Abstract
Aims
Compared to their heterosexual peers, youth who identify as lesbian, gay or bisexual (LGB) tend to suffer higher rates of peer victimisation from bullying. However, studies of LGB adolescents' participation as bullies are scarce. We aimed to examine the possible association of sexual minority identity and the heightened risk of not only being bullied but bullying others as well. We also explored the effect of one's sexual identity on their involvement in bullying through the mediation of coping strategies and mood states.
Methods
A total of 12 218 students were recruited from 18 secondary schools in China. The demographic information, positive and negative coping strategies, mood state (anxiety, depression and hypomania) and information related to bullying and being bullied were collected. Multinomial regression was used to assess the heightened risk of sexual minority groups in comparison to their heterosexual adolescents' counterparts. A structural equation model (SEM) was used to test the mediating role of coping strategy and mood state between one's sex, sexual identity and bullying experience.
Results
Two trends could be observed: (1) LGB groups reported heightened risks of being bullied and bullying others at school than heterosexual peers. However, being a sexual-undeveloped girl seemed to have a protective effect on bullying-related problems. (2) Birth-assigned males were more likely to be bullied as well as bullying others at school when compared to birth-assigned females. SEM analysis revealed that being a sexual minority was directly associated with a higher frequency of being bullied (B = 0.16, 95% CI [0.10, 0.22], p < 0.001) but not bullying others (B = 0.02, 95% CI [−0.02, 0.06], p = 0.398) when compared to the heterosexual group. Negative coping, hypomania, anxiety and depression were associated with a higher frequency of being bullied, while positive coping was associated with a lower frequency of being bullied. Moreover, negative coping, hypomania and depression were associated with a higher frequency of bullying others, while positive coping was associated with a reduced likelihood of bullying others. In addition, being bullied and bullying others were significantly correlated in the SEM model.
Conclusions
This novel research investigated the dynamic nature of the interaction between victim and bullying of LGB school adolescents in China, with a specific exploration of the psychological mechanism behind the pattern of being bullied and bullying others. School-level interventions aimed at teaching positive coping strategies to lower psychological distress are recommended to support sexual minority students.
Key words: Adolescents, bullying, coping strategies, LGB, sexual minority, victim-bully cycle
Introduction
Bullying has been defined as intentional and repeated aggressive behaviours that occur in power and imbalanced interpersonal relationships (Whitney and Smith, 1993; Olweus, 1994). Bullying is a highly stressful experience and victims can have numerous negative outcomes (Duong and Bradshaw, 2014). Peer bullying experienced by adolescents is correlated with severe mental health problems – including suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, non-suicidal self-injury, depression and anxiety – and can have long-term detrimental life consequence (Klomek et al., 2007; Drydakis, 2019; Li et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2020). Due to the marginalised sexual orientation, lesbian, gay and bisexual (LGB) adolescents are more likely to face noticeable challenges and adverse experiences, including the victim-bully cycle (Button et al., 2012).
Bullying in sexual minority individuals
Studies across different countries have demonstrated that sexual minorities tend to be victims of verbal, physical and social bullying (Birkett et al., 2009; Robinson and Espelage, 2012; Collier et al., 2013; Robinson et al., 2013; Duong and Bradshaw, 2014). A previous meta-analysis showed that identifying as a sexual minority is a risk factor for suffering from bullying at school (Moyano and del Mar Sánchez-Fuentes, 2020). Researchers have consistently found that homophobic bullying is linked to negative mental health outcomes (Espelage et al., 2019; Peng et al., 2019). Much of the literature has focused on the experiences of sexual minority adolescents being bullied, while studies on sexual minority adolescents' participation in bullying are scarce. Previous research on the victim-bully cycle in middle school indicates that the relationship from bully to victim was reciprocal (Ma, 2001). Bully-victims can be defined as an individual who was a victim of bulling who then in turn reciprocates and bullies others (Swearer et al., 2001). Research on the victim and bully roles at school has found that the victim role was unstable and that the bully role was only moderately stable (Schäfer et al., 2005). Many studies have suggested the roles oscillate between bully and victim (Olweus, 1994; Slee, 1995; Swearer et al., 2001). The victim-bully cycle can be explained by social learning theory; the victims' bullying behaviours could be a socially learned behaviour as a response to coping with the situation (Ma, 2001). Bullying research has also found that some of the most extreme victims are also among the most aggressive of bullies (Perry et al., 1988). In addition, sexual minority youth who experience school bullying are more likely to engage in aggressive behaviours such as physical fights (Duong and Bradshaw, 2014). It is important to note that those who take on the role of both the victim and bully may be at the highest risk for depression and anxiety (Swearer et al., 2001).
Bullying and mood problems
Research has shown that victims of bullying are at risk of mood disorders (Kochenderfer-Ladd and Skinner, 2002; Tenenbaum et al., 2011). There is ample documentation of the sexual minority population being at risk for depression and anxiety (D'augelli and Grossman, 2001; Meyer, 2003; Cochran and Mays, 2009; Bostwick et al., 2010; Chakraborty et al., 2011; Marshal et al., 2011; Fredriksen-Goldsen et al., 2013). Considering that sexual minority individuals have a higher likelihood of being bullied and a higher risk of having mood problems, bullying and mood disorders are likely to be prevalent in sexual minority adolescent at schools. Although the role of bullying within hypomania is not clear, a previous study suggests that bullying victimisation may increase the vulnerability of developing psychotic symptoms which could result in further hypomanic symptoms (Trotta et al., 2013). Sexual minority identity has been associated with psychosis (Pakula and Shoveller, 2013; Jacob et al., 2019), and researchers propose that stressful life events, such as bullying victimisation, may function as part of the underlying mechanism that results in hypomania (Jacob et al., 2019).
Coping strategies and bullying
Many studies have investigated the association between coping strategies and bullying (Varjas et al., 2009; Tenenbaum et al., 2011). A previous longitudinal study in the USA found that bullying was more persistent for victims who applied negative coping strategies (i.e. fought back) than those who applied positive coping strategies (i.e. having a friend help) (Kochenderfer and Ladd, 1997). Researchers have indicated that victims of bullying generally found that the implementation of coping strategies was not effective in solving their problems (Tenenbaum et al., 2011). The application of adaptive coping strategies may help to prevent future bullying and victimisation (Varjas et al., 2009). Sexual minority adolescents with effective coping strategies are also less likely to experience adverse events such as being marginalised and being bullied (Kiperman et al., 2014).
Hypothesis
To the best of our knowledge, no existing published research has investigated the associative variables on the interaction between bullying others and being bullied among sexual minority adolescents. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the influence of the sex orientation on bullying and being bullied through the mediation of coping strategies and mood states. It is hypothesised that engaging in positive coping strategies could reduce the risk of being bullied. Moreover, previous studies have noted that sex difference also leads to adolescents applying different coping strategies in response to bullying (Naylor et al., 2001). Thus, the current study will assess the influence of sex together with the influence of the sexual orientation as part of the bullying mechanism within the victim-bully cycle. This study also assessed the different odds ratio of sexual minority groups in comparison to heterosexual adolescents for a variety of bullying-related behaviours, in order to examine the disparities among the sexual minority groups.
Methods
Participants
Data were collected from 18 public secondary schools in Suzhou, a medium-size metropolitan city in China. Schoolteachers aided in the recruitment of subjects and it was made clear to potential subjects that participation was voluntary, and there were no adverse consequences for refusing to participate or for later if they chose to withdraw. A total of 12 354 questionnaires were completed and returned and the response rate was 83.2%. The study design and study participants have been described in a previous publication (Duan et al., 2020). All students (6688 boys and 5666 girls) answered the question about their birth-assigned sex; however, there were 43 boys and 73 girls who did not specify to which sex they were attracted to and were therefore excluded from further analysis. As such, the sample in the analysis consisted of 6625 birth-assigned boys (Mage = 14.94, s.d. = 1.48) and 5593 birth-assigned girls (Mage = 14.95, s.d. = 1.48).
The student's sexual orientation was measured by two questions (Denny et al., 2016): ‘What was your biological sex assigned at birth? (choose from male or female)’ and ‘Which sex are you attracted to? (choose from male, female, both, and none)’. Students were categorised into six groups based on their birth-assigned sex and sexual: Those boys and girls who were attracted to the opposite sex were classified as opposite-sex-attraction-boys and opposite-sex-attraction-girls, respectively. Birth-assigned males attracted to other males were categorised as same-sex-attraction-boys, while birth-assigned females attracted to females were categorised as same-sex-attraction-girls. Birth-assigned boys who reported being attracted to both sexes were designated as both-sex-attraction-boys and birth-assigned girls attracted to both sexes as both-sex-attraction-girls (Denny et al., 2016). As Fenaughty et al. (2019) point out, the choice of ‘to neither males nor females’ was not a particular measure of asexuality. Instead, we categorised the 2625 boys and 2395 girls who reported attracted to neither male nor female as sexual-undeveloped-boys and sexual-undeveloped-girls, because they are more likely to not yet experience sexual due to their young age rather than identifying as asexual. We believe these groups have meaningful differences, and a similar method of grouping among Chinese adolescents has been used to in a previous study (Huang et al., 2018).
Measures
The Chinese Trait Coping Style Questionnaire
The Trait Coping Style Questionnaire (TCSQ) was used to measure positive and negative coping styles among the adolescents. There were 20 items, with ten items assessing each sub-scale. One example for positive coping was ‘I focus on the positive side and reappraise the situation’; and one example for negative coping was ‘If I had a confrontation with someone, I would cut the communication with the person for a long time’. Responses were rated on a 1–5 Likert scale from 1 (not me at all) to 5 (I do things completely this way). A higher composite score indicates a higher inclination to adopt the positive or negative coping style, respectively. The Cronbach's α was 0.85 for the positive coping style sub-scale, and 0.88 for the negative coping style in this sample.
The Patient Health Questionnaire
The Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) was used to measure the severity of depressive symptoms. There were nine items (e.g. ‘Little interest or pleasure in doing things’). Participants were asked to rate how often they had been bothered by any of the problems over the previous 2 weeks on a 0–3 point scale, where 0 = Not at all to 3 = Nearly every day. The Cronbach's α was 0.93 in this sample.
The 32-item Hypomania Checklist Chinese Version
The Chinese version of the Hypomania Checklist (HCL-32) was used to measure the level of hypomania in the adolescents. Participants were asked to choose yes or no on 32 statements about when they were in a state of ‘high spirit’. One example was ‘you are more talkative’. The Cronbach's α was 0.87 in this sample.
The Generalised Anxiety Disorder Screener
The Generalised Anxiety Disorder Screener (GAD-7) , which was previously validated in the general population, was used to measure anxiety symptoms; there are seven items (e.g. ‘worrying too much about different things’). Similar to the PHQ-9, participants were asked to report based on the previous 2 weeks' experiences, rated on a 0–3 point scale, where 0 = Not at all to 3 = Nearly every day. The Cronbach's α was 0.94 in this sample.
Frequency of being bullied at school
The frequency of being bullied at school was measured by five items. Participants were asked to rate their experience in the past academic year on a 1–4 point scale. Response options for this question were 0 = never, 1 = sometimes (1–2 per month), 2 = often (1–2 per week) and 3 = every day. One example was ‘Were you afraid of being kicked, pushed, or beaten at school?’ The total score of being bullied was calculated and the range of the composite score was between 0 and 15, with a higher score indicating a higher frequency of being bullied at school in the past academic year. The Cronbach's α was 0.68 in this sample. In the multinomial analyses, ratings of 1, 2 and 3 for each item were further grouped as a ‘yes’ response to the experience, in contrast to those who had not experienced bullying at school.
Frequency of bullying others at school
The frequency of bullying others at school was measured by five items. Participants were asked to rate their behaviours in the past academic year on a 1–4 point scale. Response options for this question were 0 = never, 1 = sometimes (1–2 per month), 2 = often (1–2 per week) and 3 = every day. One example was ‘Have you kicked, pushed, or beaten others at school?’ The total score of being bullied was calculated and the range of the composite score was between 0 and 15, with a higher score indicating a higher frequency of bullying others at school in the past academic year. The Cronbach's α was 0.66 in this sample. In the multinomial analyses, ratings of 1, 2 and 3 for each item were further grouped as a ‘yes’ response to the experience, in contrast to those who had experienced bullying at school.
Analysis
All analyses were carried out using R software Mac version 3.6.1. Total numbers and valid percentages were calculated for each sexual orientation group. Given the large sample size of the survey, p < 0.01 was taken to indicate statistical significance in all analyses. To assess the difference in measured variables among the sex and sexual attraction groups, a MANOVA was conducted. To assess the increased risk of being bullied and bullying others, in association with different groups, a series of multinomial regression were conducted. To assess the psychological mechanism behind the association between sexual orientation and the frequency of being bullied as well as bullying others, a structural equation model (SEM) was constructed using R Lavaan package using negative and positive coping, hypomanic behavioural pattern, anxiety and depression as the mediators. The analysis incorporated several regression analyses simultaneously, also allowing correlations between theoretically related variables; in particular: negative and positive coping, anxiety and depression, as well as the frequency of being bullied and bullying others.
Results
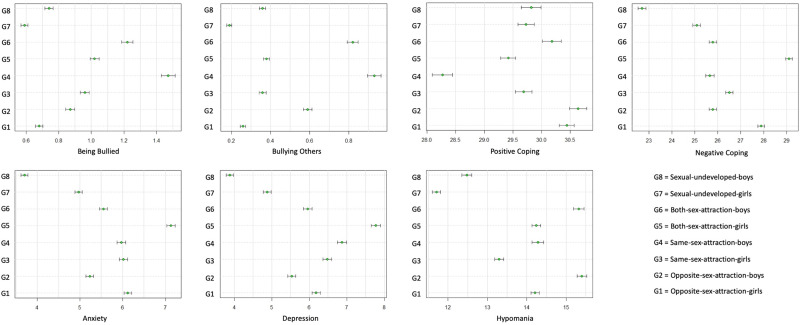
The means and s.d.s of the variables used in the study by sexual attraction groups are shown in Table 1. A 2 × 4 MANOVA was conducted to test the potential effect of sex and sexual on all measured variables, including being bullied, bullying others, positive and negative coping, hypomania, anxiety and depression. There was a significant main effect of sex, F(7, 10799) = 44.48, p < 0.001, Wilks' Λ = 0.97, partial η2 = 0.03, a significant main effect of sexual, F(21, 31009) = 27.86, p < 0.001, Wilks' Λ = 0.95, partial η2 = 0.02, and a significant main interaction of sex and sexual, F(21, 31009) = 6.04, p < 0.001, Wilks' Λ = 0.98, partial η2 = 0.01. As the interaction term was significant, follow-up post hoc comparisons were done by comparing the eight sexual groups. The results are summarised in Fig. 1, which indicates the estimated mean (the mid-point) and 95% confidence interval (the bars extended from the mid-point) for each group on all the measured variables. Any two groups with non-overlapping bars in each panel of the graph showed significant group difference.
Table 1.
Means and s.d.s of study variables by sexual attraction
| N | % | Age | Positive Coping | Negative Coping | Hypomania | Anxiety | Depression | Being Bullied | Bullying Others | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opposite-sex-at-girl | 1998 | 16.35% | 15.42 (1.53) | 30.44 (7.31) | 27.89 (7.80) | 14.21 (5.87) | 6.12 (5.07) | 6.18 (6.22) | 0.68 (1.27) | 0.26 (0.76) |
| Opposite-sex-at-boy | 3136 | 25.67% | 15.48 (1.56) | 30.64 (8.45) | 25.78 (8.71) | 15.40 (6.94) | 5.23 (5.02) | 5.53 (6.02) | 0.87 (1.50) | 0.59 (1.23) |
| Same-sex-at-girl | 274 | 2.24% | 14.47 (1.27) | 29.69 (8.17) | 26.50 (9.25) | 13.30 (6.29) | 6.02 (5.42) | 6.48 (6.66) | 0.96 (1.53) | 0.36 (1.00) |
| Same-sex-at-boy | 212 | 1.74% | 14.65 (1.62) | 28.27 (9.97) | 25.65 (10.20) | 14.28 (8.26) | 5.97 (5.66) | 6.87 (7.16) | 1.47 (2.43) | 0.93 (1.94) |
| Both-sex-at-girl | 926 | 7.58% | 14.90 (1.49) | 29.42 (7.39) | 29.10 (8.26) | 14.24 (6.19) | 7.13 (5.49) | 7.77 (7.03) | 1.02 (1.52) | 0.38 (0.86) |
| Both-sex-at-boy | 652 | 5.34% | 14.77 (1.40) | 30.18 (9.20) | 25.78 (9.34) | 15.32 (7.65) | 5.55 (5.39) | 5.96 (6.50) | 1.22 (1.96) | 0.82 (1.58) |
| Sexual-undevelop-girl | 2395 | 19.60% | 14.64 (1.34) | 29.73 (7.97) | 25.08 (9.34) | 11.71 (5.99) | 4.97 (4.90) | 4.88 (5.86) | 0.59 (1.20) | 0.19 (0.71) |
| Sexual-undevelop-boy | 2635 | 21.57% | 14.38 (1.10) | 29.82 (9.62) | 22.70 (9.48) | 12.48 (6.98) | 3.70 (4.48) | 3.88 (5.37) | 0.74 (1.39) | 0.36 (0.88) |
| Total | 12 218 | 100% | 14.95 (1.48) | 30.08 (8.45) | 25.59 (8.89) | 13.68 (6.75) | 5.18 (5.07) | 5.39 (6.13) | 0.80 (1.45) | 0.41 (1.03) |
Note. at, attraction; undevelop, underdeveloped.
Fig. 1.
Centipede plot of group difference: means and 95% confidence interval of each sexual attraction group on study variables. Note. The mid-point indicates the mean and the bars indicate the 95% confidence interval. In each panel, any two groups with non-overlapping bars were significantly different on the measured variable.
A series of multinomial logistic regressions were conducted to test whether being a sexual minority was associated with a greater risk of being bullied and a higher or lower likelihood of bullying others. The birth-assigned sex and sexual attraction category was used as the predictor, and the YES/NO answers to the being bullied or to bullying others were used as dependent variables (the opposite-sex-attraction-girls were treated as the reference group). Details of the ORs and effect sizes are summarised in Table 2; but two trends could be observed: (1) sexual minority groups reported heightened risks of being bullied and bullying others at school than heterosexual girls. However, being a sexual-undeveloped girl seemed to have a protective effect on bullying-related problems; and (2) birth-assigned males were more likely to be involved in being bullied as well as bullying others at school than birth-assigned females.
Table 2.
Multinomial regression results indicating associations between sexual attraction and being bullied or bullying others
| n (No) | n (Yes) | Yes% | Odds ratio | 95% CI of odds ratio | Z | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Have you ever been bullied at school in this academic year? | |||||||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-girl | 1882 | 113 | 5.66% | 1.00 | |||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-boy | 2836 | 294 | 9.39% | 1.73 | [1.39, 2.16] | 4.77 | <0.001 |
| Same-sex-attraction-girl | 254 | 19 | 6.96% | 1.24 | [0.75, 2.08] | 0.86 | 0.392 |
| Same-sex-attraction-boy | 167 | 41 | 19.71% | 4.09 | [2.77, 6.05] | 7.06 | <0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-girl | 863 | 63 | 6.80% | 1.22 | [0.90, 1.66] | 1.20 | 0.229 |
| Both-sex-attraction-boy | 556 | 92 | 14.20% | 2.76 | [2.05, 3.67] | 6.83 | <0.001 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-girl | 2270 | 122 | 5.10% | 0.90 | [0.70, 1.15] | −0.83 | 0.409 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-boy | 2399 | 221 | 8.44% | 1.53 | [1.21, 1.93] | 3.58 | <0.001 |
| Have you ever missed school because you were concerned about safety? | |||||||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-girl | 1822 | 171 | 8.58% | 1.00 | |||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-boy | 2918 | 205 | 6.56% | 0.75 | [0.61, 0.93] | −2.68 | 0.007 |
| Same-sex-attraction-girl | 242 | 29 | 10.70% | 1.28 | [0.84, 1,92] | 1.15 | 0.249 |
| Same-sex-attraction-boy | 180 | 29 | 13.88% | 1.72 | [1.12, 2.64] | 2.50 | 0.012 |
| Both-sex-attraction-girl | 809 | 114 | 12.35% | 1.50 | [1.17, 1.93] | 3.17 | 0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-boy | 588 | 61 | 9.40% | 1.10 | [0.81, 1.51] | 0.64 | 0.522 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-girl | 2239 | 150 | 6.28% | 0.71 | [0.57, 0.89] | −2.90 | 0.004 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-boy | 2473 | 136 | 5.21% | 0.59 | [0.47, 0.75] | −4.49 | <0.001 |
| Were you afraid of being kicked, pushed or beaten at school? | |||||||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-girl | 1768 | 213 | 10.75% | 1.00 | |||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-boy | 2775 | 333 | 10.71% | 1.00 | [0.84, 1.20] | −0.04 | 0.966 |
| Same-sex-attraction-girl | 226 | 45 | 16.61% | 1.65 | [1.16, 2.34] | 2.81 | 0.005 |
| Same-sex-attraction-boy | 170 | 39 | 18.66% | 1.90 | [1.31, 2.74] | 3.36 | <0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-girl | 770 | 150 | 16.30% | 1.62 | [1.27, 2.05] | 4.18 | <0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-boy | 544 | 100 | 15.53% | 1.53 | [1.17, 1.95] | 3.23 | 0.001 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-girl | 2160 | 218 | 9.17% | 0.84 | [0.68, 1.02] | −1.74 | 0.081 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-boy | 2350 | 249 | 9.58% | 0.88 | [0.72, 1.07] | −1.30 | 0.192 |
| Have your belongings being stolen or damaged (e.g. books or bike)? | |||||||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-girl | 1668 | 325 | 16.31% | 1.00 | |||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-boy | 2342 | 786 | 25.13% | 1.72 | [1.49, 1.97] | 7.42 | <0.001 |
| Same-sex-attraction-girl | 208 | 65 | 23.81% | 1.60 | [1.20, 2.14] | 3.05 | 0.002 |
| Same-sex-attraction-boy | 154 | 56 | 26.67% | 1.86 | [1.34, 2.58] | 3.72 | <0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-girl | 688 | 236 | 25.54% | 1.76 | [1.43, 2.14] | 5.84 | <0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-boy | 445 | 204 | 31.43% | 2.35 | [1.93, 2.89] | 8.22 | <0.001 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-girl | 2013 | 380 | 15.88% | 0.97 | [0.83, 1.14] | −0.38 | 0.701 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-boy | 2060 | 557 | 21.28% | 1.39 | [1.18, 1.63] | 4.24 | <0.001 |
| Were you afraid of your belongings being stolen or damaged at school? | |||||||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-girl | 1619 | 376 | 18.85% | 1.00 | |||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-boy | 2458 | 670 | 21.42% | 1.17 | [1.02, 1.35] | 2.22 | 0.026 |
| Same-sex-attraction-girl | 217 | 55 | 20.22% | 1.09 | [0.80, 1.49] | 0.54 | 0.588 |
| Same-sex-attraction-boy | 160 | 50 | 23.81% | 1.34 | [0.97. 1.88] | 1.73 | 0.084 |
| Both-sex-attraction-girl | 679 | 245 | 26.52% | 1.55 | [1.30, 1.86] | 4.69 | <0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-boy | 492 | 158 | 24.31% | 1.38 | [1.10, 1.72] | 3.00 | 0.003 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-girl | 2006 | 386 | 16.14% | 0.83 | [0.70, 0.97] | −2.36 | 0.018 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-boy | 2157 | 461 | 17.61% | 0.92 | [0.79, 1.08] | −1.08 | 0.280 |
| Have you ever bullied or laughed at others? | |||||||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-girl | 1754 | 241 | 12.08% | 1.00 | |||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-boy | 2366 | 755 | 24.19% | 2.32 | [1.97, 2.72] | 10.48 | <0.001 |
| Same-sex-attraction-girl | 229 | 43 | 15.81% | 1.37 | [0.96, 1.93] | 1.74 | 0.082 |
| Same-sex-attraction-boy | 156 | 54 | 25.71% | 2.52 | [1.80, 3.49] | 5.36 | <0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-girl | 767 | 157 | 16.99% | 1.49 | [1.20, 1.86] | 3.58 | <0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-boy | 460 | 185 | 28.68% | 2.93 | [2.34, 3.60] | 9.68 | <0.001 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-girl | 2202 | 184 | 7.71% | 0.61 | [0.50, 0.75] | −4.83 | <0.001 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-boy | 2217 | 392 | 15.02% | 1.29 | [1.07, 1.54] | 2.87 | 0.004 |
| Have you kicked, pushed, or beaten others at school? | |||||||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-girl | 1895 | 93 | 4.68% | 1.00 | |||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-boy | 2760 | 357 | 11.45% | 2.64 | [2.08, 3.32] | 8.06 | <0.001 |
| Same-sex-attraction-girl | 259 | 13 | 4.78% | 1.02 | [0.56, 1.84] | 0.07 | 0.943 |
| Same-sex-attraction-boy | 177 | 33 | 15.71% | 3.80 | [2.46, 5.81] | 6.14 | <0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-girl | 868 | 57 | 6.16% | 1.34 | [0.96, 1.86] | 1.68 | 0.093 |
| Both-sex-attraction-boy | 548 | 100 | 15.43% | 3.72 | [2.77, 4.95] | 8.64 | <0.001 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-girl | 2316 | 72 | 3.02% | 0.63 | [0.46, 0.86] | −2.85 | 0.004 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-boy | 2428 | 180 | 6.90% | 1.51 | [1.17, 1.93] | 3.14 | 0.002 |
| Have you stolen or damage others' belongings such as books or bikes? | |||||||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-girl | 1969 | 25 | 1.25% | 1.00 | |||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-boy | 3038 | 89 | 2.85% | 2.31 | [1.48, 3.63] | 3.66 | <0.001 |
| Same-sex-attraction-girl | 268 | 4 | 1.47% | 1.18 | [0.41, 3.39] | 0.30 | 0.765 |
| Same-sex-attraction-boy | 196 | 15 | 7.11% | 6.02 | [3.13, 11.82] | 5.36 | <0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-girl | 907 | 15 | 1.63% | 1.30 | [0.68, 2.48] | 0.80 | 0.421 |
| Both-sex-attraction-boy | 616 | 32 | 4.94% | 4.09 | [2.41, 6.96] | 5.20 | <0.001 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-girl | 2360 | 33 | 1.38% | 1.10 | [0.65, 1.88] | 0.36 | 0.718 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-boy | 2561 | 53 | 2.03% | 1.63 | [1.02, 2.61] | 2.00 | 0.046 |
| Have you brought weapons (‘aggressive tools’ in Chinese) to school? | |||||||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-girl | 1920 | 68 | 3.42% | 1.00 | |||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-boy | 2927 | 204 | 6.52% | 1.97 | [1.49, 2.58] | 4.73 | <0.001 |
| Same-sex-attraction-girl | 259 | 14 | 5.13% | 1.52 | [0.84, 2.72] | 1.40 | 0.160 |
| Same-sex-attraction-boy | 191 | 18 | 8.61% | 2.66 | [1.54, 4.62] | 3.55 | <0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-girl | 872 | 54 | 5.83% | 1.75 | [1.21, 2.53] | 2.99 | 0.003 |
| Both-sex-attraction-boy | 595 | 53 | 8.18% | 2.51 | [1.73, 3.63] | 4.88 | <0.001 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-girl | 2319 | 70 | 2.93% | 0.85 | [0.61, 1.18] | −0.92 | 0.355 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-boy | 2506 | 107 | 4.09% | 1.20 | [0.90, 1.62] | 1.18 | 0.237 |
| Did you often get into fight at school in the past academic year? | |||||||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-girl | 1972 | 20 | 1.00% | 1.00 | |||
| Opposite-sex-attraction-boy | 2997 | 127 | 4.07% | 4.18 | [2.61, 6.68] | 5.90 | <0.001 |
| Same-sex-attraction-girl | 266 | 6 | 2.21% | 2.22 | [0.89, 5.58] | 1.70 | 0.089 |
| Same-sex-attraction-boy | 196 | 15 | 7.11% | 7.55 | [3.78, 15.03] | 5.78 | <0.001 |
| Both-sex-attraction-girl | 915 | 9 | 0.97% | 0.97 | [0.44, 2.12] | −0.08 | 0.939 |
| Both-sex-attraction-boy | 607 | 41 | 6.33% | 6.66 | [3.86, 11.59] | 6.85 | <0.001 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-girl | 2365 | 23 | 0.96% | 0.96 | [0.55, 1.66] | −0.14 | 0.892 |
| Sexual-undeveloped-boy | 2544 | 69 | 2.64% | 2.67 | [1.56, 4.44] | 3.85 | <0.001 |
Bolded value <0.05, significant level was set at <0.05.
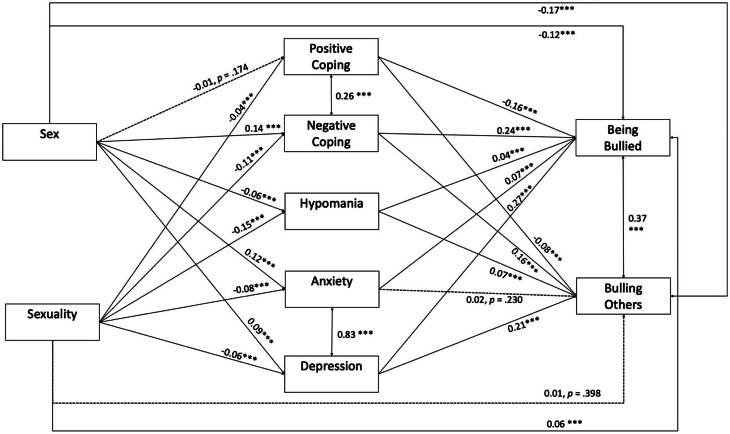
An SEM (Fig. 2) was constructed to examine the mechanism behind the association between sex and sexual attraction and the frequency of being bullied and bullying behaviours, with positive and negative coping, hypomania, anxiety as well as depression as mediators. The results are summarised in Table 3. SEM analysis revealed that being a heterosexual girl was associated with a reduced risk of being bullied and bullying others in comparison to being a heterosexual boy. On the other hand, being a sexual minority was associated with a heightened risk of being bullied. Negative coping, hypomania, anxiety and depression were associated with a higher frequency of being bullied; while positive coping had a significant protective effect on the frequency of being bullied. Negative coping, hypomania and depression were associated with a higher frequency of bullying others, whereas positive coping was associated with a lower frequency of bullying others. Moreover, positive coping and negative coping were positively correlated, and so were anxiety and depression, as well as bullying others and being bullied.
Fig. 2.
Final SEM model with the standardized coefficients labelled for each path. Note. ***p < 0.001. Sex: 0 = boys; 1 = girls. Sexuality: 0 = opposite-sex attraction; 1 = all other sexual preference.
Table 3.
Summary of the SEM model
| Model description | Path | Unstandardised coefficient | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct effect | Sex --> Being bullied | −0.33 | [−0.39, −0.27] | <0.001 |
| Sex --> Bullying others | −0.34 | [−0.38, −0.30] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> Being bullied | 0.16 | [0.10, 0.22] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> Bullying others | 0.02 | [−0.02, 0.06] | 0.398 | |
| Mediators --> DV | Positive coping --> Being bullied | −0.03 | [−0.034, −0.026] | <0.001 |
| Negative coping --> Being bullied | 0.04 | [0.036, 0.044] | <0.001 | |
| Hypomania --> Being bullied | 0.01 | [0.006, 0.014] | <0.001 | |
| Anxiety --> Being bullied | 0.02 | [0.01, 0.03] | <0.001 | |
| Depression --> Being bullied | 0.06 | [0.05, 0.07] | <0.001 | |
| Positive coping --> Bullying others | −0.01 | [−0.012, −0.008] | <0.001 | |
| Negative coping --> Bullying others | 0.02 | [0.018, 0.022] | <0.001 | |
| Hypomania --> Bullying others | 0.01 | [0.006, 0.014] | <0.001 | |
| Anxiety --> Bullying others | 0.004 | [−0.002, 0.010] | 0.230 | |
| Depression --> Bullying others | 0.03 | [0.024, 0.036] | <0.001 | |
| IV --> Mediators | Sex --> Positive coping | −0.22 | [−0.53, 0.09] | 0.174 |
| Sex --> Negative coping | 2.51 | [2.18, 2.84] | <0.001 | |
| Sex --> Hypomania | −0.87 | [−1.12, −0.62] | <0.001 | |
| Sex --> Anxiety | 1.26 | [1.06, 1.46] | <0.001 | |
| Sex --> Depression | 1.12 | [0.88, 1.36] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> Positive coping | −0.71 | [−1.02, −0.40] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> Negative coping | −2.00 | [−2.33, −1.67] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> Hypomania | −2.05 | [−2.30, −1.80] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> Anxiety | −0.82 | [−1.02, −0.62] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> Depression | −0.81 | [−1.04, −0.58] | <0.001 | |
| Correlations | Positive coping <--> Negative coping | 19.58 | [17.56, 21.60] | <0.001 |
| Anxiety <--> Depression | 25.12 | [24.14, 26.10] | <0.001 | |
| Being bullied <--> Bullying others | 0.46 | [0.37, 0.55] | <0.001 | |
| Indirect Effect | Sex --> M1 --> DV1 | 0.006 | [−0.00, 0.01] | 0.177 |
| Sex --> M2 --> DV1 | 0.10 | [0.08, 0.12] | <0.001 | |
| Sex --> M3 --> DV1 | −0.01 | [−0.014, −0.006] | 0.001 | |
| Sex --> M4 --> DV1 | 0.02 | [0.01, 0.03] | <0.001 | |
| Sex --> M5 --> DV1 | 0.07 | [0.05, 0.09] | <0.001 | |
| Sex --> M1 --> DV2 | 0.002 | [−0.002, 0.006] | 0.183 | |
| Sex --> M2 --> DV2 | 0.05 | [0.04, 0.06] | <0.001 | |
| Sex --> M3 --> DV2 | −0.01 | [−0.014, −0.006] | <0.001 | |
| Sex --> M4 --> DV2 | 0.005 | [−0.003, 0.013] | 0.231 | |
| Sex --> M5 --> DV2 | 0.04 | [0.03, 0.05] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> M1 --> DV1 | 0.02 | [0.01, 0.03] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> M2 --> DV1 | −0.08 | [−0.09, −0.07] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> M3 --> DV1 | −0.02 | [−0.03, −0.01] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> M4 --> DV1 | −0.02 | [−0.02, −0.01] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> M5 --> DV1 | −0.05 | [−0.06, −0.03] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> M1 --> DV2 | 0.007 | [0.003, 0.011] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> M2 --> DV2 | −0.04 | [−0.05, −0.03] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> M3 --> DV2 | −0.02 | [−0.03, −0.01] | <0.001 | |
| Sexuality --> M4 --> DV2 | −0.003 | [−0.01, 0.00] | 0.235 | |
| Sexuality --> M5 --> DV2 | −0.03 | [−0.04, −0.02] | <0.001 |
Note. Sex: 0 = boys; 1 = girls. Sexuality: 0 = opposite-sex attraction; 1 = all other sexual minority groups. M1 = positive coping; M2 = negative coping; M3 = hypomania; M4 = anxiety; M5 = depression. DV1 = being bullied; DV2 = bullying other.
Bolded value <0.05, significant level was set at <0.05.
In addition, heterosexual girls reported a similar level of using positive coping, a higher level of using negative coping, a lower score on hypomania, a higher score on anxiety and depression in comparison to heterosexual boys. On the other hand, the sexual minority group reported lower usage of positive coping, higher usage of negative coping, a lower score on hypomania, anxiety and depression in comparison to opposite-sex attraction group.
Discussion
This is the first study examining the psychological mechanism behind the pattern of being bullied and bullying others in relation to one's birth-assigned sex and sexual attraction. This study provides insights into how being bullied and bullying others are associated, increases knowledge about related factors of the victim-bully cycle, identifies the importance of coping strategies and mood states, and explores the dynamic nature of being bullying and bullying others in school settings.
Specific socio-demographic features
The current study was composed of 2.2% same-sex-attraction girls, 1.7% same-sex-attraction boys, 7.6% both-sex-attraction-girls and 5.3% both-sex-attraction-boys out of the total sample. According to recent Chinese adolescent research, 4.1% of adolescents self-report as sexual minorities and 17.3% are unsure (Huang et al., 2018). Huang et al.'s study covered four regional areas of China, including less economically developed areas. This study was conducted in Suzhou, one of the well-developed economical cities of China. Due to the higher tolerance and friendly environment, adolescents in this study may have been more likely to disclose their sexual minority status rather than report as unsure.
The current research also shed light on a new phenomenon that has not been discussed in previous studies: there could be a number of adolescents who may not have experienced a romantic relationship or have reached a mature sexuality. In previous research, adolescents who reported being sexually attracted to neither male nor female were usually treated as asexual in their sexuality; and the number of adolescents who reported being sexually attracted to neither male nor female is usually quite small (Fenaughty et al., 2019). However, in this current study, 2625 boys and 2395 girls reported being sexually attracted to neither male nor female. Accordingly, new categories of sexuality were added (sexually-undeveloped boys and girls). The results showed that this subgroup of adolescents seem to be ‘protected’ from the heightened risk of being bullied or bullying others; and they also seem to report better mental health, such as lower hypomania, lower anxiety and lower depression. This may be a culturally specific phenomenon in China since Chinese parents and schools openly discourage adolescent children to be involved in romantic relationships (Li et al., 2010). Those adolescents who obey these suggestions tend to have a closer relationship with their parents (Li et al., 2010) and receive more positive feedback from school teachers. Consequently, those factors may lead to better mental health and fewer bully-related problems.
Mood problems and bullying
It is well-documented that a sexual minority orientation is a risk factor for bullying and stressful life events (King et al., 2003; Berlan et al., 2010). Previous studies have shown that compared with heterosexual counterparts, sexual minority participants experience a significantly higher rate of bullying victimisation, with 31–33.9% being bullied v. 18–19.3%, respectively (Jacob et al., 2019; Qi et al., 2020). In the current results, the prevalence of bullying among sexual minorities was much lower than previous studies. It is possible that participants may feel embarrassed about bullying experiences and the lower prevalence could partly be due to underreporting. Importantly, our results confirmed our hypothesis that being bullied and bullying others are significantly correlated. In addition, a previous study indicated bully-victims may experience the greatest internal distress (Swearer et al., 2001). It is therefore critical that research and interventions continue to primarily focus on individuals who are being bullied and participate in the bullying others.
There is a lack of research on the association between bullying and hypomania in sexual minority individuals. A previous study in a Dutch school setting showed that both bullying and being bullied were associated with an increased risk of subclinical psychotic experiences (Horrevorts et al., 2014). Sexual minorities have an elevated risk of psychosis, which could be due to the experiences of social adversity such as bullying (Qi et al., 2020) and this association between psychological health and bullying is well-documented (Kaltiala-Heino et al., 2000; Bond et al., 2001; Fekkes et al., 2006; Arseneault et al., 2010). Our results showed that individuals with mood problems had a higher risk of being involved in bullying. Individuals with mood problems could face discriminations towards their mental health problems, which makes them more likely to be bullied. Meanwhile, individuals with mood problems have less control over their mood status, which could make them more likely to be involved in aggressive behaviours such as bullying others.
Coping strategies and bullying
This study showed that positive coping had a significant protective effect on being bullied and a preventive effect on bullying others; negative coping was positively associated with being bullied and bullying others. In order to reduce the victim-bully cycle, it is important to coach adolescents to adopt positive coping strategies. Importantly, researchers have noted that sexual minority and heterosexual samples use different coping strategies. For example, gay men preferred to use emotional-oriented coping strategies while heterosexual men preferred to use problem-oriented coping strategies (Sandfort et al., 2009), with a lack of current research to understand different types of coping skills based on sexual orientation. Emotional-oriented coping strategies are associated with poorer mental health outcomes, and problem-oriented coping strategies were associated with better mental health outcomes (Sandfort et al., 2009). It would be useful for future research to explore the association between sexual orientation (i.e. sexual minority v. heterosexual) and their preferred coping strategies and bullying related information in Chinese adolescents in order to create tailored interventions for each subgroup. Furthermore, it is meaningful to design distinct forms of coping strategies between LGB groups, since sexual minority subgroups might have different needs.
Practical implications
School-age bullying experienced by sexual orientation minorities tends to result in long-term consequences for their overall health and well-being. Recent research in England found that school-age bullying of sexual minority people is positively associated with victims' lower educational level and workplace bullying, while negatively associated with job satisfaction (Drydakis, 2019). Policies merely aimed at reducing bullying may not be effective, and additional policies are needed to promote safe and supportive school environments (Robinson and Espelage, 2012). According to a previous meta-analysis of longitudinal research, school victimisation was positively associated with students' psychological distress (Reijntjes et al., 2010). Many studies have emphasised the benefits of warmth, support and care for sexual minority youth (Shilo and Savaya, 2012; Hsieh, 2014; Watson et al., 2019). This study highlighted the importance of providing a supportive school environment to reduce bullying.
Although social support could promote positive psychosocial adjustment for sexual minority youth, the sources of social support for sexual minority youth are sparse (Button et al., 2012; Watson et al., 2019). It is important to provide social support to sexual minority youth from parents, clinicians, teachers and classmates (Watson et al., 2019). It is essential to provide supportive learning environments for sexual minorities, such as training teachers and staff in sexuality diversity and discussing homophobia in education (Robinson and Espelage, 2012; Robinson et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020). In addition, in terms of school counselling, it is inappropriate to narrowly defined victims and bullies as two separate groups (Ma, 2001); the results from this study instead indicate that victims and bullies can belong to the same categories.
Limitations
There are several limitations in the current study. First, we were unable to confirm the causality direction of the measured aspects. Second, the data are from an economically developed region of China, which may not be generalisable to all school settings in Chinese regions. Third, many other variables could affect the victim-bully cycle. Besides sexual minority personal variables, it is also critical to consider variables such as effect on school climate, discipline climate, parental and teacher involvement, academic press and school size (Ma, 2001). Future studies should aim to measure those relevant variables and establish a more comprehensive framework of the victim-bully cycle for LGB adolescents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this research is pioneering in exploring the interaction of being bullied and bullying others among sexual minority adolescents. We investigated the relationship between sexual orientation, mood problems, coping strategies and the victim-bully cycle. It has expanded the understanding of the possible mechanism of bullying others and being bullied among sexual minority adolescents in school settings. Unlike previous studies which investigated sexual minorities as a whole group, we identified the subgroup differences among LGB adolescents, which provided in-depth details for sexual minority adolescents. The current research highlights the importance of providing a supportive and safe learning environment for sexual minority students.
Acknowledgements
N/A.
Author contributions
Study design: WY, YH, YY, CR; Data collection: LR, YY, WS; Data analysis: WY, YH, YY, CR; Data interpretation: WY, YH, YY, CR, DJ, AW; Manuscript preparing: WY, YH, YY, CR, DJ, YY, AW.
Financial support
The study was supported by the Young Medical Talent of Jiangsu Province (QNRC2016229), Suzhou Municipal Sci-Tech Bureau Program (SS2019009), Suzhou Key Diagnosis and Treatment Program (LCZX201616) and Suzhou Clinical Medicine Expert Team (szyjtd201715). The funding body had no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis and interpretation of data or in writing the manuscript.
Ethical standards
The authors assert that all procedures contributing to this work comply with the ethical standards of the relevant national and institutional committees on human experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000. Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Suzhou Guangji Hospital, Suzhou University.
Data
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflict of interest
None.
References
- Arseneault L, Bowes L and Shakoor S (2010) Bullying victimization in youths and mental health problems: ‘much ado about nothing’? Psychological Medicine 40, 717–729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlan ED, Corliss HL, Field AE, Goodman E and Austin SB (2010) Sexual orientation and bullying among adolescents in the growing up today study. Journal of Adolescent Health 46, 366–371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkett M, Espelage DL and Koenig B (2009) LGB and questioning students in schools: the moderating effects of homophobic bullying and school climate on negative outcomes. Journal of Youth and Adolescence 38, 989–1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond L, Carlin JB, Thomas L, Rubin K and Patton G (2001) Does bullying cause emotional problems? A prospective study of young teenagers. BMJ 323, 480–484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostwick WB, Boyd CJ, Hughes TL and McCabe SE (2010) Dimensions of sexual orientation and the prevalence of mood and anxiety disorders in the United States. American Journal of Public Health 100, 468–475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Button DM, O'Connell DJ and Gealt R (2012) Sexual minority youth victimization and social support: the intersection of sexuality, gender, race, and victimization. Journal of Homosexuality 59, 18–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty A, McManus S, Brugha TS, Bebbington P and King M (2011) Mental health of the non-heterosexual population of England. British Journal of Psychiatry 198, 143–148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R, Liu J, Cao X, Duan S, Wen S, Zhang S, Xu J, Lin L, Xue Z and Lu J (2020) The relationship between mobile phone use and suicide-related behaviors among adolescents: the mediating role of depression and interpersonal problems. Journal of Affective Disorders 269, 101–107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran SD and Mays VM (2009) Burden of psychiatric morbidity among lesbian, gay, and bisexual individuals in the California Quality of Life Survey. Journal of Abnormal Psychology 118, 647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier KL, Van Beusekom G, Bos HM and Sandfort TG (2013) Sexual orientation and gender identity/expression related peer victimization in adolescence: a systematic review of associated psychosocial and health outcomes. Journal of Sex Research 50, 299–317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'augelli AR and Grossman AH (2001) Disclosure of sexual orientation, victimization, and mental health among lesbian, gay, and bisexual older adults. Journal of Interpersonal Violence 16, 1008–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Denny S, Lucassen MF, Stuart J, Fleming T, Bullen P, Peiris-John R, Rossen FV and Utter J (2016) The association between supportive high school environments and depressive symptoms and suicidality among sexual minority students. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology 45, 248–261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drydakis N (2019) School-age bullying, workplace bullying and job satisfaction: experiences of LGB people in Britain. The Manchester School 87, 455–488. [Google Scholar]
- Duan S, Duan Z, Li R, Wilson A, Wang Y, Jia Q, Yang Y, Xia M, Wang G, Jin T, Wang S and Chen R (2020) Bullying victimization, bullying witnessing, bullying perpetration and suicide risk among adolescents: a serial mediation analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders 273, 274–279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duong J and Bradshaw C (2014) Associations between bullying and engaging in aggressive and suicidal behaviors among sexual minority youth: the moderating role of connectedness. Journal of School Health 84, 636–645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espelage DL, Valido A, Hatchel T, Ingram KM, Huang Y and Torgal C (2019) A literature review of protective factors associated with homophobic bullying and its consequences among children & adolescents. Aggression Violent Behavior 45, 98–110. [Google Scholar]
- Fekkes M, Pijpers FI, Fredriks AM, Vogels T and Verloove-Vanhorick SP (2006) Do bullied children get ill, or do ill children get bullied? A prospective cohort study on the relationship between bullying and health-related symptoms. Pediatrics 117, 1568–1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenaughty J, Lucassen MF, Clark T and Denny S (2019) Factors associated with academic achievement for sexual and gender minority and heterosexual cisgender students: implications from a nationally representative study. Journal of Youth and Adolescence 48, 1883–1898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredriksen-Goldsen KI, Kim H-J, Barkan SE, Muraco A and Hoy-Ellis CP (2013) Health disparities among lesbian, gay, and bisexual older adults: results from a population-based study. American Journal of Public Health 103, 1802–1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horrevorts EM, Monshouwer K, Wigman JT and Vollebergh WA (2014) The relation between bullying and subclinical psychotic experiences and the influence of the bully climate of school classes. European Child Adolescent Psychiatry 23, 765–772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh N (2014) Explaining the mental health disparity by sexual orientation: the importance of social resources. Society Mental Health 4, 129–146. [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y, Li P, Guo L, Gao X, Xu Y, Huang G, Deng X and Lu C (2018) Sexual minority status and suicidal behaviour among Chinese adolescents: a nationally representative cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 8, e020969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob L, Smith L, McDermott D, Haro JM, Stickley A and Koyanagi A (2019) Relationship between sexual orientation and psychotic experiences in the general population in England. Psychological Medicine, 1–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltiala-Heino R, Rimpelä M, Rantanen P and Rimpelä A (2000) Bullying at school – an indicator of adolescents at risk for mental disorders. Journal of Adolescence 23, 661–674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M, McKeown E, Warner J, Ramsay A, Johnson K, Cort C, Wright L, Blizard R and Davidson O (2003) Mental health and quality of life of gay men and lesbians in England and Wales: controlled, cross-sectional study. British Journal of Psychiatry 183, 552–558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiperman S, Varjas K, Meyers J and Howard A (2014) LGB Youth's perceptions of social support: implications for school psychologists. School Psychology Forum 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Klomek AB, Marrocco F, Kleinman M, Schonfeld IS and Gould MS (2007) Bullying, depression, and suicidality in adolescents. Journal of the American Academy of Child Adolescent Psychiatry 46, 40–49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochenderfer-Ladd B and Skinner K (2002) Children's coping strategies: moderators of the effects of peer victimization? Developmental Psychology 38, 267–278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochenderfer BJ and Ladd GW (1997) Victimized children's responses to peers’ aggression: behaviors associated with reduced versus continued victimization. Development and Psychopathology 9, 59–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li ZH, Connolly J, Jiang D, Pepler D and Craig W (2010) Adolescent romantic relationships in China and Canada: a cross-national comparison. International Journal of Behavioral Development 34, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Li X, Zheng H, Tucker W, Xu W, Wen X, Lin Y, Jia Z, Yuan Z and Yang W (2019) Research on relationships between sexual identity, adverse childhood experiences and non-suicidal self-injury among rural high school students in less developed areas of China. International Journal of Environmental Research Public Health 16, 3158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma X (2001) Bullying and being bullied: to what extent are bullies also victims? American Educational Research Journal 38, 351–370. [Google Scholar]
- Marshal MP, Dietz LJ, Friedman MS, Stall R, Smith HA, McGinley J, Thoma BC, Murray PJ, D'Augelli AR and Brent DA (2011) Suicidality and depression disparities between sexual minority and heterosexual youth: a meta-analytic review. Journal of Adolescent Health 49, 115–123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer IH (2003) Prejudice, social stress, and mental health in lesbian, gay, and bisexual populations: conceptual issues and research evidence. Psychological Bulletin 129, 674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyano N and del Mar Sánchez-Fuentes M (2020) Homophobic bullying at schools: a systematic review of research, prevalence, school-related predictors and consequences. Aggression and Violent Behavior 53, 101441. [Google Scholar]
- Naylor P, Cowie H and Rey RD (2001) Coping strategies of secondary school children in response to being bullied. Child Psychology Psychiatry Review 6, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Olweus D (1994) Bullying at school: basic facts and an effective intervention programme. Promotion Education 1, 27–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakula B and Shoveller JA (2013) Sexual orientation and self-reported mood disorder diagnosis among Canadian adults. BMC Public Health 13, 209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng K, Zhu X, Gillespie A, Wang Y, Gao Y, Xin Y, Qi J, Ou J, Zhong S and Zhao L (2019) Self-reported rates of abuse, neglect, and bullying experienced by transgender and gender-nonbinary adolescents in China. JAMA Network Open 2, e1911058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry DG, Kusel SJ and Perry LC (1988) Victims of peer aggression. Developmental Psychology 24, 807. [Google Scholar]
- Qi R, Palmier-Claus J, Simpson J, Varese F and Bentall R (2020) Sexual minority status and symptoms of psychosis: the role of bullying, discrimination, social support, and drug use – findings from the Adult Psychiatric Morbidity Survey 2007. Psychology and Psychotherapy 93, 503–519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijntjes A, Kamphuis JH, Prinzie P and Telch MJ (2010) Peer victimization and internalizing problems in children: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Child Abuse & Neglect 34, 244–252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson JP and Espelage DL (2012) Bullying explains only part of LGBTQ–heterosexual risk disparities: implications for policy and practice. Educational Researcher 41, 309–319. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson JP, Espelage DL and Rivers I (2013) Developmental trends in peer victimization and emotional distress in LGB and heterosexual youth. Pediatrics 131, 423–430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandfort TG, Bakker F, Schellevis F and Vanwesenbeeck I (2009) Coping styles as mediator of sexual orientation-related health differences. Archives of Sexual Behavior 38, 253–263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer M, Korn S, Brodbeck FC, Wolke D and Schulz H (2005) Bullying roles in changing contexts: the stability of victim and bully roles from primary to secondary school. International Journal of Behavioral Development 29, 323–335. [Google Scholar]
- Shilo G and Savaya R (2012) Mental health of lesbian, gay, and bisexual youth and young adults: differential effects of age, gender, religiosity, and sexual orientation. Journal of Research on Adolescence 22, 310–325. [Google Scholar]
- Slee PT (1995) Peer victimization and its relationship to depression among Australian primary school students. Personality Individual Differences 18, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Swearer SM, Song SY, Cary PT, Eagle JW and Mickelson WT (2001) Psychosocial correlates in bullying and victimization: the relationship between depression, anxiety, and bully/victim status. Journal of Emotional Abuse 2, 95–121. [Google Scholar]
- Tenenbaum LS, Varjas K, Meyers J and Parris L (2011) Coping strategies and perceived effectiveness in fourth through eighth grade victims of bullying. School Psychology International 32, 263–287. [Google Scholar]
- Trotta A, Di Forti M, Mondelli V, Dazzan P, Pariante C, David A, Mule A, Ferraro L, Formica I, Murray RM and Fisher HL (2013) Prevalence of bullying victimisation amongst first-episode psychosis patients and unaffected controls. Schizophrenia Research 150, 169–175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varjas K, Meyers J, Meyers B, Kim S, Henrich CC and Tenebaum LS (2009) Positive psychology and the prevention of school-based victimization. Handbook of Positive Psychology in Schools 20, 323–338. [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Hu Z, Peng K, Xin Y, Yang Y, Drescher J and Chen R (2019) Discrimination against LGBT populations in China. The Lancet Public Health 4, e440–e441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Hu Z, Peng K, Rechdan J, Yang Y, Wu L, Xin Y, Lin J, Duan Z and Zhu X (2020) Mapping out a spectrum of the Chinese public's discrimination toward the LGBT community: results from a national survey. BMC Public Health 20, 1–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson RJ, Grossman AH and Russell ST (2019) Sources of social support and mental health among LGB youth. Youth & Society 51, 30–48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney I and Smith PK (1993) A survey of the nature and extent of bullying in junior/middle and secondary schools. Educational Research 35, 3–25. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.