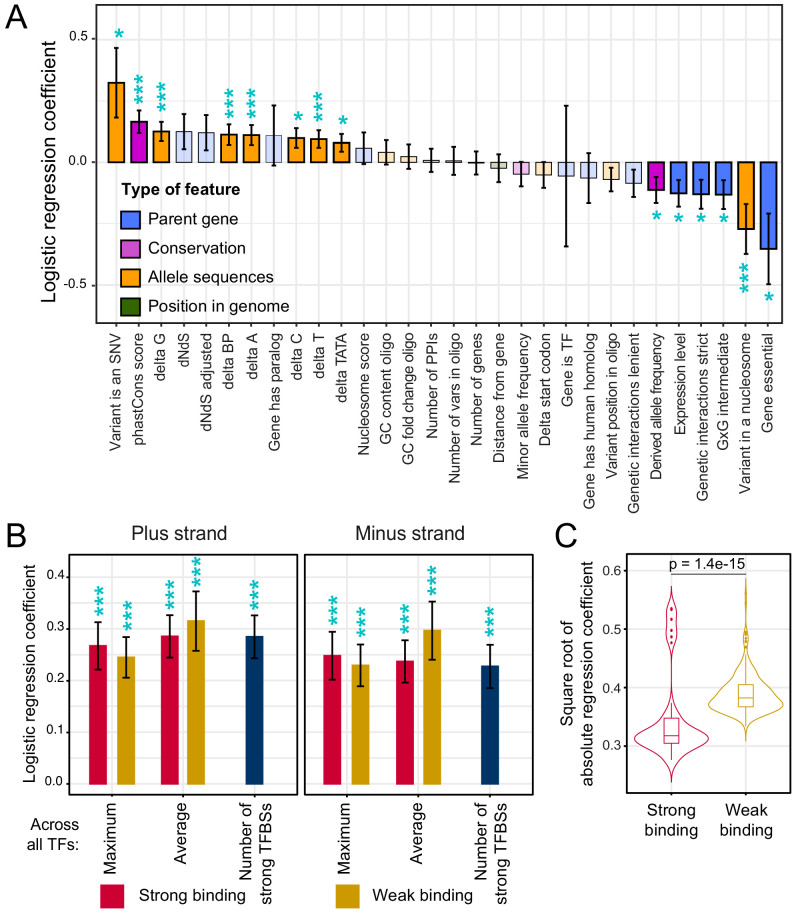
Figure 5. Association of features with variant causality.
(A) Non-TF features. The figure shows the strength of association between each feature and variant causality. Error bars show the standard error of the mean. Significant associations are indicated by three stars (FDR < 5%) or one star (nominal p-value<0.05). Non-significant features are shown in lighter coloring. (B) TF summary features aggregated across all 196 TFs, separated by strand, mode of aggregation across TFs, strength of binding (weak or strong), and mode of comparing allelic PWM scores across sliding sequence windows spanning each variant (Materials and methods). Each of these summary features was significantly associated with variant causality at an FDR of <5%. (C) Distributions of logistic regression estimates for strong vs. weak binding for individual TFs. The p-value shows the result of a Wilcoxon rank test. See also Figure 5—figure supplement 1.