Abstract
The goal of the present investigation is to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between SARS-CoV-2 infected and normal control samples to investigate the molecular mechanisms of infection with SARS-CoV-2. The microarray data of the dataset E-MTAB-8871 were retrieved from the ArrayExpress database. Pathway and Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment study, protein–protein interaction (PPI) network, modules, target gene–miRNA regulatory network, and target gene–TF regulatory network have been performed. Subsequently, the key genes were validated using an analysis of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. In SARS-CoV-2 infection, a total of 324 DEGs (76 up- and 248 down-regulated genes) were identified and enriched in a number of associated SARS-CoV-2 infection pathways and GO terms. Hub and target genes such as TP53, HRAS, MAPK11, RELA, IKZF3, IFNAR2, SKI, TNFRSF13C, JAK1, TRAF6, KLRF2, CD1A were identified from PPI network, target gene–miRNA regulatory network, and target gene–TF regulatory network. Study of the ROC showed that ten genes (CCL5, IFNAR2, JAK2, MX1, STAT1, BID, CD55, CD80, HAL-B, and HLA-DMA) were substantially involved in SARS-CoV-2 patients. The present investigation identified key genes and pathways that deepen our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and could be used for SARS-CoV-2 infection as diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 infection, Bioinformatics analysis, Biomarkers, Protein–protein interaction (PPI) network, Differentially expressed genes
Introduction
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is known as novel coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) and has spread widely throughout the globe in an epidemic proportion with the current pandemic risk (Li et al. 2020). This infection is related to respiratory diseases, and this virus mainly infects respiratory epithelial cells and transmits from human to human primarily through the respiratory tract, contributing to more deaths (Zou et al. 2020; Madurai Elavarasan and Pugazhendhi 2020). In the present situation, the survival rate of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection has been slightly increased, and patients with this infection have no apparent benefit from the current antiviral drugs (Hoffmann et al. 2020). Knowing the molecular pathogenesis of the viral infections and their routes of transmission is completely necessary for the creation of new therapeutic targets.
Present situation for investigating the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection is needed in molecular biology. Although the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection remains to be clarified, abnormal gene expression in nasal epithelial cells can serve significant roles (Sungnak et al. 2020). Entry factors related genes such as angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) (Zhang et al. 2020); TMPRSS2 (Sungnak et al. 2020); and inflammatory related genes (IL-2, IL-7, IL-10, GCSF, IP-10, MCP-1, MIP-1A, and TNF-α) (Fu et al. 2020) were linked with pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infections. Therefore, targeted regulation of these genes may reveal potential strategies for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infections. Therefore, targeted regulation of entry factors and inflammatory-related genes could become potential strategies for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Throughout this investigation, we used bioinformatics methods to examine differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between SARS-CoV-2-infected samples and standard control samples. We performed pathway enrichment and gene ontology (GO) analysis of DEGs, and established the protein–protein interactions (PPI) network, modules analysis, target gene–miRNA regulatory network, and target gene–TF regulatory network to reveal molecular mechanisms in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Finally, we performed validation hub genes by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. Finally, through receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, we conducted validation hub genes. The aim of this study is thus to have a better understanding of the exact mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 infection and to identify potential novel diagnostic or therapeutic targets through bioinformatics analysis.
Materials and methods
Microarray data selection
Microarray data of gene expression profile (E-MTAB-8871) was downloaded from ArrayExpress (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress), which is the largest resource of gene expression publicly available (Kolesnikov et al. 2015). Samples from this dataset were RNA extracted from the blood sample and processed for hybridization on NanoString nCounter Human Immunology V2 Panel Array. A total of 32 samples were investigated, including 22 SARS-CoV-2-infected samples, and 10 normal control samples. The study was designed according to the flowchart (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
The workflow representing the methodology and the major outcome of the study. SARS-CoV-2—Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection - breast cancer, GO—gene ontology, miRNA—MicroRNA, TF-transcription factor, DEGs—deferential expressed genes
Identification of DEGs
The DEGs between the SARS-CoV-2-infected samples and normal control samples were analyzed with various methods including data preparation (data normalization and summarization) and DEGs identification (up- and down-regulated genes). The limma package in R Software was used for background correction, quantile normalization and probe summarization, and limma package was also applied for DEGs identification (Ritchie et al. 2015). The development of DEGs choice included model design, linear model fitness, contrast matrix generation, bayesian model building and gene filtering, all of which were managed by the functions in the limma package. Genes with the p < 0.05, |log Fc| (fold change) > 1.5 were considered as DEGs (up- and down-regulated genes).
Pathway enrichment analysis for DEGs
BIOCYC (https://biocyc.org/) (Caspi et al. 2016), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/pathway.html) (Kanehisa et al. 2019), Pathway Interaction Database (PID) (https://wiki.nci.nih.gov/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=315491760) (Schaefer et al. 2009), REACTOME (https://reactome.org/) (Fabregat et al. 2018), GenMAPP (http://www.genmapp.org/) (Dahlquist et al. 2002), MSigDB C2 BIOCARTA (http://software.broadinstitute.org/gsea/msigdb/collections.jsp) (Subramanian et al. 2005), PantherDB (http://www.pantherdb.org/) (Mi et al. 2017), Pathway Ontology (http://www.obofoundry.org/ontology/pw.html) (Petri et al. 2014) and Small Molecule Pathway Database (SMPDB) (http://smpdb.ca/) (Jewison et al. 2014) are a data resource for genes and genomes with assigned corresponding functional importance. The ToppGene (ToppFun) (https://toppgene.cchmc.org/enrichment.jsp) (Chen et al. 2009) is an online resource for interpreting genes originating from genomic investigation with bioinformatics data. The p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis for DEGs
GO (http://www.geneontology.org/) (Lewis et al. 2017) was used to determine gene actions in three aspects: biological process (BP), cellular component (CC) and molecular function (MF). ToppGene (ToppFun) (https://toppgene.cchmc.org/enrichment.jsp) (Chen et al. 2009) is an online website that provides an extensive set of functional annotation tools to understand the biological meaning behind a massive list of genes. In the current investigation, the GO enrichment analyses for statistically important DEGs. The p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
PPI network construction and module analysis
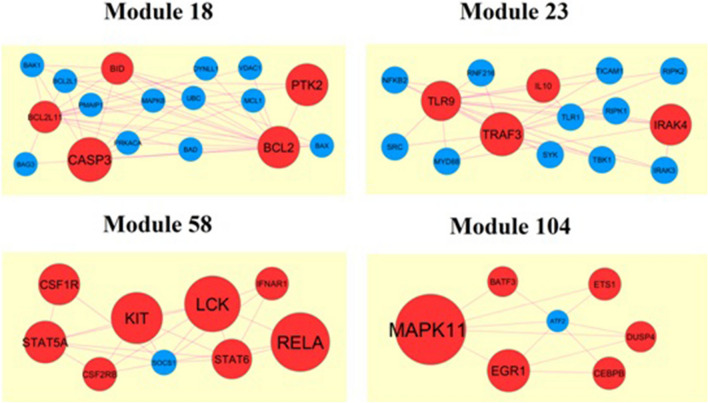
The common up and down-regulated genes of E-MTAB-8871 was analyzed using the online website STRING (https://string-db.org/, version 11) (Szklarczyk et al. 2019), with 0.700 (moderate confidence) as the minimum required interaction score. Then, the software Cytoscape (http://www.cytoscape.org/, version 3.8.0) (Shannon et al. 2003) was used to establish a PPI network. The Network Analyzer in Cytoscape was utilized to calculate node degree (Przulj et al. 2004), betweenness centrality (Nguyen et al. 2011), stress centrality (Shi and Zhang 2011), closeness centrality (Nguyen and Liu 2011) and clustering coefficient (Wang et al. 2012). PEWCC1 (http://apps.cytoscape.org/apps/PEWCC1) (Zaki et al. 2013) was used to perform module analysis.
Construction of target gene–miRNA regulatory network
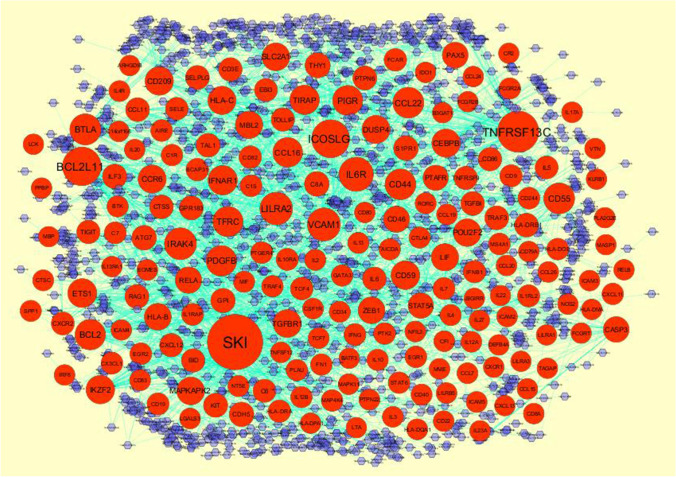
miRNet database (https://www.mirnet.ca/) (Fan and Xia 2018) provides certain target gene–miRNA regulatory association pairs, which are verified by experiments and predicted by ten programs, including TarBase (http://diana.imis.athena-innovation.gr/DianaTools/index.php?r=tarbase/index) (Vlachos et al. 2015), miRTarBase (http://mirtarbase.mbc.nctu.edu.tw/php/download.php) (Chou et al. 2018), miRecords (http://miRecords.umn.edu/miRecords) (Xiao et al. 2009), miR2Disease (http://www.mir2disease.org/) (Jiang et al. 2009), HMDD (http://www.cuilab.cn/hmdd) (Huang et al. 2019), PhenomiR (http://mips.helmholtz-muenchen.de/phenomir/) (Ruepp et al. 2010), SM2miR (http://bioinfo.hrbmu.edu.cn/SM2miR/) (Liu et al. 2013), PharmacomiR (http://www.pharmaco-mir.org/) (Rukov et al. 2014), EpimiR (http://bioinfo.hrbmu.edu.cn/EpimiR/) (Dai et al. 2014) and starBase (http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/) (Li et al. 2014). This investigation inputted the up- and down-regulated genes into the database to examine the regulatory association pairs between target gene and miRNA. Target gene–miRNA regulatory network was constructed and visualized by Cytoscape 3.8.0 software to show the target genes and miRNA. Therefore, these target genes and miRNA might play a potential role in the pathogenesis and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Construction of target gene–TF regulatory network
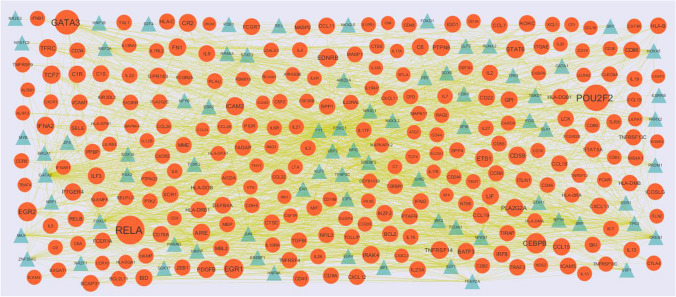
NetworkAnalyst database (https://www.networkanalyst.ca/) (Zhou et al. 2019) provides certain target gene–TF regulatory association pairs, which are verified by experiments and predicted by JASPAR (http://jaspar.genereg.net/) (Khan et al. 2018) database. This investigation inputted the up- and down-regulated genes into the database to examine the regulatory association pairs between target gene and TF. Target gene–TF regulatory network was constructed and visualized by Cytoscape 3.8.0 software to show the target genes and TF. Therefore, these target genes and TF may play a potential role in the pathogenesis and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Validation of hub genes
Receiver‐operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were operated to calculate the diagnostic value of the hub genes for SARS-CoV-2 infection. The ROC curve with area under curve (AUC) was determined using R “pROC” package (Robin et al. 2011).
Results
Identification of DEGs
Microarray dataset (E-MTAB-8871) was obtained from ArrayExpress database and normalized mRNA expression data through R language (Fig. 2). Volcano plot was generated to manifest up-regulated (green) and down-regulated (red) genes between SARS-CoV-2-infected samples and normal controls samples (Fig. 3) and were also visualized on a heatmap for up- and down-regulated genes (Figs. 4, 5). This approach indicated presence of a total of 324 statistically significant genes (P < 0.05, |log Fc| (fold change) > 1.5), of which 76 genes were up-regulated and 248 genes were down-regulated (Table 1).
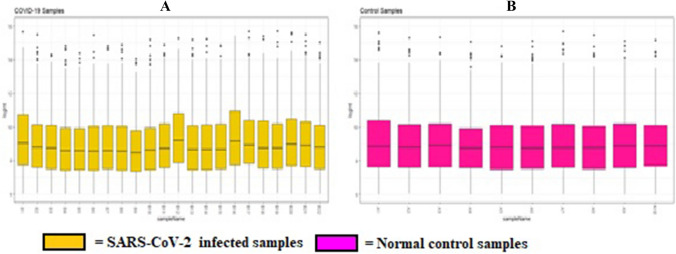
Fig. 2.
Box plots of the normalized data. a 22 SARS-CoV-2 infected samples b 10 normal control samples. Horizontal axis represents the sample symbol and the vertical axis represents the gene expression values. The black line in the box plot represents the median value of gene expression
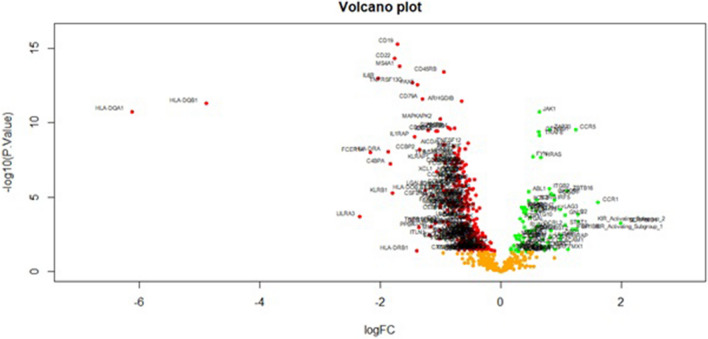
Fig. 3.
Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes. Genes with a significant change of more than twofold were selected. Green dot on right side (
 ) represented up regulated significant genes and red dot on left side (
) represented up regulated significant genes and red dot on left side ( ) represented down regulated significant genes
) represented down regulated significant genes
Fig. 4.
Heat map of up regulated differentially expressed genes. Legend on the top left indicate log fold change of genes. White represents decreased expression of genes; light green represents not significant expression of genes; dark green represents increased expression of genes. (A1–A10 = Normal control samples; B1–B22 = SARS-CoV-2 infected samples)
Fig. 5.
Heat map of down regulated differentially expressed genes. Legend on the top left indicate log fold change of genes. White represents decreased expression of genes; light pink represents not significant expression of genes; dark pink represents increased expression of genes. (A1–A10 = Normal control samples; B1–B22 = SARS-CoV-2 infected samples)
Table 1.
The statistical metrics for key differentially expressed genes (DEGs)
| Gene Symbol | logFC | pValue | adj.P.Val | t value | Regulation | Gene Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JAK1 | 0.641818 | 1.84E − 11 | 1.84E − 11 | 9.973193 | Up | Janus kinase 1 |
| ZAP70 | 0.810545 | 2.91E − 10 | 2.91E − 10 | 8.897328 | Up | Zeta chain of T cell receptor associated protein kinase 70 |
| CCR5 | 1.239182 | 3.04E − 10 | 3.04E − 10 | 8.880753 | Up | C–C motif chemokine receptor 5 (gene/pseudogene) |
| CTNNB1 | 0.633545 | 4.11E − 10 | 4.11E − 10 | 8.766907 | Up | Catenin beta 1 |
| TRAF6 | 0.644773 | 7.11E − 10 | 7.11E − 10 | 8.561082 | Up | TNF receptor associated factor 6 |
| FYN | 0.536182 | 1.96E − 08 | 1.96E − 08 | 7.357891 | Up | FYN proto-oncogene, Src family tyrosine kinase |
| HRAS | 0.668773 | 2.14E − 08 | 2.14E − 08 | 7.325507 | Up | HRas proto-oncogene, GTPase |
| ITGB2 | 0.805182 | 2.8E − 06 | 2.8E − 06 | 5.644273 | Up | Integrin subunit beta 2 |
| ZBTB16 | 1.099955 | 3.88E − 06 | 3.88E − 06 | 5.53388 | Up | Zinc finger and BTB domain containing 16 |
| ABL1 | 0.468091 | 4.46E − 06 | 4.46E − 06 | 5.486138 | Up | ABL proto-oncogene 1, non-receptor tyrosine kinase |
| CX3CR1 | 0.834227 | 6.3E − 06 | 6.3E − 06 | 5.369313 | Up | C-X3-C motif chemokine receptor 1 |
| PDCD1 | 0.880955 | 7.79E − 06 | 7.79E − 06 | 5.297093 | Up | Programmed cell death 1 |
| IRF5 | 0.884364 | 1.56E − 05 | 1.56E − 05 | 5.062275 | Up | Interferon regulatory factor 5 |
| IL2RG | 0.590818 | 1.7E − 05 | 1.7E − 05 | 5.032467 | Up | Interleukin 2 receptor subunit gamma |
| IKZF3 | 0.467273 | 1.78E − 0E − 05 | 1.78E − 05 | 5.016592 | Up | IKAROS family zinc finger 3 |
| CCR1 | 1.613727 | 2.3E − 05 | 2.3E − 05 | 4.929543 | Up | C–C motif chemokine receptor 1 |
| CD99 | 0.398773 | 4.76E − 05 | 4.76E − 05 | 4.681138 | Up | CD99 molecule (Xg blood group) |
| SMAD5 | 0.349818 | 5.02E − 05 | 5.02E − 05 | 4.662446 | Up | SMAD family member 5 |
| CD247 | 0.51 | 5.34E − 05 | 5.34E − 05 | 4.641555 | Up | CD247 molecule |
| TP53 | 0.372273 | 5.85E − 05 | 5.85E − 05 | 4.609909 | Up | Tumor protein p53 |
| LAG3 | 0.988591 | 6.64E − 05 | 6.64E − 05 | 4.566916 | Up | Lymphocyte activating 3 |
| LCP2 | 0.432682 | 6.74E − 05 | 6.74E − 05 | 4.561553 | Up | Lymphocyte cytosolic protein 2 |
| SLAMF7 | 0.577409 | 8.58E − 05 | 8.58E − 05 | 4.478485 | Up | SLAM family member 7 |
| TMEM173 | 0.377318 | 0.000103 | 0.000103 | 4.416144 | Up | Transmembrane protein 173 |
| CUL9 | 0.4155 | 0.000119 | 0.000119 | 4.366647 | Up | Cullin 9 |
| C2 | 1.280182 | 0.000153 | 0.000153 | 4.279415 | Up | Complement C2 |
| GNLY | 1.067364 | 0.000167 | 0.000167 | 4.248083 | Up | Granulysin |
| ATG10 | 0.490955 | 0.000234 | 0.000234 | 4.130655 | Up | Autophagy related 10 |
| IKZF1 | 0.321682 | 0.000285 | 0.000285 | 4.061503 | Up | IKAROS family zinc finger 1 |
| KIR_Activating_Subgroup_2 | 1.279318 | 0.00043 | 0.00043 | 3.915229 | Up | Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptorSubgroup 2 |
| ITGAL | 0.370273 | 0.000461 | 0.000461 | 3.890576 | Up | Integrin subunit alpha L |
| SERPING1 | 1.992773 | 0.00057 | 0.00057 | 3.815201 | Up | Serpin family G member 1 |
| STAT1 | 1.066864 | 0.000762 | 0.000762 | 3.711251 | Up | signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 |
| CCRL2 | 0.621773 | 0.000844 | 0.000844 | 3.674266 | Up | C–C motif chemokine receptor like 2 |
| RUNX1 | 0.392409 | 0.001035 | 0.001035 | 3.600334 | Up | RUNX family transcription factor 1 |
| KIR_Activating_Subgroup_1 | 1.243455 | 0.001444 | 0.001444 | 3.478418 | Up | Killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor Subgroup 1 |
| IFIH1 | 1.189 | 0.001492 | 0.001492 | 3.466339 | Up | Interferon induced with helicase C domain 1 |
| GP1BB | 1.252364 | 0.001517 | 0.001517 | 3.460324 | Up | Glycoprotein Ib platelet subunit beta |
| TBX21 | 0.557591 | 0.001716 | 0.001716 | 3.414736 | Up | T-box transcription factor 21 |
| BST2 | 0.825727 | 0.00183 | 0.00183 | 3.390875 | Up | Bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 |
| JAK2 | 0.436727 | 0.001927 | 0.001927 | 3.371677 | Up | Janus kinase 2 |
| PSMB9 | 0.490864 | 0.001928 | 0.001928 | 3.371431 | Up | Proteasome 20S subunit beta 9 |
| XBP1 | 0.485455 | 0.002051 | 0.002051 | 3.348399 | Up | X-box binding protein 1 |
| GBP1 | 0.999545 | 0.003627 | 0.003627 | 3.133218 | Up | Guanylate binding protein 1 |
| STAT4 | 0.295591 | 0.003667 | 0.003667 | 3.129061 | Up | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 |
| MAP4K1 | 0.2385 | 0.003959 | 0.003959 | 3.099644 | Up | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinasekinasekinase 1 |
| CCND3 | 0.326591 | 0.004076 | 0.004076 | 3.08846 | Up | cyclin D3 |
| LILRA6 | 0.817091 | 0.004839 | 0.004839 | 3.022071 | Up | Leukocyte immunoglobulin like receptor A6 |
| GFI1 | 0.495591 | 0.005741 | 0.005741 | 2.955427 | Up | Growth factor independent 1 transcriptional repressor |
| HLA-A | 0.385909 | 0.005824 | 0.005824 | 2.949825 | Up | Major histocompatibility complex, class I, A |
| IL18RAP | 0.982227 | 0.006135 | 0.006135 | 2.929331 | Up | Interleukin 18 receptor accessory protein |
| C1QBP | 0.264182 | 0.006145 | 0.006145 | 2.928686 | Up | Complement C1q binding protein |
| CCL5 | 0.3105 | 0.006563 | 0.006563 | 2.902767 | Up | C–C motif chemokine ligand 5 |
| SOCS1 | 0.704318 | 0.007115 | 0.007115 | 2.870801 | Up | Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 |
| STAT3 | 0.370545 | 0.010179 | 0.010179 | 2.72698 | Up | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| CEACAM1 | 0.784909 | 0.011682 | 0.011682 | 2.670737 | Up | CEA cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| TLR2 | 0.589773 | 0.013287 | 0.013287 | 2.617647 | Up | toll like receptor 2 |
| KLRK1 | 0.358136 | 0.014239 | 0.014239 | 2.588898 | Up | killer cell lectin like receptor K1 |
| MAP4K2 | 0.221227 | 0.018828 | 0.018828 | 2.471244 | Up | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinasekinasekinase 2 |
| KLRC1 | 0.7945 | 0.019896 | 0.019896 | 2.4477 | Up | Killer cell lectin like receptor C1 |
| ATG5 | 0.327 | 0.020137 | 0.020137 | 2.44253 | Up | Autophagy related 5 |
| IL18R1 | 0.713136 | 0.020905 | 0.020905 | 2.426467 | Up | Interleukin 18 receptor 1 |
| IKBKB | 0.1695 | 0.027641 | 0.027641 | 2.304841 | Up | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase subunit beta |
| STAT5B | 0.2575 | 0.032278 | 0.032278 | 2.235871 | Up | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5B |
| MX1 | 1.111727 | 0.032817 | 0.032817 | 2.228441 | Up | MX dynamin like GTPase 1 |
| IRF7 | 0.898909 | 0.033248 | 0.033248 | 2.222589 | Up | Interferon regulatory factor 7 |
| TRAF2 | 0.171955 | 0.034273 | 0.034273 | 2.208908 | Up | TNF receptor associated factor 2 |
| IFI35 | 0.725909 | 0.035093 | 0.035093 | 2.198229 | Up | Interferon induced protein 35 |
| IKBKE | 0.236545 | 0.035149 | 0.035149 | 2.197514 | Up | Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase subunit epsilon |
| CLEC7A | 0.421227 | 0.037828 | 0.037828 | 2.164155 | Up | C-type lectin domain containing 7A |
| LTB4R | 0.465227 | 0.03902 | 0.03902 | 2.149988 | Up | Leukotriene B4 receptor |
| GZMB | 0.437364 | 0.040654 | 0.040654 | 2.131179 | Up | Granzyme B |
| NLRP3 | 0.290364 | 0.04286 | 0.04286 | 2.106829 | Up | NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| LILRB2 | 0.299364 | 0.042931 | 0.042931 | 2.106059 | Up | Leukocyte immunoglobulin like receptor B2 |
| IFNAR2 | 0.184136 | 0.048633 | 0.048633 | 2.047965 | Up | Interferon alpha and beta receptor subunit 2 |
| KLRD1 | 0.4455 | 0.049759 | 0.049759 | 2.037205 | Up | Killer cell lectin like receptor D1 |
| CD19 | − 1.7175 | 5.18E − 16 | 5.18E − 16 | − 14.7177 | Down | CD19 molecule |
| CD22 | − 1.757 | 4.93E − 15 | 4.93E − 15 | − 13.592 | Down | CD22 molecule |
| MS4A1 | − 1.67741 | 1.67E − 14 | 1.67E − 14 | − 13.0082 | Down | Membrane spanning 4-domains A1 |
| CD45RB | − 0.94709 | 4.17E − 14 | 4.17E − 14 | − 12.5832 | Down | Receptor-Type Tyrosine-Protein Phosphatase C |
| IL6R | − 2.0375 | 1.05E − 13 | 1.05E − 13 | − 12.164 | Down | interleukin 6 receptor |
| TNFRSF13C | − 1.46186 | 2.18E − 13 | 2.18E − 13 | − 11.8375 | Down | TNF receptor superfamily member 13C |
| PAX5 | − 1.37636 | 2.92E − 13 | 2.92E − 13 | − 11.7085 | Down | Paired box 5 |
| CD79A | − 1.29577 | 2.53E − 12 | 2.53E − 12 | − 10.7841 | Down | CD79a molecule |
| ARHGDIB | − 0.65064 | 3.68E − 12 | 3.68E − 12 | − 10.6278 | Down | Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor beta |
| HLA-DQB1 | − 4.88305 | 5.18E − 12 | 5.18E − 12 | − 10.4865 | Down | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ beta 1 |
| HLA-DQA1 | − 6.1155 | 1.8E − 11 | 1.8E − 11 | − 9.98021 | Down | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1 |
| MAPKAPK2 | − 0.99755 | 5.49E − 11 | 5.49E − 11 | − 9.53915 | Down | MAPK activated protein kinase 2 |
| SLAMF6 | − 0.87414 | 2.16E − 10 | 2.16E − 10 | − 9.01008 | Down | SLAM family member 6 |
| PTGER4 | − 0.76932 | 2.43E − 10 | 2.43E − 10 | − 8.96519 | Down | Prostaglandin E receptor 4 |
| CD79B | − 0.84082 | 2.75E − 10 | 2.75E − 10 | − 8.91788 | Down | CD79b molecule |
| CD97 | − 1.1985 | 3.22E − 10 | 3.22E − 10 | − 8.85915 | Down | Leukocyte antigen CD97 |
| IL1RL2 | − 1.04873 | 3.57E − 10 | 3.57E − 10 | − 8.81964 | Down | Interleukin 1 receptor like 2 |
| CD1A | − 1.07114 | 3.6E − 10 | 3.6E − 10 | − 8.81626 | Down | CD1a molecule |
| IL1RAP | − 1.43418 | 8.92E − 10 | 8.92E − 10 | − 8.47672 | Down | Interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein |
| TNFSF12 | − 0.53718 | 2.42E − 09 | 2.42E − 09 | − 8.10915 | Down | TNF superfamily member 12 |
| AICDA | − 0.94759 | 2.89E − 09 | 2.89E − 09 | − 8.04473 | Down | Activation induced cytidinedeaminase |
| MBP | − 0.77614 | 4.02E − 09 | 4.02E − 09 | − 7.92468 | Down | myelin basic protein |
| TRAF4 | − 0.67777 | 5.69E − 09 | 5.69E − 09 | − 7.79888 | Down | TNF receptor associated factor 4 |
| MIF | − 0.59309 | 5.94E − 09 | 5.94E − 09 | − 7.78344 | Down | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor |
| CCBP2 | − 1.34027 | 6.31E − 09 | 6.31E − 09 | − 7.76207 | Down | Chemokine-binding protein 2 |
| CCL22 | − 0.68986 | 8.3E − 09 | 8.3E − 09 | − 7.66358 | Down | C–C motif chemokine ligand 22 |
| HLA-DRA | − 1.87223 | 9.28E − 09 | 9.28E − 09 | − 7.62328 | Down | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR alpha |
| FCER1A | − 2.15768 | 9.79E − 09 | 9.79E − 09 | − 7.60411 | Down | Fc fragment of IgE receptor Ia |
| LILRB5 | − 0.76595 | 1.11E − 08 | 1.11E − 08 | − 7.55809 | Down | Leukocyte immunoglobulin like receptor B5 |
| CCL15 | − 0.7105 | 1.48E − 08 | 1.48E − 08 | − 7.4567 | Down | C–C motif chemokine ligand 15 |
| IL12B | − 0.99886 | 1.5E − 08 | 1.5E − 08 | − 7.45174 | Down | Interleukin 12B |
| TFRC | − 1.07782 | 1.61E − 08 | 1.61E − 08 | − 7.42698 | Down | Transferrin receptor |
| EBI3 | − 0.72195 | 1.86E − 08 | 1.86E − 08 | − 7.37653 | Down | Epstein-Barr virus induced 3 |
| IL4 | − 0.69941 | 2.72E − 08 | 2.72E − 08 | − 7.24189 | Down | Interleukin 4 |
| ICAM2 | − 0.74745 | 2.86E − 08 | 2.86E − 08 | − 7.22422 | Down | Intercellular adhesion molecule 2 |
| KLRAP1 | − 1.0865 | 3.09E − 08 | 3.09E − 08 | − 7.19683 | Down | Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily A pseudogene 1 |
| CD40 | − 0.79436 | 3.29E − 08 | 3.29E − 08 | − 7.17439 | Down | CD40 molecule |
| IL22RA2 | − 0.6365 | 4.34E − 08 | 4.34E − 08 | − 7.07766 | Down | Interleukin 22 receptor subunit alpha 2 |
| IL2 | − 0.64395 | 4.65E − 08 | 4.65E − 08 | − 7.05298 | Down | Interleukin 2 |
| IL29 | − 0.64395 | 4.65E − 08 | 4.65E − 08 | − 7.05298 | Down | Interleukin 29 |
| CD3E | − 0.73018 | 5.24E − 08 | 5.24E − 08 | − 7.01159 | Down | CD3e molecule |
| CD55 | − 0.92114 | 5.29E − 08 | 5.29E − 08 | − 7.00828 | Down | CD55 molecule (Cromer blood group) |
| IL19 | − 0.6555 | 5.33E − 08 | 5.33E − 08 | − 7.00515 | Down | Interleukin 19 |
| NOS2 | − 0.81432 | 5.6E − 08 | 5.6E − 08 | − 6.98829 | Down | Nitric oxide synthase 2 |
| C4BPA | − 1.83359 | 5.78E − 08 | 5.78E − 08 | − 6.97697 | Down | Complement component 4 binding protein alpha |
| CCL26 | − 0.57677 | 6.5E − 08 | 6.5E − 08 | − 6.93596 | Down | C–C motif chemokine ligand 26 |
| CDH5 | − 0.60586 | 7.09E − 08 | 7.09E − 08 | − 6.90577 | Down | Cadherin 5 |
| IL9 | − 0.60586 | 7.09E − 08 | 7.09E − 08 | − 6.90577 | Down | Interleukin 9 |
| FCGRT | − 0.75709 | 8.18E − 08 | 8.18E − 08 | − 6.85603 | Down | Fc fragment of IgG receptor and transporter |
| C8B | − 0.6555 | 1.1E − 07 | 1.1E − 07 | − 6.75159 | Down | Complement C8 beta chain |
| IL5 | − 0.64086 | 1.16E − 07 | 1.16E − 07 | − 6.7344 | Down | Interleukin 5 |
| PIGR | − 0.66695 | 1.33E − 07 | 1.33E − 07 | − 6.68821 | Down | Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor |
| XCL1 | − 1.06423 | 1.98E − 07 | 1.98E − 07 | − 6.54928 | Down | X-C motif chemokine ligand 1 |
| AIRE | − 0.78032 | 2.01E − 07 | 2.01E − 07 | − 6.5441 | Down | Autoimmune regulator |
| IL3 | − 0.60723 | 2.08E − 07 | 2.08E − 07 | − 6.53283 | Down | Interleukin 3 |
| CCL16 | − 0.6195 | 2.31E − 07 | 2.31E − 07 | − 6.4973 | Down | C–C motif chemokine ligand 16 |
| CCL7 | − 0.6195 | 2.31E − 07 | 2.31E − 07 | − 6.4973 | Down | C–C motif chemokine ligand 7 |
| CSF2 | − 0.6195 | 2.31E − 07 | 2.31E − 07 | − 6.4973 | Down | Colony stimulating factor 2 |
| ITLN2 | − 0.6195 | 2.31E − 07 | 2.31E − 07 | − 6.4973 | Down | Intelectin 2 |
| THY1 | − 0.6195 | 2.31E − 07 | 2.31E − 07 | − 6.4973 | Down | Thy-1 cell surface antigen |
| IL21 | − 0.70245 | 3.28E − 07 | 3.28E − 07 | − 6.37574 | Down | Interleukin 21 |
| BCL2 | − 0.7385 | 4.11E − 07 | 4.11E − 07 | − 6.29854 | Down | BCL2 apoptosis regulator |
| EDNRB | − 0.60541 | 4.11E − 07 | 4.11E − 07 | − 6.29833 | Down | Endothelin receptor type B |
| CCR6 | − 0.88205 | 4.78E − 07 | 4.78E − 07 | − 6.24666 | Down | C–C motif chemokine receptor 6 |
| TIRAP | − 0.70182 | 5.91E − 07 | 5.91E − 07 | − 6.17398 | Down | TIR domain containing adaptor protein |
| STAT6 | − 0.52186 | 6.37E − 07 | 6.37E − 07 | − 6.14848 | Down | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 |
| PSMB10 | − 0.43945 | 6.43E − 07 | 6.43E − 07 | − 6.14519 | Down | Proteasome 20S subunit beta 10 |
| SKI | − 0.52182 | 7.16E − 07 | 7.16E − 07 | − 6.10886 | Down | SKI proto-oncogene |
| RAG2 | − 0.56723 | 8.47E − 07 | 8.47E − 07 | − 6.05149 | Down | Recombination activating 2 |
| CD209 | − 0.7285 | 8.56E − 07 | 8.56E − 07 | − 6.04758 | Down | CD209 molecule |
| VTN | − 0.68305 | 9.43E − 07 | 9.43E − 07 | − 6.01488 | Down | Vitronectin |
| IFNB1 | − 0.57768 | 9.97E − 07 | 9.97E − 07 | − 5.99573 | Down | Interferon beta 1 |
| EOMES | − 0.77505 | 1.47E − 06 | 1.47E − 06 | − 5.8643 | Down | Eomesodermin |
| CD74 | − 0.69905 | 1.52E − 06 | 1.52E − 06 | − 5.85145 | Down | CD74 molecule |
| CCR10 | − 0.60368 | 1.7E − 06 | 1.7E − 06 | − 5.81503 | Down | C–C motif chemokine receptor 10 |
| LGALS3 | − 1.12309 | 1.85E − 06 | 1.85E − 06 | − 5.78563 | Down | Galectin 3 |
| PDGFB | − 0.64241 | 1.86E − 06 | 1.86E − 06 | − 5.78395 | Down | Platelet derived growth factor subunit B |
| ICAM4 | − 0.96814 | 1.96E − 06 | 1.96E − 06 | − 5.76557 | Down | Intercellular adhesion molecule 4 (Landsteiner-Wiener blood group) |
| ICOSLG | − 0.74791 | 2.07E − 06 | 2.07E − 06 | − 5.74698 | Down | Inducible T cell costimulator ligand |
| C9 | − 0.52132 | 2.66E − 06 | 2.66E − 06 | − 5.66169 | Down | Complement C9 |
| IL16 | − 0.45973 | 2.88E − 06 | 2.88E − 06 | − 5.63467 | Down | Interleukin 16 |
| RELA | − 0.47205 | 3.09E − 06 | 3.09E − 06 | − 5.61097 | Down | RELA proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit |
| DEFB1 | − 0.8105 | 3.38E − 06 | 3.38E − 06 | − 5.58051 | Down | Defensin beta 1 |
| IL13RA1 | − 0.90159 | 3.41E − 06 | 3.41E − 06 | − 5.57755 | Down | Interleukin 13 receptor subunit alpha 1 |
| HLA-DOB | − 1.24595 | 3.65E − 06 | 3.65E − 06 | − 5.55493 | Down | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DO beta |
| KIR3DL3 | − 0.56905 | 3.78E − 06 | 3.78E − 06 | − 5.54244 | Down | Killer cell immunoglobulin like receptor, three Ig domains and long cytoplasmic tail 3 |
| HLA-C | − 0.93941 | 3.97E − 06 | 3.97E − 06 | − 5.52568 | Down | Major histocompatibility complex, class I, C |
| KLRB1 | − 1.79632 | 5.31E − 06 | 5.31E − 06 | − 5.42732 | Down | Killer cell lectin like receptor B1 |
| HLA-DMB | − 0.85005 | 5.86E − 06 | 5.86E − 06 | − 5.39367 | Down | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DM beta |
| KLRF2 | − 0.53859 | 6E − 06 | 6E − 06 | − 5.3857 | Down | Killer cell lectin like receptor F2 |
| ICAM3 | − 0.66718 | 6.38E − 06 | 6.38E − 06 | − 5.36481 | Down | Intercellular adhesion molecule 3 |
| IL28A | − 0.55718 | 7.03E − 06 | 7.03E − 06 | − 5.33194 | Down | Interleukin 28A |
| SIGIRR | − 0.41545 | 7.52E − 06 | 7.52E − 06 | − 5.30925 | Down | Single Ig and TIR domain containing |
| MASP2 | − 0.68927 | 7.93E − 06 | 7.93E − 06 | − 5.29109 | Down | Mannan binding lectin serine peptidase 2 |
| CSF2RB | − 1.12332 | 8.36E − 06 | 8.36E − 06 | − 5.27318 | Down | Colony stimulating factor 2 receptor beta common subunit |
| CD46 | − 0.59905 | 9.11E − 06 | 9.11E − 06 | − 5.24408 | Down | CD46 molecule |
| S1PR1 | − 0.60436 | 9.23E − 06 | 9.23E − 06 | − 5.23966 | Down | Sphingosine − 1-phosphate receptor 1 |
| TLR9 | − 0.56841 | 1.05E − 05 | 1.05E − 05 | − 5.19438 | Down | Toll like receptor 9 |
| HLA-DPB1 | − 0.70064 | 1.07E − 05 | 1.07E − 05 | − 5.19046 | Down | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP beta 1 |
| CCL13 | − 0.57018 | 1.16E − 05 | 1.16E − 05 | − 5.16161 | Down | C–C motif chemokine ligand 13 |
| PLA2G2E | − 0.67155 | 1.19E − 05 | 1.19E − 05 | -5.15362 | Down | Phospholipase A2 group IIE |
| IL20 | − 0.67032 | 1.29E − 05 | 1.29E − 05 | -5.12687 | Down | Interleukin 20 |
| PTAFR | − 0.91373 | 1.37E − 05 | 1.37E − 05 | -5.10671 | Down | Platelet activating factor receptor |
| TGFBI | − 0.59209 | 1.44E − 05 | 1.44E − 05 | -5.08943 | Down | Transforming growth factor beta induced |
| IL26 | − 0.50514 | 1.52E − 05 | 1.52E − 05 | -5.07029 | Down | Interleukin 26 |
| IFNAR1 | − 0.78755 | 2.03E − 05 | 2.03E − 05 | − 4.97214 | Down | Interferon alpha and beta receptor subunit 1 |
| LTA | − 0.56282 | 2.17E − 05 | 2.17E − 05 | − 4.94915 | Down | Lymphotoxin alpha |
| FCGR2B | − 0.85355 | 2.4E − 05 | 2.4E − 05 | − 4.91443 | Down | Fc fragment of IgG receptor IIb |
| EGR1 | − 0.63082 | 2.41E − 05 | 2.41E − 05 | − 4.9133 | Down | Early growth response 1 |
| CD86 | − 0.76691 | 2.54E − 05 | 2.54E − 05 | − 4.89525 | Down | CD86 molecule |
| CD82 | − 0.99568 | 2.76E − 05 | 2.76E − 05 | − 4.86674 | Down | CD82 molecule |
| CD34 | − 0.56045 | 2.79E − 05 | 2.79E − 05 | − 4.86293 | Down | CD34 molecule |
| TRAF3 | − 0.46214 | 2.87E − 05 | 2.87E − 05 | − 4.85429 | Down | TNF receptor associated factor 3 |
| CTLA4 | − 0.53577 | 3E − 05 | 3E − 05 | − 4.83886 | Down | Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Associated Protein 4 |
| HAMP | − 0.61205 | 3E − 05 | 3E − 05 | − 4.83856 | Down | Hepcidin antimicrobial peptide |
| EGR2 | − 0.78873 | 3.15E − 05 | 3.15E − 05 | − 4.82228 | Down | Early growth response 2 |
| ICAM5 | − 0.53214 | 3.22E − 05 | 3.22E − 05 | − 4.81493 | Down | Intercellular adhesion molecule 5 |
| CSF1R | − 0.70273 | 3.45E − 05 | 3.45E − 05 | − 4.79056 | Down | Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor |
| NT5E | − 0.85836 | 3.68E − 05 | 3.68E − 05 | − 4.76884 | Down | 5′-nucleotidase ecto |
| IL7 | − 0.74464 | 4.3E − 05 | 4.3E − 05 | − 4.71548 | Down | Interleukin 7 |
| CTSS | − 0.62991 | 4.34E − 05 | 4.34E − 05 | − 4.71277 | Down | Cathepsin S |
| IL17B | − 0.55268 | 4.82E − 05 | 4.82E − 05 | − 4.6769 | Down | Interleukin 17B |
| CR2 | − 1.00786 | 4.86E − 05 | 4.86E − 05 | − 4.67369 | Down | Complement C3d receptor 2 |
| CD44 | − 0.35164 | 5.25E − 05 | 5.25E − 05 | − 4.64701 | Down | CD44 molecule (Indian blood group) |
| PLA2G2A | − 0.53655 | 5.77E − 05 | 5.77E − 05 | − 4.61492 | Down | Phospholipase A2 group IIA |
| BTK | − 0.45495 | 5.87E − 05 | 5.87E − 05 | − 4.60896 | Down | Bruton tyrosine kinase |
| C6 | − 0.65964 | 5.95E − 05 | 5.95E − 05 | − 4.60439 | Down | Complement C6 |
| IRGM | − 0.62291 | 6.21E − 05 | 6.21E − 05 | − 4.58953 | Down | Immunity related GTPase M |
| IL22 | − 0.65314 | 7.15E − 05 | 7.15E − 05 | − 4.54121 | Down | Interleukin 22 |
| CEBPB | − 0.88709 | 7.69E − 05 | 7.69E − 05 | − 4.51625 | Down | CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta |
| IL6 | − 0.69105 | 7.91E − 05 | 7.91E − 05 | − 4.50639 | Down | Interleukin 6 |
| IFNA2 | − 0.77586 | 8.23E − 05 | 8.23E − 05 | − 4.49296 | Down | Interferon alpha 2 |
| TGFBR1 | − 0.40336 | 8.66E − 05 | 8.66E − 05 | − 4.47511 | Down | Transforming growth factor beta receptor 1 |
| IL17F | − 0.54009 | 8.83E − 05 | 8.83E − 05 | − 4.4686 | Down | Interleukin 17F |
| IL28A/B | − 0.55282 | 0.000163 | 0.000163 | − 4.25674 | Down | Interleukin 28A/B |
| IL17A | − 0.53723 | 0.00018 | 0.00018 | − 4.22236 | Down | Interleukin 17A |
| LILRA2 | − 0.68495 | 0.000195 | 0.000195 | − 4.194 | Down | Leukocyte immunoglobulin like receptor A2 |
| LILRA3 | − 2.33691 | 0.000203 | 0.000203 | − 4.18055 | Down | Leukocyte immunoglobulin like receptor A3 |
| VCAM1 | − 0.60605 | 0.000219 | 0.000219 | − 4.15259 | Down | Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| SPP1 | − 0.6555 | 0.000221 | 0.000221 | − 4.1496 | Down | Secreted phosphoprotein 1 |
| CARD9 | − 0.55227 | 0.000269 | 0.000269 | − 4.0818 | Down | Caspase recruitment domain family member 9 |
| LCK | − 0.40364 | 0.000299 | 0.000299 | − 4.04398 | Down | LCK proto-oncogene, Src family tyrosine kinase |
| SELE | − 0.52332 | 0.000306 | 0.000306 | − 4.03551 | Down | selectin E |
| SLC2A1 | − 0.44118 | 0.00036 | 0.00036 | − 3.97865 | Down | solute carrier family 2 member 1 |
| LIF | − 0.50555 | 0.000368 | 0.000368 | − 3.97037 | Down | LIF interleukin 6 family cytokine |
| IDO1 | − 0.95541 | 0.000417 | 0.000417 | − 3.92685 | Down | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 |
| TNFRSF10C | − 0.88564 | 0.000471 | 0.000471 | − 3.88294 | Down | TNF receptor superfamily member 10c |
| IL23A | − 0.87541 | 0.000557 | 0.000557 | − 3.82374 | Down | interleukin 23 subunit alpha |
| CD80 | − 0.58964 | 0.000567 | 0.000567 | − 3.81702 | Down | CD80 molecule |
| GPR183 | − 1.088 | 0.00057 | 0.00057 | − 3.81527 | Down | G protein-coupled receptor 183 |
| C1R | − 0.41727 | 0.000592 | 0.000592 | − 3.8018 | Down | Complement C1r |
| CCL11 | − 0.55055 | 0.000611 | 0.000611 | − 3.79064 | Down | C–C motif chemokine ligand 11 |
| HLA-DPA1 | − 0.6385 | 0.000637 | 0.000637 | − 3.77577 | Down | major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP alpha 1 |
| IFNG | − 0.877 | 0.00073 | 0.00073 | − 3.72658 | Down | Interferon gamma |
| DUSP4 | − 0.70741 | 0.000789 | 0.000789 | − 3.69861 | Down | Dual specificity phosphatase 4 |
| IL27 | − 0.44905 | 0.000852 | 0.000852 | − 3.67089 | Down | Interleukin 27 |
| CD48 | − 1.15805 | 0.000953 | 0.000953 | − 3.6304 | Down | CD48 molecule |
| FN1 | − 0.56177 | 0.001005 | 0.001005 | − 3.61111 | Down | fibronectin 1 |
| CD244 | − 0.39427 | 0.001018 | 0.001018 | − 3.60646 | Down | CD244 molecule |
| PPBP | − 1.35464 | 0.001091 | 0.001091 | − 3.58105 | Down | pro-platelet basic protein |
| IL13 | − 0.599 | 0.001204 | 0.001204 | − 3.54515 | Down | interleukin 13 |
| CCL24 | − 0.45395 | 0.001221 | 0.001221 | − 3.53987 | Down | C–C motif chemokine ligand 24 |
| GATA3 | − 0.55041 | 0.001228 | 0.001228 | − 3.53797 | Down | GATA binding protein 3 |
| BID | − 0.46636 | 0.001281 | 0.001281 | − 3.52243 | Down | BH3 interacting domain death agonist |
| BCL2L11 | − 0.40091 | 0.001565 | 0.001565 | − 3.44881 | Down | BCL2 like 11 |
| KIT | − 0.52868 | 0.001589 | 0.001589 | − 3.44316 | Down | KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase |
| MME | − 1.00591 | 0.001596 | 0.001596 | − 3.44151 | Down | Membrane metalloendopeptidase |
| ZEB1 | − 0.38082 | 0.001667 | 0.001667 | − 3.42548 | Down | Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 |
| C4A/B | − 0.62314 | 0.001738 | 0.001738 | − 3.40994 | Down | Complement C4A/B |
| FCAR | − 0.50423 | 0.00198 | 0.00198 | − 3.36169 | Down | Fc fragment of IgA receptor |
| BTLA | − 0.45623 | 0.002033 | 0.002033 | − 3.35183 | Down | B and T lymphocyte associated |
| TAGAP | − 0.38886 | 0.002261 | 0.002261 | − 3.31206 | Down | T cell activation RhoGTPase activating protein |
| CD83 | − 0.39914 | 0.002292 | 0.002292 | − 3.307 | Down | CD83 molecule |
| SELPLG | − 0.37564 | 0.002362 | 0.002362 | -3.29575 | Down | Selectin P ligand |
| B3GAT1 | − 0.66791 | 0.002423 | 0.002423 | − 3.28614 | Down | Beta-1,3-glucuronyltransferase 1 |
| CCRL1 | − 0.39195 | 0.002543 | 0.002543 | − 3.26788 | Down | C–C chemokine receptor type 11 |
| TNFRSF14 | − 0.29986 | 0.002557 | 0.002557 | − 3.26588 | Down | TNF receptor superfamily member 14 |
| CSF3R | − 0.65318 | 0.003003 | 0.003003 | − 3.20507 | Down | Colony stimulating factor 3 receptor |
| CD9 | − 0.87091 | 0.003004 | 0.003004 | − 3.20497 | Down | CD9 molecule |
| C1S | − 0.52059 | 0.003211 | 0.003211 | − 3.17969 | Down | complement C1s |
| PECAM1 | − 0.30873 | 0.003251 | 0.003251 | − 3.17496 | Down | platelet and endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| DEFB103B | − 0.4315 | 0.003466 | 0.003466 | − 3.15055 | Down | Defensin beta 103B |
| ITLN1 | − 1.17682 | 0.003488 | 0.003488 | − 3.14815 | Down | Intelectin 1 |
| CXCL13 | − 0.46586 | 0.003554 | 0.003554 | − 3.14101 | Down | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 13 |
| RAG1 | − 0.47836 | 0.003917 | 0.003917 | − 3.10376 | Down | Recombination activating 1 |
| TNFRSF4 | − 0.55123 | 0.004154 | 0.004154 | − 3.08112 | Down | TNF receptor superfamily member 4 |
| C14orf166 | − 0.35727 | 0.004255 | 0.004255 | − 3.07189 | Down | Chromosome 14 open reading frame 166 |
| IL10RA | − 0.26059 | 0.004423 | 0.004423 | − 3.0569 | Down | Interleukin 10 receptor subunit alpha |
| POU2F2 | − 0.292 | 0.004614 | 0.004614 | − 3.04059 | Down | POU class 2 homeobox 2 |
| C7 | − 0.41223 | 0.004688 | 0.004688 | − 3.03441 | Down | complement C7 |
| RORC | − 0.52768 | 0.005006 | 0.005006 | − 3.00891 | Down | RAR related orphan receptor C |
| CXCL11 | − 0.83891 | 0.005151 | 0.005151 | − 2.99784 | Down | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 11 |
| MASP1 | − 0.50677 | 0.005182 | 0.005182 | − 2.99543 | Down | Mannan binding lectin serine peptidase 1 |
| MAP4K4 | − 0.37777 | 0.005449 | 0.005449 | − 2.97583 | Down | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinasekinasekinase 4 |
| CX3CL1 | − 0.50445 | 0.005597 | 0.005597 | − 2.96535 | Down | C-X3-C motif chemokine ligand 1 |
| BATF3 | − 0.62586 | 0.005862 | 0.005862 | − 2.94725 | Down | Basic leucine zipper ATF-like transcription factor 3 |
| CCR8 | − 0.51627 | 0.005946 | 0.005946 | − 2.94164 | Down | C–C motif chemokine receptor 8 |
| TAL1 | − 1.01455 | 0.006016 | 0.006016 | − 2.93707 | Down | TAL bHLH transcription factor 1, erythroid differentiation factor |
| NFIL3 | − 0.723 | 0.007 | 0.007 | − 2.87725 | Down | Nuclear factor, interleukin 3 regulated |
| CD8A | − 0.50595 | 0.007337 | 0.007337 | − 2.85858 | Down | CD8a molecule |
| CLEC6A | − 0.62323 | 0.007445 | 0.007445 | − 2.85274 | Down | C-type lectin domain containing 6A |
| TCF4 | − 0.37827 | 0.007904 | 0.007904 | − 2.8289 | Down | Transcription factor 4 |
| FCGR2A | − 0.664 | 0.009089 | 0.009089 | − 2.77283 | Down | Fc fragment of IgG receptor IIa |
| HLA-B | − 0.31677 | 0.00918 | 0.00918 | − 2.76877 | Down | major histocompatibility complex, class I, B |
| IRF8 | − 0.39477 | 0.009346 | 0.009346 | − 2.76157 | Down | Interferon regulatory factor 8 |
| MAPK11 | − 0.60427 | 0.010152 | 0.010152 | − 2.72804 | Down | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 11 |
| ILF3 | − 0.17055 | 0.010366 | 0.010366 | − 2.71958 | Down | Interleukin enhancer binding factor 3 |
| XCR1 | − 0.34541 | 0.01065 | 0.01065 | − 2.70856 | Down | X–C motif chemokine receptor 1 |
| ITGAE | − 0.33509 | 0.011424 | 0.011424 | − 2.67988 | Down | Integrin subunit alpha E |
| IL4R | − 0.69064 | 0.012538 | 0.012538 | − 2.64162 | Down | Interleukin 4 receptor |
| CTSC | − 0.16718 | 0.012619 | 0.012619 | − 2.63897 | Down | Cathepsin C |
| ETS1 | − 0.39405 | 0.013255 | 0.013255 | − 2.61865 | Down | ETS proto-oncogene 1, transcription factor |
| CFI | − 0.30082 | 0.013335 | 0.013335 | − 2.61614 | Down | Complement factor I |
| STAT5A | − 0.27168 | 0.014802 | 0.014802 | − 2.57273 | Down | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A |
| C8A | − 0.37964 | 0.016204 | 0.016204 | − 2.53478 | Down | Complement C8 alpha chain |
| DEFB4A | − 0.36691 | 0.017835 | 0.017835 | − 2.49428 | Down | Defensin beta 4A |
| RELB | − 0.45095 | 0.019351 | 0.019351 | − 2.45958 | Down | RELB proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit |
| ATG7 | − 0.32859 | 0.01984 | 0.01984 | − 2.4489 | Down | Autophagy related 7 |
| DPP4 | − 0.38823 | 0.01999 | 0.01999 | − 2.44568 | Down | Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 |
| GPI | − 0.21382 | 0.020424 | 0.020424 | − 2.43646 | Down | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase |
| CD59 | − 0.24032 | 0.020561 | 0.020561 | − 2.43359 | Down | CD59 molecule (CD59 blood group) |
| CASP3 | − 0.40573 | 0.025629 | 0.025629 | − 2.33807 | Down | Caspase 3 |
| TIGIT | − 0.3615 | 0.025963 | 0.025963 | − 2.33239 | Down | T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains |
| CFD | − 0.36627 | 0.026073 | 0.026073 | − 2.33053 | Down | Complement factor D |
| CCL18 | − 0.42077 | 0.026944 | 0.026944 | − 2.3161 | Down | C–C motif chemokine ligand 18 |
| PLAU | − 0.34086 | 0.028132 | 0.028132 | − 2.29706 | Down | Plasminogen activator, urokinase |
| PTPN22 | − 0.20086 | 0.028829 | 0.028829 | − 2.28623 | Down | Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22 |
| TOLLIP | − 0.27377 | 0.028911 | 0.028911 | − 2.28497 | Down | Toll interacting protein |
| CXCR2 | − 0.49195 | 0.029438 | 0.029438 | − 2.27696 | Down | C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 2 |
| CCL20 | − 0.34555 | 0.029871 | 0.029871 | − 2.27048 | Down | C–C motif chemokine ligand 20 |
| IL12A | − 0.40759 | 0.03046 | 0.03046 | − 2.26179 | Down | Interleukin 12A |
| IL10 | − 0.33555 | 0.03205 | 0.03205 | − 2.23904 | Down | Interleukin 10 |
| LILRA1 | − 0.26991 | 0.033542 | 0.033542 | − 2.21862 | Down | leukocyte immunoglobulin like receptor A1 |
| PTPN6 | − 0.16109 | 0.034722 | 0.034722 | − 2.20304 | Down | protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 6 |
| CCL19 | − 0.37718 | 0.035605 | 0.035605 | − 2.19168 | Down | C–C motif chemokine ligand 19 |
| IKBKAP | − 0.15505 | 0.035624 | 0.035624 | − 2.19144 | Down | IκB kinase complex-associated protein |
| TNFRSF9 | − 0.50786 | 0.036235 | 0.036235 | − 2.18372 | Down | TNF receptor superfamily member 9 |
| TCF7 | − 0.60091 | 0.036564 | 0.036564 | − 2.17963 | Down | Transcription factor 7 |
| HLA-DMA | − 0.30777 | 0.036925 | 0.036925 | − 2.17516 | Down | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DM alpha |
| CXCL12 | − 0.69291 | 0.037168 | 0.037168 | − 2.17218 | Down | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 |
| MBL2 | − 0.37009 | 0.037623 | 0.037623 | − 2.16664 | Down | Mannose binding lectin 2 |
| IKZF2 | − 0.46655 | 0.039489 | 0.039489 | − 2.14452 | Down | IKAROS family zinc finger 2 |
| BCAP31 | − 0.10632 | 0.04075 | 0.04075 | − 2.13009 | Down | B cell receptor associated protein 31 |
| HLA-DRB1 | − 1.39495 | 0.041403 | 0.041403 | − 2.12278 | Down | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 1 |
| IRAK4 | − 0.23727 | 0.041428 | 0.041428 | − 2.12251 | Down | Interleukin 1 receptor associated kinase 4 |
| CXCR1 | − 0.49741 | 0.041833 | 0.041833 | − 2.11802 | Down | C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 1 |
| PTK2 | − 0.33609 | 0.043242 | 0.043242 | − 2.10272 | Down | Protein tyrosine kinase 2 |
| CD45R0 | − 0.46514 | 0.043373 | 0.043373 | − 2.10132 | Down | A member of leucocyte common antigen family |
Pathway enrichment analysis for DEGs
Pathway enrichment analysis of integrated DEGs showed the up-regulated genes were mainly involved in measles, herpes simplex infection, IL12-mediated signaling events, IL2-mediated signaling events, cytokine signaling in immune system, innate immune system, IL22 soluble receptor signaling pathway, bioactive peptide-induced signaling pathway, JAK/STAT signaling pathway, Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway, G protein signaling, platelet-derived growth factor signaling, intracellular signalling through adenosine receptor A2a and adenosine, insulin signalling and other pathways (Table 2); the down-regulated genes were mainly involved in citrulline–nitric oxide cycle, phospholipases, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, hematopoietic cell lineage, IL4-mediated signaling events, IL12-mediated signaling events, cytokine signaling in immune system, signaling by interleukins, phenylalanine tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis, MAP kinase activity, genes encoding secreted soluble factors, cytokine network, interleukin signaling pathway, inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway, intrinsic apoptotic, interleukin-10 signaling, sulindac pathway, glycolysis and other pathways (Table 3).
Table 2.
The enriched pathway terms of the up regulated differentially expressed genes
| KEGG | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathway ID | Pathway Name | P-value | FDR B&H | FDR B&Y | Bonferroni | Gene Count | Gene |
| 213306 | Measles | 3.21E − 17 | 4.46E − 15 | 2.46E − 14 | 4.46E − 15 | 16 | CCND3, JAK1, JAK2, IFIH1, TRAF6, IKBKE, TLR2, IRF7, FYN, IL2RG, STAT1, TP53, STAT3, MX1, STAT5B, IFNAR2 |
| 377873 | Herpes simplex infection | 1.19E − 13 | 8.24E − 12 | 4.54E − 11 | 1.65E − 11 | 15 | JAK1, JAK2, IFIH1, TRAF2, TRAF6, HLA-A, IKBKE, TLR2, C1QBP, CCL5, IRF7, IKBKB, STAT1, TP53, IFNAR2 |
| 83079 | Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | 5.40E − 13 | 2.50E − 11 | 1.38E − 10 | 7.51E − 11 | 13 | KLRK1, CD247, HLA-A, GZMB, HRAS, LCP2, ITGAL, FYN, ITGB2, KLRC1, ZAP70, KLRD1, IFNAR2 |
| 193147 | Osteoclast differentiation | 1.85E − 10 | 3.32E − 09 | 1.83E − 08 | 2.57E − 08 | 11 | JAK1, TRAF2, TRAF6, LILRB2, LILRA6, SOCS1, IKBKB, LCP2, FYN, STAT1, IFNAR2 |
| 83077 | Jak-STAT signaling pathway | 1.31E − 09 | 1.83E − 08 | 1.01E − 07 | 1.83E − 07 | 11 | CCND3, JAK1, JAK2, HRAS, SOCS1, IL2RG, STAT1, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5B, IFNAR2 |
| 217173 | Influenza A | 3.94E − 09 | 4.56E − 08 | 2.51E − 07 | 5.47E − 07 | 11 | JAK1, JAK2, IFIH1, IKBKE, CCL5, IRF7, IKBKB, STAT1, NLRP3, MX1, IFNAR2 |
| 373901 | HTLV-I infection | 2.27E − 08 | 2.11E − 07 | 1.16E − 06 | 3.16E − 06 | 12 | CCND3, JAK1, HLA-A, HRAS, XBP1, CTNNB1, IKBKB, ITGAL, ITGB2, IL2RG, TP53, STAT5B |
| 658418 | Viral carcinogenesis | 2.16E − 07 | 1.67E − 06 | 9.20E − 06 | 3.00E − 05 | 10 | CCND3, JAK1, TRAF2, HLA-A, HRAS, IRF7, CCR5, TP53, STAT3, STAT5B |
| 83080 | T cell receptor signaling pathway | 2.05E − 06 | 1.36E − 05 | 7.47E − 05 | 2.85E − 04 | 7 | PDCD1, CD247, HRAS, IKBKB, LCP2, FYN, ZAP70 |
| 125138 | Viral myocarditis | 2.21E − 05 | 1.18E − 04 | 6.51E − 04 | 3.07E − 03 | 5 | ABL1, HLA-A, ITGAL, FYN, ITGB2 |
| 213780 | Tuberculosis | 7.57E − 05 | 3.63E − 04 | 2.00E − 03 | 1.05E − 02 | 7 | JAK1, JAK2, TRAF6, TLR2, CLEC7A, ITGB2, STAT1 |
| 83051 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | 1.59E − 04 | 6.69E − 04 | 3.69E − 03 | 2.21E − 02 | 8 | CCR1, CCL5, CCR5, IL18RAP, IL2RG, IL18R1, CX3CR1, IFNAR2 |
| 152665 | Malaria | 1.79E − 04 | 7.32E − 04 | 4.04E − 03 | 2.49E − 02 | 4 | KLRK1, TLR2, ITGAL, ITGB2 |
| Pathway interaction database | |||||||
| 137922 | IL12-mediated signaling events | 1.37E − 17 | 1.56E − 15 | 8.29E − 15 | 1.56E − 15 | 13 | JAK2, CD247, HLA-A, TBX21, GZMB, SOCS1, CCR5, IL18RAP, IL2RG, IL18R1, STAT1, STAT3, STAT4 |
| 137976 | IL2-mediated signaling events | 5.15E − 10 | 2.94E − 08 | 1.56E − 07 | 5.88E − 08 | 8 | JAK1, IKZF3, SOCS1, FYN, IL2RG, STAT1, STAT3, STAT5B |
| 138055 | TCR signaling in naive CD8 + T cells | 9.79E − 09 | 2.35E − 07 | 1.25E − 06 | 1.12E − 06 | 7 | TRAF6, CD247, HLA-A, IKBKB, LCP2, FYN, ZAP70 |
| 138071 | PDGFR-beta signaling pathway | 6.28E − 07 | 7.16E − 06 | 3.81E − 05 | 7.16E − 05 | 6 | ABL1, HRAS, FYN, STAT1, STAT3, STAT5B |
| 137988 | IL2 signaling events mediated by STAT5 | 2.52E − 05 | 2.21E − 04 | 1.17E − 03 | 2.87E − 03 | 4 | CCND3, JAK1, IL2RG, STAT5B |
| 138019 | p75(NTR)-mediated signaling | 5.25E − 03 | 2.32E − 02 | 1.23E − 01 | 5.99E − 01 | 3 | TRAF6, IKBKB, TP53 |
| 138021 | Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 | 5.29E − 03 | 2.32E − 02 | 1.23E − 01 | 6.03E − 01 | 2 | ITGAL, ITGB2 |
| 137940 | Signaling events mediated by VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 | 5.75E − 03 | 2.43E − 02 | 1.29E − 01 | 6.55E − 01 | 3 | HRAS, CTNNB1, FYN |
| 137983 | ALK2 signaling events | 6.18E − 02 | 1.22E − 01 | 6.47E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | SMAD5 |
| 138046 | Syndecan-1-mediated signaling events | 9.40E − 02 | 1.70E − 01 | 9.04E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | CCL5 |
| REACTOME | |||||||
| 1269310 | Cytokine Signaling in Immune system | 3.94E − 16 | 2.05E − 13 | 1.40E − 12 | 2.05E − 13 | 28 | JAK1, JAK2, TRAF2, TRAF6, HLA-A, BST2, HRAS, PSMB9, GBP1, SOCS1, CCR1, IRF5, CCL5, IRF7, CCR5, IKBKB, FYN, IFI35, IL18RAP, ITGB2, IL2RG, IL18R1, STAT1, TP53, STAT3, MX1, STAT5B, IFNAR2 |
| 1269203 | Innate Immune System | 1.61E − 13 | 4.19E − 11 | 2.86E − 10 | 8.38E − 11 | 32 | KLRK1, ATG5, JAK1, JAK2, IFIH1, TRAF2, TRAF6, CD247, ABL1, HLA-A, IKBKE, BST2, LILRB2, TLR2, HRAS, PSMB9, CLEC7A, SOCS1, C2, IRF7, GNLY, CTNNB1, IKBKB, LCP2, ITGAL, FYN, ITGB2, IL2RG, KLRD1, TP53, NLRP3, CEACAM1 |
| 1269318 | Signaling by Interleukins | 9.69E − 11 | 1.06E − 08 | 7.24E − 08 | 5.04E − 08 | 19 | JAK1, JAK2, TRAF6, HRAS, PSMB9, SOCS1, CCR1, CCL5, CCR5, IKBKB, FYN, IL18RAP, ITGB2, IL2RG, IL18R1, STAT1, TP53, STAT3, STAT5B |
| 1269171 | Adaptive Immune System | 1.02E − 10 | 1.06E − 08 | 7.24E − 08 | 5.30E − 08 | 23 | KLRK1, PDCD1, TRAF6, CD247, ZBTB16, HLA-A, LILRB2, TLR2, LAG3, HRAS, LILRA6, PSMB9, SOCS1, SLAMF7, IKBKB, LCP2, ITGAL, FYN, ITGB2, KLRC1, ZAP70, KLRD1, TP53 |
| 1269340 | Hemostasis | 5.49E − 07 | 2.20E − 05 | 1.50E − 04 | 2.86E − 04 | 16 | JAK1, JAK2, ABL1, CD99, HRAS, C1QBP, SERPING1, IRF7, LCP2, ITGAL, FYN, ITGB2, IL2RG, TP53, CEACAM1, GP1BB |
| 1269260 | TRAF3-dependent IRF activation pathway | 9.84E − 05 | 1.55E − 03 | 1.06E − 02 | 5.12E − 02 | 3 | IFIH1, IKBKE, IRF7 |
| 1268854 | Disease | 1.26E − 03 | 1.24E − 02 | 8.44E − 02 | 6.55E − 01 | 13 | JAK2, CD247, HLA-A, TLR2, HRAS, PSMB9, CCR5, CTNNB1, IKBKB, FYN, STAT1, STAT3, STAT5B |
| 1268855 | Diseases of signal transduction | 1.35E − 03 | 1.30E − 02 | 8.90E − 02 | 7.03E − 01 | 8 | JAK2, HRAS, PSMB9, CTNNB1, FYN, STAT1, STAT3, STAT5B |
| 1269562 | Leukotriene receptors | 2.86E − 02 | 8.96E − 02 | 6.12E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | LTB4R |
| 1269248 | Activation of C3 and C5 | 3.98E − 02 | 1.18E − 01 | 8.08E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | C2 |
| MSigDB C2 BIOCARTA (v6.0) | |||||||
| M8066 | IL22 Soluble Receptor Signaling Pathway | 2.31E − 10 | 3.56E − 08 | 2.00E − 07 | 3.56E − 08 | 6 | JAK1, JAK2, STAT1, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5B |
| M13494 | Bioactive Peptide Induced Signaling Pathway | 4.38E − 09 | 3.38E − 07 | 1.90E − 06 | 6.75E − 07 | 7 | JAK2, HRAS, FYN, STAT1, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5B |
| M1462 | CTL mediated immune response against target cells | 1.61E − 08 | 7.50E − 07 | 4.21E − 06 | 2.48E − 06 | 5 | CD247, HLA-A, GZMB, ITGAL, ITGB2 |
| M6231 | NO2-dependent IL 12 Pathway in NK cells | 2.31E − 06 | 3.24E − 05 | 1.82E − 04 | 3.56E − 04 | 4 | JAK2, CD247, CCR5, STAT4 |
| M13863 | MAPKinaseSignaling Pathway | 1.06E − 05 | 1.08E − 04 | 6.09E − 04 | 1.63E − 03 | 6 | TRAF2, MAP4K1, HRAS, IKBKB, MAP4K2, STAT1 |
| M6427 | T Helper Cell Surface Molecules | 6.45E − 05 | 4.73E − 04 | 2.66E − 03 | 9.93E − 03 | 3 | CD247, ITGAL, ITGB2 |
| M4047 | Selective expression of chemokine receptors during T-cell polarization | 6.08E − 04 | 3.12E − 03 | 1.75E − 02 | 9.37E − 02 | 3 | CCR1, CCR5, IL18R1 |
| M11358 | Tumor Suppressor Arf Inhibits Ribosomal Biogenesis | 4.24E − 03 | 1.28E − 02 | 7.19E − 02 | 6.53E − 01 | 2 | ABL1, TP53 |
| M17400 | ALK in cardiac myocytes | 1.93E − 02 | 4.37E − 02 | 2.45E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 2 | CTNNB1, SMAD5 |
| M5885 | Ensemble of genes encoding ECM-associated proteins including ECM-affilaited proteins, ECM regulators and secreted factors | 8.19E − 01 | 8.30E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 3 | CLEC7A, SERPING1, CCL5 |
| Panther DB | |||||||
| P00038 | JAK/STAT signaling pathway | 1.76E − 12 | 5.64E − 11 | 2.29E − 10 | 5.64E − 11 | 7 | JAK1, JAK2, SOCS1, STAT1, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5B |
| P00031 | Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway | 1.44E − 06 | 2.31E − 05 | 9.37E − 05 | 4.62E − 05 | 9 | JAK2, CCRL2, CCR1, CCL5, CCR5, IKBKB, ITGAL, CX3CR1, STAT3 |
| P00054 | Toll receptor signaling pathway | 1.94E − 04 | 1.03E − 03 | 4.19E − 03 | 6.20E − 03 | 4 | TRAF6, IKBKE, TLR2, IKBKB |
| P00006 | Apoptosis signaling pathway | 3.03E − 04 | 1.39E − 03 | 5.62E − 03 | 9.69E − 03 | 5 | TRAF2, GZMB, IKBKB, MAP4K2, TP53 |
| P00010 | B cell activation | 4.43E − 02 | 9.45E − 02 | 3.83E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 2 | HRAS, IKBKB |
| P00052 | TGF-beta signaling pathway | 9.73E − 02 | 1.67E − 01 | 6.78E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 2 | HRAS, SMAD5 |
| P00011 | Blood coagulation | 2.07E − 01 | 2.89E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | GP1BB |
| P00012 | Cadherin signaling pathway | 2.34E − 01 | 3.00E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 2 | CTNNB1, FYN |
| P00057 | Wntsignaling pathway | 2.59E − 01 | 3.07E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 3 | CTNNB1, TP53, SMAD5 |
| P00056 | VEGF signaling pathway | 2.86E − 01 | 3.27E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | HRAS |
| Pathway Ontology | |||||||
| PW:0000125 | G protein signaling | 5.82E − 03 | 3.10E − 02 | 1.26E − 01 | 1.86E − 01 | 1 | LTB4R |
| PW:0000297 | platelet-derived growth factor signaling | 5.82E − 03 | 3.10E − 02 | 1.26E − 01 | 1.86E − 01 | 1 | JAK2 |
| PW:0000143 | insulin signaling | 1.05E − 02 | 3.36E − 02 | 1.36E − 01 | 3.37E − 01 | 2 | SOCS1, STAT5B |
| PW:0000330 | Bone morphogenetic proteins signaling | 2.86E − 02 | 6.53E − 02 | 2.65E − 01 | 9.15E − 01 | 1 | SMAD5 |
| PW:0000599 | altered canonical Wntsignaling | 2.86E − 02 | 6.53E − 02 | 2.65E − 01 | 9.15E − 01 | 1 | CTNNB1 |
| PW:0000508 | platelet aggregation | 3.42E − 02 | 6.84E − 02 | 2.78E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | GP1BB |
| PW:0000234 | innate immune response | 6.18E − 02 | 1.10E − 01 | 4.46E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | TLR2 |
| PW:0000278 | autophagy | 1.04E − 01 | 1.39E − 01 | 5.65E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | ATG10 |
| PW:0000243 | vascular endothelial growth factor signaling | 1.30E − 01 | 1.49E − 01 | 6.03E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | FYN |
| PW:0000490 | transforming growth factor-beta Smad dependent signaling | 1.40E − 01 | 1.55E − 01 | 6.28E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | RUNX1 |
| SMPDB | |||||||
| SMP00320 | Intracellular Signalling Through Adenosine Receptor A2a and Adenosine | 1.55E − 02 | 2.46E − 02 | 4.52E − 02 | 4.65E − 02 | 2 | HRAS, IKBKB |
| SMP00391 | Insulin Signalling | 1.89E − 01 | 1.89E − 01 | 3.46E − 01 | 5.66E − 01 | 1 | HRAS |
Table 3.
The enriched pathway terms of the down regulated differentially expressed genes
| BIOCYC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathway ID | Pathway Name | P-value | FDR B&H | FDR B&Y | Bonferroni | Gene Count | Gene |
| 703092 | Citrulline-nitric oxide cycle | 8.83E − 02 | 2.53E − 01 | 8.24E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | NOS2 |
| 142419 | Phospholipases | 9.82E − 02 | 2.53E − 01 | 8.24E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | PLA2G2E, PLA2G2A |
| 545273 | Glycoaminoglycan-protein linkage region biosynthesis | 1.05E − 01 | 2.53E − 01 | 8.24E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | B3GAT1 |
| 545323 | Urate biosynthesis/inosine 5′-phosphate degradation | 1.05E − 01 | 2.53E − 01 | 8.24E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | NT5E |
| 142383 | Tryptophan degradation to 2-amino-3-carboxymuconate semialdehyde | 1.21E − 01 | 2.53E − 01 | 8.24E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | IDO1 |
| KEGG | |||||||
| 83051 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | 3.05E − 61 | 5.54E − 59 | 3.21E − 58 | 5.54E − 59 | 69 | IL10, IL10RA, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IL13RA1, TNFRSF9, IL17A, PDGFB, TNFSF12, IL17B, TNFRSF14, TNFRSF10C, CCL26,IL17F, TNFRSF4, IL22RA2, IL21, CCL7, CCR6, CCL11, CCL13, CCR8, CCL15, CCL16, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, KIT, CX3CL1, CXCL12, IL19, CCR10, XCR1, CXCL13, PPBP, IL23A, IFNA2, IFNAR1, IFNB1, IFNG, TGFBR1, LIF, CSF1R, CSF2, CSF2RB, CSF3R, IL20, IL22,, CD40, TNFRSF13C, LTA, IL1RAP, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL4R, IL5, IL6, IL6R, IL7, IL26, CXCR1, IL9, CXCR2 |
| 83078 | Hematopoietic cell lineage | 4.22E − 35 | 3.84E − 33 | 2.22E − 32 | 7.67E − 33 | 34 | HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, CD55, MME, KIT, CR2, TFRC, CD1A, CD3E, CSF1R, CSF2, CD8A, CD9, CSF3R, CD19, MS4A1, CD22, CD34, CD44, CD59, IL3, IL4, IL4R, IL5, IL6, IL6R, IL7 |
| 842771 | Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | 4.58E − 32 | 2.78E − 30 | 1.61E − 29 | 8.34E − 30 | 28 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IL17A, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, GATA3, IL17F, STAT6, IL21, RELA, IL23A, IFNG, IL22, RORC, IL2, IL4, IL4R, IL5, IL6 |
| 83077 | Jak-STAT signaling pathway | 4.56E − 26 | 1.19E − 24 | 6.86E − 24 | 8.30E − 24 | 33 | IL10, IL10RA, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IL13RA1, BCL2, STAT5A, STAT6, PTPN6, IL22RA2, IL21, IL19, IL23A, IFNA2, IFNAR1, IFNB1, IFNG, LIF, CSF2, CSF2RB, CSF3R, IL20, IL22, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL4R, IL5, IL6, IL6R, IL7, IL9 |
| 213780 | Tuberculosis | 3.41E − 25 | 6.89E − 24 | 3.99E − 23 | 6.20E − 23 | 34 | IL10, IL10RA, IL12A, IL12B, CEBPB, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, BCL2, CD209, BID, FCGR2A, FCGR2B, CARD9, NOS2, CASP3, RELA, TLR9, IL23A, IFNA2, IFNB1, IFNG, TIRAP, IRAK4, CD74, MAPK11, CTSS, IL6 |
| 83120 | Asthma | 4.56E − 24 | 8.30E − 23 | 4.80E − 22 | 8.30E − 22 | 18 | IL10, IL13, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, FCER1A, CCL11, CD40, IL3, IL4, IL5, IL9 |
| 125138 | Viral myocarditis | 2.26E − 16 | 2.06E − 15 | 1.19E − 14 | 4.12E − 14 | 17 | HLA-B, HLA-C, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, CD55, BID, CASP3, CD80, CD86, CD40 |
| 373901 | HTLV-I infection | 2.85E − 15 | 2.35E − 14 | 1.36E − 13 | 5.18E − 13 | 29 | HLA-B, PDGFB, HLA-C, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, ETS1, STAT5A, VCAM1, RELA, RELB, LCK, SLC2A1, TGFBR1, CD3E, CSF2, EGR1, EGR2, CD40, TNFRSF13C, LTA, IL2, IL6 |
| 213306 | Measles | 4.04E − 12 | 2.53E − 11 | 1.47E − 10 | 7.35E − 10 | 19 | IL12A, IL12B, IL13, CD46, TNFRSF10C, CD209, STAT5A, FCGR2B, RELA, TLR9, IFNA2, IFNAR1, IFNB1, IFNG, CD3E, IRAK4, IL2, IL4, IL6 |
| 83074 | Antigen processing and presentation | 7.12E − 12 | 4.32E − 11 | 2.50E − 10 | 1.30E − 09 | 15 | HLA-B, HLA-C, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, IFNG, CD8A, CD74, CTSS |
| 217173 | Influenza A | 4.98E − 11 | 2.75E − 10 | 1.59E − 09 | 9.07E − 09 | 20 | IL12A, IL12B, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1,HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, TNFRSF10C, RELA, IFNA2, IFNAR1, IFNB1, IFNG, IRAK4, MAPK11, IL6 |
| Pathway interaction database | |||||||
| 137933 | IL4-mediated signaling events | 7.74E − 16 | 8.36E − 14 | 4.40E − 13 | 8.36E − 14 | 17 | IL10, IL13RA1, CEBPB, AICDA, ETS1, CCL26, STAT5A, STAT6, PTPN6, PIGR, CCL11, THY1, EGR2, LTA, IL4, IL4R, IL5 |
| 137922 | IL12-mediated signaling events | 9.23E − 15 | 4.99E − 13 | 2.62E − 12 | 9.97E − 13 | 16 | IL12A, IL12B, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, STAT5A, STAT6, EOMES, NOS2, RELA, RELB, LCK, IFNG, CD3E, CD8A, IL2, IL4 |
| 138000 | IL23-mediated signaling events | 1.32E − 12 | 4.75E − 11 | 2.50E − 10 | 1.42E − 10 | 12 | IL12B, IL17A, IL17F, STAT5A, NOS2, IL19, RELA, IL23A, IFNG, CD3E, IL2, IL6 |
| 137929 | IL27-mediated signaling events | 1.43E − 11 | 3.87E − 10 | 2.04E − 09 | 1.55E − 09 | 10 | IL12A, IL12B, IL17A, GATA3, STAT5A, IFNG, EBI3, IL2, IL6, IL27 |
| 138058 | BCR signaling pathway | 3.00E − 07 | 4.05E − 06 | 2.13E − 05 | 3.24E − 05 | 10 | ETS1, PTPN6, FCGR2B, BTK, POU2F2, RELA, CD19, CD22, CD79A, CD79B |
| 138055 | TCR signaling in naive CD8 + T cells | 2.28E − 04 | 1.30E − 03 | 6.82E − 03 | 2.46E − 02 | 6 | PTPN6, LCK, CD3E, CD8A, CD80, CD86 |
| 137939 | Direct p53 effectors | 2.95E − 03 | 1.33E − 02 | 7.00E − 02 | 3.18E − 01 | 8 | SPP1, BCL2, TNFRSF10C, BID, CD82, MAP4K4, CX3CL1, LIF |
| 138081 | FAS (CD95) signaling pathway | 3.67E − 03 | 1.42E − 02 | 7.46E − 02 | 3.97E − 01 | 4 | BID, BTK, CASP3, MAPK11 |
| 137995 | HIV-1 Nef: Negative effector of Fas and TNF-alpha | 3.67E − 03 | 1.42E − 02 | 7.46E − 02 | 3.97E − 01 | 4 | BCL2, BID, CASP3, RELA |
| 137944 | IL1-mediated signaling events | 2.58E − 02 | 6.45E − 02 | 3.40E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 3 | TOLLIP, RELA, IRAK4 |
| REACTOME | |||||||
| 1269310 | Cytokine Signaling in Immune system | 3.81E − 46 | 2.02E − 43 | 1.39E − 42 | 2.02E − 43 | 86 | IL10, IL10RA, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IL13RA1, IL16, TRAF3, TNFRSF9, IL17A, HLA-B, PDGFB, HLA-C, TNFSF12, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, TNFRSF14, GATA3, PSMB10, BCL2, PTAFR, IL1RL2, IL17F, PTK2, STAT5A, STAT6, TNFRSF4, PTPN6, IL22RA2, TOLLIP, CCL11, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, KIT, NOS2, VCAM1, IL19, RAG1, RAG2, ZEB1, FN1, DUSP4, IRF8, CASP3, RELA, RELB, LCK, IL23A, S1PR1, IFNA2, IFNAR1, IFNB1, IFNG, LIF, CSF1R, CSF2, CSF2RB, CSF3R, EBI3, EGR1, IL20, CD80, CD86, IL22, CD40, IRAK4, CD44, TNFRSF13C, LTA, RORC, IL1RAP, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL4R, IL5, IL6, IL6R, IL7, IL27, IL9 |
| 1269318 | Signaling by Interleukins | 2.98E − 33 | 7.91E − 31 | 5.42E − 30 | 1.58E − 30 | 62 | IL10, IL10RA, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IL13RA1, IL16, IL17A, PDGFB, GATA3, PSMB10, BCL2, PTAFR, IL1RL2, IL17F, PTK2, STAT5A, STAT6, PTPN6, IL22RA2, TOLLIP, CCL11, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, KIT,NOS2, VCAM1, IL19, RAG1, RAG2, ZEB1, FN1, DUSP4, CASP3, RELA, LCK, IL23A, S1PR1, LIF, CSF1R, CSF2, CSF2RB, CSF3R, EBI3, IL20, CD80, CD86, IL22, IRAK4, RORC, IL1RAP, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL4R, IL5, IL6, IL6R,IL7, IL27, IL9 |
| 1269203 | Innate Immune System | 4.93E − 25 | 8.72E − 23 | 5.98E − 22 | 2.62E − 22 | 82 | MASP1, TRAF3, HLA-B, PDGFB, HLA-C, MAPKAPK2, CTSC, PECAM1, MBL2, PSMB10, CD55, CD46, BCL2, DEFB103B, PTAFR, CD209, PTK2, STAT6, DEFB1, DEFB4A, CFD, PTPN6, FCAR, FCER1A, PIGR, FCGR2A, CARD9, BTK, MIF, PLA2G2A, TOLLIP, C1R, C1S, C4A, PLAU, C4BPA, CCR6, MME, C6, C7, C8A, C8B, C9, KIT, NOS2, GPI, LILRA3, VTN, CLEC6A, FN1, ATG7, ITLN1, DUSP4, ICAM2, ICAM3, RELA, RELB, TLR9, LCK, PPBP, CFI, IFNA2, LGALS3, IFNB1, CSF2, CSF2RB, CD19, SIGIRR, CD80, CD86, TIRAP, IRAK4, CD44, CD59, MAPK11, IL2, IL3, IL5, CTSS, CXCR1, MASP2, CXCR2 |
| 1269171 | Adaptive Immune System | 1.51E − 15 | 1.15E − 13 | 7.86E − 13 | 8.03E − 13 | 52 | HLA-B, PDGFB, HLA-C, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, CTSC, HLA-DRB1, TNFRSF14, PSMB10, PTPN22, CD209, PTPN6, SLAMF6, FCGR2B, BTK, KIT, KLRB1, LILRB5, VCAM1, ICOSLG, LILRA1, LILRA3, LILRA2, ATG7, ICAM2, ICAM3, ICAM4, RELA, BTLA, LCK, CD1A, CD3E, CD8A, CD19, CD22, CD80, CD86, ICAM5, TIRAP, CD34, CD40, CD74, CD79A, CD79B, CTLA4, CTSS |
| 1269201 | Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell | 5.01E − 14 | 2.66E − 12 | 1.82E − 11 | 2.66E − 11 | 21 | HLA-B, HLA-C, SLAMF6, FCGR2B, KLRB1, LILRB5, VCAM1, LILRA1, LILRA3, LILRA2, ICAM2, ICAM3, ICAM4, CD1A, CD3E, CD8A, CD19, CD22, ICAM5, CD34, CD40 |
| 1269546 | Peptide ligand-binding receptors | 6.17E − 08 | 1.82E − 06 | 1.25E − 05 | 3.27E − 05 | 17 | CCR6, CCL13, CCR8, CCL16, CCL19, CCL20, CXCL11, XCL1, CX3CL1, CXCL12, CCR10, XCR1, CXCL13, PPBP, EDNRB, CXCR1, CXCR2 |
| 1269545 | Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors) | 4.71E − 07 | 1.14E − 05 | 7.79E − 05 | 2.50E − 04 | 21 | PTAFR, PTGER4, CCR6, CCL13,CCR8,CCL16, CCL19, CCL20, CXCL11, XCL1, CX3CL1, CXCL12, CCR10, XCR1, CXCL13, GPR183, PPBP, S1PR1, EDNRB, CXCR1, CXCR2 |
| 1269340 | Hemostasis | 1.15E − 04 | 1.47E − 03 | 1.01E − 02 | 6.09E − 02 | 26 | CD244, PDGFB, PECAM1, GATA3, PTK2, CFD, PTPN6, MIF, PLAU, NOS2, SELE, SELPLG, FN1, LCK, PPBP, IFNA2, IFNB1, CSF2, CSF2RB, CD9, CD44, CD48, CD74, IL2, IL3, IL5 |
| 1269501 | MAPK family signaling cascades | 3.27E − 04 | 3.40E − 03 | 2.33E − 02 | 1.74E − 01 | 15 | PDGFB, PSMB10, PTK2, KIT, RAG1, RAG2, FN1, DUSP4, CSF2, CSF2RB, IL2, IL3, IL5, IL6, IL6R |
| 1269240 | Toll Like Receptor TLR6:TLR2 Cascade | 3.46E − 04 | 3.40E − 03 | 2.33E − 02 | 1.84E − 01 | 8 | MAPKAPK2, BTK, DUSP4, RELA, SIGIRR, TIRAP, IRAK4, MAPK11 |
| Gen MAPP | |||||||
| MAP00400 | Phenylalanine tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis | 1.38E − 01 | 5.02E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | BID |
| MAP_kinase_activity | MAP kinase activity | 1.38E − 01 | 5.02E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | MAPK11 |
| MAP00010 | Glycolysis Gluconeogenesis | 2.47E − 01 | 5.02E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 2 | BID, GPI |
| MAP00030 | Pentose phosphate | 2.70E − 01 | 5.02E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | GPI |
| MAP00590 | Prostaglandin and leukotriene metabolism | 2.96E − 01 | 5.02E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | PLA2G2A |
| MAP00500 | Starch and sucrose metabolism | 3.34E − 01 | 5.02E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | GPI |
| MAP00330 | Arginine and proline metabolism | 5.05E − 01 | 5.81E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | NOS2 |
| MAP00380 | Tryptophan metabolism | 5.73E − 01 | 5.81E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | IDO1 |
| MAP00561 | Glycerolipid metabolism | 5.81E − 01 | 5.81E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | PLA2G2A |
| MSigDB C2 BIOCARTA (v6.0) | |||||||
| M5883 | Genes encoding secreted soluble factors | 4.86E − 27 | 7.82E − 25 | 4.43E − 24 | 7.82E − 25 | 46 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IL16, IL17A, PDGFB, TNFSF12, IL17B, CCL26, IL17F, CCL7, CCL11, CCL13, CCL15, CCL16, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, CX3CL1, CXCL12, IL19, CXCL13, PPBP, IL23A, IFNA2, IFNB1, IFNG, LIF, CSF2, EBI3, IL20, IL22, LTA, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL5, IL6, IL7, IL26, IL9 |
| M17406 | Cytokine Network | 2.71E − 22 | 2.18E − 20 | 1.24E − 19 | 4.36E − 20 | 15 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IL16, IL17A, IFNB1, IFNG, LTA, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL5, IL6, IL9 |
| M6910 | Cytokines and Inflammatory Response | 5.19E − 21 | 2.78E − 19 | 1.58E − 18 | 8.35E − 19 | 16 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, IFNB1, IFNG, CSF2, LTA, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL5, IL6, IL7 |
| M5885 | Ensemble of genes encoding ECM-associated proteins including ECM-affilaited proteins, ECM regulators and secreted factors | 7.80E − 21 | 3.14E − 19 | 1.78E − 18 | 1.26E − 18 | 57 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, MASP1, IL16, IL17A, PDGFB, TNFSF12, CTSC, IL17B, MBL2, CCL26, IL17F, CD209, PLAU, CCL7, CCL11, CCL13, CCL15, CCL16, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, CX3CL1, CXCL12, IL19, CLEC6A, ITLN1, CXCL13, ITLN2, PPBP, IL23A, IFNA2, LGALS3, IFNB1, IFNG, LIF, CSF2, EBI3, IL20, IL22, LTA, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL5, CTSS, IL6, IL7, IL26, IL9, MASP2 |
| M5889 | Ensemble of genes encoding extracellular matrix and extracellular matrix-associated proteins | 4.62E − 17 | 1.49E − 15 | 8.43E − 15 | 7.44E − 15 | 61 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, MASP1, IL16, IL17A, PDGFB, TNFSF12, SPP1, CTSC,IL17B, MBL2, CCL26, IL17F, CD209, PLAU, CCL7,CCL11, CCL13, CCL15,CCL16, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20,CCL22, CCL24, CXCL11,XCL1, CX3CL1, CXCL12, IL19, VTN,CLEC6A, FN1, ITLN1, CXCL13,ITLN2, PPBP, IL23A,IFNA2, LGALS3, IFNB1, IFNG, TGFBI, LIF, CSF2, EBI3, IL20, IL22, LTA, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL5, CTSS, IL6, IL7, IL26, IL9, MASP2 |
| M1467 | The Co-Stimulatory Signal During T-cell Activation | 4.81E − 11 | 7.03E − 10 | 3.98E − 09 | 7.74E − 09 | 9 | HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, ICOSLG, LCK, CD3E, CD80, CD86, CTLA4, IL2 |
| M3952 | Cells and Molecules involved in local acute inflammatory response | 1.02E − 05 | 7.46E − 05 | 4.22E − 04 | 1.64E − 03 | 5 | C6, C7, VCAM1, SELPLG,IL6 |
| M18215 | Role of Tob in T-cell activation | 3.16E − 05 | 2.21E − 04 | 1.25E − 03 | 5.08E − 03 | 5 | IFNG, TGFBR1, CD3E, IL2, IL4 |
| M13968 | HIV-I Nef: negative effector of Fas and TNF | 6.46E − 04 | 3.15E − 03 | 1.78E − 02 | 1.04E − 01 | 6 | BCL2,PTK2, BID, CASP3, RELA, ARHGDIB |
| M13247 | T Cytotoxic Cell Surface Molecules | 1.90E − 03 | 6.80E − 03 | 3.85E − 02 | 3.06E − 01 | 3 | CD3E, CD8A, THY1 |
| Panther DB | |||||||
| P00036 | Interleukin signaling pathway | 6.51E − 19 | 2.47E − 17 | 1.05E − 16 | 2.47E − 17 | 22 | IL10,IL10RA, IL12A,IL13, IL13RA1, IL17A, MAPKAPK2, IL17F, STAT5A, STAT6, IL21, IL23A, IL2, IL4, IL4R, IL5, IL6, IL6R, IL7, CXCR1, IL9, CXCR2 |
| P00031 | Inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway | 4.36E − 07 | 8.28E − 06 | 3.50E − 05 | 1.66E − 05 | 16 | CCL26, CCL7, CCR6, CCL11, CCL13, CCR8, CCL18, CCL20, CCL22, CX3CL1, CCR10, XCR1, IFNAR1, IFNG, CXCR1, CXCR2 |
| P00053 | T cell activation | 7.23E − 05 | 8.13E − 04 | 3.44E − 03 | 2.75E − 03 | 8 | HLA-DPA1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DRA, LCK, CD3E, CD80, CD86, CD74 |
| P00010 | B cell activation | 8.56E − 05 | 8.13E − 04 | 3.44E − 03 | 3.25E − 03 | 7 | PTPN6, BTK, CD19, CD22, CD79A, CD79B, MAPK11 |
| P00054 | Toll receptor signaling pathway | 2.14E − 03 | 1.62E − 02 | 6.86E − 02 | 8.12E − 02 | 5 | TOLLIP, RELA, TLR9, IFNB1, IRAK4 |
| P00006 | Apoptosis signaling pathway | 2.67E − 03 | 1.69E − 02 | 7.14E − 02 | 1.01E − 01 | 7 | BCL2, BID, BCL2L11, CASP3, RELA, RELB, LTA |
| P00035 | Interferon-gamma signalingpathway | 1.42E − 02 | 7.69E − 02 | 3.25E − 01 | 5.39E − 01 | 3 | PTPN6, IFNG, MAPK11 |
| P00046 | Oxidative stress response | 5.17E − 02 | 1.86E − 01 | 7.88E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 3 | BCL2, DUSP4, MAPK11 |
| P00047 | PDGF signaling pathway | 8.39E − 02 | 2.44E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 5 | PDGFB, MAPKAPK2, ETS1, STAT5A, STAT6 |
| P00034 | Integrin signalling pathway | 5.94E − 01 | 7.28E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 3 | ITGAE, PTK2, FN1 |
| Pathway Ontology | |||||||
| PW:0000104 | intrinsic apoptotic | 1.82E − 03 | 7.63E − 02 | 3.30E − 01 | 7.63E − 02 | 4 | BCL2, BID, BCL2L11, CASP3 |
| PW:0000515 | Interleukin-10 signaling | 7.84E − 01 | 1.57E − 01 | 6.78E − 01 | 6.78E − 01 | 1 | IL10 |
| PW:0000516 | Interleukin-6 signaling | 7.84E − 01 | 1.57E − 01 | 6.78E − 01 | 6.78E − 01 | 1 | IL6 |
| PW:0000499 | Nuclear Factor Kappa B signaling | 9.58E − 01 | 1.60E − 01 | 6.91E − 01 | 6.91E − 01 | 2 | RELA, RELB |
| PW:0000009 | programmed cell death | 1.00E + 00 | 1.80E − 01 | 7.78E − 01 | 7.78E − 01 | 2 | BCL2, CASP3 |
| PW:0000102 | The extracellular signal-regulated RAF/MEK/ERK signaling | 8.14E − 02 | 2.18E − 01 | 9.44E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 2 | SPP1, S1PR1 |
| PW:0000529 | angiotensin (1-7) signaling | 8.83E − 02 | 2.18E − 01 | 9.44E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | MME |
| PW:0000106 | extrinsic apoptotic | 1.05E − 01 | 2.45E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | CASP3 |
| PW:0000559 | hexosamine biosynthetic | 1.21E − 01 | 2.55E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | GPI |
| PW:0000228 | G protein signaling via Galphai family | 1.53E − 01 | 2.80E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | S1PR1 |
| SMPDB | |||||||
| SMP00094 | Sulindac Pathway | 1.21E − 01 | 4.52E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | PLA2G2A |
| SMP00040 | Glycolysis | 2.14E − 01 | 4.52E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | GPI |
| SMP00063 | Tryptophan Metabolism | 2.70E − 01 | 4.52E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | IDO1 |
| SMP00379 | NifedipinePathway | 2.83E − 01 | 4.52E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | EDNRB |
| SMP00006 | Tyrosine Metabolism | 3.59E − 01 | 4.84E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | MIF |
| SMP00320 | Intracellular Signalling Through Adenosine Receptor A2a and Adenosine | 4.57E − 01 | 4.84E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 1 | MAPK11 |
Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis for DEGs
The GO enrichment analysis of up- and down-regulated genes can be split into three groups: BP, CC, and MF are listed in Tables 4, 5. In terms of BP, the up-regulated genes were mainly involved in regulation of immune system process, response to biotic stimulus and other functions; the down-regulated genes were mainly associated in regulation of immune system process, cytokine-mediated signaling pathway and other functions. As far as CC is concerned, the up-regulated genes were mainly involved in the side of membrane, receptor complex and other functions; the down-regulated genes were mainly located in the cell surface, leaflet of membrane layers and other functions. As for MF, the up-regulated genes mainly participated in kinase binding, signaling receptor binding and other functions; the down-regulated genes mainly participated in cytokine receptor binding, signaling receptor binding and other functions (Tables 4, 5).
Table 4.
The enriched GO terms of the up regulated differentially expressed genes
| GO ID | CATEGORY | GO Name | P Value | FDR B&H | FDR B&Y | Bonferroni | Gene Count | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0002682 | BP | Regulation of immune system process | 1.53E − 44 | 5.68E − 41 | 5.00E − 40 | 5.68E − 41 | 56 | KLRK1, ATG5, JAK1, JAK2, IFIH1, PDCD1, TRAF2, TRAF6, IKZF3, CD247, ZBTB16, ABL1, HLA-A, IKBKE, CD99, BST2, LILRB2, TBX21, TLR2, LAG3, HRAS, PSMB9, C1QBP, CLEC7A, SERPING1, XBP1, GBP1, SOCS1, C2, CCR1, IKZF1, CCL5, IRF7, CTNNB1, RUNX1, SLAMF7, IKBKB, LCP2, ITGAL, FYN, IL18RAP, ITGB2, IL2RG, IL18R1, KLRC1, ZAP70, GFI1, KLRD1, CX3CR1, STAT1, TP53, NLRP3, STAT3, STAT5B, CEACAM1, IFNAR2 |
| GO:0009607 | BP | Response to biotic stimulus | 6.86E − 35 | 6.36E − 32 | 5.59E − 31 | 2.54E − 31 | 48 | KLRK1, ATG5, JAK1, JAK2, IFIH1, TRAF6, IKZF3, ATG10, ABL1, HLA-A, IKBKE, BST2, LILRB2, TBX21, TLR2, GZMB, LAG3, HRAS, PSMB9, C1QBP, CLEC7A, SERPING1, XBP1, GBP1, SOCS1, C2, IRF5, CCL5, IRF7, CCR5, GNLY, SLAMF7, IKBKB, FYN, IFI35, IL18RAP, ITGB2, MAP4K2, GFI1, KLRD1, CX3CR1, STAT1, TP53, NLRP3, MX1, STAT5B, CEACAM1, IFNAR2 |
| GO:0006952 | BP | Defense response | 1.12E − 33 | 5.92E − 31 | 5.21E − 30 | 4.14E − 30 | 49 | KLRK1, JAK1, JAK2, IFIH1, TRAF6, HLA-A, IKBKE, BST2, LILRB2, TLR2, GZMB, LAG3, HRAS, PSMB9, C1QBP, CLEC7A, SERPING1, GBP1, CCRL2, SOCS1, C2, CCR1, IRF5, CCL5, IRF7, CCR5, GNLY, LTB4R, SLAMF7, IKBKB, ITGAL, FYN, IFI35, IL18RAP, ITGB2, IL18R1, MAP4K2, GFI1, KLRD1, CX3CR1, STAT1, TP53, NLRP3, STAT3, STAT4, MX1, STAT5B, CEACAM1, IFNAR2 |
| GO:0001816 | BP | Cytokine production | 3.84E − 27 | 1.29E − 24 | 1.14E − 23 | 1.42E − 23 | 34 | KLRK1, ATG5, JAK2, IFIH1, TRAF2, TRAF6, CD247, ABL1, IKBKE, BST2, LILRB2, TBX21, TLR2, LAG3, HRAS, C1QBP, CLEC7A, XBP1, GBP1, SOCS1, IRF5, CCL5, IRF7, CTNNB1, RUNX1, LCP2, IL18RAP, IL18R1, CX3CR1, STAT1, NLRP3, STAT3, STAT5B, CEACAM1 |
| GO:0034097 | BP | Response to cytokine | 2.23E − 26 | 6.90E − 24 | 6.07E − 23 | 8.28E − 23 | 38 | JAK1, JAK2, IFIH1, TRAF2, TRAF6, HLA-A, IKBKE, BST2, TLR2, PSMB9, XBP1, GBP1, CCRL2, SOCS1, CCR1, IRF5, CCL5, IRF7, CCR5, CTNNB1, RUNX1, IKBKB, FYN, IFI35, IL18RAP, ITGB2, IL2RG, IL18R1, GFI1, CX3CR1, STAT1, TP53, STAT3, STAT4, MX1, STAT5B, CEACAM1, IFNAR2 |
| GO:0042110 | BP | T cell activation | 1.68E − 25 | 4.43E − 23 | 3.90E − 22 | 6.21E − 22 | 28 | CCND3, KLRK1, ATG5, PDCD1, TRAF6, ZBTB16, ABL1, LILRB2, TBX21, LAG3, CLEC7A, XBP1, SOCS1, IKZF1, CCL5, CTNNB1, RUNX1, ITGAL, FYN, ITGB2, IL2RG, IL18R1, ZAP70, TP53, NLRP3, STAT3, STAT5B, CEACAM1 |
| GO:0045321 | BP | Leukocyte activation | 6.65E − 23 | 1.30E − 20 | 1.14E − 19 | 2.47E − 19 | 36 | CCND3, KLRK1, ATG5, JAK2, PDCD1, TRAF6, IKZF3, ZBTB16, ABL1, BST2, LILRB2, TBX21, TLR2, LAG3, CLEC7A, XBP1, SOCS1, IKZF1, CCL5, CTNNB1, RUNX1, SLAMF7, LCP2, ITGAL, FYN, IL18RAP, ITGB2, IL2RG, IL18R1,ZAP70, CX3CR1,TP53, NLRP3, STAT3, STAT5B, CEACAM1 |
| GO:0001775 | BP | Cell activation | 2.83E − 22 | 5.00E − 20 | 4.40E − 19 | 1.05E − 18 | 37 | CCND3, KLRK1, ATG5, JAK2, PDCD1, TRAF6, IKZF3, ZBTB16, ABL1, BST2, LILRB2, TBX21, TLR2, LAG3, CLEC7A, XBP1, SOCS1, IKZF1, CCL5, CTNNB1, RUNX1, SLAMF7, LCP2, ITGAL, FYN, IL18RAP, ITGB2, IL2RG, IL18R1, ZAP70, CX3CR1, TP53, NLRP3, STAT3, STAT5B, CEACAM1, GP1BB |
| GO:0080134 | BP | Regulation of response to stress | 3.88E − 18 | 3.59E − 16 | 3.16E − 15 | 1.44E − 14 | 34 | KLRK1, JAK1, JAK2, IFIH1, TRAF2, TRAF6, ABL1, IKBKE, MAP4K1, TLR2, LAG3, HRAS, PSMB9, C1QBP, CLEC7A, SERPING1, XBP1, SOCS1, CCL5, IRF7, CTNNB1, IKBKB, FYN, IL18RAP, ITGB2, MAP4K2, GFI1, CX3CR1, STAT1, TP53, NLRP3, STAT5B, CEACAM1, IFNAR2 |
| GO:0051094 | BP | Positive regulation of developmental process | 1.52E − 15 | 1.00E − 13 | 8.79E − 13 | 5.64E − 12 | 31 | JAK1, JAK2, TRAF6, ZBTB16, ABL1, LILRB2, TBX21, TLR2, C1QBP, CLEC7A, XBP1, SOCS1, CCR1, IKZF1, CCL5, CTNNB1, RUNX1, IKBKB, FYN, ITGB2, IL2RG, ZAP70, GFI1, CX3CR1, STAT1, TP53, NLRP3, STAT3, STAT5B, SMAD5, CEACAM1 |
| GO:0098552 | CC | Side of membrane | 1.17E − 11 | 1.54E − 09 | 9.47E − 09 | 3.08E − 09 | 18 | KLRK1, PDCD1, TRAF2, TRAF6, HLA-A, TLR2, LAG3, CCRL2, CCR1, CCR5, SLAMF7, IKBKB, ITGAL, FYN, ITGB2, IL2RG, KLRD1, CX3CR1 |
| GO:0043235 | CC | Receptor complex | 3.20E − 10 | 2.81E − 08 | 1.73E − 07 | 8.44E − 08 | 15 | TRAF2, TRAF6, CD247, TLR2, IKBKB, LCP2, ITGAL, IL18RAP, ITGB2, IL2RG, IL18R1, KLRC1, ZAP70, KLRD1, CEACAM1 |
| GO:0009986 | CC | Cell surface | 2.20E − 09 | 9.68E − 08 | 5.96E − 07 | 5.81E − 07 | 19 | KLRK1, PDCD1, HLA-A, BST2, LILRB2, TLR2, LAG3, C1QBP, CLEC7A, CCRL2, CCR1, CCR5, SLAMF7, ITGAL, ITGB2, IL2RG, KLRD1, CX3CR1, CEACAM1 |
| GO:0005887 | CC | Integral component of plasma membrane | 2.88E − 07 | 6.90E − 06 | 4.25E − 05 | 7.59E − 05 | 21 | KLRK1, TRAF2, TRAF6, CD99, LILRB2, TLR2, CCRL2, CCR1, CCR5, LTB4R, IKBKB, ITGAL, IL18RAP, ITGB2, IL2RG, IL18R1, KLRC1, CX3CR1, CEACAM1, GP1BB, IFNAR2 |
| GO:0098805 | CC | Whole membrane | 8.24E − 06 | 1.55E − 04 | 9.56E − 04 | 2.18E − 03 | 19 | ATG5, JAK2, TRAF2, TRAF6, HLA-A, IKBKE, BST2, LILRB2, TLR2, IRF7, LTB4R, CTNNB1, IKBKB, LCP2, ITGAL, FYN, ITGB2, ZAP70, CEACAM1 |
| GO:0044194 | CC | cytolytic granule | 1.84E − 04 | 2.70E − 03 | 1.66E − 02 | 4.87E − 02 | 2 | GZMB, GNLY |
| GO:0000790 | CC | Nuclear chromatin | 9.72E − 04 | 1.17E − 02 | 7.18E − 02 | 2.57E − 01 | 16 | IKZF3, ZBTB16, TBX21, XBP1, IRF5, IKZF1, IRF7, CTNNB1, RUNX1, GFI1, STAT1, TP53, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5B, SMAD5 |
| GO:0090575 | CC | RNA polymerase II transcription factor complex | 5.30E − 03 | 4.21E − 02 | 2.59E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 4 | CTNNB1, RUNX1, TP53, STAT3 |
| GO:0005667 | CC | Transcription factor complex | 5.46E − 03 | 4.21E − 02 | 2.59E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 6 | IKZF1, CTNNB1, RUNX1, TP53, STAT3, SMAD5 |
| GO:0048471 | CC | Perinuclear region of cytoplasm | 8.69E − 03 | 4.78E − 02 | 2.94E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 8 | TRAF6, ABL1, HRAS, CTNNB1, FYN, CX3CR1, STAT1, MX1 |
| GO:0019900 | MF | Kinase binding | 6.20E − 10 | 1.90E − 07 | 1.27E − 06 | 2.82E − 07 | 19 | CCND3, KLRK1, JAK2, TRAF2, TRAF6, CD247, ABL1, C1QBP, XBP1, SOCS1, CCL5, CTNNB1, IKBKB, ITGB2, MAP4K2, TP53, STAT3, CEACAM1, IFNAR2 |
| GO:0005102 | MF | Signaling receptor binding | 7.06E − 08 | 3.57E − 06 | 2.39E − 05 | 3.21E − 05 | 23 | KLRK1, JAK1, JAK2, TRAF2, TRAF6, ABL1, HLA-A, LILRB2, TLR2, LAG3, C1QBP, CLEC7A, CCRL2, SOCS1, CCL5, CTNNB1, FYN, ITGB2, KLRD1, STAT1, TP53, STAT3, STAT5B |
| GO:0044212 | MF | Transcription regulatory region DNA binding | 1.45E − 07 | 5.42E − 06 | 3.63E − 05 | 6.57E − 05 | 17 | TRAF6, IKZF3, ZBTB16, TBX21, XBP1, IRF5, IKZF1, IRF7, CTNNB1, RUNX1, GFI1, STAT1, TP53, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5B, SMAD5 |
| GO:0038023 | MF | Signaling receptor activity | 3.46E − 07 | 1.13E − 05 | 7.54E − 05 | 1.58E − 04 | 21 | KLRK1, CD247, LILRB2, TLR2, LAG3, CLEC7A, CCRL2, CCR1, CCL5, CCR5, LTB4R, ITGAL, IL18RAP, ITGB2, IL2RG, IL18R1, KLRC1, KLRD1, CX3CR1, GP1BB, IFNAR2 |
| GO:0043565 | MF | Sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding | 5.76E − 06 | 9.35E − 05 | 6.27E − 04 | 2.62E − 03 | 16 | IKZF3, ZBTB16, ABL1, TBX21, XBP1, IRF5, IKZF1, IRF7, RUNX1, STAT1, TP53, NLRP3, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5B, SMAD5 |
| GO:0016772 | MF | Transferase activity, transferring phosphorus-containing groups | 8.11E − 06 | 1.19E − 04 | 7.98E − 04 | 3.69E − 03 | 20 | CCND3, JAK1, JAK2, TRAF2, TRAF6, ABL1, IKBKE, MAP4K1, HRAS, SOCS1, CCL5, CTNNB1, IKBKB, LCP2, FYN, ZAP70, MAP4K2, TP53, STAT3, CEACAM1 |
| GO:0070011 | MF | Peptidase activity, acting on L-amino acid peptides | 1.03E − 05 | 1.38E − 04 | 9.27E − 04 | 4.66E − 03 | 16 | ATG5, JAK2, IFIH1, TRAF2, TRAF6, BST2, GZMB, PSMB9, CLEC7A, SERPING1, C2, FYN, STAT1, TP53, NLRP3, STAT3 |
| GO:0000977 | MF | RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | 1.25E − 05 | 1.58E − 04 | 1.06E − 03 | 5.67E − 03 | 13 | IKZF3, ZBTB16, TBX21, XBP1, IKZF1, IRF7, RUNX1, STAT1, TP53, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5B, SMAD5 |
| GO:0035639 | MF | Purine ribonucleoside triphosphate binding | 3.00E − 04 | 1.75E − 03 | 1.17E − 02 | 1.37E − 01 | 17 | JAK1, JAK2, IFIH1, ABL1, IKBKE, MAP4K1, HRAS, CUL9, GBP1, RUNX1, IKBKB, FYN, ZAP70, MAP4K2, TP53, NLRP3, MX1 |
| GO:0032559 | MF | Adenylribonucleotide binding | 1.44E − 03 | 6.51E − 03 | 4.36E − 02 | 6.57E − 01 | 14 | JAK1, JAK2, IFIH1, ABL1, IKBKE, MAP4K1, CUL9, RUNX1, IKBKB, FYN, ZAP70, MAP4K2, TP53, NLRP3 |
BP biological process, CC cellular component, MF molecular functions
Table 5.
The enriched GO terms of the down regulated differentially expressed genes
| GO ID | Category | GO Name | P Value | FDR B&H | FDR B&Y | Bonferroni | Gene Count | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0002682 | BP | Regulation of immune system process | 1.87E − 103 | 9.66E − 100 | 8.82E − 99 | 9.66E − 100 | 153 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IRGM, MASP1, TRAF3, IL17A, CEBPB, CD244, HLA-B, HLA-C, IDO1, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, MAPKAPK2, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, CTSC, HLA-DRB1, PECAM1, MBL2, TNFRSF14, GATA3, ETS1, PSMB10, CD55, PTPN22, CD46, BCL2, PTAFR, CD83, PTGER4, IL1RL2, CD209, PTK2, STAT5A, STAT6, TNFRSF4, CFD, PTPN6, SLAMF6, FCER1A, PIGR, FCGR2A, FCGR2B, CARD9, BTK, MIF, IL21, C1R, C1S, C4A, C4BPA, CCL7, CCR6, C6, C7, C8A, CCL19, C8B, CCL20, C9, CCL24, TAL1, XCL1, KIT, CX3CL1, KLRB1, CXCL12, VCAM1, SELE, GPI, RAG1, DPP4, ICOSLG, LILRA1, LILRA2, ZEB1, VTN, CLEC6A, ATG7, ICAM2, ICAM3, ICAM4, CXCL13, CASP3, AIRE, RELA, BTLA, RELB, GPR183, TLR9, LCK, CFI, CR2, IL23A, IFNA2, LGALS3, TFRC,IFNB1, IFNG, LIF, CD1A, CD3E, CSF1R, CSF2, CD8A, THY1, CD9, CSF3R, CD19, TIGIT, MS4A1, EBI3, CD22, IL20, CD80, CD86, ICAM5, TIRAP, CD34, CD40, IRAK4, CD44, CD48, TNFRSF13C, CD59, CD74, CD79A, CD79B, LTA, RORC, CTLA4, PAX5, HAMP, MAPK11, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL4R, IL5, CTSS, IL6, IL6R, IL7, IL27, MASP2, CXCR2 |
| GO:0019221 | BP | Cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | 1.05E − 84 | 1.35E − 81 | 1.23E − 80 | 5.40E − 81 | 131 | IL10, IL10RA, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IRGM, MASP1, TRAF3, IL17A, ILF3, CEBPB, CD244, HLA-B, AICDA, HLA-C, IDO1, TAGAP, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, MAPKAPK2, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, MBL2, TNFRSF14, GATA3, PSMB10, CD55, PTPN22, CD46, BCL2, DEFB103B, PTAFR, PTGER4, IL1RL2, CCL26, CD209, STAT5A, BID, DEFB1, DEFB4A, CFD, PTPN6, SLAMF6, FCGR2B, CARD9, BTK, KLRF2, MIF, IL21, PLA2G2A, TOLLIP, C1R, C1S, C4A, C4BPA, CCL7, CCL11, CCL13, BATF3, CCL15, CCL16, C6, C7, CCL18, C8A, CCL19, C8B, CCL20, CCL22, C9, CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, CX3CL1, NOS2, CXCL12, VCAM1, SELE, RAG2, LILRA2, CLEC6A, BCL2L11, ATG7, ITLN1, ICAM2, ICAM3, IRF8, CXCL13, CASP3, RELA, RELB, TLR9, PPBP, CFI, CR2, IL23A, IFNA2, EDNRB, LGALS3, IFNAR1, IFNB1, IFNG, CSF1R, CSF2, CD8A, CSF2RB, MS4A1, EGR1, SIGIRR, CD80, CD86, TIRAP, CD40, IRAK4, CD44, CD74, CD79B, LTA, HAMP, MAPK11, IL1RAP, IL2, IL4, IL4R, CTSS, IL6, IL6R, IL27, MASP2 |
| GO:0009607 | BP | RESPONSE to biotic stimulus | 7.42E − 81 | 7.65E − 78 | 6.99E − 77 | 3.83E − 77 | 120 | IL10, IL10RA, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IL13RA1, IRGM, IL16, TRAF3, TNFRSF9, IL17A, CEBPB, HLA-B, PDGFB, HLA-C, TNFSF12, SPP1, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, MAPKAPK2, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, TNFRSF14, GATA3, ETS1, PSMB10, BCL2, PTAFR, IL1RL2, CCL26, IL17F,STAT5A, STAT6, TNFRSF4, PTPN6, IL22RA2, NFIL3, BTK, MIF, IL21, TOLLIP, CCL7, CCR6, CCL11, CCL13, CCR8, CCL15, MME, CCL16, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22,CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, KIT, CX3CL1, NOS2, CXCL12, VCAM1, IL19, SELE, SELPLG, CCR10, XCR1, TCF7, ZEB1, FN1, IRF8, CXCL13, CASP3, RELA, RELB, PPBP, IL23A, S1PR1, IFNA2, TFRC, IFNAR1, IFNB1, IFNG, LIF, CSF1R, CSF2, CSF2RB, CSF3R, EBI3, EGR1, SIGIRR, IL20, CD80, CD86, TIRAP, IL22, CD40, IRAK4, CD44, TNFRSF13C, CD74, LTA, RORC, HAMP, MAPK11, IL1RAP, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL4R, IL5, IL6, IL6R, IL7, IL26, IL27, CXCR1, IL9, CXCR2 |
| GO:0009607 | BP | Response to biotic stimulus | 7.42E − 81 | 7.65E − 78 | 6.99E − 77 | 3.83E − 77 | 131 | IL10, IL10RA, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IRGM, MASP1, TRAF3, IL17A, ILF3, CEBPB, CD244, HLA-B, AICDA, HLA-C, IDO1, TAGAP, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, MAPKAPK2, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, MBL2, TNFRSF14, GATA3, PSMB10, CD55, PTPN22, CD46, BCL2, DEFB103B, PTAFR, PTGER4, IL1RL2, CCL26, CD209, STAT5A, BID, DEFB1, DEFB4A, CFD, PTPN6, SLAMF6, FCGR2B, CARD9, BTK, KLRF2, MIF, IL21, PLA2G2A, TOLLIP, C1R, C1S, C4A, C4BPA, CCL7, CCL11, CCL13, BATF3, CCL15, CCL16, C6, C7, CCL18, C8A, CCL19, C8B, CCL20, CCL22, C9, CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, CX3CL1, NOS2, CXCL12, VCAM1, SELE, RAG2, LILRA2, CLEC6A, BCL2L11, ATG7, ITLN1, ICAM2, ICAM3, IRF8, CXCL13, CASP3, RELA, RELB, TLR9, PPBP, CFI, CR2, IL23A, IFNA2, EDNRB, LGALS3, IFNAR1, IFNB1, IFNG, CSF1R, CSF2, CD8A, CSF2RB, MS4A1, EGR1, SIGIRR, CD80, CD86, TIRAP, CD40, IRAK4, CD44, CD74, CD79B, LTA, HAMP, MAPK11, IL1RAP, IL2, IL4, IL4R, CTSS, IL6, IL6R, IL27, MASP2 |
| GO:0034097 | BP | Response to cytokine | 3.04E − 80 | 2.61E − 77 | 2.39E − 76 | 1.57E − 76 | 120 | IL10, IL10RA, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IL13RA1, IRGM, IL16, TRAF3, TNFRSF9, IL17A, CEBPB, HLA-B, PDGFB, HLA-C, TNFSF12, SPP1, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, MAPKAPK2, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, TNFRSF14, GATA3, ETS1, PSMB10, BCL2, PTAFR, IL1RL2, CCL26, IL17F, STAT5A, STAT6, TNFRSF4, PTPN6, IL22RA2, NFIL3, BTK, MIF, IL21, TOLLIP, CCL7, CCR6, CCL11, CCL13, CCR8, CCL15, MME, CCL16, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, KIT, CX3CL1, NOS2, CXCL12, VCAM1, IL19, SELE, SELPLG, CCR10, XCR1, TCF7, ZEB1, FN1, IRF8, CXCL13, CASP3, RELA, RELB, PPBP, IL23A, S1PR1, IFNA2, TFRC, IFNAR1, IFNB1, IFNG, LIF, CSF1R, CSF2, CSF2RB, CSF3R, EBI3, EGR1, SIGIRR, IL20, CD80, CD86, TIRAP, IL22, CD40, IRAK4, CD44, TNFRSF13C, CD74, LTA, RORC, HAMP, MAPK11, IL1RAP, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL4R, IL5, IL6, IL6R, IL7, IL26, IL27, CXCR1, IL9, CXCR2 |
| GO:0042110 | BP | T cell activation | 8.30E − 63 | 2.25E − 60 | 2.06E − 59 | 4.28E − 59 | 77 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, CEBPB, CD244, IDO1, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, TNFRSF14, GATA3, PSMB10, CD55, PTPN22, CD46, BCL2, CD83, PTGER4, IL1RL2, CD209, STAT5A, STAT6, TNFRSF4, EOMES, PTPN6, SLAMF6, FCGR2B, IL21, CCR6, CCL19, CCL20, XCL1, KIT, CXCL12, VCAM1, RAG1, RAG2, DPP4, ICOSLG, TCF7, ZEB1, CASP3, AIRE, BTLA, RELB, GPR183, LCK, IL23A, IFNA2, LGALS3, TFRC, IFNAR1, IFNB1, IFNG, CD3E, CD8A, THY1, TIGIT, EBI3, EGR1, CD80, CD86, CD44, CD48, TNFRSF13C, CD74, RORC, CTLA4, IL2, IL4, IL4R, IL6, IL6R, IL7, IL27 |
| GO:0001816 | BP | Cytokine production | 8.07E − 58 | 1.81E − 55 | 1.65E − 54 | 4.16E − 54 | 87 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, TRAF3, TNFRSF9, IL17A, CEBPB, CD244, IDO1, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, MAPKAPK2, IL17B, MBP, TNFRSF14, GATA3, CD55, PTPN22, CD46, PTAFR, CD83, PTGER4, IL1RL2, IL17F, STAT5A, STAT6, TNFRSF4, EOMES, PTPN6, SLAMF6, FCER1A, FCGR2B, CARD9, BTK, KLRF2, MIF, IL21, CCL19, CCL20, XCL1, KIT, CX3CL1, NOS2, IL19, ICOSLG, LILRA2, CLEC6A, FN1, IRF8, AIRE, RELA, RELB, TLR9, IL23A, IFNA2, IFNAR1, IFNB1, IFNG, CD3E, CSF1R, CSF2, TIGIT, EBI3, EGR1,SIGIRR, CD80, CD86, TIRAP, CD34, CD40, IRAK4, TNFRSF13C, CD74,LTA, RORC, MAPK11, IL1RAP, IL2, IL4, IL4R, IL6, IL6R, IL7, IL26, IL27, IL9 |
| GO:0002694 | BP | Regulation of leukocyte activation | 7.07E − 57 | 1.52E − 54 | 1.39E − 53 | 3.65E − 53 | 77 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, CEBPB, CD244, IDO1, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, CTSC, TNFRSF14, GATA3, CD55, PTPN22, CD46, BCL2, PTAFR, CD83, IL1RL2, CD209, STAT5A, STAT6, TNFRSF4, PTPN6, FCER1A, FCGR2B, BTK, MIF, IL21, CCR6, CCL19, CCL20, XCL1, CX3CL1, VCAM1, RAG1, DPP4, ICOSLG, ZEB1, CASP3, BTLA, GPR183, TLR9, LCK, IL23A, IFNA2, LGALS3, TFRC, IFNB1, IFNG, CD3E, THY1, CD19, TIGIT, EBI3, CD22, CD80, CD86, TIRAP, CD40, CD44, TNFRSF13C, CD74, RORC, CTLA4, HAMP, IL2, IL4, IL4R, IL5, IL6, IL6R, IL7, IL27 |
| GO:0006954 | BP | Inflammatory response | 5.64E − 55 | 1.12E − 52 | 1.02E − 51 | 2.91E − 51 | 82 | IL10, IL12B, IL13, IRGM, IL17A, CEBPB, IDO1, SPP1, MAPKAPK2, CTSC, IL17B, MBL2, GATA3, ETS1, PTAFR, PLA2G2E, PTGER4, IL1RL2, CCL26, IL17F, STAT5A, TNFRSF4, IL22RA2, FCER1A, FCGR2B, BTK,MIF, IL21, PLA2G2A, TOLLIP, C4A, CCL7, CCR6,CCL11, CCL13, CCL15, CCL16, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, KIT, CX3CL1, NOS2, VCAM1, SELE, XCR1, FN1, NT5E, CXCL13, RELA, RELB, TLR9, PPBP, IL23A, IFNA2, EDNRB, IFNG, CSF1R, SIGIRR, IL20, TIRAP, IL22, CD40, CD44, LTA, HAMP, IL1RAP, IL2, CDH5, IL4, IL4R, IL5, CTSS, IL6, IL6R, IL27, IL9, CXCR2 |
| GO:0007155 | BP | Cell adhesion | 3.87E − 42 | 3.50E − 40 | 3.20E − 39 | 2.00E − 38 | 91 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, CEBPB,CD244, IDO1, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, SPP1, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, PECAM1, MBP, TNFRSF14, GATA3, ETS1, CD55, PTPN22, CD46, BCL2, PTAFR, CD83, ITGAE, PTGER4, IL1RL2, CD209, PTK2, STAT5A, PTPN6, FCGR2B, IL21, PLAU, CCL11, CCR8, CCL19, XCL1, KIT, MAP4K4, CX3CL1, CXCL12, VCAM1, SELE, SELPLG, RAG1, DPP4, ICOSLG, VTN, FN1, BCL2L11, NT5E, ICAM2, ICAM3, ICAM4, CXCL13, CASP3, RELA, BTLA, LCK, IL23A, S1PR1, IFNA2, LGALS3, TFRC, IFNB1, IFNG, TGFBI, ARHGDIB, CD3E, THY1, CD9, CSF3R, TIGIT, EBI3, CD22, CD80, CD86, ICAM5, CD34, CD44, TNFRSF13C, CD74, CTLA4,IL1RAP, IL2, CDH5, IL4, IL4R, IL6, IL6R, IL7 |
| GO:0009986 | CC | Cell surface | 8.40E − 48 | 1.04E − 45 | 6.72E − 45 | 3.09E − 45 | 83 | IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IL13RA1, TNFRSF9, IL17A, CD244, HLA-B, PDGFB, HLA-C, HLA-DMA, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, PECAM1, MBL2, MBP, TNFRSF14, CD55, CD46, TNFRSF10C, CD83, ITGAE, CD209, TNFRSF4, FCER1A, FCGR2B, FCGRT, MIF, PLAU, CCR6, CCR8, MME, KIT, CX3CL1, CXCL12, VCAM1, CCR10, DPP4, ICOSLG, XCR1, NT5E, BTLA, CR2, S1PR1, LGALS3, TFRC, IFNG, TGFBR1, CD1A, CD3E, CSF1R, CD8A, THY1, CD9, CSF3R, CD19, TIGIT, MS4A1, EBI3, CD22, CD80, CD86, CD34, CD40, CD44, CD48, TNFRSF13C, CD59, CD74, CD79A, CD79B, RORC, CTLA4, CDH5, IL4, CTSS, IL6, IL6R, CXCR1, CXCR2 |
| GO:0097478 | CC | Leaflet of membrane bilayer | 8.80E − 48 | 1.04E − 45 | 6.72E − 45 | 3.24E − 45 | 70 | IL12B, IL13, IL13RA1, TRAF3, TNFRSF9, IL17A, CD244, HLA-B, HLA-C, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, PECAM1, TNFRSF14, PTPN22, CD83, ITGAE, CD209, TNFRSF4, FCER1A, FCGR2B, FCGRT, CCR6, CCR8, KIT, CXCL12, VCAM1, CCR10, ICOSLG, XCR1, BTLA, LCK, CR2, S1PR1, LGALS3, TFRC, IFNG, CD1A, CD3E, BCAP31, CD8A, THY1, CD9, CSF3R, CD19, MS4A1, EBI3, CD22, CD80, CD86, CD34,CD40, CD44, CD48, TNFRSF13C, CD59,CD74, CD79A, CD79B, RORC, CTLA4, CDH5, IL4, IL6, IL6R, CXCR1, CXCR2 |
| GO:0031226 | CC | Intrinsic component of plasma membrane | 4.10E − 24 | 3.01E − 22 | 1.96E − 21 | 1.51E − 21 | 75 | IL13RA1, TRAF3, TNFRSF9,TNFSF12, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DRA, CD46,PTAFR, CD83, ITGAE, IL1RL2, TNFRSF4, CD82, SLAMF6,FCAR, FCER1A, PIGR, FCGR2B, KLRF2, TOLLIP, CCR6, CCR8, MME, C6, C7, C8A, C8B, C9, KIT, VCAM1, SELE, SELPLG, CCR10, ICOSLG, XCR1, LILRA2, ICAM2, ICAM3, ICAM4, BTLA, GPR183, S1PR1, SLC2A1, EDNRB, TFRC, IFNAR1, TGFBR1,CD1A, CD3E, BCAP31, CSF1R, CD8A, THY1, CSF2RB, CD9, CSF3R, CD19, MS4A1, EBI3, CD22, ICAM5, CD34, CD40, CD44, CD48, CD59, CD74, CD79B, CTLA4, IL1RAP, IL4R, IL6, IL6R, CXCR2 |
| GO:0098589 | CC | Membrane region | 7.35E − 11 | 1.93E − 09 | 1.25E − 08 | 2.70E − 08 | 24 | PECAM1, CD55, CD46, STAT6, FCER1A, BTK, MME, SELE, SELPLG, DPP4, ITLN1, CASP3, LCK, S1PR1, SLC2A1, EDNRB, TGFBR1, CD1A, CD8A, THY1, CD19, MS4A1, CD48, CD79A |
| GO:0043235 | CC | Receptor complex | 3.10E − 10 | 6.71E − 09 | 4.35E − 08 | 1.14E − 07 | 26 | IL12B, IL13RA1, TRAF3, ITGAE, PTPN6, PIGR, TOLLIP, KIT, ITLN1, CR2, TFRC, TGFBR1, CD3E, CSF1R, CD8A, CSF2RB, CSF3R, EBI3, CD40, CD44, CD74, CD79A, CD79B, IL4R, IL6, IL6R |
| GO:0030141 | CC | Secretory granule | 3.67E − 07 | 5.20E − 06 | 3.37E − 05 | 1.35E − 04 | 29 | PDGFB, CTSC, PECAM1, CD55, CD46, PTAFR, CFD, PTPN6, FCAR, PIGR, FCGR2A, MIF, PLA2G2A, TOLLIP, PLAU, MME, KIT, GPI, LILRA3, FN1, ATG7, PPBP, LGALS3, CD9, CD44, CD59, CTSS, CXCR1, CXCR2 |
| GO:0005764 | CC | Lysosome | 1.31E − 06 | 1.49E − 05 | 9.69E − 05 | 4.81E − 04 | 25 | IL13, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, CTSC, HLA-DRB1, FCER1A, PIGR, BTK, TOLLIP,KIT, DPP4, TLR9, IFNAR1, CD34, CD74, IL4, IL4R, CTSS, CXCR2 |
| GO:0005794 | CC | Golgi apparatus | 4.18E − 03 | 2.00E − 02 | 1.30E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 31 | IRGM, HLA-B, PDGFB, HLA-C,SPP1, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, CTSC, HLA-DRB1, CD55, CD46, DEFB103B, DEFB1,DEFB4A, MME, VCAM1, DPP4, VTN, TLR9, SLC2A1, TGFBI, BCAP31, CD44, CD59, CD74, CD79B, B3GAT1, CTLA4 |
| GO:0048471 | CC | Perinuclear region of cytoplasm | 2.87E − 02 | 8.46E − 02 | 5.49E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 16 | TNFSF12, SPP1, PTPN22, BCL2, BTK, PLA2G2A, TOLLIP, CX3CL1, NOS2, SELE, ATG7,TFRC, TRAF4, BCAP31, CD34, CTLA4 |
| GO:0044297 | CC | Cell body | 9.03E − 02 | 2.08E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 14 | PDGFB, MBP, PTGER4, FCGR2B, C4A, MME, CX3CL1, CASP3,IFNG, CD3E, THY1, CD22, CD40, IL6R |
| GO:0030054 | CC | Cell junction | 9.70E − 02 | 2.20E − 01 | 1.00E + 00 | 1.00E + 00 | 21 | PECAM1, CD46, PTK2, PTPN6, C4A, PLAU, MME, KIT, MAP4K4, DPP4, LCK, SLC2A1, TGFBR1, TRAF4, CD3E, THY1, CD9, CD44,CD59, HAMP, CDH5 |
| GO:0005126 | MF | Cytokine receptor binding | 8.37E − 54 | 6.01E − 51 | 4.30E − 50 | 6.01E − 51 | 59 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, TRAF3, TNFSF12, GATA3, DEFB103B, CCL26, IL17F, BID, DEFB1, DEFB4A, MIF, IL21, TOLLIP, CCL7, CCL11, CCL13, CCL15, CCL16, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, CX3CL1, CXCL12, CXCL13, CASP3, TLR9, PPBP, IL23A, IFNA2, IFNB1, IFNG, TGFBR1, LIF, TRAF4, CSF2, EBI3, IL20, IL22,IRAK4, CD44, LTA, IL1RAP, IL2,IL3, CDH5,IL4, IL5, IL6, IL6R, IL7, IL27, IL9 |
| GO:0005102 | MF | Signaling receptor binding | 3.78E − 49 | 9.05E − 47 | 6.48E − 46 | 2.72E − 46 | 108 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IL16, TRAF3, IL17A, CEBPB, CD244, HLA-B, PDGFB, HLA-C, TNFSF12, HLA-DOB, SPP1, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, IL17B, MBL2, GATA3, DEFB103B, CCL26, IL17F, PTK2, BID, DEFB1, DEFB4A, PTPN6, PIGR, MIF, IL21, TOLLIP, CCL7, CCL11, CCL13, CCL15, CCL16, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, CX3CL1, CXCL12, VCAM1, IL19, SELPLG, GPI, DPP4, ICOSLG, VTN, FN1, ATG7, ICAM2, ICAM3, ICAM4, CXCL13, CASP3, TLR9, LCK, PPBP, IL23A, S1PR1, IFNA2, EDNRB, LGALS3, IFNB1, IFNG, TGFBI, TGFBR1, LIF, TRAF4, CD3E,BCAP31, CSF2, CD8A, THY1, CD9, TIGIT, MS4A1, EBI3, CD22, IL20, CD86, ICAM5, TIRAP, IL22, IRAK4, CD44, CD74, LTA, HAMP, IL1RAP, IL2, IL3, CDH5, IL4, IL5, IL6, IL6R, IL7, IL26, IL27, IL9 |
| GO:0030545 | MF | Chemokine receptor binding | 2.63E − 22 | 2.36E − 20 | 1.69E − 19 | 1.89E − 19 | 20 | DEFB103B, CCL26, DEFB1, DEFB4A, CCL7, CCL11,CCL13, CCL15, CCL16, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, CX3CL1, CXCL12, CXCL13, PPBP |
| GO:0098772 | MF | Molecular function regulator | 1.42E − 18 | 6.80E − 17 | 4.86E − 16 | 1.02E − 15 | 71 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, IL13, IRGM, IL16, IL17A, PDGFB, TNFSF12, SPP1, TAGAP, CTSC, IL17B, CD46, BCL2, DEFB103B, CCL26, IL17F, EOMES, DEFB4A, MIF, IL21, C4A, CCL7, CCL11, CCL13, CCL15, CCL16, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, CX3CL1, NOS2, CXCL12, IL19, GPI, FN1, CXCL13, CASP3, SKI, PPBP, IL23A, IFNA2, LGALS3, IFNB1, IFNG, LIF, ARHGDIB, TRAF4, CSF2, THY1, EBI3, IL20, TIRAP, IL22, LTA, HAMP, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL5, IL6, IL6R, IL7, IL26,IL27, IL9 |
| GO:0004888 | MF | Transmembranesignaling receptor activity | 2.09E − 12 | 8.81E − 11 | 6.31E − 10 | 1.50E − 09 | 50 | IL10RA, IL12B, IL13RA1, HLA-DOB, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA, TNFRSF14, TNFRSF10C, PTAFR, PTGER4, IL1RL2, TNFRSF4, PTPN6, IL22RA2, FCER1A, PIGR, FCGR2B, CCR6, CCR8, KIT, KLRB1, LILRB5, SELE, CCR10, XCR1, LILRA1, GPR183, TLR9, CR2, S1PR1, EDNRB, IFNAR1, IFNG, TGFBR1, CD3E, CSF1R, CSF2RB, CSF3R, EBI3, CD44, CD74, CD79A, CD79B, IL1RAP, IL4R, IL6R, CXCR1, CXCR2 |
| GO:0001664 | MF | G protein-coupled receptor binding | 3.80E − 12 | 1.52E − 10 | 1.08E − 09 | 2.73E − 09 | 23 | DEFB103B, CCL26, DEFB1, DEFB4A, CCL7, CCL11, CCL13, CCL15, CCL16, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, CCL24, CXCL11, XCL1, CX3CL1, CXCL12, CXCL13, PPBP, S1PR1, EDNRB, IL2 |
| GO:0044877 | MF | Protein-containing complex binding | 1.24E − 11 | 4.46E − 10 | 3.19E − 09 | 8.92E − 09 | 48 | PDGFB, HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, SPP1, HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, PTK2, FCAR, FCER1A, PIGR, FCGR2A, FCGR2B, FCGRT, MIF, C8A, C8B, CX3CL1, CXCL12, VCAM1, DPP4, LILRA2, VTN, FN1, BCL2L11, ICAM2, ICAM3, ICAM4, CASP3, RELA, LCK, IFNA2, LGALS3, IFNB1, TGFBI, TGFBR1, CD3E, BCAP31, CD8A, THY1, CD9, MS4A1, CD22, ICAM5, CD44, CD74, CDH5, CTSS |
| GO:0042802 | MF | IDENTICAL protein binding | 1.81E − 07 | 3.93E − 06 | 2.81E − 05 | 1.30E − 04 | 51 | IL12B, MASP1, CEBPB, AICDA, PDGFB, CTSC, PECAM1, ETS1, BCL2, IL17F, PTK2, STAT6, DEFB1, CARD9, BTK, KLRF2, MIF, C1S, MME, XCL1, KIT, NOS2, RAG1, DPP4, ICOSLG, TCF4, IKZF2, VTN, FN1, ATG7, ITLN1, AIRE, RELA, RELB, TLR9, LCK, CR2, SLC2A1, LGALS3, TFRC, TRAF4, CD3E, CSF1R, CD8A, TIGIT, TIRAP, CD74, CD79A, CD79B, CDH5, IL6R |
| GO:0046983 | MF | Protein dimerization activity | 6.79E − 07 | 1.19E − 05 | 8.51E − 05 | 4.88E − 04 | 42 | IL10, IL12A, IL12B, MASP1, CEBPB, PDGFB, HLA-DQA1, PECAM1, GATA3, BCL2, IL17F, BID, CARD9, KLRF2, CCL11, MME, TAL1, XCL1, KIT, NOS2, RAG1, DPP4, TCF4, IKZF2, BCL2L11, ATG7, CXCL13, RELA, TLR9, CR2, LGALS3, TFRC, TGFBR1, TRAF4, CD3E, CSF1R, CD8A, TIRAP, CD79A, CD79B, CDH5, IL6R |
| GO:0016301 | MF | Kinase activity | 1.16E − 05 | 1.54E − 04 | 1.10E − 03 | 8.29E − 03 | 40 | IL12B, IRGM, PDGFB, MAPKAPK2, PTPN22, PTK2, TNFRSF4, PTPN6, FCER1A, BTK, MIF, CCL19, TAL1, KIT, MAP4K4, NOS2, GPI, DUSP4, CASP3, TLR9, LCK, IL23A, IFNG, TGFBR1, TRAF4, CSF1R, THY1, CD19, EGR1, TIRAP, CD40, IRAK4, CD44, CD74, MAPK11, IL2, IL3, IL4, IL6, IL6R |
BP biological process, CC cellular component, MF molecular functions
PPI network construction and module analysis
To determine the expression relationships among up- and down-regulated genes, we inputted the up- and down-regulated genes to STRING PPI database. Then, PPI networks were visualized using the cytoscape software. As a result, a PPI network for up-regulated genes had 2912 nodes and 5967 edges (Fig. 6). Among these nodes, TP53, HRAS, CTNNB1, FYN, ABL1, STAT3, STAT1, JAK2, C1QBP, XBP1, BST2, CD99 and IFI35 were identified as hub genes with highest node degree distribution, betweenness centrality, stress centrality, closeness centrality and lowest clustering coefficient are listed in Table 6. The scatter plots for this network are shown in Fig. 7a–e. Enrichment analysis showed that the genes were mainly associated with measles, natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity, HTLV-I infection, regulation of immune system process, viral myocarditis, Jak-STAT signaling pathway, herpes simplex infection, hemostasis, response to biotic stimulus, cytokine signaling in immune system, integral component of plasma membrane and response to biotic stimulus. A PPI network for down-regulated genes had 3083 nodes and 6491 edges (Fig. 8). Among these nodes, MAPK11, RELA, LCK, KIT, EGR1, IL20, ILF3, CASP3, IL19, ATG7, GPI and S1PR1 were identified as hub genes with highest node degree distribution, betweenness centrality, stress centrality, closeness centrality and lowest clustering coefficient are listed in Table 6. The scatter plots for this network are shown in Fig. 9a–e. Enrichment analysis showed that the genes were mainly associated with tuberculosis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), HTLV-I infection, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, cytokine-mediated signaling pathway, regulation of immune system process, response to biotic stimulus, response to cytokine, cytokine production, innate immune system, glycolysis, gluconeogenesis and the extracellular signal-regulated RAF/MEK/ERK signaling.
Fig. 6.
Protein–protein interaction network of up regulated genes. Green nodes ( ) denotes up regulated genes; Blue lines (
) denotes up regulated genes; Blue lines ( ) denotes edges (Interactions)
) denotes edges (Interactions)
Table 6.
Topology table for up and down regulated genes
| Regulation | Node | Degree | Betweenness | Stress | Closeness | Clustering Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up | TP53 | 682 | 0.308256 | 69419762 | 0.44613 | 0.001042 |
| Up | HRAS | 543 | 0.243425 | 36147274 | 0.454702 | 0.003568 |
| Up | CTNNB1 | 454 | 0.17049 | 60805652 | 0.403018 | 0.002042 |
| Up | FYN | 396 | 0.117564 | 12570856 | 0.436236 | 0.010907 |
| Up | ABL1 | 362 | 0.118179 | 7631538 | 0.470883 | 0.015228 |
| Up | JAK2 | 258 | 0.054758 | 7164820 | 0.434802 | 0.021748 |
| Up | STAT3 | 253 | 0.05294 | 16470742 | 0.398767 | 0.02108 |
| Up | JAK1 | 223 | 0.032981 | 6336566 | 0.40235 | 0.019876 |
| Up | TRAF6 | 216 | 0.074546 | 12176648 | 0.395301 | 0.010207 |
| Up | STAT1 | 213 | 0.045072 | 12845532 | 0.387307 | 0.023031 |
| Up | TRAF2 | 171 | 0.047572 | 11238720 | 0.357837 | 0.007981 |
| Up | ZAP70 | 153 | 0.018814 | 3346658 | 0.375226 | 0.028294 |
| Up | IKBKB | 140 | 0.040639 | 5153454 | 0.403521 | 0.017575 |
| Up | MX1 | 125 | 0.057134 | 6475242 | 0.352549 | 0.002194 |
| Up | STAT5B | 118 | 0.012758 | 2934924 | 0.377415 | 0.057801 |
| Up | ZBTB16 | 105 | 0.029011 | 4339392 | 0.371064 | 0.00696 |
| Up | GP1BB | 104 | 0.024662 | 2308816 | 0.350596 | 0.009335 |
| Up | RUNX1 | 95 | 0.021204 | 3579930 | 0.370309 | 0.010526 |
| Up | C1QBP | 89 | 0.043687 | 7011558 | 0.334675 | 0 |
| Up | TLR2 | 85 | 0.019615 | 2401022 | 0.374839 | 0.034734 |
| Up | SOCS1 | 85 | 0.019595 | 1846156 | 0.398713 | 0.072829 |
| Up | SMAD5 | 82 | 0.024208 | 4462604 | 0.336687 | 0.003011 |
| Up | ITGB2 | 72 | 0.025976 | 3349086 | 0.351061 | 0.008607 |
| Up | IKZF1 | 72 | 0.011714 | 1722502 | 0.373157 | 0.034038 |
| Up | CCND3 | 71 | 0.025956 | 2361424 | 0.357661 | 0.008048 |
| Up | ATG5 | 60 | 0.020131 | 2294688 | 0.333219 | 0.00678 |
| Up | IFIH1 | 59 | 0.023459 | 2059722 | 0.333945 | 0.001753 |
| Up | STAT4 | 58 | 0.002561 | 797810 | 0.366902 | 0.082275 |
| Up | PSMB9 | 55 | 0.0248 | 2740768 | 0.310739 | 0 |
| Up | IKZF3 | 47 | 0.005026 | 756292 | 0.361346 | 0.053654 |
| Up | GFI1 | 46 | 0.007563 | 811180 | 0.357266 | 0.013527 |
| Up | IRF7 | 44 | 0.010411 | 1198488 | 0.338804 | 0.008457 |
| Up | MAP4K1 | 44 | 0.006432 | 851692 | 0.348957 | 0.046512 |
| Up | CD247 | 43 | 0.00724 | 710792 | 0.349292 | 0.058693 |
| Up | LCP2 | 41 | 0.003353 | 442356 | 0.338331 | 0.07439 |
| Up | CCR5 | 39 | 0.010719 | 942222 | 0.343359 | 0.043185 |
| Up | IRF5 | 34 | 0.006222 | 736764 | 0.339277 | 0.012478 |
| Up | GZMB | 29 | 0.01009 | 1297184 | 0.313584 | 0 |
| Up | IL2RG | 27 | 0.005284 | 347620 | 0.3463 | 0.071225 |
| Up | TBX21 | 23 | 0.003781 | 493896 | 0.328704 | 0.023715 |
| Up | XBP1 | 21 | 0.004344 | 440004 | 0.329933 | 0 |
| Up | HLA-A | 19 | 0.007447 | 822622 | 0.311637 | 0 |
| Up | MAP4K2 | 18 | 0.002038 | 190802 | 0.334636 | 0.045752 |
| Up | CCR1 | 18 | 0.004542 | 722956 | 0.323912 | 0.019608 |
| Up | IFNAR2 | 17 | 0.003686 | 214358 | 0.335872 | 0.169118 |
| Up | ITGAL | 17 | 0.004258 | 302784 | 0.285588 | 0.058824 |
| Up | ATG10 | 16 | 0.00303 | 204222 | 0.278618 | 0.075 |
| Up | CEACAM1 | 15 | 0.003567 | 815206 | 0.308991 | 0 |
| Up | CLEC7A | 13 | 0.006223 | 422114 | 0.302253 | 0 |
| Up | CUL9 | 10 | 0.001917 | 66468 | 0.352806 | 0.111111 |
| Up | SERPING1 | 10 | 0.004857 | 805696 | 0.203225 | 0 |
| Up | NLRP3 | 10 | 0.002325 | 208526 | 0.304371 | 0 |
| Up | LTB4R | 9 | 0.002812 | 970594 | 0.242059 | 0 |
| Up | GBP1 | 9 | 0.001571 | 66852 | 0.307489 | 0 |
| Up | LILRB2 | 9 | 0.004803 | 191694 | 0.287677 | 0 |
| Up | CD99 | 8 | 0.002792 | 99752 | 0.324129 | 0 |
| Up | KLRK1 | 7 | 0.003445 | 544176 | 0.26256 | 0 |
| Up | BST2 | 7 | 1.93E − 04 | 36836 | 0.324273 | 0 |
| Up | KLRD1 | 7 | 0.001389 | 97132 | 0.22517 | 0.047619 |
| Up | KLRC1 | 5 | 0.003221 | 307724 | 0.286234 | 0.1 |
| Up | IL18R1 | 4 | 0.00118 | 348338 | 0.245924 | 0 |
| Up | PDCD1 | 4 | 0.001374 | 55018 | 0.303894 | 0.166667 |
| Up | SLAMF7 | 4 | 0.00206 | 191070 | 0.233272 | 0 |
| Up | C2 | 4 | 0.001446 | 96444 | 0.245447 | 0 |
| Up | IFI35 | 3 | 6.93E − 04 | 23710 | 0.323301 | 0 |
| Up | LAG3 | 2 | 4.23E − 06 | 1074 | 0.245695 | 0 |
| Up | IL18RAP | 2 | 1.95E − 04 | 52194 | 0.233609 | 0 |
| Down | MAPK11 | 421 | 0.179413 | 26118522 | 0.388195 | 0.003744 |
| Down | RELA | 285 | 0.126824 | 20931198 | 0.37804 | 0.004645 |
| Down | LCK | 267 | 0.108492 | 11305268 | 0.405534 | 0.014108 |
| Down | KIT | 221 | 0.051071 | 10158794 | 0.36783 | 0.015014 |
| Down | EGR1 | 195 | 0.060886 | 6334914 | 0.384414 | 0.016178 |
| Down | ILF3 | 179 | 0.093546 | 7805892 | 0.330116 | 3.14E − 04 |
| Down | CASP3 | 175 | 0.070326 | 10842834 | 0.355181 | 0.005123 |
| Down | PTK2 | 153 | 0.049652 | 8738870 | 0.356704 | 0.005246 |
| Down | PTPN6 | 150 | 0.044684 | 5323296 | 0.365645 | 0.021477 |
| Down | BCL2 | 150 | 0.062256 | 5772430 | 0.365862 | 0.009128 |
| Down | BTK | 137 | 0.022999 | 3449618 | 0.35359 | 0.019429 |
| Down | STAT5A | 126 | 0.024378 | 5096524 | 0.35745 | 0.027429 |
| Down | TGFBR1 | 123 | 0.048955 | 6050368 | 0.349257 | 0.007464 |
| Down | CSF1R | 117 | 0.01327 | 3411424 | 0.344835 | 0.005894 |
| Down | FN1 | 116 | 0.052141 | 5201654 | 0.335331 | 0.003148 |
| Down | TCF4 | 115 | 0.044569 | 5794596 | 0.333586 | 0.005492 |
| Down | TRAF3 | 113 | 0.038869 | 4088284 | 0.341886 | 0.010588 |
| Down | STAT6 | 102 | 0.026319 | 3212830 | 0.363486 | 0.039216 |
| Down | GATA3 | 97 | 0.03064 | 3006348 | 0.350689 | 0.018471 |
| Down | IRAK4 | 90 | 0.015953 | 2526624 | 0.344064 | 0.010986 |
| Down | TCF7 | 90 | 0.029254 | 4190222 | 0.323796 | 9.99E − 04 |
| Down | ATG7 | 88 | 0.032475 | 4557368 | 0.323761 | 0 |
| Down | PSMB10 | 86 | 0.037084 | 3948650 | 0.316536 | 0 |
| Down | EGR2 | 78 | 0.014472 | 2942228 | 0.323966 | 0.002331 |
| Down | CEBPB | 77 | 0.01563 | 2080316 | 0.347208 | 0.028708 |
| Down | TLR9 | 75 | 0.01613 | 2504516 | 0.335623 | 0.017658 |
| Down | ETS1 | 74 | 0.015119 | 2229504 | 0.345493 | 0.023695 |
| Down | MBP | 69 | 0.02034 | 1946892 | 0.33211 | 0.008099 |
| Down | CD40 | 63 | 0.012367 | 1565636 | 0.343144 | 0.030722 |
| Down | PTPN22 | 63 | 0.005103 | 648768 | 0.333009 | 0.039939 |
| Down | CXCL13 | 62 | 0.033409 | 4616616 | 0.255924 | 0.002644 |
| Down | CD44 | 61 | 0.027234 | 2621678 | 0.352941 | 0.016393 |
| Down | DUSP4 | 56 | 0.005964 | 877004 | 0.343106 | 0.046753 |
| Down | TOLLIP | 55 | 0.020841 | 1681614 | 0.32948 | 0.011448 |
| Down | TRAF4 | 54 | 0.017367 | 1322968 | 0.327447 | 0.012579 |
| Down | TFRC | 51 | 0.020865 | 2030850 | 0.323932 | 7.84E − 04 |
| Down | TAL1 | 49 | 0.012074 | 1294452 | 0.327273 | 0.02551 |
| Down | BATF3 | 48 | 0.009925 | 1237560 | 0.309471 | 0.011525 |
| Down | SKI | 47 | 0.009912 | 1441494 | 0.325026 | 0.010176 |
| Down | MAP4K4 | 46 | 0.00723 | 923942 | 0.334966 | 0.025121 |
| Down | ARHGDIB | 43 | 0.008007 | 998356 | 0.325267 | 0.00443 |
| Down | BID | 40 | 0.007734 | 665116 | 0.336026 | 0.046154 |
| Down | BCL2L11 | 39 | 0.006742 | 718322 | 0.327935 | 0.032389 |
| Down | NOS2 | 39 | 0.012743 | 915032 | 0.332218 | 0.010796 |
| Down | AICDA | 38 | 0.016444 | 2864544 | 0.288094 | 0 |
| Down | GPI | 37 | 0.009895 | 1400722 | 0.322202 | 0 |
| Down | CSF2RB | 37 | 0.005071 | 681430 | 0.345571 | 0.100601 |
| Down | TIRAP | 37 | 0.009595 | 1070880 | 0.324 | 0.033033 |
| Down | CD9 | 36 | 0.01001 | 838100 | 0.302685 | 0.019048 |
| Down | CDH5 | 35 | 0.00845 | 737334 | 0.306177 | 0.013445 |
| Down | AIRE | 35 | 0.010893 | 2140272 | 0.292753 | 0 |
| Down | CD82 | 32 | 0.008605 | 911074 | 0.323659 | 0.020161 |
| Down | IFNAR1 | 31 | 0.006943 | 536824 | 0.340902 | 0.062366 |
| Down | CD3E | 30 | 0.006779 | 602042 | 0.338614 | 0.078161 |
| Down | LGALS3 | 30 | 0.009645 | 633882 | 0.302536 | 0 |
| Down | VTN | 30 | 0.009755 | 750034 | 0.299445 | 0.006897 |
| Down | CD8A | 29 | 0.008368 | 709958 | 0.334638 | 0.029557 |
| Down | CSF3R | 28 | 0.008229 | 711320 | 0.334093 | 0.029101 |
| Down | EOMES | 28 | 0.005201 | 513270 | 0.277597 | 0.018519 |
| Down | VCAM1 | 28 | 0.008841 | 718322 | 0.31732 | 0.010582 |
| Down | ZEB1 | 27 | 0.006122 | 1257304 | 0.288851 | 0 |
| Down | MME | 27 | 0.009061 | 1835908 | 0.290624 | 0.014245 |
| Down | MIF | 27 | 0.00826 | 611016 | 0.321596 | 0.005698 |
| Down | IKZF2 | 26 | 0.003358 | 390862 | 0.3129 | 0 |
| Down | MAPKAPK2 | 26 | 0.004801 | 451358 | 0.310909 | 0.024615 |
| Down | PLAU | 25 | 0.008975 | 593824 | 0.317844 | 0.01 |
| Down | DPP4 | 25 | 0.010538 | 1418468 | 0.265231 | 0.006667 |
| Down | RORC | 25 | 0.00722 | 1661398 | 0.278729 | 0.013333 |
| Down | CD55 | 24 | 0.010279 | 705586 | 0.303102 | 0 |
| Down | IL4R | 24 | 0.00238 | 270352 | 0.331181 | 0.083333 |
| Down | CD19 | 23 | 0.001702 | 211728 | 0.304301 | 0.090909 |
| Down | IRF8 | 23 | 0.005195 | 372574 | 0.329904 | 0.019763 |
| Down | IL4 | 23 | 0.004905 | 441962 | 0.296246 | 0.019763 |
| Down | RELB | 23 | 0.003464 | 286340 | 0.326336 | 0.055336 |
| Down | PAX5 | 22 | 0.002896 | 300204 | 0.291726 | 0.021645 |
| Down | CXCR2 | 22 | 0.006344 | 1097670 | 0.26098 | 0.047619 |
| Down | IL16 | 22 | 0.008141 | 455702 | 0.300821 | 0 |
| Down | SPP1 | 21 | 0.005095 | 320668 | 0.307124 | 0.014286 |
| Down | THY1 | 21 | 0.008614 | 468640 | 0.309285 | 0.004762 |
| Down | SLC2A1 | 20 | 0.00547 | 544898 | 0.316244 | 0 |
| Down | EDNRB | 20 | 0.006473 | 488214 | 0.313729 | 0 |
| Down | SELE | 20 | 0.005852 | 411150 | 0.300615 | 0.031579 |
| Down | HLA-DRA | 18 | 0.004735 | 398954 | 0.319992 | 0.052288 |
| Down | CD79A | 18 | 0.00478 | 297512 | 0.338726 | 0.176471 |
| Down | HLA-B | 17 | 0.006176 | 428434 | 0.315111 | 0.022059 |
| Down | BCAP31 | 17 | 0.005172 | 568664 | 0.289476 | 0.058824 |
| Down | IL1RAP | 17 | 0.003059 | 257852 | 0.322101 | 0.088235 |
| Down | PDGFB | 16 | 0.003308 | 533330 | 0.27399 | 0 |
| Down | S1PR1 | 16 | 0.002256 | 404754 | 0.320025 | 0 |
| Down | CD46 | 15 | 0.004006 | 360234 | 0.31814 | 0.047619 |
| Down | RAG1 | 15 | 0.002698 | 229148 | 0.267304 | 0.019048 |
| Down | CD22 | 15 | 0.003395 | 414458 | 0.289123 | 0.07619 |
| Down | POU2F2 | 14 | 0.00252 | 256428 | 0.313506 | 0 |
| Down | TNFRSF14 | 14 | 0.002863 | 205148 | 0.290131 | 0.054945 |
| Down | FCGR2B | 14 | 0.001419 | 233096 | 0.299854 | 0.087912 |
| Down | CSF2 | 14 | 0.001964 | 189924 | 0.271764 | 0.076923 |
| Down | SELPLG | 14 | 0.004641 | 618406 | 0.266933 | 0.010989 |
| Down | IL10 | 13 | 0.001286 | 131502 | 0.275387 | 0.025641 |
| Down | CCL7 | 13 | 0.002891 | 346838 | 0.240789 | 0 |
| Down | CD79B | 13 | 3.06E − 04 | 78608 | 0.337796 | 0.423077 |
| Down | HLA-C | 13 | 0.003625 | 407006 | 0.310407 | 0.025641 |
| Down | IL6R | 13 | 0.004275 | 289876 | 0.288689 | 0.051282 |
| Down | IL17A | 13 | 0.002334 | 388710 | 0.280328 | 0.025641 |
| Down | FCGR2A | 13 | 0.002143 | 252800 | 0.318403 | 0 |
| Down | LTA | 12 | 0.002886 | 476206 | 0.257315 | 0 |
| Down | CXCL12 | 12 | 0.005496 | 372448 | 0.27655 | 0.030303 |
| Down | CTSS | 12 | 0.00407 | 451030 | 0.260472 | 0 |
| Down | CD59 | 12 | 0.004363 | 207460 | 0.290405 | 0.030303 |
| Down | CXCR1 | 12 | 8.07E − 04 | 176404 | 0.242095 | 0.166667 |
| Down | IL2 | 12 | 0.002493 | 217616 | 0.290487 | 0.030303 |
| Down | C6 | 12 | 9.26E − 04 | 133246 | 0.24911 | 0 |
| Down | CD74 | 12 | 0.003192 | 267306 | 0.315369 | 0.121212 |
| Down | CR2 | 11 | 0.001319 | 143504 | 0.267072 | 0.036364 |
| Down | CCR10 | 11 | 0.003702 | 303034 | 0.222963 | 0.072727 |
| Down | CTSC | 11 | 0.004925 | 257558 | 0.302268 | 0 |
| Down | TGFBI | 10 | 7.77E − 04 | 51700 | 0.253167 | 0.155556 |
| Down | CD209 | 10 | 4.47E − 04 | 37928 | 0.243628 | 0.044444 |
| Down | NT5E | 10 | 0.003249 | 169846 | 0.314627 | 0.022222 |
| Down | IL10RA | 10 | 0.001722 | 123836 | 0.32116 | 0.155556 |
| Down | MBL2 | 9 | 0.002733 | 247190 | 0.248106 | 0.027778 |
| Down | TNFRSF9 | 9 | 0.001065 | 77604 | 0.309005 | 0.305556 |
| Down | HLA-DQA1 | 9 | 8.50E − 04 | 84902 | 0.306147 | 0.194444 |
| Down | NFIL3 | 9 | 0.002148 | 269802 | 0.253063 | 0 |
| Down | MS4A1 | 9 | 6.53E − 04 | 54246 | 0.308664 | 0.083333 |
| Down | PTAFR | 9 | 0.001839 | 146258 | 0.315401 | 0.055556 |
| Down | MASP1 | 9 | 0.002137 | 326806 | 0.225528 | 0.083333 |
| Down | PLA2G2A | 8 | 0.002039 | 625578 | 0.228338 | 0 |
| Down | TNFRSF4 | 8 | 7.20E − 04 | 87330 | 0.26198 | 0.321429 |
| Down | IL13RA1 | 8 | 6.92E − 04 | 54632 | 0.3129 | 0.214286 |
| Down | CD48 | 8 | 0.001004 | 75166 | 0.297881 | 0.142857 |
| Down | CD244 | 8 | 0.001314 | 270208 | 0.265574 | 0.071429 |
| Down | HLA-DRB1 | 8 | 0.001343 | 119046 | 0.273066 | 0.142857 |
| Down | IL12A | 8 | 0.003272 | 296440 | 0.241412 | 0.071429 |
| Down | ICAM3 | 8 | 6.74E − 04 | 94610 | 0.255118 | 0.035714 |
| Down | ICAM2 | 7 | 7.74E − 04 | 115578 | 0.242687 | 0.047619 |
| Down | CD86 | 7 | 0.00143 | 76566 | 0.302417 | 0.190476 |
| Down | IL6 | 7 | 0.001988 | 115352 | 0.260582 | 0.095238 |
| Down | CD80 | 7 | 0.001335 | 74000 | 0.254317 | 0.190476 |
| Down | CCL13 | 7 | 3.79E − 04 | 117758 | 0.239347 | 0 |
| Down | CARD9 | 6 | 0.001358 | 152030 | 0.262583 | 0 |
| Down | MASP2 | 6 | 8.34E − 04 | 73116 | 0.210649 | 0.2 |
| Down | HLA-DMA | 6 | 0.001965 | 186844 | 0.252792 | 0.2 |
| Down | FCER1A | 6 | 0.001958 | 462984 | 0.26283 | 0 |
| Down | IL13 | 6 | 9.18E − 04 | 81904 | 0.260164 | 0.2 |
| Down | PIGR | 6 | 0.001383 | 46460 | 0.267211 | 0 |
| Down | ICAM4 | 6 | 7.08E − 04 | 122662 | 0.244131 | 0 |
| Down | CCL11 | 6 | 4.36E − 04 | 106892 | 0.239682 | 0 |
| Down | FCAR | 6 | 0.001325 | 60556 | 0.281404 | 0.066667 |
| Down | PTGER4 | 6 | 0.001594 | 111600 | 0.311981 | 0 |
| Down | RAG2 | 6 | 0.002235 | 108180 | 0.302893 | 0.133333 |
| Down | PPBP | 6 | 0.00149 | 101978 | 0.25057 | 0.066667 |
| Down | IL3 | 6 | 1.42E − 05 | 4398 | 0.276848 | 0.133333 |
| Down | HLA-DQB1 | 5 | 1.37E − 04 | 32052 | 0.304361 | 0.5 |
| Down | IDO1 | 5 | 0.002598 | 124836 | 0.300263 | 0 |
| Down | TNFRSF10C | 5 | 6.74E − 04 | 112660 | 0.252006 | 0 |
| Down | TNFRSF13C | 5 | 6.50E − 04 | 58590 | 0.256308 | 0.3 |
| Down | IL17F | 5 | 2.32E − 04 | 81308 | 0.256031 | 0.2 |
| Down | CFD | 5 | 0.001535 | 135276 | 0.301765 | 0 |
| Down | CCL19 | 5 | 8.76E − 05 | 9268 | 0.219387 | 0.4 |
| Down | CD34 | 5 | 0.001329 | 226272 | 0.243224 | 0 |
| Down | IFNG | 5 | 0.001405 | 110736 | 0.270285 | 0 |
| Down | IL23A | 5 | 0.00132 | 310874 | 0.180846 | 0.1 |
| Down | EBI3 | 5 | 0.001288 | 90012 | 0.222769 | 0.1 |
| Down | C8B | 4 | 2.59E − 04 | 21386 | 0.208212 | 0.166667 |
| Down | CCL20 | 4 | 0.001697 | 215266 | 0.242974 | 0 |
| Down | C4BPA | 4 | 0.001305 | 202342 | 0.207217 | 0 |
| Down | C8A | 4 | 5.17E − 04 | 27442 | 0.225528 | 0.333333 |
| Down | SLAMF6 | 4 | 6.38E − 06 | 766 | 0.274209 | 0.333333 |
| Down | CCR6 | 4 | 0.001956 | 273648 | 0.209231 | 0 |
| Down | BTLA | 4 | 6.84E − 04 | 61880 | 0.275584 | 0.333333 |
| Down | CCR8 | 4 | 6.64E − 04 | 48144 | 0.196954 | 0 |
| Down | CXCL11 | 4 | 8.55E − 05 | 11782 | 0.220629 | 0 |
| Down | SIGIRR | 4 | 3.08E − 06 | 666 | 0.277147 | 0.333333 |
| Down | ITLN1 | 4 | 0.001313 | 85710 | 0.272679 | 0 |
| Down | ICAM5 | 4 | 3.97E − 05 | 5052 | 0.242936 | 0 |
| Down | FCGRT | 4 | 0.001307 | 236680 | 0.210779 | 0 |
| Down | CCL22 | 4 | 5.04E − 04 | 43848 | 0.247169 | 0 |
| Down | IL12B | 4 | 1.64E − 04 | 39054 | 0.194859 | 0.5 |
| Down | IL27 | 3 | 2.87E − 04 | 26194 | 0.215697 | 0.333333 |
| Down | IL22 | 3 | 6.54E − 04 | 37474 | 0.199417 | 0 |
| Down | C7 | 3 | 1.54E − 04 | 29126 | 0.226657 | 0 |
| Down | TIGIT | 3 | 0.001299 | 79710 | 0.18742 | 0 |
| Down | DEFB4A | 3 | 0.002265 | 309432 | 0.250917 | 0 |
| Down | IL22RA2 | 3 | 8.49E − 04 | 82918 | 0.216806 | 0 |
| Down | IL21 | 3 | 2.06E − 05 | 882 | 0.21301 | 0 |
| Down | C9 | 3 | 1.97E − 05 | 976 | 0.229359 | 0.333333 |
| Down | LIF | 3 | 1.35E − 05 | 994 | 0.252689 | 0 |
| Down | ITGAE | 3 | 6.54E − 04 | 122018 | 0.226607 | 0 |
| Down | IL5 | 3 | 2.60E − 05 | 1936 | 0.26283 | 0.333333 |
| Down | HLA-DPB1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.240356 | 1 |
| Down | CFI | 2 | 6.50E − 04 | 65960 | 0.196527 | 0 |
| Down | IFNB1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.254275 | 1 |
| Down | IFNA2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.254275 | 1 |
| Down | XCL1 | 2 | 0.001299 | 97076 | 0.208706 | 0 |
| Down | CD1A | 2 | 6.50E − 04 | 79654 | 0.20475 | 0 |
| Down | XCR1 | 2 | 6.50E − 04 | 48540 | 0.172698 | 0 |
| Down | DEFB103B | 2 | 6.50E − 04 | 91060 | 0.173057 | 0 |
| Down | IL7 | 2 | 6.20E − 07 | 68 | 0.219497 | 0 |
| Down | KLRB1 | 2 | 6.50E − 04 | 58078 | 0.267815 | 0 |
| Down | IL20 | 2 | 0.666667 | 4 | 0.75 | 0 |
| Down | HLA-DMB | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.201796 | 0 |
| Down | HLA-DOB | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.16794 | 0 |
| Down | ICOSLG | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.200469 | 0 |
| Down | CD83 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.300029 | 0 |
| Down | GPR183 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.300029 | 0 |
| Down | IKBKAP | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.250938 | 0 |
| Down | DEFB1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.173038 | 0 |
| Down | IL1RL2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.20772 | 0 |
| Down | IL19 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 |
Fig. 7.
Scatter plot for up regulated genes. (A—Node degree; B—Betweenness centrality; C—Stress centrality; D—Closeness centrality; E—Clustering coefficient)
Fig. 8.
Protein–protein interaction network of down regulated genes. Red nodes ( ) denotes down regulated genes; Pink lines (
) denotes down regulated genes; Pink lines ( ) denotes edges (Interactions)
) denotes edges (Interactions)
Fig. 9.
Scatter plot for down regulated genes. (A—Node degree; B—Betweenness centrality; C—Stress centrality; D—Closeness centrality; E—Clustering coefficient)
Based on STRING database, plug-ins PEWCC1 was used to carry out module analysis in Cytoscape software. We identified total 566 and 548 modules from the PPI network of up- and down-regulated genes according to the degree of importance and further analyzed with the plug-in PEWCC1. The top four significant modules of up-regulated were selected for further analysis (Fig. 10). Module 48 had 10 nodes and 34 edges, module 50 had 10 nodes and 33 edges, Module 64 had 10 nodes and 17 edges and module 65 had 10 nodes and 17 edges, respectively. Enrichment analysis showed that the genes in these modules were mainly involved in natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity, measles, Jak-STAT signaling pathway, viral myocarditis, herpes simplex infection, influenza A, osteoclast differentiation, HTLV-I infection, IL12-mediated signaling events, IL2-mediated signaling events, tuberculosis, malaria, paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1, TCR signaling in naive CD8 + T cells and cytokine signaling in Immune system. The top four significant modules of down-regulated were selected for further analysis (Fig. 11). Module 18 had 17 nodes and 44 edges, module 23 had 15 nodes and 20 edges, module 58 had 9 nodes and 22 edges and module 104 had 7 nodes and 12 edges, respectively. Enrichment analysis showed that the genes in these modules were mainly involved in apoptosis signaling pathway, tuberculosis, viral myocarditis, Jak-STAT signaling pathway, cytokine signaling in immune system, measles, innate immune system, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, influenza A, hematopoietic cell lineage, HTLV-I infection, signaling by interleukins, adaptive immune system, IL12-mediated signaling events, interleukin signaling pathway, inflammation mediated by chemokine and cytokine signaling pathway, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), FAS (CD95) signaling pathway, cytokine-mediated signaling pathway, response to biotic stimulus, IL4-mediated signaling events, MAPK family signaling cascades and regulation of immune system process.
Fig. 10.
Modules in PPI network. The green nodes denote the up regulated genes. Green nodes ( ) denotes up regulated genes; Blue lines (
) denotes up regulated genes; Blue lines ( ) denotes edges (Interactions)
) denotes edges (Interactions)
Fig. 11.
Modules in PPI network. The red nodes denote the down regulated genes. Red nodes ( ) denotes down regulated genes; Pink lines (
) denotes down regulated genes; Pink lines ( ) denotes edges (Interactions)
) denotes edges (Interactions)
Construction of target gene–miRNA regulatory network
Using the miRNet database, target gene–miRNA regulatory network for up-regulated genes had 1008 nodes and 1613 interactions (Fig. 12). The network marked that each target genes have interactions with miRNAs. IKZF3 regulates 134 miRNAs (ex, hsa-mir-6860), TP53 regulates 130 miRNAs (ex, hsa-mir-5703), IFNAR2 regulates 109 miRNAs (ex, hsa-mir − 4510), SMAD5 regulates 83 miRNAs (ex, hsa-mir-6086) and STAT3 regulates by 80 miRNAs (ex, hsa-mir − 4270) are listed in Table 8. Enrichment analysis showed that the target genes in this network were mainly involved in IL2-mediated signaling events, measles, herpes simplex infection, ALK2 signaling events and cytokine signaling in immune system. Similarly, target gene–miRNA regulatory network for down-regulated genes had 1791 nodes and 3951 interactions (Fig. 13). SKI regulates 210 miRNAs (ex, hsa-mir-5100), TNFRSF13C regulates 136 miRNAs (ex, hsa-mir-3197), BCL2L11 regulates 122 miRNAs (ex, hsa-mir-8064), ICOSLG regulates 119 miRNAs (ex, hsa-mir-3672) and IL6R regulates 94 miRNAs (ex, hsa-mir-7641) are listed in Table 7. Enrichment analysis showed that the target genes in this network were mainly involved in molecular function regulator, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, apoptosis signaling pathway, adaptive immune system and cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction.
Fig. 12.
The network of up regulated genes and their related miRNAs. The green circles nodes ( ) are the up regulated genes; yellow diamond nodes (
) are the up regulated genes; yellow diamond nodes ( ) are the miRNAs; Pink lines (
) are the miRNAs; Pink lines ( ) denotes edges (Interactions)
) denotes edges (Interactions)
Table 8.
TF—target gene interaction table
| Regulation | TF | Degree | Target Gene | Regulation | TF | Degree | Target Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up | FOXC1 | 46 | JAK1 | Down | FOXC1 | 127 | KLRF2 |
| Up | GATA2 | 31 | TRAF6 | Down | GATA2 | 102 | CD1A |
| Up | YY1 | 25 | CLEC7A | Down | YY1 | 75 | TNFRSF4 |
| Up | CREB1 | 22 | STAT1 | Down | FOXL1 | 63 | MME |
| Up | TFAP2A | 21 | IKZF1 | Down | NFKB1 | 61 | CXCL12 |
| Up | PPARG | 20 | IRF7 | Down | USF2 | 48 | DEFB1 |
| Up | NFKB1 | 20 | TRAF2 | Down | SRF | 48 | STAT5A |
| Up | E2F1 | 19 | PSMB9 | Down | CREB1 | 46 | TNFRSF10C |
| Up | RELA | 18 | IFI35 | Down | TP53 | 45 | C1S |
| Up | USF2 | 17 | LTB4R | Down | STAT3 | 45 | IL26 |
| Up | SREBF1 | 16 | CCND3 | Down | PPARG | 43 | ICAM4 |
| Up | HINFP | 15 | GP1BB | Down | JUN | 42 | FCGRT |
| Up | JUN | 15 | TLR2 | Down | E2F1 | 42 | GATA3 |
| Up | FOXL1 | 12 | LCP2 | Down | HINFP | 40 | BCL2L11 |
| Up | BRCA1 | 11 | CD99 | Down | TFAP2A | 38 | EOMES |
| Up | NFIC | 11 | FYN | Down | NFIC | 38 | IFNA2 |
| Up | SRF | 11 | IL18RAP | Down | MEF2A | 31 | CTSS |
| Up | GATA3 | 9 | CX3CR1 | Down | NFYA | 29 | GPI |
| Up | PRDM1 | 9 | GNLY | Down | TEAD1 | 28 | LTA |
| Up | POU2F2 | 9 | SLAMF7 | Down | HOXA5 | 28 | PPBP |
| Up | USF1 | 8 | ATG5 | Down | MAX | 27 | IL12B |
| Up | FOS | 8 | CCL5 | Down | SREBF2 | 26 | CD80 |
| Up | TEAD1 | 8 | CCR1 | Down | SREBF1 | 26 | DEFB4A |
| Up | TFAP2C | 8 | CEACAM1 | Down | JUND | 26 | HLA-DPB1 |
| Up | ELK4 | 8 | GBP1 | Down | TFAP2C | 26 | HLA-DQA1 |
| Up | HOXA5 | 8 | GZMB | Down | RUNX2 | 25 | C1R |
| Up | E2F6 | 8 | HRAS | Down | ARID3A | 24 | SKI |
| Up | HNF4A | 8 | IFNAR2 | Down | HNF4A | 23 | CR2 |
| Up | RUNX2 | 8 | KLRK1 | Down | ZNF354C | 22 | C8A |
| Up | NFYA | 7 | ATG10 | Down | NR3C1 | 22 | FCGR2B |
| Up | SREBF2 | 7 | C1QBP | Down | IRF2 | 22 | XCR1 |
| Up | MAX | 7 | CCRL2 | Down | PRDM1 | 21 | IL13 |
| Up | CEBPB | 7 | CD247 | Down | FOS | 20 | CCL15 |
| Up | PRRX2 | 7 | CTNNB1 | Down | USF1 | 20 | IRAK4 |
| Up | ZNF354C | 7 | GFI1 | Down | FOXA1 | 19 | ITLN1 |
| Up | MEF2A | 7 | IL18R1 | Down | PRRX2 | 19 | TLR9 |
| Up | ARID3A | 6 | ABL1 | Down | STAT1 | 18 | LCK |
| Up | ESR1 | 6 | C2 | Down | SP1 | 16 | CD82 |
| Up | PDX1 | 6 | HLA-A | Down | ELK4 | 16 | PAX5 |
| Up | NR3C1 | 6 | ITGAL | Down | NKX3-2 | 16 | PLA2G2E |
| Up | KLF5 | 6 | ITGB2 | Down | KLF5 | 15 | ICOSLG |
| Up | ELK1 | 6 | JAK2 | Down | ELK1 | 15 | IDO1 |
| Up | SP1 | 6 | MAP4K2 | Down | BRCA1 | 15 | LGALS3 |
| Up | EGR1 | 6 | MX1 | Down | ESR1 | 15 | MASP2 |
| Up | EN1 | 6 | SMAD5 | Down | TP63 | 12 | CD19 |
| Up | IRF2 | 5 | RUNX1 | Down | PAX2 | 12 | CD48 |
| Up | PAX2 | 5 | STAT5B | Down | NR2F1 | 12 | CEBPB |
| Up | NR2F1 | 4 | CUL9 | Down | E2F6 | 11 | CD8A |
| Up | FOXF2 | 4 | IKBKE | Down | EN1 | 11 | IL22 |
| Up | TP63 | 4 | IKZF3 | Down | SPIB | 11 | PTAFR |
| Up | FOXA1 | 4 | IL2RG | Down | FOXF2 | 10 | SELE |
| Up | NRF1 | 4 | MAP4K1 | Down | SOX10 | 9 | POU2F2 |
| Up | JUND | 4 | NLRP3 | Down | SRY | 8 | EDNRB |
| Up | SPIB | 4 | ZBTB16 | Down | NRF1 | 8 | IFNAR1 |
| Up | REL | 3 | IKZF3 | Down | SOX17 | 7 | TNFRSF14 |
| Up | NKX3-1 | 3 | IRF5 | Down | SOX5 | 6 | BTK |
| Up | SOX5 | 3 | KLRD1 | Down | NKX2-5 | 6 | PIGR |
| Up | SOX10 | 3 | STAT3 | Down | ELF5 | 5 | BATF3 |
| Up | MYB | 3 | JAK2 | Down | NFATC2 | 5 | IL4 |
| Up | SRY | 2 | KLRK1 | Down | PDX1 | 5 | ITGAE |
| Up | ELF5 | 2 | TLR2 | Down | NFYB | 3 | PTPN6 |
| Up | NFIL3 | 1 | CX3CR1 | Down | ZFX | 3 | THY1 |
| Up | NR4A2 | 1 | C2 | Down | NR4A2 | 2 | CSF2 |
| Up | FEV | 1 | ATG5 | Down | FEV | 2 | IL23A |
| Up | FOXI1 | 1 | CCL5 | Down | MYB | 2 | MIF |
| Up | NKX3-2 | 1 | GZMB | Down | HNF1B | 2 | SPP1 |
| Up | E2F4 | 1 | IKZF1 | Down | REL | 2 | STAT6 |
| Up | TFCP2L1 | 1 | LCP2 | Down | ESR2 | 1 | CCL22 |
| Up | NR2E3 | 1 | HLA-A | Down | FOXI1 | 1 | CD209 |
| Up | GATA1 | 1 | HLA-A | Down | FOXD1 | 1 | HLA-DOB |
| Up | HNF1B | 1 | IL18R1 | Down | ESRRB | 1 | ICAM2 |
| Up | SOX17 | 1 | LILRA6 | Down | NR2E3 | 1 | IL2 |
| Down | E2F4 | 1 | S1PR1 | ||||
| Down | GATA1 | 1 | PDGFB |
Degree—No of TF interact with target gene. We taken any one TF in table
Fig. 13.
The network of down regulated genes and their related miRNAs. The red circles nodes ( ) are the down regulated genes; blue diamond nodes (
) are the down regulated genes; blue diamond nodes ( ) are the miRNAs; Sku blue lines (
) are the miRNAs; Sku blue lines ( ) denotes edges (Interactions)
) denotes edges (Interactions)
Table 7.
miRNA - target gene interaction table
| Regulation | Target Genes | Degree | MicroRNA | Regulation | Target Genes | Degree | MicroRNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up | IKZF3 | 134 | hsa-mir-6860 | Down | SKI | 210 | hsa-mir-5100 |
| Up | TP53 | 130 | hsa-mir-5703 | Down | TNFRSF13C | 136 | hsa-mir-3197 |
| Up | IFNAR2 | 109 | hsa-mir − 4510 | Down | BCL2L11 | 122 | hsa-mir-8064 |
| Up | SMAD5 | 83 | hsa-mir-6086 | Down | ICOSLG | 119 | hsa-mir-3672 |
| Up | STAT3 | 80 | hsa-mir − 4270 | Down | IL6R | 94 | hsa-mir-7641 |
| Up | TRAF6 | 71 | hsa-mir-6745 | Down | VCAM1 | 86 | hsa-mir − 4270 |
| Up | RUNX1 | 67 | hsa-mir − 4467 | Down | LILRA2 | 83 | hsa-mir − 4780 |
| Up | ABL1 | 64 | hsa-mir − 4511 | Down | IRAK4 | 78 | hsa-mir-520e |
| Up | KLRD1 | 60 | hsa-mir-5094 | Down | BTLA | 72 | hsa-mir-3133 |
| Up | CCL5 | 49 | hsa-mir − 4775 | Down | CD55 | 71 | hsa-mir-6124 |
| Up | CTNNB1 | 48 | hsa-mir − 4255 | Down | CCL22 | 71 | hsa-mir-5190 |
| Up | MAP4K2 | 47 | hsa-mir-6131 | Down | CD44 | 70 | hsa-mir-5696 |
| Up | PSMB9 | 44 | hsa-mir-3658 | Down | PDGFB | 69 | hsa-mir-6132 |
| Up | ZBTB16 | 43 | hsa-mir − 4287 | Down | BCL2 | 68 | hsa-mir-184 |
| Up | SOCS1 | 42 | hsa-mir − 4495 | Down | TFRC | 67 | hsa-mir-6070 |
| Up | HLA-A | 39 | hsa-mir-6129 | Down | PIGR | 66 | hsa-mir − 4486 |
| Up | SERPING1 | 38 | hsa-mir-1262 | Down | CCL16 | 63 | hsa-mir-7703 |
| Up | CCR5 | 33 | hsa-mir-3183 | Down | IFNAR1 | 61 | hsa-mir − 4430 |
| Up | CLEC7A | 33 | hsa-mir − 4792 | Down | TIRAP | 61 | hsa-mir − 4325 |
| Up | CD99 | 32 | hsa-mir-3199 | Down | ETS1 | 58 | hsa-mir-3972 |
| Up | LILRB2 | 30 | hsa-mir-3941 | Down | CD59 | 56 | hsa-mir-3919 |
| Up | ATG10 | 29 | hsa-mir − 4309 | Down | IKZF2 | 55 | hsa-mir-5096 |
| Up | CCND3 | 29 | hsa-mir-1321 | Down | CEBPB | 54 | hsa-mir − 4510 |
| Up | STAT5B | 25 | hsa-mir-8485 | Down | CD209 | 54 | hsa-mir-3188 |
| Up | TRAF2 | 21 | hsa-mir-6165 | Down | HLA-C | 53 | hsa-mir − 4660 |
| Up | HRAS | 21 | hsa-mir-1268a | Down | DUSP4 | 53 | hsa-mir-6089 |
| Up | STAT1 | 19 | hsa-mir-1183 | Down | CCR6 | 52 | hsa-mir − 4539 |
| Up | JAK1 | 17 | hsa-mir-107 | Down | TGFBR1 | 51 | hsa-mir-8083 |
| Up | CCRL2 | 16 | hsa-mir − 4469 | Down | MAPKAPK2 | 50 | hsa-mir − 4468 |
| Up | ITGAL | 14 | hsa-mir-764 | Down | SLC2A1 | 50 | hsa-mir − 4448 |
| Up | FYN | 14 | hsa-mir-3924 | Down | POU2F2 | 49 | hsa-mir − 4307 |
| Up | JAK2 | 14 | hsa-mir-5692a | Down | LIF | 47 | hsa-mir-3655 |
| Up | PDCD1 | 13 | hsa-mir-922 | Down | MBL2 | 47 | hsa-mir-3689c |
| Up | C1QBP | 11 | hsa-mir − 484 | Down | HLA-B | 44 | hsa-mir-5047 |
| Up | IKBKB | 10 | hsa-mir − 451a | Down | ZEB1 | 43 | hsa-mir-2113 |
| Up | TLR2 | 10 | hsa-mir-105-5p | Down | RELA | 41 | hsa-mir-7515 |
| Up | XBP1 | 10 | hsa-mir-320c | Down | CD46 | 39 | hsa-mir − 4780 |
| Up | TMEM173 | 9 | hsa-mir-5093 | Down | PAX5 | 37 | hsa-mir-6127 |
| Up | ATG5 | 9 | hsa-mir-299-5p | Down | CASP3 | 36 | hsa-mir − 4666b |
| Up | ZAP70 | 4 | hsa-mir-631 | Down | STAT5A | 34 | hsa-mir − 4457 |
| Up | IFIH1 | 4 | hsa-mir − 424-5p | Down | PTAFR | 33 | hsa-mir − 4301 |
| Up | KLRC1 | 4 | hsa-mir-9-5p | Down | THY1 | 32 | hsa-mir − 4269 |
| Up | IKZF1 | 4 | hsa-mir-19a-3p | Down | ATG7 | 29 | hsa-mir − 4518 |
| Up | KLRK1 | 3 | hsa-mir-148b-3p | Down | S1PR1 | 29 | hsa-mir-7977 |
| Up | IKBKE | 3 | hsa-mir-296-5p | Down | C8A | 29 | hsa-mir-1299 |
| Up | GFI1 | 3 | hsa-mir-142-3p | Down | CDH5 | 28 | hsa-mir-544a |
| Up | NLRP3 | 3 | hsa-mir-223-3p | Down | GPI | 27 | hsa-mir-760 |
| Up | ITGB2 | 3 | hsa-mir-146a-5p | Down | ILF3 | 27 | hsa-mir − 4314 |
| Up | IL18RAP | 2 | hsa-mir − 4677-3p | Down | KIT | 25 | hsa-mir − 4490 |
| Up | IRF7 | 2 | hsa-mir-762 | Down | GPR183 | 24 | hsa-mir-1303 |
| Up | C2 | 2 | hsa-mir-335-5p | Down | TRAF3 | 24 | hsa-mir-8085 |
| Up | MX1 | 2 | hsa-mir-211-5p | Down | PTPN6 | 24 | hsa-mir − 4525 |
| Up | CCR1 | 2 | hsa-mir-181d-3p | Down | SELPLG | 23 | hsa-mir-1470 |
| Up | CUL9 | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | Down | RAG1 | 23 | hsa-mir-3666 |
| Up | IL18R1 | 1 | hsa-mir-124-3p | Down | HLA-DRB1 | 23 | hsa-mir-3978 |
| Up | GBP1 | 1 | hsa-mir-124-3p | Down | TAL1 | 23 | hsa-mir − 4719 |
| Up | TBX21 | 1 | hsa-mir-29b-3p | Down | CCL11 | 23 | hsa-mir-6077 |
| Up | GP1BB | 1 | hsa-mir-26b-5p | Down | IL6 | 22 | hsa-mir − 451a |
| Up | IRF5 | 1 | hsa-mir-22-3p | Down | TGFBI | 22 | hsa-mir-1322 |
| Down | CTSS | 22 | hsa-mir-8066 | ||||
| Down | CXCL12 | 20 | hsa-mir-886-3p | ||||
| Down | BID | 20 | hsa-mir-623 | ||||
| Down | TOLLIP | 20 | hsa-mir-6078 | ||||
| Down | CD86 | 20 | hsa-mir-8056 | ||||
| Down | TIGIT | 20 | hsa-mir-3941 | ||||
| Down | CD3E | 20 | hsa-mir − 4510 | ||||
| Down | TNFRSF9 | 19 | hsa-mir-1305 | ||||
| Down | CXCR2 | 18 | hsa-mir-588 | ||||
| Down | C6 | 18 | hsa-mir − 4310 | ||||
| Down | IL5 | 17 | hsa-mir-604 | ||||
| Down | EBI3 | 17 | hsa-mir-6069 | ||||
| Down | TCF4 | 15 | hsa-let-7e-5p | ||||
| Down | BCAP31 | 15 | hsa-mir − 4514 | ||||
| Down | CD82 | 15 | hsa-mir-1470 | ||||
| Down | FCAR | 15 | hsa-mir-1976 | ||||
| Down | SELE | 14 | hsa-mir-630 | ||||
| Down | HLA-DRA | 14 | hsa-mir-3915 | ||||
| Down | IFNB1 | 13 | hsa-mir-6080 | ||||
| Down | CD9 | 13 | hsa-mir-5688 | ||||
| Down | IL10RA | 12 | hsa-mir-8064 | ||||
| Down | IL1RL2 | 12 | hsa-mir − 4301 | ||||
| Down | IL1RAP | 11 | hsa-mir − 4635 | ||||
| Down | IL7 | 11 | hsa-mir-203a-3p | ||||
| Down | CD19 | 11 | hsa-mir − 466 | ||||
| Down | IFNG | 10 | hsa-mir-15b-5p | ||||
| Down | EGR2 | 10 | hsa-mir-100-5p | ||||
| Down | PTGER4 | 10 | hsa-mir-101-3p | ||||
| Down | C1S | 10 | hsa-mir-548 s | ||||
| Down | CX3CL1 | 10 | hsa-mir-5093 | ||||
| Down | CD244 | 10 | hsa-mir-5702 | ||||
| Down | C7 | 10 | hsa-mir-1827 | ||||
| Down | PTK2 | 9 | hsa-mir-543 | ||||
| Down | MS4A1 | 9 | hsa-mir-644a | ||||
| Down | AIRE | 9 | hsa-mir − 4770 | ||||
| Down | HLA-DOB | 9 | hsa-mir-1260a | ||||
| Down | MAP4K4 | 8 | hsa-mir-520e | ||||
| Down | TRAF4 | 8 | hsa-mir − 4284 | ||||
| Down | FN1 | 8 | hsa-mir-200b-3p | ||||
| Down | STAT6 | 8 | hsa-mir-361-5p | ||||
| Down | CXCL11 | 8 | hsa-mir − 4511 | ||||
| Down | EGR1 | 8 | hsa-mir-377-3p | ||||
| Down | C1R | 8 | hsa-mir-326 | ||||
| Down | IL10 | 7 | hsa-mir-106a-5p | ||||
| Down | IL12B | 7 | hsa-mir-103b | ||||
| Down | PLAU | 7 | hsa-mir-23b-3p | ||||
| Down | GATA3 | 7 | hsa-mir-10b-5p | ||||
| Down | FCGR2A | 7 | hsa-mir − 4275 | ||||
| Down | AICDA | 7 | hsa-mir-6873-3p | ||||
| Down | NT5E | 6 | hsa-mir − 422a | ||||
| Down | CTLA4 | 6 | hsa-mir-3924 | ||||
| Down | SPP1 | 6 | hsa-mir-299-5p | ||||
| Down | BTK | 6 | hsa-mir-1253 | ||||
| Down | MIF | 6 | hsa-mir-320a | ||||
| Down | IL13 | 5 | hsa-let-7i-5p | ||||
| Down | CD34 | 5 | hsa-mir-106b-5p | ||||
| Down | IL4 | 5 | hsa-mir − 429 | ||||
| Down | RORC | 5 | hsa-mir-148b-3p | ||||
| Down | CTSC | 5 | hsa-mir-199a-5p | ||||
| Down | CD40 | 5 | hsa-mir-503-5p | ||||
| Down | IL2 | 5 | hsa-mir-181c-5p | ||||
| Down | TCF7 | 4 | hsa-mir-22-3p | ||||
| Down | ICAM5 | 4 | hsa-mir − 4707-5p | ||||
| Down | CD83 | 4 | hsa-mir-122-5p | ||||
| Down | HLA-DQA1 | 4 | hsa-mir − 4673 | ||||
| Down | IL4R | 4 | hsa-mir-331-3p | ||||
| Down | MAPK11 | 3 | hsa-let-7a-5p | ||||
| Down | TNFSF12 | 3 | hsa-mir-17-5p | ||||
| Down | CCL7 | 3 | hsa-mir-135b-3p | ||||
| Down | IL12A | 3 | hsa-mir-10a-5p | ||||
| Down | CSF1R | 3 | hsa-mir-155-5p | ||||
| Down | CFI | 3 | hsa-mir-181a-5p | ||||
| Down | IL3 | 3 | hsa-mir − 452-5p | ||||
| Down | NFIL3 | 3 | hsa-mir-183-5p | ||||
| Down | ICAM3 | 3 | hsa-mir-3943 | ||||
| Down | EOMES | 3 | hsa-mir-7855-5p | ||||
| Down | PTPN22 | 3 | hsa-mir-624-3p | ||||
| Down | LGALS3 | 3 | hsa-mir-744-5p | ||||
| Down | CCL19 | 3 | hsa-mir-148b-3p | ||||
| Down | IL17A | 3 | hsa-mir-16-1-3p | ||||
| Down | CD22 | 2 | hsa-mir-19a-3p | ||||
| Down | CCL20 | 2 | hsa-mir-21-5p | ||||
| Down | CCL26 | 2 | hsa-mir-25-3p | ||||
| Down | DEFB4A | 2 | hsa-mir-26b-5p | ||||
| Down | CXCR1 | 2 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | MME | 2 | hsa-mir-1-3p | ||||
| Down | VTN | 2 | hsa-mir-26b-5p | ||||
| Down | LILRB5 | 2 | hsa-mir-128-3p | ||||
| Down | IL13RA1 | 2 | hsa-mir-143-3p | ||||
| Down | SIGIRR | 2 | hsa-mir-149-5p | ||||
| Down | C14orf166 | 2 | hsa-mir-331-3p | ||||
| Down | CD8A | 2 | hsa-mir-196b-5p | ||||
| Down | IRF8 | 2 | hsa-mir-646 | ||||
| Down | FCGR2B | 1 | hsa-mir-18a-5p | ||||
| Down | NOS2 | 1 | hsa-mir-26a-5p | ||||
| Down | RELB | 1 | hsa-mir-26b-5p | ||||
| Down | CXCL13 | 1 | hsa-mir-26b-5p | ||||
| Down | BATF3 | 1 | hsa-mir-26b-5p | ||||
| Down | ICAM4 | 1 | hsa-mir-93-5p | ||||
| Down | IL23A | 1 | hsa-mir-10a-5p | ||||
| Down | ARHGDIB | 1 | hsa-mir-34a-5p | ||||
| Down | LTA | 1 | hsa-mir-34a-5p | ||||
| Down | ICAM2 | 1 | hsa-mir-125b-5p | ||||
| Down | CR2 | 1 | hsa-mir-132-3p | ||||
| Down | B3GAT1 | 1 | hsa-mir-132-3p | ||||
| Down | IDO1 | 1 | hsa-mir-153-3p | ||||
| Down | MASP1 | 1 | hsa-mir-153-3p | ||||
| Down | CD80 | 1 | hsa-mir-146a-5p | ||||
| Down | HLA-DPA1 | 1 | hsa-mir-155-5p | ||||
| Down | TAGAP | 1 | hsa-mir-374a-5p | ||||
| Down | CD79A | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | FCGRT | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | HLA-DMA | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | KLRB1 | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | LCK | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | PPBP | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | CCL15 | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | CCL24 | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | LILRA1 | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | LILRA3 | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | PLA2G2E | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | IL22 | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | IL27 | 1 | hsa-mir-335-5p | ||||
| Down | MBP | 1 | hsa-mir-127-5p | ||||
| Down | IL20 | 1 | hsa-mir-624-3p |
Degree – No of miRNA interact with target gene. We taken any one miRNA in table
Construction of target gene–TF regulatory network
Using the NetworkAnalyst database, target gene–TF regulatory network for up-regulated genes had 145 nodes and 634 interactions (Fig. 14). The network marked that each target genes have interactions with transcription factors (TFs). JAK1 regulates 46 TFs (ex, FOXC1), TRAF6 regulates 31 TFs (ex, GATA2), CLEC7A regulates 25 TFs (ex, YY1), STAT1 regulates 22 TFs (ex, CREB1) and IKZF1 regulates 22 TFs (ex, TFAP2A) are listed in Table 8. Enrichment analysis showed that the target genes in this network were mainly involved in measles, herpes simplex infection, tuberculosis, osteoclast differentiation and regulation of immune system process. Similarly, target gene–TF regulatory network of down-regulated genes had 1788 nodes and 235 interactions (Fig. 15). KLRF2 regulates 127 TFs (ex, FOXC1), CD1A regulates 102 TFs (ex, GATA2), TNFRSF4 regulates 75 TFs (ex, YY1), MME regulates 63 TFs (ex, FOXL1) and CXCL12 regulates 63 TFs (ex, FOXL1) are listed in Table 7. Enrichment analysis showed that the target genes in this network were mainly involved in cytokine-mediated signaling pathway, hematopoietic cell lineage, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, innate immune system and peptide ligand-binding receptors.
Fig. 14.
The network of up regulated genes and their related TFs. The green circles nodes ( ) are the up regulated genes; Blue triangle nodes (
) are the up regulated genes; Blue triangle nodes ( ) are the TFs; Purple line (
) are the TFs; Purple line ( ) denotes edges (Interactions)
) denotes edges (Interactions)
Fig. 15.
The network of down regulated genes and their related TFs. The Red circles nodes ( ) are the down regulated genes; Blue triangle nodes (
) are the down regulated genes; Blue triangle nodes ( ) are the TFs; Yelow line (
) are the TFs; Yelow line ( ) denotes edges (Interactions)
) denotes edges (Interactions)
Validation of hub genes
The ROC curve analysis was accomplished to assess the diagnostic values of hub genes. Our finding revealed that CCL5 (AUC = 0.784), IFNAR2 (AUC = 0.750), JAK2 (AUC = 0.859), MX1 (AUC = 0.773), STAT1 (AUC = 0.873), BID (AUC = 0.848), CD55 (AUC = 0.973), CD80 (AUC = 0.870), HAL-B (AUC = 0.816) and HLA-DMA (AUC = 0.730) had significant diagnostic values for discriminating SARS-CoV-2 samples and normal controls (Fig. 16).
Fig. 16.
ROC curve validated the sensitivity, specificity of hub genes as a predictive biomarker for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis. a CCL5 b IFNAR2 c JAK2 d MX1 e STAT1 f BID g CD55 h CD80 i HAL-B j HLA-DMA
Discussion
Currently, genetic and genomic-related exploration progress speedily and provide new prospect to illuminate the molecular pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infections. And bioinformatics analysis also has developed phenomenally and is committed to search for candidate biomarkers to implement more correct screening, prompt diagnosis for SARS-CoV-2-infected patients based on enormous genetic and genomics data.
In the current investigation, a bioinformatics approach was used to identify candidate biomarker and therapeutic targets of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Following the analysis, 324 DEGs, including 76 up-regulated genes and 248 down-regulated genes were identified. Shi et al. (2007) found that expression of JAK1 was responsible for progression of adenovirus infection, but this gene may be linked with advancement of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Previously reported genes such as ZAP70 (Guntermann et al. 1997), CD22 (Ma et al. 2013) and MAPKAPK2 (Yang et al. 2012) are expressed and responsible for progression various viral infections, but our study found that these genes may important for development of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Previously reported genes such as CCR5 (Dawson et al. 2000) and TRAF6 (Tian et al. 2018) were highly expressed and involved in progression of influenza A viral infections, but these genes may be liable for advancement of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Zhivaki et al. (2017) noticed that expression of CX3CR1 is associated in progression of respiratory syncytial virus infection, but this gene may be linked with development of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Previous studies had reported that expression of CD45RB was key for progression of sendai virus infection (Hou and Doherty 1993), but this gene may liable for advancement of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Corominas et al. (2020) showed the possible involvement of IL6R in the development of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Evidence from Chi et al. (2013) study indicated that the HLA-DQB1 expression level is down-regulated in varicella-zoster virus infection, but low expression of this gene may be associated in progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Pathway enrichment analysis results for up- and down-regulated gene might play important roles in the SARS-CoV-2 infection. Studies have found that over expression of enriched genes such as CCND3 (Fan et al. 2017), IRF7 (Rosenberger et al. 2017), MX1 (Pillai et al. 2016) and STAT4 (Bot et al. 2003) in influenza viral infection, but these genes may be important for progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. JAK2 is a protein-coding gene which was first reported aberrantly expressed and plays important roles in SARS-CoV-2 infection (Wu and Yang 2020). After that, enriched up-regulated genes such as IFIH1 (Asgari et al. 2017), FYN (FYN proto-oncogene, Src family tyrosine kinase) (Kenney and Meng 2015), STAT1 (Patel et al. 2010), GZMB (granzyme B) (Loebbermann et al. 2012a, b), TRAF2 (Liu et al. 2019) and BST2 (Wang et al. 2019) were found to be involved in development of severe viral respiratory infections. Rice et al. (2016) suggested that TLR2 activity was involved in progression of pneumovirus infection, but this gene may be involved in development of SARS-CoV-2 infection. IL2RG has been shown to have an important role in adeno-associated viral infection (Hiramoto et al. 2018), but this gene may be involved in progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Reported enriched up-regulated genes such as STAT3 (Mizutani et al. 2004) and HLA-A (Ohno et al. 2009) contributes to the progression of SARS coronavirus infection, but this gene may be involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Several studies have reported that enriched genes such as STAT5B (Mukherjee et al. 2014), SOCS1 (Zheng et al. 2015), CCR1 (Miller et al. 2006) and CCL5 (Sali mi et al. 2017) were highly expressed in respiratory syncytial virus infection, but elevated expression these genes may be involved in development of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Increasing evidence shows that the enriched genes such as IFNAR2 (Romporn et al. 2013), TBX21 (Zhu et al. 2015), GBP1 (Anderson et al. 1999), IRF5 (Vandenbroeck et al. 2011) and IFI35 (Estrabaud et al. 2015) were over expressed in various viral infections, but high expression of these genes may be involved in infection of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Novel biomarkers such as IKBKE (inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase subunit epsilon), TP53, CD247, IL18RAP, IL18R1, HRAS (HRas proto-oncogene, GTPase), PSMB9, IKBKB (inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase subunit beta), ITGB2 and LTB4R were highly expressed and might be involved in progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Sanders et al. (2001) revealed that NOS2 was down-regulated in rhinovirus infection, but this gene may be involved in development of SARS-CoV-2 infection. The enriched down-regulated genes found in this study include IL10 (Loebbermann et al. 2012a, b), IL13 (Castilow et al. 2008), IL21 (Antunes et al. 2019), CCR6 (Shi et al. 2017), CXCL13 (Alturaiki et al. 2018), CCL20 (Shi et al. 2017), IL19 (Ermers et al. 2011), IL20 (Ermers et al. 2011), CD40 (Harcourt et al. 2003a, b), IL2 (Noma et al. 1996), IL3 (Bertrand et al. 2015), IL4 (Puthothu et al. 2006), IL9 (Dodd et al. 2009) and STAT6 (Srinivasa et al. 2016) were responsible for progression of respiratory syncytial virus infection, but these genes may be linked with progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Many previous studies have confirmed the roles of enriched down-regulated genes such as IL12B (Mueller et al. 2004), TNFRSF9 (Rodriguez et al. 2019), TNFRSF14 (Soroosh et al. 2014), IL17F (Wang et al. 2016), CCR8 (Calado et al. 2010), CCL18 (Malhotra et al. 2019), CCL22 (Yang et al. 2012), CXCL11 (Pineda-Tenor et al. 2014), CX3CL1 (Bertin et al. 2014), CXCL12 (Durrant et al. 2014), CCR10 (Nakayama et al. 2002), IFNA2 (Chen et al. 2017), IFNB1 (Gagné et al. 2017), IL7 (Golden‐Mason et al. 2006), IL26 (Miot et al. 2015), CXCR1 (Xu et al. 2016), CEBPB (CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta) (Liu et al. 2009), ETS1 (Posada et al. 2000), STAT5A (Warby et al. 2003), THY1 (Lu et al. 2011), IL16 (Caufour et al. 2001), HLA-B (Martin et al. 2007), HLA-C (Apps et al. 2013), HLA-DPA1 (Wasityastuti et al. 2016), HLA-DPB1 (Lambert et al. 2015), HLA-DQA1 (Tibbs et al. 1996), HLA-DRB1 (Chi et al. 2013), PSMB10 (Deng et al. 2019), BCL2 (Zuckerman et al. 2001), TOLLIP (toll interacting protein) (Li et al. 2016a, b), VCAM1 (Koraka et al. 2004), RAG1 (Winkler et al. 2017), IRF8 (Terry et al. 2015), EBI3 (Gehlert et al. 2004), EGR1 (Baer et al. 2016), IL27 (Swaminathan et al. 2013) and BID (BH3 interacting domain death agonist) (Hsu et al. 2003) were linked with development of various viral infections, but these genes may be associated with advancement of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Previous investigation demonstrated that enriched down-regulated genes such as IL17A (Wang et al. 2016), CCL11 (Suryadevara et al. 2013), CCL19 (Fleming-Canepa et al. 2011), XCR1 (Fossum et al. 2015), IFNAR1 (Lin et al. 2014), IL22 (Kumar et al. 2013), LTA (lymphotoxin alpha) (Morales-García et al. 2012), IL5 (Gorski et al. 2013), EGR2 (Du et al. 2014), RAG2 (Wu et al. 2010), CASP3 (Takahashi et al. 2013), S1PR1 (Zhao et al. 2019), CD80 (Lumsden et al. 2000), CD86 (Lumsden et al. 2000) and CD44 (Liu et al. 2014) were key for advancement of influenza virus infection, but these genes may be involved in progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Enriched down-regulated genes such as CCL7 (Girkin et al. 2015) and CXCR2 (Nagarkar et al. 2009) have been reported to be associated with rhinovirus 1B infection, but these genes may be responsible for infection of SARS-CoV-2. Accumulating evidence shows that enriched genes such as IFNG (interferon gamma) (Sainz et al. 2004) and TRAF3 (Siu et al. 2009) were low expressed in SARS-CoV, but decreased expression of these genes may be key for progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Conti et al. (2020) showed that IL6 was liable for progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Novel biomarkers such as IL10RA, IL12A, IL13RA1, PDGFB (platelet-derived growth factor subunit B), TNFSF12, IL17B, TNFRSF10C, CCL26, TNFRSF4, IL22RA2, CCL15, CCL16, CCL24, XCL1, KIT (KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase), CCL13, PPBP (pro-platelet basic protein), IL23A, TGFBR1, LIF (LIF interleukin 6 family cytokine), CSF1R, CSF2, CSF2RB, CSF3R, TNFRSF13C, IL1RAP, IL4R, AICDA (activation-induced cytidinedeaminase), PTPN6, PIGR (polymeric immunoglobulin receptor), GATA3, PTAFR (platelet activating factor receptor), IL1RL2, PTK2, FN1, DUSP4, RELA (RELA proto-oncogene, NF-kA subunit), RELB (RELB proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit), LCK (LCK proto-oncogene, Src family tyrosine kinase), IRAK4, RORC (RAR-related orphan receptor C), BCL2L11 and PLA2G2A were low expressed and might be involved in progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
GO enrichment analysis results for up- and down-regulated gene might play important roles in the SARS-CoV-2 infection. Enriched up-regulated genes such as ATG5 (Guévin et al. 2010), PDCD1 (Nasi et al. 2013), ABL1 (García et al. 2012), CD99 (Tochikura et al. 2003), LILRB2 (Alaoui et al. 2018), LAG3 (Tian et al. 2015), SERPING1 (Sanfilippo et al. 2017), XBP1 (Sharma et al. 2017), CTNNB1 (Tucci et al. 2013), RUNX1 (Zhao et al. 2016), SLAMF7 (O’Connell et al. 2019), ITGAL (integrin subunit alpha L) (Xu et al. 2018) and CEACAM1 (Hirai et al. 2010) appeared to be related in various types of viral infections, but these genes may be responsible for progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Hu et al. (2017) observed that high expression of C1QBP was liable for progression of respiratory syncytial viral infection, but elevated expression this gene may be associated with advancement of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Evidence demonstrated that high expression of enriched genes such as KLRD1 (Bongen et al. 2018) and NLRP3 (Pothlichet et al. 2013) were important for progression of influenza virus infection, but increased expression of these genes may be involved in advancement of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Novel biomarkers such as KLRK1, IKZF3, ZBTB16, CLEC7A, C2 (complement C2), IKZF1, LCP2, KLRC1, GFI1, CCRL2 and MAP4K2 were highly expressed and might be involved in progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Studies have reported that low expression of enriched genes such as IRGM (immunity-related GTPase M) (Hansen et al. 2017), MASP1 (El Saadany et al. 2011), CD244 (Raziorrouh et al. 2010), MBL2 (Spector et al. 2010), CD46 (Gaggar et al. 2003), C4A (Imakiire et al. 2012), C9 (Kim et al. 2013), ZEB1 (Lacher et al. 2011), ICAM2 (Wang et al. 2009), BTLA (B and T lymphocyte associated) (Cai et al. 2013), CD1A (Sacchi et al. 2007), CD19 (Zehender et al. 1997), ICAM5 (Wei et al. 2016), CD34 (Fahrbach et al. 2007), CD48 (Ezinne et al. 2014), CD59 (Amet et al. 2012), CD74 (Le Noury et al. 2015) and DEFB1 (Estrada-Aguirre et al. 2014) were linked with development of various viral infections, but low expression of these genes may be liable for progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Recent studies reported that enriched genes such as IDO1 (Fox et al. 2015), CD55 (Li et al. 2016), PTPN22 (Crabtree et al. 2016), FCGR2A (Maestri et al. 2016), CARD9 (Uematsu et al. 2015), MIF (macrophage migration inhibitory factor) (Arndt et al. 2002) and PLAU (plasminogen activator, urokinase) (Sidenius et al. 2000) were low expressed in influenza virus infection, but decrease expression of these genes may be key for progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Low expression of genes such as PECAM1 (Wang et al. 1998), TLR9 (Shafique et al. 2012) and CTLA4 (Ayukawa et al. 2004) were observed in respiratory syncytial virus infection, but decrease expression these genes may be associated with progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Chen et al. (2017) demonstrated CD83 was important for progression of respiratory syndrome virus, but decrease expression of this gene may be linked with advancement of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Many studies have reported the enriched down-regulated gene such as CD209 (Chan et al. 2010), DPP4 (Letko et al. 2018), ICAM3 (Chan et al. 2007), CD9 (Earnest et al. 2017) and MASP2 (Wang et al. 2009) were liable for advancement of SARS-CoV, but these genes may be linked with progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Treon et al. (2020) indicated that low expression of BTK (Bruton tyrosine kinase) was key for progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Novel biomarkers such as HLA-DMA, HLA-DMB, HLA-DOB, HLA-DRA, CTSC (cathepsin C), PTGER4, CFD (complement factor D), SLAMF6, FCER1A, FCGR2B, C1R, C1S, C4BPA, C6, C7, C8A, C8B, TAL1, KLRB1, SELE (selectin E), GPI (glucose-6-phosphate isomerase), ICOSLG (inducible T cell costimulator ligand), LILRA1, LILRA2, VTN (vitronectin), CLEC6A, ATG7, ICAM4, AIRE (autoimmune regulator), GPR183, CFI, CR2, LGALS3, TFRC (transferrin receptor), CD3E, CD8A, TIGIT (T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains), MS4A1, TIRAP (TIR domain containing adaptor protein), CD79A, CD79B, PAX5, HAMP (hepcidin antimicrobial peptide), MAPK11, CTSS (cathepsin S), MBP (myelin basic protein), ITGAE (integrin subunit alpha E), FCGRT (Fc fragment of IgG receptor and transporter), MME (membrane metalloendopeptidase), NT5E, CDH5, DEFB103B, DEFB4A and TRAF4 were low expressed and might be involved in progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Construction of PPI network of up- and down-regulated genes might be helpful for understanding the relationship of developmental SARS-CoV-2 infection. Desai et al. (2018) showed that BATF3 was involved in progression of respiratory poxvirus infection, but this gene may be key for development of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Novel biomarker ILF3 was low expressed and might be involved in progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
A target gene–miRNA regulatory and target gene–TF regulatory network for up- and down-regulated genes were generated to determine the key target genes and provide valuable information for the analysis of cellular functions and biological processes in SARS-CoV-2 infection. SMAD5 was highly expressed in SARS-CoV-2 infection and might be consider as novel biomarker. Novel biomarkers such as SKI (SKI proto-oncogene) and KLRF2 were low expressed and might be involved in progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Conclusion
It in earnestly hoped that this research will help in enhancing attempts to further understand the molecular characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 infection progression. CCL5, IFNAR2, JAK2, MX1, STAT1, BID, CD55, CD80, HAL-B and HLA-DMA may be used as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. This research, it is hoped promote ultimate molecularly targeted therapies for SARS-CoV-2 infection and provide acceptable local control and survival.
Acknowledgements
We thank Eugenia Ong, Experimental Therapeutics Centre, Agency for Science, Technology and Research, Singapore, Singapore, very much, the author who deposited their microarray dataset, E-MTAB-8871, into the public ArrayExpress database.
Author contributions
Basavaraj Vastrad participated in writing original draft and investigation, Chanabasayya Vastrad performed software, supervision, formal analysis and validation. Anandkumar Tengli performed editing and reviewing the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are available in the ArrayExpress (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress) repository. [(E-MTAB-8871) (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-8871/)].
Compliance with ethical standards
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
No informed consent, because this study does not contain human or animals participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
References
- Alaoui L, Palomino G, Zurawski S, Zurawski G, Coindre S, Dereuddre-Bosquet N, Lecuroux C, Goujard C, Vaslin B, Bourgeois C, et al. Early SIV and HIV infection promotes the LILRB2/MHC-I inhibitory axis in cDCs. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(10):1871–1887. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2712-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alturaiki W, McFarlane AJ, Rose K, Corkhill R, McNamara PS, Schwarze J, Flanagan BF. Expression of the B cell differentiation factor BAFF and chemokine CXCL13 in a murine model of respiratory syncytial virus infection. Cytokine. 2018;110:267–271. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amet T, Ghabril M, Chalasani N, Byrd D, Hu N, Grantham A, Liu Z, Qin X, He JJ, Yu Q. CD59 incorporation protects hepatitis C virus against complement-mediated destruction. Hepatology. 2012;55(2):354–363. doi: 10.1002/hep.24686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson SL, Carton JM, Lou J, Xing L, Rubin BY. Interferon-induced guanylate binding protein-1 (GBP-1) mediates an antiviral effect against vesicular stomatitis virus and encephalomyocarditis virus. Virology. 1999;256(1):8–14. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.9614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antunes KH, Becker A, Franceschina C, de Freitas DD, Lape I, da Cunha MD, Leitão L, Rigo MM, Pinto LA, Stein RT, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus reduces STAT3 phosphorylation in human memory CD8 T cells stimulated with IL-21. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):17766. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54240-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apps R, Qi Y, Carlson JM, Chen H, Gao X, Thomas R, Yuki Y, Del Prete GQ, Goulder P, Brumme ZL, et al. Influence of HLA-C expression level on HIV control. Science. 2013;340(6128):87–91. doi: 10.1126/science.1232685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt U, Wennemuth G, Barth P, Nain M, Al-Abed Y, Meinhardt A, Gemsa D, Bacher M. Release of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and CXCL8/interleukin-8 from lung epithelial cells rendered necrotic by influenza A virus infection. J Virol. 2002;76(18):9298–9306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.18.9298-9306.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asgari S, Schlapbach LJ, Anchisi S, Hammer C, Bartha I, Junier T, Mottet-Osman G, Posfay-Barbe KM, Longchamp D, Stocker M, et al. Severe viral respiratory infections in children with IFIH1 loss-of-function mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114(31):8342–8347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1704259114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayukawa H, Matsubara T, Kaneko M, Hasegawa M, Ichiyama T, Furukawa S. Expression of CTLA − 4 (CD152) in peripheral blood T cells of children with influenza virus infection including encephalopathy in comparison with respiratory syncytial virus infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004;137(1):151–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer A, Lundberg L, Swales D, Waybright N, Pinkham C, Dinman JD, Jacobs JL, Kehn-Hall K. Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus induces apoptosis through the unfolded protein response activation of EGR1. J Virol. 2016;90(7):3558–3572. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02827-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertin J, Jalaguier P, Barat C, Roy MA, Tremblay MJ. Exposure of human astrocytes to leukotriene C4 promotes a CX3CL1/fractalkine-mediated transmigration of HIV-1-infected CD4+ T cells across an in vitro blood-brain barrier model. Virology. 2014;454–455:128–138. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand P, Lay MK, Piedimonte G, Brockmann PE, Palavecino CE, Hernández J, León MA, Kalergis AM, Bueno SM. Elevated IL-3 and IL-12p40 levels in the lower airway of infants with RSV-induced bronchiolitis correlate with recurrent wheezing. Cytokine. 2015;76(2):417–423. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bongen E, Vallania F, Utz PJ, Khatri P. KLRD1-expressing natural killer cells predict influenza susceptibility. Genome Med. 2018;10(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13073-018-0554-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bot A, Rodrigo E, Wolfe T, Bot S, Von Herrath MG. Infection-triggered regulatory mechanisms override the role of STAT 4 in control of the immune response to influenza virus antigens. J Virol. 2003;77(10):5794–5800. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.10.5794-5800.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai G, Nie X, Li L, Hu L, Wu B, Lin J, Jiang C, Wang H, Wang X, Shen Q. B and T lymphocyte attenuator is highly expressed on intrahepatic T cells during chronic HBV infection and regulates their function. J Gastroenterol. 2013;48(12):1362–1372. doi: 10.1007/s00535-013-0762-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calado M, Matoso P, Santos-Costa Q, Espirito-Santo M, Machado J, Rosado L, Antunes F, Mansinho K, Lopes MM, Maltez F, et al. Coreceptor usage by HIV-1 and HIV-2 primary isolates: the relevance of CCR8 chemokine receptor as an alternative coreceptor. Virology. 2010;408(2):174–182. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.09.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspi R, Billington R, Ferrer L, Foerster H, Fulcher CA, Keseler IM, Kothari A, Krummenacker M, Latendresse M, Mueller LA, et al. The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(D1):D471–D480. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilow EM, Meyerholz DK, Varga SM. IL-13 is required for eosinophil entry into the lung during respiratory syncytial virus vaccine-enhanced disease. J Immunol. 2008;180(4):2376–2384. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.4.2376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caufour P, Le Grand R, Chéret A, Neildez O, Thiébot H, Théodoro F, Boson B, Vaslin B, Venet A, Dormont D. Longitudinal analysis of CD8(+) T-cell phenotype and IL-7, IL-15 and IL-16 mRNA expression in different tissues during primary simian immunodeficiency virus infection. Microbes Infect. 2001;3(3):181–191. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(01)01370-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan KY, Ching JC, Xu MS, Cheung AN, Yip SP, Yam LY, Lai ST, Chu CM, Wong AT, Song YQ, et al. Association of ICAM3 genetic variant with severe acute respiratory syndrome. J Infect Dis. 2007;196(2):271–280. doi: 10.1086/518892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan KY, Xu MS, Ching JC, So TM, Lai ST, Chu CM, Yam LY, Wong AT, Chung PH, Chan VS, et al. CD209 (DC-SIGN) -336A > G promoter polymorphism and severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong Chinese. Hum Immunol. 2010;71(7):702–707. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2010.03.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J, Bardes EE, Aronow BJ, Jegga AG. ToppGene Suite for gene list enrichment analysis and candidate gene prioritization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(Web Server issue):W305–W311. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C, Zhu X, Xu W, Yang F, Zhang G, Wu L, Zheng Y, Gao Z, Xie C, Peng L. IFNA2 p.Ala120Thr impairs the inhibitory activity of Interferon-α2 against the hepatitis B virus through altering its binding to the receptor. Antiviral Res. 2017;147:11–18. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X, Zhang Q, Bai J, Zhao Y, Wang X, Wang H, Jiang P. The nucleocapsid protein and nonstructural protein 10 of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus enhance CD83 production via NF-κB and Sp1 signaling pathways. J Virol. 2017;91(18):e00986. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00986-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi CY, Chu CC, Liu JP, Lin CH, Ho MW, Lo WJ, Lin PC, Chen HJ, Chou CH, Feng JY, et al. Anti-IFN-γ autoantibodies in adults with disseminated nontuberculous mycobacterial infections are associated with HLA-DRB1*16:02 and HLA-DQB1*05:02 and the reactivation of latent varicella-zoster virus infection. Blood. 2013;121(8):1357–1366. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-08-452482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou CH, Shrestha S, Yang CD, Chang NW, Lin YL, Liao KW, Huang WC, Sun TH, Tu SJ, Lee WH, et al. miRTarBase update 2018: a resource for experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D296–D302. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti P, Ronconi G, Caraffa A, Gallenga CE, Ross R, Frydas I, Kritas SK. Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): anti-inflammatory strategies. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020;34(2):1. doi: 10.23812/CONTI-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corominas H, Castellví I, Domingo P, Casademont J. Facing the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) outbreak with IL-6R antagonists. Eur J Rheumatol. 2020 doi: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2020.20061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree JN, He W, Guan W, Flage M, Miller MS, Peterson EJ. Autoimmune Variant PTPN22 C1858T Is Associated With Impaired Responses to Influenza Vaccination. J Infect Dis. 2016;214(2):248–257. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlquist KD, Salomonis N, Vranizan K, Lawlor SC, Conklin BR. GenMAPP, a new tool for viewing and analyzing microarray data on biological pathways. Nat Genet. 2002;31(1):19–20. doi: 10.1038/ng0502-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai E, Yu X, Zhang Y, Meng F, Wang S, Liu X, Liu D, Wang J, Li X, Jiang W. EpimiR: a database of curated mutual regulation between miRNAs and epigenetic modifications. Database (Oxford). 2014;2014:bau023. doi: 10.1093/database/bau023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson TC, Beck MA, Kuziel WA, Henderson F, Maeda N. Contrasting effects of CCR5 and CCR2 deficiency in the pulmonary inflammatory response to influenza A virus. Am J Pathol. 2000;156(6):1951–1959. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65068-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng S, Yang C, Nie K, Fan S, Zhu M, Zhu J, Chen Y, Yuan J, Zhang J, Xu H, et al. Host cell protein PSMB10 interacts with viral NS3 protein and inhibits the growth of classical swine fever virus. Virology. 2019;537:74–83. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2019.05.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai P, Tahiliani V, Abboud G, Stanfield J, Salek-Ardakani S. Batf3-dependent dendritic cells promote optimal CD8 T cell responses against respiratory poxvirus infection. J Virol. 2018;92(16):e00495. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00495-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd JS, Lum E, Goulding J, Muir R, Van Snick J, Openshaw PJ. IL-9 regulates pathology during primary and memory responses to respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Immunol. 2009;183(11):7006–7013. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du N, Kwon H, Li P, West EE, Oh J, Liao W, Yu Z, Ren M, Leonard WJ. EGR2 is critical for peripheral naïve T-cell differentiation and the T-cell response to influenza. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(46):16484–16489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417215111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrant DM, Daniels BP, Klein RS. IL-1R1 signaling regulates CXCL12-mediated T cell localization and fate within the central nervous system during West Nile Virus encephalitis. J Immunol. 2014;193(8):4095–4106. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnest JT, Hantak MP, Li K, McCray PB, Jr, Perlman S, Gallagher T. The tetraspanin CD9 facilitates MERS-coronavirus entry by scaffolding host cell receptors and proteases. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13(7):e1006546. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Saadany SA, Ziada DH, Farrag W, Hazaa S. Fibrosis severity and mannan-binding lectin (MBL)/MBL-associated serine protease 1 (MASP-1) complex in HCV-infected patients. Arab J Gastroenterol. 2011;12(2):68–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ajg.2011.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ermers MJ, Janssen R, Onland-Moret NC, Hodemaekers HM, Rovers MM, Houben ML, Kimpen JL, Bont LJ. IL10 family member genes IL19 and IL20 are associated with recurrent wheeze after respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Pediatr Res. 2011;70(5):518–523. doi: 10.1203/pdr.0b013e31822f5863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estrabaud E, Appourchaux K, Bieche I, Carrat F, Lapalus M, Lada O, Martinot-Peignoux M, Boyer N, Marcellin P, Vidaud M, et al. IFI35, mir-99a and HCV genotype to predict sustained virological response to pegylated-interferon plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(4):e0121395. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-Aguirre JA, Osuna-Ramírez I, Montes Prado, de Oca E, Ochoa-Ramirez LA, Ramirez M, Magallon-Zazueta LG, Gonzalez-Beltran MS, Cazarez-Salazar SG, Rangel-Villalobos H, Velarde-Felix JS. DEFB1 5′UTR polymorphisms modulate the risk of HIV-1 infection in Mexican women. Curr HIV Res. 2014;12(3):220–226. doi: 10.2174/1570162x12666140708102722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezinne CC, Yoshimitsu M, White Y, Arima N. HTLV-1 specific CD8 + T cell function augmented by blockade of 2B4/CD48 interaction in HTLV-1 infection. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(2):e87631. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabregat A, Jupe S, Matthews L, Sidiropoulos K, Gillespie M, Garapati P, Haw R, Jassal B, Korninger F, May B, et al. The reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D649–D655. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrbach KM, Barry SM, Ayehunie S, Lamore S, Klausner M, Hope TJ. Activated CD34-derived Langerhans cells mediate transinfection with human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 2007;81(13):6858–6868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02472-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan Y, Xia J. miRNet-functional analysis and visual exploration of mirna-target interactions in a network context. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1819:215–233. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8618-7_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan Y, Mok CK, Chan MC, Zhang Y, Nal B, Kien F, Bruzzone R, Sanyal S. Cell cycle-independent role of cyclin D3 in host restriction of influenza virus infection. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(12):5070–5088. doi: 10.1074/jbc.m117.776112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming-Canepa X, Brusnyk C, Aldridge JR, Ross KL, Moon D, Wang D, Xia J, Barber MR, Webster RG, Magor KE. Expression of duck CCL19 and CCL21 and CCR7 receptor in lymphoid and influenza-infected tissues. Mol Immunol. 2011;48(15–16):1950–1957. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2011.05.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossum E, Grødeland G, Terhorst D, Tveita AA, Vikse E, Mjaaland S, Henri S, Malissen B, Bogen B. Vaccine molecules targeting Xcr1 on cross-presenting DCs induce protective CD8 + T-cell responses against influenza virus. Eur J Immunol. 2015;45(2):624–635. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox JM, Crabtree JM, Sage LK, Tompkins SM, Tripp RA. Interferon lambda upregulates IDO1 expression in respiratory epithelial cells after influenza virus infection. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015;35(7):554–562. doi: 10.1089/jir.2014.0052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y, Cheng Y, Wu Y. Understanding SARS-CoV-2-mediated inflammatory responses: from mechanisms to potential therapeutic tools. Virol Sin. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s12250-020-00207-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaggar A, Shayakhmetov DM, Lieber A. CD46 is a cellular receptor for group B adenoviruses. Nat Med. 2003;9(11):1408–1412. doi: 10.1038/nm952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagné B, Tremblay N, Park AY, Baril M, Lamarre D. Importin β1 targeting by hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protein restricts IRF3 and NF-κB signaling of IFNB1 antiviral response. Traffic. 2017;18(6):362–377. doi: 10.1111/tra.12480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García M, Cooper A, Shi W, Bornmann W, Carrion R, Kalman D, Nabel GJ. Productive replication of Ebola virus is regulated by the c-Abl1 tyrosine kinase. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(123):123ra24. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlert T, Devergne O, Niedobitek G. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection and expression of the interleukin-12 family member EBV-induced gene 3 (EBI3) in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. J Med Virol. 2004;73(3):432–438. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girkin J, Hatchwell L, Foster P, Johnston SL, Bartlett N, Collison A, Mattes J. CCL7 and IRF-7 Mediate Hallmark Inflammatory and IFN Responses following Rhinovirus 1B Infection. J Immunol. 2015;194(10):4924–4930. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden-Mason L, Burton JR, Jr, Castelblanco N, Klarquist J, Benlloch S, Wang C, Rosen HR. Loss of IL-7 receptor alpha-chain (CD127) expression in acute HCV infection associated with viral persistence. Hepatology. 2006;44(5):1098–1109. doi: 10.1002/hep.21365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski SA, Hahn YS, Braciale TJ. Group 2 innate lymphoid cell production of IL-5 is regulated by NKT cells during influenza virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(9):e1003615. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guévin C, Manna D, Bélanger C, Konan KV, Mak P, Labonté P. Autophagy protein ATG5 interacts transiently with the hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase (NS5B) early during infection. Virology. 2010;405(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.05.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guntermann C, Dye J, Nye KE. Human immunodeficiency virus infection abolishes CD4-dependent activation of ZAP-70 by inhibition of p56lck. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1997;14(3):204–212. doi: 10.1097/00042560-199703010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen MD, Johnsen IB, Stiberg KA, Sherstova T, Wakita T, Richard GM, Kandasamy RK, Meurs EF, Anthonsen MW. Hepatitis C virus triggers Golgi fragmentation and autophagy through the immunity-related GTPase M. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114(17):E3462–E3471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1616683114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harcourt JL, Brown MP, Anderson LJ, Tripp RA. CD40 ligand (CD154) improves the durability of respiratory syncytial virus DNA vaccination in BALB/c mice. Vaccine. 2003;21(21–22):2964–2979. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(03)00119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai A, Ohtsuka N, Ikeda T, Taniguchi R, Blau D, Nakagaki K, Miura HS, Ami Y, Yamada YK, Itohara S, et al. Role of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) receptor murine CEACAM1 in the resistance of mice to MHV infection: studies of mice with chimeric mCEACAM1a and mCEACAM1b. J Virol. 2010;84(13):6654–6666. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02680-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramoto T, Li LB, Funk SE, Hirata RK, Russell DW. Nuclease-free adeno-associated virus-mediated Il2rg gene editing in X-SCID mice. Mol Ther. 2018;26(5):1255–1265. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.02.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH, Nitsche A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou S, Doherty PC. Partitioning of responder CD8 + T cells in lymph node and lung of mice with Sendai virus pneumonia by LECAM-1 and CD45RB phenotype. J Immunol. 1993;150(12):5494–5500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu EC, Hsi B, Hirota-Tsuchihara M, Ruland J, Iorio C, Sarangi F, Diao J, Migliaccio G, Tyrrell DL, Kneteman N, et al. Modified apoptotic molecule (BID) reduces hepatitis C virus infection in mice with chimeric human livers. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21(5):519–525. doi: 10.1038/nbt817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M, Li HM, Bogoyevitch MA, Jans DA. Mitochondrial protein p32/HAPB1/gC1qR/C1qbp is required for efficient respiratory syncytial virus production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;489(4):460–465. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.05.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Z, Shi J, Gao Y, Cui C, Zhang S, Li J, Zhou Y, Cui Q. HMDD v.30: a database for experimentally supported human microRNA-disease associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D1013–D1017. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1010z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imakiire K, Uto H, Sato Y, Sasaki F, Mawatari S, Ido A, Shimoda K, Hayashi K, Stuver SO, Ito Y, et al. Difference in serum complement component C4a levels between hepatitis C virus carriers with persistently normal alanine aminotransferase levels or chronic hepatitis C. Mol Med Rep. 2012;6(2):259–264. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2012.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewison T, Su Y, Disfany FM, Liang Y, Knox C, Maciejewski A, Poelzer J, Huynh J, Zhou Y, Arndt D, et al. SMPDB 2.0: big improvements to the Small Molecule Pathway Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue):D478–D484. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Q, Wang Y, Hao Y, Juan L, Teng M, Zhang X, Li M, Wang G, Liu Y. miR2Disease: a manually curated database for microRNA deregulation in human disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(Database issue):D98–D104. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Morishima K, Tanabe M. New approach for understanding genome variations in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D590–D595. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney SP, Meng XJ. An SH3 binding motif within the nucleocapsid protein of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus interacts with the host cellular signaling proteins STAMI, TXK, Fyn, Hck, and cortactin. Virus Res. 2015;204:31–39. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A, Fornes O, Stigliani A, Gheorghe M, Castro-Mondragon JA, van der Lee R, Bessy A, Chèneby J, Kulkarni SR, Tan G, et al. JASPAR 2018: update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles and its web framework. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D260–D266. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H, Meyer K, Di Bisceglie AM, Ray R. Hepatitis C virus suppresses C9 complement synthesis and impairs membrane attack complex function. J Virol. 2013;87(10):5858–5867. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00174-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnikov N, Hastings E, Keays M, Melnichuk O, Tang YA, Williams E, Dylag M, Kurbatova N, Brandizi M, Burdett T, Megy K. Arrayexpress update–simplifying data submissions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(Database issue):D1113–D1116. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koraka P, Murgue B, Deparis X, van Gorp EC, Setiati TE, Osterhaus AD, Groen J. Elevation of soluble VCAM-1 plasma levels in children with acute dengue virus infection of varying severity. J Med Virol. 2004;72(3):445–450. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar P, Thakar MS, Ouyang W, Malarkannan S. IL-22 from conventional NK cells is epithelial regenerative and inflammation protective during influenza infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2013;6(1):69–82. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacher MD, Shiina M, Chang P, Keller D, Tiirikainen MI, Korn WM. ZEB1 limits adenoviral infectability by transcriptionally repressing the coxsackie virus and adenovirus receptor. Mol Cancer. 2011;10:91. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert ND, Haralambieva IH, Kennedy RB, Ovsyannikova IG, Pankratz VS, Poland GA. Polymorphisms in HLA-DPB1 are associated with differences in rubella virus-specific humoral immunity after vaccination. J Infect Dis. 2015;211(6):898–905. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Noury DA, Mosebi S, Papathanasopoulos MA, Hewer R. Functional roles of HIV-1 Vpu and CD74: details and implications of the Vpu-CD74 interaction. Cell Immunol. 2015;298(1–2):25–32. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letko M, Miazgowicz K, McMinn R, Seifert SN, Sola I, Enjuanes L, Carmody A, Van Doremalen N, Munster V. Adaptive evolution of MERS-CoV to Species Variation in DPP4. Cell Rep. 2018;24(7):1730–1737. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis SE. The vision and challenges of the gene ontology. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1446:291–302. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3743-1_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, Yang JH. starBase v20: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Databse Issue):D92–D97. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C, Kuang WD, Qu D, Wang JH. Toll-interacting protein inhibits HIV-1 infection and regulates viral latency. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;475(2):161–168. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.05.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Johnson JB, Parks GD. Parainfluenza virus 5 upregulates CD55 expression to produce virions with enhanced resistance to complement-mediated neutralization. Virology. 2016;497:305–313. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.07.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li YK, Peng S, Li LQ, Wang Q, Ping W, Zhang N, Fu XN. Clinical and transmission characteristics of Covid-19—a retrospective study of 25 cases from a single thoracic surgery department. Curr Med Sci. 2020;40(2):295–300. doi: 10.1007/s11596-020-2176-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin SJ, Lo M, Kuo RL, Shih SR, Ojcius DM, Lu J, Lee CK, Chen HC, Lin MY, Leu CM, et al. The pathological effects of CCR2 + inflammatory monocytes are amplified by an IFNAR1-triggered chemokine feedback loop in highly pathogenic influenza infection. J Biomed Sci. 2014;21(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12929-014-0099-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y, Nonnemacher MR, Wigdahl B. CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins and the pathogenesis of retrovirus infection. Future Microbiol. 2009;4(3):299–321. doi: 10.2217/fmb.09.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X, Wang S, Meng F, Wang J, Zhang Y, Dai E, Yu X, Li X, Jiang W. SM2miR: a database of the experimentally validated small molecules’ effects on microRNA expression. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(3):409–411. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B, Zhang X, Deng W, Liu J, Li H, Wen M, Bao L, Qu J, Liu Y, Li F, et al. Severe influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 infection induces thymic atrophy through activating innate CD8(+)CD44(hi) T cells by upregulating IFN-γ. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5(10):e1440. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X, Bi J, Zhao Q, Li M, Zuo Q, Wang X, Lan R, Li X, Yang G, Liu J, et al. Overexpression of RACK1 enhanced the replication of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in Marc-145 cells and promoted the NF-κB activation via upregulating the expression and phosphorylation of TRAF2. Gene. 2019;709:75–83. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.05.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loebbermann J, Schnoeller C, Thornton H, Durant L, Sweeney NP, Schuijs M, O’Garra A, Johansson C, Openshaw PJ. IL-10 regulates viral lung immunopathology during acute respiratory syncytial virus infection in mice. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(2):e32371. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loebbermann J, Thornton H, Durant L, Sparwasser T, Webster KE, Sprent J, Culley FJ, Johansson C, Openshaw PJ. Regulatory T cells expressing granzyme B play a critical role in controlling lung inflammation during acute viral infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2012;5(2):161–172. doi: 10.1038/mi.2011.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu JW, Chang JG, Yeh KT, Chen RM, Tsai JJ, Hu RM. Overexpression of Thy1/CD90 in human hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with HBV infection and poor prognosis. Acta Histochem. 2011;113(8):833–838. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2011.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden JM, Roberts JM, Harris NL, Peach RJ, Ronchese F. Differential requirement for CD80 and CD80/CD86-dependent costimulation in the lung immune response to an influenza virus infection. J Immunol. 2000;164(1):79–85. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma DY, Suthar MS, Kasahara S, Gale M, Jr, Clark EA. CD22 is required for protection against West Nile virus Infection. J Virol. 2013;87(6):3361–3375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02368-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madurai Elavarasan R, Pugazhendhi R. Restructured society and environment: a review on potential technological strategies to control the COVID-19 pandemic. Sci Total Environ. 2020;725:138858. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maestri A, Sortica VA, Ferreira DL, de Almeida Ferreira J, Amador MA, de Mello WA, Santos SE, Sousa RC. The His131Arg substitution in the FCGR2A gene (rs1801274) is not associated with the severity of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 infection. BMC Res Notes. 2016;9:296. doi: 10.1186/s13104-016-2096-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra P, Haslett P, Sherry B, Shepp DH, Barber P, Abshier J, Roy U, Schmidtmayerova H. Increased plasma levels of the TH2 chemokine CCL18 associated with low CD4 + T cell counts in HIV-1-infected patients with a suppressed viral load. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):5963. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41588-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin MP, Qi Y, Gao X, Yamada E, Martin JN, Pereyra F, Colombo S, Brown EE, Shupert WL, Phair J, et al. Innate partnership of HLA-B and KIR3DL1 subtypes against HIV-1. Nat Genet. 2007;39(6):733–740. doi: 10.1038/ng2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mi H, Huang X, Muruganujan A, Tang H, Mills C, Kang D, Thomas PD. PANTHER version 11: expanded annotation data from Gene Ontology and Reactome pathways, and data analysis tool enhancements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D183–D189. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller AL, Gerard C, Schaller M, Gruber AD, Humbles AA, Lukacs NW. Deletion of CCR1 attenuates pathophysiologic responses during respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Immunol. 2006;176(4):2562–2567. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.4.2562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miot C, Beaumont E, Duluc D, Le Guillou-Guillemette H, Preisser L, Garo E, Blanchard S, Fouchard IH, Créminon C, Lamourette P, et al. IL-26 is overexpressed in chronically HCV-infected patients and enhances TRAIL-mediated cytotoxicity and interferon production by human NK cells. Gut. 2015;64(9):1466–1475. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani T, Fukushi S, Murakami M, Hirano T, Saijo M, Kurane I, Morikawa S. Tyrosine dephosphorylation of STAT3 in SARS coronavirus-infected Vero E6 cells. FEBS Lett. 2004;577(1–2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.10.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales-García G, Falfán-Valencia R, García-Ramírez RA, Camarena Á, Ramirez-Venegas A, Castillejos-López M, Pérez-Rodríguez M, González-Bonilla C, Grajales-Muñíz C, Borja-Aburto V, et al. Pandemic influenza A/H1N1 virus infection and TNF, LTA, IL1B, IL6, IL8, and CCL polymorphisms in Mexican population: a case-control study. BMC Infect Dis. 2012;12:299. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller T, Mas-Marques A, Sarrazin C, Wiese M, Halangk J, Witt H, Ahlenstiel G, Spengler U, Goebel U, Wiedenmann B, et al. Influence of interleukin 12B (IL12B) polymorphisms on spontaneous and treatment-induced recovery from hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol. 2004;41(4):652–658. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2004.06.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee S, Rasky AJ, Lundy PA, Kittan NA, Kunkel SL, Maillard IP, Kowalski PE, Kousis PC, Guidos CJ, Lukacs NW. STAT5-induced lunatic fringe during Th2 development alters delta-like 4-mediated Th2 cytokine production in respiratory syncytial virus-exacerbated airway allergic disease. J Immunol. 2014;192(3):996–1003. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagarkar DR, Wang Q, Shim J, Zhao Y, Tsai WC, Lukacs NW, Sajjan U, Hershenson MB. CXCR2 is required for neutrophilic airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in a mouse model of human rhinovirus infection. J Immunol. 2009;183(10):6698–6707. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T, Fujisawa R, Izawa D, Hieshima K, Takada K, Yoshie O. Human B cells immortalized with Epstein-Barr virus upregulate CCR6 and CCR10 and downregulate CXCR4 and CXCR5. J Virol. 2002;76(6):3072–3077. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.6.3072-3077.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasi M, Riva A, Borghi V, D’Amico R, Del Giovane C, Casoli C, Galli M, Vicenzi E, Gibellini L, De Biasi S, et al. Novel genetic association of TNF-α-238 and PDCD1-7209 polymorphisms with long-term non-progressive HIV-1 infection. Int J Infect Dis. 2013;17(10):e845–e850. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2013.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen TP, Liu WC, Jordán F. Inferring pleiotropy by network analysis: linked diseases in the human PPI network. BMC Syst Biol. 2011;5:179. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-5-179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma T, Mori A, Yoshizawa I. Induction of allergen-specific IL-2 responsiveness of lymphocytes after respiratory syncytial virus infection and prediction of onset of recurrent wheezing and bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;98(4):816–826. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(96)70131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Connell P, Pepelyayeva Y, Blake MK, Hyslop S, Crawford RB, Rizzo MD, Pereira-Hicks C, Godbehere S, Dale L, Gulick P, et al. SLAMF7 is a critical negative regulator of IFN-α-mediated CXCL10 production in chronic HIV infection. J Immunol. 2019;202(1):228–238. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S, Kohyama S, Taneichi M, Moriya O, Hayashi H, Oda H, Mori M, Kobayashi A, Akatsuka T, Uchida T, et al. Synthetic peptides coupled to the surface of liposomes effectively induce SARS coronavirus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes and viral clearance in HLA-A*0201 transgenic mice. Vaccine. 2009;27(29):3912–3920. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D, Nan Y, Shen M, Ritthipichai K, Zhu X, Zhang YJ. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus inhibits type I interferon signaling by blocking STAT1/STAT2 nuclear translocation. J Virol. 2010;84(21):11045–11055. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00655-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri V, Jayaraman P, Tutaj M, Hayman GT, Smith JR, De Pons J, Laulederkind SJ, Lowry TF, Nigam R, Wang SJ. The pathway ontology - updates and applications. J Biomed Semant. 2014;5(1):7. doi: 10.1186/2041-1480-5-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillai PS, Molony RD, Martinod K, Dong H, Pang IK, Tal MC, Solis AG, Bielecki P, Mohanty S, Trentalange M, et al. Mx1 reveals innate pathways to antiviral resistance and lethal influenza disease. Science. 2016;352(6284):463–466. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf3926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pineda-Tenor D, Berenguer J, Jiménez-Sousa MA, Guzmán-Fulgencio M, Aldámiz-Echevarria T, Carrero A, García-Álvarez M, Diez C, Tejerina F, Briz V, et al. CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11 polymorphisms are associated with sustained virologic response in HIV/HCV-coinfected patients. J Clin Virol. 2014;61(3):423–429. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2014.08.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada R, Pettoello-Mantovani M, Sieweke M, Graf T, Goldstein H. Suppression of HIV type 1 replication by a dominant-negative Ets-1 mutant. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000;16(18):1981–1989. doi: 10.1089/088922200750054710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothlichet J, Meunier I, Davis BK, Ting JP, Skamene E, von Messling V, Vidal SM. Type I IFN triggers RIG-I/TLR3/NLRP3-dependent inflammasome activation in influenza A virus infected cells. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(4):e1003256. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przulj N, Wigle DA, Jurisica I. Functional topology in a network of protein interactions. Bioinformatics. 2004;20(3):340–348. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puthothu B, Krueger M, Forster J, Heinzmann A. Association between severe respiratory syncytial virus infection and IL13/IL4 haplotypes. J Infect Dis. 2006;193(3):438–441. doi: 10.1086/499316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziorrouh B, Schraut W, Gerlach T, Nowack D, Grüner NH, Ulsenheimer A, Zachoval R, Wächtler M, Spannagl M, Haas J, et al. The immunoregulatory role of CD244 in chronic hepatitis B infection and its inhibitory potential on virus-specific CD8 + T-cell function. Hepatology. 2010;52(6):1934–1947. doi: 10.1002/hep.23936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice TA, Brenner TA, Percopo CM, Ma M, Keicher JD, Domachowske JB, Rosenberg HF. Signaling via pattern recognition receptors NOD2 and TLR2 contributes to immunomodulatory control of lethal pneumovirus infection. Antiviral Res. 2016;132:131–140. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.06.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu DI, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, Smyth GK. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(7):e47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N, Lisacek F, Sanchez JC, Müller M. pROC: an open-source package for R and S + to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:77. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez R, Fournier B, Cordeiro DJ, Winter S, Izawa K, Martin E, Boutboul D, Lenoir C, Fraitag S, Kracker S, et al. Concomitant PIK3CD and TNFRSF9 deficiencies cause chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection of T cells. J Exp Med. 2019;216(12):2800–2818. doi: 10.1084/jem.20190678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romporn S, Hirankarn N, Tangkijvanich P, Kimkong I. Association of IFNAR2 and IL10RB genes in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Tissue Antigens. 2013;82(1):21–25. doi: 10.1111/tan.12133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger CM, Podyminogin RL, Diercks AH, Treuting PM, Peschon JJ, Rodriguez D, Gundapuneni M, Weiss MJ, Aderem A. miR-144 attenuates the host response to influenza virus by targeting the TRAF6-IRF7 signaling axis. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13(4):e1006305. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruepp A, Kowarsch A, Schmidl D, Buggenthin F, Brauner B, Dunger I, Fobo G, Frishman G, Montrone C, Theis FJ. PhenomiR: a knowledgebase for microRNA expression in diseases and biological processes. Genome Biol. 2010;11(1):R6. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-1-r6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rukov JL, Wilentzik R, Jaffe I, Vinther J, Shomron N. Pharmaco-miR: linking microRNAs and drug effects. Brief Bioinform. 2014;15(4):648–659. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbs082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi A, Cappelli G, Cairo C, Martino A, Sanarico N, D’Offizi G, Pupillo LP, Chenal H, De Libero G, Colizzi V, et al. Differentiation of monocytes into CD1a- dendritic cells correlates with disease progression in HIV-infected patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007;46(5):519–528. doi: 10.1097/qai.0b013e31815b1278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sainz B, Jr, Mossel EC, Peters CJ, Garry RF. Interferon-beta and interferon-gamma synergistically inhibit the replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) Virology. 2004;329(1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2004.08.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salimi V, Ramezani A, Mirzaei H, Tahamtan A, Faghihloo E, Rezaei F, Naseri M, Bont L, Mokhtari-Azad T, Tavakoli-Yaraki M. Evaluation of the expression level of 12/15 lipoxygenase and the related inflammatory factors (CCL5, CCL3) in respiratory syncytial virus infection in mice model. Microb Pathog. 2017;109:209–213. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.05.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders SP, Siekierski ES, Richards SM, Porter JD, Imani F, Proud D. Rhinovirus infection induces expression of type 2 nitric oxide synthase in human respiratory epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;107(2):235–243. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.112028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanfilippo C, Cambria D, Longo A, Palumbo M, Avola R, Pinzone M, Nunnari G, Condorelli F, Musumeci G, Imbesi R. SERPING1 mRNA overexpression in monocytes from HIV + patients. Inflamm Res. 2017;66(12):1107–1116. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer CF, Anthony K, Krupa S, Buchoff J, Day M, Hannay T, Buetow KH. PID: the pathway interaction database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(1):D674–D679. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafique M, Wilschut J, de Haan A. Induction of mucosal and systemic immunity against respiratory syncytial virus by inactivated virus supplemented with TLR9 and NOD2 ligands. Vaccine. 2012;30(3):597–606. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.11.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13(11):2498–2504. doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma M, Bhattacharyya S, Sharma KB, Chauhan S, Asthana S, Abdin MZ, Vrati S, Kalia M. Japanese encephalitis virus activates autophagy through XBP1 and ATF6 ER stress sensors in neuronal cells. J Gen Virol. 2017;98(5):1027–1039. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Z, Zhang B. Fast network centrality analysis using GPUs. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:149. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi L, Ramaswamy M, Manzel LJ, Look DC. Inhibition of Jak1-dependent signal transduction in airway epithelial cells infected with adenovirus. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007;37(6):720–728. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0158oc. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi T, He Y, Sun W, Wu Y, Li L, Jie Z, Su X. Respiratory Syncytial virus infection compromises asthma tolerance by recruiting interleukin-17A-producing cells via CCR6-CCL20 signaling. Mol Immunol. 2017;88:45–57. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.05.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidenius N, Sier CF, Ullum H, Pedersen BK, Lepri AC, Blasi F, Eugen-Olsen J. Serum level of soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor is a strong and independent predictor of survival in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood. 2000;96(13):4091–4095. doi: 10.1182/blood.V96.13.4091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu KL, Kok KH, Ng MH, Poon VK, Yuen KY, Zheng BJ, Jin DY. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus M protein inhibits type I interferon production by impeding the formation of TRAF3.TANK.TBK1/IKKepsilon complex. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(24):16202–16209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.m109.008227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soroosh P, Doherty TA, So T, Mehta AK, Khorram N, Norris PS, Scheu S, Pfeffer K, Ware C, Croft M. Interactions between herpesvirus entry mediator (TNFRSF14) and latency-associated transcript during herpes simplex virus 1 latency. J Virol. 2014;88(4):1961–1971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02467-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector SA, Singh KK, Gupta S, Cystique LA, Jin H, Letendre S, Schrier R, Wu Z, Hong KX, Yu X, et al. APOE epsilon4 and MBL-2 O/O genotypes are associated with neurocognitive impairment in HIV-infected plasma donors. AIDS. 2010;24(10):1471–1479. doi: 10.1097/qad.0b013e328339e25c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasa BT, Restori KH, Shan J, Cyr L, Xing L, Lee S, Ward BJ, Fixman ED. STAT6 inhibitory peptide given during RSV infection of neonatal mice reduces exacerbated airway responses upon adult reinfection. J Leukoc Biol. 2017;101(2):519–529. doi: 10.1189/jlb.4a0215-062rr. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(43):15545–15550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sungnak W, Huang N, Bécavin C, Berg M, Queen R, Litvinukova M, Talavera-López C, Maatz H, Reichart D, Sampaziotis F, et al. SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes. Nat Med. 2020 doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0868-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suryadevara M, Bonville CA, Rosenberg HF, Domachowske JB. Local production of CCL3, CCL11, and IFN-γ correlates with disease severity in murine parainfluenza virus infection. Virol J. 2013;10:357. doi: 10.1186/1743-422x-10-357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan S, Dai L, Lane HC, Imamichi T. Evaluating the potential of IL-27 as a novel therapeutic agent in HIV-1 infection. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013;24(6):571–577. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.07.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A, Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork P, et al. STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D607–D613. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T, Takaguchi M, Kawakami T, Suzuki T. Sulfatide regulates caspase-3-independent apoptosis of influenza A virus through viral PB1-F2 protein. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(4):e61092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry RL, Deffrasnes C, Getts DR, Minten C, Van Vreden C, Ashhurst TM, Getts MT, Xie RD, Campbell IL, King NJ. Defective inflammatory monocyte development in IRF8-deficient mice abrogates migration to the West Nile virus-infected brain. J Innate Immun. 2015;7(1):102–112. doi: 10.1159/000365972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian X, Zhang A, Qiu C, Wang W, Yang Y, Qiu C, Liu A, Zhu L, Yuan S, Hu H, et al. The upregulation of LAG-3 on T cells defines a subpopulation with functional exhaustion and correlates with disease progression in HIV-infected subjects. J Immunol. 2015;194(8):3873–3882. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian J, Jiao X, Wang X, Geng J, Wang R, Liu N, Gao X, Griffin N, Shan F. Novel effect of methionine enkephalin against influenza A virus infection through inhibiting TLR7-MyD88-TRAF6-NF-κB p65 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;55:38–48. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbs C, Donaldson P, Underhill J, Thomson L, Manabe K, Williams R. Evidence that the HLA DQA1*03 allele confers protection from chronic HCV-infection in Northern European Caucasoids. Hepatology. 1996;24(6):1342–1345. doi: 10.1053/jhep.1996.v24.pm0008938158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tochikura TS, Xiao S, Ego T, Sagara J, Kawai A. Further characterization of a CD99-related 21-kDa transmembrane protein (VAP21) expressed in Syrian hamster cells and its possible involvement in vesicular stomatitis virus production. Microbiol Immunol. 2003;47(10):745–757. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2003.tb03444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treon SP, Castillo J, Skarbnik AP, Soumerai JD, Ghobrial IM, Guerrera ML, Meid KE, Yang G. The BTK-inhibitor ibrutinib may protect against pulmonary injury in COVID-19 infected patients. Blood. 2020 doi: 10.1182/blood.2020006288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucci FA, Broering R, Johansson P, Schlaak JF, Küppers R. B cells in chronically hepatitis C virus-infected individuals lack a virus-induced mutation signature in the TP53, CTNNB1, and BCL6 genes. J Virol. 2013;87(5):2956–2962. doi: 10.1128/jvi.03081-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uematsu T, Iizasa E, Kobayashi N, Yoshida H, Hara H. Loss of CARD9-mediated innate activation attenuates severe influenza pneumonia without compromising host viral immunity. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17577. doi: 10.1038/srep17577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbroeck K, Alloza I, Swaminathan B, Antigüedad A, Otaegui D, Olascoaga J, Barcina MG, De Las Heras V, Bartolomé M, Fernández-Arquero M, et al. Validation of IRF5 as multiple sclerosis risk gene: putative role in interferon beta therapy and human herpes virus-6 infection. Genes Immun. 2011;12(1):40–45. doi: 10.1038/gene.2010.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlachos IS, Paraskevopoulou MD, Karagkouni D, Georgakilas G, Vergoulis T, Kanellos I, Anastasopoulos IL, Maniou S, Karathanou K, Kalfakakou D, et al. DIANA-TarBase v7.0: indexing more than half a million experimentally supported miRNA:mRNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(1):D153–D159. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang SZ, Smith PK, Lovejoy M, Bowden JJ, Alpers JH, Forsyth KD. Shedding of L-selectin and PECAM-1 and upregulation of Mac-1 and ICAM-1 on neutrophils in RSV bronchiolitis. Am J Physiol. 1998;275(5):L983–L989. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1998.275.5.l983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang JH, Kwas C, Wu L. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), but not ICAM-2 and -3, is important for dendritic cell-mediated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmission. J Virol. 2009;83(9):4195–4204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00006-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Yan J, Shi Y, Li P, Liu C, Ma Q, Yang R, Wang X, Yang X, Cao C. Lack of association between polymorphisms of MASP2 and susceptibility to SARS coronavirus infection. BMC Infect Dis. 2009;9:51. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-9-51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Li M, Wang H, Pan Y. Identification of essential proteins based on edge clustering coefficient. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2012;9(4):1070–1080. doi: 10.1109/tcbb.2011.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Liu Y, Xie L, Li S, Qin X. Association of IL-17A and IL-17F gene polymorphisms with chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis in a Chinese population: a case-control study. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2016;40(3):288–296. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2015.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X, Ma K, Chen M, Ko KH, Zheng BJ, Lu L. IL-17A promotes pulmonary B-1a cell differentiation via induction of blimp-1 expression during influenza virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12(1):e1005367. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang SM, Huang KJ, Wang CT. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein counteracts BST2-mediated restriction of virus-like particle release. J Med Virol. 2019;91(10):1743–1750. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warby TJ, Crowe SM, Jaworowski A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection inhibits granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced activation of STAT5A in human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Virol. 2003;77(23):12630–12638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.23.12630-12638.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasityastuti W, Yano Y, Ratnasari N, Triyono T, Triwikatmani C, Indrarti F, Heriyanto DS, Yamani LN, Liang Y, Utsumi T, et al. Protective effects of HLA-DPA1/DPB1 variants against Hepatitis B virus infection in an Indonesian population. Infect Genet Evol. 2016;41:177–184. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.03.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei W, Guo H, Chang J, Yu Y, Liu G, Zhang N, Willard SH, Zheng S, Yu XF. ICAM-5/telencephalin is a functional entry receptor for enterovirus D68. Cell Host Microbe. 2016;20(5):631–641. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler CW, Woods TA, Rosenke R, Scott DP, Best SM, Peterson KE. Sexual and Vertical Transmission of Zika Virus in anti-interferon receptor-treated Rag1-deficient mice. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):7176. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07099-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D, Yang XO. TH17 responses in cytokine storm of COVID-19: an emerging target of JAK2 inhibitor Fedratinib. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020;S1684–1182(20):30065–30067. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H, Haist V, Baumgärtner W, Schughart K. Sustained viral load and late death in Rag2-/- mice after influenza A virus infection. Virol J. 2010;7:172. doi: 10.1186/1743-422x-7-172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X, Li T. miRecords: an integrated resource for microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(Database Issue):D105–D110. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu R, Bao C, Huang H, Lin F, Yuan Y, Wang S, Jin L, Yang T, Shi M, Zhang Z, et al. Low expression of CXCR1/2 on neutrophils predicts poor survival in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38714. doi: 10.1038/srep38714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X, Li Y, Liang Y, Yin M, Zhang Y, Huang L, Yu Z, Ni J. Low responsiveness to a hepatitis B virus vaccine in a Chinese population lacks association with ITGAL, CD58, TNFSF15, CCL15, TGFB3, and BCL6 gene variants. Infect Genet Evol. 2018;64:126–130. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang P, Li QJ, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Markowitz GJ, Ning S, Deng Y, Zhao J, Jiang S, Yuan Y, et al. TGF-β-miR-34a-CCL22 signaling-induced Treg cell recruitment promotes venous metastases of HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2012;22(3):291–303. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.07.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaki N, Efimov D, Berengueres J. Protein complex detection using interaction reliability assessment and weighted clustering coefficient. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14:163. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehender G, Meroni L, De Maddalena C, Varchetta S, Monti G, Galli M. Detection of hepatitis C virus RNA in CD19 peripheral blood mononuclear cells of chronically infected patients. J Infect Dis. 1997;176(5):1209–1214. doi: 10.1086/514114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H, Penninger JM, Li Y, Zhong N, Slutsky AS. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(4):586–590. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-05985-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X, Song X, Bai X, Fei N, Huang Y, Zhao Z, Du Q, Zhang H, Zhang L, Tong D. miR-27b attenuates apoptosis induced by transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) infection via targeting runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) PeerJ. 2016;4:e1635. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J, Zhu M, Jiang H, Shen S, Su X, Shi Y. Combination of sphingosinE − 1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1PR1) agonist and antiviral drug: a potential therapy against pathogenic influenza virus. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):5272. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41760-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Zheng J, Yang P, Tang Y, Zhao D. A respiratory syncytial virus persistent-infected cell line system reveals the involvement of SOCS1 in the innate antiviral response. Virol Sin. 2015;30(3):190–199. doi: 10.1007/s12250-015-3597-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhivaki D, Lemoine S, Lim A, Morva A, Vidalain PO, Schandene L, Casartelli N, Rameix-Welti MA, Hervé PL, Dériaud E, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus infects regulatory B cells in human neonates via chemokine receptor CX3CR1 and promotes lung disease severity. Immunity. 2017;46(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.01.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou G, Soufan O, Ewald J, Hancock REW, Basu N, Xia J. NetworkAnalyst 3.0: a visual analytics platform for comprehensive gene expression profiling and meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu DY, Jiang LF, Deng XZ, Xiao W, Pei JP, Li BJ, Wang CJ, Zhang JH, Zhang Q, Zhou ZX, et al. TBX21 polymorphisms are associated with virus persistence in hepatitis C virus infection patients from a high-risk Chinese population. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;34(7):1309–1318. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2337-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou L, Ruan F, Huang M, Liang L, Huang H, Hong Z, Yu J, Kang M, Song Y, Xia J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Upper Respiratory Specimens of Infected Patients. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(12):1177–1179. doi: 10.1056/nejmc2001737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman E, Zuckerman T, Sahar D, Streichman S, Attias D, Sabo E, Yeshurun D, Rowe JM. bcl-2 and immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in patients with hepatitis C virus infection. Br J Haematol. 2001;112(2):364–369. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are available in the ArrayExpress (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress) repository. [(E-MTAB-8871) (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-8871/)].