotations made by the medical experts were used to generate the gold standard to assess the performance of EHRead's output; performance is calculated in terms of the standard metrics of accuracy (P), recall (R) and their harmonic mean F-score [22].
All statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS software (version 25.0; IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Unless otherwise indicated, qualitative variables are expressed as absolute frequencies and percentages, while quantitative variables are expressed as mean±sd. For the assessment of statistical significance of numerical variables, we used independent-samples t-tests or ANOVA. To measure the relative distribution of patients assigned to different categories of qualitative variables, we used Chi-squared tests. In all cases, a p-value for statistical significance was set at 0.05.
Results
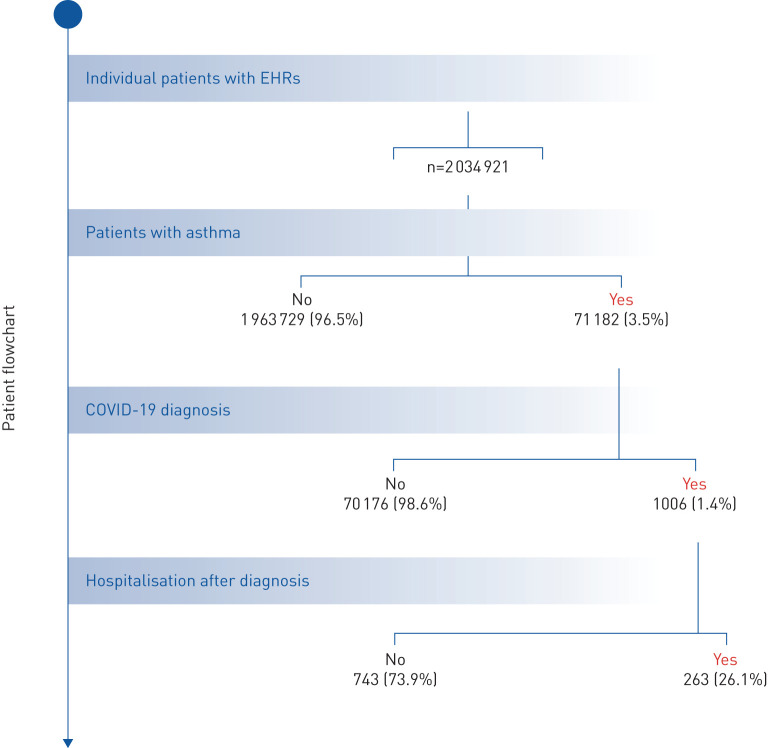
We identified 71 182 patients with asthma during the study period (January 1, 2019 to May 10, 2020). The search terms used to identify patients with bronchial asthma are listed in supplementary table S1. For the linguistic evaluation of the variable “asthma”, we obtained precision, recall and F-scores of 0.88, 0.75 and 0.81, respectively; these metrics indicate that patients with asthma were properly identified within the target population. The patient flowchart for asthmatics with and without COVID-19 is depicted in figure 1.
FIGURE 1.
Flowchart depicting the total number of patients with available electronic health records (EHRs), the number of patients with asthma, the number of patients diagnosed with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), and of those, the number of hospitalisations after diagnosis during the study period (January 1 to May 10, 2020). All percentage values are computed in relation to the level immediately above.
Mean±sd age was 42±20 years; 59% of patients were female. Overall, 1006 (1.41%) asthma patients were also diagnosed with COVID-19. EHRead identified COVID-19 with precision 0.99, recall 0.75 and F-score 0.93; again, these results indicate that within our population with asthma, COVID-19 cases were accurately identified. COVID-19 diagnosis was confirmed using PCR in 61% (n=611) of patients; in the remaining cases, and considering the epidemiological context of the pandemic in the study area between March and May 2020, diagnosis was based on rapid serological tests or clinical, radiological and/or analytical evaluation. Notably, the percentage (95% CI) of patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in the population of patients with asthma (1.41%, 1.33–1.50%) was significantly higher than in the general population of Castilla La-Mancha (Spain) (0.86%, 0.85–0.87%; p<0.001).
Patients with asthma who also had a diagnosis of COVID-19 were older, predominantly female and had higher prevalence rates of hypertension, dyslipidaemia, diabetes, obesity and smoking habits than asthmatic individuals without COVID-19 (all p<0.05). By contrast, atopy-related factors such as rhinitis or eczema were significantly more frequent in patients without COVID-19 (table 1). The higher prevalence of hypertension, dyslipidaemia, diabetes and obesity was further confirmed in those patients requiring hospital admission, as compared with those who only required outpatient management (table 2).
TABLE 1.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with asthma with/without coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
| Asthma | Asthma without COVID-19 | Asthma with COVID-19 | OR (95% CI) | p-value# | |
| Patients n | 71 182 | 70 176 | 1006 | ||
| Age years | 42±24 | 41±24 | 55±20 | <0.001 | |
| Female | 59 | 59 | 66 | 1.34 (1.18–1.54) | <0.001 |
| Tobacco use | 10 | 9 | 11 | 1.25 (1.03–1.53) | 00.02 |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Arterial hypertension | 24 | 24 | 39 | 2.02 (1.78–2.30) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 17 | 17 | 26 | 1.72 (1.49–1.98) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 11 | 10 | 16 | 1.72 (1.45–2.03) | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 10 | 10 | 13 | 1.35 (1.12–1.62) | <0.001 |
| Rhinitis | 33 | 33 | 17 | 0.42 (0.35–0.49) | <0.001 |
| Eczema | 7 | 7 | 1 | 0.50 (0.40–0.76) | <0.001 |
Data are presented as mean±sd or %, unless otherwise stated. #: patients with asthma with COVID-19 versus patients with asthma without COVID-19.
TABLE 2.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with asthma and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) who required hospital admission
| Asthma+COVID-19 |
Asthma+COVID-19 non-hospitalised |
Asthma+COVID-19 hospitalised |
OR (95% CI) | p-value# | |
| Patients n | 1006 | 743 | 263 | ||
| Age years | 55±20 | 52±20 | 63±18 | <0.001 | |
| Female | 66 | 67 | 61 | 0.76 (0.57–1.02) | 0.07 |
| Tobacco use | 7 | 7 | 6 | 0.69 (0.37–1.29) | 0.29 |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Arterial hypertension | 39 | 34 | 54 | 2.27 (1.71–3.03) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 27 | 21 | 38 | 2.31 (1.70–3.13) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 15 | 13 | 21 | 1.76 (1.22–2.54) | 0.002 |
| Obesity | 13 | 12 | 18 | 1.60 (1.09–2.35) | 0.02 |
Data are presented as mean±sd or %, unless otherwise stated. #: non-hospitalised patients versus hospitalised patients.
The proportion of patients with asthma using inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) was significantly lower in individuals requiring hospital admission (48.3% versus 61.5%), with an OR (95% CI) of 0.58 (0.44–0.77). The most common diagnosis in hospitalised patients was pneumonia (91% of patients; n=239), with great variability of radiological expression. Different diagnoses associated with respiratory failure but with normal lung radiology (data not shown) were found in 9% (n=24) of patients.
Regardless of previous ICS or bronchodilator use, a total of 865 (1.21%) patients in the study population of 71 182 asthmatics were being treated with biologics (omalizumab n=641, mepolizumab n=308, benralizumab n=98, reslizumab n=26) during the study period, due to previous poor control of the disease (table 3). Biologic-treated patients showed a high frequency of rhinitis and polyposis (50% in both cases) and a greater number of bronchospasm episodes before treatment onset with biologics. Of note, there were only 20 patients with asthma under treatment with biologics with confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19; of these, two (10%) patients were admitted to the hospital. Despite increased severity and comorbidity of symptoms at the ear, nose and throat (ENT) level, the need for COVID-19-related hospital admission in biologic-treated patients with asthma was relatively marginal (0.23%, 95% CI 0.03–0.83%). This proportion significantly differs from the observed in both the general population and in the population of patients with asthma not being treated with biologics; in both cases 26% of patients required hospitalisation due to COVID-19. Only one patient undergoing treatment with biologics died; he was a 52-year-old male with high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidaemia.
TABLE 3.
Treatment of patients with asthma and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) and biologics in hospitalised versus non-hospitalised patients between January 1 and May 10, 2020
| Patients | Asthma+COVID-19 |
Asthma+COVID-19 hospitalised |
p-value | |
| Patients with asthma | 71 182 | 1006 | 263 | |
| Asthma + ≤1 ICS | 42 171 (59.23% of asthmatic patients) | 619 | 127 | <0.001 |
| Asthma + ≤1 biologic# | 865 (1.21% of asthmatic patients) | 18 | 2 | |
| Omalizumab | 641 | 9 | 0 | |
| Mepolizumab | 308 | 7 | 2 | |
| Benralizumab | 98 | 2 | 0 | |
| Reslizumab | 26 | 1 | 0 |
Data are presented as n, unless otherwise stated. #: 54% of the patients treated with mepolizumab had been treated previously with omalizumab; 65% of patients treated with benralizumab had been treated previously with omalizumab and 35% with mepolizumab. Most of the patients treated with reslizumab had been treated previously with omalizumab and mepolizumab.
Compared with information from patients with asthma available since January 2019, the data collected during the study period (January 1 to May 10, 2020) show that COVID-19 significantly increased in-hospital mortality in this population (0.54% versus 2.29%), with an associated OR (95% CI) of 4.35 (2.84–6.66). For both periods, in-hospital mortality mainly affected elderly patients, with a mean±sd age of 76±12 years in patients with both asthma and COVID-19, and 78±17 years in COVID-19-free patients with asthma (p<0.001); most of these patients were female in both study periods (61% and 71%, respectively), and had previously diagnosed comorbidities (table 4). The mean±sd age of patients without asthma who died from COVID-19 was 79±11 years, and 63% (n=296) of them were male.
TABLE 4.
In-hospital mortality in asthmatic patients with/without coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
| Asthma with COVID-19 | Asthma without COVID-19 | OR (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Age years | 78±17 | 76±17 | <0.001 | |
| Female | 61 | 71 | 0.64 (0.56–0.73) | |
| Mortality | 2.29 | 0.54 | 2.29 (4.35–6.66) |
Data are presented as mean±sd or %, unless otherwise stated.
Discussion
The World Health Organization declared the COVID-19 outbreak a global pandemic on March 11, 2020. Since then, clinicians worldwide have been particularly concerned about the impact of patients’ pre-existing chronic conditions (particularly lung and cardiovascular diseases) on the course of this new disease. Whereas high blood pressure and diabetes have been closely associated with increased frequency of cases and severity of COVID-19, care-related data suggest that COVID-19 has not affected patients with asthma to nearly the same extent [15, 23–25].
To shed light on this question, we have applied big-data analytics and AI to analyse the clinical information of a large cohort of patients with asthma and COVID-19. Big-data applications in healthcare (specifically the use of new technologies to manage and extract the complex data generated in large volumes of EHRs) is an inescapable reality [26]. Crucially, most of the information contained in EHRs is found in an unstructured form (e.g. as free-text narratives or clinical notes). The use of big-data analytics and cutting-edge methods in the realm of AI (i.e. NLP, machine learning) now allows for the extraction and analysis of this valuable information in real time. The software use in the present study enable the rapid evaluation of the main indicators of various clinical processes while avoiding the selection biases that occur in audit or case-series studies, where only specialised centres and medical professionals participate in the study. Importantly, the Spanish autonomous community of Castilla-La Mancha has different features that optimise the use of this technology to analyse the clinical impact of COVID-19 on patients with asthma. First, this region has been one of the most affected by the pandemic in Spain, which in turn has been one of the most hard-hit countries in Europe. Second, it has a good EHR system, which has been standardised and is shared across all five provinces. Finally, the SAVANA Manager tool is widely available in the region, allowing access to large amounts of clinical information [27].
In the present study, we analysed clinical data from the largest population of asthma patients published to date (n=71 182); 1006 of these patients were diagnosed with COVID-19. The study period was January 1, 2019 to May 10, 2020. Although the system allows us to analyse data from 2011 onwards, we selected this temporal cut-off to include asthmatic patients with updated follow-up information and with the active form of the disease.
The proportion of patients with both asthma and COVID-19 during the study period was 1.41%, which is markedly higher than the 0.86% observed in the general population. Although these data show a higher frequency of COVID-19 in patients with asthma, the manifestation of the disease in this clinical population was not particularly severe, with low rate of hospital admissions. In addition, this proportion is lower than the reported for patients with other chronic diseases. Some of the reasons that may explain this phenomenon include remission of seasonal influenza, lack of exposure to environmental factors, greater monitoring of hygiene measures during lockdown in these patients, the significant reduction in air pollution during this period and/or better control of the disease by improving adherence to treatment due to fear of worsening symptomatology. This trend has been observed since the initial phases of the pandemic in patient populations with other respiratory diseases, such as COPD [28].
Comorbidities play a major role in the manifestation of COVID-19-related complications. In our study, the manifestation of COVID-19 in patients with asthma was favoured by older age, male sex and the presence of several comorbidities. High blood pressure, dyslipidaemia, diabetes and obesity were the main risk factors for hospital admission due to poor prognosis. The lower risk associated with rhinitis and eczema is consistent with previous observations that allergic sensitisation in asthma is linked to lower expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)2 receptors in both upper and lower respiratory airways, suggesting a potential protective effect [29]. As previously observed in the general population, mortality due to COVID-19 in patients with asthma mainly occurred in the elderly.
The possibility that different therapeutic options in patients with chronic respiratory diseases affects the incidence and prognosis of COVID-19 has been a matter of intense debate. As for asthma, it has been suggested that the use of ICS might yield a protective effect against COVID-19 [30, 31]. Although an antiviral effect has been described in rhinovirus-induced exacerbations, these results are highly controversial. Peters et al. [32] showed an association of ICS use and reduced expression of both ACE2 and TMPRSS2 receptors, thus implying that ICS may reduce the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and decrease COVID-19-related morbidity. Although our data cannot answer this question in a conclusive manner, they show that the proportion of patients who used ICS was significantly reduced in asthmatics who required hospitalisation due to COVID-19. These findings are consistent with other studies showing that a combination of glycopyrronium, formoterol and budesonide prevents the replication of HCoV-229E (via inhibition of receptor expression and/or endosomal function), and that these drugs modulate infection-related inflammation in the respiratory tract [33]. In our study, the three corticosteroid-dependent patients diagnosed with COVID-19 did not die from it; however, there is no experimental evidence to date regarding the effect of systemic corticosteroids in patients with asthma and COVID-19.
Whether treatment with biologics in patients with asthma impacts SARS-CoV-2 infection or the incidence and prognosis of COVID-19 remains unknown. In this context, there is no evidence supporting that either omalizumab or other drugs that suppress eosinophils directly modulate viral processes in patients with asthma [34, 35]. In our study, we identified a total of 865 patients treated with biologics. Among these, two patients required admission and only one died from COVID-19; however, this patient had other comorbidities in addition to severe asthma, which may have contributed to his poor clinical outcome. Overall, our results support the safety of these drugs for the treatment of asthma in patients diagnosed with COVID-19. As with ICS use, our data suggest that biologics might be associated with a protective effect on the clinical course of these patients. However, we cannot rule out that the aforementioned favourable factors also contributed to a better disease prognosis.
Our findings are consistent with a clinical series of 220 asthmatic patients with COVID-19 in Chicago and surrounding Illinois suburbs, where asthma was not associated with an increased risk of hospitalisation after adjusting for age, sex, sex and comorbidities (relative risk (RR) 0.96, 95% CI 0.77–1.19) [36]. However, ICS use was associated with a statistically nonsignificant increased risk of hospitalisation (RR 1.39, 95% CI 0.90–2.15); however, in the same report, the interpretation of the effects of combined use of ICS and long-acting β-agonists and levels of care in these patients was not straightforward. These results warrant further research in patients with asthma and other clinical populations.
Strengths and limitations
The strengths of the present study include immediacy, large sample size and access to real-world evidence. In addition, our results must be interpreted in light of the following limitations. First, the main limitation of this type of studies is perhaps the lack of documented information. In Castilla-La Mancha, the digitalisation of clinical records has been optimal since 2011. Not only is the EHR system homogenous throughout the region, but its use has been universal for the past 5 years. Second, unlike classical research methods, reproducibility is not generally considered in big-data studies, since the latter involve large amounts of information collected from the whole target population. Because we exclusively analysed the data captured in EHRs, the quality of the results reported for some variables is directly tied to the quality of the clinical records; in many cases, EHRs may be partially incomplete and not capture all the relevant clinical information from a given patient. Third, because this study was not designed to collect variables in a strict, a priori fashion, there were some variables that were not properly documented and which were therefore not analysed. Fourth, the subanalysis presented in table 3 is based on the experience of only 20 patients with both COVID-19 and asthma, and under treatment with biologics. Thus, these results must be interpreted considering the limited statistical power. In addition, the more positive outcomes reported in these patients may be partly due to a more consistent avoidance of external hazards and compliance with both their asthma treatment and protective interventions (i.e. face masks, social distancing, hand hygiene). Finally, our study sample comprised COVID-19 cases confirmed by both PCR/serological tests and clinical criteria (i.e. symptomatology, imaging and laboratory results). Of note, PCR and other rapid laboratory tests for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 were not routinely used in Spain during the onset of the pandemic. The decision to include clinically diagnosed COVID-19 cases is further supported by recent data questioning the clinical validity and sensitivity of symptom- and image-based identification of patients with COVID-19, especially in the early stages of the disease [37–39].
Conclusion
We conclude that 1) the frequency of SARS-CoV-2 infection has been low in patients with asthma, although higher than in the general population; 2) the increased risk of hospitalisation due to COVID-19 in patients with asthma is largely associated with age and related comorbidities; mortality mainly affected elderly patients; 3) ICS showed a safe profile; compared to asthmatic patients who required hospitalisation due to COVID-19, a significantly higher percentage of non-hospitalised patients used ICS; and 4) although biologic-treated patients with asthma typically present with the most severe manifestations of the disease, and considering the caveats associated with a reduced sample size in this subanalysis, we found that the number of COVID-19-related admissions and mortality in these patients was strikingly low; thus, further exploration of a possible protective effect associated with the use of these therapeutic agents is warranted.
Supplementary material
Please note: supplementary material is not edited by the Editorial Office, and is uploaded as it has been supplied by the author.
Supplementary material ERJ-03142-2020.SUPPLEMENT (38.8KB, pdf)
Shareable PDF
Footnotes
This article has an editorial commentary: https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.04451-2020
This article has supplementary material available from erj.ersjournals.com
Conflict of interest: J.L. Izquierdo reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, Grifols, Menarini, Novartis, Orion, Pfizer, Sandoz and Teva.
Conflict of interest: C. Almonacid reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, Menarini, Novartis and ALK.
Conflict of interest: Y. González reports that they are an employee at Savana Medica.
Conflict of interest: C. Del Rio-Bermudez reports that they are an employee at Savana Medica.
Conflict of interest: J. Ancochea has nothing to disclose.
Conflict of interest: R. Cárdenas has nothing to disclose.
Conflict of interest: S. Lumbreras has nothing to disclose.
Conflict of interest: J.B. Soriano has nothing to disclose.
Support statement: Grant COVID-19 UAH 2019/00003/016/001/005 from the University of Alcalá (Spain). Funding information for this article has been deposited with the Crossref Funder Registry.
References
- 1.Global Asthma Network . The Global Asthma Report 2014. www.globalasthmareport.org/2014/burden/burden.php
- 2.GBD Chronic Respiratory Disease Collaborators . Prevalence and attributable health burden of chronic respiratory diseases, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Respir Med 2020; 8: 585–596. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30105-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fergeson JE, Patel SS, Lockey RF. Acute asthma, prognosis, and treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2017; 139: 438–447. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.06.054 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gibson GJ, Loddenkemper R, Lundbäck B, et al. Respiratory health and disease in Europe: the new European Lung White Book. Eur Respir J 2013; 42: 559–563. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00105513 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Urrutia I, Aguirre U, Sunyer J, et al. Cambios en la prevalencia de asma en la población española del Estudio de Salud Respiratoria de la Comunidad Europea (ECRHS-II). [Changes in the prevalence of asthma in the Spanish cohort of the European Community Respiratory Health Survey (ECRHS-II)]. Arch Bronconeumol 2007; 43: 425–430. doi: 10.1157/13108781 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Quirce S, Plaza V, Picado C, et al. Prevalence of uncontrolled severe persistent asthma in pneumology and allergy hospital units in Spain. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 2011; 21: 466–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Olaguibel JM, Quirce S, Juliá B, et al. Measurement of asthma control according to Global Initiative for Asthma guidelines: a comparison with the Asthma Control Questionnaire. Respir Res 2012; 13: 50. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-13-50 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jackson DJ, Trujillo-Torralbo MB, del-Rosario J, et al. The influence of asthma control on the severity of virus-induced asthma exacerbations. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015; 136: 497–500. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.01.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Papi A, Brightling C, Pedersen SE, et al. Asthma. Lancet 2018; 391: 783–800. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33311-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ritchie AI, Jackson DJ, Edwards MR, et al. Airway epithelial orchestration of innate immune function in response to virus infection. A focus on asthma. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2016; 13: Suppl. 1, S55–S63. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201507-421MG [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.World Health Organization . Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Events as They Happen www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-as-they-happen Date last accessed: November 5, 2020. Date last updated: July 30, 2020.
- 12.Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia. N Engl J Med 2020; 382: 1199–1207. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001316 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chow EJ, Doyle JD, Uyeki TM. Influenza virus-related critical illness: prevention, diagnosis, treatment. Crit Care 2019; 23: 214. doi: 10.1186/s13054-019-2491-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Goyal P, Choi JJ, Pinheiro LC, et al. Clinical characteristics of Covid-19 in New York City. N Engl J Med 2020; 382: 2372–2374. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2010419 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li X, Xu S, Yu M, et al. Risk factors for severity and mortality in adult COVID-19 inpatients in Wuhan. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2020; 146: 110–118. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Johnston SL. Asthma and COVID-19: is asthma a risk factor for severe outcomes? Allergy 2020; 75: 1543–1545. doi: 10.1111/all.14348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mallappallil M, Sabu J, Gruessner A, et al. A review of big data and medical research. SAGE Open Med 2020; 8: 2050312120934839. doi: 10.1177/2050312120934839 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hernández Medrano I, Tello Guijarro J, Belda C, et al. SAVANA: re-using electronic health records with artificial intelligence. Int J Interact Multimedia Artif Intell 2017; 4: 8–12. 10.9781/ijimai.2017.03.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Espinosa-Anke LT, Pardo A, Medrano I, et al. SAVANA: a global information extraction and terminology expansion framework in the medical domain. Proces de Leng Nat 2016; 57: 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- 20.von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, et al. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007; 370: 1453–1457. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61602-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Benson T. Principles of Health Interoperability HL7 and SNOMED. London, Springer, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Baeza-Yates RA, Ribeiro-Neto B. Modern Information Retrieval. Boston, Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang J-J, Dong X, Cao Y-Y, et al. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy 2020; 75: 1730–1741. doi: 10.1111/all.14238 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liu S, Zhi Y, Ying S. COVID-19 and asthma: reflection during the pandemic. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2020; 59: 78–88. 10.1007/s12016-020-08797-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gupta A, Bush A, Nagakumar P. Asthma in children during the COVID-19 pandemic: lessons from lockdown and future directions for management. Lancet Respir Med 2020; 8: 1070–1071. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30278-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Almonacid Sánchez C, Melero Moreno C, Quirce Gancedo S, et al. PAGE study: summary of a study protocol to estimate the prevalence of severe asthma in Spain using big-data methods. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 2020; in press [ 10.18176/jiaci.0483]. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0483 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Izquierdo JL, Morena D, Gonzalez Y, et al. Clinical management of COPD in a real-world setting. A big data analysis. Arch Bronconeumol 2020; in press doi.org/10.1016/j.arbres.2019.12.025. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2019.12.025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Guan W-J, Liang W-H, Zhao Y, et al. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis. Eur Respir J 2020; 55: 2000547. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00547-2020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wang R, Bikov A, Fowler SJ. Treating asthma in the COVID-19 pandemic. Thorax 2020; 75: 822–823. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-215118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Halpin DMG, Singh D, Hadfield RM. Inhaled corticosteroids and COVID-19: a systematic review and clinical perspective. Eur Respir J 2020; 55: 2001009, doi: 10.1183/13993003.01009-2020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Grünberg K, Sharon RF, Sont JK, et al. Rhinovirus-induced airway inflammation in asthma: effect of treatment with inhaled corticosteroids before and during experimental infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 164: 1816–1822. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.164.10.2102118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Peters MC, Sajuthi S, Deford P, et al. COVID-19 related genes in sputum cells in asthma: relationship to demographic features and corticosteroids. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2020; 202: 83–90. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202003-0821OC [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yamaya M, Nishimura H, Deng X, et al. Inhibitory effects of glycopyrronium, formoterol, and budesonide on coronavirus HCoV-229E replication and cytokine production by primary cultures of human nasal and tracheal epithelial cells. Respir Investig 2020; 58: 155–168. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2019.12.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Esquivel A, Busse WW, Calatroni A, et al. Effects of omalizumab on rhinovirus infections, illnesses, and exacerbations of asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2017; 196: 985–992. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201701-0120OC [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sabogal Piñeros YS, Bal SM, van de Pol MA, et al. Anti-IL-5 in mild asthma alters rhinovirus-induced macrophage, B-cell, and neutrophil responses (MATERIAL). A placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2019; 199: 508–517. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201803-0461OC [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chhiba KD, Patel GB, Vu THT, et al. Prevalence and characterization of asthma in hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2020; 146: 307–314. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.06.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Long C, Xu H, Shen Q, et al. Diagnosis of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): rRT-PCR or CT? Eur J Radiol 2020; 126: 108961. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108961 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wang W, Xu Y, Gao R, et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in different types of clinical specimens. JAMA 2020; 323: 1843–1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ai T, Yang Z, Hou H, et al. Correlation of chest CT and RT-PCR testing in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: a report of 1014 cases. Radiology 2020; 296: E32–E40. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020200642 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Please note: supplementary material is not edited by the Editorial Office, and is uploaded as it has been supplied by the author.
Supplementary material ERJ-03142-2020.SUPPLEMENT (38.8KB, pdf)
This one-page PDF can be shared freely online.
Shareable PDF ERJ-03142-2020.Shareable (276.5KB, pdf)