Abstract
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is largely considered an autoimmune disease leading to the destruction of insulin-producing pancreatic β cells. Further, patients with T1D have 3–4-fold increased risk of developing micro- and macrovascular complications. However, the contribution of immune-related factors contributing to these diabetes complications are poorly understood. Individuals with long-term T1D who do not progress to vascular complications offer a great potential to evaluate end-organ protection. The aim of the present study was to investigate the association of inflammatory protein levels with vascular complications (retinopathy, nephropathy, cardiovascular disease) in individuals with long-term T1D compared to individuals who rapidly progressed to complications. We studied a panel of inflammatory markers in plasma of patients with long-term T1D with (n = 81 and 26) and without (n = 313 and 25) vascular complications from two cross-sectional Scandinavian cohorts (PROLONG and DIALONG) using Luminex technology. A subset of PROLONG individuals (n = 61) was screened for circulating immune cells using multicolor flow cytometry. We found that elevated plasma levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor alpha (sIL-2R) were positively associated with the complication phenotype. Risk carriers of polymorphisms in the IL2RA and PTPN2 gene region had elevated plasma levels of sIL-2R. In addition, cell surface marker analysis revealed a shift from naïve to effector T cells in T1D individuals with vascular complications as compared to those without. In contrast, no difference between the groups was observed either in IL-2R cell surface expression or in regulatory T cell population size. In conclusion, our data indicates that IL2RA and PTPN2 gene variants might increase the risk of developing vascular complications in people with T1D, by affecting sIL-2R plasma levels and potentially lowering T cell responsiveness. Thus, elevated sIL-2R plasma levels may serve as a biomarker in monitoring the risk for developing diabetic complications and thereby improve patient care.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease, Cluster of Differentiation 25 (CD25), diabetes complications, nephropathy, regulatory T cells, retinopathy, sIL-2R
Introduction
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is characterised by T cell mediated autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing pancreatic β cells (1, 2), causing T1D individuals to become insulin-dependent throughout their life (3). Most of the patients with T1D develop macrovascular complications such as cardiovascular disease (CVD), and microvascular complications, including proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), chronic kidney disease (CKD), and peripheral neuropathy (PN) (4). The rising prevalence of T1D and its associated long-term vascular complications clearly confer a humanistic (5) and socio-economic burden (6). Vascular complications in T1D individuals are a common cause of mortality related to end-organ damage as compared to the non-diabetic population (4, 7). Remarkably, few patients with T1D do not progress to these vascular complications despite long disease duration and chronic hyperglycaemia, and therefore exert great potential to evaluate end-organ protection (8).
Although T1D individuals with complications show considerable derangement in immunological processes like having elevated concentrations of C-reactive protein (CRP), a marker of inflammation, proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) as compared to individuals without complications (9), the extent of contribution of immunological factors to the development of vascular complications in patients with T1D is poorly understood.
Over the past decades, both genetic (10, 11) and immunological (12, 13) studies revealed IL-2 receptor (IL-2R) and its downstream signalling pathways as central players in the pathogenesis of T1D (14). Upon binding of IL-2 to its receptor IL-2R, a cascade of signalling events is initiated. These events are negatively regulated by the ubiquitously expressed phosphatase tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 2 (PTPN2) (14, 15). IL-2 signalling is critical for the function of regulatory T cells (Tregs), a type of suppressive immune cell, which plays an indispensable role in maintaining immune homeostasis (16) and prevention of autoimmune diseases (17, 18). In addition, elevated levels of soluble IL-2R alpha (sIL-2R; alternative: IL-2RA, CD25) have been reported to be an important factor in the development of diabetic retinopathy in non-insulin-dependent diabetes patients (19) and coronary artery calcification in T1D patients (20). However, a limitation of both studies was that the patient group without complications had a considerably shorter diabetes duration compared to the patient group with the respective complications. Therefore, some of the patients in the complications-free group could have later progressed to vascular complications. Furthermore, Colombo et al. (2019) reported that elevated levels of sIL-2R were associated with a decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in T1D patients (21).
The aim of the present study was to evaluate plasma levels of inflammatory proteins including but not limited to sIL-2R in long-term T1D individuals with and without vascular complications. Additionally, a subset of patients was screened for circulating immune cells to investigate cell populations associated with developing vascular complications in T1D individuals. Finally, plasma sIL-2R levels were correlated to genetic risk variants in IL2RA and PTPN2.
Methods
Study Design
This immunological investigation forms a part of the PROtective genetic and non-genetic factors in diabetic complications and LONGevity (PROLONG) study, which was launched to identify protective factors against complications in long-term T1D individuals. Patients were recruited from seven departments of endocrinology/diabetes outpatient clinics in Sweden and at the Steno Diabetes Center in Denmark. As an extended collaborative effort, we included T1D individuals from a Norwegian cohort, DIALONG. The DIALONG study also included non-diabetic spouses or friends as a control group.
We classified T1D patients into two groups comparing their diabetes complications status. Non-progressors (NP) were defined as patients with a T1D duration of over 30 years without having progressed to any of the specified complications. Patients who progressed to complications within 25 years of T1D diagnosis were defined as rapid progressors (RP). We defined late progressors (LP) as T1D patients that did progress to complications >25 years post diagnosis. For this study RPs and LPs were pooled into one group referred to as progressors (P).
In PROLONG, PDR was defined by the presence of proliferative retinopathy in at least one eye, confirmed laser treatment (panretinal photocoagulation) or blindness. For CKD we used the following inclusion criteria: presence of nighttime albuminuria over 200 µg/min, macroalbuminuria over 300 mg/g or a documented diabetic kidney disease diagnosis. None of the PROLONG participants were treated with SGLT2 inhibitors. Documented events including non-fatal myocardial infarction, stroke (haemorrhagic or ischemic), balloon angioplasty, or coronary artery bypass were defined as CVD. There was limited information on CVD, as the original focus of PROLONG was on microvascular complications.
In DIALONG (22) macro- and microvascular complications were defined using similar criteria as in PROLONG. PDR was defined by the presence of proliferative retinopathy or blindness. Laser treatment was not used as criteria here as it was not exclusively applied to proliferative retinopathy in this study. CKD was adjusted to include patients with persistent microalbuminuria or proteinuria. None of the DIALONG participants were treated with SGLT2 inhibitors. CVD was defined by stroke or myocardial infarction events, coronary artery bypass or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), diagnosed peripheral vascular disease or heart failure.
The regional ethical committees approved the studies (PROLONG: Denmark H-2-2013-073, Sweden 777/2009, Norway 2019/1324; DIALONG: Norway 2014/851) and all participants provided written informed consent.
Blood Sampling
Collected EDTA plasma was aliquoted and stored at -80°C for ~6 years (PROLONG) and ~3 years (DIALONG).
For peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) isolation, peripheral blood from patients with T1D (PROLONG) with and without complications was collected in CPT tubes (BD Vacutainer) at the Steno Diabetes Center, Denmark. PBMCs were subsequently isolated by density gradient centrifugation and cryopreserved in human AB serum containing 10% DMSO at -80°C for ~5 years.
Cytokine Analysis
In DIALONG, plasma cytokines were measured in 79 individuals using an Invitrogen™ Human Cytokine 30-Plex kit (LHC6003M, Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The following adjustments were made to the protocol: (a) one additional standard was included in the serial dilution, making the standard range from 1:3 to 1:2,187; (b) undiluted plasma samples that underwent one freeze-thaw cycle were measured. The following biomarkers were detected in >90% of samples (CCL11, IFN-α, IL-12, sIL-2R, CXCL10, CCL2, CCL3, CCL4 and CCL5), whereas others were only detected in 40–75% (FGF basic, G-CSF, HGF, IL-13, IL-1RA, CXCL9, VEGF) and <17% of patients (EGF, IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-15, IL-17A, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, TNF-α). GM-CSF, IL-5, IL-7, and IL-8 were not detected in any samples.
In PROLONG, we used a custom-designed ProCartaPlex™ Human Cytokine Panel (sIL-2R, CCL2, CCL11, IFN-α; Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to manufacturer’s instructions to measure plasma cytokines. The following adjustments were made to the protocol: (a) one additional standard was included in the serial dilution, making the standard range from 1:4 to 1:32,768 (in pg/ml: sIL-2R 10.06–82,425; CCL2 0.45–3,650; CCL11 0.07–550; IFN-α 0.08–625); (b) undiluted plasma samples that underwent one freeze-thaw cycle were measured.
Data was acquired on a Luminex® 100™, counting 3,000 (DIALONG) and 600 (PROLONG) beads per well. The five-parameter logistic algorithm [weighted by 1/y, (V2.4)] and raw median fluorescence intensity values were used for the creation of standard curves.
Genetic Analysis
The DNA samples in the PROLONG study were genotyped using InfiniumCoreExome-24v1-1 array. Standard quality control steps for GWAS were performed. Imputation was performed using Michigan Imputation Server (https://imputationserver.sph.umich.edu/index.html) using Haplotype Reference Consortium Release 1.1 (HRC.r1-1, GRCh37) as a reference panel. Variants with minor allele frequency (MAF) <5% were excluded before imputation. In the present study, we extracted the region for the IL2RA (Chromosome 10: 6,052,652-6,104,288, build GRch37) and PTPN2 gene (Chromosome 18: 12,785,477-12,929,642, build GRch37) for analysis. Only variants with imputation quality R2 >0.4 and with MAF >5% were included in the analysis.
Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed on pruned, directly genotyped SNPs using 1,000 Genomes’ reference panel version 5A. Population outliers were examined based on visual inspection of PC1 and PC2, and outliers were excluded from the further analysis. Only individuals with complete data on sIL-2R, sex, complication group, HbA1c and age at visit were included. In total, there were 330 individuals analyzed. We used linear regression adjusted for sex, age, and complication group to identify associations between genetic variants and log-transformed plasma levels of sIL-2R.
Antibodies Used for Flow Cytometry
We designed two flow cytometry panels using multiple fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies. Panel 1 includes 14 markers (14 colors), which can discriminate the main mononuclear immune cell types (B cells, T cells, NK cells, monocytes, dendritic cells), and endothelial progenitor cells. Panel 2 includes 16 markers (15 colors) and focuses specifically on different types of T cells. Pacific orange dye (250 ng/ml; Life Technologies) was used as a live/dead marker in both panels. The monoclonal antibodies used in the two panels during the flow cytometry protocol are listed in Supplementary Table 1 .
Fluorescent Staining for Flow Cytometry
Before staining, cryopreserved PBMCs were rapidly thawed using a water bath set to 37°C and washed once in cold PBS (without calcium and magnesium, Lonza) containing 5% AB serum and Benzonase® Nuclease (1:10,000; Merck Millipore) by centrifugation at 450 x g for 5 min at 4°C. The PBMCs were then resuspended in cold PBS and stained with pacific orange (250 ng/ml; Life Technologies) for 20 min on ice in the dark. Following live/dead staining, cells were washed once, taken up in cold FACS-buffer (PBS containing 0.5% BSA) and incubated with 2 µl Fc receptor block (Miltenyi Biotec) per 1 x 106 cells for 10 min on ice. Cells were then subdivided into two parts and incubated for 30 min on ice in the dark with the respective antibody staining panel. The samples were subsequently washed once and re-suspended in FACS-buffer prior to analysis at the flow cytometer.
Flow Cytometry Analysis
Samples were acquired on a LSRI Fortessa flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) with BD FACSDiva™ Software (BD Biosciences) at the Bergen Flow Cytometry Core Facility, University of Bergen, Norway. The flow cytometer was equipped with 407, 488, 561, and 635 nm lasers, and emission filters for PerCP-Cy5.5 (Long Pass (LP): 685, Band Pass (BP): 695/40), Alexa Fluor 488 (LP: 505, BP: 530/30), PE-Cy7 (LP: 750, BP: 780/60), PE (LP: -, BP: 582/15), APC (LP: -, BP: 670/14), Pacific blue (LP: -, BP: 450/50), Pacific orange (LP: 570, BP: 585/42), and BV786 (LP: 750, BP: 780/60). The cytometer was routinely calibrated with BD cytometer setup and tracking beads (BD Biosciences). An average of 138,635 (panel 1) and 122,287 (panel 2) events were recorded in the intact single cell gate and mean percentage of live cells was 98 and 96% for panels 1 and 2, respectively. Flow cytometry data was analyzed in FlowJo™ 10 (Tree Star). Compensation beads (eBioscience) stained with the respective antibody were used as controls to calculate the compensation matrix. The representative gating strategies for both panels are shown in Supplementary Figures 1 and 2 and were validated with the unsupervised gating method using the tSNE algorithm ( Supplementary Figures 3B, C ). For accurate gating, fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls were run regularly for both panels.
Statistical Analysis
sIL-2R was log2 transformed prior to analysis. Values above the ordinary range were removed by biological consideration and literature review. The Mann-Whitney U test was used in the comparison between the complication groups in the analyses of plasma cytokines. To evaluate the association between two variables we used the Pearson correlation formula. In flow cytometry analysis, multiple linear regression was applied and adjusted for the age and sex covariates. Differences were considered statistically significant when p <0.05. The study was of exploratory nature and hence no correction was made for multiple comparisons. Comparisons between patient groups, correlations and the production of associated graphs were done using R Studio (Version 1.1.456). Figures were arranged in Adobe Illustrator CS6.
Results
Elevated sIL-2R in T1D Individuals
Baseline characteristics of DIALONG study participants are given in Table 1 . There were 26 T1D individuals with vascular complications (progressor, P), of whom 10 had CKD, 11 had CVD, and all apart from one had PDR. As the matching groups we included 25 T1D individuals without any vascular complications (non-progressors, NP) and 28 healthy controls. In brief, progressors had significantly higher BMI and slightly elevated HbA1c. The groups were balanced regarding age, sex, and eGFR.
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the DIALONG study participants.
| Cohort | Healthy control | NP | Progressors | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 28 | 25 | 26 | |
| Age (years) | 62.2 ± 6.3 | 63.1 ± 6.5 | 62.2 ± 6.5 | ns |
| BMI (kg/m3) | 26.6 ± 4.2a | 25.1 ± 3.3 | 27.3 ± 3.9 | 3.66 × 10-2 |
| Diabetes duration (years) | NA | 50.5 ± 3.4 | 51.3 ± 5.1 | ns |
| Age at diagnosis (years) | NA | 12.6 ± 5.6 | 10.8 ± 6.5 | ns |
| Sex (% female) | 57% | 48% | 54% | ns |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.5 ± 0.2 | 7.3 ± 0.8 | 7.6 ± 0.8 | ns |
| GAD AA positive (%) | 7% | 29%b | 32%c | ns |
| IA-2 AA positive (%) | 4% | 8%b | 16%c | ns |
| Insulin AA positive (%) | 0% | 71%b | 68%c | ns |
| ZnT8 AA positive (%) | 0% | 4%b | 8%c | ns |
| AA positive (%) | 7% | 75%b | 80%c | ns |
| eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m3) | 83.4 ± 16.4 | 85.4 ± 15.1 | 78.5 ± 26.1 | ns |
| C-peptide (nmol/L) | 718.3 ± 225.3 | undetectable | undetectable | ns |
| CRP (mg/L) | 1.8 ± 2.3d | 3.3 ± 6.1e | 3.0 ± 3.3e | ns |
| Statins | 6 (21%) | 9 (36%) | 17 (65%) | 3.87 × 10-2 |
| Beta-blocker | 1 (4%) | 2 (8%) | 10 (38%) | 1.16 × 10-2 |
| ACEi/ARB | 6 (21%) | 7 (28%) | 19 (73%) | 1.49 × 10-3 |
| Antiplatelet agent | 6 (21%) | 1 (4%) | 14 (54%) | 1.16 × 10-4 |
| Loop diuretics | 0 (0%) | 1 (4%) | 7 (27%) | 2.69 × 10-2 |
| PDR/CKD/CVD (n) | NA | NA | 25/10/11 |
Values for continuous variables are presented as mean ± SD. P-values were calculated between NPs and progressors by Mann–Whitney U test. NP, non-progressor; BMI, body mass index; HbA1c, haemoglobin A1c; GAD, glutamic acid decarboxylase; AA, autoantibody; IA2, islet cell antigen-2; ZnT8, zink transporter 8; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; C-peptide, connecting peptide; CRP, C-reactive protein; ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; PDR, proliferative diabetic retinopathy; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CVD, cardiovascular disease.
an = 27, bn = 24; cn = 25, dn = 21, en = 20.
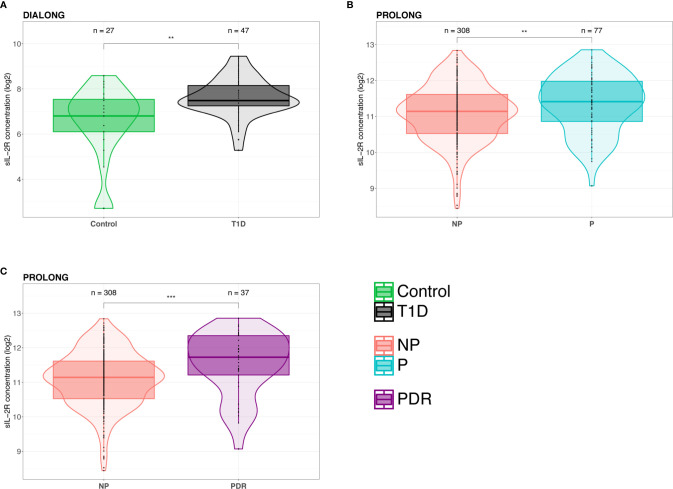
There was a significant increase of sIL-2R (p = 0.0011) in T1D as compared to healthy individuals ( Figure 1A ). The increase was gradual in relation to vascular complication status, being highest in the progressor group (Control vs. NP: p = 0.014; Control vs. P: p = 0.0021; NP vs. P: p = 0.47) ( Supplementary Figure 4A ). None of the other analyzed cytokines showed significant differences between the T1D groups in relation to their complication status ( Supplementary Figure 5A ). An overview over the detection rate for each investigated cytokine is provided in Supplementary Figure 5B .
Figure 1.
Elevated plasma levels of sIL-2R in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D). (A) Patients with T1D from the DIALONG cohort had significantly elevated sIL-2R plasma levels compared to healthy controls. (B) In PROLONG, sIL-2R plasma levels were significantly increased in T1D with vascular complications (progressors, P) compared to T1D patients without complications (non-progressors, NP). (C) PROLONG progressors with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) showed significantly higher sIL-2R plasma levels compared to progressors with other vascular complications. (The Mann-Whitney U test was used in the comparison between the different groups. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001).
To investigate complication status further, we stratified progressors into those with CKD, CVD, or PDR. These analyses revealed that progressors with CVD had significantly elevated sIL-2R plasma levels (p = 0.029) as compared to NPs ( Supplementary Figure 4B ). Plasma sIL-2R was slightly increased in progressors with CKD (p = 0.19) as compared to NPs ( Supplementary Figure 4C ), and sIL-2R correlated negatively with eGFR (T1D: R = -0.42, p = 0.0037) ( Supplementary Figure 4D ). Adjusting for eGFR did not change the observed result with CKD (p = 0.35). Plasma sIL-2R was elevated in progressors with PDR compared to NPs (p = 0.36) ( Supplementary Figure 4E ). Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (CCL2, alternative: MCP-1) plasma levels were significantly higher in progressors with CKD (p = 0.021) and CVD (p = 0.013) compared to NPs ( Supplementary Figures 4F, G ). CCL2 was slightly elevated in progressors with PDR compared to NPs (p = 0.09) ( Supplementary Figure 4H ).
Elevated sIL-2R in T1D Individuals with Vascular Complications
In order to confirm our cytokine findings in DIALONG in a larger and independent cohort, we measured 4 nominally associated cytokines (sIL-2R, CCL2, CCL11, IFN-α) in plasma from PROLONG patients with T1D with and without complications (n = 394). Clinical characteristics for this cohort are summarized in Table 2 . We included 81 patients with T1D with vascular complications (progressors, P), of whom 40 had PDR, 58 had CKD, and on 2 we had information on CVD. Those individuals were compared to 313 T1D individuals without any vascular complications (non-progressors, NP). Progressors were significantly younger in age, displayed significantly higher BMI and HbA1c and lower eGFR and diabetes duration compared to NPs. The groups were balanced regarding sex.
Table 2.
Clinical characteristics of the PROLONG participants.
| Cohort | Cytokine assay | Flow cytometry | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP | Progressors | p-value | NP | Progressors | p-value | |
| n | 313 | 81 | 44 | 17 | ||
| Age (yrs.) | 58.1 ± 10.6 | 44.6 ± 13.7a | 1.08 × 10-13 | 50.6 ± 7.2 | 50.8 ± 15.5 | ns |
| BMI (kg/m3) | 24.8 ± 3.7b | 26.4 ± 4.7 | 3.94 × 10-3 | 25.3 ± 4.2 | 25.3 ± 4.7 | ns |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 40.6 ± 8.6 | 22.4 ± 8.3 | <2.2 × 10-16 | 37.7 ± 5.1 | 29.9 ± 13.4 | 9.49 × 10-3 |
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 17.5 ± 9.9 | 22.0 ± 14.4a | ns | 12.9 ± 6.0 | 20.9 ± 13.2 | 4.63 × 10-2 |
| Sex (% female) | 58% | 53% | ns | 59% | 53% | ns |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.6 ± 0.9 | 8.9 ± 1.5 | 3.33 × 10-14 | 7.4 ± 0.9 | 8.5 ± 0.8 | 6.35 × 10-5 |
| GAD AA positive (%) | 50%c | 68% | 8.15 × 10-3 | 50%d | 90%e | 2.41 × 10-2 |
| eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m3) | 90.2 ± 15.5 | 97.4 ± 30.8f | 3.66 × 10-3 | 94.6 ± 16.6 | 93.3 ± 29.7 | ns |
| C-peptide (nmol/L) | 0.03 ± 0.07g | 0.03 ± 0.05h | ns | 0.01 ± 0.02i | 0.02 ± 0.01j | 3.37 × 10-2 |
| PDR/CKD/CVD (n) | NA | 40/58/2 | NA | 10/12/0 | ||
Values for continuous variables are presented as mean ± SD. P-values were calculated by Mann–Whitney U test. NP, non-progressor; BMI, body mass index; HbA1c, haemoglobin A1c; GAD, glutamic acid decarboxylase; AA, autoantibody; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; C-peptide, connecting peptide; PDR, proliferative diabetic retinopathy; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CVD, cardiovascular disease.
an = 77; bn = 308; cn = 303; dn = 40; en = 10; fn = 76; gn = 296; hn = 68; in = 35; jn = 7.
Three cytokines were detected in 100% of samples (sIL-2R, CCL2, CCL11), while IFN-α was only detected <16% of samples ( Supplementary Figure 6B ). We observed a significant increase of sIL-2R (p = 0.0064) in progressors compared to NPs ( Figure 1B ). This observed difference was even more pronounced (p = 0.00084) when comparing NPs with progressors with PDR ( Figure 1C ). Additionally, sIL-2R was slightly increased in patients with CKD (p = 0.077) compared to NPs ( Supplementary Figure 6C ), and sIL-2R correlated negatively with eGFR (R = -0.12, p = 0.025) ( Supplementary Figure 6D ). Adjusting for eGFR using linear regression, resulted in a significant increase in sIL-2R between progressors with CKD and NPs (p = 0.041). Comparisons for CVD could not be made due to the small sample size of progressors with information on CVD (n = 2). As observed in the DIALONG cohort, there was no significant difference between the complication groups in CCL2 (p = 0.46), CCL11 (p = 0.25), and IFN- α (p = 0.40) ( Supplementary Figure 6A ). In PROLONG, CCL2 was not elevated in progressors with CKD (p = 0.39) ( Supplementary Figure 6E ). Progressors with PDR and NPs showed similar levels of CCL2 (p = 0.97) ( Supplementary Figure 6F ).
Association of sIL-2R Levels With IL2RA and PTPN2 Gene Variants
To identify associations between genetic variants in IL2RA and plasma levels of sIL-2R, we used linear regression adjusting for sex, age, and group. Plasma levels of sIL-2R were significantly associated with 68 SNPs in the IL2RA gene ( Table 3 ), with rs12722489 showing the statistically strongest association (p = 5,19 × 10-7). Two of our identified SNPs are located in exon 8, namely rs12722606 and rs12722605. The majority of the associated SNPs (n = 51) are located in the large intron 1 area of IL2RA.
Table 3.
Imputed IL2RA genotypes and their significant associations with sIL-2R in plasma.
| Chr | SNP | bp* | Intron/Exon | A1 | n | Beta (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | rs12722489 | 6102012 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | −0.28 (−0.39, −0.17) | 5.19 × 10−7 |
| 10 | rs12722517 | 6081040 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | −0.24 (−0.34, −0.14) | 2.23 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs9663421 | 6055604 | Intron 7 | T | 330 | 0.25 (0.15, 0.35) | 3.17 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs12722553 | 6071284 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | −0.26 (−0.37, −0.15) | 3.30 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs12722551 | 6071379 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | −0.26 (−0.37, −0.15) | 3.30 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs791593 | 6083292 | Intron 1 | G | 330 | −0.23 (−0.33, −0.14) | 4.22 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs2104286 | 6099045 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | −0.24 (−0.33, −0.14) | 4.63 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs41294713 | 6080354 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | −0.25 (−0.36, −0.15) | 5.23 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs12722515 | 6081230 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | −0.25 (−0.36, −0.15) | 5.23 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs791590 | 6090322 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | −0.25 (−0.36, −0.15) | 5.23 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs2246031 | 6092210 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | −0.25 (−0.36, −0.15) | 5.23 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs7078614 | 6075831 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | −0.21 (−0.30, −0.12) | 5.50 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs7920946 | 6074634 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | −0.22 (−0.31, −0.13) | 5.53 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs4625363 | 6072504 | Intron 1 | G | 330 | −0.25 (−0.36, −0.15) | 5.54 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs12722527 | 6077328 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | −0.25 (−0.36, −0.15) | 5.54 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs12722523 | 6078390 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | −0.25 (−0.36, −0.15) | 5.54 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs12722561 | 6069893 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | −0.25 (−0.36, −0.15) | 6.22 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs12722559 | 6070273 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | −0.25 (−0.36, −0.15) | 6.22 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs12722606 | 6053133 | Exon 8 | A | 330 | 0.25 (0.14, 0.36) | 6.98 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs11256335 | 6055222 | Intron 7 | A | 330 | 0.25 (0.14, 0.36) | 6.98 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs12722605 | 6053163 | Exon 8 | A | 330 | 0.29 (0.17, 0.42) | 7.27 × 10−6 |
| 10 | rs12722497 | 6095928 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.35 (0.20, 0.50) | 1.22 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs11256464 | 6082558 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | 0.32 (0.18, 0.47) | 2.55 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs11597237 | 6079017 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | −0.23 (−0.33, −0.12) | 3.07 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs11256416 | 6075359 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | −0.21 (−0.31, −0.11) | 3.67 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs7910961 | 6077796 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | 0.20 (0.11, 0.30) | 4.04 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs4747837 | 6058735 | Intron 7 | G | 330 | −0.23 (−0.34, −0.12) | 4.34 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs7900385 | 6062748 | Intron 4 | A | 330 | −0.23 (−0.34, −0.12) | 4.34 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs12722588 | 6060433 | Intron 6 | T | 330 | −0.22 (−0.33, −0.11) | 5.83 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs12722587 | 6060630 | Intron 6 | T | 330 | −0.22 (−0.33, −0.11) | 5.83 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs7093069 | 6063319 | Intron 4 | T | 330 | −0.22 (−0.33, −0.11) | 5.83 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs11816044 | 6074082 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.20 (0.10, 0.30) | 8.91 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs7100984 | 6078539 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.20 (0.10, 0.30) | 9.07 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs12722574 | 6066462 | Intron 2 | A | 330 | −0.20 (−0.29, −0.10) | 9.63 × 10−5 |
| 10 | rs4749894 | 6058323 | Intron 7 | G | 330 | 0.22 (0.11, 0.33) | 1.00 × 10−4 |
| 10 | rs4749924 | 6082396 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | 0.20 (0.10, 0.29) | 1.00 × 10−4 |
| 10 | rs6602398 | 6082953 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | 0.20 (0.10, 0.29) | 1.00 × 10−4 |
| 10 | rs7900744 | 6065611 | Intron 3 | G | 330 | −0.20 (−0.29, −0.10) | 1.19 × 10−4 |
| 10 | rs791588 | 6089342 | Intron 1 | G | 330 | 0.15 (0.06, 0.24) | 7.71 × 10−4 |
| 10 | rs11256342 | 6057231 | Intron 7 | G | 330 | 0.17 (.07, 0.26) | 8.37 × 10−4 |
| 10 | rs12253981 | 6092346 | Intron 1 | G | 330 | 0.16 (0.07, 0.25) | 8.84 × 10−4 |
| 10 | rs2025345 | 6067688 | Intron 2 | G | 330 | 0.16 (0.07, 0.26) | 9.75 × 10−4 |
| 10 | rs12358961 | 6066195 | Intron 3 | A | 330 | 0.16 (0.07, 0.26) | 1.03 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs1924138 | 6096158 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.16 (0.06, 0.25) | 1.06 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs11256497 | 6087794 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.15 (0.06, 0.25) | 1.36 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs10795752 | 6072354 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | 0.15 (0.06, 0.25) | 1.51 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs2245675 | 6095577 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.16 (0.06, 0.25) | 1.55 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs2256852 | 6096923 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.16 (0.06, 0.25) | 1.55 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs791587 | 6088699 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.14 (0.05, 0.23) | 1.62 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs12251836 | 6091281 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.15 (0.06, 0.24) | 1.65 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs6602368 | 6062915 | Intron 4 | C | 330 | 0.15 (0.06, 0.24) | 1.67 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs2476491 | 6095410 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | 0.16 (0.06, 0.26) | 1.74 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs4749926 | 6085312 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.15 (0.05, 0.24) | 2.60 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs11256457 | 6080794 | Intron 1 | G | 330 | 0.15 (0.05, 0.24) | 2.72 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs10905641 | 6072293 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | 0.14 (0.05, 0.23) | 3.41 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs6602379 | 6073374 | Intron 1 | G | 330 | 0.14 (0.05, 0.24) | 3.51 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs809356 | 6091148 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | 0.13 (0.04, 0.22) | 3.60 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs2256774 | 6097165 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | 0.14 (0.05, 0.23) | 3.87 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs1323657 | 6072427 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.13 (0.04, 0.23) | 3.95 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs7072398 | 6079846 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.13 (0.04. 0.22) | 5.33 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs10795763 | 6096199 | Intron 1 | G | 330 | 0.13 (0.04. 0.22) | 5.34 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs7917726 | 6096600 | Intron 1 | G | 330 | 0.13 (0.04. 0.22) | 5.34 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs706779 | 6098824 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | 0.12 (0.03. 0.21) | 7.97 × 10−3 |
| 10 | rs10905656 | 6086093 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.11 (0.02. 0.20) | 1.51 × 10−2 |
| 10 | rs3793713 | 6059704 | Intron 7 | G | 330 | 0.11 (0.01. 0.20) | 2.56 × 10−2 |
| 10 | rs4749920 | 6071453 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | 0.11 (0.01. 0.21) | 3.73 × 10−2 |
| 10 | rs4749921 | 6071654 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | 0.11 (0.01. 0.21) | 3.73 × 10−2 |
| 10 | rs4747845 | 6074441 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | 0.11 (0.01. 0.21) | 3.73 × 10−2 |
*SNP positions according to the Genome Reference Consortium Human Build 37 (GRch37).
Linear regression model: p-value = adjusted for age, sex and complication group. Chr, chromosome; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; bp, base pair; A1, minor allele; CI, confidence interval.
Furthermore, sIL-2R levels were significantly associated with 53 intronic SNPs in the PTPN2 gene region ( Table 4 ). The variant rs12971201 showed the strongest association with plasma sIL-2R (p = 1.09 × 10-3). When we conditioned this analysis for the T1D-associated SNP rs2104286 in IL2RA, we could still identify 42 PTPN2 variants to be independently associated with sIL-2R ( Table 4 ). Here rs592390 had the strongest association with plasma sIL-2R (p = 2.16 × 10-3).
Table 4.
Imputed PTPN2 genotypes and their significant associations with sIL-2R in plasma.
| Chr | SNP | bp* | Intron/Exon | A1 | n | Beta (95% CI) | p-Valuea | p-Valueb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | rs12971201 | 12830538 | Intron 4 | A | 330 | 0.16 (0.07, 0.26) | 1.09 × 10−3 | 3.01 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs2542162 | 12820900 | Intron 5 | T | 330 | 0.16 (0.06, 0.26) | 1.13 × 10−3 | 2.91 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs2847281 | 12821593 | Intron 5 | G | 330 | 0.16 (0.06, 0.26) | 1.13 × 10−3 | 2.91 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs2852151 | 12841176 | Intron 2 | A | 330 | 0.16 (0.06, 0.26) | 1.16 × 10−3 | 3.38 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs3826557 | 12843263 | Intron 2 | T | 330 | 0.16 (0.06, 0.26) | 1.16 × 10−3 | 3.38 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs674222 | 12848349 | Intron 2 | C | 330 | 0.16 (0.06, 0.26) | 1.16 × 10−3 | 3.38 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs2847273 | 12856908 | Intron 2 | C | 330 | 0.16 (0.06, 0.26) | 1.16 × 10−3 | 3.38 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs641085 | 12824930 | Intron 5 | T | 330 | 0.15 (0.06, 0.24) | 1.61 × 10−3 | 2.22 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs592390 | 12822314 | Intron 5 | C | 330 | 0.15 (0.06, 0.24) | 1.67 × 10−3 | 2.16 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs12957037 | 12829065 | Intron 4 | G | 330 | 0.15 (0.06, 0.24) | 1.67 × 10−3 | 2.16 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs588447 | 12832842 | Intron 3 | C | 330 | 0.15 (0.06, 0.24) | 1.69 × 10−3 | 2.48 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs8087237 | 12834359 | Intron 3 | A | 330 | 0.15 (0.06, 0.24) | 1.69 × 10−3 | 2.48 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs478582 | 12835976 | Intron 3 | C | 330 | 0.15 (0.06, 0.24) | 1.69 × 10−3 | 2.48 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs559406 | 12857002 | Intron 2 | G | 330 | −0.14 (−0.24, −0.05) | 1.94 × 10−3 | 2.44 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs960550 | 12827697 | Intron 4 | T | 330 | 0.15 (0.06, 0.25) | 2.08 × 10−3 | 6.02 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs4797709 | 12882359 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | 0.15 (0.05, 0.24) | 2.43 × 10−3 | 6.64 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs2292759 | 12884343 | upstream | A | 330 | 0.15 (0.05, 0.24) | 2.43 × 10−3 | 8.09 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs2542157 | 12787247 | Intron 10 | G | 330 | 0.14 (0.04, 0.23) | 5.57 × 10−3 | 4.98 × 10−3 |
| 18 | rs2847291 | 12808713 | Intron 8 | A | 330 | 0.14 (0.04, 0.24) | 6.86 × 10−3 | 1.43 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs11663472 | 12810471 | Intron 8 | A | 330 | 0.14 (0.04, 0.24) | 6.86 × 10−3 | 1.43 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs2847286 | 12817815 | Intron 6 | G | 330 | 0.14 (0.04, 0.24) | 6.86 × 10−3 | 1.43 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs2847285 | 12818224 | Intron 6 | A | 330 | 0.14 (0.04, 0.24) | 6.86 × 10−3 | 1.43 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs45456495 | 12792228 | Intron 10 | T | 330 | 0.13 (0.03, 0.24) | 9.11 × 10−3 | 1.77 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs2542167 | 12795849 | Intron 9 | T | 330 | 0.13 (0.03, 0.24) | 9.11 × 10−3 | 1.77 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs2847298 | 12800120 | Intron 9 | G | 330 | 0.13 (0.03, 0.24) | 9.11 × 10−3 | 1.77 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs2542160 | 12789246 | Intron 10 | C | 330 | 0.13 (0.03, 0.23) | 1.06 × 10−2 | 1.94 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs2847299 | 12801337 | Intron 9 | A | 330 | 0.14 (0.03, 0.24) | 1.10 × 10−2 | 3.06 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs7227207 | 12819616 | Intron 5 | T | 330 | −0.13 (−0.23, −0.03) | 1.15 × 10−2 | 2.13 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs72872125 | 12876915 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | 0.19 (0.04, 0.34) | 1.24 × 10−2 | 1.72 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs60474474 | 12792736 | Intron 10 | T | 330 | −0.14 (−0.25, −0.03) | 1.68 × 10−2 | 2.03 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs45450798 | 12792940 | Intron 10 | G | 330 | −0.14 (−0.25, −0.03) | 1.68 × 10−2 | 2.03 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs60751993 | 12795420 | Intron 9 | A | 330 | −0.14 (−0.25, −0.03) | 1.68 × 10−2 | 2.03 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs60735058 | 12795470 | Intron 9 | A | 330 | −0.14 (−0.25, −0.03) | 1.68 × 10−2 | 2.03 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs8096138 | 12808140 | Intron 8 | G | 330 | −0.14 (−0.25, −0.03) | 1.68 × 10−2 | 2.03 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs1893217 | 12809340 | Intron 8 | G | 330 | −0.14 (−0.25, −0.03) | 1.68 × 10−2 | 2.03 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs11663253 | 12789556 | Intron 10 | G | 330 | −0.13 (−0.25, −0.02) | 1.84 × 10−2 | 2.12 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs10502416 | 12822702 | Intron 5 | T | 330 | −0.13 (−0.24, −0.02) | 2.01 × 10−2 | 2.14 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs78637414 | 12826836 | Intron 4 | A | 330 | −0.13 (−0.24, −0.02) | 2.01 × 10−2 | 2.14 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs62097820 | 12834649 | Intron 3 | T | 330 | −0.13 (−0.24, −0.02) | 2.01 × 10−2 | 2.14 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs8096327 | 12887750 | Upstream | G | 330 | −0.10 (−0.19, −0.01) | 2.91 × 10−2 | 3.71 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs3737361 | 12831324 | Intron 3 | C | 330 | −0.11 (−0.22, −0.01) | 3.07 × 10−2 | 5.45 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs16939910 | 12837993 | Intron 2 | A | 330 | −0.11 (−0.22, −0.01) | 3.07 × 10−2 | 5.45 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs3786158 | 12843275 | Intron 2 | A | 330 | −0.11 (−0.22, −0.01) | 3.07 × 10−2 | 5.45 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs11080605 | 12847329 | Intron 2 | C | 330 | −0.11 (−0.22, −0.01) | 3.07 × 10−2 | 5.45 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs62097858 | 12862581 | Intron 1 | A | 330 | −0.11 (−0.22, −0.01) | 3.07 × 10−2 | 5.45 × 10−−2 |
| 18 | rs8091720 | 12865186 | Intron 1 | T | 330 | −0.11 (−0.22, −0.01) | 3.07 × 10−2 | 5.45 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs7244152 | 12854294 | Intron 2 | C | 330 | −0.11 (−0.22, −0.01) | 3.23 × 10−2 | 5.44 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs11080606 | 12867969 | Intron 1 | C | 330 | −0.11 (−0.22, −0.01) | 3.23 × 10−2 | 5.44 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs7242788 | 12820330 | Intron 5 | A | 330 | −0.11 (−0.22, −0.01) | 3.30 × 10−2 | 5.79 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs12959799 | 12900695 | Upstream | G | 330 | 0.11 (0.01, 0.21) | 4.01 × 10−2 | 5.41 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs80262450 | 12818922 | Intron 6 | A | 330 | −0.13 (−0.25, −0.01) | 4.13 × 10−2 | 3.45 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs56946650 | 12916943 | Upstream | T | 330 | −0.11 (−0.22, −0.00) | 4.16 × 10−2 | 6.45 × 10−2 |
| 18 | rs2847282 | 12819820 | Intron 5 | G | 330 | −0.09 (−0.19, −0.00) | 4.79 × 10−2 | 6.62 × 10−2 |
*SNP positions according to the Genome Reference Consortium Human Build 37 (GRch37)
Linear regression models: p-valuea = adjusted for age, sex and complication group; p-valueb = adjusted for age, sex, complication group and rs2104286. Chr, chromosome; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; bp, base pair; A1, minor allele; CI, confidence interval.
Cell-Surface Marker Analysis on PBMC of T1D Individuals
Our flow cytometry panels enabled us to investigate a range of different cell populations, which are summarized in Supplementary Figure 3A . The applied gating strategies are provided in Supplementary Figure 1 and 2 . Baseline characteristics for this subset of PROLONG patients are provided in Table 2 . In total, we performed flow cytometry analysis on 61 T1D samples, of which 17 were from progressors. The groups were balanced regarding age and sex.
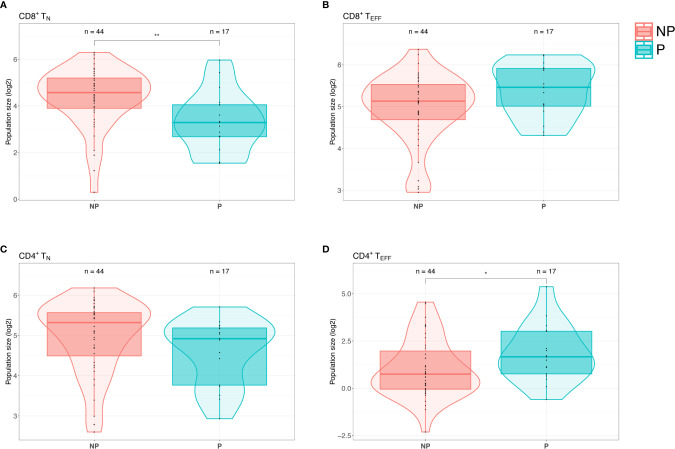
We identified a significant decrease of CD8+ naïve T cells (CD3+CD8+CD45RA+CCR7+CCR5-) (p = 0.0046) and increase of CD8+ effector T cells (CD3+CD8+CD45RA+CCR7-) (p = 0.070) in progressors compared to NPs ( Figures 2A, B ). Furthermore, progressors had significantly increased CD4+ effector T cells (CD3+CD4+CD45RA+CCR7-) (p = 0.045) and decreased CD4+ naïve T cells (CD3+CD4+CD45RA+CCR7+CCR5-) (p = 0.14) compared to NPs ( Figures 2C, D ). To summarize, we observed a shift from naïve to effector T cells (CD4+ and CD8+) in PBMCs from T1D patients with vascular complications compared to those without.
Figure 2.
Patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D) with complications display a shift from naïve T cells to effector T cells. (A) Flow cytometry screening of PBMCs from PROLONG patients revealed a significant decrease of CD8+ naïve T (TN) cells (CD3+CD4+CD45RA+CCR7+CCR5-) in progressors (P) compared to non-progressors (NP). (B) Progressors displayed elevated CD8+ effector T (TEFF) cells (CD3+CD4+CD45RA+CCR7-) simultaneously (p = ns). (C) CD4+ TN cells were also declined in patients with T1D with complications as compared to NPs (p = ns). (D) In progressors CD4+ TEFF cells were significantly elevated compared to NPs. (For the comparison between the different groups, multiple linear regression was applied and adjusted for the age and sex covariates. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01).
Since we observed significant differences in plasma sIL-2R in the two PROLONG groups, we also investigated cell surface expression of interleukin-2 receptor alpha (CD25) on PBMCs. Remarkably, we did not see differences between NPs and progressors in neither CD25+ T cells (p = 0.84) nor Tregs (CD3+CD4+CD25++CD127-) (p = 0.27) ( Supplementary Figures 7A, B ).
Discussion
The present study revealed that plasma sIL-2R levels are reproducibly elevated in individuals with long-term T1D with severe vascular complications as compared to those who remained free from to vascular complications despite more than 30 years of diabetes duration. Further, plasma levels of sIL-2R were associated with SNPs in the IL2RA and PTPN2 gene regions, which might suggest underlying genetic determinants and possibly biological causal inference. Finally, our results are in agreement with published studies confirming an increase of circulating sIL-2R in patients with T1D when compared to healthy controls, which might further emphasize that immune factors contributing to diabetes pathogenesis might early on govern progression to vascular complications (12, 23).
The biological function of sIL-2R is not yet completely understood, but there is evidence that it reflects an imbalance in Treg and effector T cell (TEFF) activity (14, 24). It has been suggested that there is a reduced immunosuppressive function of Tregs due to impaired IL-2 signalling in T1D (24–28), a defect which may subsequently lead to a more aggressive immune destruction of pancreatic β cells by TEFF (12, 28). In addition, defects in the intracellular IL-2 pathways and a decreased regulatory function have recently been reported in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) (29). In many autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) (30), rheumatoid arthritis (31), primary Sjögren’s syndrome (32), scleroderma (33), and inflammatory myopathies (34), but also in various cancers (31), sIL-2R has been proposed to be a biomarker for disease activity.
Patients with T1D develop the disease at an early age and a large proportion of them will progress to devastating vascular complications representing a major problem because the tools for monitoring when and how disease deteriorates are not available (4). Diabetes retinopathy is the most common vascular complication of diabetes (35) and the proliferative form of diabetic retinopathy (PDR) is the leading cause of vision loss in adults (36). Previous studies show that several inflammatory cytokines are involved in the pathogenesis and progression of PDR, including sIL-2R (19), however, not all of the results have been replicated. In the present study, both PROLONG and DIALONG progressors with PDR had higher plasma levels of sIL-2R compared to NPs, supporting the notion that sIL-2R could emerge as a contributing player not only in the pathogenesis of T1D but also in disease progression.
An additional evidence in the present study to biological importance of sIL-2R were our findings that 68 IL2RA SNPs are associated with sIL-2R plasma levels in PROLONG patients with T1D and correlated with the elevated sIL-2R levels observed in progressors accordingly. IL2RA rs12722489 showed the strongest association with sIL-2R plasma levels in patients with T1D and is located in the large intron 1. This particular SNP has been identified as a risk factor for MS in several studies (37–39). However, a secondary association was suggested due to the nearby location of rs2104286 (Linkage disequilibrium D’ = 1, R2 = 0.58), which is a well-recognized T1D risk factor (11, 37) and also significantly associated with plasma sIL-2R in our dataset. Interestingly, one of our identified SNPs, rs2256774, was associated with higher levels of Rubella antibodies (40), and Rubella viral infections have been associated with the onset of T1D (41, 42). Additionally, multiple IL2RA variants have been shown to correlate with sIL-2R levels in T1D (10) and MS (37) and IL2RA gene variants are associated with susceptibility of T1D (10, 11, 43). Further, functional studies support these results by suggesting that specific IL2RA variants cause defects in immune homeostasis due to impaired IL-2 signalling in Tregs (25, 27, 44).
Interestingly, seventeen of our identified SNPs are positioned within the first 15 kb of the first intron of the IL2RA gene, which has been described as a super-enhancer region due to a cluster of histone 3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) elements in this area (45). Notably, many of the IL2RA SNPs related to autoimmune diseases fall into this region and affect transcription factor binding and enhancer activity (46). Several of our identified SNPs have been reported to be associated with DNA methylation at the IL2RA promoter locus, particularly rs6602398 and rs4749926 (47). Despite having detected a number of IL2RA SNPs to be associated with sIL-2R, it is challenging to conclude the direct effect of those mostly intronic SNPs on the expression of IL-2R itself and in-depth research is scarce. However, it has been reported that one of our identified SNPs, rs12251836, is associated with IL2RA expression on acutely triggered TEFF, but not in Tregs (48), suggesting a likely biological causal inference of IL-2R gene locus in T1D.
Another exciting and supporting genetic observation included 53 PTPN2 SNPs to be significantly associated with sIL-2R plasma levels, importantly 42 of which were associations independent of IL2RA variant rs2104286. Our most significant SNP in PTPN2 is rs12971201, which has previously been associated with T1D, however a secondary association has been suggested due to rs1893217 (49). This particular variant is considered a risk variant for T1D and celiac disease (50, 51), and correlated with impaired IL-2 signalling in CD4+ T cells as measured by decreased phosphorylation of STAT5 (pSTAT5) but also reduced PTPN2 expression (52). One of our identified SNPs, rs2847281, was shown to significantly associate with CRP levels along many other PTPN2 variants (53). PTPN2 is a negative regulator in the IL-2 signalling cascade and several SNPs in the PTPN2 gene region have been linked to different autoimmune diseases including T1D, rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease (54, 55). Furthermore, different genetic variants in PTPN2 were reported to be associated with diminished IL-2 responsiveness in naïve Tregs from patients with long-standing T1D (56). PTPN2 has been shown to modulate interferon gamma signal transduction in pancreatic β cells and regulate cytokine-induced apoptosis, which could potentially contribute to the pathogenesis of T1D (57).
As described above, elevated sIL-2R levels are likely to reflect an imbalance in Treg and TEFF activity. PBMCs from PROLONG patients with T1D with vascular complications displayed a shift from naïve T cells (TN) to TEFF, however, we cannot distinguish whether this shift is the cause or the result of diabetic complications. The interpretation of these results was difficult due to the small and heterogeneous sample size in the progressors group. One can speculate that progressors have increased TEFF due to impaired Treg suppression leading to a more destructive form of T1D, thereby more active course of the disease. This systemic long-term inflammation could subsequently drive the development of vascular complications by affecting tissues aside from the pancreas. Further studies testing suppression capacity of Tregs isolated from patients with T1D with and without complications are crucial to confirm this notion.
In PROLONG, we observed significantly higher levels of sIL-2R in progressors which associated with IL2RA SNPs, however the surface expression of IL-2R on circulating immune cells was similar between progressors and NPs. This may be confirmatory for the theory that it is not the number of cells expressing IL-2R making a difference, but the efficiency of IL-2 signalling within the cells themselves. Paradoxically, the IL-2/IL-2R signalling pathway is important in immunity and tolerance, which is further complicated by shedding of sIL-2R. How sIL-2R is involved in the pathogenesis of different diseases remains a puzzle. The high-affinity receptor for IL-2 consists of 3 protein chains, namely IL-2Rα, IL-2Rβ, and IL-2Rγ. Upon proteolytic cleavage of the ectodomains of the membrane-bound IL-2Rα and release into the extracellular space, sIL-2R retains the ability to bind IL-2 with low affinity, which can lead to different outcomes. Firstly, sIL-2R may function as a decoy-receptor reducing the bioavailability of IL-2 and favor tolerance controlled by Tregs over immunity. Tregs constitutively express the high-affinity IL-2R, which enables them to out-compete conventional T cells with the intermediate-affinity receptor (IL-2Rβ and IL-2Rγ) when less IL-2 is available, thereby boosting immune tolerance (58). This difference in affinity is exploited in clinical trials in T1D where the administration of low-dose IL-2 has shown promising effects expanding and activating Tregs (59, 60). Alternatively, the binding of sIL-2R to IL-2 can enable in trans presentation of IL-2 to T-cells which only express the intermediate-affinity IL-2R. Overall, increased shedding of sIL-2R and it binding to IL-2 can have opposing effects depending on the cell type affected (58).
Stratified analysis of different vascular complications revealed increased sIL-2R and CCL2 levels in DIALONG patients with CVD in comparison to patients with T1D with other diabetic complications. Elevated sIL-2R has been described as a marker for coronary artery calcification progression in both individuals with and without T1D independent of traditional CVD risk factors (20). CCL2 plays a critical role in the development of atherosclerotic plaque formation by attracting monocytes to the vessel lumen where they will differentiate into macrophages and become foam cells by the uptake of low-density lipoprotein (61). Elevated plasma levels of CCL2 have also been associated with CVD (61–63). The observed increases in sIL-2R and CCL2 were based on a small sample set in DIALONG, however, the patient characterisation for CVD was performed thoroughly using computed tomography coronary angiography, which enabled the identification of asymptomatic coronary artery disease (64). Nevertheless, we were not able to investigate this finding in PROLONG due to the limited information on CVD.
Previously it was shown in the EURODIAB study that patients with T1D with complications have increased IL-6 and TNF-α as compared to individuals without complications (9). We could neither confirm nor confound this finding due to the low detection rate of IL-6 and TNF-α (< 20%) in our study, which statistically did not allow for reliable comparisons. In general, the detection rates in our cytokine screening were considerably low, where many of the investigated biomarkers were not detected at all. This could be due to technical differences and kit quality, however all kits used were validated for plasma usage by the respective providers, we followed manufacturer’s instructions accordingly and did not experience technical issues during analysis.
Our future perspective is to unravel the role of IL-2R in the progression to diabetic complications in general, larger cohorts analyzing sIL-2R levels in other types of diabetes, such as T2D with no autoimmunity and latent autoimmune diabetes of adults, are of importance. To investigate the predictive power of sIL-2R levels in the development of diabetic complications, longitudinal studies in children and adolescents would be a great asset. Furthermore, it is of great interest to study the relationship between sIL-2R and IL-2 signalling efficacy and Treg function in patients with T1D.
In summary, we conclude that IL2RA and PTPN2 gene variants may not only increase the risk of T1D, but in addition the development of diabetic complications possibly by influencing sIL-2R plasma levels and lowering T cell responsiveness. Thus, sIL-2R could potentially act as a biomarker for monitoring vascular complications in people with T1D thereby enabling early treatment and improving patient care.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because of GDPR and ethical restrictions. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to valeriya.lyssenko@uib.no.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by PROLONG-Sweden: Regional Ethics Review Board, Department 1, Lund, Sweden, Dnr 777/2009; PROLONG-Denmark: Scientific-Ethical Committee for the Capital Region of Denmark, Hillerød, Denmark, Dnr H-2-2013-073; DIALONG: Regional Committees for Medical and Health Research Ethics (REC), South-East regional health authority, panel D, Norway, 2014/851; Data analysis of both studies at University of Bergen: REC, West regional health authority, Norway 2019/1324. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
VL, RJ, and SA conceived the study, and MK and SA designed the immunological part of the study. TM, CL, HF, TN, S-BC, GJ, LG, ME, BE, KB, and PN contributed to the study design and data collection. VL is the PI of the PROLONG study. TB is the PI of the DIALONG study. MK conducted the flow cytometric and cytokine analysis and wrote the manuscript. MK, OF, EP, BB, and SA analyzed and processed the data. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
Financial support was obtained from the Swedish Research Council (Dnr2015-03574, Dnr349-2006-237), the Novo Nordisk Foundation (NNF12OC1016467), the Family Erling-Person Foundation, the Steno Diabetes Center Copenhagen, the Bergen Research Foundation (BFS811294), and the University of Bergen. The DIALONG study is supported by the Oslo Diabetes Research Centre and the Norwegian Diabetics’ Centre.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. At the time when the data from Steno was collected, CLM was affiliated with Steno Diabetes Centre. During revisions and the finalization of the article, CLM have changed affiliation from Steno to Novo Nordisk as of 6-Jun-2016.
Acknowledgments
We thank all PROLONG and DIALONG patients and blood donors, nurses, and researchers involved in the planning and implementation of the studies. Additionally, we are grateful for the help from Karl A. Brokstad with the Luminex assay. We appreciate the help from the Flow Cytometry Core Facility, Department of Clinical Science, University of Bergen, where the flow cytometry analysis was performed. Furthermore, we acknowledge Richard Davies and Timothy Holmes for their continuous assistance designing, conducting, and analyzing multicolor flow cytometry measurements. We are very thankful for the help we received from Türküler Özgümüş with data analysis.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2020.575469/full#supplementary-material
References
- 1. Castano a L, Eisenbarth GS. Type-I Diabetes: A Chronic Autoimmune Disease of Human, Mouse, and Rat. Annu Rev Immunol (1990) 8(1):647–79. 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003243 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Roep BO. The role of T-cells in the pathogenesis of Type 1 diabetes: From cause to cure. Diabetologia (2003) 46(3):305–21. 10.1007/s00125-003-1089-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Tisch R, McDevitt H. Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Cell (1996) 85(3):291–7. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81106-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Harcourt BE, Penfold SA, Forbes JM. Coming full circle in diabetes mellitus: from complications to initiation. Nat Rev Endocrinol (2013) 9:113. 10.1038/nrendo.2012.236 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Rydén A, Sörstadius E, Bergenheim K, Romanovschi A, Thorén F, Witt EA, et al. The Humanistic Burden of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Europe: Examining Health Outcomes and the Role of Complications. PLoS One (2016) 11(11):e0164977. 10.1371/journal.pone.0164977 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Forlenza GP, Rewers M. The epidemic of type 1 diabetes: what is it telling us? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes (2011) 18(4):248–51. 10.1097/MED.0b013e32834872ce [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Park M, Katon WJ, Wolf FM. Depression and risk of mortality in individuals with diabetes: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Gen Hosp Psychiatry (2013) 35(3):217–25. 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2013.01.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Sun JK, Keenan HA, Cavallerano JD, Asztalos BF, Schaefer EJ, Sell DR, et al. Protection from retinopathy and other complications in patients with type 1 diabetes of extreme duration: the joslin 50-year medalist study. Diabetes Care (2011) 34(4):968–74. 10.2337/dc10-1675 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Schram MT, Chaturvedi N, Schalkwijk C, Giorgino F, Ebeling P, Fuller JH, et al. Vascular Risk Factors and Markers of Endothelial Function as Determinants of Inflammatory Markers in Type 1 Diabetes. EURODIAB Prospect Complications Study (2003) 26(7):2165–73. 10.2337/diacare.26.7.2165 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Lowe CE, Cooper JD, Brusko T, Walker NM, Smyth DJ, Bailey R, et al. Large-scale genetic fine mapping and genotype-phenotype associations implicate polymorphism in the IL2RA region in type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet (2007) 39:1074. 10.1038/ng2102 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Tang W, Cui D, Jiang L, Zhao L, Qian W, Long SA, et al. Association of common polymorphisms in the IL2RA gene with type 1 diabetes: evidence of 32,646 individuals from 10 independent studies. J Cell Mol Med (2015) 19(10):2481–8. 10.1111/jcmm.12642 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Downes K, Marcovecchio ML, Clarke P, Cooper JD, Ferreira RC, Howson JM, et al. Plasma concentrations of soluble IL-2 receptor α (CD25) are increased in type 1 diabetes and associated with reduced C-peptide levels in young patients. Diabetologia (2014) 57(2):366–72. 10.1007/s00125-013-3113-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Krause S, Beyerlein A, Winkler C, Gavrisan A, Kayser C, Puff R, et al. Soluble interleukin-2 receptor alpha in preclinical type 1 diabetes. Acta Diabetol (2014) 51(3):517–8. 10.1007/s00592-013-0512-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Hulme MA, Wasserfall CH, Atkinson MA, Brusko TM. Central role for interleukin-2 in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes (2012) 61(1):14–22. 10.2337/db11-1213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Kovanen PE, Leonard WJ. Cytokines and immunodeficiency diseases: critical roles of the γc-dependent cytokines interleukins 2, 4, 7, 9, 15, and 21, and their signaling pathways. Immunol Rev (2004) 202(1):67–83. 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00203.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M. Regulatory T Cells and Immune Tolerance. Cell (2008) 133(5):775–87. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Lan Q, Fan H, Quesniaux V, Ryffel B, Liu Z, Zheng SG. Induced Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells: a potential new weapon to treat autoimmune and inflammatory diseases? J Mol Cell Biol (2012) 4(1):22–8. 10.1093/jmcb/mjr039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Ye C, Brand D, Zheng SG. Targeting IL-2: an unexpected effect in treating immunological diseases. Signal Transduct Targeted Ther (2018) 3(1):2. 10.1038/s41392-017-0002-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Doganay S, Evereklioglu C, Er H, Türköz Y, Sevinç A, Mehmet N, et al. Comparison of serum NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, sIL-2R, IL-6 and IL-8 levels with grades of retinopathy in patients with diabetes mellitus. Eye (2002) 16(2):163–70. 10.1038/sj.eye.6700095 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Wadwa RP, Kinney GL, Ogden L, Snell-Bergeon JK, Maahs DM, Cornell E, et al. Soluble interleukin-2 receptor as a marker for progression of coronary artery calcification in type 1 diabetes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol (2006) 38(5):996–1003. 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.09.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Colombo M, Valo E, McGurnaghan SJ, Sandholm N, Blackbourn LAK, Dalton RN, et al. Biomarker panels associated with progression of renal disease in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia (2019) 62(9):1616–27. 10.1007/s00125-019-4915-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Holte KB, Juel NG, Brox JI, Hanssen KF, Fosmark DS, Sell DR, et al. Hand, shoulder and back stiffness in long-term type 1 diabetes; cross-sectional association with skin collagen advanced glycation end-products. The Dialong study. J Diabetes Complications (2017) 31(9):1408–14. 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2017.06.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Giordano C, Galluzzo A, Marco A, Panto F, Amato MP, Caruso C, et al. Increased soluble interleukin-2 receptor levels in the sera of type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res (Edinburgh Scotland) (1988) 8(3):135–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Yu H, Paiva R, Flavell RA. Harnessing the power of regulatory T-cells to control autoimmune diabetes: overview and perspective. Immunology (2018) 153(2):161–70. 10.1111/imm.12867 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Garg G, Tyler JR, Yang JH, Cutler AJ, Downes K, Pekalski M, et al. Type 1 diabetes-associated IL2RA variation lowers IL-2 signaling and contributes to diminished CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell function. J Immunol (Baltimore Md 1950) (2012) 188(9):4644–53. 10.4049/jimmunol.1100272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Lawson JM, Tremble J, Dayan C, Beyan H, Leslie RD, Peakman M, et al. Increased resistance to CD4+CD25hi regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in patients with type 1 diabetes. Clin Exp Immunol (2008) 154(3):353–9. 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2008.03810.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Long SA, Buckner JH. CD4+FOXP3+ T regulatory cells in human autoimmunity: more than a numbers game. J Immunol (Baltimore Md 1950) (2011) 187(5):2061–6. 10.4049/jimmunol.1003224 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Hughson A, Bromberg I, Johnson B, Quataert S, Jospe N, Fowell DJ. Uncoupling of proliferation and cytokines from suppression within the CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T-cell compartment in the 1st year of human type 1 diabetes. Diabetes (2011) 60(8):2125–33. 10.2337/db10-1661 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Sheikh V, Zamani A, Mahabadi-Ashtiyani E, Tarokhian H, Borzouei S, Alahgholi-Hajibehzad M. Decreased regulatory function of CD4+CD25+CD45RA+ T cells and impaired IL-2 signalling pathway in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Scand J Immunol (2018) 88(4):e12711. 10.1111/sji.12711 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Sharief MK, Thompson EJ. Correlation of interleukin-2 and soluble interleukin-2 receptor with clinical activity of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry (1993) 56(2):169–74. 10.1136/jnnp.56.2.169 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Witkowska AM. On the role of sIL-2R measurements in rheumatoid arthritis and cancers. Mediators Inflamm (2005) 2005(3):121–30. 10.1155/mi.2005.121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Akiyama M, Sasaki T, Kaneko Y, Yasuoka H, Suzuki K, Yamaoka K, et al. Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor is a useful biomarker for disease activity but not for differential diagnosis in IgG4-related disease and primary Sjogren’s syndrome adults from a defined population. Clin Exp Rheumatol (2018) 36 Suppl 112(3):157–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Uziel Y, Krafchik BR, Feldman B, Silverman ED, Rubin LA, Laxer RM. Serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor. A marker of disease activity in localized scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum (1994) 37(6):898–901. 10.1002/art.1780370618 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Tournadre A, Dubost JJ, Soubrier M, Ruivard M, Souteyrand P, Schmidt J, et al. Soluble IL-2 receptor: a biomarker for assessing myositis activity. Dis Markers (2014) 2014:472624. 10.1155/2014/472624 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Hietala K, Harjutsalo V, Forsblom C, Summanen P, Groop PH. Age at onset and the risk of proliferative retinopathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care (2010) 33(6):1315–9. 10.2337/dc09-2278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Semeraro F, Cancarini A, dell’Omo R, Rezzola S, Romano MR, Costagliola C. Diabetic Retinopathy: Vascular and Inflammatory Disease. J Diabetes Res (2015) 2015:582060. 10.1155/2015/582060 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Maier LM, Lowe CE, Cooper J, Downes K, Anderson DE, Severson C, et al. IL2RA Genetic Heterogeneity in Multiple Sclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility and Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor Production. PLoS Genet (2009) 5(1):e1000322. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000322 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Consortium IMSG, Hafler DA, Compston A, Sawcer S, Lander ES, Daly MJ, et al. Risk Alleles for Multiple Sclerosis Identified by a Genomewide Study. N Engl J Med (2007) 357(9):851–62. 10.1056/NEJMoa073493 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Alcina A, Fedetz M, Ndagire D, Fernández O, Leyva L, Guerrero M, et al. IL2RA/CD25 gene polymorphisms: uneven association with multiple sclerosis (MS) and type 1 diabetes (T1D). PLoS One (2009) 4(1):e4137. 10.1371/journal.pone.0004137 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Pankratz VS, Vierkant RA, O’Byrne MM, Ovsyannikova IG, Poland GA. Associations between SNPs in candidate immune-relevant genes and rubella antibody levels: a multigenic assessment. BMC Immunol (2010) 11(1):48. 10.1186/1471-2172-11-48 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Ramondetti F, Sacco S, Comelli M, Bruno G, Falorni A, Iannilli A, et al. Type 1 diabetes and measles, mumps and rubella childhood infections within the Italian Insulin-dependent Diabetes Registry. Diabetic Med (2012) 29(6):761–6. 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2011.03529.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Korkmaz HA, Ermiş Ç. A case of immune-mediated type 1 diabetes mellitus due to congenital rubella ınfection. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab (2019) 24(1):68–70. 10.6065/apem.2019.24.1.68 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Vella A, Cooper JD, Lowe CE, Walker N, Nutland S, Widmer B, et al. Localization of a type 1 diabetes locus in the IL2RA/CD25 region by use of tag single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet (2005) 76(5):773–9. 10.1086/429843 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Maier LM, Anderson DE, Severson CA, Baecher-Allan C, Healy B, Liu DV, et al. Soluble IL-2RA levels in multiple sclerosis subjects and the effect of soluble IL-2RA on immune responses. J Immunol (Baltimore Md 1950) (2009) 182(3):1541–7. 10.4049/jimmunol.182.3.1541 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Farh KK-H, Marson A, Zhu J, Kleinewietfeld M, Housley WJ, Beik S, et al. Genetic and epigenetic fine mapping of causal autoimmune disease variants. Nature (2014) 518:337. 10.1038/nature13835 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Schwartz AM, Demin DE, Vorontsov IE, Kasyanov AS, Putlyaeva LV, Tatosyan KA, et al. Multiple single nucleotide polymorphisms in the first intron of the IL2RA gene affect transcription factor binding and enhancer activity. Gene (2017) 602:50–6. 10.1016/j.gene.2016.11.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Belot M-P, Fradin D, Mai N, Le Fur S, Zélénika D, Kerr-Conte J, et al. CpG methylation changes within the IL2RA promoter in type 1 diabetes of childhood onset. PLoS One (2013) 8(7):e68093–e. 10.1371/journal.pone.0068093 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Ye CJ, Feng T, Kwon H-K, Raj T, Wilson MT, Asinovski N, et al. Intersection of population variation and autoimmunity genetics in human T cell activation. Science (2014) 345(6202):1254665–. 10.1126/science.1254665 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Onengut-Gumuscu S, Chen W-M, Burren O, Cooper NJ, Quinlan AR, Mychaleckyj JC, et al. Fine mapping of type 1 diabetes susceptibility loci and evidence for colocalization of causal variants with lymphoid gene enhancers. Nat Genet (2015) 47(4):381–6. 10.1038/ng.3245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Johnson MB, Cerosaletti K, Flanagan SE, Buckner JH. Genetic Mechanisms Highlight Shared Pathways for the Pathogenesis of Polygenic Type 1 Diabetes and Monogenic Autoimmune Diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rep (2019) 19(5):20. 10.1007/s11892-019-1141-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Dubois PCA, Trynka G, Franke L, Hunt KA, Romanos J, Curtotti A, et al. Multiple common variants for celiac disease influencing immune gene expression. Nat Genet (2010) 42(4):295–302. 10.1038/ng.543 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Long SA, Cerosaletti K, Wan JY, Ho JC, Tatum M, Wei S, et al. An autoimmune-associated variant in PTPN2 reveals an impairment of IL-2R signaling in CD4+ T cells. Genes Immun (2010) 12:116. 10.1038/gene.2010.54 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Dehghan A, Dupuis J, Barbalic M, Bis JC, Eiriksdottir G, Lu C, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies in >80 000 subjects identifies multiple loci for C-reactive protein levels. Circulation (2011) 123(7):731–8. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.948570 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Todd JA, Walker NM, Cooper JD, Smyth DJ, Downes K, Plagnol V, et al. Robust associations of four new chromosome regions from genome-wide analyses of type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet (2007) 39(7):857–64. 10.1038/ng2068 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Wellcome Trust Case Control C Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature (2007) 447(7145):661–78. 10.1038/nature05911 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Yang JH, Cutler AJ, Ferreira RC, Reading JL, Cooper NJ, Wallace C, et al. Natural Variation in Interleukin-2 Sensitivity Influences Regulatory T-Cell Frequency and Function in Individuals With Long-standing Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes (2015) 64(11):3891–902. 10.2337/db15-0516 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Moore F, Colli ML, Cnop M, Esteve MI, Cardozo AK, Cunha DA, et al. PTPN2, a candidate gene for type 1 diabetes, modulates interferon-gamma-induced pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis. Diabetes (2009) 58(6):1283–91. 10.2337/db08-1510 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Damoiseaux J. The IL-2 – IL-2 receptor pathway in health and disease: The role of the soluble IL-2 receptor. Clin Immunol (2020) 218:108515. 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108515 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Rosenzwajg M, Churlaud G, Mallone R, Six A, Dérian N, Chaara W, et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 fosters a dose-dependent regulatory T cell tuned milieu in T1D patients. J Autoimmun (2015) 58:48–58. 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.01.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Yu A, Snowhite I, Vendrame F, Rosenzwajg M, Klatzmann D, Pugliese A, et al. Selective IL-2 Responsiveness of Regulatory T Cells Through Multiple Intrinsic Mechanisms Supports the Use of Low-Dose IL-2 Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes (2015) 64(6):2172–83. 10.2337/db14-1322 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Niu J, Kolattukudy P E. Role of MCP-1 in cardiovascular disease: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Clin Sci (2009) 117(3):95–109. 10.1042/cs20080581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Piemonti L, Calori G, Lattuada G, Mercalli A, Ragogna F, Garancini MP, et al. Association between plasma monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 concentration and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. Diabetes Care (2009) 32(11):2105–10. 10.2337/dc09-0763 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Gonzalez-Quesada C, Frangogiannis NG. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1/CCL2 as a biomarker in acute coronary syndromes. Curr Atheroscl Rep (2009) 11(2):131–8. 10.1007/s11883-009-0021-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Holte KB, Svanteson M, Hanssen KF, Haig Y, Solheim S, Berg TJ. Undiagnosed coronary artery disease in long-term type 1 diabetes. The Dialong study. J Diabetes Complications (2019) 33(5):383–9. 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2019.01.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because of GDPR and ethical restrictions. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to valeriya.lyssenko@uib.no.