Abstract
Background
Liver metastasis (LIM) of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) is associated with poor prognosis. The present study aimed at developing and validating nomogram to predict LIM in patients with GIST, thus helping clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Methods
The data of GIST patients derived from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database from 2010 to 2016, which were then screened by univariate and multivariate logistic regression for the construction of LIM nomogram. The model discrimination of LIM nomogram was evaluated by concordance index (C-index) and calibration plots, while the predictive accuracy and clinical values were measured by decision curve analysis (DCA) and clinical impact plot. Furthermore, we validated predictive nomogram in the internal testing set.
Results
A total of 3797 patients were enrolled and divided randomly into training and validating groups in a 3-to-1 ratio. After logistic regression, the significant variables were sex, tumor location, tumor size, N stage and mitotic rate. The calibration curves showed the perfect agreement between nomogram predictions and actual observations, while the DCA and clinical impact plot showed the clinical utility of LIM nomogram. C-index of the nomogram was 0.812. What’s more, receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC) also showed good discrimination and calibration in the training set (AUC = 0.794, 95% CI 0.778–0.808) and the testing set (AUC = 0.775, 95% CI 0.748–0.802).
Conclusion
The nomogram for patients with GIST can effectively predict the individualized risk of liver metastasis and provide insightful information to clinicians to optimize therapeutic regimens.
Keywords: Gastrointestinal stromal tumors, Liver metastasis, Nomogram, SEER
Background
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) is a rare neoplasm of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, which is considered to originate from the multipotential mesenchymal stem cells and differentiate to interstitial Cajal’s cells (ICC) [1–3]. The incidence of GIST has increased in the recent years, possibly related to the rapid development of endoscopic technology [1]. GIST can occur anywhere throughout the GI tract, stomach and small intestine are the most common site, followed by colon, rectum, esophagus [4, 5]. However, there were several studies indicated that GISTs can also arise outside of the GI tract, including pancreas, gallbladder, liver, retroperitoneum and so on [4, 6, 7].
It was reported that more than half of the GIST patients had metastases upon presentation at medical institutions, and the liver was the most common site [8]. Although complete surgical resection with negative margins is the standard treatment for GIST, over 50% of patients develop recurrence or metastasis [9, 10], with liver metastasis being the main metastatic pattern of GIST [11, 12]. Hence, the poor prognosis of GISTs might be related to the status of liver metastasis (LIM). Prior to the introduction of adjuvant therapy, the treatment of metastatic GIST was limited and the outcomes were dismal [13]. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) like imatinib have revolutionized the management of metastatic GIST for the marked improvements in survival outcomes [14]. Nonetheless, secondary mutations and drug resistance appeared during the adjuvant TKIs treatment, indicating that it is difficult to obtain the complete cure by the use of TKIs [15, 16]. Hence, the tools for predicting the biological behavior and clinical outcome of GIST assumed a crucial role in the management of GIST [17].
In recent years, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) nomogram has been worldwide used to generate the probability of a clinical event through a complex computational formula [18, 19]. With the aid of nomogram, clinicians can assess the risk of the clinical event and then design individual treatment plans, determine the use of adjuvant therapy, optimize aspects of therapies and consider appropriate patient counselling [20]. Considering the important role of LIM in the prognosis of GIST, the study presented in evaluating patients with GIST and discovering patients with high-risk scores in liver metastasis by the use of nomogram.
Methods
Data source and inclusion criteria
Considering that Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database started to provide data regarding the specific sites of metastatic GIST since 2010 [21, 22], we extracted data about patients with known histological diagnosis of GIST between 2010 and 2016 by the use of the SEER*Stat software version 8.3.6. The International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, 3rd edition (ICD-O-3) morphology codes (8936/3) were used to identify GIST.
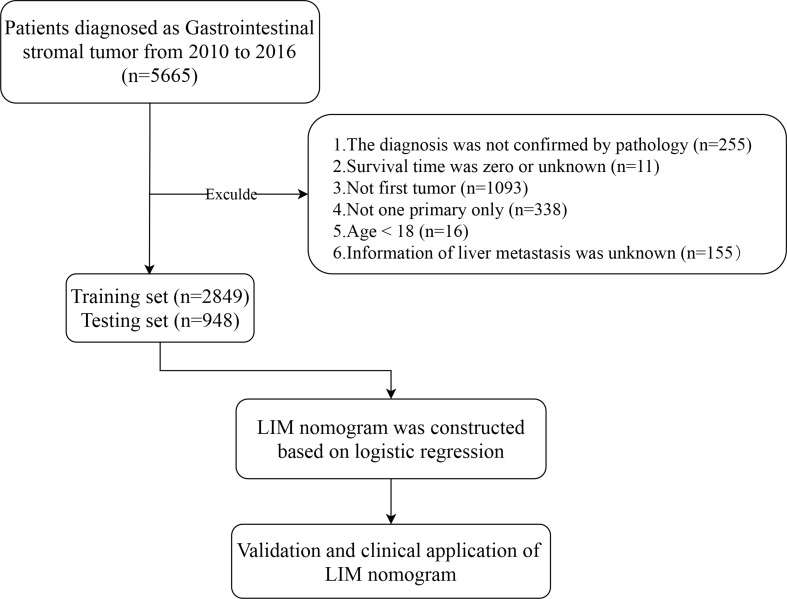
The patient's inclusion and elimination process are shown in Fig. 1. We excluded the cases if they: (1) had no positive pathology; (2) had unknown survival time; (3) had not been the first tumor; (4) had more than one primary tumor; (5) age < 18 [23, 24]; (6) had unknown liver metastasis information.
Fig. 1.
Study flowchart
We extracted the data from the SEER database including age, sex, race, marriage, primary site, N stage, tumor size, and mitotic rate, which was identified by the variable “CS site-specific factor 6”. The N stage was established according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Cancer Staging Manual (7th edition). “SEER Combined Mets at DX-liver (2010+)” was used to identify the presence of liver metastasis in a newly diagnosed GIST patient. We classified patients as married, unmarried (including single, divorced, separated, and widowed) and unknown. Age was categorized into two groups: less than or equal to 65 years old and more than 65 years old [25]. Tumor locations with less than 20 cases were classified as “Others” [25].
Construction, validation and clinical utility of nomogram
The GIST patients who met the inclusion criteria were randomly divided into training and testing sets in a 3-to-1 ratio. Afterward, the following variables were selected into the research: age, sex, marriage, race, tumor location, tumor size, mitotic rate and N stage. Univariate and multivariate binary logistic regressions were then used to identify the significant characteristics with the help of the forwarding stepwise selection method [26]. By the use of Hosmer–Lemeshow test, bootstrapping with 1,000 samples were utilized to internal validation of the nomogram and to draw calibration plots, which can indicate the association among the apparent curve, bias-corrected curve and ideal curve [27]. Harrell’s concordance index (C-index) and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) were also employed to estimate the predictive performance of the nomogram. The higher C-index and the area under ROC curve (AUC) were, the better discrimination ability or prognostic accuracy the variables would be. Meanwhile, sensitivity and specificity of the cutoff values were then obtained [28]. Furthermore, the decision curve analysis (DCA), which plots net benefit (NB) at a range of reasonable risk thresholds that conform with the clinical practice, was applied to evaluate the clinical utility of nomograms for decision making [29]. Based on DCA, we developed clinical impact plots to visually show the estimated high-risk patients' number for each risk threshold [30].
Statistical methodologies and software
Continuous variables were presented as mean values ± standard deviation (SD), and categorical variables were summarized as proportions. Continuous variables and categorical variables were compared by the Student’s t-test and Chi-squared test, respectively. IBM SPSS Statistics, version 26.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA) and R software version 3.6.2 (http://www.r-project.org) performed the statistical methods mentioned above, and several R packages, including regplot, rms, rmda and pROC were applied to draw graphs, such as nomogram, calibration plot, DCA plot, and ROC curve. All P values were two-sided with values of P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant, and confidence intervals (CIs) stated at the 95% confidence level.
Results
Demographic baseline characteristics
3797 patients (Additional file 1: Table S1) fulfilled the inclusion criteria being enrolled and divided randomly into training and validating groups in a 3-to-1 ratio, with a training group (n = 2849) (Additional file 2: Table S2) for the construction of nomogram and a testing group (n = 948) (Additional file 3: Table S3) for internal verification, which was then summarized in Table 1. There was no statistically significant difference between training and testing sets (P > 0.05). LIM was present in 320 of 2849 patients (11.3%) in the training set, while the proportion that LIM occupied in the testing group was 11.5% (109 of 948). Afterward, as indicated in Table 2, in the correlation analysis, five clinical characteristics, including sex, tumor location, tumor size, N stage and mitotic rate were significantly correlated (P < 0.05) with LIM both in the training and testing groups.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patients
| Characteristics | SEER cohort (%) | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire cohort n = 3797 | Training n = 2849 | Testing n = 948 |
||
| Age | 62.25 ± 13.67 | 62.12 ± 13.90 | 62.38 ± 13.43 | 0.616 |
| Sex | 0.962 | |||
| Male | 1908(50.2) | 1431(50.2) | 477(47.1) | |
| Female | 1889(49.8) | 1418(49.8) | 471(52.9) | |
| Marriage | 0.158 | |||
| Married | 2143(56.4) | 1609(56.4) | 534(56.3) | |
| Unmarried | 1447(38.1) | 1096(38.4) | 351(37.0) | |
| Unknown | 207(5.5) | 144(5.2) | 6.6(6.7) | |
| Race | 0.359 | |||
| White | 2534(66.7) | 1909(67.0) | 625(65.9) | |
| Black | 684(18.0) | 519(18.2) | 165(17.4) | |
| Others | 579(15.3) | 421(14.8) | 158(16.7) | |
| Tumor location | 0.716 | |||
| Stomach | 1509(39.7) | 1119(39.2) | 390(41.1) | |
| Duodenum | 213(5.6) | 158(5.5) | 55(5.8) | |
| Jejunum | 272(7.1) | 208(7.3) | 64(6.7) | |
| Ileum | 104(2.7) | 86(3.0) | 18(1.8) | |
| Colon | 79(2.0) | 60(2.1) | 19(2.0) | |
| Rectum | 104(2.7) | 79(2.7) | 25(2.6) | |
| Others | 457(12.0) | 340(11.9) | 117(12.3) | |
| Unknown | 1059(28.2) | 799(28.3) | 260(27.7) | |
| Tumor size | 0.003 | |||
| ≤ 2 cm | 446(11.7) | 356(12.4) | 90(9.4) | |
| 2–5 cm | 1066(28.0) | 797(27.9) | 269(28.3) | |
| 5–10 cm | 1088(28.6) | 839(29.4) | 249(26.2) | |
| > 10 cm | 896(23.5) | 645(22.6) | 251(26.4) | |
| Unknown | 301(8.2) | 212(7.7) | 89(9.7) | |
| N stage | 0.319 | |||
| N0 | 3531(93.1) | 2658(93.4) | 873(92.2) | |
| N1 | 131(3.4) | 97(3.4) | 34(3.5) | |
| Unknown | 135(3.5) | 94(3.2) | 41(4.3) | |
| Mitotic rate | 0.794 | |||
| < 5/50 HPFs | 1835(48.3) | 1386(48.6) | 449(47.3) | |
| ≥ 5/50 HPFs | 814(21.4) | 610(21.4) | 204(21.5) | |
| Unknown | 1148(30.3) | 853(30.0) | 295(31.2) | |
| Liver metastasis | 0.823 | |||
| No | 3368(88.7) | 2529(88.7) | 839(88.5) | |
| Yes | 429(11.3) | 320(11.3) | 109(11.5) | |
SEER Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results, HPFs high power fields
Table 2.
Correlations between characteristics of patients with liver metastasis in the training and testing groups
| Characteristics | Training set (%) | Testing set (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | P | Negative | Positive | P | |
| Age | 62.18 ± 13.77 | 61.67 ± 14.86 | 0.560 | 62.41 ± 13.62 | 62.10 ± 11.96 | 0.802 |
| Sex | < 0.001 | 0.004 | ||||
| Male | 1238(48.9) | 193(60.3) | 408(48.6) | 69(63.3) | ||
| Female | 1291(51.1) | 127(39.7) | 431(51.4) | 40(36.7) | ||
| Marriage | 0.254 | 0.818 | ||||
| Married | 1442(57.0) | 167(52.1) | 474(56.4) | 60(55.0) | ||
| Unmarried | 960(37.9) | 136(42.5) | 308(36.7) | 43(39.4) | ||
| Unknown | 127(5.1) | 17(5.4) | 57(6.9) | 6(5.6) | ||
| Race | 0.144 | < 0.001 | ||||
| White | 1695(67.0) | 214(66.8) | 556(66.2) | 69(63.4) | ||
| Black | 451(17.8) | 68(21.2) | 145(17.2) | 20(18.3) | ||
| Others | 383(15.2) | 38(12.0) | 138(16.6) | 20(18.3) | ||
| Tumor location | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | ||||
| Stomach | 1026(40.5) | 93(29.0) | 357(42.5) | 33(30.2) | ||
| Duodenum | 140(5.5) | 18(5.6) | 51(6.0) | 4(3.6) | ||
| Jejunum | 186(7.3) | 22(6.8) | 59(7.0) | 5(4.5) | ||
| Ileum | 83(3.2) | 3(0.9) | 16(2.1) | 2(1.8) | ||
| Colon | 51(2.0) | 9(2.8) | 18(2.1) | 1(0.9) | ||
| Rectum | 75(2.9) | 4(1.2) | 23(2.7) | 2(1.8) | ||
| Others | 266(10.5) | 74(23.1) | 85(10.1) | 32(29.1) | ||
| Unknown | 702(28.1) | 97(30.6) | 228(27.5) | 32(29.1) | ||
| Tumor size | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | ||||
| ≤ 2 cm | 338(13.3) | 18(5.6) | 86(10.2) | 4(3.6) | ||
| 2–5 cm | 755(29.8) | 42(13.1) | 256(30.5) | 13(11.9) | ||
| 5–10 cm | 766(30.2) | 73(22.8) | 221(26.3) | 28(25.6) | ||
| > 10 cm | 534(21.1) | 111(34.6) | 215(25.6) | 36(33.3) | ||
| Unknown | 136(5.6) | 76(23.9) | 61(7.4) | 28(25.6) | ||
| N stage | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | ||||
| N0 | 2412(95.3) | 246(77.0) | 791(94.2) | 82(75.2) | ||
| N1 | 60(2.4) | 37(11.5) | 28(3.3) | 6(5.5) | ||
| Unknown | 57(2.3) | 37(11.5) | 20(2.5) | 21(19.3) | ||
| Mitotic rate | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | ||||
| < 5/50HPFs | 1329(52.5) | 57(17.5) | 428(51.0) | 21(19.2) | ||
| ≥ 5/50HPFs | 557(22.0) | 53(16.5) | 187(22.2) | 17(15.5) | ||
| Unknown | 643(25.5) | 210(66.0) | 224(26.8) | 71(65.3) | ||
HPFs high power fields
Univariate and multivariate logistic regression results
In the univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses, there were finally five parameters significantly correlated with LIM (Table 3), namely sex (female: odds ratio (OR) 0.723, 95% CI 0.577–0.939, P = 0.015), tumor location (rectum: 0.226, 0.079–0.647, P = 0.006), tumor size (> 10 cm: 2.842, 1.649–4.897, P < 0.001; unknown: 4.251, 2.359–7.660, P < 0.001), N stage (positive: 3.313, 2.057–5.337, P < 0.001; unknown: 2.851, 1.723–4.716, P < 0.001) and mitotic rate (≥ 5/50 HPFs: 1.803, 1.210–2.687, P = 0.004; unknown: 5.763, 4.091–8.116, P < 0.001).
Table 3.
Risk factors for liver metastasis identified by univariate logistic regression analysis and multivariate logistic regression analysis
| Characteristics | Univariate logistic regression analysis | Multivariate logistic regression analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | P | OR | 95% CI | P | |
| Age | 0.336 | |||||
| ≤ 65 | 1 | |||||
| > 65 | 0.890 | 0.701–1.129 | 0.336 | |||
| Sex | < 0.001 | 0.015 | ||||
| Male | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Female | 0.631 | 0.498–0.800 | 0.723 | 0.557–0.939 | 0.015 | |
| Race | 0.146 | |||||
| White | 1 | |||||
| Black | 1.194 | 0.892–1.599 | 0.233 | |||
| Others | 0.786 | 0.547–1.129 | 0.192 | |||
| Marriage | 0.254 | |||||
| Married | 1 | |||||
| Unmarried | 1.223 | 0.962–1.556 | 0.101 | |||
| Unknown | 1.156 | 0.680–1.965 | 0.593 | |||
| Tumor location | < 0.001 | 0.057 | ||||
| Stomach | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Duodenum | 1.418 | 0.831–2.421 | 0.200 | 0.994 | 0.554–1.784 | 0.985 |
| Jejunum | 1.305 | 0.799–2.130 | 0.287 | 1.403 | 0.826–2.381 | 0.210 |
| Ileum | 0.399 | 0.124–1.286 | 0.124 | 0.377 | 0.110–1.293 | 0.121 |
| Colon | 1.947 | 0.929–4.079 | 0.078 | 0.686 | 0.312–1.511 | 0.350 |
| Rectum | 0.588 | 0.210–1.645 | 0.312 | 0.226 | 0.079–0.647 | 0.006 |
| Others | 3.069 | 2.198–4.285 | < 0.001 | 1.043 | 0.708–1.537 | 0.831 |
| Unknown | 1.524 | 1.129–2.058 | 0.006 | 1.049 | 0.752–1.463 | 0.778 |
| Tumor size | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | ||||
| ≤ 2 cm | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 2–5 cm | 1.045 | 0.593–1.841 | 0.880 | 1.123 | 0.623–2.024 | 0.700 |
| 5–10 cm | 1.790 | 1.052–3.045 | 0.032 | 1.584 | 0.910–2.755 | 0.104 |
| > 10 cm | 3.903 | 2.329–6.541 | < 0.001 | 2.842 | 1.649–4.897 | < 0.001 |
| Unknown | 10.493 | 6.048–18.026 | < 0.001 | 4.251 | 2.359–7.660 | < 0.001 |
| N stage | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | ||||
| N0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| N1 | 6.046 | 3.932–9.296 | < 0.001 | 3.313 | 2.057–5.337 | < 0.001 |
| Unknown | 6.365 | 4.123–9.824 | < 0.001 | 2.851 | 1.723–4.716 | < 0.001 |
| Mitotic rate | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | ||||
| < 5/50 HPFs | 1 | 1 | ||||
| ≥ 5/50 HPFs | 2.219 | 1.507–3.266 | < 0.001 | 1.803 | 1.210–2.687 | 0.004 |
| Unknown | 7.615 | 5.599–10.365 | < 0.001 | 5.763 | 4.091–8.116 | < 0.001 |
OR odds ratio, 95% CI 95% confidence interval, HPFs high power fields
Construction and validation of LIM nomogram
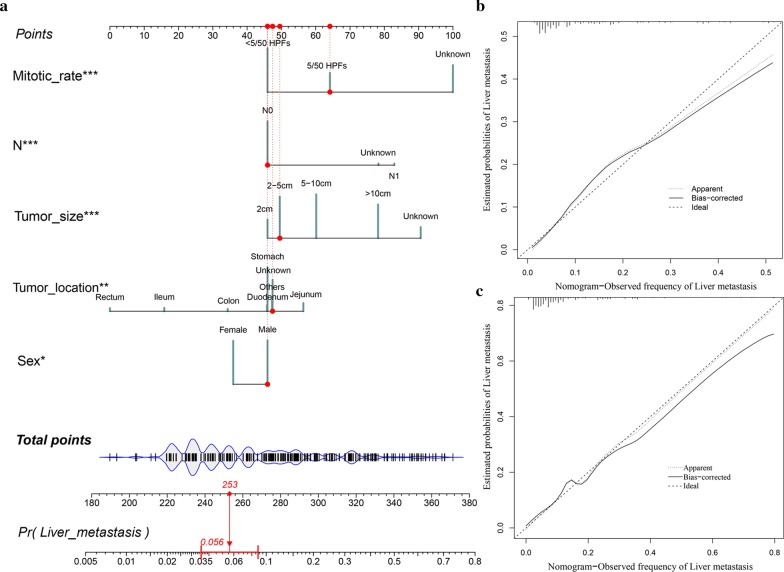
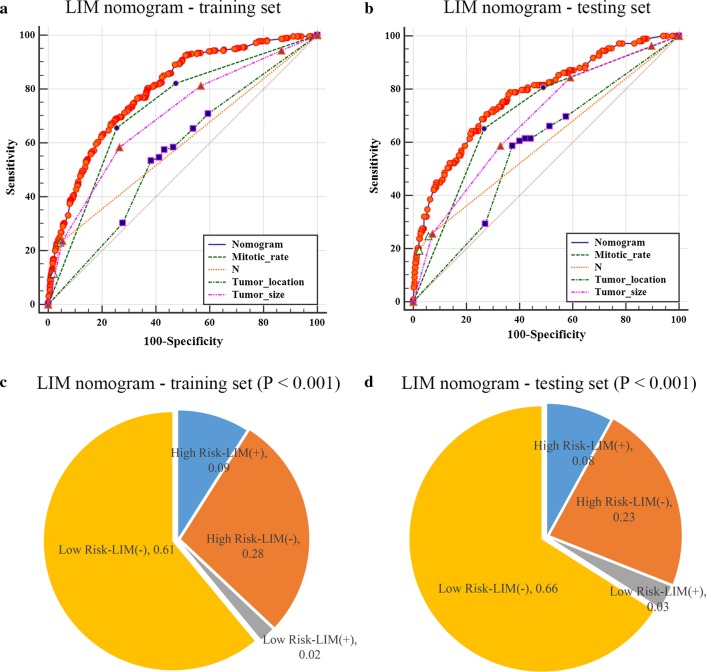
The results of univariate and multivariate logistic regression were then used to construct LIM nomogram (Fig. 2a). As demonstrated in the LIM nomogram, mitotic rate was expectedly to be the best predictor, followed by the tumor size, tumor location, N stage and sex. Afterward, the calibration plots of the nomogram (Fig. 2b, c) indicated that apparent curve, bias-corrected curve, and ideal curve were well numerically agreed both in the training and testing groups. Respectively, the AUC values of the nomogram were 0.794 (95% CI 0.778–0.808) and 0.775 (95% CI 0.748–0.802) in the training and testing groups (Fig. 3a, b). According to the ROC curves in the training set, the value of nomogram was more significant than other variables, including tumor location (AUC 0.562, 95% CI 0.544–0.581, P < 0.001), mitotic rate (0.725, 0.708–0.741, P < 0.001), tumor size (0.697, 0.679–0.714, P < 0.001) and N stage (0.593, 0.574–0.611, P < 0.001). Similarly, in the testing set, the value of nomogram was also more significant than mitotic rate (0.711, 0.680–0.739, P < 0.001), tumor size (0.682, 0.652–0.712, P < 0.001), N stage (0.598, 0.566–0.629, P < 0.001) and tumor location (0.574, 0.542–0.606, P < 0.001). Furthermore, by the use of the maximum Youden index in the training group [19], the cutoff values of 170 and 188 were get, the patients were then divided into high-risk and low-risk groups with the results shown as pie charts (Fig. 3c, d).
Fig. 2.
Nomogram and calibration curves for the prediction of liver metastasis in the patients with GIST. There are five characteristics enrolled in the LIM nomogram (a), and the patient #77784053 is illustrated by mapping its values to the covariate scales. Calibration curves for predicting LIM in the training groups (b) and testing groups (c) are shown in the right side (Bootstrap = 1000 repetitions). The detailed statistics are provided in Additional file 2: Table S2 and Additional file 3: Table S3. Abbreviations: LIM liver metastasis, Pr prediction
Fig. 3.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis for LIM nomogram and pie charts for indicating the discriminatory power of LIM nomogram. In the training (a) and testing (b) groups of LIM nomogram, the AUC was respectively 0.794 (95% CI 0.778–0.808) and 0.775 (95% CI 0.748–0.802). The P values were two-sided. The maximum Youden index of the ROC curves were employed to distinguish the risk of liver metastasis in the training group (c) and the testing groups (d), respectively. The detailed statistics are provided in Additional file 2: Table S2 and Additional file 3: Table S3. The P values were two-sided and tested by Chi-square test. Abbreviations: ROC receiver operating characteristic, LIM liver metastasis, 95% CI 95% confidence interval
Clinical utility of LIM nomogram
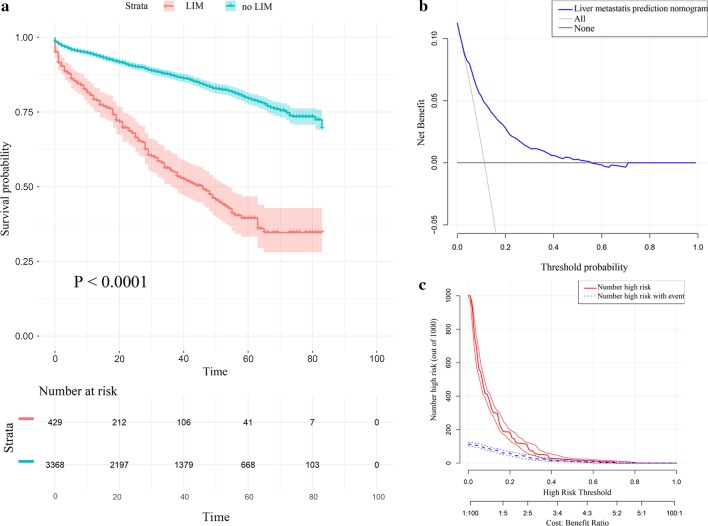
Firstly, we developed Kaplan–Meier survival curves of overall survival (OS) for all 3797 patients (Fig. 4a) enrolled in the study and there were significant differences between the Kaplan–Meier survival curves of the two sets (P < 0.001), which indicated that patients with GIST who were predicted to have LIM would have significant survival disadvantage. Afterward, as shown in DCA curve (Fig. 4b), threshold probabilities of 0.02–0.54 was the best benefit to LIM. Furthermore, clinical impact plot (Fig. 4c) of the training set indicated that, during the most beneficial threshold probabilities range, the predicted high-risk patients were always more than the patients actually had LIM, accompanying with acceptable cost–benefit ratios.
Fig. 4.
Kaplan–Meier survival curve, decision curve analysis, and clinical impact plot of patients with GIST. The entire cohort of patients with GIST were enrolled to construct the Kaplan–Meier survival curve (a). The decision curve analysis (DCA) and clinical impact of the LIM nomogram (b, c) in the training group are plotted. The detailed statistics are provided in Additional file 2: Table S2 and Additional file 3: Table S3. The P value was two-sided. Abbreviations: LIM liver metastasis
Discussion
GIST was mistaken for schwannomas, leiomyomas or leiomyosarcomas until the introduction of ultrastructural, immunohistochemical, and molecular biological techniques, which uncovered that GIST originated from myenteric nervous system [31], and ICCs were further suggested to be the cells of origin [32]. Subsequently, gain-of-function mutations in the tyrosine kinase receptor KIT and platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α (PDGFRA) were groundbreakingly found as the main oncogenic driver in GIST [33, 34], which encouraged the development of GIST targeted therapies [5]. In recent researches, Etwenty-six (ETS) variant 1 (ETV1) was also reported to overexpress in GIST and enhance the expression of KIT when binding target genes [1, 35]. However, nearly 10–15% of adult GIST and 85% of pediatric GIST are negative for KIT and PDGFRA mutations, as called wild-type (WT) GIST, which is a component of the Carney-Stratakis syndrome caused by the succinyl dehydrogenase (SDH)-mutations [36]. Whereas, liver was the most common site that GIST metastatic to, both in WT GIST and non-WT GIST, and LIM of GIST was always suggested to be related to the poor prognosis [37].
Nomogram, a quantitative tool for assessing risk and benefit, has been widespread applied in the medical domain for clinical decision-making [38]. In the previous studies, several nomograms have been developed and validated to predict the OS, cancer-specific survival (CSS) of GIST, recurrence-free survival (RFS) and disease-free survival (DFS) after surgical resection of GIST [25, 39–41]. However, the nomogram for predicting LIM of GIST has not yet been reported.
In the present research, we ultimately obtained 3797 GIST cases from SEER database and the LIM nomogram was further established based on five significant patient features, namely sex, tumor location, tumor size, N stage and mitotic rate. The discrimination performance, as demonstrated in the calibration plots (Fig. 2b, c), was assessed by an internal bootstrap resampling approach. Furthermore, as shown in the ROC curves (Fig. 3a, b), the LIM nomogram displayed better diagnostic efficiencies when compared with the other single variables, and the AUCs of the nomogram were 0.794 (0.778–0.808) and 0.775 (0.748–0.802) in the training and testing groups, respectively.
Although the classification, line(s) of differentiation, prognostication have long been the confusion and controversy of GIST, tumor size and mitotic rate were the widely accepted risk factors. By means of tumor size and mitotic rate, the first risk classification of GIST, constructed by Fletcher et al. [42], divided GIST patients into four sets, including very low risk, low risk, intermediate risk, and high risk. Previous studies indicated that the size and mitotic rate of GIST were proportional to poor prognosis [25, 39, 40], which corroborated our results. However, metastatic measures were not uncommon for postoperative GISTs, even that with small tumor size and low mitotic rate [43]. The results obtained from the multivariate analysis of Yang et al.’s study [11] presented that GIST size was not a significant prognostic factor of the liver metastatic GIST. In contrast, Mietinenn et al. suggested tumor size was the metastatic risk of GIST, rather than mitotic rate [44]. In our opinions, GIST with larger tumor size or higher mitotic rate tend to subject to earlier adjuvant therapy and more extensive resections, which may be a reason for the discrepancy in the previous studies [11, 45, 46]. Additionally, male GIST patients were more likely to have LIM than female ones, which was in accordance with the previous studies that indicated GIST had a mild male predominance [11, 47], however, the underlying mechanism remains unclear.
Recently, controversy exists surrounding the relationship between primary tumor location and prognosis of GIST. It is a common dogma that gastric GIST (G-GIST) has a more favorable behavior when compared with small intestinal GIST (SI-GIST) [17]. Together with tumor size and mitotic rate, Miettinnen et al. added tumor location as a poor prognostic factor for the construction of Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) classification [42, 48]. Based on approximately 2000 cases, SI-GIST resulted in a relatively higher risk of metastasis and tumor-related death, particularly with the tumor size exceeding 5 cm [48]. Anatomic site was also reported to be the significant independent predictor of OS [49], CSS [50] and RFS [51], with SI-GIST accompanied with significant disadvantage in the prognosis as compared to G-GIST. Furthermore, Kukar et al. found that younger patients with SI-GIST had a tendency to be presented with distant metastatic disease and larger tumor size [50]. In addition, the proportion of KIT exon 9 mutation was strikingly higher in SI-GIST than that in G-GIST, which may be the explanation of poorer prognosis of SI-GIST [52]. Inversely, several studies based on SEER database revealed comparable prognosis between small bowel and gastric GIST. After adjusting the confounding variables on a population based level, Guller et al. found that SI-GIST and G-GIST shared similar OS and CSS, which was contrary to common belief [17]. These results reflect those of Giuliano et al. [53] who further found that, although SI-GIST did have more aggressive features, SI-GIST patients were also more likely to undergo surgery than G-GIST (89.8% SI-GIST vs. 78.7% G-GIST), leading to the comparable survival outcomes. However, the previous studies always investigated SI-GIST as an entire cohort. As displayed in Fig. 2a, G-GIST seemed to share similar score with duodenal GIST (D-GIST), while jejunal GIST (J-GIST) patients were more likely to have LIM than ileal GIST (I-GIST) patients. Although I-GIST and J-GIST were reported to share compared prognosis in the study of Feng et al. [54], we suggested that more aggressive treatment should be taken into consideration to J-GIST for the high risk of LIM. In comparison with colon GIST (C-GIST), rectal GIST (R-GIST) tended to have more positive prognosis in spite of the less likelihood of surgical resection [50], analogous result could be found in the current study. Moreover, the aggressive course of extra-gastrointestinal GIST (EGIST) was suggested to be akin to SI-GIST [55], whereas according to the present LIM nomogram, EGIST seemed to shared similar prognosis with D-GIST, irrespective of I-GIST and J-GIST. Sample size and potential bias may result in such differences.
Unlike other solid tumors, lymph nodal involvement is extremely rare in GIST patients and lymph node dissection is not routinely suggested during the surgical treatment [56, 57]. However, in the present study, although the rate of lymph node metastasis (LNM) in the entire cohort was low (3.3%), LNM was significantly associated with LIM. This finding was consistent with that of Gaitanidis et al. who also found LNM was an independent prognostic factor of worse overall survival in patients with metastatic GIST [58], which further revealed that the evaluation of regional lymph nodes could be taken into consideration when undergoing surgical resection in patients with metastatic GIST. In addition, Li et al. found that lymphadenectomy was associated with an risk of mortality in GIST patients, which may be attributed to the destroy of the immune micro-environment in the normal lymph nodes and increasing postoperative morbidity and mortality caused by surgical trauma [59, 60]. What’s more, GIST patients with SDH complex deficiencies tended to have LNM. The SDH-deficient related disease like WT GIST (a component of the Carney-Stratakis syndrome) was reported to have high rates of LNM (29%) [61], hence the resection of enlarged nodes in SDH-deficient neoplasms was recommended in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines [62].
However, the current study is subject to several limitations. The study is a retrospective analysis, systematic and prospective data were lacked. External validation at other institutions was also lacked in our research, which may lead LIM nomogram to be overfitting. In addition, several critical clinicopathologic variables were required, especially the administration of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. If the information of co-morbidities, immunohistochemistry, and other laboratory values could be available for the construction of LIM nomogram, the results of our study might provide more valuable therapeutic measures for clinician.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a large population-based cohort derived from the SEER dataset was screened for the construction of the novel nomogram for predicting LIM in patients with GIST. According to the results of the internal validation, DCA curve, and clinical impact plot, our nomogram could effectively predict the individualized risk of LIM. We hoped that the LIM nomogram could be further employed and improved in the clinical work, clinicians can choose better medical examinations and optimize therapeutic regimens with the help of LIM nomogram.
Supplementary information
Additional file 1: Table S1. A database of the information of GIST patients obtained from SEER database.
Additional file 2: Table S2. A database of training set.
Additional file 3: Table S3. A database of testing set.
Acknowledgements
We thank the SEER database for the available data sets.
Abbreviations
- SEER
Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results
- GIST
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- LIM
Liver metastasis
- LNM
Lymph node metastasis
- C-index
Concordance index
- DCA
Decision curve analysis
- OS
Overall survival
- CSS
Cancer-specific survival
- RFS
Recurrence-free survival
- DFS
Disease-free survival
- HPFs
High power fields
- TKIs
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- OR
Odds ratio
- 95% CI
95% Confidence interval
- ROC
Receiver operating characteristic
- AUC
Area under ROC curve
Authors’ Contributions
ZWJ, XXL and CQM conceived and designed the study. GWZ, KSX and GWG acquired and analyzed the data. GWZ, KSX, YZ and JBW interpreted the data and drafted the manuscript. All authors contributed to and revised the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 8170151341) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20161086 and BK20181506). The funders of the study had no role in study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or writing of the report. The corresponding author had full access to all the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declared no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Guowei Zhou and Keshuai Xiao have contributed equally to this work
Contributor Information
Guanwen Gong, Email: love_ggw2@163.com.
Chaoqun Ma, Email: doctormachaoqun@gmail.com.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1186/s12893-020-00969-4.
References
- 1.Mantese G. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor: epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2019;35(6):555–559. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nilsson B, Bumming P, Meis-Kindblom JM, Oden A, Dortok A, Gustavsson B, Sablinska K, Kindblom LG. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: the incidence, prevalence, clinical course, and prognostication in the preimatinib mesylate era—a population-based study in western Sweden. Cancer. 2005;103(4):821–829. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Perez EA, Livingstone AS, Franceschi D, Rocha-Lima C, Lee DJ, Hodgson N, Jorda M, Koniaris LG. Current incidence and outcomes of gastrointestinal mesenchymal tumors including gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;202(4):623–629. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2006.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Liu Z, Tian Y, Liu S, Xu G, Guo M, Lian X, Fan D, Zhang H, Feng F. Clinicopathological feature and prognosis of primary hepatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Cancer Med. 2016;5(9):2268–2275. doi: 10.1002/cam4.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schaefer IM, Marino-Enriquez A, Fletcher JA. What is new in gastrointestinal stromal tumor? Adv Anat Pathol. 2017;24(5):259–267. doi: 10.1097/PAP.0000000000000158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yamaura K, Kato K, Miyazawa M, Haba Y, Muramatsu A, Miyata K, Koide N. Stromal tumor of the pancreas with expression of c-kit protein: report of a case. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;19(4):467–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2003.02891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhou B, Zhang M, Yan S, Zheng S. Primary gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the liver: report of a case. Surg Today. 2014;44(6):1142–1146. doi: 10.1007/s00595-013-0521-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.DeMatteo RP, Lewis JJ, Leung D, Mudan SS, Woodruff JM, Brennan MF. Two hundred gastrointestinal stromal tumors: recurrence patterns and prognostic factors for survival. Ann Surg. 2000;231(1):51–58. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200001000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4(7):540–550. doi: 10.1038/nrc1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang HC, Li TY, Chao YJ, Hou YC, Hsueh YS, Hsu KH, Shan YS. KIT exon 11 codons 557–558 deletion mutation promotes liver metastasis through the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(14):3477–3487. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yang DY, Wang X, Yuan WJ, Chen ZH. Metastatic pattern and prognosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): a SEER-based analysis. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019;21(12):1654–1662. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02094-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shi YN, Li Y, Wang LP, Wang ZH, Liang XB, Liang H, Zhang L, Li B, Fan LQ, Zhao Q, et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) with liver metastases: an 18-year experience from the GIST cooperation group in North China. Medicine. 2017;96(46):e8240. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ng EH, Pollock RE, Romsdahl MM. Prognostic implications of patterns of failure for gastrointestinal leiomyosarcomas. Cancer. 1992;69(6):1334–1341. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920315)69:6<1334::AID-CNCR2820690606>3.0.CO;2-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Casali PG, Abecassis N, Aro HT, Bauer S, Biagini R, Bielack S, Bonvalot S, Boukovinas I, Bovee J, Brodowicz T, et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: ESMO-EURACAN Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(Suppl 4):iv68–iv78. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Blanke CD, Rankin C, Demetri GD, Ryan CW, von Mehren M, Benjamin RS, Raymond AK, Bramwell VH, Baker LH, Maki RG, et al. Phase III randomized, intergroup trial assessing imatinib mesylate at two dose levels in patients with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors expressing the kit receptor tyrosine kinase: S0033. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(4):626–632. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.4452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Haller F, Detken S, Schulten HJ, Happel N, Gunawan B, Kuhlgatz J, Fuzesi L. Surgical management after neoadjuvant imatinib therapy in gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GISTs) with respect to imatinib resistance caused by secondary KIT mutations. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14(2):526–532. doi: 10.1245/s10434-006-9228-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Guller U, Tarantino I, Cerny T, Ulrich A, Schmied BM, Warschkow R. Revisiting a dogma: similar survival of patients with small bowel and gastric GIST. A population-based propensity score SEER analysis. Gastric Cancer. 2017;20(1):49–60. doi: 10.1007/s10120-015-0571-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang H, Zhang J, Bao S, Liu J, Hou F, Huang Y, Chen H, Duan S, Hao D, Liu J. Preoperative MRI-based radiomic machine-learning nomogram may accurately distinguish between benign and malignant soft-tissue lesions: a two-center study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 doi: 10.1002/jmri.27111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yan Y, Liu H, Mao K, Zhang M, Zhou Q, Yu W, Shi B, Wang J, Xiao Z. Novel nomograms to predict lymph node metastasis and liver metastasis in patients with early colon carcinoma. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1940-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Khoo CY, Chai X, Quek R, Teo MCC, Goh BKP. Systematic review of current prognostication systems for primary gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44(4):388–394. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2017.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li Q, Zou J, Jia M, Li P, Zhang R, Han J, Huang K, Qiao Y, Xu T, Peng R, et al. Palliative gastrectomy and survival in patients with metastatic gastric cancer: a propensity score-matched analysis of a large population-based study. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2019;10(5):1–8. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Li H, Pang Y, Cheng X. Surgery of primary sites for stage IVB cervical cancer patients receiving chemoradiotherapy: a population-based study. J Gynecol Oncol. 2020;31(1):e8. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2020.31.e8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Murphy JD, Ma GL, Baumgartner JM, Madlensky L, Burgoyne AM, Tang CM, Martinez ME, Sicklick JK. Increased risk of additional cancers among patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a population-based study. Cancer. 2015;121(17):2960–2967. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Güller U, Tarantino I, Cerny T, Schmied BM, Warschkow R. Population-based SEER trend analysis of overall and cancer-specific survival in 5138 patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:557. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1554-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rossi S, Miceli R, Messerini L, Bearzi I, Mazzoleni G, Capella C, Arrigoni G, Sonzogni A, Sidoni A, Toffolatti L, et al. Natural history of imatinib-naive GISTs: a retrospective analysis of 929 cases with long-term follow-up and development of a survival nomogram based on mitotic index and size as continuous variables. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011;35(11):1646–1656. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31822d63a7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Taylor J, Tibshirani RJ. Statistical learning and selective inference. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(25):7629–7634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1507583112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tang J, Cui Q, Zhang D, Liao X, Zhu J, Wu G. An estrogen receptor (ER)-related signature in predicting prognosis of ER-positive breast cancer following endocrine treatment. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(8):4980–4990. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dong D, Tang L, Li ZY, Fang MJ, Gao JB, Shan XH, Ying XJ, Sun YS, Fu J, Wang XX, et al. Development and validation of an individualized nomogram to identify occult peritoneal metastasis in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Ann Oncol. 2019;30(3):431–438. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Van Calster B, Wynants L, Verbeek JFM, Verbakel JY, Christodoulou E, Vickers AJ, Roobol MJ, Steyerberg EW. Reporting and interpreting decision curve analysis: a guide for investigators. Eur Urol. 2018;74(6):796–804. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.08.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kerr KF, Brown MD, Zhu K, Janes H. Assessing the clinical impact of risk prediction models with decision curves: guidance for correct interpretation and appropriate use. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(21):2534–2540. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.65.5654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lillemoe HA, Brudvik KW, Vauthey JN. Treatment options for metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors to the liver: a review. Semin Liver Dis. 2019;39(3):395–402. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1685517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Perez-Atayde AR, Shamberger RC, Kozakewich HW. Neuroectodermal differentiation of the gastrointestinal tumors in the Carney triad. An ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993;17(7):706–714. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199307000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Duensing A, McGreevey L, Chen CJ, Joseph N, Singer S, Griffith DJ, Haley A, Town A, et al. PDGFRA activating mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science (New York, NY) 2003;299(5607):708–710. doi: 10.1126/science.1079666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hirota S, Isozaki K, Moriyama Y, Hashimoto K, Nishida T, Ishiguro S, Kawano K, Hanada M, Kurata A, Takeda M, et al. Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science (New York, NY) 1998;279(5350):577–580. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5350.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chi P, Chen Y, Zhang L, Guo X, Wongvipat J, Shamu T, Fletcher JA, Dewell S, Maki RG, Zheng D, et al. ETV1 is a lineage survival factor that cooperates with KIT in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Nature. 2010;467(7317):849–853. doi: 10.1038/nature09409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pasini B, McWhinney SR, Bei T, Matyakhina L, Stergiopoulos S, Muchow M, Boikos SA, Ferrando B, Pacak K, Assie G, et al. Clinical and molecular genetics of patients with the Carney-Stratakis syndrome and germline mutations of the genes coding for the succinate dehydrogenase subunits SDHB, SDHC, and SDHD. Eur J Hum Genet. 2008;16(1):79–88. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Boikos SA, Pappo AS, Killian JK, LaQuaglia MP, Weldon CB, George S, Trent JC, von Mehren M, Wright JA, Schiffman JD, et al. Molecular subtypes of KIT/PDGFRA wild-type gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a report from the National Institutes of Health Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Clinic. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2(7):922–928. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.0256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhou ZR, Wang WW, Li Y, Jin KR, Wang XY, Wang ZW, Chen YS, Wang SJ, Hu J, Zhang HN, et al. In-depth mining of clinical data: the construction of clinical prediction model with R. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(23):796. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.08.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bischof DA, Kim Y, Behman R, Karanicolas PJ, Quereshy FA, Blazer DG, 3rd, Maithel SK, Gamblin TC, Bauer TW, Pawlik TM. A nomogram to predict disease-free survival after surgical resection of GIST. J Gastrointest Surg. 2014;18(12):2123–2129. doi: 10.1007/s11605-014-2658-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Gold JS, Gonen M, Gutierrez A, Broto JM, Garcia-del-Muro X, Smyrk TC, Maki RG, Singer S, Brennan MF, Antonescu CR, et al. Development and validation of a prognostic nomogram for recurrence-free survival after complete surgical resection of localised primary gastrointestinal stromal tumour: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(11):1045–1052. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70242-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Guller U, Tarantino I, Cerny T, Schmied BM, Warschkow R. Population-based SEER trend analysis of overall and cancer-specific survival in 5138 patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:557. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1554-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fletcher CD, Berman JJ, Corless C, Gorstein F, Lasota J, Longley BJ, Miettinen M, O'Leary TJ, Remotti H, Rubin BP, et al. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a consensus approach. Hum Pathol. 2002;33(5):459–465. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2002.123545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Akahoshi K, Oya M, Koga T, Shiratsuchi Y. Current clinical management of gastrointestinal stromal tumor. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24(26):2806–2817. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i26.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Miettinen M, Sobin LH, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors of the stomach: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 1765 cases with long-term follow-up. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29(1):52–68. doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000146010.92933.de. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Karakousis GC, Singer S, Zheng J, Gonen M, Coit D, DeMatteo RP, Strong VE. Laparoscopic versus open gastric resections for primary gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs): a size-matched comparison. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(6):1599–1605. doi: 10.1245/s10434-010-1517-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Vassos N, Agaimy A, Hohenberger W, Croner RS. Management of liver metastases of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) Ann Hepatol. 2015;14(4):531–539. doi: 10.1016/S1665-2681(19)31175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kramer K, Knippschild U, Mayer B, Bögelspacher K, Spatz H, Henne-Bruns D, Agaimy A, Schwab M, Schmieder M. Impact of age and gender on tumor related prognosis in gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) BMC Cancer. 2015;15:57. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1054-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: pathology and prognosis at different sites. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2006;23(2):70–83. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2006.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Emory TS, Sobin LH, Lukes L, Lee DH, O'Leary TJ. Prognosis of gastrointestinal smooth-muscle (stromal) tumors: dependence on anatomic site. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23(1):82–87. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199901000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kukar M, Kapil A, Papenfuss W, Groman A, Grobmyer SR, Hochwald SN. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) at uncommon locations: a large population based analysis. J Surg Oncol. 2015;111(6):696–701. doi: 10.1002/jso.23873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Dematteo RP, Gold JS, Saran L, Gonen M, Liau KH, Maki RG, Singer S, Besmer P, Brennan MF, Antonescu CR. Tumor mitotic rate, size, and location independently predict recurrence after resection of primary gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) Cancer. 2008;112(3):608–615. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Antonescu CR, Viale A, Sarran L, Tschernyavsky SJ, Gonen M, Segal NH, Maki RG, Socci ND, DeMatteo RP, Besmer P. Gene expression in gastrointestinal stromal tumors is distinguished by KIT genotype and anatomic site. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(10):3282–3290. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Giuliano K, Nagarajan N, Canner J, Najafian A, Wolfgang C, Schneider E, Meyer C, Lennon AM, Johnston FM, Ahuja N. Gastric and small intestine gastrointestinal stromal tumors: do outcomes differ? J Surg Oncol. 2017;115(3):351–357. doi: 10.1002/jso.24514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Feng F, Wang F, Wang Q, Zheng G, Xu G, Liu S, Liu Z, Guo M, Lian X, Zhang H. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor located in the jejunum and ileum. Dig Surg. 2019;36(2):153–157. doi: 10.1159/000487147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Reith JD, Goldblum JR, Lyles RH, Weiss SW. Extragastrointestinal (soft tissue) stromal tumors: an analysis of 48 cases with emphasis on histologic predictors of outcome. Mod Pathol. 2000;13(5):577–585. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3880099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Agaimy A, Wunsch PH. Lymph node metastasis in gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST) occurs preferentially in young patients < or = 40 years: an overview based on our case material and the literature. Langenbeck's Arch Surg. 2009;394(2):375–381. doi: 10.1007/s00423-008-0449-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Antonescu CR, DeMatteo RP, Ganjoo KN, Maki RG, Pisters PW, Raut CP, Riedel RF, Schuetze S, et al. NCCN Task Force report: update on the management of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2010;8(Suppl 2):S1–41; quiz S42–44. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2010.0116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Gaitanidis A, El Lakis M, Alevizakos M, Tsaroucha A, Pitiakoudis M. Predictors of lymph node metastasis in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) Langenbeck's Arch Surg. 2018;403(5):599–606. doi: 10.1007/s00423-018-1683-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Vuletic A, Jovanic I, Jurisic V, Milovanovic Z, Nikolic S, Spurnic I, Konjevic G. Decreased interferon gamma production in CD3+ and CD3- CD56+ lymphocyte subsets in metastatic regional lymph nodes of melanoma patients. Pathol Oncol Res. 2015;21(4):1109–1114. doi: 10.1007/s12253-015-9938-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Li C, Su D, Xie C, Chen Q, Zhou J, Wu X. Lymphadenectomy is associated with poor survival in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(20):558. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.09.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zhang L, Smyrk TC, Young WF, Jr, Stratakis CA, Carney JA. Gastric stromal tumors in Carney triad are different clinically, pathologically, and behaviorally from sporadic gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors: findings in 104 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34(1):53–64. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181c20f4f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.von Mehren M, Randall RL, Benjamin RS, Boles S, Bui MM, Conrad EU, 3rd, Ganjoo KN, George S, Gonzalez RJ, Heslin MJ, et al. Soft Tissue Sarcoma, Version 2.2016, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2016;14(6):758–786. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2016.0078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. A database of the information of GIST patients obtained from SEER database.
Additional file 2: Table S2. A database of training set.
Additional file 3: Table S3. A database of testing set.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.