To the Editor:
The electrical impedance tomography (EIT), a noninvasive, radiation-free, bedside lung imaging method, has gained attention in the diagnosis of acute respiratory failure (ARF), pleural effusion, and pneumothorax (1, 2) and monitoring of regional lung ventilation in mechanically ventilated patients (3, 4). Besides, EIT was proposed to quantitatively assess regional lung perfusion with saline bolus injection, which was validated in small animal studies (5, 6). We demonstrated the clinical use of this method to detect acute pulmonary embolism (PE) in a recent case (7). To further confirm the feasibility of bedside detection of acute PE, we conducted a larger prospective observational clinical study using EIT.
Methods
The study was approved by the Institutional Research and Ethics Committee of the Peking Union Medical College Hospital (JS-1896). Informed consent was obtained from all patients or next of kin before the study. The patients, who were sequentially admitted to the ICU with ARF or who had a new onset of ARF in ICU, were screened for eligibility (PaO2/FiO2 <300 mm Hg and/or peripheral oxygen saturation as measured by pulse oximetry <94% under air condition and/or dyspnea) when the research team was available. Patients were eligible when they had a central venous catheter in the jugular or the subclavian vein placed upon clinical decision outside the study prior to enrollment. The position of the tip of the venous catheter was in the upper part of the right atrium and verified by chest radiograph. Further exclusion criteria were age <18 years, pregnancy, body mass index over 50 kg/m2, ribcage malformation, and any contraindication to the use of EIT (chest wounds limiting electrode belt placement, automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillator, and implantable pumps).
EIT measurements were obtained with PulmoVista500 (Dräger Medical). An EIT belt with 16 surface electrodes was placed around the patient’s thorax at the fourth intercostal space level. A bolus of 10 ml 10% NaCl was injected during a respiratory pause (≥8 s) through the central venous catheter. The respiratory pause was conducted via an end-expiratory hold maneuver with the ventilator in the intubated patients. The conscious patients were asked to hold their breath at the end of expiration. The maneuver was repeated maximum once in 30 minutes in case significant tortuosity and/or interruption in global time-impedance curve was observed, and the patient with poor quality global time–impedance curve was excluded from the study after two attempts.
EIT data analysis was achieved using customized software developed with MATLAB (R2015a; MathWorks). Functional ventilation map was derived from averaging the tidal impedance variation images (8). Functional perfusion map was calculated as the slope of regional impedance–time curves after saline bolus injection (7). To minimize the influence of heart on the perfusion image, the initial impedance fall of global time-impedance curve was excluded from the analysis (a period of one cardiac cycle). Ventilated and perfused regions were defined as pixels higher than 20% maximum of the functional ventilation and perfusion maps, respectively. Subsequently, three regions were identified: regions that were only ventilated (RV), regions that were only perfused (RP), and regions both ventilated and perfused (RV+P). The following EIT-derived parameters were calculated:
| (1) |
| (2) |
| (3) |
The three above-mentioned parameters were used to assess regional mismatching pattern. The cardiac-related pulsatility signal was computed via band-pass filtering the EIT data (second-order Butterworth, 0.7–2 Hz), and the results were compared with the lung perfusion calculated during saline bolus injection in the patients with PE.
The statistical analysis was performed by using the software package SPSS 24.0 (SPSS Inc.) and MedCalc 11.4.3.0 (MedCalc Software). Mann-Whitney test was used to compare groups on continuous variables. The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves were compared using a Hanley-McNeil test.
Results
A total of 129 patients with ARF were screened. Sixty-one were excluded (11 patients were unable to hold their breaths after two attempts; 50 because of absence of study team or the exclusion criteria met). Sixty-eight patients with ARF were enrolled to the study, including 11 patients with PE (10 confirmed by computed tomographic pulmonary angiography [CTPA] and 1 by medical history and bedside ultrasound) and 57 patients without PE (ARF caused by other reasons such as diffuse lung interstitial disease, lung edema/pneumonia, or pleural effusion). Time interval between the CPTA and EIT examination was 1.5 ± 1.1 days, and time lag between ICU admission and EIT was 2.4 ± 2.1 days. Three patients with PE and three without PE were awake. Two patients without PE received muscle paralysis for lung protection. The rest of the patients were sedated and intubated.
Clinical and EIT data of individual patients with PE are summarized in Table 1. Typical matching images of patients with PE, diffuse lung disease, and hemothorax are shown in Figures 1A–1C. No recognizable defects in regional ventilation and perfusion were observed in the patient with diffuse lung disease, whereas a defect in regional perfusion with normal ventilation was observed in the PE patient. Defects in both regional ventilation and perfusion were found in a patient with hemothorax.
Table 1.
Individual Clinical Data, CTPA, and EIT Examination of the 11 Patients with PE
| Pts No. | Weight (kg) | Primary Diagnosis | Clinical Presentation | PaO2/FiO2 (mm Hg) | Origin of Embolism | Diagnosis of PE | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 69 | Right atrium tumor | Acute cardiac shock and hypoxemia during operation | 50 | Right atrium | Ultrasound: acute cor pulmonale was diagnosed, and acute lung edema/pneumothorax/atelectasis were excluded. CTPA: N/A | Dead |
| 2 | 70 | Right atrial thrombus, anticardiolipin antibody syndrome | Acute hypoxemia | 80 | Right atrium | CTPA: embolism in both left and right main pulmonary arteries and branches | Dead |
| 3 | 85 | Lung cancer | Acute dyspnea after out-of-bed physical activities during postoperative period | 207 | DVT | CTPA: embolism in both left and right pulmonary artery branches | Alive |
| 4 | 65 | Chronic pulmonary embolism | Sudden hypoxemia | 120 | Unknown | CTPA: multiple embolisms and worse in lower right lobe | Alive |
| 5 | 80 | Chronic portal mesentery and vein thrombosis | Hypoxemia after vascular bypass operation | 141 | Unknown | CTPA: embolism in pulmonary artery of left superior lobe lingual segment | Alive |
| 6 | 75 | Suspected cancer and lung interstitial disease | Refractory hypoxemia | 134 | Unknown | CTPA: embolism in both left and right pulmonary branches and worse in left lung | Dead |
| 7 | 50 | Pelvic malignant neoplasm | Acute dyspnea after out-of-bed physical activities during postoperative period | 272 | DVT | CTPA: embolism in both left and right pulmonary branches | Alive |
| 8 | 68 | Thymoma | Acute dyspnea and sudden cardiac arrest after out-of-bed physical activities during postoperative period | 86 | DVT | CTPA: embolism in both left and right main pulmonary artery branches | Alive |
| 9 | 72 | Left lung cancer | Sudden dyspnea after out-of-bed physical activities during postoperative period | 206 | Unknown | CTPA: embolism in right pulmonary artery branches | Alive |
| 10 | 80 | Postoperative coronary bypass surgery | Acute dyspnea after out-of-bed physical activities during postoperative period | 210 | DVT | CTPA: embolism in right pulmonary artery branches | Alive |
| 11 | 83 | Tumor of right atrium | Hypoxemia after operation | 171 | Right atrium | CTPA: embolism in right and left pulmonary artery branches | Alive |
Definition of abbreviations: CTPA = computed tomographic pulmonary angiography; DVT = deep vein thrombosis; EIT = electrical impedance tomography; PE = pulmonary embolism; Pts = patients; N/A = not available.
Figure 1.
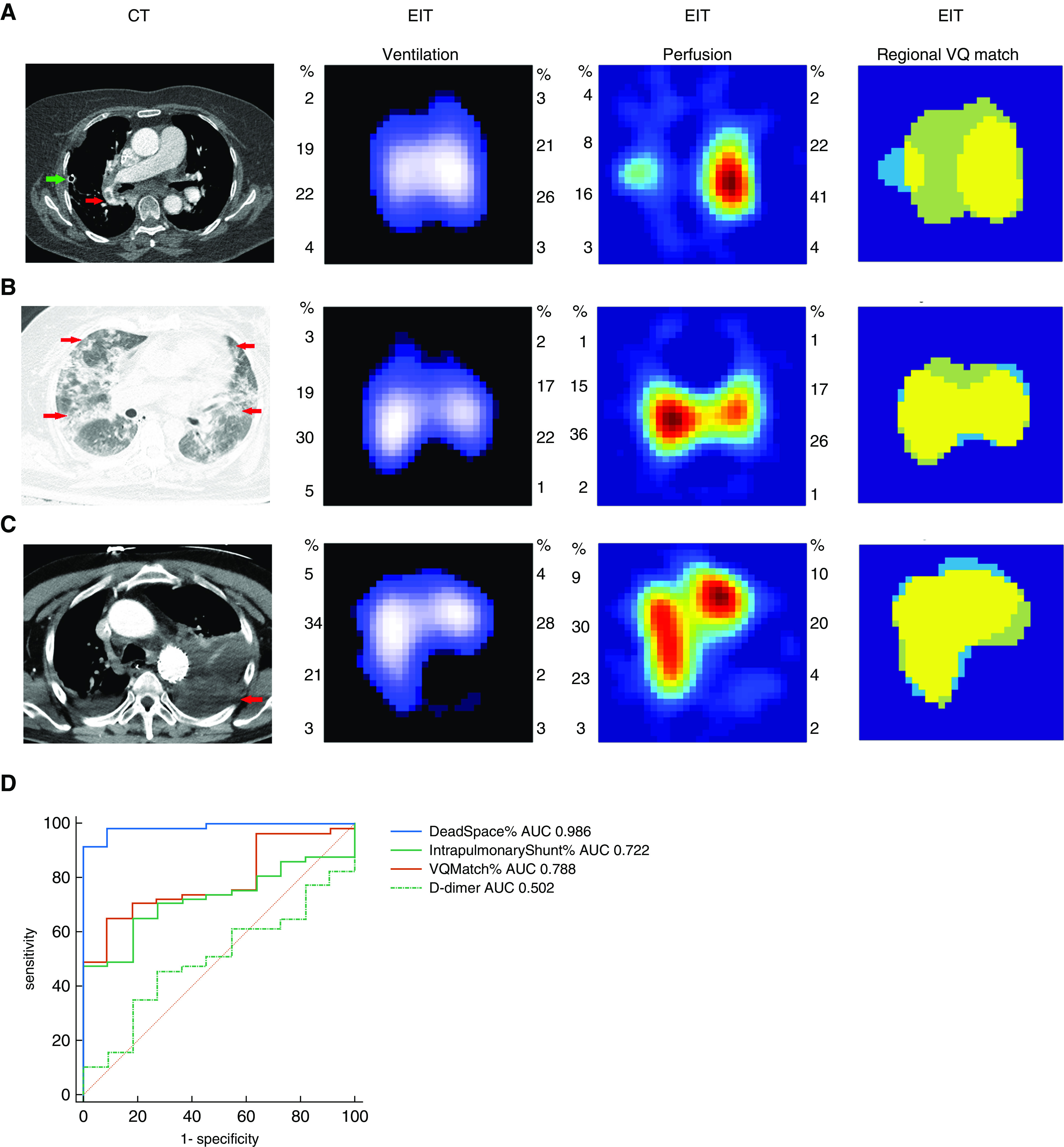
(A) Computed tomographic (CT) pulmonary angiography and electrical impedance tomography measurement of a patient, who developed acute pulmonary embolism after left upper lung lobe resection. In the CT pulmonary angiography image, the red arrow shows an embolus in the right pulmonary artery. Ventilation and perfusion images indicated poor regional perfusion in the left lung with a normal ventilation distribution. Low-ventilated regions are marked in dark blue and high-ventilated regions in white; regions with high perfusion are marked in red and low perfusion in green. In the match image, dead-space fraction area percentage marked as light green was 54.01%, percentage of intrapulmonary shunt area marked as light blue was 9.50%, and percentage of match region marked as yellow was 36.50%. Please refer to the text for the parameters’ calculation. Green arrow shows a chest tube, which was placed at the end of the surgery. (B) A patient with diffuse lung disease with ground-glass opacity (CT: red arrows show diffuse opacities in both lungs; ventilation and perfusion images: relative normal distribution of regional ventilation and distribution; match image: dead-space fraction was 15.29%, intrapulmonary shunt ratio was 6.27%, and match region percentage was 78.43%). (C) A patient with hemothorax (CT: red arrow shows the hemothorax in the lower left chest zone; ventilation and perfusion images: defects in regional ventilation and distribution in the lower left lung; match image: dead-space fraction was 12.19%, intrapulmonary shunt ratio was 11.25%, and match region percentage was 76.56%). (D) Areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUC) comparing the ability of dead space %, match %, intrapulmonary shunt %, and D-dimer to discriminate pulmonary embolism in the 68 patients. AUC of dead space % was significantly higher than AUC of the other parameters (P < 0.05). EIT = electrical impedance tomography.
The PE group had a significantly lower PaO2/FiO2 compared with the non-PE group (153 ± 67 vs. 230 ± 86 mm Hg; P = 0.005). As confirmed by EIT, the PE group had a significantly higher dead space % (43.1 ± 11.1 vs. 15.7 ± 9.2%; P < 0.0001), lower intrapulmonary shunt % (9.5 ± 4.5 vs. 21.3 ± 16.2%; P = 0.02), and match % (47.2 ± 10.8 vs. 62.9 ± 16.1%; P = 0.003) than the non-PE group. Dead space % had the best performance in diagnosing PE among the examined parameters (also significantly better than D-dimer [Figure 1D]). A cutoff value of 30.37 for dead space % resulted in a sensitivity of 90.9% and a specificity of 98.6% for the PE diagnosis.
A correlation between saline injection and pulsatility methods was not found in the investigated parameters (intrapulmonary shunt %, r = −0.173, P = 0.612; dead space %, r = 0.164, P = 0.631; match %, r = −0.018, P = 0.958) in the patients with PE.
Discussion
In the present study, we described for the first time EIT-based regional ventilation and perfusion measures that were able to discriminate patients with acute PE from other patients with ARF. With these measures, EIT might be used to confirm PE at the bedside already during the initial patient assessment. This is potentially relevant especially for patients with unstable clinical status and high risk of transfer for CTPA examination.
Injection of 10% NaCl might cause the elevation of serum Na+ and Cl− concentrations, which might be harmful for brain and kidney function. In the present study, only 10 ml of 10% NaCl was injected, and the amount was taken into account for the acceptable daily intake of NaCl in the patient management. No adverse events (electrolyte disturbance, catheter related infection, etc.) were recorded. A lower concentration was used in a recent study (9) with longer breath holding time, where the lung volume drops because of oxygen intake may become a significant influencing factor.
A mild agreement between the locations of regions exhibiting perfusion loss by EIT and CTPA was found. Functional EIT measurement does not reflect anatomical location of PE but rather regions with perfusion gain/loss. Patients with PE may have single or multiple embolisms. CTPA provides morphological information capturing the location of PE, but the influence of PE on perfusion might not be limited to that region. Besides, diseases other than PE may also cause loss of regional perfusion (e.g., Figure 1C). Therefore, we recommend combining regional ventilation and perfusion for PE diagnosis. With limited spatial resolution, EIT is unlikely to detect small embolism as effectively as CTPA. For adjacent current driving pattern, the EIT measurement sensitivity falls for objects toward the center of measurement field. In theory, in case the emboli are located centrally within the chest, the sensitivity may be reduced regarding the detectable sizes. But in fact, it is easier to detect central PE that always causes more regions perfusion loss than peripheral PE.
Among the EIT-based measures proposed in our study combining perfusion and ventilation, dead space % caused by regionally diminished perfusion and normal ventilation has a significantly higher sensitivity and specificity to diagnose PE compared with other examined parameters. In our study, D-dimer did not show a good ability to diagnose PE in the mixed patient population (Figure 1C). It was previously reported that high D-dimer concentration was considered as an indication of anticoagulation treatment in the patients with ARF with suspected PE (10). However, some factors such as operation, tumor, and inflammation could also cause an increase in D-dimer. For comparison, we also calculated the cardiac-related pulsatility signal. Although the pulsatility method might not measure exactly the regional lung perfusion in regard to blood flow distribution, it may contain valuable information regarding regional blood volume and regional pulmonary vascular mechanics, which warrants further investigations.
There were several limitations in the present study. 1) Our proof-of-concept study was performed in a single center and with a small number of patients, which limited the statistical power. 2) The investigators were not blinded to the patient’s clinical data; however, the EIT data analysis method was established prior to the study, and the developer was not aware of the clinical data. 3) The use of thresholds to identify ventilated and perfused regions could reduce the influence of noise in the signal but at the same time decrease the sensitivity to small changes. The threshold values used in the present study were not optimized, which could be further investigated.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first clinical study confirming PE at the bedside with EIT showing high sensitivity and specificity. Further study is required to validate the impact of the described EIT-based method on decision-making, therapeutic management, and outcomes in the suspected PE patients.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
Supported by Capital’s Funds for Health Improvement and Research (No. 2020-2-40111), Peking Union Medical College Hospital of Medical Novel Medical Technology Project (No. XJS20190210), Everest Program of AFMU (Grant No. 2019ZFB002), BMBF MOVE (FKZ 13FH628IX6), and H2020 MCSA Rise (872488—DCPM).
Author Contributions: H.H., Y.C., Y.L., S.Y., R.Z., and Z.Z. conceived the study protocol. H.H., Y.C., Y.L., S.Y., R.Z., and Z.Z. participated in the design and coordination of the study. H.H., Y.C., Y.L., S.Y., and R.Z. collected study data. H.H., Y.C., Y.L., S.Y., R.Z., I.F., K.M., F.F., and Z.Z. participated in data interpretation. H.H., Y.C., Y.L., S.Y., and Z.Z. drafted the present manuscript. H.H., Y.C., Y.L., S.Y., R.Z., I.F., K.M., F.F., and Z.Z. revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Originally Published in Press as DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202005-1780LE on June 25, 2020
Author disclosures are available with the text of this letter at www.atsjournals.org.
References
- 1.Becher T, Bußmeyer M, Lautenschläger I, Schädler D, Weiler N, Frerichs I. Characteristic pattern of pleural effusion in electrical impedance tomography images of critically ill patients. Br J Anaesth. 2018;120:1219–1228. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2018.02.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rahtu M, Frerichs I, Waldmann A, Strodthoff C, Becher T, Bayford R, et al. Early recognition of pneumothorax in neonatal respiratory distress syndrome with electrical impedance tomography. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2019;200:1060–1061. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201810-1999IM. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kobylianskii J, Murray A, Brace D, Goligher E, Fan E. Electrical impedance tomography in adult patients undergoing mechanical ventilation: a systematic review. J Crit Care. 2016;35:33–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.04.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Frerichs I, Amato MB, van Kaam AH, Tingay DG, Zhao Z, Grychtol B, et al. TREND study group. Chest electrical impedance tomography examination, data analysis, terminology, clinical use and recommendations: consensus statement of the TRanslational EIT developmeNt stuDy group. Thorax. 2017;72:83–93. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-208357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nguyen DT, Bhaskaran A, Chik W, Barry MA, Pouliopoulos J, Kosobrodov R, et al. Perfusion redistribution after a pulmonary-embolism-like event with contrast enhanced EIT. Physiol Meas. 2015;36:1297–1309. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/36/6/1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Borges JB, Suarez-Sipmann F, Bohm SH, Tusman G, Melo A, Maripuu E, et al. Regional lung perfusion estimated by electrical impedance tomography in a piglet model of lung collapse. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2012;112:225–236. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01090.2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.He H, Long Y, Frerichs I, Zhao Z. Detection of acute pulmonary embolism by electrical impedance tomography and saline bolus injection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;202:881–882. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202003-0554IM. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhao Z, Yun PJ, Kuo YL, Fu F, Dai M, Frerichs I, et al. Comparison of different functional EIT approaches to quantify tidal ventilation distribution. Physiol Meas. 2018;39:01NT01. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/aa9eb4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mauri T, Spinelli E, Scotti E, Colussi G, Basile MC, Crotti S, et al. Potential for lung recruitment and ventilation-perfusion mismatch in patients with the acute respiratory distress syndrome from coronavirus disease 2019. Crit Care Med. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004386. [online ahead of print] 17 Apr 2020; DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kearon C, de Wit K, Parpia S, Schulman S, Afilalo M, Hirsch A, et al. PEGeD Study Investigators. Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism with d-dimer adjusted to clinical probability. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:2125–2134. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1909159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


