Figure 1.
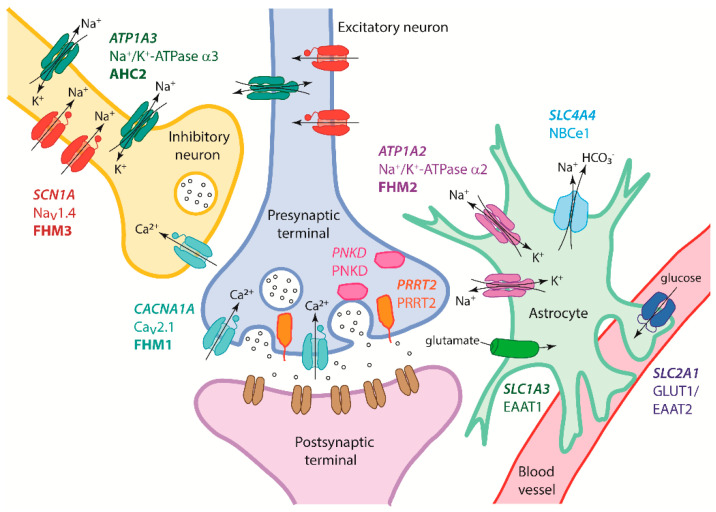
Genes and their encoded proteins involved in hemiplegic migraine (HM) shown at a tripartite glutamatergic synapse in the central nervous system (adapted from Russell and Ducros [1]). A presynaptic excitatory neuron along with an inhibitory gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic interneuron is shown with a postsynaptic neuron, their surrounding astrocyte, and an associated blood vessel. The three major HM genes—CACNA1A, ATP1A2, and SCN1A—cause FHM1, FHM2, and FHM3, respectively. Cav2.1 channels encoded by CACNA1A are located in the presynaptic terminal of excitatory and inhibitory neurons and, in response to an action potential, allow entry of Ca2+, triggering glutamate release into the synaptic cleft. ATP1A2 encodes the Na+-K+ ATPase α2 pump subunit, expressed on the surface of astrocytic glial cells, and removes K+ from the synaptic cleft to limit neuronal excitability and maintain a Na+ gradient across the cell membrane. Nav1.1 channels, encoded by SCN1A, are mainly expressed on GABAergic neurons and inhibitory interneurons, mediating voltage-dependent Na+ influx and regulating their excitability. The PRRT2 protein encoded by PRRT2 is localised at glutamatergic synapses where it interacts with proteins (e.g., SNAP25 and Ca2+ sensors Syt1/2) to mediate the activation of fast and synchronous neurotransmitter release. Similarly, paroxysmal non-kinesigenic dyskinesia (PNKD) protein encoded by PNKD interacts with synaptic active zone proteins (e.g., RIM1 and RIM2) to modulate neurotransmitter release. SLC4A4 encodes the electrogenic Na+-HCO3 cotransporter NBCe1, with some isoforms expressed in the brain and on glial cells, which play a role in regulation of synaptic pH and neurotransmission. ATP1A3 encodes the Na+-K+ ATPase α3 pump subunit, which functions to maintain the electrochemical gradient across neuronal membranes to regulate their excitability and has a likely role at inhibitory synapses. Mutations in ATP1A3 can cause alternating hemiplegia of childhood (AHC). EAAT1 encoded by SLC1A3 is a Na+/K+-dependent glutamate transporter that recaptures glutamate from the synaptic cleft into glial cells including astrocytes to terminate its postsynaptic action. SLC2A1 encodes the GLUT1 glucose transporter and is present at the blood–brain barrier to facilitate glucose transport into the brain. Na+, sodium ion; K+, potassium ion; Ca2+, calcium ion.