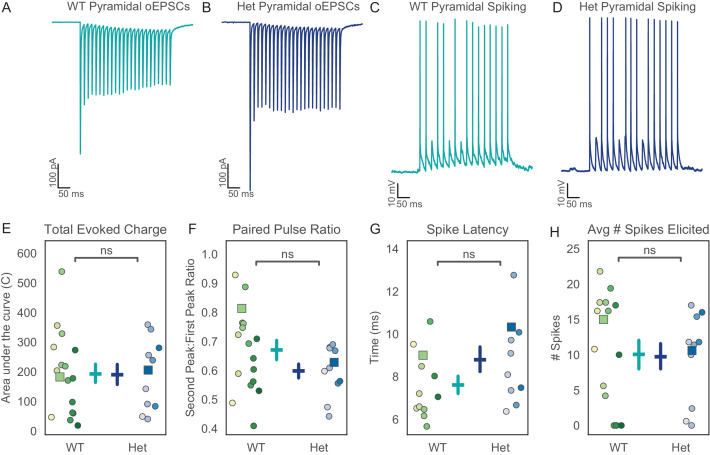
Figure 5. Excitatory hippocampal input to prefrontal pyramidal neurons is not changed in Pogz mutants.
(A, B) Representative examples of optically-evoked excitatory post-synaptic currents (oEPSCs) recorded from prefrontal pyramidal neurons in wildtype (A) or Pogz+/- mice (B). (C, D) Optically-evoked excitatory post-synaptic potentials (oEPSPs) and action potentials in wildtype (C) or Pogz+/- (D) pyramidal neurons. (E) Total oEPSC charge in pyramidal neurons, U = 1.0736, p=0.28. (F) Paired-pulse ratio for oEPSCs in pyramidal neurons, U = 1.4347, p=0.15 (G) Latency to first optically-evoked action potential in pyramidal neurons, U = −0.305, p=0.76. (H) Number of action potentials elicited by oEPSPs in pyramidal neurons, U = 0.2822, p=0.78. In E-H, different hues correspond to specific mice, and squares indicate datapoints from cells that were used for the representative traces shown in A-D. All p-values from Wilcoxon rank sum, WT N = 13 animals, n = 17 cells. Het N = 8 animals, n = 11 cells.