Abstract
Introduction
Vasodilatory hypotension is common among intensive care unit (ICU) patients; vasopressors are considered standard of care. However, optimal mean arterial pressure (MAP) targets for vasopressor titration are unknown. The objective of the Optimal VAsopressor TitraTION in patients 65 years and older (OVATION-65) trial is to ascertain the effect of permissive hypotension (vasopressor titration to achieve MAP 60–65 mm Hg) versus usual care on biomarkers of organ injury in hypotensive patients aged ≥65 years.
Methods and analysis
OVATION-65 is an allocation-concealed randomised trial in 7 Canadian hospitals. Eligible patients are ≥65 years of age, in an ICU with vasodilatory hypotension, receiving vasopressors for ≤12 hours to maintain MAP ≥65 mm Hg during or after adequate fluid resuscitation, and expected to receive vasopressors for ≥6 additional hours. Patients are excluded for any of the following: active treatment for spinal cord or acute brain injury; vasopressors given solely for bleeding, ventricular failure or postcardiopulmonary bypass vasoplegia; withdrawal of life-sustaining treatments expected within 48 hours; death perceived as imminent; previous enrolment in OVATION-65; organ transplant within the last year; receiving extracorporeal life support or lack of physician equipoise. Patients are randomised to permissive hypotension versus usual care for up to 28 days. The primary outcome is high-sensitivity troponin T, a biomarker of cardiac injury, on day 3. Secondary outcomes include biomarkers of injury to other organs (brain, liver, intestine, skeletal muscle); lactate (a biomarker of global tissue dysoxia); resource utilisation; adverse events; mortality (90 days and 6 months) and cognitive function (6 months). Assessors of biomarkers, mortality and cognitive function are blinded to allocation.
Ethics and dissemination
This protocol has been approved at all sites. Consent is obtained from the eligible patient, the substitute decision-maker if the patient is incapable, or in a deferred fashion where permitted. End-of-grant dissemination plans include presentations, publications and social media platforms and discussion forums.
Trial registration number
Keywords: adult intensive & critical care, clinical trials, clinical chemistry
Strengths and limitations of this study.
Optimal VAsopressor TitraTION-65 is an allocation-concealed randomised clinical trial of permissive hypotension versus usual care in patients aged 65 years and older with hypotension from a vasodilatory cause, a population that may be more vulnerable to adverse effects of vasopressors.
Vasopressor titration is understudied in critically ill patients, compared with other interventions such as mechanical ventilation.
The primary and many secondary outcomes, selected with input from a patient representative, focus on biomarkers of organ injury; although these are not patient-centred outcomes, results will complement clinical outcome data from larger trials.
Because of the nature of the intervention, clinician blinding is not feasible; however, outcome assessors are blinded.
The modest sample size implies that the trial is underpowered for clinical outcomes.
Introduction
Shock, a clinical syndrome of which hypotension is a cardinal feature, is common and associated with high mortality. Vasopressors are used to treat hypotension that is potentially life-threatening because they raise blood pressure by inducing vasoconstriction.1 However, these medications are associated with adverse effects,2–4 some of which are direct consequences of vasoconstriction-induced reduction in blood flow to vital organs. Therefore, titrating vasopressors implies balancing the risks of end-organ failure caused by hypotension and potential vasopressor-induced harm, including myocardial injury and arrhythmia, excessive vasoconstriction, hyperglycaemia and immunosuppression.2–5 Permissive hypotension is a strategy of targeting a lower blood pressure when prescribing vasopressors, compared with usual care. Benefits have been associated with other ‘permissive’ therapies in critically ill patients, including hypoxia,6 underfeeding,7 hypercapnia,8 red blood cell transfusion9 and hypotension in thoracic penetrating trauma.10
Clinicians in the intensive care unit (ICU) use mean arterial pressure (MAP) targets to determine the intensity of vasopressor therapy. Current international practice guidelines recommend titrating vasopressors to a MAP of 65 mm Hg,11 but because the target lacks an upper boundary, clinicians commonly put more emphasis on preventing hypotension than on minimising vasopressor exposure. This underappreciation of the risks associated with vasopressor overuse was apparent in a multicentre observational study12 that reported an average MAP of 75 (SD 6) mm Hg in patients receiving vasopressors, approximately 10 mm Hg above the recommended MAP and self-reported practice.13 Given the relative lack of studies about vasopressor dosing, in contrast to other common ICU treatments such as mechanical ventilation, editorialists have advocated for better characterisation of the lowest acceptable blood pressure target to avoid vasopressor-induced harm.3
Existing evidence
Observational studies have described independent associations between dose and duration of vasopressor therapy and poor outcomes, such as adverse cardiac events and increased mortality.14 15 However, these studies are limited by indication bias, as patients who are sicker have a greater risk of unfavourable outcomes and are therefore more likely to be exposed to higher doses of vasopressor therapy.
Two randomised clinical trials (RCTs; combined n=894) published prior to the initiation of this study compared blood pressure targets in patients receiving vasopresors.16 17 The Sepsis and Mean Arterial Pressure (SEPSISPAM) trial compared a MAP target of 65–70 mm Hg vs 80–85 mm Hg for 5 days in 776 patients with septic shock from 29 French ICUs. This study reported no difference in 28-day mortality (lower MAP 34.0% vs higher MAP 36.6%, p=0.57), but a greater risk of atrial fibrillation in the higher MAP arm (6.7% vs 2.8%, p=0.02).16 However, actual MAP values were 74–76 mm Hg in the lower MAP arm, precluding conclusions regarding permissive hypotension. The Optimal VAsopressor TitraTION (OVATION) pilot feasibility trial randomly assigned 118 patients from 1 US and 10 Canadian ICUs to a lower (60–65 mm Hg) or higher (75–80 mm Hg) MAP target.17 This trial was not powered to detect differences in mortality. A subsequent individual patient data meta-analysis (IPDMA)18 included data from both RCTs and found that higher MAP targets (75–85 mm Hg) may be associated with an increased risk of 28-day mortality in older patients (p=0.1 for interaction between age and MAP).
Based on these RCTs, guidelines state that no evidence supports the use of vasopressors to achieve MAP values >65 mm Hg for patients receiving vasopressors.19 Subsequently, the 65 trial randomised 2600 patients aged ≥65 years in the UK to permissive hypotension versus usual care using a similar protocol as OVATION-65.20 21 Patients in the permissive hypotension arm had a lower exposure to vasopressors and a lower 90-day mortality (41.0% vs 43.8%, p=0.15), but the difference was not statistically significant. However, an analysis adjusting for baseline covariates found lower mortality with permissive hypotension (OR 0.82, 95% CI 0.68 to 0.98).22 The 65 trial collected no biological samples, precluding exploration of mechanisms underlying the effect of vasopressor dosing in that trial.
Objective and specific aims
The main objective of OVATION-65 is to determine whether permissive hypotension (MAP 60–65 mm Hg) in patients aged ≥65 years with a vasodilatory cause of hypotension and receiving vasopressors, compared with usual MAP targets, reduces organ injury as measured by biomarkers. Specific aims are to ascertain the effect of permissive hypotension versus usual care on: (1) biomarkers of organ injury (heart (primary outcome), brain, liver, intestine, skeletal muscle); (2) biomarker of global tissue dysoxia (lactate); (3) organ function (assessed by Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score);23 (4) resource utilisation; (5) prespecified adverse events; (6) mortality at 90 days and 6 months; (7) cognitive impairment in survivors at 6 months (table 1).
Table 1.
Summary of objectives and outcomes
| Objectives | Outcomes |
| Biomarkers of organ injury | |
| Heart | High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (primary outcome) |
| N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide | |
| Brain | Glial fibrillar acidic protein |
| Myelin basic protein | |
| Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) | |
| Liver | Alanine aminotransferase |
| Intestine | Intestinal-type fatty acid binding protein |
| Skeletal muscle | Creatine kinase |
| Global tissue dysoxia | Lactate |
| Organ function | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score on days 2, 3, 4, 7, 10, 14 and 28 while in the ICU (an additional measurement is taken on day 1 (baseline)) |
| Resource utilisation | Duration of mechanical ventilation |
| Duration of renal replacement therapy | |
| Duration of vasopressor therapy | |
| Duration of ICU stay | |
| Duration of hospital stay | |
| Adverse events | Clinically detected supraventricular arrhythmia |
| Stroke | |
| Acute kidney injury (KDIGO stage 3) | |
| Limb ischaemia | |
| Intestinal ischaemia | |
| Mortality | 90 days |
| 6 months | |
| Cognitive impairment | Telephone Interview for Cognitive Status at 6 months |
All biomarkers of organ injury and lactate are measured in plasma (except for NSE, measured in serum) at days 3 and 7, with an additional measurement at baseline (day 1).
ICU, intensive care unit; KDIGO, kidney disease improving global outcomes.
The primary outcome and several secondary outcomes are focused on biomarkers because of well-documented limitations of mortality in critical care trials24 and the challenges of developing valid surrogate end points.25 OVATION-65 was designed to be complementary to the 65 trial.22 A larger version of OVATION-65 (n=800) was abandoned in 2018 after funding applications to the Canadian Institutes for Health Research and the Canadian Frailty Network were rejected. As discussed in the ‘Statistical Analysis’ section, the Data and Safety Monitoring Committee (DSMC) recommended termination of enrolment in the current smaller version of OVATION-65 on 21 February 2020; patient follow-up is ongoing.
Methods and analysis
OVATION-65 is a multicentre, parallel-group, allocation-concealed, superiority RCT. We developed OVATION-65 on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group (CCCTG), a 350-member organisation of clinicians and researchers, incorporating feedback received since January 2012 at each of its thrice yearly scientific meetings. Table 2 shows a timeline of trial activities. The Standard Protocol Items: Recommendations for Interventional Trials checklist is available in online supplementary file S1.
Table 2.
OVATION-65 trial timeline
| Study period | |||||||||||||
| Days | Days | Months |
|||||||||||
| Enrolment/Allocation | Post-allocation | ||||||||||||
| Time points | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5–6 | 7 | 8–9 | 10 | 11–13 | 14 | 15–27 | 28 | 6 months |
| Enrolment | |||||||||||||
| Eligibility screen | x | ||||||||||||
| Informed consent | x | ||||||||||||
| Allocation | x | ||||||||||||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||
| Permissive hypotension (MAP 60–65 mm Hg) versus usual care* |

|
||||||||||||
| Assessments | |||||||||||||
| Baseline variables | |||||||||||||
| Diagnosis of admission | x | ||||||||||||
| Severity of illness (APACHE II score) |
x | ||||||||||||
| Pre-existing comorbidities (Clinical Frailty Score) |
x | ||||||||||||
| Outcomes | |||||||||||||
| hsTnT† | x | x | x | ||||||||||
| Biomarkers of organ injury‡ | x | x | x | ||||||||||
| Global tissue dysoxia (lactate) |
x | x | x | ||||||||||
| Organ function including renal function (SOFA score) | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||
| Resource utilisation§ |

|
||||||||||||
| Mortality at 90 days and 6 months |

|
x | |||||||||||
| Cognitive impairment (TICS) at 6 months | x | ||||||||||||
| Stroke |

|
||||||||||||
| Clinically detected supraventricular arrhythmia |

|
||||||||||||
| Limb or intestinal ischaemia |

|
||||||||||||
| Stage 3 acute kidney injury¶ |

|
||||||||||||
| Other variables | |||||||||||||
| Protocol adherence** |

|
||||||||||||
| Co-interventions†† |

|
||||||||||||
*MAP target while receiving vasopressor therapy up to day 28, or discontinuation for >24 hours.
†hsTnT at day 3 is the primary outcome and at day 7 is a secondary outcome.
‡NT-proBNP, GFAP, MBP, NSE, ALT, FABP, CK.
§Duration of mechanical ventilation, renal replacement therapy, vasopressor therapy, ICU and hospital stay.
¶As defined by KDIGO criteria.
**See text for definition.
††See text for definition.
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; APACHE II, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; CK, creatine kinase; FABP, intestinal-type fatty acid binding protein; GFAP, glial fibrillar acidic protein; hsTnT, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T; KDIGO, Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes; MAP, mean arterial pressure; MBP, myelin basic protein; NSE, neuron-specific enolase; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; OVATION-65, Optimal VAsopressor TitraTION in patients 65 years and older; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; TICS, Telephone Interview for Cognitive Status.
bmjopen-2020-037947supp001.pdf (63.4KB, pdf)
Study setting and management
Many study procedures for OVATION-65 are the same as those described for another trial conducted by our group.26 OVATION-65 is conducted in adult ICUs in seven sites in Canada. OVATION-65 team members, including research personnel at clinical sites active at the time of submission of this manuscript, are listed in online supplementary file S2. The procedures in place for OVATION-65 were piloted during the OVATION pilot RCT.17 The Unité de Recherche Clinique et Épidémiologique (URCE) is coordinating this trial and is responsible for construction and maintenance of the randomisation system and the REDCap27 28 electronic data capture (EDC) system. The URCE also oversees the storage and analysis of blood and urine samples in the OVATION-65 core laboratory.
bmjopen-2020-037947supp002.pdf (82.4KB, pdf)
Inclusion criteria
Patients are included if they meet all the following criteria: (1) age ≥65 years; (2) diagnosis of vasodilatory hypotension as assessed by the treating team; (3) vasopressors started ≤12 hours ago (after or during adequate fluid resuscitation, as assessed by treating physician) and (4) vasopressors expected for ≥6 additional hours, as assessed by the treating team. Aligned with the 65 trial,22 we do not specify a minimum volume of fluid or specific examinations for volume status prior to the clinical (prerandomisation) decision to commence a vasopressor.
Exclusion criteria
Patients are excluded if they meet any of the following criteria: (1) actively treated for spinal cord injury or acute brain injury; (2) vasopressors given solely for bleeding, acute ventricular failure or postcardiopulmonary bypass vasoplegia; (3) lacking commitment to life-sustaining therapies (expected withdrawal of life-sustaining treatments within the next 48 hours); (4) death perceived as imminent; (5) previously enrolled in OVATION-65; (6) organ transplant within the last year; (7) receiving extracorporeal life support at baseline and (8) lack of treating physician equipoise regarding the overall effects of permissive hypotension versus usual care on patient important outcomes.
Rationale for eligibility criteria
The inclusion criteria strive to identify patients most likely to benefit from permissive hypotension, namely elderly patients not already exposed to a prolonged duration of higher MAP but expected to require an additional period of vasopressor therapy. The exclusion criteria are designed to exclude patients for whom clinicians commonly apply different MAP targets (criterion 1) or whose prognosis may be dominated by factors other than the MAP target (criteria 2, 3, 4, 6, 7).
Study intervention
Treatment allocation
Using a web randomisation service available 24 hours/7 days per week, patients are randomised immediately after confirming eligibility following a 1:1 sequence to permissive hypotension or usual care. We use permuted blocks of variable and undisclosed size (4, 6 and 8) and stratify randomisation by site. Stratifying by site ensures equal distribution of patients between arms at each site and decreases the probability that site-specific practices confound treatment effects.
Permissive hypotension arm
The intervention minimises dose and duration of vasopressors. Treating teams adjust vasopressors to a target MAP range of 60–65 mm Hg. A MAP of 60 mm Hg was selected as lowest tolerable limit because it corresponds to the threshold at which Canadian intensivists usually initiate vasopressors.13 Accordingly, it is not uncommon for patients to have MAP as low as 60 mm Hg before vasopressors are instituted under usual care. The same MAP range was used in the OVATION pilot RCT.17
The duration of the trial intervention is determined, as it was in the pilot RCT, by the duration of the hypotensive episode, up to a maximum of 28 days. For trial purposes, the episode of hypotension ends when vasopressors are discontinued for 24 consecutive hours. As soon as patients are able to maintain the target MAP without vasopressors, the infusions are stopped. If MAP drops below 60 mm Hg after this 24-hour period, and if the treating team determines that vasopressors should be reinstituted, they are titrated to the allocated target of 60–65 mm Hg. If patients are discharged and then readmitted to the ICU, vasopressor therapy is left at the discretion of the treating team. We do not mandate resumption of the permissive hypotension strategy to enhance trial feasibility, and we anticipate relatively few readmissions overall and rare readmissions before ascertainment of our primary outcome on day 3.
Usual care arm
Patients in the control arm receive usual care, as per local practice. This constitutes an improvement to the protocol of the OVATION pilot trial, which imposed a higher target MAP range of 75–80 mm Hg. Given preliminary evidence suggesting that this higher MAP target may increase risk of death in older patients, we believe that mandating a higher MAP would be ethically questionable. By comparing permissive hypotension with usual care, we improve acceptance from clinicians and reduce the risk that the control group will diverge widely from usual care.29 Risks of contamination are negligible given observational data showing that MAP values of patients treated with vasopressors are much higher than the currently recommended target of 65 mm Hg. Moreover, changing the behaviour of physicians and nurses is challenging even when there is consensus on the benefit of a new intervention,30 and such a consensus does not exist for permissive hypotension.31 To further decrease the risk of contamination (ie, lack of separation of MAP between arms), we monitor separation of actual MAP between study arms and communicate regularly with sites.
Selection of vasopressors
We do not mandate the use of any specific vasopressor or combination of vasopressors. In OVATION-65, the term ‘vasopressor’ refers to the following medications given by infusion: norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, phenylephrine and vasopressin. In patients receiving multiple vasopressors, we calculate the total vasopressor dose as norepinephrine equivalent as previously reported.32 In addition, we collect information on orally administered catecholaminergic medications (ie, midodrine and ephedrine).
Other interventions
As per usual care of patients receiving vasopressors, we expect central venous catheters (to avoid extravasation) and arterial catheters (for close MAP monitoring) to be in place for most patients. MAP is measured by an arterial line if present or by a non-invasive blood pressure cuff otherwise; values are taken from the nursing vital signs flowsheet. Peripheral venous lines to deliver vasopressors or non-invasive blood pressure measurements do not constitute protocol deviations, consistent with a pragmatic study design. Use of pure inotropes, intravenous fluids and corticosteroids are recorded but left to the discretion of the treating team.
Outcomes
Primary outcome
The primary outcome of OVATION-65 is plasma high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hsTnT) at day 3, or before anticipated death or withdrawal of life-sustaining therapies, whichever comes first. A baseline sample (day 1) is collected before assignment to the intervention but after vasopressors have started. Cardiac troponins are consistently associated with worse outcomes in critical illness,33–37 and cardiac biomarkers may be modifiable by administration of albumin34 and medications.35 Given that coronary blood flow is maintained over a broad range of coronary perfusion pressures under most circumstances,38 we hypothesise that increasing vasopressors to achieve a higher MAP will have little effect on coronary perfusion but may increase the severity of demand-related myocardial ischaemia via increased heart rate (ie, reduced coronary perfusion time) and transmural pressure (ie, afterload). If OVATION-65 shows that permissive hypotension prevents or limits hsTnT elevation, then patients at increased risk of secondary myocardial ischaemia, possibly identified by baseline hsTnT, may benefit the most from this strategy. Similarly, this biomarker could be used to identify vasopressor-induced harm earlier and modify vasopressor use accordingly.
Secondary outcomes
Secondary outcomes include hsTnT at day 7; biomarkers associated with cardiac wall stress (N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP)34); tissue injury to the brain39 (glial fibrillar acidic protein (GFAP),40 myelin basic protein (MBP),41 neuron-specific enolase (NSE)42), liver (alanine aminotransferase (ALT)43), intestine (intestinal-type fatty acid binding protein (FABP)44) and skeletal muscle (creatine kinase (CK)45) and global tissue dysoxia (lactate). As for hsTnT, these biomarker outcomes are measured at day 3 and 7, along with a baseline sample; all biomarkers are measured in plasma, except for NSE, which is measured in serum. We selected lactate as a reasonable measure of tissue hypoxia in critically ill patients but recognise that hyperlactataemia may result from other factors, including aerobic glycolysis, reduced oxidative phosphorylation and decreased clearance.46
We measure secondary clinical outcomes, including organ function using SOFA score (measured on days 2, 3, 4, 7, 10, 14 and 28 while in the ICU, along with a baseline (day 1) measurement). We describe healthcare utilisation in terms of days of mechanical ventilation, renal replacement therapy, vasopressor therapy and ICU and hospital stay. We report the incidence of the prespecified adverse events of stroke, acute kidney injury (kidney disease improving global outcomes (KDIGO) stage 3),47 clinically detected supraventricular arrhythmia5 48 and limb or intestinal ischaemia as defined in the OVATION pilot trial.17 Investigators will adjudicate these adverse events using medical records, if necessary. We ascertain mortality at 90 days and 6 months. For 6-month survivors, we assess cognition using the Telephone Interview for Cognitive Status (TICS), a validated questionnaire used in ICU cohorts.49
We had originally planned to measure additional secondary outcomes but lacked resources to do so for each participant. We have described these additional secondary outcomes as planned ancillary studies in online supplementary file S3.
bmjopen-2020-037947supp003.pdf (35.3KB, pdf)
Adverse events
OVATION-65 is testing a common intervention to treat a common problem in critically ill patients. All eligible patients are at risk of adverse events due to their underlying critical illness. Following Canadian guidelines for serious adverse event (SAE) reporting in academic drug trials in critical care,50 expected SAEs (stroke, KDIGO stage 3 acute kidney injury, clinically detected supraventricular arrhythmia, limb or intestinal ischaemia, death) are already incorporated as trial outcomes, defined a priori. SAEs are limited to events not already labelled as trial outcomes and that might reasonably occur as a consequence of the trial interventions. SAEs must be reported in the participant’s medical notes, on the OVATION-65 dedicated case report form and to the coordinating centre within 24 hours of observing or learning of the event. Such events are promptly discussed with the DSMC.
Data collection
We collect the following data: (1) baseline data (day 1)—demographics, admitting diagnosis, aetiology of hypotension, severity of illness (acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II (APACHE II) score51), vasopressor name, dose and start time, organ dysfunction (SOFA score23), comorbidities (including chronic hypertension, coronary, cerebral or peripheral vascular disease, congestive heart failure, chronic kidney disease, severe cognitive impairment, Clinical Frailty Scale,52 co-enrolment in other prospective observational studies or RCTs; (2) daily data—protocol adherence (hourly MAP while receiving vasopressors and corresponding vasopressor names, doses and modifications) and relevant co-interventions (fluid balance, inotropes, corticosteroids, life-support interventions, sedation) and (3) primary and secondary outcomes. We collect data on the times from hospital admission and ICU admission to the start of vasopressors. We collect data on fluid balance (total intake–total output) on the day of randomisation, but we do not collect data on volume of intravenous fluid administered before initiation of vasopressors.
Study samples
To minimise the treating teams’ workload, study samples (blood and urine) coincide as much as possible with clinical sampling on day 1 (baseline) and on day 3 and 7 (or the day of ICU discharge or before anticipated death or withdrawal of life-sustaining therapies, whichever comes first).
To ensure consistent measurement of biomarkers, the study samples are processed on site and shipped to URCE, where they are stored at −80°C and batched for analyses at the end of the trial. Clinicians are blinded to the results of study biomarker assays but can order any laboratory tests available at their hospital. Participants are also approached for participation in a parallel Acute Care Biobank, via a separate consent form, which allows samples remaining following completion of OVATION-65 specified analyses to be stored for future projects.
Risk of bias
Randomisation is concealed, with variable and undisclosed block size, thereby reducing risk of bias. Although clinical teams are not blinded to treatment arms, assessors of biomarkers, prespecified adverse events, mortality and TICS are blinded to treatment allocation. Specimen processing and analysis are standardised as described. Finally, we record co-interventions to detect performance bias.
A risk of bias related to the biomarker outcomes is that early death or live discharge from the ICU, which may be related to treatment allocation, are competing risks for ongoing treatment in the ICU and ascertainment of these outcomes. Our analysis plan (see ‘Statistical analysis’ section) accounts for this possibility.
Vasopressor management and protocol adherence
In the permissive hypotension arm, a protocol deviation is defined as a failure to reduce the dose of (or discontinue) vasopressors while the MAP is >65 mm Hg for three consecutive hours. Sites report protocol deviations on study forms and are asked to specify a reason for the deviation, which may include a physician’s decision to target a higher MAP because of particular clinical circumstances. Investigators will adjudicate protocol deviations using source data.
For each day on protocol, we record the MAP value recorded nearest to each hour. In the permissive hypotension arm, clinical teams are reminded to consider discontinuing vasopressor therapy if the patients are able to maintain MAP values of at least 60 mm Hg. Every participating site receives on-site training, to which all ICU bedside staff are invited. We distribute standard operating procedures and protocol adherence reports generated from MAP and vasopressor data entered in the electronic case report form (CRF). Regular newsletters and trial website updates (https://www.ccctg.ca/Programs/OVATION65.aspx) keep participating sites informed of study progress, overall adherence and answers to frequently asked questions. Research staff are available 24/7.
We will report vasopressor management in each arm in terms of duration and total dose of vasopressor therapy received, hourly MAP values and corresponding vasopressor infusion rates and the number of episodes of vasopressor therapy. In the permissive hypotension arm, we will report the number and proportion of patients with any protocol deviation. As in the 65 trial,22 patient-level adherence will be defined as not having experienced a protocol deviation. We will also report total time on vasopressors with recorded MAP within target range; total time on vasopressors with recorded MAP above target range; total time on vasopressors with recorded MAP >5 mm Hg above upper limit of target and total time on vasopressors with recorded MAP below target range. These measures will be summarised with descriptive statistics.
Follow-up
Participants are followed to hospital discharge by local research teams. Either the coordinating centre or the enrolling site ascertains 90-day and 6-month mortality and 6-month cognitive status in survivors by telephone. Prior verification of known vital status with local research teams and calibrated telephone scripts mitigate the risk of emotional distress in the event that a patient has died since hospital discharge. We selected TICS to measure cognitive function in survivors because telephone administration reduces risk of bias, improves measurement consistency, reduces patient burden and enhances feasibility.
Patient and public involvement
The protocol was developed with input from two ICU survivors (EB and DC), who participated in protocol development meetings, contributed to the selection of 6-month cognitive function as a secondary outcome and are coauthors of this manuscript.
Statistical analysis
Sample size
OVATION-65 is supported by several modest operating grants, each of which required a distinct objective, sample size calculation and analysis plan. By combining funds from multiple sources, we had planned to enrol 200 participants, which provides 80% power to detect an effect size of 0.4 in the difference between day 3 hsTnT in the permissive hypotension group compared with usual care, where 0.5 is considered to be medium.53
After the 65 trial22 was published, the OVATION-65 Executive Committee forwarded the publication to the DSMC, which requested a meeting to discuss the results. The DSMC subsequently issued a letter on 21 February 2020 recommending termination of enrolment in OVATION-65. The DSMC ‘reasoned that in light of the accumulated evidence, mostly from the 65 trial22 but also with some consideration of SEPSISPAM,16 the posterior probability of lower MAP targets now being better was sufficiently high that there is no longer equipoise between the interventions being compared in OVATION-65’. As of 21 February 2020, 159 patients had been randomised.
Patient flow
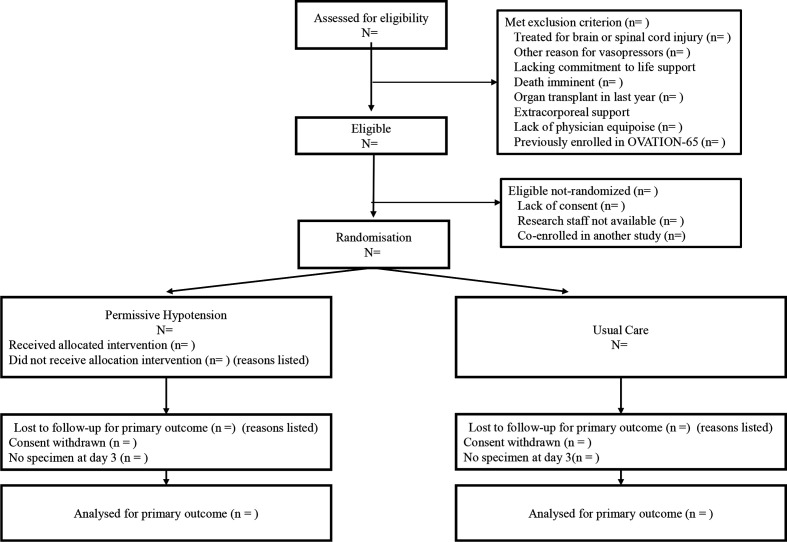
A sample Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials diagram is presented in figure 1.
Figure 1.
Progress of patients through the trial. ‘Co-enrolled in another study’ refers to a study for which the principal investigators of Optimal VAsopressor TitraTION-65 (OVATION-65) or the other study had prespecified that co-enrolment would not be allowed.
Data analysis
Analyses will be performed after all follow-up is completed, data queries are resolved and the database is locked. Analyses will follow the intention-to-treat principle, with data from participants analysed by allocated group. All participant data will be analysed unless consent to retain data is withdrawn. Statistical testing will use a superiority framework, with two-sided p<0.05 interpreted as statistically significant. Estimates of effect will be reported with 95% CIs. No adjustments for multiplicity will be made. All analyses will use SAS V.9.4 (Cary, USA). Given the modest sample size and focus on biomarkers of organ injury, no interim analysis was planned. Continuous data will be summarised as means (SD) if normally distributed and as medians (Q1, Q3) otherwise. Categorical data will be summarised as frequencies and proportions. Baseline data will be summarised as shown in table 3.
Table 3.
Baseline characteristics
| Characteristic | Permissive hypotension (n=) | Usual care (n=) |
| Demographics | ||
| Age, years, mean (SD) | ||
| Female sex, n (%) | ||
| Weight, kg; mean (SD) | ||
| Clinical Frailty Scale* >4, n (%) | ||
| APACHE II†, mean (SD) | ||
| SOFA‡, mean (SD) | ||
| Comorbidities | ||
| Cardiac | ||
| Supraventricular arrhythmia, n (%) | ||
| Ventricular arrhythmia, n (%) | ||
| Coronary artery disease§, n (%) | ||
| Congestive Heart Failure, class 1–3, n (%) | ||
| Congestive Heart Failure, class 4, n (%) | ||
| Left ventricular ejection fraction, % (mean, SD) | ||
| Vascular, n (%) | ||
| Known hypertension | ||
| Peripheral vascular disease or claudication | ||
| Cerebrovascular disease | ||
| Diabetes (type 1 or 2), n (%) | ||
| Renal, n (%) | ||
| Receiving chronic dialysis | ||
| Baseline creatinine¶, μmol/L, mean (SD) | ||
| Child’s B or C cirrhosis, n (%) | ||
| Chronic lung disease, n (%) | ||
| Immunosuppression, n (%) | ||
| Cognitive impairment or dementia, n (%) | ||
| ICU admission data | ||
| Primary ICU diagnosis, n (%) | ||
| Medical | ||
| Surgical | ||
| Transfer from another hospital, n (%) | ||
| Time from hospital admission to randomisation, hours; mean (SD) | ||
| Time from ICU admission to randomisation, hours; mean (SD) | ||
| Vasopressor dose, mean norepinephrine equivalents (mean µg/kg/min (SD)) | ||
| Vasopressors, n (%) | ||
| Norepinephrine | ||
| Epinephrine | ||
| Dopamine | ||
| Phenylephrine | ||
| Vasopressin | ||
| Inotropes, n (%) | ||
| Dobutamine | ||
| Milrinone | ||
| Mean arterial pressure, mm Hg; mean (SD) | ||
*The Clinical Frailty Scale52 ranges from 1 to 7, with scores of 5–7 denoting frailty.
†Scores on the APACHE II51 range from 0 to 71, with higher scores indicating more severe disease and a higher risk of death.
‡Scores on the SOFA23 range from 0 to 24, with higher scores indicating more severe disease and a higher risk of death.
§Coronary artery disease included angina and previous MI, PCI or CABG.
¶Baseline creatinine was determined from the outpatient creatinine within the last 12 months and closest to admission (n=) or, if not available, then the lowest inpatient creatinine before ICU admission (n=).
APACHE II, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting; ICU, intensive care unit; MI, myocardial infarction; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment.
The primary outcome of day 3 hsTnT will be analysed adjusting for the day 1 value. We will use the original scale and analysis of covariance if the data are not skewed; if skewed we will log-transform and use robust regression to obtain more interpretable estimates. We will use pooled logistic regression to estimate the probabilities of missing values due to either death or live discharge from the ICU. Based on these models, we will compute the inverse probability of attrition weights for each observation and use generalised estimating equation models to test the differences in hsTnT between the permissive hypotension and usual care arm,54 adjusting for centre using fixed effects. As a sensitivity analysis, for patients that die before day 3, we will impute the worst (highest) value and for patients discharged alive before day 3, we will impute the best (lowest) value.
For the secondary outcome of day 7 hsTnT, we will use the same approach. For patients who die before day 7, we will impute the worst (highest) value. For patients discharged alive before day 7, we will impute based on data available for other patients alive at day 7. The approach for all other biomarkers will be the same as for hsTnT.
For SOFA over the first 7 days, we will use a linear mixed effects model to account for repeated measures within patients as well as the centre effect. For patients who die before day 7, we will impute the worst (highest) value. For patients discharged alive before day 7, we will impute based on data available for patients in the same group alive at day 7. We will look for interaction between time and group as well as time trends. For TICS, we will use ordinal logistic regression with fixed effect for centre to compare the distribution of patients at 6 months in four categories (death and three cognitive status categories (non-impaired, mild impairment and moderate-to-severe impairment)). If proportional odds assumption does not hold, we will use multinomial regression to compare the two groups. If there is >5% loss to follow-up for TICS, we will conduct sensitivity analyses using multiple imputation techniques for the missing values. We will also report the proportion of patients in each category by arm and test for differences in separate categories of mortality and cognitive impairment. For mortality, we will use a generalised linear mixed effect model with logit link for 90 and 365 days separately. For prespecified adverse events, we will report the proportion of patients in each arm with the outcome and test for differences using χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate.
In sensitivity analyses, we will also adjust for prespecified baseline covariates: APACHE II, total dose of vasopressor administration before randomisation (in norepinephrine equivalents),55 and history of hypertension, or coronary artery disease (angina, myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularisation).
No subgroup analyses are prespecified due to the small sample size. An updated IPDMA18 including data from existing trials,16 17 the 65 trial22 and the current trial is under consideration.
Registration
The trial was registered on www.clinicaltrials.gov on 13 February 2018 before enrolling the first patient in the study. Initially, the primary outcome was listed as hsTnT at day 7; this error was subsequently corrected on 28 May 2020. Data will not be analysed until trial follow-up is complete in August 2020.
Data management
Site research personnel record data on paper or electronic CRFs within the secure REDCap EDC system. Data collected initially on paper are re-entered into REDCap.
Monitoring
Quality control measures include: (1) training of site research and clinical personnel on eligibility assessment, study procedures and data collection; (2) standard operating procedures for processing, storage and shipping of blood and urine samples; (3) ongoing assessment of trial conduct, with monthly review of screening logs and reports for site enrolment, protocol adherence in the permissive hypotension arm and quality of study samples and feedback to the clinical sites on recruitment and protocol adherence, benchmarked with other sites; (4) ongoing review of missing data and outlying values and (5) rapid responses to frequently asked questions on the study website and monthly newsletter. For one site, we also conducted monitoring visits for two of the first five participants and 10% of the subsequent participants. Coordinating Centre staff and the Principal Investigators are available to answer study-related questions.
Trial oversight
Executive Committee
The Executive Committee comprised Neill KJ Adhikari, M Elizabeth Wilcox and François Lamontagne (co-principal investigators), Marie-Claude Battista (core laboratory) and Marie-Hélène Masse (project leader). The Executive Committee is responsible for day-to-day management.
Data safety monitoring committee
The independent DSMC is responsible for safeguarding the interests of study participants, assessing the safety and efficacy of study procedures and monitoring study conduct. DSMC members include a senior methodologist with DSMC Chair experience for international RCTs, an experienced biostatistician and a critical care clinician scientist (online supplementary file S1). The DSMC met on an ad hoc basis to review reports of unanticipated SAEs not predefined as study outcomes. In accordance with a prespecified DSMC Charter, the DSMC advised the Executive Committee of concerns related to participant safety and trial conduct. Following each meeting, the DSMC made a recommendation for study continuation, continuation with modifications, temporary suspension of enrolment or termination. As noted above, the DSMC recommended termination of enrolment in response to data from the 65 trial.22
Ethics and dissemination
This protocol was approved by the Comité d’éthique de la recherche du Centre intégré universitaire de santé et de services sociaux de l’Estrie—Centre hospitalier universitaire de Sherbrooke (MP-31-2018-1789). Before enrolment of the first participant, each clinical site received local research ethics board (REB) approval and provided the Coordinating Centre with their REB approval letter and informed consent form (sample in online supplementary file S4). Protocol amendments were submitted to each REB and disseminated to all investigators.
bmjopen-2020-037947supp004.pdf (168.7KB, pdf)
Site research personnel obtained informed consent by approaching eligible capable patients directly. For eligible incapable patients, research personnel approached the substitute decision-maker to obtain consent in person or by telephone. Alternatively, where permitted by the site REB, the patient was randomised with consent obtained later under a deferred consent model. Consent was also requested for possible future laboratory analyses.
Participants may discontinue participation in the OVATION-65 trial at any time. If a participant wished to withdraw consent, we offered the following alternatives: (1) complete withdrawal, which included no further study intervention (only relevant for participants in the permissive hypotension arm), data deletion and sample destruction; (2) discontinuation of study intervention but permission for data collection (clinical data, sample collection, telephone follow-up); (3) discontinuation of study intervention, in-person follow-up and sample collection but permission for telephone follow-up; or 4) discontinuation study intervention, sample collection and in-person and telephone follow-up, but permission for access to medical records.
All personal health information collected remains confidential in a secure database. Participants are identified by an alphanumeric code, and the file linking the alphanumeric code to identifying information is securely stored by the local principal investigator.
There was no compensation for harm suffered from trial participation; details on data collection for adverse events are given above. Patients enrolled in this trial were critically ill, with daily care provided by intensivists. There was no provision for post-trial care.
Plans for end-of-grant dissemination include presentations at international critical care conferences and journal publications. In addition, building on the experience with social media during the OVATION pilot trial, we will disseminate our results via social media platforms and discussion forums managed by partner organisations.
Authorship of the trial manuscript will be based on leadership roles in trial management and at clinical sites, specific expertise (eg, methodological, laboratory) and contributions as defined by International Committee of Medical Journal Editors criteria.
Data statement
The OVATION-65 protocol is freely accessible via this publication. The principal investigators, project leader and study statisticians will have access to the full trial dataset; there are no contractual limitations to such access. Requests for access to the participant-level dataset and statistical code will be considered by the Executive Committee after publication of primary results and planned secondary studies by co-investigators.
Trial status
The current protocol is V.6, dated 29 November 2019. Participant recruitment began on 17 February 2018 and was scheduled to continue until approximately June 2020. As noted, the DSMC recommended termination of enrolment on 21 February 2020. The database will be locked after the last enrolled patient completes the 6-month follow-up in August 2020, and 6 additional months will be required to address remaining data queries and to finalise the analyses.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Unité de Recherche Clinique et Épidémiologique of the Centre de Recherche du Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Sherbrooke for their commitment to the coordination of the study; and Claudio Martin for a careful review of an earlier version of this manuscript, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group Grants and Manuscripts Committee.
Footnotes
FLam and NKJA contributed equally.
Collaborators: OVATION-65 team members: Executive Committee: Neill KJ Adhikari (PI, co-chair), François Lamontagne (PI, co-chair), M Elizabeth Wilcox, (PI), Marie-Claude Battista (co-I), Marie-Hélène Masse (PL); Data Safety Monitoring Committee: Andreas Laupacis (chair), Lauren Griffith, Scott Halpern; Coordinating Centre Personnel: Marie-Claude Battista, Marie-Hélène Masse, Louise Robert-Petit, Marie-Ève Thibault; Contributors to ancillary studies: François-Michel Boisvert, Lee Hwa Tai, Jean-Luc Parent, Xavier Roucou; Participating Clinical Site Personnel: CIUSSS de l’Estrie – Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Sherbrooke: François Lamontagne (PI), Frédérick D’Aragon (Co-I), Marc-André Leclair (Co-I), Michaël Mayette (Co-I), Yannick Poulin (Co-I), Hector Quiroz-Martinez (Co-I), Charles St-Arnaud (Co-I), Élaine Carbonneau (RC), Line Côté (RC), Marilène Ladouceur (RC), Joannie Marchand (RA), Marie-Hélène Masse (RC), Noémie Turcotte (RA); Centre Hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal: Michaël Chassé (PI), Martine Lebrasseur (RC), Fatna Benettaib (RC), Dounia Boumahni (RC), Marie-Ève Cantin (RA), Ali Ghamraoui (RC), Maya Salame (RC); The Ottawa Hospital (General Campus and Civic Campus): Andrew Seely (PI), Irene Watpool (RC), Rebecca Porteous (RC), Sydney Miezitis (RA); Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre: Neill KJ Adhikari (PI), Andre Carlos Amaral (Co-I), Brian H Cuthbertson (Co-I), Robert A Fowler(Co-I), Damon C Scales (Co-I), Nicole Marinoff (RC), Navjot Kaur (RC), Wael Mohammed (RC); Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Québec-Université Laval: François Lauzier (PI), Alexis Turgeon (Co-I), Charles Francoeur (Co-I), Guillaume Leblanc (CoI), David Bellemare (RC), Olivier Costerousse (RC), Stéphanie Grenier (RA), Gabrielle Guilbault (RA), Marjorie Daigle (RA), Ève Cloutier (RA), Isabelle St-Hilaire (RA); Mount Sinai Hospital: Sangeeta Mehta (PI), Laveena Munshi (Co-I), Sumesh Shah (RC); Toronto Western Hospital: Mary Elizabeth Wilcox (PI), Jeffrey Singh (Co-I), Karolina Walczak (RC); Juravinski Hospital (activation in progress and no patients enrolled at the time of manuscript submission): Bram Rochwerg (PI), Tina Millen (RC); Abbreviations: Co-I – co-investigator; PI – principal investigator; PL – project leader; RA – research assistant; RC – research coordinator
Contributors: NKJA and FLam drafted the protocol for the OVATION-65 trial and drafted the manuscript; they contributed equally and co-senior authors. M-HM, M-CB, MEW, RPi, NM, FD’A, CS-A, MM, M-AL, HQM, BG-B, YP, ECa, AJES, IW, RPo, MC, ML, FLau, AFT, DB, SM, ECh, EB-C, EB and DC contributed to protocol development and revised the manuscript. M-HM, M-CB, MEW, FLam and NKJA are on the Executive Committee. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding: OVATION-65 is funded by the Lotte and John Hecht Memorial Foundation (grant no. 4410); internal grants from the Université de Sherbrooke/Merck Sharp and Dohme and the Centre de recherche du CHUS/Projet Structurant and a research chair awarded to FLam (Chaire de recherche axée sur le patient et les soins hospitaliers aigus). FLam is supported by an award from the Fonds de recherche du Québec—Santé.
Disclaimer: The funders and institutional sponsor had no role in the design of the study, ongoing data collection, planned data analysis and interpretation or writing of this manuscript or of the study protocol.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient and public involvement: Patients and/or the public were involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research. Refer to the Methods section for further details.
Patient consent for publication: Not required.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Contributor Information
OVATION-65 team members:
Neill KJ Adhikari, François Lamontagne, Mary Elizabeth Wilcox, Marie-Claude Battista, Marie-Hélène Masse, Andreas Laupacis, Lauren Griffith, Scott Halpern, Louise Robert-Petit, Marie-Ève Thibault, François-Michel Boisvert, Lee Hwa Tai, Jean-Luc Parent, Xavier Roucou, Frédérick D’Aragon, Marc-André Leclair, Michaël Mayette, Yannick Poulin, Hector Quiroz-Martinez, Charles St-Arnaud, Élaine Carbonneau, Line Côté, Marilène Ladouceur, Joannie Marchand, Noémie Turcotte, Michaël Chassé, Martine Lebrasseur, Fatna Benettaib, Dounia Boumahni, Marie-Ève Cantin, Ali Ghamraoui, Maya Salame, Andrew Seely, Irene Watpool, Rebecca Porteous, Sydney Miezitis, Andre Carlos Amaral, Brian H Cuthbertson, Robert A Fowler, Damon C Scales, Nicole Marinoff, Navjot Kaur, Wael Mohammed, François Lauzier, Alexis Turgeon, Charles Francoeur, Guillaume Leblanc, David Bellemare, Olivier Costerousse, Stéphanie Grenier, Gabrielle Guilbault, Marjorie Daigle, Ève Cloutier, Isabelle St-Hilaire, Sangeeta Mehta, Laveena Munshi, Sumesh Shah, Jeffrey Singh, Karolina Walczak, Bram Rochwerg, and Tina Millen
References
- 1. Hollenberg SM. Vasoactive drugs in circulatory shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011;183:201006-0972CI:847–55. 10.1164/rccm.201006-0972CI [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Andreis DT, Singer M. Catecholamines for inflammatory shock: a Jekyll-and-Hyde conundrum. Intensive Care Med 2016;42:1387–97. 10.1007/s00134-016-4249-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Singer M. Catecholamine treatment for shock--equally good or bad? Lancet 2007;370:636–7. 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61317-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Singer M, Glynne P. Treating critical illness: the importance of first doing no harm. PLoS Med 2005;2:e167. 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020167 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Walkey AJ, Adhikari NKJ, Day AG, et al. Mediation analysis of high blood pressure targets, arrhythmias, and shock mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2019;199:802–5. 10.1164/rccm.201808-1435LE [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Girardis M, Busani S, Damiani E, et al. Effect of conservative vs conventional oxygen therapy on mortality among patients in an intensive care unit: the Oxygen-ICU randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016;316:1583–9. 10.1001/jama.2016.11993 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Arabi YM, Aldawood AS, Al-Dorzi HM, et al. Permissive underfeeding or standard enteral feeding in high- and Low-Nutritional-Risk critically ill adults. post hoc analysis of the permit trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2017;195:652–62. 10.1164/rccm.201605-1012OC [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network, Brower RG, Matthay MA, et al. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1301–8. 10.1056/NEJM200005043421801 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Hébert PC, Wells G, Blajchman MA, et al. A multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial of transfusion requirements in critical care. transfusion requirements in critical care Investigators, Canadian critical care Trials Group. N Engl J Med 1999;340:409–17. 10.1056/NEJM199902113400601 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Bickell WH, Wall MJ, Pepe PE, et al. Immediate versus delayed fluid resuscitation for hypotensive patients with penetrating torso injuries. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1105–9. 10.1056/NEJM199410273311701 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med 2017;43:304–77. 10.1007/s00134-017-4683-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Lamontagne F, Cook DJ, Meade MO, et al. Vasopressor use for severe Hypotension-A multicentre prospective observational study. PLoS One 2017;12:e0167840. 10.1371/journal.pone.0167840 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Lamontagne F, Cook DJ, Adhikari NKJ, et al. Vasopressor administration and sepsis: a survey of Canadian intensivists. J Crit Care 2011;26:532.e1 10.1016/j.jcrc.2011.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Schmittinger CA, Torgersen C, Luckner G, et al. Adverse cardiac events during catecholamine vasopressor therapy: a prospective observational study. Intensive Care Med 2012;38:950–8. 10.1007/s00134-012-2531-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Dünser MW, Ruokonen E, Pettilä V, et al. Association of arterial blood pressure and vasopressor load with septic shock mortality: a post hoc analysis of a multicenter trial. Crit Care 2009;13:cc8167 10.1186/cc8167 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Asfar P, Meziani F, Hamel J-F, et al. High versus low blood-pressure target in patients with septic shock. N Engl J Med 2014;370:1583–93. 10.1056/NEJMoa1312173 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Lamontagne F, Meade MO, Hébert PC, et al. Higher versus lower blood pressure targets for vasopressor therapy in shock: a multicentre pilot randomized controlled trial. Intensive Care Med 2016;42:542–50. 10.1007/s00134-016-4237-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Lamontagne F, Day AG, Meade MO, et al. Pooled analysis of higher versus lower blood pressure targets for vasopressor therapy septic and vasodilatory shock. Intensive Care Med 2018;44:12–21. 10.1007/s00134-017-5016-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Rochwerg B, Hylands M, Møller M, et al. CCCS-SSAI WikiRecs clinical practice guideline: vasopressor blood pressure targets in critically ill adults with hypotension. Can J Anaesth 2017;64:763–5. 10.1007/s12630-017-0878-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Richards-Belle A, Mouncey PR, Grieve RD, et al. Evaluating the clinical and cost-effectiveness of permissive hypotension in critically ill patients aged 65 years or over with vasodilatory hypotension: protocol for the 65 randomised clinical trial. J Intensive Care Soc 2019:1751143719870088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Thomas K, Patel A, Sadique MZ, et al. Evaluating the clinical and cost-effectiveness of permissive hypotension in critically ill patients aged 65 years or over with vasodilatory hypotension: statistical and health economic analysis plan for the 65 trial. J Intensive Care Soc 2019;21:1751143719860387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Lamontagne F, Richards-Belle A, Thomas K, et al. Effect of reduced exposure to vasopressors on 90-day mortality in older critically ill patients with vasodilatory hypotension: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2020;323:938–49. 10.1001/jama.2020.0930 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, et al. The SOFA (sepsis-related organ failure assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. on behalf of the Working group on sepsis-related problems of the European Society of intensive care medicine. Intensive Care Med 1996;22:707–10. 10.1007/BF01709751 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Petros AJ, Marshall JC, van Saene HK. Should morbidity replace mortality as an endpoint for clinical trials in intensive care? Lancet 1995;345:369–71. 10.1016/S0140-6736(95)90347-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Svensson S, Menkes DB, Lexchin J. Surrogate outcomes in clinical trials: a cautionary tale. JAMA Intern Med 2013;173:611–2. 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.3037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Masse M-H, Ménard J, Sprague S, et al. Lessening organ dysfunction with vitamin C (LOVIT): protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2020;21:42. 10.1186/s13063-019-3834-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Harris PA, Taylor R, Minor BL, et al. The REDCap Consortium: building an international community of software platform partners. J Biomed Inform 2019;95:103208. 10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, et al. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)--a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform 2009;42:377–81. 10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Angriman F, Masse M-H, Adhikari NKJ. Defining standard of practice: pros and cons of the usual care arm. Curr Opin Crit Care 2019;25:498–504. 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000642 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, et al. Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries. JAMA 2016;315:788–800. 10.1001/jama.2016.0291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Schortgen F, Schetz M. Does this critically ill patient with oliguria need more fluids, a vasopressor, or neither? Intensive Care Med 2017;43:907–10. 10.1007/s00134-017-4744-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Brown SM, Lanspa MJ, Jones JP, et al. Survival after shock requiring high-dose vasopressor therapy. Chest 2013;143:664–71. 10.1378/chest.12-1106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Lim W, Qushmaq I, Devereaux PJ, et al. Elevated cardiac troponin measurements in critically ill patients. Arch Intern Med 2006;166:2446–54. 10.1001/archinte.166.22.2446 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Masson S, Caironi P, Fanizza C, et al. Sequential N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin measurements during albumin replacement in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Crit Care Med 2016;44:707–16. 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001473 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Poe S, Vandivier-Pletsch RH, Clay M, et al. Cardiac troponin measurement in the critically ill: potential for guiding clinical management. J Investig Med 2015;63:905–15. 10.1097/JIM.0000000000000239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Røsjø H, Varpula M, Hagve T-A, et al. Circulating high sensitivity troponin T in severe sepsis and septic shock: distribution, associated factors, and relation to outcome. Intensive Care Med 2011;37:77–85. 10.1007/s00134-010-2051-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Waxman DA, Hecht S, Schappert J, et al. A model for troponin I as a quantitative predictor of in-hospital mortality. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;48:1755–62. 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.05.075 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Goodwill AG, Dick GM, Kiel AM, et al. Regulation of coronary blood flow. Compr Physiol 2017;7:321–82. 10.1002/cphy.c160016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Glushakova OY, Glushakov AV, Miller ER, et al. Biomarkers for acute diagnosis and management of stroke in neurointensive care units. Brain Circ 2016;2:28–47. 10.4103/2394-8108.178546 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Shemilt M, Boutin A, Lauzier F, et al. Prognostic value of glial fibrillary acidic protein in patients with moderate and severe traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med 2019;47:e522–9. 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003728 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Fink EL, Berger RP, Clark RSB, et al. Serum biomarkers of brain injury to classify outcome after pediatric cardiac arrest*. Crit Care Med 2014;42:664–74. 10.1097/01.ccm.0000435668.53188.80 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Anderson BJ, Reilly JP, Shashaty MGS, et al. Admission plasma levels of the neuronal injury marker neuron-specific enolase are associated with mortality and delirium in sepsis. J Crit Care 2016;36:18–23. 10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.06.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Thomson SJ, Cowan ML, Johnston I, et al. 'Liver function tests' on the intensive care unit: a prospective, observational study. Intensive Care Med 2009;35:1406–11. 10.1007/s00134-009-1511-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Derikx JPM, Schellekens DHSM, Acosta S. Serological markers for human intestinal ischemia: a systematic review. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2017;31:69–74. 10.1016/j.bpg.2017.01.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Shapiro ML, Baldea A, Luchette FA. Rhabdomyolysis in the intensive care unit. J Intensive Care Med 2012;27:335–42. 10.1177/0885066611402150 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Kraut JA, Madias NE. Lactic acidosis. N Engl J Med 2014;371:2309–19. 10.1056/NEJMra1309483 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO) acute kidney injury work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl 2012;2:1–138. [Google Scholar]
- 48. Walkey AJ, Wiener RS, Ghobrial JM, et al. Incident stroke and mortality associated with new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients hospitalized with severe sepsis. JAMA 2011;306:2248–54. 10.1001/jama.2011.1615 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Knopman DS, Roberts RO, Geda YE, et al. Validation of the telephone interview for cognitive status-modified in subjects with normal cognition, mild cognitive impairment, or dementia. Neuroepidemiology 2010;34:34–42. 10.1159/000255464 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Cook D, Lauzier F, Rocha MG, et al. Serious adverse events in academic critical care research. CMAJ 2008;178:1181–4. 10.1503/cmaj.071366 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, et al. Apache II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med 1985;13:818–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Rockwood K, Song X, MacKnight C, et al. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. CMAJ 2005;173:489–95. 10.1503/cmaj.050051 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed New York: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 54. Weuve J, Tchetgen Tchetgen EJ, Glymour MM, et al. Accounting for bias due to selective attrition: the example of smoking and cognitive decline. Epidemiology 2012;23:119–28. 10.1097/EDE.0b013e318230e861 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Russell JA, Walley KR, Singer J, et al. Vasopressin versus norepinephrine infusion in patients with septic shock. N Engl J Med 2008;358:877–87. 10.1056/NEJMoa067373 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
bmjopen-2020-037947supp001.pdf (63.4KB, pdf)
bmjopen-2020-037947supp002.pdf (82.4KB, pdf)
bmjopen-2020-037947supp003.pdf (35.3KB, pdf)
bmjopen-2020-037947supp004.pdf (168.7KB, pdf)