Management of the compromised airway during theCOVID-19 era is associated with significant risk of infectious transmission to health care workers (HCWs), particularly when urgent tracheotomy is required.1 In some instances, super spreader events have been associated with airway management.2,3 Although several modifications to open and percutaneous tracheostomy have been described,2,4 evidence is limited regarding the relative safety of techniques and some controversies are unresolved.5,6 In this clinical case, we describe a patient who demonstrated external tracheal compression with superimposed acute COVID-19 infection. The surgical approach involved open tracheotomy with Bjork flap under local anesthesia, as previously performed in 23 of our COVID-19 patients with tracheostomy (not published data). The approach has mitigated risk of aerosol generation, ensured adequate oxygenation, and achieved a safe, secure airway. The study was approved by the institutional review board and conducted in accordance with Helsinki rules for human rights.
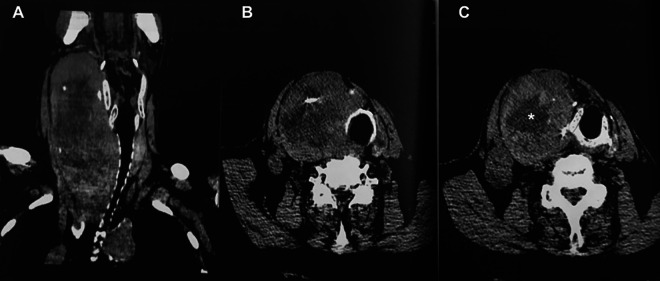
An 81-year-old man with long-standing history of goiter presented to the emergency department with shortness of breath and a large right-sided neck mass with rapid growth. He reported a 10-day history of increasing difficulty with breathing, which had dramatically worsened in the last 24 hours. The patient had tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) by nasopharyngeal swab, performed by a home nurse 3 days prior. His examination demonstrated labored breathing, hypoxemia on pulse oximetry (saturation <85%), and a large, fixed mass of the right neck. Neck computed tomography (CT; Figure 1) showed voluminous thyroid struma arising from right thyroid lobe extending into his mediastinum, resulting in compression and displacement of the larynx and trachea, with reduced airway patency. In addition, patient’s chest CT demonstrated diffuse interstitial pneumonia and multiple nodules consistent with tumor metastasis (Figure 2).
Figure 1.
Neck computer tomography scan. A, Coronal view that shows the mass which compresses and displaces the upper airway tract with partial obstruction. B and C, Axial view of upper and lower level of larynx that shows rotation on the right without reduction of the airway space. The asterisk shows diffuse edema in the struma that contributed to acute exacerbation of respiratory compromise.
Figure 2.
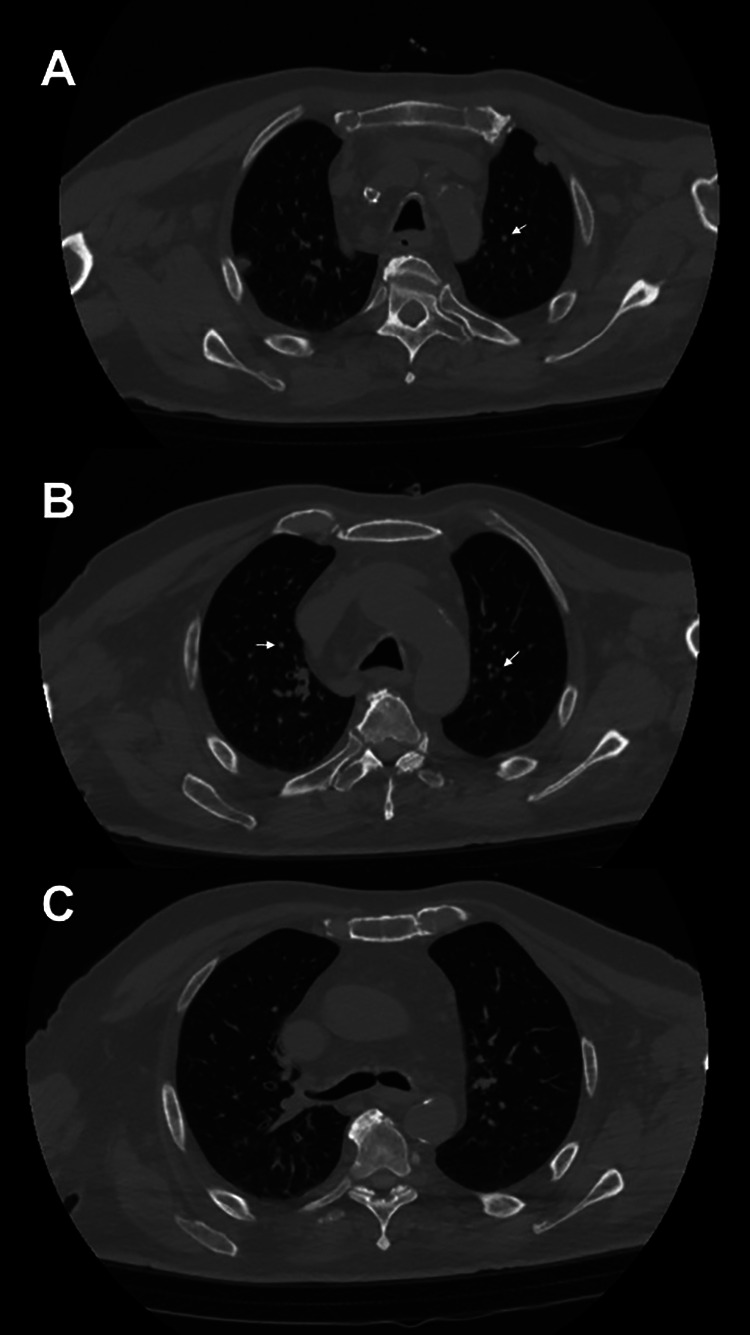
Chest computed tomography (CT) scan. A, The arrow shows an apical pulmonary metastasis. B, The arrows show the multiple bilateral nodules in the context of interstitial COVID-19 pneumonitis. C, The infection, laryngeal displacement, and compression of the trachea all contribute to respiratory distress.
Desaturation was attributed to the presence of both progressive interstitial pneumonia and external compression. Given clinical deterioration and the need for ventilatory support to improve oxygen saturation, the patient underwent endotracheal intubation, which was maintained for 10 days. The patients demonstrated no progress with weaning, and therefore, a tracheostomy was performed in the operating room in accordance with international guidelines,7 with all members of the team wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
The procedure was performed as follows:
Neck skin incision was placed 2 cm inferior to the cricoid cartilage, and after dividing the midline raphe, the thyroid isthmus was visualized and retracted cephalad, with discrete use of cautery along Berry’s ligament to minimize bleeding and facilitate surgical access to the airway.
After the patient was preoxygenated (100% oxygen) for 3 minutes, mechanical ventilation was paused and positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) allowed to dissipate, so as to minimize aerosol generation when entering the airway.
The trachea was entered with a scalpel, fashioning an inferiorly based flap (Björk flap) while leaving the endotracheal tube hyperinflated just between the carina and the tracheotomy site.
The endotracheal cuff was then deflated, and the endotracheal tube was slowly retracted until the cuff was positioned just superior to the tracheal window. Suction procedures were avoided.
The tracheostomy tube cannula (previously connected to Halyard system)6 was swiftly placed into the tracheal lumen and insufflated at the appropriate pressure level.
The correct position of the cannula was verified with capnography, and once oximetry values demonstrated saturation >97%, the endotracheal tube was removed, and the patient was safely transferred to the COVID-19 cohort unit.
During the tracheotomy, multiple biopsies of the thyroid tissue were performed, given presence of chest nodules. Computed tomography scan of the neck performed 2 days after surgery demonstrated appropriate position of cannula, which allowed for favorable ventilation (97% saturation; Figure 3). Histologic examination of the thyroid biopsy demonstrated histiocytic sarcoma in the context of normal thyroid tissue. The immunohistochemistry was PMG1 and KP1 positive for CD4 and CD68, CD163, CD31, and vimentin with high proliferation index (Ki67 60%-70%).
Figure 3.
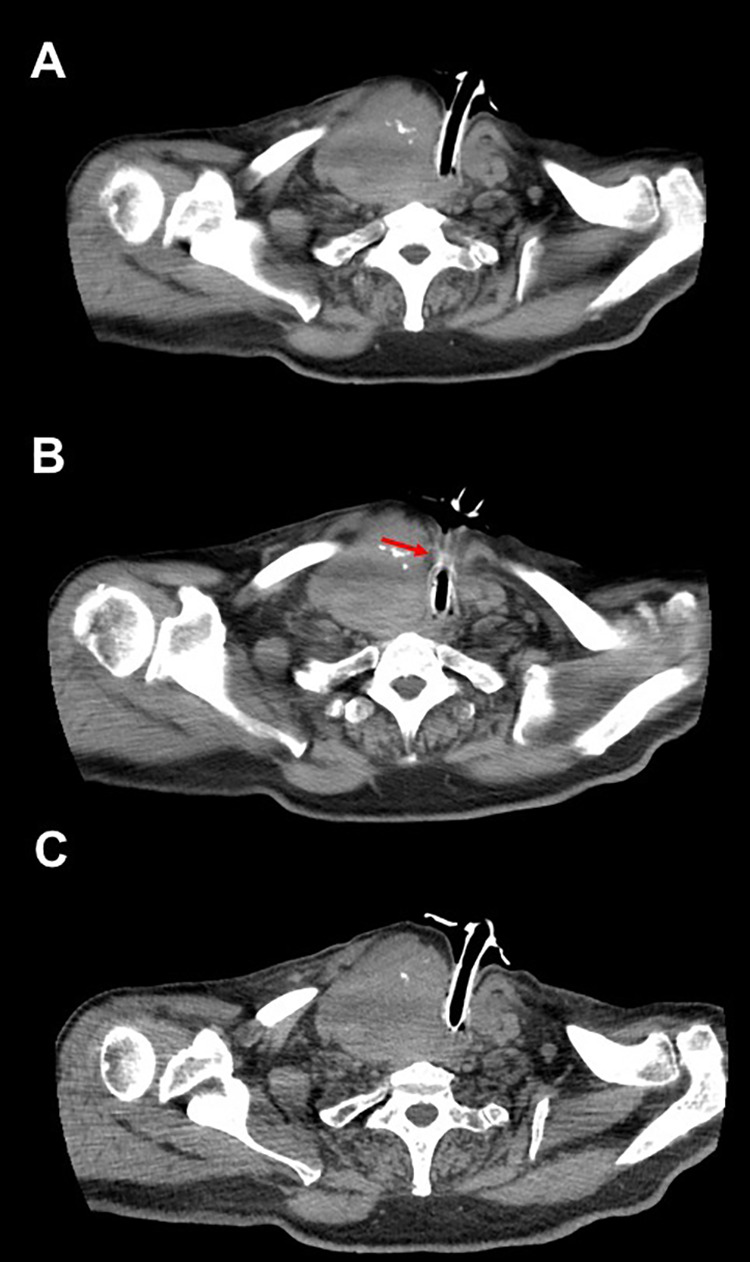
Neck computed tomography (CT) postsurgery. From top to bottom (A-C), the position of the tracheostomy tube cannula is shown in relation to the thyroid struma and airway. The red arrow shows the inferiorly based Björk flap.
The multifactorial etiology of respiratory distress included laryngeal edema, external tracheal compression, and interstitial pneumonia from COVID-19. Tracheotomy in the COVID-19 era often favors approaches that allow the tracheostoma to close swiftly following decannulation. In contrast, the Björk flap may delay closure of the site, but it reduces the risk of false passages, simplifies changes of the tracheostomy tube, and reduces risk of stenosis, particularly in patients with bulky thyroid disease or other head and neck cancer.8,9 Preoxygenation with 100% oxygen minimizes desaturation and cold technique is used to enter the airway. Last, while the pause in ventilation reduces risk of HCWs exposure10 the associated loss of PEEP will also result in derecruitment, so cannula insertion is performed expeditiously to minimize loss in the amount of aerated lung tissue.
This approach may be considered in conjunction with a multidisciplinary team approach that engages patients and other stakeholders to achieve safe, effective airway management. In difficult neck with altered tracheal anatomy, the Björk flap stabilizes the tracheostoma, and this procedure can be safely performed with proper PPE to protect medical staff while assuring a safe outcomes for the patient.
Footnotes
Authors’ Note: A.D.S., L.D’.A., M.J.B. contributed to study design and article writing; G.L., P.G., M.P., and C.G. collection of clinical data; G.R. and M.M. literature review, criticism, and review of paper. Original data are available under request to the corresponding author. The study was approved by the IRB of the hospital without releasing of an authorization number. The patient signed a written consent before being included in the study. The patient authorized to publish his data previous anonymization.
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
ORCID iD: Arianna Di Stadio  https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5510-3814
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5510-3814
Michael J. Brenner  https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4926-0957
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4926-0957
References
- 1.Smith JD, Chen MM, Balakrishnan K, et al. The Difficult airway and aerosol-generating procedures in COVID-19: timeless principles for uncertain times. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020;23:194599820936615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.McGrath BA, Brenner MJ, Warrillow SJ, et al. Tracheostomy in the COVID-19 era: global and multidisciplinary guidance. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(7):717–725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Balakrishnan K, Schechtman S, Hogikyan ND, Teoh AYB, McGrath B, Brenner MJ. COVID-19 pandemic: what every otolaryngologist-head and neck surgeon needs to know for safe airway management. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020;162(6):804–808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Foster P, Cheung T, Craft P, et al. Novel approach to reduce transmission of COVID-19 during tracheostomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2020;230(6):1102–1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pichi B, Mazzola F, Bonsembiante A, et al. CORONA-steps for tracheotomy in COVID-19 patients: a staff-safe method for airway management. Oral Oncol. 2020;105:104682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.D’Ascanio L, Latini G, Pandolfini M, Giardini D.Corona-steps for tracheotomy in COVID-19 patients: a staff-safe method for airway management. Oral Oncol. 2020;106:104731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bier-Lanning C, Cramer JD, Roy S, et al. Tracheostomy during COVID-19 pandemic: comparison of international perioperative care protocols and practices in 26 countries. OTO-HNS in press. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 8.Stathopoulos P, Stassen L. A modification of the Bjork flap in tracheostomies for head and neck cancer patients. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;119(5):444–445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Janik S, Kliman J, Hacker P, Erovic BM. Preserving the thyroidal isthmus during low tracheostomy with creation of a Björk flap. Laryngoscope. 2018;128(12):2783–2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Restrepo RD. AARC clinical practice guidelines: from “reference-based” to “evidence-based”. Respir Care. 2010;55(6):787–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]