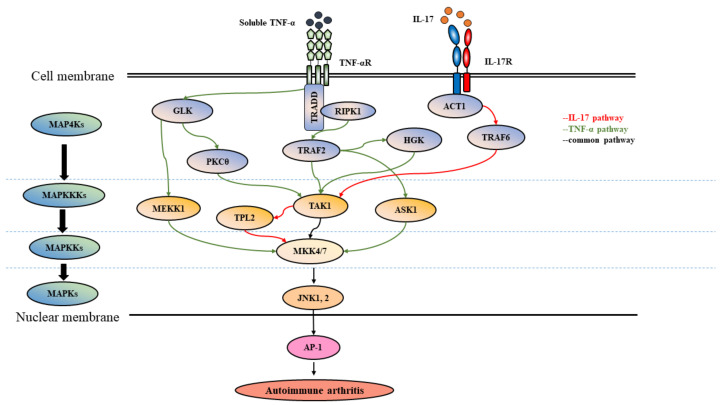
Figure 1.
Activation of JNK by proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-17 leading to autoimmune arthritis. Binding of proinflammatory cytokine TNF-α or IL-17 to its receptor induces activation of JNK-AP-1 leading to autoimmune arthritis. Along the signaling pathways, many adaptors and kinases are involved. The sequences of activation are indicated with arrows. The TNF-α- and IL-17-mediated signaling pathways are shown in red color and green color, respectively. The common pathway shared by both TNF-α and IL-17 signals is illustrated in black color. Abbreviations: TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TNF-αR, TNF-α receptor; IL-17, interleukin-17; TNFR1, TNF receptor 1; TRADD, TNFR1-associated DD protein; RIPK1, receptor interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1; GCK, germinal center kinase; HPK, hematopoietic progenitor kinase; HGK, HPK1/GCK-like kinase; GLK, GCK-like kinase; ACT1, also known as CIKS (connection to inhibitor of κB (IκB) kinase and stress-activated protein kinases); HGK, HPK/GCK-like kinase; PKC-θ, protein kinase C-θ; TRAF2, TNFR-associated factor; TAK1, transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)-activated kinase 1; ASK1, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; TPL2, tumor progression locus 2; MAPK4K, MAP kinase kinase kinase kinase; MAPK3K, MAP kinase kinase kinase; MAP2K, MAP kinase kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MEKK1, MAPK/ERK kinase kinase 1; MKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; AP-1, activator protein-1; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal Kinase.