Abstract
Background: We aimed to assess whether nucleated red blood cells (NRBCs) count could serve as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for morbidity and mortality in critically ill neonates. Methods: The association between NRBCs count and neonatal morbidity and mortality was evaluated in an observational cohort of critically ill neonates hospitalized in our neonatal intensive care unit over a period of 69 months. The discriminative ability of NRBCs count as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers was evaluated by performing the Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) curve analysis. Results: Among 467 critically ill neonates included in the study, 45 (9.6%) of them experienced in-hospital mortality. No statistically significant difference was found with regards to NRBCs count between survivors and non-survivors, although the median value for NRBCs was sometimes higher for non-survivors. ROC curve analysis showed that NRBCs is a good discriminator marker for the diagnosis of perinatal hypoxia in neonates with area under the curve (AUC) [AUC 0.710; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.660–0.759] and predominantly in preterm neonates (AUC 0.921 (95% CI, 0.0849–0.0993)) by using a cut-off value of ≥11.2%, with 80% sensitivity and 88.7% specificity. NRBCs also revealed significant prognostic power for mortality in septic neonates (AUC 0.760 (95% CI, 0.631–0.888)) and especially in preterms with sepsis (AUC 0.816 (95% CI, 0.681–0.951)), with cut-off value ≥ 1%, resulting in 81.6% sensitivity and 78.1% specificity. Conclusion: NRBCs count may be included among the early diagnostic and prognostic markers for sick neonates.
Keywords: critically ill neonates, nucleated red blood cells, mortality, morbidity, perinatal hypoxia, sepsis
1. Introduction
Critically ill neonates constitute a fragile population with very special characteristics compared to children and adults; hence, early diagnosis and management of critical illness are of great importance for their short-term outcome and lifelong prognosis. Various scoring systems have been established to estimate illness severity in neonates, such as the Score for Neonatal Acute Physiology (SNAP), SNAP-Perinatal Extension (SNAPPE) and SNAPPE-II, Neonatal Multiple Organ Dysfunction (NEOMOD) score, and Clinical Risk Index for Babies scoring system (CRIB II) [1,2,3,4]. These systems aim to achieve early identification of ill neonates with increased risk of morbidity and mortality and may contribute to improved patient care.
Advances in neonatal medicine have focused on several clinical and laboratory parameters as diagnostic and prognostic markers. The management of critically ill newborns such as septic newborns and those with perinatal hypoxia might be improved and more targeted using novel biomarkers, which could help for the detection of the disease within the critical time window. Previous studies have reported that hematological and serum biochemical variables such as leukocyte and neutrophil count, nucleated red blood cells (NRBCs), C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), arterial blood gas analysis, lactate, hepatic enzymes, plasma creatinine (Cr), and troponin high sensitivity (hsTn) have been used for this purpose [5,6,7,8,9,10,11].
NRBCs are early erythrocyte precursors not detectable in the peripheral blood of healthy adults under normal conditions. Contrarily, NRBCs constitute a normal finding in the circulation of the fetus and the neonates during the first week of life, depending on their gestational age and health status [12]. NRBCs count reflects high production of erythropoietin as a result of decreased arterial oxygen partial tension and/or increased concentrations of inflammatory cytokines. In critically ill adults, NRBCs are strongly prognostic of mortality [13]. In a recent study, Menk et al. [14] reported that the presence of NRBCs in the circulation might be regarded as a marker of disease severity indicating a higher risk of intensive care unit (ICU) death. Although, several studies have reported that elevated NRBCs count correlates with perinatal hypoxia and inflammation severity (sepsis) [6,7,15,16,17]. Christensen et al. [18] found that “neonates with an elevated NRBC count at birth had the onset of hypoxia at least 28 to 29 h before birth”. To date, relevant data regarding NRBCs diagnostic and prognostic value in critically ill neonates are limited.
Our aim was to investigate if the detection of elevated NRBCs count in critically ill neonates could serve as diagnostic and prognostic marker of neonatal morbidity and mortality.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This single-center, observational study was conducted at the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) of Nikaia General Hospital “Aghios Panteleimon”, Piraeus, Greece, from July 2014 to April 2020. The study protocol, designed, conducted, and reported in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki, was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Nikaia General Hospital (15 July 2014, 32/2). Parental informed consent was obtained prior to recruitment.
2.2. Participants
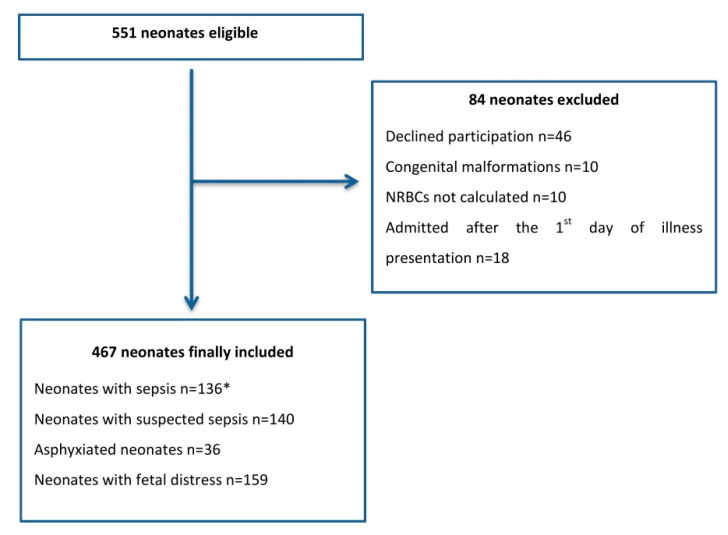
Patients eligible for data collection were critically ill neonates hospitalized in our NICU during the study period. Critically ill neonates were characterized as: preterm neonates with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), neonates with suspected or confirmed sepsis, and neonates with perinatal asphyxia/fetal distress. The definitions and the inclusion criteria for neonates mentioned above are in accordance with References [19,20,21]. Neonates with congenital malformations were excluded from the study. Data for the recruitment procedure are presented in the flow chart in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Flowchart of study population. * 4 neonates with perinatal hypoxia were also included in this subgroup, as they suffered from late-onset sepsis. Abbreviation: NRBCs, nucleated red blood cell counts.
2.3. Variables’ Measurements
Data on demographics (birth weight, gestational age, sex), maternal and pregnancy history, neonatal physiological parameters, clinical findings, laboratory results, day of establishing full enteral feeding, and length of hospital stay were recorded for all study neonates. For preterm neonates (gestational age <37 weeks), severe morbidity such as respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) [19], neonatal sepsis [22], bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) [23], necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) [24], retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) [25], intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) ≥ grade 2 [26], periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) [27], and patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) [28], were recorded. Morbidities recorded for term neonates were: respiratory morbidity including supplemental oxygen therapy, need for continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) or ventilation support [29], sepsis, asphyxia [30], hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) [31], and seizures. Mortality was defined as death before discharge. Delivery room deaths were not included as data were not available. Multiple organ dysfunction (MOD) was defined as the presence of dysfunction of at least two organ systems [32]. Organ involvement was determined by using laboratory tests and clinical evaluation.
In all study neonates, the SNAPPE score and modified NEOMOD scoring system [33] were calculated on admission to the NICU (for preterm neonates with RDS or neonates with perinatal asphyxia/fetal distress) and on the onset of the disease (for neonates with suspected or confirmed sepsis).
In the first 6–12 h of life (for preterm neonates with RDS and those with perinatal asphyxia/fetal distress), prior to initiating antibiotic therapy—if required, blood specimens for culture and biochemical tests (serum glutamil oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), complete blood count, (CRP) were performed, while on the second day of life (DOL), further biochemical parameters (sodium, potassium, SGOT, serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (SGPT), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine plasma level (Cr), bilirubin, albumin (ALB)) were measured in all neonates, as per our NICU protocol. As for neonates with suspected or confirmed sepsis, the aforementioned laboratory tests were performed and recorded at the onset of clinical deterioration [median day of life: 12, interquartile range (IQR) 7–20]. Chest radiograph was performed whenever clinically indicated.
Complete blood count was performed on a Sysmex XE-2100 analyzer (Roche, IL, USA). Peripheral blood smears prepared with Giemsa stain were examined, and band forms, NRBCs, myelocytes and metamyelocytes (evaluated as immature neutrophils in leukocyte formula), and Immature to Total Neutrophil Ratio (I/T ratio) were calculated.
NRBCs measurement, expressed as NRBC count per 100 White Blood Cells (WBC), was carried out both automatically by the formerly mentioned analyzer and also by manual correction so that the results would be accurate.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics of the baseline data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD), median (ranges), or as percentages when appropriate. The differences in categorized and continuous data were compared using the chi-square contingency test and the with Mann-Whitney U test. Time-to-event analysis was carried out in order to evaluate the variables independently associated with the in-hospital survival. Univariate Cox’s proportional hazards analysis for relevant prognostic variables was performed. The hazards ratios or relative hazards derived from Cox’s proportional hazards models are presented with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and the respective p-values. A ratio higher than unity implies a higher probability of death than in the reference group.
NRBCs count was evaluated to predict mortality in the study group. Their discriminative ability as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers was evaluated by performing the Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) curve analysis. The optimal cut-off thresholds were identified with the Youden index, and the sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values were also evaluated. All statistical tests were two-sided. Stata statistical software was used for all statistical analyses (Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA). For all tests, a p-value lower than 0.05 indicates statistical significance.
3. Results
A total of 467 critically ill neonates were included in the study, of which 45 (9.6%) did not survive. The baseline characteristics of the neonates are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the study population.
| Descriptive Statistics | Value |
|---|---|
| Population (n) | 467 |
| Gender (Male) | 300 (64.2%) |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 35.3 ± 4.3 |
| Birth weight (g) | 2452.4 ± 976.9 |
| Delivery mode (Caesarian session) | 312 (66.8%) |
| Maternal diseases * | 176 (42.1%) |
* Preeclampsia, thyroid disease, gestational diabetes mellitus.
Comorbidities recorded in study neonates are presented in Table 2.
Table 2.
Morbidities recorded in all neonates (n = 467).
| All Study Neonates n = 467 |
Term Neonates n = 248 |
Preterm Neonates n = 219 |
Terms vs. Preterms | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | ||||
| Gestational age (weeks) | 35.3 ± 4.3 | 38.7 ± 1.2 | 31.5 ± 3.2 | 0.000 |
| Birth weight (g) | 2452.4 ± 976.9 | 3147 ± 554 | 1665 ± 722 | 0.000 |
| Death | 45 (9.6%) | 23 (9.3%) | 22 (10%) | 0.875 |
| Respiratory Distress Syndrome | 244 (52.6%) | 88 (35.5%) | 156 (71.2%) | 0.000 |
| Intrauterine Growth Retardation | 56 (12.0%) | 24 (9.7%) | 32 (14.6%) | 0.117 |
| Sepsis | 136 (29.1%) | 52 (21%) | 84 (38.4%) | 0.000 |
| Infection | 140 (30.0%) | 67 (27%) | 73 (33.3%) | 0.157 |
| Perinatal hypoxia | 195 (41.8%) | 136 (54.8%) | 59 (27%) | 0.000 |
| Perinatal asphyxia | 36 (7.7%) | 31 (12.5%) | 5 (2.3%) | 0.000 |
| Fetal distress | 159 (34%) | 105 (42.3%) | 54 (24.7%) | 0.000 |
| Acute Kidney Injury | 75 (16.1%) | 37 (14.9%) | 38 (17.4%) | 0.528 |
| Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy | 78 (16.7%) | 36 (14.5%) | 42 (19.2%) | 0.174 |
| Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome | 82 (17.6%) | 45 (18.1%) | 37 (16.9%) | 0.808 |
| Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia | 70 (15%) | - | 70 (32%) | - |
| Mild | 19 (0.04%) | 19 (8.7%) | ||
| Moderate | 14 (0.03%) | 14 (6.4%) | ||
| Severe | 56 (12%) | 56 (25.5%) | ||
| Retinopathy of Prematurity | 77 (16.5%) | - | 77 (35.1%) | - |
| Laser treatment | 29 (0.06%) | 29 (13.2%) | ||
| No treatment | 48 (10.3%) | 48 (22%) | ||
| Patent Ductus Arteriosus | 24 (5.1%) | - | 24 (11%) | - |
| Pharmacological treatment | 16 (0.03%) | 16 (7.3%) | ||
| Surgical ligation | 5 (0.01%) | 5 (2.3%) | ||
| Conservative treatment | 3 (0.006%) | 3 (1.4%) | ||
| Periventricular Leukomalacia | 71 (15.2%) | - | 71 (32.4%) | - |
| Intra-Ventricular Hemorrhage ≥ grade 2 | 61 (13%) | - | 61 (27.8%) | - |
| Necrotizing Enterocolitis | 15 (0.03%) | - | 15 (6.8%) | - |
Subsequently, we investigated the role of several parameters, and specifically, NRBCs, in the survival of the neonates (Table 3).
Table 3.
Baseline characteristics and laboratory data of survivors vs. non-survivors.
| Survivors (n = 422) | Non-Survivors (n = 45) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | p Value |
| Gestational_Age (weeks) | 37 (32–39) | 37 (32–40) | 0.1089 |
| Birth_Weight (g) | 2640 (1490–3230) | 2550 (1420–3300) | 0.9921 |
| Base Deficit (mmol/L) | 3.4 (1.5–5.5) | 4.2 (1.1–12) | 0.1617 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.6 (2.3–2.8) | 2.3 (2.1–2.5) | 0.0001 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 41.2 (37–45.9) | 35.1 (33–41.2) | 0.0000 |
| WBC (/mL) | 13,045 (9680–17,930) | 14,600 (9030–20,430) | 0.5954 |
| Neutrophils (%) | 61 (47.3–72) | 55 (40–75.1) | 0.7930 |
| NRBC (%) | 0.4 (0–2.3) | 1.6 (0–7.9) | 0.1649 |
| PLT (/mL) | 229,500 (120,000–297,000) | 57,000 (13,000–169,000) | 0.0000 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 13.4 (3.4–40.2) | 49.1 (7.2–85.2) | 0.0010 |
| SGOT (IU/L) | 55 (33–83) | 89 (54–235.5) | 0.0000 |
| SGPT (IU/L) | 18 (12–30) | 43 (23–141) | 0.0000 |
| T_BIL (mg/dL) | 6 (3.8–9) | 8.2 (3.9–25.4) | 0.0053 |
| D_BIL (mg/dL) | 0.3 (0.2–0.4) | 0.9 (0.3–17) | 0.0000 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 27.5 (19–47) | 57 (35–92) | 0.0000 |
| Cr (mg/dL) | 0.6 (0.4–0.8) | 0.7 (0.5–1.2) | 0.0105 |
| Modified NEOMOD score | 2 (1–4) | 8 (5–10) | 0.0000 |
| SNAPPE score | 9 (2–17) | 19 (13–36) | 0.0000 |
| TOLLNER score | 0.1 (0–3.5) | 10 (0–13.5) | 0.0019 |
Abbreviations: IQR: interquartile range; WBC, white blood count; NRBC, nucleated red blood cells; PLT, platelets; CRP, C-reactive protein; SGOT, serum glutamil oxaloacetic transaminase; SGPT, serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase; T_BIL, total bilirubin; D_BIL, direct bilirubin; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; Cr, creatinine plasma level; Modified NEOMOD score, modified Neonatal Multiple Organ Dysfunction scoring system; SNAPPE score, Score for Neonatal Acute Physiology with Perinatal extension.
No statistically significant difference between survivors and non-survivors regarding GA and BW was found. Almost all laboratory studied parameters had a significant role in the survival of the neonates except for neutrophils percentage, WBC, and NRBC. Although the median value for NRBCs was sometimes times higher for non-survivors, this finding did not allow for proving a statistical significance under the condition of p < 0.05, probably because of the great variability in NRBCs and the small number of cases. In addition, this analysis proved that all scoring systems (i.e., SNAPPE, modified NEOMOD, and TOLLNER scores) were significantly different between survivors and non-survivors.
The analysis of study population mortality (as a dependent variable) in relation to comorbidities revealed that all conditions had a significant role in survivability except for intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR) and NEC (Table 4).
Table 4.
Univariate analysis results for morbidities affecting neonates’ survival.
| Morbidity | OR and 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Kidney Injury | 28.65 (13.5–60.79) | <0.0001 |
| Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia | 0.3 (0.09–1) | 0.0377 |
| Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy | 10.88 (5.6–21.15) | <0.0001 |
| Intrauterine Growth Retardation | 1.4 (0.59–3.31) | 0.4388 |
| Multi-organ Dysfunction Syndrome | 32.7 (14.81–72.19) | <0.0001 |
| Necrotizing Enterocolitis | 2.82 (0.89–8.97) | 0.0670 |
| Patent Ductus Arteriosus | 4.36 (1.7–11.16) | 0.0009 |
| Perinatal Hypoxia | 2.27 (1.21–4.25) | 0.0090 |
| Periventricular Leucomalakia | 14.52 (7.35–28.66) | <0.0001 |
| Respiratory Distress Syndrome | 5.61 (2.45–12.85) | <0.0001 |
| Sepsis | 2.58 (1.39–4.82) | 0.0021 |
Abbreviations: OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
The performance of ROC curve analysis for the discriminative ability of NRBCs as diagnostic and prognostic markers in all study neonates is displayed in Table 5.
Table 5.
Receiver Operating Characteristics curve analysis for NRBCs in study population.
| AUC | 95% CI | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sepsis diagnosis | 0.615 | 0.559–0.671 | 0.000 |
| Hypoxia diagnosis | 0.710 | 0.660–0.759 | 0.000 |
| Mortality prognosis in all neonates | 0.565 | 0.461–0.670 | 0.000 |
| Mortality prognosis in septic neonates | 0.760 | 0.631–0.888 | 0.001 |
| Mortality prognosis in asphyxiated neonates | 0.671 | 0.465–0.876 | 0.145 |
Abbreviations: AUC, area under the curve; CI, confidence interval.
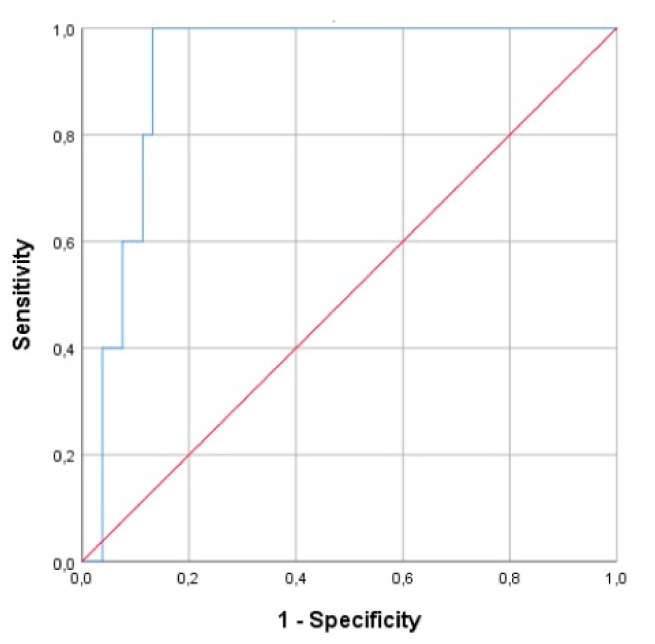
Subsequently, study neonates were subclassified as term and preterm neonates. ROC curve analysis showed that NRBCs is a good discriminator marker for the diagnosis of perinatal hypoxia in preterm neonates (Figure 2), with AUC 0.921(95% CI, 0.0849–0.0993). Using a cut-off value of ≥11.2%, NRBCs resulted in 80% sensitivity and 88.7% specificity.
Figure 2.
Area under the ROC curves of NRBCs for diagnosis of perinatal hypoxia in critically ill preterm neonates.
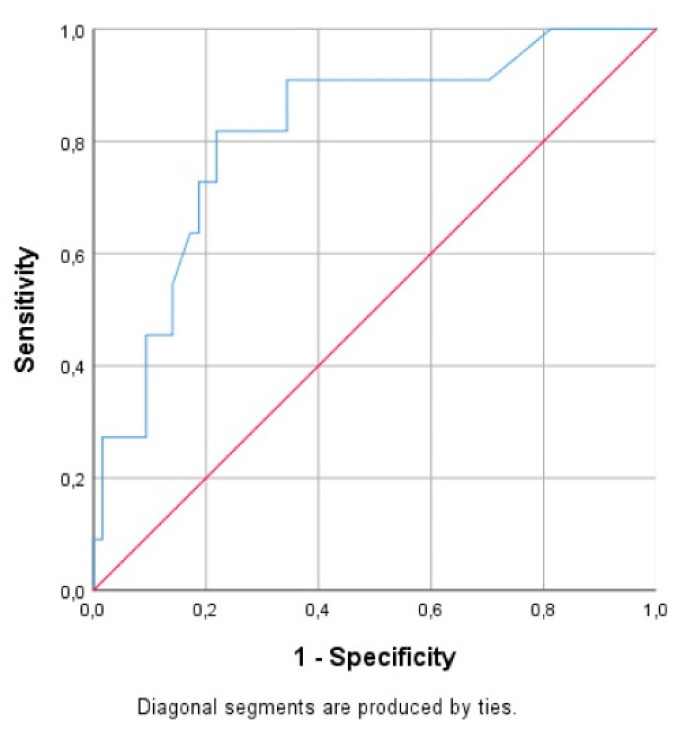
NRBCs also revealed significant prognostic power for mortality in preterm neonates with sepsis (AUC 0.816 (95% CI, 0.681–0.951)), with cut-off value ≥1%, resulting in 81.6% sensitivity and 78.1% specificity (Figure 3). This low cut-off value probably attributed to the day of measurement (median: 12 (IQR 7–20)).
Figure 3.
Area under the ROC curves of NRBCs for mortality prognosis in preterm neonates with sepsis.
Contrarily, ROC curve analysis showed that NRBCs could not discriminate diagnosis or prognosis of sepsis or perinatal hypoxia between the term neonates of our study.
4. Discussion
In the present study, we evaluated the role of NRBCs count in the diagnosis and prognosis of morbidity and mortality in critically ill neonates. Our results revealed that NRBCs could serve, among others, as prognostic and diagnostic markers in this population, especially in preterm neonates. In healthy adults, NRBCs are not present in the peripheral blood but studies have reported their detection in 10–30% of critically ill patients [13]. Inflammation, hypoxia, or massive hemorrhage seem responsible for the appearance of NRBCs in peripheral blood, as these situations increase erythropoietic pressure and result in failure of the spleen to remove these cells from the circulation. Purtle et al. [34] demonstrated that the presence of NRBCs is associated with a significant increase in the odds of post-discharge hospital mortality in critically ill adults.
Schaer et al. [15] found that NRBCs are not an independent risk factor for bad outcomes in pediatric intensive care; however, they may have a prognostic value in the first month of life, although their association with outcome is much less pronounced beyond the neonatal period.
The presence of NRBCs in the circulation at birth and during the first week of life is an expected and rather physiological finding. In healthy neonates, NRBCs disappear from the peripheral blood within a few weeks of life, but they can return to the circulation in several pathological situations and their elevated value has been often correlated with poor short outcome and risk factors for poor neurodevelopment in neonates [16,35].
In septic neonates, data show that excess NRBCs in peripheral blood may help with the diagnosis of sepsis and correlates with the mortality of these neonates [36]. In our study, NRBCs showed a good performance as a prognostic marker for mortality in neonates with sepsis, especially in preterms.
NRBCs could also serve as hematologic markers for placental dysfunction, hypoxemia, and asphyxia as hypoxemia triggers erythropoietin release, resulting in stimulation of red blood cells. NRBCs count elevation at birth or persistence is linked to adverse short-term and long-term outcomes of neonates with perinatal hypoxia [18]. Boskabadi et al. [17] found that NRBC count in neonates with birth asphyxia were significantly higher than healthy controls and associated with poorer short-term outcome. In accordance with these findings, the current study showed that NRBCs count could serve as a discriminator marker for early diagnosis of perinatal hypoxia with excellent performance in preterm neonates (AUC 0.921) by using a cut-off value of ≥11.2%, with 80% sensitivity and 88.7% specificity. In a more recent study, Boskabadi et al. [7] demonstrated that theNRBC count can be used as a prognostic marker for neonatal asphyxia, which in combination with the HIE grade could indicate high infant mortality, and complications of asphyxia. Furthermore, NRBCs were found to be very useful in differentiating the neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, leading to appropriate management and better outcome of these newborns [37]. The role of NRBCs count in critically ill neonates is confirmed by Morton et al. [38], who reported that among critically ill neonates, NRBCs are associated with significantly elevated mortality risk. In our study, although the median value for NRBCs count was found to be sometimes times higher for non-survivors, this parameter did not have good discriminative ability for predicting mortality in all the study population, probably because of the great variability in NRBCs and the small number of cases.
This single-center study also has some limitations which arise from the variability in NRBCs count and the small number of subjects. Another limitation might be the evaluation of NRBCs count only at the disease onset and this perhaps weakens the strength of the study with regards to the prognostic role of NRBCs in mortality.
In conclusion, NRBCs count may be encompassed among the early diagnostic and prognostic markers for neonatal intensive care unit patients. Further studies are needed to assess trends in NRBC values for critically ill neonates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: R.S. and A.K.; methodology: R.S. and A.K.; software: A.K., R.S., G.I., A.G.T. and M.L.; validation A.K. and R.S.; formal analysis: R.S., A.K. and A.P.; data curation: R.S., A.K., G.I. and M.L.; writing—original draft preparation: A.K. and R.S.; writing—review and editing: A.K., R.S., N.I., A.E.T., G.I., A.G.T. and M.L.; visualization: R.S. and A.K.; supervision: A.K.; project administration: R.S. and A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Dorling J.S., Field D.J., Manktelow B. Neonatal disease severity scoring systems. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005;90:F11–F16. doi: 10.1136/adc.2003.048488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Richardson D.K., Corcoran J.D., Escobar G.J., Lee S.K. SNAP-II and SNAPPE-II: Simplified newborn illness severity and mortality risk scores. J. Pediatr. 2001;138:92–100. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2001.109608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Janota J., Stranák Z., Statecná B., Dohnalová A., Sípek A., Simák J. Characterization of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in very low birthweight infants: A new sequential scoring system. Shock. 2001;15:348–352. doi: 10.1097/00024382-200115050-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Parry G., Tucker J., Tarnow-Mordi W. CRIB II: An update of the clinical risk index for babies score. Lancet. 2003;361:1789–1791. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13397-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Goel M., Dwivedi R., Gohiya P., Hegde D. Nucleated red blood cell in cord blood as a marker of perinatal asphyxia. J. Clin. Neonatol. 2013;2:179–182. doi: 10.4103/2249-4847.123097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dulay A.T., Buhimschi I.A., Zhao G., Luo G., Abdel-Razeq S., Cackovic M., Rosenberg V.A., Pettker C.M., Thung S.F., Bahtiyar M.O., et al. Nucleated red blood cells are a direct response to mediators of inflammation in newborns with early-onset neonatal sepsis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008;198:426.e1–426.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2008.01.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Boskabadi H., Zakerihamidi M., Sadeghian M.H., Avan A., Ghayour-Mobarhan M., Ferns G.A. Nucleated red blood cells count as a prognostic biomarker in predicting the complications of asphyxia in neonates. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017;30:2551–2556. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2016.1256988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sharma D., Farahbakhsh N., Shastri S., Sharma P. Biomarkers for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: A literature review. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018;31:1646–1659. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2017.1322060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bhandari V. Effective Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Neonatal Sepsis. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2014;3:234–245. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piu063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Islam M.T., Islam M.N., Mollah A.H., Hoque M.A., Hossain M.A., Nazir F., Ahsan M.M. Status of liver enzymes in babies with perinatal asphyxia. Mymensingh Med. J. 2011;20:446–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hadzimuratovic E., Skokic F., Hadzimuratovic A., Nazdrajic A., Mujic M., Hadzimuratovic A. Acute renal failure in term newborn following perinatal asphyxia. Sanamed. 2017;12:11. doi: 10.24125/sanamed.v1i1.162. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Christensen R.D., Henry E., Andres R.L., Bennett S.T. Reference ranges for blood concentrations of nucleated red blood cells in neonates. Neonatology. 2011;99:289–294. doi: 10.1159/000320148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Stachon A., Segbers E., Holland-Letz T., Kempf R., Hering S., Krieg M. Nucleated red blood cells in the blood of medical intensive care patients indicate increased mortality risk: A prospective cohort study. Crit. Care. 2007;11:R62. doi: 10.1186/cc5932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Menk M., Giebelhäuser L., Vorderwülbecke G., Gassner M., Graw J.A., Weiss B., Zimmermann M., Wernecke K.-D., Weber-Carstens S. Nucleated red blood cells as predictors of mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): An observational study. Ann. Intensive Care. 2018;8:42. doi: 10.1186/s13613-018-0387-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schaer C., Schmugge M., Frey B. Prognostic value of nucleated red blood cells in critically ill children. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2014;144:w13944. doi: 10.4414/smw.2014.13944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Baschat A.A., Gungor S., Kush M.L., Berg C., Gembruch U., Harman C.R. Nucleated red blood cell counts in the first week of life: A critical appraisal of relationships with perinatal outcome in preterm growth-restricted neonates. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007;197:286.e281–286.e288. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.06.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Boskabadi H., Maamouri G., Sadeghian M., Ghayour-Mobarhan M., Heidarzade M., Shakeri M.-T., Ferns G. Early Diagnosis of Perinatal Asphyxia by Nucleated Red Blood Cell Count: A Case-control Study. Arch. Iran. Med. 2010;13:275–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Christensen R.D., Lambert D.K., Richards D.S. Estimating the nucleated red blood cell ‘emergence time’ in neonates. J. Perinatol. 2014;34:116–119. doi: 10.1038/jp.2013.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Walti H., Couchard M., Relier J.P. Neonatal diagnosis of respiratory distress syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. Suppl. 1989;3:22s–26s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sokou R., Giallouros G., Konstantinidi A., Pantavou K., Nikolopoulos G., Bonovas S., Lytras T., Kyriakou E., Lambadaridis I., Gounaris A., et al. Thromboelastometry for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis-associated coagulopathy: An observational study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018;177:355–362. doi: 10.1007/s00431-017-3072-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Konstantinidi A., Sokou R., Tsantes A.G., Parastatidou S., Bonovas S., Kouskouni E., Gounaris A.K., Tsantes A.E., Iacovidou N. Thromboelastometry variables in neonates with perinatal hypoxia. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2020;46:428–434. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1709473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.McGovern M., Giannoni E., Kuester H., Turner M.A., van den Hoogen A., Bliss J.M., Koenig J.M., Keij F.M., Mazela J., Finnegan R., et al. Challenges in developing a consensus definition of neonatal sepsis. Pediatr. Res. 2020 doi: 10.1038/s41390-020-0785-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jobe A.H., Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001;163:1723–1729. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.163.7.2011060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Neu J., Walker W.A. Necrotizing enterocolitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011;364:255–264. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1005408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hellström A., Smith L.E.H., Dammann O. Retinopathy of prematurity. Lancet. 2013;382:1445–1457. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60178-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Khanafer-Larocque I., Soraisham A., Stritzke A., Al Awad E., Thomas S., Murthy P., Kamaluddeen M., Scott J.N., Mohammad K. Intraventricular Hemorrhage: Risk Factors and Association With Patent Ductus Arteriosus Treatment in Extremely Preterm Neonates. Front. Pediatr. 2019;7 doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zaghloul N., Ahmed M. Pathophysiology of periventricular leukomalacia: What we learned from animal models. Neural. Regen. Res. 2017;12:1795–1796. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.219034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Benitz W.E. Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants. Pediatrics. 2016;137:e20153730. doi: 10.1542/peds.2015-3730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ghartey K., Coletta J., Lizarraga L., Murphy E., Ananth C.V., Gyamfi-Bannerman C. Neonatal respiratory morbidity in the early term delivery. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2012;207:292.e291–292.e294. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2012.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hankins G.D.V. Neonatal Organ System Injury in Acute Birth Asphyxia Sufficient to Result in Neonatal Encephalopathy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003;101:203–204. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(02)02577-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yıldız E.P., Ekici B., Tatlı B. Neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: An update on disease pathogenesis and treatment. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2017;17:449–459. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2017.1259567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Aufieri R., Picone S., Paolillo P. Multiple organ failure in the newborn. J. Pediatr. Neonatal Individ. Med. 2014;3 doi: 10.7363/030254. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Çetinkaya M., Köksal N., Özkan H. A New Scoring System for Evaluation of Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome in Premature Infants. Am. J. Crit. Care Publ. Am. Assoc. Crit. Care Nurses. 2012;21:328–337. doi: 10.4037/ajcc2012312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Purtle S.W., Horkan C.M., Moromizato T., Gibbons F.K., Christopher K.B. Nucleated red blood cells, critical illness survivors and postdischarge outcomes: A cohort study. Crit. Care. 2017;21:154. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1724-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.May J.E., Marques M.B., Reddy V.V.B., Gangaraju R. Three neglected numbers in the CBC: The RDW, MPV, and NRBC count. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2019;86:167. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.86a.18072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sadeghinasab J., Boskabadi H., Sadeghian M. Investigation of Changes in Nucleated Red Blood Cells in Neonatal Infection. Iran. J. Neonatol. 2017;8 doi: 10.22038/ijn.2017.14811.1227. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kanodia P., Bhatta N., Shah G., Yadav S., Yadav S. Nucleated Red Blood Cell in Cord Blood as a Marker of Perinatal Asphyxia. J. Nepal Paediatr. Soc. 2016;35:264–268. doi: 10.3126/jnps.v35i3.14487. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Morton S., Brettin K., Feldman H., Leeman K. Association of Nucleated Red Blood Cell Count with Mortality among Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Patients. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2020.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]