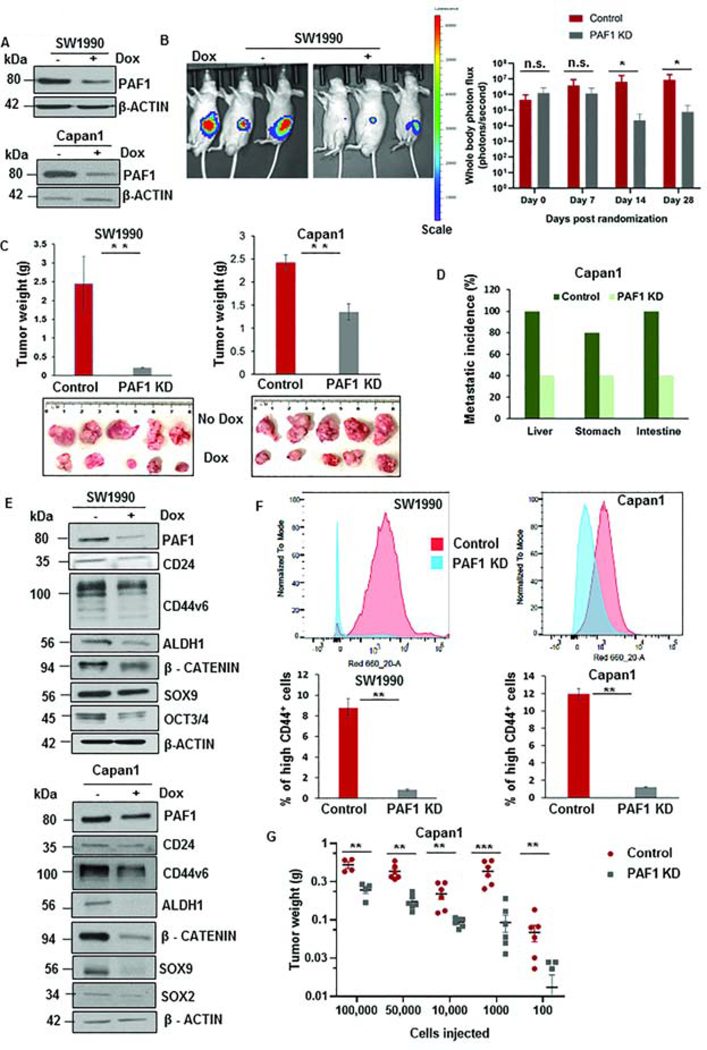
Figure 1: Loss of PAF1 reduces pancreatic tumorigenesis and proportions of CSCs.
A. Immunoblot depicting the efficiency of PAF1 KD using a doxycycline-based inducible shRNA system. B. Representative IVIS image of mice from control and PAF1 KD group. The right panel represents a quantification of total photon counts at indicated time points. Data represented as mean ± SD (n = 10 mice per group). C. Representative images and quantification of tumor weights generated with orthotopic implantation of engineered SW1990 and Capan1 cells in pancreas of athymic nude mice. D. Graphical representation of metastatic incidence in xenografts generated from orthotopic implantation of control and PAF1-depleted Capan1 cells. E. Immunoblot analysis of PAF1 and CSC markers with and without doxycycline treatment in engineered SW1990 and Capan1 cells. F. Percentage of high CD44+ cells in control and PAF1 KD SW1990 and Capan1 cells. G. Graphical representation of tumor weights of control and PAF1 KD cohorts versus the number of cells injected per tumor subcutaneously.*P <0.05, **P <0.01, ***P <0.001.