Abstract
Aquaporin 3 (AQP3) is a transporter of water, glycerol and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) that is expressed in various epithelial cells and in macrophages. Here, we developed an anti-AQP3 monoclonal antibody (mAb) that inhibited AQP3-facilitated H2O2 and glycerol transport, and prevented liver injury in experimental animal models. Using AQP3 knockout mice in a model of liver injury and fibrosis produced by CCl4, we obtained evidence for involvement of AQP3 expression in nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) cell signaling, hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation in macrophages during liver injury. The activated macrophages caused stellate cell activation, leading to liver injury, by a mechanism involving AQP3-mediated H2O2 transport. Administration of an anti-AQP3 mAb, which targeted an extracellular epitope on AQP3, prevented liver injury by inhibition of AQP3-mediated H2O2 transport and macrophage activation. These findings implicate the involvement of macrophage AQP3 in liver injury, and provide evidence for mAb inhibition of AQP3-mediated H2O2 transport as therapy for macrophage-dependent liver injury.
Subject terms: Drug discovery, Liver diseases, Molecular medicine
Aquaporin 3 (AQP3) is a transporter of water, glycerol and hydrogen peroxide, and hydrogen peroxide mediated oxidative stress has been implicated in liver injury. Here, the authors report the development of an anti-AQP3 monoclonal antibody, which alleviates liver injury in multiple mouse models.
Introduction
Chronic liver injury with inflammation and fibrosis occurs in various etiologies, including viral infection, autoimmune disorders, alcohol or drug abuse, metabolic disorders, and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis1,2. Liver fibrosis has been implicated in many types of liver diseases such as cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma1,3,4. Although multiple cell populations in the liver contribute to various inflammatory and fibrogenic pathways, hepatic macrophages are considered a key contributor to acute and chronic liver inflammation and fibrosis1,5–9. Regardless of the underlying cause, it is now generally accepted that resident macrophages (Kupffer cells) and infiltrating macrophages are activated after acute liver cell death, which then exacerbates the initial liver injury by secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines that activate hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Activated HSCs transdifferentiate into myofibroblasts, which amplify the progression of chronic liver fibrosis1,2,7.
Previous studies have suggested the involvement of redox state and oxidative stress in the progression of liver fibrosis10,11. During liver injury, hepatocytes, neutrophils, and macrophages generate high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS; O2−, OH, and hydrogen peroxide [H2O2]), which are thought to increase oxidative stress, cause direct cytotoxicity, or act as intracellular signaling mediators10,11. Pro-inflammatory macrophages show an increase in the inflammatory mediators nitric oxide and ROS, and enhanced aerobic glycolysis12,13. NADPH oxidase (Nox) and the mitochondrial respiratory pathway are the two major producers of endogenous ROS14–17. Previous studies have shown that Nox1, 2, and 4 in hepatocytes or HSCs are involved in liver inflammation and fibrosis via ROS production18–20. Thus, a variety of mechanisms for liver injury and fibrosis have been proposed though their relative importance remains unclear. Because advanced liver fibrosis is largely irreversible1,3, there remains an unmet need for development of novel therapeutics to reduce liver inflammation and fibrosis in a variety of disorders including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Aquaporin-3 (AQP3), a member of the aquaporin water channel family, functions as a transporter of water and small molecules, including glycerol and H2O221. We previously reported that AQP3-mediated H2O2 transport and increased intracellular H2O2 concentration acted as a secondary messenger for cell signaling involving factors such as NF-κB and PTEN, which increased inflammation, cell proliferation, and cell migration22–25. AQP3 knockout (AQP3−/−) mice showed reduced inflammation in models of contact hypersensitivity and psoriasis, and in cancer progression22,23,25,26. We speculated herein that AQP3 might regulate cellular ROS levels and thereby oxidative stress in oxidative stress-related diseases including liver fibrosis.
The present study examines the involvement and downstream mechanisms of AQP3-mediated H2O2 transport in liver injury in an experimental mouse model. An anti-AQP3 monoclonal antibody was generated that inhibited AQP3-mediated H2O2 transport and prevented acute and chronic liver injury.
Results
Reduced CCl4-induced acute liver injury in AQP3−/− mice
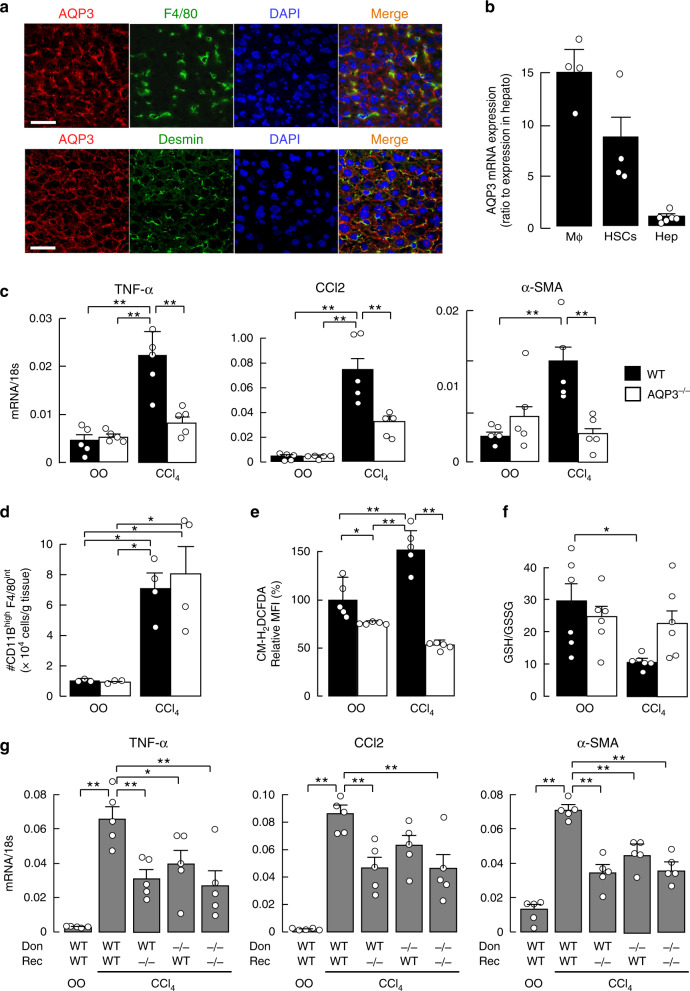
AQP3 expression has been reported in human liver macrophages by immunostaining27. Double immunofluorescence staining of normal human liver with anti-AQP3 and anti-CD68 (human macrophage marker) showed AQP3 expression predominantly in CD68+ macrophages (Supplementary Fig. 1a). The AQP3 expression pattern was studied in mouse liver tissue. AQP3 immunostaining with anti-F4/80 (macrophage marker) and anti-desmin (HSC marker) showed AQP3 expression in macrophages and HSCs (Fig. 1a). RT-PCR in isolated hepatic cells from naive wild-type (WT) mouse liver showed high AQP3 expression in hepatic macrophages and HSCs, and little AQP3 expression in hepatocytes (Fig. 1b, Supplementary Fig. 1b).
Fig. 1. Reduced CCl4-induced acute liver injury in AQP3−/− mice.
a AQP3 immunofluorescence in mouse liver. Immunostaining with anti-AQP3 (Cy3, red), and anti-F4/80 (FITC, green, upper) or anti-desmin (FITC, green, lower). Bar, 100 µm. b AQP3 mRNA expression in hepatic macrophages (Mϕ), hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), and hepatocytes (Hep) from WT liver determined by real-time RT-PCR (mean ± SE, n = 6 for hepatocytes, n = 4 for macrophages and HSCs biologically independent samples). Data are expressed as the ratio to 18 s RNA. c–f CCl4 (1 ml/kg) or vehicle olive oil (OO) was injected intraperitoneally, and livers were excised at 24 h. c Expression of mRNAs encoding TNF-α, CCl2, and α-SMA by real-time RT-PCR (mean ± SE, n = 5 mice/group, **p < 0.01). Data are expressed as the ratio to 18 s RNA. d Dispersed liver cells were stained with anti-F4/80 and anti-CD11B, and analyzed by FACS, as shown in Supplementary Fig. 1d. Cell number of CD11Bhigh F4/80intermediate hepatic macrophages (mean ± SE, n = 3 for OO, n = 4 for CCl4 mice/group, *p < 0.05). e Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of CM-H2DCFDA by FACS analysis in hepatocytes (mean ± SE, n = 5 biologically independent samples *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). f Ratio of GSH to GSSG in liver homogenate (mean ± SE, n = 6 mice/group, *p < 0.05). Statistical analysis for (c)–(f) was performed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. g Mice (WT or AQP3−/−, age 8–10 weeks) were gamma-irradiated (900 rad) and injected intravenously with bone marrow from WT or AQP3−/− mice. The study was performed at 60 days after bone marrow transfer (mean ± SE, n = 5 mice/group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). Source data, including exact p values, are provided as a Source data file.
A CCl4 model of acute liver injury was done in WT and AQP3−/− mice to investigate the potential role of AQP3 in the pathogenesis of liver injury28,29. Previous studies have shown macrophages play an important role in this model via the secretion of chemokines (e.g., CCL2 and CCL5) and inflammatory cytokines (e.g., tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α] and IL-1β) that promote HSC activation and transdifferentiation, and induce α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and collagen α11,5. CCl4 injection greatly increased expression of mRNA encoding TNF-α, CCL2, and α-SMA in WT liver, which were much reduced in AQP3−/− liver (Fig. 1c). AQP3−/− mice also showed a significant reduction in the elevations in serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), the common biomarkers of liver injury30 (Supplementary Fig. 1c). The numbers of CD11Bhigh F4/80int-positive recruited macrophages increased after CCl4 injection, as described previously28,29,31, but comparable in WT and AQP3−/− livers (Fig. 1d, Supplementary Fig. 1d), indicating similar macrophage infiltration into the liver.
We next determined whether AQP3 expression affects cellular ROS levels and oxidative stress during acute liver injury. Hepatocytes were isolated from liver 1 day after CCl4 injection, and cellular ROS levels were assayed using the fluorescent dye CM-H2DCFDA that reacts with ROS including H2O222,23,32. Figure 1e shows that CCl4 injection increased cellular ROS levels in WT hepatocytes but not in AQP3−/− hepatocytes. Oxidative stress, as detected by decreased glutathione (GSH)/glutathione disulfide (GSSG) ratio, was significantly increased in CCl4-injected WT but not AQP3−/− liver homogenates (Fig. 1f). These findings support the involvement of AQP3 in the development of acute liver injury and oxidative stress in the CCl4 model.
To investigate the role of AQP3 in macrophages and HSCs in liver injury, lethally irradiated WT and AQP3−/− mice (recipients) were reconstituted with bone marrow (BM) cells from WT and AQP3−/− mice (donors) in a CCl4-induced acute liver injury model (Supplementary Fig. 1e). The chimeric mice produced by transferring WT BM cells into AQP3−/− recipients showed reduced CCl4-induced increased expression of mRNA encoding TNF-α, CCL2, and α-SMA compared to the WT mice with WT BM transfer, suggesting that the development of liver injury requires AQP3 expression in non-hematopoietic cells such as HSCs and Kupffer cells. Transfer of AQP3−/− BM into WT or AQP3−/− recipients also reduced CCl4-induced liver injury, suggesting the involvement of AQP3 expression in hematopoietic cells, most likely in recruited macrophages (Fig. 1g).
AQP3-dependent macrophage activation is required for acute liver injury
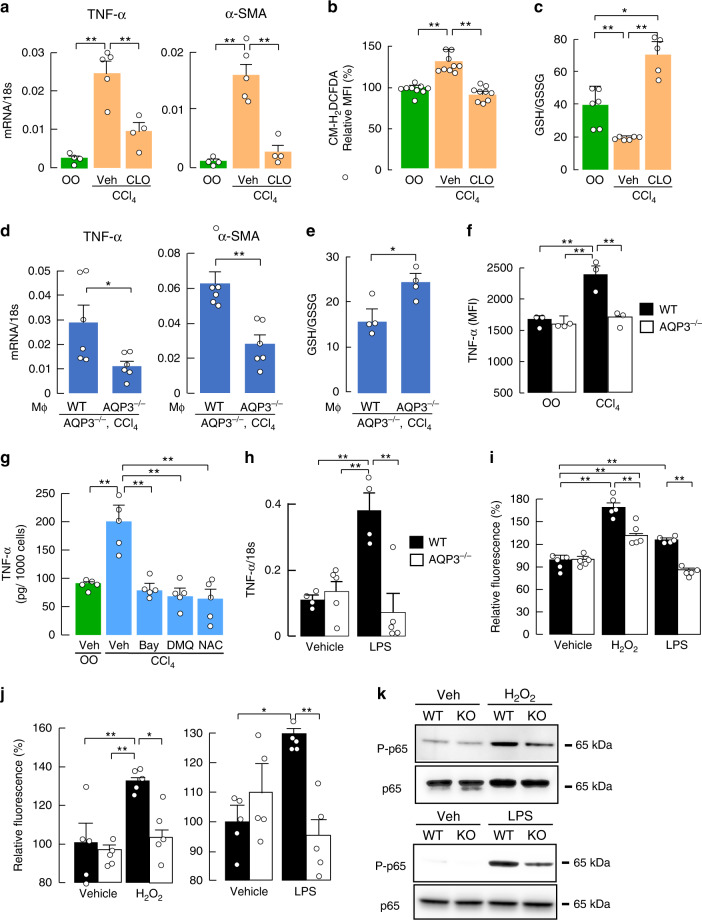
To investigate the involvement of macrophages in HSC activation and hepatic inflammation in CCl4-induced acute liver injury, WT mice were administered clodronate liposomes, which depleted macrophages33 as confirmed by anti-F4/80 immunostaining (Supplementary Fig. 2a). CCl4-induced increases in TNF-α and α-SMA mRNA expression were suppressed by clodronate liposomes (Fig. 2a), as were hepatocyte ROS levels and oxidative stress (Fig. 2b, c), implicating the involvement of macrophages in HSC activation, increased hepatocyte ROS, and oxidative stress during acute liver injury.
Fig. 2. AQP3-dependent macrophages activation is required for acute liver injury.
a–c Clodronate liposomes (CLO, 10 ml/kg) were injected intravenously, and injected CCl4 intraperitoneally (1 ml/kg) or vehicle olive oil (OO) after 48 h. a mRNA expression of TNF-α and α-SMA in liver homogenates determined by real-time RT-PCR (mean ± SE, n = 4 for olive oil and clodronate/CCl4, n = 5 for vehicle/CCl4 mice/group, **p < 0.01). b MFI of CM-H2DCFDA by FACS analysis in hepatocytes (mean ± SE, n = 9 biologically independent samples, **p < 0.01). c Ratio of GSH to GSSG in the liver homogenate (mean ± SE, n = 6 for olive oil and vehicle/CCl4, n = 5 for clodronate/CCl4 mice/group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Statistical analysis for (a)–(c) was performed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. d, e WT or AQP3−/− mouse-derived macrophages (5 × 106 cells/200 μl PBS/head) were injected intravenously into AQP3−/− mice 1 h before CCl4 injection. d mRNA expression of indicated genes in liver homogenates (mean ± SE, n = 6 mice/group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 by two-tailed unpaired Student t-test). e Ratio of GSH to GSSG in liver homogenate (mean ± SE, n = 4 mice/group, *p < 0.05 by two-tailed unpaired Student t-test). f TNF-α expression in CD11B+ F4/80+ hepatic macrophage after CCl4 injection or olive oil (OO) was analyzed by FACS as shown in Supplementary Fig. 2c. MFI of TNF-α (mean ± SE, n = 3 biologically independent samples, **p < 0.01 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). g TNF-α amount in culture medium by ELISA assay. CD11B+ macrophages were magnetically isolated from WT liver with or without CCl4 injection, and cultured with BAY11-7082 (20 μM), DHMEQ (1 μg/ml), or NAC (50 μM) (mean ± SE, n = 5 biologically independent samples, **p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). h, i CD11B+ macrophages were magnetically isolated from WT or AQP3−/− mouse liver. h Cells were treated with LPS (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. mRNA expression of TNF-α as the ratio to 18 s (mean ± SE, n = 4 for WT, n = 5 for AQP3−/− biologically independent samples, **p < 0.01). i H2O2 uptake into CD11B+ liver macrophages. Cells were stimulated with H2O2 (30 μM) for 30 s or LPS (100 ng/ml) for 1 min, and cellular H2O2 was detected with CM-H2DCFDA fluorescence using a plate reader (mean ± SE, n = 5 biologically independent samples, **p < 0.01). j–k Bone marrow-derived macrophages were generated from WT or AQP3−/− mice. j Cells were stimulated with H2O2 (30 μM) for 30 s or LPS (100 ng/ml) for 1 min. Cellular H2O2 was detected using CM-H2DCFDA fluorescence using a plate reader (mean ± SE, n = 5 biologically independent samples, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Statistical analysis for (h)–(j) was performed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. k Cells were incubated with H2O2 (300 μM) or LPS (100 ng/ml) for 30 min. Representative immunoblot using antibodies against phospho-p65 or p65. Source data, including exact p values and uncropped immunoblot image, are provided as a Source data file.
We next investigated the requirement of AQP3 expression in macrophages for CCl4-induced acute liver injury. Macrophages from WT and AQP3−/− bone marrow (Supplementary Fig. 2b) were injected intravenously 3 h before CCl4 administration into AQP3−/− mice as described previously34–36. Adoptive transfer of WT macrophages rescued the reduction in mRNA expression of TNF-α and α-SMA when compared with transfer of AQP3−/− macrophages (Fig. 2d). In addition, CCl4-induced oxidative stress was greater with WT than AQP3−/− macrophage transfer (Fig. 2e), supporting the requirement of AQP3 in macrophages for CCl4-induced liver injury.
Previous studies have shown that CCl4-induced TNF-α production by activated macrophages contributes to the development of liver inflammation and fibrogenesis, which is dependent on NF-κB signaling and ROS status1,5,28,29. FACS analysis showed significantly greater TNF-α expression in CD11B+ macrophages in WT than in AQP3−/− liver after CCl4 injection, suggesting the involvement of AQP3 in TNF-α production by hepatic macrophages (Fig. 2f, Supplementary Fig. 2c). TNF-α production (assessed by ELISA assay) by isolated CD11B+ hepatic macrophages from CCl4-treated WT mice was reduced by the NF-κB inhibitors BAY11-7082 and DHMEQ37, or the ROS scavenger N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) (Fig. 2g). These findings show that CCl4-induced TNF-α production by macrophages depends in part on NF-κB and ROS levels.
Reduced H2O2 transport and NF-κB activation in AQP3−/− macrophages
There is evidence that H2O2 plays an important role in the regulation of NF-κB38,39. We previously showed that AQP3-facilitated transport of H2O2 is involved in NF-κB activation as a secondary messenger in keratinocytes23. To study the involvement of AQP3 in NF-κB activation of macrophages during liver injury, sorted liver macrophages from naive WT or AQP3−/− mice were incubated with LPS for 24 h. Quantitative RT-PCR showed increased TNF-α expression in WT macrophages with LPS, which is related to inflammation in response to NF-κB activation, with little effect in AQP3−/− cells (Fig. 2h). We next investigated whether AQP3 could transport extracellular H2O2 into naive macrophages, as was found in keratinocytes, epithelial cells, and cancer cells22–25,40–42. Following extracellular addition of H2O2, intracellular H2O2 was significantly greater in WT than AQP3−/− macrophages within seconds (Fig. 2i). The increase in cellular ROS levels with LPS stimulation was also reduced in AQP3−/− macrophages (Fig. 2i).
In addition to liver macrophages, we confirmed the involvement of AQP3 in H2O2 transport and NF-κB activation in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Both H2O2 and LPS stimulation increased intracellular H2O2 level greater in WT compared to AQP3−/− cells (Fig. 2j). Moreover, both H2O2 and LPS stimulation induced p65 phosphorylation as seen by immunoblotting (Fig. 2k, Supplementary Fig. 2d) and p65 translocation into the nucleus as seen by immunofluorescence (Supplementary Fig. 2e), as markers of NF-κB activation in WT naive cells, which were reduced in AQP3−/− cells. Pretreatment with NAC and diphenyleneiodonium (DPI), a general Nox inhibitor, or incubation with catalase, which depletes extracellular H2O2, greatly suppressed LPS-induced NF-κB activation, suggesting that LPS-induced NF-κB activation in macrophages is partially dependent on extracellular ROS levels (Supplementary Fig. 2f). These results suggest that AQP3-mediated H2O2 transport regulates NF-κB activation in macrophages during acute inflammation.
Activated macrophages are involved in HSC activation and hepatocyte oxidative stress
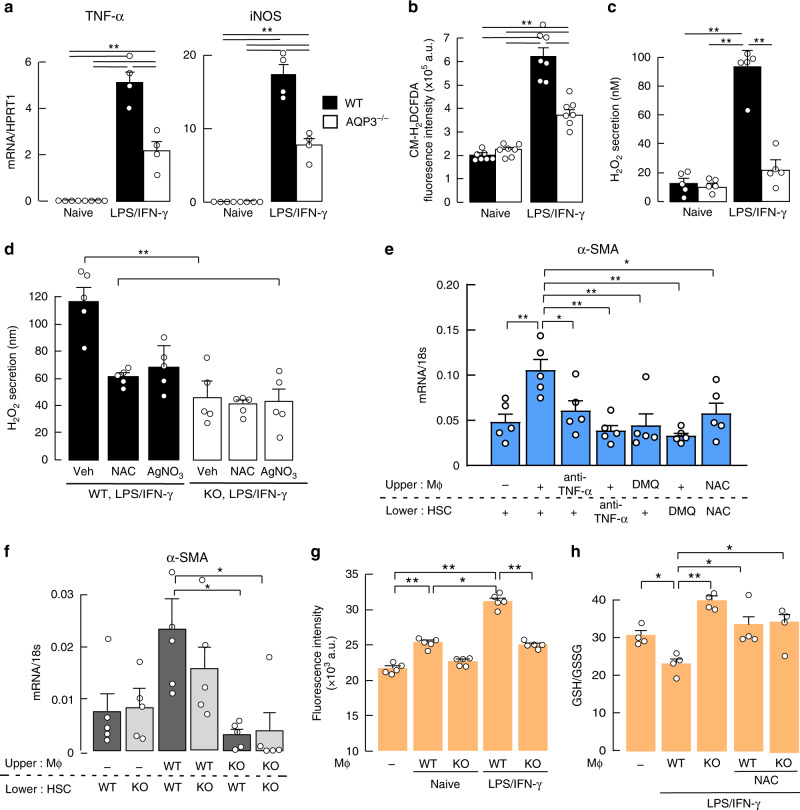
In response to environmental signals, macrophages are polarized into M1 or M2 types4–6. M1 macrophages with an inflammatory phenotype are induced by LPS and IFN-γ, and release pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as TNF, IL-1β), iNOS, and ROS. The inflammatory response with sustained LPS and IFN-γ stimulation, as seen by the increases in TNF-α and iNOS mRNA, was reduced in AQP3 deficiency (Fig. 3a). In contrast, differentiation of macrophages into the M2 subtype by IL-4 stimulation, quantified by arginase 1 (ARG1) as one of the M2 markers, was comparable in WT and AQP3−/− macrophages, while AQP3 expression level was greater in IL-4 treated macrophages than control or LPS/IFN-γ treated macrophages (Supplementary Fig. 3b, c). Cellular ROS levels were significantly higher in LPS/IFN-γ-treated inflammatory macrophages than in naive WT macrophages (Fig. 3b). H2O2 secretion from macrophages into the culture medium was remarkably greater in LPS/IFN-γ-treated than in naive macrophages, with much reduced secretion in AQP3−/− macrophages (Fig. 3c). Treatment with the AQP3 inhibitor AgNO3 reduced H2O2 release from WT macrophages, suggesting AQP3-mediated H2O2 release (Fig. 3d). These findings support the conclusion that activated macrophages secrete H2O2 through AQP3.
Fig. 3. Activated macrophages are involved in HSC activation and hepatocyte oxidative stress.
a–d Naive bone marrow-derived macrophages from WT or AQP3−/− mice were treated with LPS/IFN-γ (1 ng/ml; 10 ng/ml) for 24 h. a mRNA expression of TNF-α and iNOS. Data are expressed as the ratio to HPRT1 (mean ± SE, n = 4 biologically independent samples, **p < 0.01). b Cellular ROS level (mean ± SE, n = 7 biologically independent samples, **p < 0.01). c H2O2 release into the culture medium (mean ± SE, n = 5 biologically independent samples, **p < 0.01). d H2O2 release to the culture medium from WT and AQP3−/− cells. After 24 h of LPS/IFN-γ treatment, cells were incubated with NAC (50 μM) or AgNO3 (AQP3 inhibitor, 20 μM, 1 h), and H2O2 release to the culture medium measured (mean ± SE, n = 5 biologically independent samples, **p < 0.01). Statistical analysis for (a)–(d) was performed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. e, f HSCs from naive mice were co-cultured with hepatic macrophages from CCl4-injected mice using a polycarbonate transwell membrane filter. e WT-derived HSCs or macrophages were incubated with anti-TNF-α (1 μg/ml) or DHMEQ (DMQ, 1 μg/ml) and then co-cultured. NAC (50 μM) was added to the culture medium. mRNA expression of α-SMA in HSCs (mean ± SE, n = 5 biologically independent samples, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). f HSCs from WT or AQP3−/− mice were co-cultured with WT or AQP3−/− mouse-derived macrophages for 24 h. mRNA expression of α-SMA in HSCs (mean ± SE, n = 5 biologically independent samples, *p < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). g, h WT hepatocytes were co-cultured with macrophages from WT or AQP3−/− mice. Some macrophages were treated with LPS/IFN-γ (24 h) and subsequent co-culture (24 h). g Intracellular H2O2 in hepatocytes was monitored by CM-H2DCFDA fluorescence (mean ± SE, n = 5 biologically independent samples, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). h Ratio of GSH to GSSG in hepatocytes (mean ± SE, n = 4 biologically independent samples, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Statistical analysis for (g)–(h) was performed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Source data, including exact p values, are provided as a Source data file.
Previous studies have shown that in early liver injury activated macrophages result in HSC transdifferentiation into myofibroblasts via TNF-α, as seen by the increase in α-SMA and collagen I expression, involving secretion of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)1,5. TNF-α-induced HSC activation in naive cells, as seen by the increased α-SMA and TGF-β1 expression, were similar in WT and AQP3−/− (Supplementary Fig. 3d), suggesting that HSC activation is less affected by AQP3.
To investigate whether activated macrophages cause HSC activation, isolated naive WT HSCs were co-cultured with CD11B+ macrophages from CCl4-injected WT mice. Co-cultured HSCs with activated macrophages showed increased mRNA levels of α-SMA and TGF-β when compared with the levels in the absence of macrophages (Fig. 3e, Supplementary Fig. 3e). Pretreatment of either macrophages or HSCs with a blocking monoclonal TNF-α antibody or the NF-κB inhibitor DHMEQ significantly reduced α-SMA and TGF-β expression. Further, addition of NAC to the culture medium reduced α-SMA and TGF-β expression (Fig. 3e, Supplementary Fig. 3e). These findings suggest the requirement of activated macrophages for HSC activation during CCl4-induced acute liver injury, which is dependent on TNF-α, NF-κB cell signaling, and ROS. To support the requirement of macrophage AQP3 for HSC activation, we compared HSC activation in the same co-culture system with hepatic macrophages from WT or AQP3−/− mice. WT macrophages, but not AQP3−/− macrophages, increased TGF-β and α-SMA expression, indicating that AQP3-expressing macrophages play a pivotal role in HSC activation (Fig. 3f, Supplementary Fig. 3f).
We next tested the hypothesis that activated macrophages affect hepatocytes via AQP3-mediated H2O2 secretion. In co-cultures of WT hepatocytes with macrophages, LPS and IFN-γ-induced inflammatory WT macrophages increased cellular ROS levels in hepatocytes when compared with naive control cells or AQP3−/− macrophages (Fig. 3g). Oxidative stress in hepatocytes was also increased by co-culture with activated WT but not with AQP3−/− macrophages, or NAC treatment (Fig. 3h). Taken together, these results support the involvement of macrophage AQP3 in HSC activation and hepatocyte oxidative stress during acute liver injury.
Prevention of CCl4-induced chronic liver injury in AQP3−/− mice
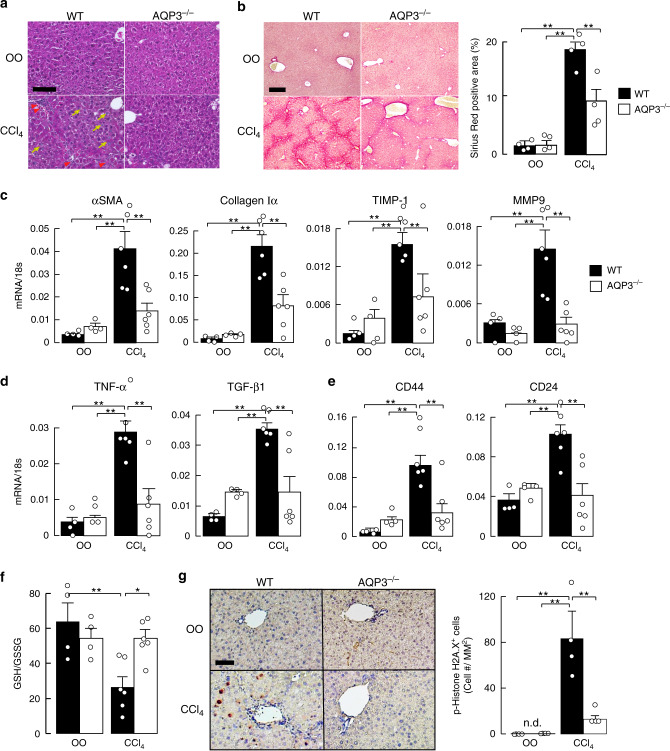
To investigate the possible role of AQP3 in the pathogenesis of chronic liver injury, CCl4 was applied for 6 weeks to induce chronic liver injury and fibrosis in WT and AQP3−/− mice43. This model resulted in chronic liver injury with many necrotic cells and marked leukocyte infiltration on hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining (Fig. 4a, Supplementary Fig. 4a). The CCl4 induced elevation in serum AST and ALT was lower in AQP3−/− mice (Supplementary Fig. 4b). Livers from WT mice showed advanced fibrosis by Sirius red staining (polymeric and monomeric collagen matrix) (Fig. 4b) and immunostaining with anti-α-SMA (Supplementary Fig. 4d), consistent with the previous reports43. Pathology was notably reduced in AQP3−/− mice, with less periportal necrosis and fibrosis (Fig. 4a, b, Supplementary Fig. 4a–c). AQP3 was found to be expressed in F4/80+ macrophages in vehicle- and CCl4-treated liver (Supplementary Fig. 4c).
Fig. 4. Reduced CCl4-induced chronic liver injury in AQP3−/− mice.
a–g CCl4 (0.5 ml/kg) or vehicle olive oil (OO) was intraperitoneally injected twice a week for 6 weeks. a Hematoxylin and eosin staining of liver from WT and AQP3−/− mice. Bar, 100 µm. Arrow: infiltrating lymphocytes. b (left) Sirius red staining. Bar, 200 µm. (right) Sirius red-positive staining area (mean ± SE, n = 4 sections from 4 individual mice, **p < 0.01). c–e mRNA expression of indicated genes in liver homogenates by real-time RT-PCR (mean ± SE, n = 4 for olive oil, n = 6 for CCl4 mice/group, **p < 0.01). Data are expressed as the ratio to 18s RNA. f Ratio of GSH to GSSG in liver homogenate (mean ± SE, n = 4 for olive oil, n = 6 for CCl4 mice/group *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). g (left) Phospho-histone H2A.X staining. Bar, 200 µm. (right) Number of phospho-histone H2A.X-positive stained cells (mean ± SE, n = 4 sections from four individual mice, >100 cells from over two different fields from one mouse, **p < 0.01). Statistical analysis for (b)–(g) was performed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Source data, including exact p values, are provided as a Source data file.
RT-PCR showed that the CCl4 injection increased fibrosis markers, including α-SMA, collagen type Iα, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1), and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), in WT liver, with significantly lesser increases in AQP3−/− liver (Fig. 4c). Pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrogenic factors (TNF-α and TGF-β) were increased in WT liver, as previously reported29, with reduced elevation in AQP3−/− liver (Fig. 4d). CD44 and CD24 expression, as cancer stem cell markers, were elevated in only WT liver with CCl4 administration (Fig. 4e).
We next investigated the involvement of AQP3 in oxidative stress in the chronic liver injury model. Six weeks of CCl4 treatment increased hepatic oxidative stress in WT liver, whereas AQP3−/− liver was unaffected (Fig. 4f). Also, the increase in DNA double-strand breaks, assessed from the number of phospho-H2AX-positive cells44, was much reduced in AQP3−/− livers from CCl4-treated mice (Fig. 4g), supporting the involvement of AQP3 in CCl4-induced DNA damage. These findings indicate the requirement of AQP3 for the development of chronic liver injury with inflammation, high oxidative stress, and fibrosis.
Monoclonal anti-AQP3 antibody inhibits H2O2 transport and macrophage activation
The above findings suggest that inhibition of AQP3-facilitated H2O2 transport in macrophages might be of benefit in liver injury, though a suitable selective inhibitor has not been available21. To develop an anti-mouse monoclonal AQP3 antibody (anti-AQP3 mAb) that specifically recognizes the extracellular domain of AQP3, we generated a fragment (oligopeptide) composed of the amino acid sequence that corresponds to positions 148–157 in loop C of the extracellular domain, which are common to human and mouse AQP3. C57BL6 mice were immunized with this synthetic peptide together with mouse AQP3-overexpressing CHO-K1 cells. After selecting AQP3-binding colonies using several screening approaches, 10 IgG clones were identified (Supplementary Table 1).
Among the 10 IgG clones, four clones (mAb-C, E, H, and J) were found to bind specifically to 148–157 oligopeptides of loop C (Supplementary Fig. 5a). These clones showed different binding sites on loop C as analyzed by peptide ELISA (Supplementary Tables 2 and 3). In CHO-K1 cells overexpressing human AQP3 (Supplementary Fig. 5b), significant binding was found of the four clones (Fig. 5a, Supplementary Fig. 5c). The anti-AQP3 mAbs significantly inhibited H2O2 uptake (Fig. 5b, Supplementary Fig. 5d, e) and glycerol uptake (Fig. 5c, Supplementary Fig. 5f, g) into AQP3-expressing cells. Some anti-AQP3 mAbs also weakly inhibited osmotically induced water transport in the AQP3-expressing CHO cells (Supplementary Fig. 5h). The apparently greater inhibitory effect on H2O2 and glycerol transport vs. water transport may be related to steric factors in the AQP3 pore. We also verified specific mAb binding to endogenous AQP3 in human keratinocytes (HaCaT), in which the binding was reduced by siRNA-mediated AQP3 knockdown (Supplementary Fig. 6a–c). The four anti-AQP3 mAbs inhibited H2O2 uptake into the cells to the same extent as with AQP3 knockdown (Supplementary Fig. 6d).
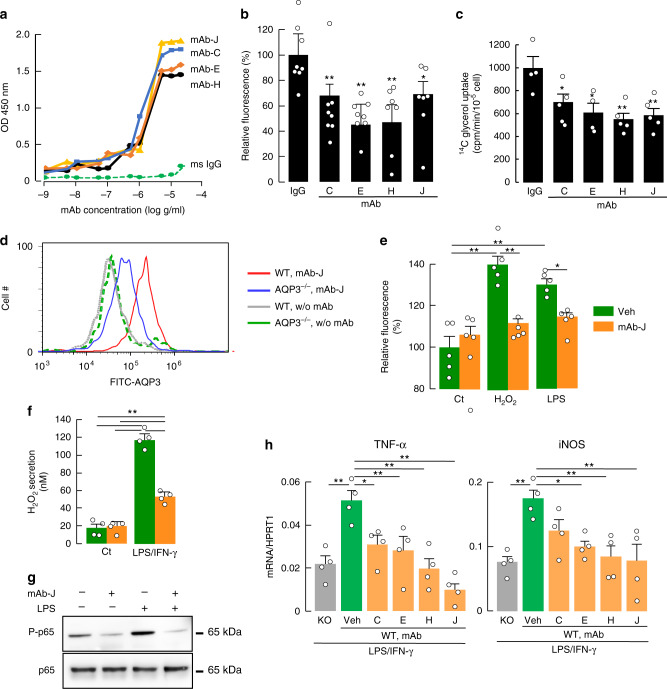
Fig. 5. Anti-AQP3 mAb inhibits H2O2 /glycerol transport and macrophage activation.
a Binding of anti-AQP3 mAb (C, E, H, and J) to human AQP3-expressing CHO-K1 cells. Experiments were performed in duplicate and repeated three times with similar results. b, c Effect of mAb on H2O2 uptake (b) or glycerol uptake (c) in human AQP3-expressing CHO-K1 cells. Cells were incubated with mAb (1 μg/ml, 37 °C) or control monoclonal anti-mouse IgG prior to transport measurements. b Cellular H2O2 measured after adding H2O2 (40 μM) using CM-H2DCFDA fluorescence (mean ± SE, n = 8 for IgG, C and E, n = 7 for H and J biologically independent samples, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. mouse IgG treated by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). c Glycerol uptake. Cellular [14C] radioactivity was measured after adding [14C]-glycerol for 1 min (mean ± SE, n = 4 for IgG and E, n = 5 for C, H, and J biologically independent samples, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. mouse IgG treated by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). d–h Bone marrow-derived macrophages generated from WT or AQP3−/− mice were used. d Flow cytometric analysis of binding of anti-AQP3 mAb-J in WT or AQP3−/− macrophages. e Cellular H2O2 after addition of H2O2 (30 μM, 30 s) or LPS (100 ng/ml, 1 min) in WT macrophages treated with anti-AQP3 mAb-J (100 ng/ml, 1 h, mean ± SE, n = 5 biologically independent samples, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). f H2O2 release to the culture medium from WT macrophages treated with anti-AQP3 mAb-J (100 ng/ml, 1 h). WT Macrophages were incubated with LPS/IFN-γ (1 ng/ml; 10 ng/ml) for 24 h (mean ± SE, n = 4 biologically independent samples, **p < 0.01 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). g Representative immunoblot using antibodies against phospho-p65 and p65. WT macrophages were incubated with anti-AQP3 (mAb-J, 1 μg/ml, 1 h) and thereafter stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml, 30 min). h WT or AQP3−/− (KO) macrophages were treated with LPS/IFN-γ (1 ng/ml; 10 ng/ml) for 24 h. Some WT cells were co-incubated with anti-AQP3 mAb (C, E, H, and J, 1 μg/ml). mRNA expression of TNF-α and iNOS. Data are expressed as the ratio to HPRT1 (mean ± SE, n = 4 biologically independent samples, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. WT/vehicle by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). Source data, including exact p values and uncropped immunoblot image, are provided as a Source data file.
We next determined the effect of anti-AQP3 mAb on macrophage function. The binding of anti-AQP3 mAb-J to WT macrophages was greater than its binding to AQP3−/− macrophages (Fig. 5d). We also found binding, albeit relatively low, of mAb-J to HSC and hepatocytes (Supplementary Fig. 5i).
Cellular H2O2 uptake was reduced in WT macrophages incubated with anti-AQP3 mAbs (Fig. 5e). In addition, H2O2 secretion from LPS/IFN-γ-treated inflammatory macrophages was significantly reduced by anti-AQP3 mAb treatment (Fig. 5f). Importantly, treatment with anti-AQP3 mAb suppressed LPS-induced NF-κB activation (Fig. 5g, Supplementary Fig. 5j). In agreement with this observation, LPS/IFN-γ-induced increases in TNF-α and iNOS expression were reduced by anti-AQP3 mAb treatment (Fig. 5h). Treatment with anti-AQP3 antibody thus inhibits H2O2 transport and macrophage activation.
Anti-AQP3 antibody prevented acute and chronic liver injury in mice
We examined the effect of anti-AQP3 mAb on acute liver injury induced by CCl4 (model in Fig. 1). Anti-AQP3 mAb or mouse monoclonal antibody (as control IgG) was administered intravenously (5 mg/kg weight) 1 day before CCl4 injection. Anti-AQP3 remarkably suppressed the increases in serum AST and ALT (Fig. 6a). We verified the presence of administered fluorescein-conjugated anti-AQP3 mAb in the liver at 6–24 h after injection (Supplementary Fig. 7a). In addition, the increases in mRNAs encoding TNF-α, CCL2, α-SMA, and IL-6 in liver homogenates were greatly suppressed by anti-AQP3 mAb (Fig. 6b), as was CCl4-induced oxidative stress (Fig. 6c). Liver injury was not affected by administration of the anti-AQP3 mAb in AQP3−/− mice with CCl4 injection (Supplementary Fig. 7b, c).
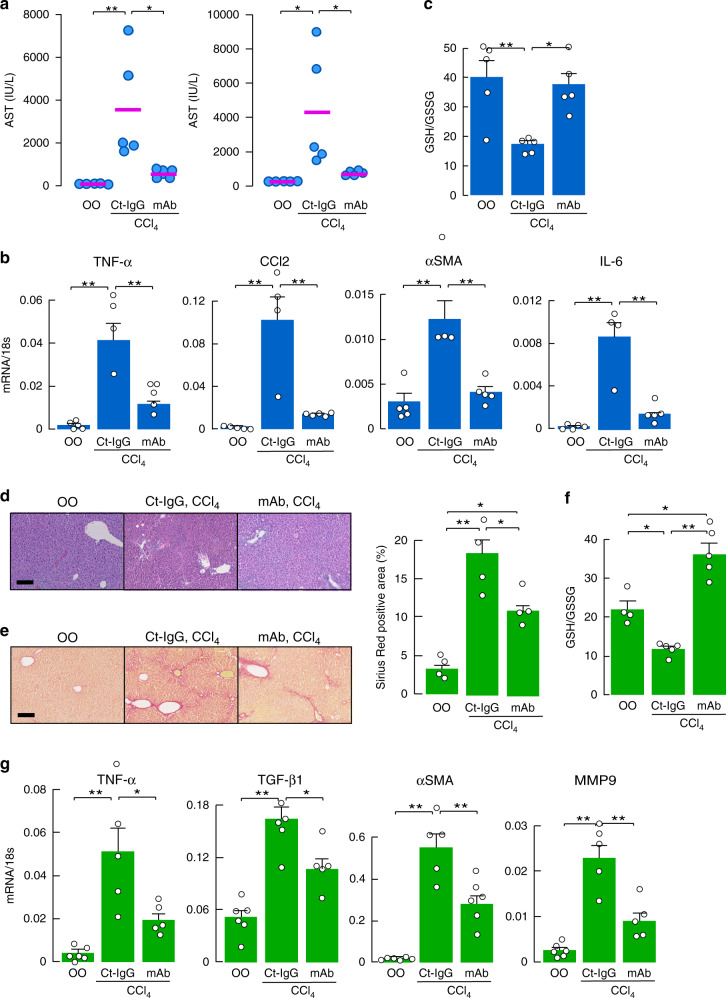
Fig. 6. Prevention of acute and chronic liver injury by anti-AQP3 mAb.
a–c Effect of anti-AQP3 mAb on acute liver injury. Anti-AQP3 (mAb-J, 10 mg/kg weight, PBS) or control monoclonal anti-mouse IgG (Ct-IgG, 10 mg/kg weight, PBS) was injected intravenously 1 day before CCl4 injection (1 ml/kg weight, olive oil; OO). Liver and blood were collected at 24 h. a Serum AST and ALT (mean ± SE, n = 5 mice/group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). b mRNA expression of indicated genes by real-time RT-PCR (mean ± SE, n = 4 for control IgG/CCl4, n = 5 for olive oil and anti-AQP3 mAb/CCl4 mice/group, **p < 0.01). Data are expressed as the ratio to 18s RNA. c Ratio of GSH to GSSG in the liver homogenate (mean ± SE, n = 5 mice/group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). d–g Effect of anti-AQP3 on chronic liver injury. CCl4 (0.5 ml/kg) or vehicle olive oil (OO) was intraperitoneally injected twice a week for 4 weeks. Anti-AQP3 mAb (mAb-J, 10 mg/kg, PBS) or control monoclonal anti-mouse IgG (Ct-IgG, 10 mg/kg, PBS) was intravenously injected 1 day before each CCl4 injection. d Hematoxylin and eosin staining of liver. Bar, 100 µm. e Sirius red staining. Bar, 200 µm. (right) Sirius red-positive staining area (mean ± SE, n = 4 sections from four individual mice, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). f Ratio of GSH to GSSG in the liver homogenate (mean ± SE, n = 4 for olive oil, n = 5 for CCl4 mice/group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). g mRNA expression of indicated genes in liver homogenates by real-time RT-PCR. Data are expressed as the ratio to 18s (mean ± SE, n = 6 for olive oil, n = 5 for CCl4 mice/group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Statistical analysis for (a)–(g) was performed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Source data, including exact p values, are provided as a Source data file.
We also investigated the effect of anti-AQP3 mAb on CCl4-induced chronic liver injury (model in Fig. 4). Administration of anti-AQP3 mAb prevented chronic liver injury, with fewer necrotic cells observed on H&E staining (Fig. 6d) and much reduced fibrosis with Sirius red staining (Fig. 6e). Anti-AQP3 mAb suppressed CCl4-induced hepatic oxidative stress (Fig. 6f) and the increases in mRNA encoding inflammatory cytokines and fibrosis-related markers (Fig. 6g).
The effect of anti-AQP3 mAb was also studied in two additional experimental mouse models of liver injury. One model involves administration of thioacetamide (TAA), which is metabolized to TAA sulfine, producing liver cell damage, inflammation, and subsequently liver fibrosis45–50. Histological examination showed more necrotic hepatocytes in WT compared to AQP3−/− liver following intraperitoneal injection of TAA (Supplementary Fig. 8a). TAA injection increased mRNA expression of inflammatory factors TNF-α and CCL2 in WT liver (at 24 and 72 h), as well as fibrogenic markers α-SMA and collagen type Iα (72 h), each of which was significantly reduced in AQP3−/− liver (Supplementary Fig. 8b). Administration of anti-AQP3 mAb one day before TAA injection suppressed necrosis as shown by H&E staining (Supplementary Fig. 8c), and reduced TNF-α and CCL2 mRNA expression at 24 h (Supplementary Fig. 8d). The anti-AQP3 mAb also suppressed TAA-induced hepatic oxidative stress (Supplementary Fig. 8e).
As a third model, we tested the azoxymethane (AOM) injection model, a well-established mouse model of colon carcinogenesis associated with liver injury51–56. We found that AOM-induced acute and chronic liver injury was reduced in AQP3−/− mice compared with WT mice (Supplementary Fig. 9a–c for chronic model; Supplementary Fig. 9d for acute model). Administration of the anti-AQP3 mAb before AOM injection reduced acute liver injury, as shown by reduced AST/ALT and oxidative stress, with reduced TNF-α, CCL2, and α-SMA (Supplementary Fig. 9e–g).
Discussion
A neutralizing anti-AQP3 mAb was generated that bound to the extracellular domain of AQP3 in macrophages and inhibited AQP3-mediated H2O2 transport and NF-κB cell signaling. Administration of the neutralizing anti-AQP3 mAb to mice suppressed inflammation and liver injury in CCl4-, TAA-, and AOM-induced models of liver injury. The anti-AQP3 mAb might block the AQP3 channel directly or neutralize its function by an allosteric mechanism. We note that a relatively high concentration of mAb was used, as the antibody was not optimized for pharmacological properties. Notwithstanding these considerations, our findings provide evidence for anti-AQP3 mAb as a novel approach for inhibition of hepatic macrophage function in liver injury. There is increasing evidence from AQP3−/− mice and AQP3-knockdown cells for the involvement of AQP3 in various inflammatory diseases including atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, allergy, and cancer progression, in which AQP3 transport function supported cell proliferation, migration, and inflammation22–26,42,57,58. Also, many descriptive studies have shown positive correlations between AQP3 expression and cancer progression and prognosis59–65. Thus, AQP3 inhibition has been suggested as a potential therapeutic target for a variety of diseases. However, as most AQP3 inhibitors contain the metals mercury, copper, or gold21, there are not at present suitable drug-like small molecule AQP3 inhibitors.
We found evidence for the requirement of AQP3 for the development of liver injury and fibrosis, which involved AQP3-mediated H2O2 transport in macrophages. In a mouse model of acute liver injury induced by a single injection of CCl4, increases in TNF-α production, α-SMA expression, and oxidative stress were greatly reduced in liver of AQP3−/− mice in a manner dependent on hepatic macrophages. The reduction in acute liver injury in AQP3−/− mice was rescued by the transfer of WT but not AQP3−/− macrophages, providing evidence for the requirement of AQP3 expression in macrophages for the early inflammatory response in the liver. In vitro studies showed that AQP3-mediated H2O2 uptake was involved in NF-κB cell signaling in naive macrophages, resulting in their activation. Moreover, excess H2O2 produced by inflammatory macrophages was transported extracellularly via AQP3, affecting surrounding cells including HSCs and hepatocytes. Consequently, in AQP3 deficiency there is reduced activation of naive macrophages and HSCs resulting in impaired inflammation and profibrotic responses. The reduced early inflammation and fibrogenesis may be responsible for the greatly reduced chronic liver injury and fibrosis in AQP3−/− mice. These findings support the involvement of AQP3 in the development of liver injury through a mechanism involving its H2O2 transport function and macrophage activation, and suggest AQP3 as a novel potential therapeutic target in liver injury.
An expanding body of literature supports an important biological effect of H2O2 on cellular functions66,67. The transient accumulation of intracellular H2O2 near the plasma membrane, though relatively small, modulates specific cell signaling pathways to control a diverse set of physiological functions, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and migration14,68. Higher concentrations of H2O2 produced by cancer cells or immune cells induces oxidative stress, leading to inflammation or cytotoxicity69,70. Oxidative stress has been linked to a myriad of pathologies including initiation and progression of liver injury10,11,71. In this study, we showed that inflammatory macrophages produced much more intracellular H2O2 compared to the quiescent cells, and hence could release larger quantities of H2O2 into extracellular space through AQP3. The increased extracellular H2O2 affected surrounding liver cells, including HSCs and hepatocytes, amplifying the liver injury (Supplementary Fig. 9). Our data support a liver injury mechanism in which AQP3 mediates crosstalk between macrophages and neighboring cells via its H2O2 transport function. Prevention of this cell–cell pro-inflammatory communication by AQP3 inhibition represents a potential novel therapeutic approach for oxidative stress-related diseases.
In summary, our findings support the novel role for AQP3 in the pathogenesis of liver injury and fibrosis in which AQP3-mediated intracellular H2O2 uptake is required for NF-κB cell signaling and subsequent macrophage activation. These findings thus support AQP3 inhibition as a potential therapeutic approach for liver injury and offer a monoclonal antibody approach to accomplish this.
Methods
Mice
C57BL/6 mice were purchased from Japan SLC, Inc. AQP3−/− mice (C57BL/6 genetic background) were generated by targeted gene disruption72. Seven- to 10-week-old mice were used. All animal experiments were approved by the President of Keio University, following the consideration by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Keio University (approval no: 16075) and by Genetic Modification Safety Committee, Keio University School of Medicine (approval no. 28-029), and were carried out in accordance with institutional procedures, national guidelines, and the relevant national laws on the protection of animals.
Development of an anti-AQP3 antibody
An oligopeptide was synthesized consisting of the amino acid sequence corresponding to positions 148–157 of the mouse/human AQP3 polypeptide. A C57BL/6 mouse was immunized by the synthetic peptide together with mouse AQP3-overexpressing CHO-K1 cells and an adjuvant. Four weeks later, immune cells were collected from the immunized mouse and an antibody gene phage library was constructed73. After several screenings, selected AQP3-binding colonies were made into IgG immunoglobulins to give ten anti-AQP3 mAbs.
Mouse models of acute and chronic liver injury by CCl4
To induce liver injury and fibrosis, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4, 0.5 ml/kg weight) or vehicle control (olive oil) was intraperitoneally injected twice weekly for 6 weeks. For acute injury, mice received an intraperitoneal injection of CCl4 (1 ml/kg weight). Mice were sacrificed at 24 h after the final CCl4 injection. To deplete macrophages in some experiments, mice were intravenously administrated chlodronate liposomes (10 μl/g weight, Xygieia Bioscience) 2 days before CCl4 injection. In some studies, anti-AQP3 mAb or mouse monoclonal antibody (as a control IgG) was administered intravenously (5 mg/kg weight) 1 day before each CCl4 injection.
Bone marrow transplantation
For bone marrow (BM) transplantation, red blood cells from WT and AQP3−/− BM cells were subjected to hypotonic cell lysis. WT and AQP3−/− recipients (8–10 weeks old) were γ-irradiated with doses of 900 rad. After irradiation, the mice received 106 BM cells intravenously. This protocol consistently gave >95% reconstitution of the recipient by donor hematopoietic cells, as evaluated by separate transplantation experiments using BM from C57BL/6-CD45.1 congenic mice (Supplementary Fig. 1e).
Primary culture of mice hepatocytes, hepatic macrophage, and HSC
Livers were perfused with liver perfusion medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, #17701-038) and then liver digest medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, #17703-034) according to manufacturer’s instructions74. The dispersed cells were centrifuged (50 × g, 1 min) to recover nonparenchymal cells-containing supernatants and pelleted hepatocytes. Isolated hepatocytes were plated on collagen I-coated plate (BD Biosciences) and cultured with HepatoZYME-SFM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, #17705-021). To obtain HSCs and macrophages, recovered nonparenchymal cells were isolated by density gradient centrifugation with Optiprep solution (11.5 and 15%) (Axis Shield, Dundee, UK) diluted with HBSS75,76. In some experiments, recovered nonparenchymal cells were sorted using anti-F4/80 or anti-CD11B microbeads with MACS separator according to manufacturer’s instructions (Milteny Biotec). Macrophages were co-cultured with HSCs or hepatocytes using a polycarbonate transwell membrane filter (0.4-μm pore size, Corning Costar, Cambridge, MA).
Bone marrow-derived macrophage preparation
Single-cell suspensions of bone marrow cells were collected from femur and tibia, and cultured in RPMI 1640 (Invitrogen) containing 10 ng/ml GM-CSF (PeproTech Inc.), 10% FBS, 50 μM 2-mercaptoethanol, 2 mM L-glutamine, 25 mM HEPES, 1 mM nonessential amino acids, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 1% penicillin-streptomycin for at least 6 days. More than 90% of cultured cells were confirmed as macrophages by FACS analysis (Supplementary Fig. 2b). To activate macrophages, cells were incubated with LPS (1 ng/ml) and IFN-γ (10 ng/ml) for over 1 day.
Cell culture and transfection
CHO-K1 cells (Riken BRC cell bank, Japan) and human keratinocyte HaCaT cells (Cell Line Service, Germany) were grown in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. The cDNA plasmid for human AQP3 (pCMV6 vector, Origine) was transfected into CHO-K1 with TransIT-X2 (Mirus) and positive cells were obtained by G418 selection. HaCaT cells were transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) with AQP3- or non-targeting-siRNA (ON-TARGET plus SMART pool, Thermo Scientific). We generally found that 70–80% of cells become positive after transfection.
RNA extraction and real-time quantitative RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted using TRIZOL (Invitrogen). The cDNA was reverse transcribed from total RNA using the Prime Script RT reagent kit (Takara Bio, Otsu, Japan). Quantitative RT-PCR was performed using SYBR Green I (Takara Bio) and StepOne Plus real-time PCR apparatus (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence
Paraffin-embedded sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, Sirius red (ScyTek Laboratories Inc.), or anti-phospho-Histone H2A.X (Cell Signaling, 1:400) with biotinylated IgG and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated ABC reagent (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA). The positive area of Sirius red staining and the number of brown color stained-H2A gamma positive cells were analyzed by Tissue Quest (TissueGnostics). Frozen sections were fixed with cold acetone, and immunostained with anti-AQP3 (Millipore, 1:100), anti-F4/80 (eBioScience, 1:400), or anti-desmin (R&D Systems, 10 μg/ml) antibodies.
Assays of cellular H2O2, extracellular H2O2, and GSH/GSSG
Cellular H2O2 was assayed using the CM-H2DCFDA reagent (Invitrogen) according to manufacturer’s instructions using flow cytometry (Gallios, Beckman, CA, USA) on a microplate reader (SpectraMax i3x; Molecular Devices). To determine cell-derived ROS level, accumulated ROS in the medium was quantified by OxiSelectTM Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Kit (Cell Biolabs, Inc.). For GSH/GSSG analysis, liver or cells were homogenized with 5% 5-sulfosalicylic acid dihydrate, and GSSG and GSH levels were measured using a GSSG/GSH Quantification kit (Dojindo, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Glycerol uptake assay
Cells were incubated with [14C]-labeled glycerol (Perkin Elmer, NEC441x, 2 μCi/ml PBS containing 10 mM glycerol) for 1 min at room temperature. After washing cells three times with ice-cold PBS, cells were disrupted with 1 M NaOH. Cell-associated radioactivity was determined by scintillation counting.
Immunoblotting
Cells were lysed with RIPA buffer (Cell Signaling Technology) and the supernatant (10,000 × g, 10 min, 4 °C) was used for immunoblotting with antibodies against phospho-p65 and p65 (Cell Signaling Technology, 1:1000). A horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary anti-rabbit antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, 1:1000) was used and visualized by chemiluminescence (GE Healthcare).
AQP3-binding assay
Human AQP3-expressing CHO-K1 or HaCaT cells plated on 96-well plates were incubated with AQP3 mAbs (0.1 ng – 1 μg/ml, 1 h, 4 °C). After washing cells, bound antibody was detected with HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (Cell Signaling Technology, 1:1000) and TMB (eBioScience), followed by stop reagent. Absorbance (450 nm) was measured on a plate reader (SpectraMax i3x, Molecular Devices).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the two-tailed Student’s t-test, one-way, or two-way ANOVA by GraphPad Prism8.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Hiroki Satooka, Sachiko Watanabe, and Catharina Sagita Moniaga for supporting preliminary experiments. We thank Drs. Shu Narumiya, Noriyuki Morikawa, and Yoshiaki Morita, and Center for Innovation in Immunoregulative Technology and Therapeutics, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University for supporting development of anti-AQP3 antibody. We thank Drs. Maruyama and Okumura for supporting the experiment using AQP3 peptide mutants. We thank Dr. Hayato Takahashi for providing CD45.1 mice. We thank Dr. Kazuo Umezawa for providing DHMEQ reagent. This work was supported in part by grants from Astellas Pharma Inc. in the Creation of Innovation Centers for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research Areas Program (M.H.-C.), the Princess Takamatsu Cancer Research Fund (15-24717, M.H.-C.), Keio University Academic Development Funds (M.H.-C.), Suntory Global Innovation Center Ltd. program “Water Channeling Life” (M.Y.), and U.S. National Institutes of Health grant DK72517 and EY13574 (A.S.V.).
Source data
Author contributions
M.H.-C. conceived the study and all authors were involved in the design of experiments. M.H.-C. and M.T. performed the experiments. M.H.-C., M.T., and M.Y. analyzed the data. M.H.-C. and A.S.V. wrote the manuscript.
Data availability
All other relevant data supporting the key findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Information file or from the corresponding authors upon request. Source data are provided with this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Peer review information Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information is available for this paper at 10.1038/s41467-020-19491-5.
References
- 1.Pellicoro A, Ramachandran P, Iredale JP, Fallowfield JA. Liver fibrosis and repair: immune regulation of wound healing in a solid organ. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014;14:181–194. doi: 10.1038/nri3623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Koyama Y, Brenner DA. Liver inflammation and fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017;127:55–64. doi: 10.1172/JCI88881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schuppan D, Kim YO. Evolving therapies for liver fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013;123:1887–1901. doi: 10.1172/JCI66028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sarin SK, Choudhury A. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: terminology, mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016;13:131–149. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2015.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tacke F, Zimmermann HW. Macrophage heterogeneity in liver injury and fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2014;60:1090–1096. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.12.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sica A, Invernizzi P, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in liver homeostasis and pathology. Hepatology. 2014;59:2034–2042. doi: 10.1002/hep.26754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lee YA, Wallace MC, Friedman SL. Pathobiology of liver fibrosis: a translational success story. Gut. 2015;64:830–841. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-306842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Seki E, Brenner DA. Recent advancement of molecular mechanisms of liver fibrosis. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2015;22:512–518. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Trautwein C, Friedman SL, Schuppan D, Pinzani M. Hepatic fibrosis: concept to treatment. J. Hepatol. 2015;62:S15–S24. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sanchez-Valle V, Chavez-Tapia NC, Uribe M, Mendez-Sanchez N. Role of oxidative stress and molecular changes in liver fibrosis: a review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012;19:4850–4860. doi: 10.2174/092986712803341520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cichoz-Lach H, Michalak A. Oxidative stress as a crucial factor in liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014;20:8082–8091. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Geeraerts X, Bolli E, Fendt SM, Ginderachter Van JA. Macrophage metabolism as therapeutic target for cancer, atherosclerosis, and obesity. Front. Immunol. 2017;8:289. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Van den Bossche J, O’Neill LA, Menon D. Macrophage Immunometabolism: Where are we (going)? Trends Immunol. 2017;38:395–406. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2017.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rhee SG. Cell signaling. H2O2, a necessary evil for cell signaling. Science. 2006;312:1882–1883. doi: 10.1126/science.1130481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Brown DI, Griendling KK. Nox proteins in signal transduction. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009;47:1239–1253. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.07.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Paulsen CE, Carroll KS. Orchestrating redox signaling networks through regulatory cysteine switches. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010;5:47–62. doi: 10.1021/cb900258z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bordt EA, Polster BM. NADPH oxidase- and mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species in proinflammatory microglial activation: a bipartisan affair? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014;76:34–46. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.07.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Paik YH, et al. The nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX) homologues NOX1 and NOX2/gp91(phox) mediate hepatic fibrosis in mice. Hepatology. 2011;53:1730–1741. doi: 10.1002/hep.24281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lan T, Kisseleva T, Brenner DA. Deficiency of NOX1 or NOX4 prevents liver inflammation and fibrosis in mice through inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0129743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bettaieb A, et al. Hepatocyte nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate reduced oxidase 4 regulates stress signaling, fibrosis, and insulin sensitivity during development of steatohepatitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:468–480. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Verkman AS, Anderson MO, Papadopoulos MC. Aquaporins: important but elusive drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Disco. 2014;13:259–277. doi: 10.1038/nrd4226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hara-Chikuma M, et al. Chemokine-dependent T cell migration requires aquaporin-3-mediated hydrogen peroxide uptake. J. Exp. Med. 2012;209:1743–1752. doi: 10.1084/jem.20112398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hara-Chikuma M, et al. Aquaporin-3-mediated hydrogen peroxide transport is required for NF-kappaB signalling in keratinocytes and development of psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:7454. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hara-Chikuma M, Watanabe S, Satooka H. Involvement of aquaporin-3 in epidermal growth factor receptor signaling via hydrogen peroxide transport in cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016;471:603–609. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Satooka H, Hara-Chikuma M. Aquaporin-3 controls breast cancer cell migration by regulating hydrogen peroxide transport and its downstream cell signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016;36:1206–1218. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00971-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nakahigashi K, et al. Upregulation of aquaporin-3 is involved in keratinocyte proliferation and epidermal hyperplasia. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011;131:865–873. doi: 10.1038/jid.2010.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gregoire F, et al. Analysis of aquaporin expression in liver with a focus on hepatocytes. Histochem Cell Biol. 2015;144:347–363. doi: 10.1007/s00418-015-1341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Karlmark KR, et al. Hepatic recruitment of the inflammatory Gr1+ monocyte subset upon liver injury promotes hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology. 2009;50:261–274. doi: 10.1002/hep.22950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chu PS, et al. C-C motif chemokine receptor 9 positive macrophages activate hepatic stellate cells and promote liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology. 2013;58:337–350. doi: 10.1002/hep.26351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kew MC. Serum aminotransferase concentration as evidence of hepatocellular damage. Lancet. 2000;355:591–592. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)00219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ramachandran P, et al. Differential Ly-6C expression identifies the recruited macrophage phenotype, which orchestrates the regression of murine liver fibrosis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2012;109:E3186–E3195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1119964109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Watanabe S, Moniaga CS, Nielsen S, Hara-Chikuma M. Aquaporin-9 facilitates membrane transport of hydrogen peroxide in mammalian cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016;471:191–197. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.01.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Van Rooijen N, Sanders A. Liposome mediated depletion of macrophages: mechanism of action, preparation of liposomes and applications. J. Immunol. Methods. 1994;174:83–93. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nishida M, et al. Adoptive transfer of macrophages ameliorates renal fibrosis in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005;332:11–16. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.04.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ke B, et al. Adoptive transfer of ex vivo HO-1 modified bone marrow-derived macrophages prevents liver ischemia and reperfusion injury. Mol. Ther. 2010;18:1019–1025. doi: 10.1038/mt.2009.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Parsa R, et al. Adoptive transfer of immunomodulatory M2 macrophages prevents type 1 diabetes in NOD mice. Diabetes. 2012;61:2881–2892. doi: 10.2337/db11-1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lin, Y., Ukaji, T., Koide, N. & Umezawa, K. Inhibition of late and early phases of cancer metastasis by the NF-kappaB inhibitor DHMEQ derived from microbial bioactive metabolite epoxyquinomicin: a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci.19, 729 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 38.Morgan MJ, Liu ZG. Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Res. 2011;21:103–115. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Oliveira-Marques V, Marinho HS, Cyrne L, Antunes F. Role of hydrogen peroxide in NF-kappaB activation: from inducer to modulator. Antioxid. redox Signal. 2009;11:2223–2243. doi: 10.1089/ars.2009.2601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Miller EW, Dickinson BC, Chang CJ. Aquaporin-3 mediates hydrogen peroxide uptake to regulate downstream intracellular signaling. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:15681–15686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005776107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Luo J, et al. Activation of TGF-beta1 by AQP3-Mediated H2O2 transport into fibroblasts of a bleomycin-induced mouse model of scleroderma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016;136:2372–2379. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Thiagarajah JR, Chang J, Goettel JA, Verkman AS, Lencer WI. Aquaporin-3 mediates hydrogen peroxide-dependent responses to environmental stress in colonic epithelia. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:568–573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1612921114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Starkel P, Leclercq IA. Animal models for the study of hepatic fibrosis. Best. Pr. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011;25:319–333. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2011.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cook PJ, et al. Tyrosine dephosphorylation of H2AX modulates apoptosis and survival decisions. Nature. 2009;458:591–596. doi: 10.1038/nature07849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Liedtke C, et al. Experimental liver fibrosis research: update on animal models, legal issues and translational aspects. Fibrogenes. Tissue Repair. 2013;6:19. doi: 10.1186/1755-1536-6-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wallace MC, et al. Standard operating procedures in experimental liver research: thioacetamide model in mice and rats. Lab Anim. 2015;49:21–29. doi: 10.1177/0023677215573040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kang JS, et al. Role of CYP2E1 in thioacetamide-induced mouse hepatotoxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2008;228:295–300. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2007.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hernandez-Gea V, et al. Autophagy releases lipid that promotes fibrogenesis by activated hepatic stellate cells in mice and in human tissues. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:938–946. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Park WJ, Kim SY, Kim YR, Park JW. Bortezomib alleviates drug-induced liver injury by regulating CYP2E1 gene transcription. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016;37:613–622. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.An P, et al. Hepatocyte mitochondria-derived danger signals directly activate hepatic stellate cells and drive progression of liver fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:2362. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16092-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Neufert C, Becker C, Neurath MF. An inducible mouse model of colon carcinogenesis for the analysis of sporadic and inflammation-driven tumor progression. Nat. Protoc. 2007;2:1998–2004. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Rosenberg DW, Giardina C, Tanaka T. Mouse models for the study of colon carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:183–196. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Matkowskyj KA, et al. Azoxymethane-induced fulminant hepatic failure in C57BL/6J mice: characterization of a new animal model. Am. J. Physiol. 1999;277:G455–G462. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1999.277.2.G455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Chastre A, et al. Inflammatory cascades driven by tumor necrosis factor-alpha play a major role in the progression of acute liver failure and its neurological complications. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e49670. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Rachakonda V, et al. M1 muscarinic receptor deficiency attenuates azoxymethane-induced chronic liver injury in mice. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:14110. doi: 10.1038/srep14110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bemeur C, Desjardins P, Butterworth RF. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of mild hypothermia in the attenuation of liver injury due to azoxymethane toxicity in the mouse. Metab. Brain Dis. 2010;25:23–29. doi: 10.1007/s11011-010-9186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hara-Chikuma M, Verkman AS. Prevention of skin tumorigenesis and impairment of epidermal cell proliferation by targeted aquaporin-3 gene disruption. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008;28:326–332. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01482-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zhu N, et al. Defective macrophage function in aquaporin-3 deficiency. FASEB J. 2011;25:4233–4239. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-182808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Li A, et al. Critical role of aquaporin-3 in epidermal growth factor-induced migration of colorectal carcinoma cells and its clinical significance. Oncol. Rep. 2013;29:535–540. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.2144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Liu S, Zhang S, Jiang H, Yang Y, Jiang Y. Co-expression of AQP3 and AQP5 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma correlates with aggressive tumor progression and poor prognosis. Med. Oncol. 2013;30:636. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0636-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Chen J, et al. Aquaporin 3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014;33:38. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-33-38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kang S, et al. Aquaporin 3 expression predicts survival in patients with her2-positive early breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015;35:2775–2782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Seleit I, Bakry OA, Al Sharaky D, Ragheb E. Evaluation of aquaporin-3 role in nonmelanoma skin cancer: an immunohistochemical study. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2015;39:306–317. doi: 10.3109/01913123.2015.1022241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Direito I, Paulino J, Vigia E, Brito MA, Soveral G. Differential expression of aquaporin-3 and aquaporin-5 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017;115:980–996. doi: 10.1002/jso.24605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zhao H, et al. Identification of AQP3 and CD24 as biomarkers for carcinogenesis of gastric intestinal metaplasia. Oncotarget. 2017;8:63382–63391. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Reuter S, Gupta SC, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: how are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010;49:1603–1616. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Schieber M, Chandel NS. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014;24:R453–R462. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hurd TR, DeGennaro M, Lehmann R. Redox regulation of cell migration and adhesion. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22:107–115. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2011.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Schroder E, Eaton P. Hydrogen peroxide as an endogenous mediator and exogenous tool in cardiovascular research: issues and considerations. Curr. Opin. Pharm. 2008;8:153–159. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2007.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Gough DR, Cotter TG. Hydrogen peroxide: a Jekyll and Hyde signalling molecule. Cell Death Dis. 2011;2:e213. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2011.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Li S, et al. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in liver diseases. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2015;16:26087–26124. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ma T, et al. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus in mice lacking aquaporin-3 water channels. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2000;97:4386–4391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.080499597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Clackson T, Hoogenboom HR, Griffiths AD, Winter G. Making antibody fragments using phage display libraries. Nature. 1991;352:624–628. doi: 10.1038/352624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Hara-Chikuma M, et al. ClC-3 chloride channels facilitate endosomal acidification and chloride accumulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:1241–1247. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407030200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Mederacke I, Dapito DH, Affo S, Uchinami H, Schwabe RF. High-yield and high-purity isolation of hepatic stellate cells from normal and fibrotic mouse livers. Nat. Protoc. 2015;10:305–315. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2015.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Fujita T, et al. Hepatic stellate cells relay inflammation signaling from sinusoids to parenchyma in mouse models of immune-mediated hepatitis. Hepatology. 2016;63:1325–1339. doi: 10.1002/hep.28112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All other relevant data supporting the key findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Information file or from the corresponding authors upon request. Source data are provided with this paper.