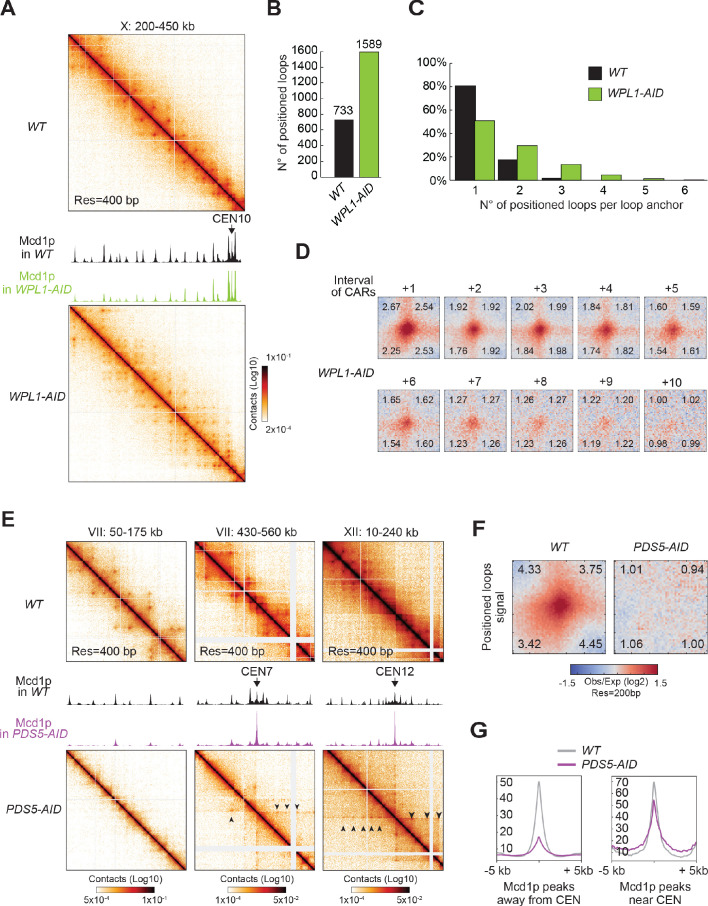
Figure 6. Wpl1p- and Pds5p-depletion perturb the looping pattern.
(A) Wpl1p-depletion causes excessive loop expansion on the contact map. Contact maps for WT (top) and WPL1-AID (bottom) show the chromatin interactions over the 200–450 kb region of chromosome X. Mcd1p ChIP-seq data for WT and WPL1-AID are overlaid across the same region. The scale for ChIP-seq is 0–200. (B) Wpl1p-depletion doubles the number of positioned loops detected. Bar chart shows the total number of positioned loops called by HiCCUPS in WT and WPL1-AID. (C) Genome-wide analysis confirms loop expansion upon Wpl1p-depletion. Bar chart shows the percentage of the number of positioned loops per anchor for WT (black) and WPL1-AID (green). (D) Wpl1p-depletion results in the expansion of the loop signal to further distal loop anchors. Heatmaps were plotted with 200 bp data for WT and WPL1-AID in ±5 kb regions surrounding the wild-type loop anchors and the corresponding CARs interval from a +1 to a +10. (E) Pds5p-depletion results in positioned loops between each centromere and surrounding CARs. Contact maps for WT (top) and PDS5-AID (bottom) shows the chromatin interactions over a chromosome arm on the 50–175 kb region of chromosome VII (left), and the centromeric region at 430–560 kb on chromosome VII (middle), or another centromeric region at 10–240 kb of chromosome XII (right). Mcd1p ChIP-seq data for WT and PDS5-AID are overlaid across the corresponding region in each panel. The scale for ChIP-seq is 0–400. (F) Pds5p-depletion results in loss of signal at wild-type anchors for positioned loops. Heatmaps were plotted with 200 bp data resolution for WT and PDS5-AID in ±5 kb regions surrounding the wild-type positioned loop anchors. (G) Pds5p-depletion causes cohesin depletion from chromosome arms, but not from pericentric regions. Average Mcd1p peak intensity for WT and PDS5-AID were plotted over ±5 kb regions around the peak center. Peaks were sorted into two groups: (1) peaks on the chromosome arms (>30 kb away from the centromeres) (left); (2) pericentric peaks (<30 kb away from the centromeres) (right).