Abstract
Background
Heart transplantation (HT) is the most useful treatment modality for heart failure. Although several studies have reported the impact of acute kidney injury (AKI) on clinical outcomes after transplantation, little is known about the impact of peri-transplant renal replacement therapy (RRT) on clinical outcomes. We compared the clinical outcomes according to RRT use status among patients with AKI during the peri-transplant period.
Material/Methods
The medical records of 21 patients who underwent HT from January 2006 to May 2019 were reviewed. We assessed the heart failure cause, comorbidities, immunosuppressant type, requirement for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, AKI incidence, and cardiac and renal functions over time. The patients were divided into 3 groups: those without AKI (non-AKI group, n=6), those who underwent perioperative RRT (RRT group, n=10), and those who did not undergo RRT (non-RRT group, n=5).
Results
The most common cause of HT was dilated cardiomyopathy (52.4%). Fifteen patients (71.4%) experienced AKI during the peri-transplant period. Among them, 9 (90%) in the RRT group underwent continuous RRT and only 1 (10%) underwent intermittent hemodialysis. Until 6 months after HT, the renal function of the RRT group was worse than that of the non-RRT group (estimated glomerular filtration rate 44.2 vs. 69.2 mL/min/1.73 m2, P=0.015), but the differences dissipated by 9 months. Finally, all patients, even in the RRT group, withdrew from dialysis.
Conclusions
RRT during the peri-transplant period in HT may be a good bridge therapy for renal function recovery in patients with cardiorenal AKI.
MeSH Keywords: Acute Kidney Injury, Cardio-Renal Syndrome, Heart Transplantation, Renal Replacement Therapy
Background
Heart transplantation (HT) is the most useful modality for treating decompensated heart failure (HF). Various complications can occur during the peri-transplant period, such as cerebrovascular accident, abnormal pulmonary gas exchange, cardiovascular complications, primary graft dysfunction, renal dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, infection, and malignancy [1,2]. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication in the peri-transplant period of HT [3]. In particular, cardiorenal syndrome, defined as disorders of the heart and kidneys in which the acute or chronic dysfunction of one organ induces subsequent functional abnormality of another, is a major cause of AKI in HF patients with normal renal function in the pre-transplant period of HT [4,5]. AKI in the peri-transplant period is a well-known independent risk factor for increased morbidity and mortality rates [3,6–10]. Previous studies reported that renal outcomes and heart transplant recipients (HTRs) survival were dependent on baseline renal function before transplantation [11–13]. Several studies reported that 5–29% of HTRs experienced AKI that requires renal replacement therapy (RRT) during the peri-transplant period [6,8,12,14–16]. These studies reported renal outcomes during the follow-up of patients with AKI after transplantation, but the impact of RRT on renal outcomes in those patients remains insufficient. Therefore, we investigated the clinical outcomes of HTRs and performed a risk-benefit assessment by RRT status in the peri-transplant period of HT.
Material and Methods
Study design and subjects
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (XC19RADI0091) of our institution and complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. This retrospective observational study included a total of 22 patients who underwent heart transplantation from January 2006 to May 2019 at Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital and Eunpyeong St. Mary’s Hospital. One out of the 22 patients was excluded because he was already on dialysis for end-stage renal disease (ESRD) before HT and underwent simultaneous heart-kidney transplantation. Finally, 21 patients were included in this study. The subjects were divided into an AKI group (n=15) and a non-AKI group (n=6). Thereafter, the AKI group (n=15) was divided into 2 groups for comparison of renal function over time according to RRT status during the peri-transplant period: those who underwent peri-transplant RRT (RRT group, n=10) and those who did not (non-RRT group, n=5). The primary outcome was the rate of renal function recovery from AKI after HT according to RRT status during the peri-transplant period. The secondary outcome included changes in renal function over time, interval from AKI to recovery of renal function, changes in cardiac function defined as left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) on echocardiogram over time, and mortality.
Data collection and definitions
Data for HTRs were collected from the electronic medical records. Basic characteristics included age, sex, emergency HT status, follow-up duration, comorbidities (hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, and myocardial infarction), underlying cardiac disease, cardiac ischemic time during transplantation, LVEF on echocardiogram at pre-transplant time, baseline serum creatinine (SCr), baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and immunosuppressant type used for induction or maintenance.
The peri-transplant period was defined as from the day of hospitalization with decompensated acute HF to the day of discharge after HT.
To evaluate cardiac and renal function over time, both LVEF and eGFR by Chronic Kidney Disease-Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI eGFR) were assessed at baseline, 1 week, and 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months after HT.
HT emergency grade was divided into emergent, urgent, and elective transplantation according to Clinical Guidelines for Adult Heart Transplantation British Columbia [17]. Emergent transplantation was defined as transplantation for patients who presented in cardiogenic shock; candidates needed to be determined within 24 h. Urgent transplantation was defined as a “fast-track” version of the routine assessment and designed for completion within 7 days. Elective transplantation was defined as transplantation for non-prioritized patients on Korean Organ Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS) wait lists.
Clinical outcomes were analyzed for cardiac function, renal function, need for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), ECMO duration, AKI incidence and stage, RRT type, and rate and interval from AKI to renal function recovery after transplantation. Cardiac function was assessed by LVEF on an echocardiogram. HF due to reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) was defined as an LVEF less than 40% [18]. Renal function was assessed according to CKD-EPI eGFR. Baseline renal function was assessed 3 months before transplantation. If previous data could not be collected because it was a patient’s first visit to our center, baseline renal function was assessed on the first day of hospitalization. AKI diagnosis and stage were defined as severity while waiting for transplantation after admission or in the first 7 days after transplantation according to the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcome (KDIGO) criteria [19]. AKI stages were stratified as follows: (1) Stage 1, 0.3 mg/dL or a 1.5–1.9 times increase in SCr from baseline; (2) Stage 2, a 2–2.9 times increase in SCr from baseline; and (3) Stage 3, a greater than 3 times increase in SCr from baseline, an increase in SCr above 4 mg/dL, or renal function requiring RRT. Baseline renal function was identified as SCr and CKD-EPI eGFR 3 months before transplantation. Renal function recovery was assessed by changes in renal function within 90 days after transplantation [20]. The assessment was performed by classifying patients as having received or not received RRT during the peri-transplant period. In patients requiring RRT, recovery from AKI was defined as sustained independence from RRT for a minimum of 14 days. In non-dialysis patients, full recovery from AKI was defined as the absence of AKI criteria, while partial recovery was defined as a downgrade in AKI stage according to the KDIGO criteria [21]. Patients who maintained normal renal function during the peri-transplant period were classified as the non-AKI group, while those with renal dysfunction were classified as the AKI group. In the AKI group, patients who underwent RRT during the peri-transplant period were classified as the RRT group, while those did not undergo RRT during the peri-transplant period were classified as the non-RRT group.
Intervention
Inotropic drugs
Post-transplant care was provided according to the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) guidelines [22]. A continuous infusion of inotropic drugs at the lowest effective dose was used to maintain hemodynamic stability after transplantation over the first 3–5 days. The following therapies were applied: dobutamine 1–10 ug/kg/min, dopamine 1–10 ug/kg/min, and α-adrenergic agonists including norepinephrine or epinephrine 1–10 ug/min to maintain adequate mean arterial pressure.
RRT setting
Patients in need of continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) were treated with continuous veno-venous hemodiafiltration (CVVHDF) mode. Patients with stable hemodynamics were treated with intermitted hemodialysis (IHD). Vascular access was set by percutaneous placement of a double-lumen catheter into the subclavian, internal jugular, or femoral veins. The CRRT setting was initiated to 30–35 ml/kg/h for the effluent volume target and 150 ml/min for the blood flow. Changes in CRRT setting according to patient condition were determined by the nephrologist.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables among the subjects’ demographics and clinical characteristics were described as the mean±standard deviation for normally distributed variables and the median (interquartile range) for non-normally distributed variables. Categorical variables were described using frequency and percentage. The chi-square test was performed to compare groups and categorical variables, while Fisher’s exact test was performed if it did not meet the assumptions required for parametric testing. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov t test was performed to compare normally distributed continuous variables. The Mann-Whitney U test was performed to compare non-normally distributed continuous variables. The cumulative rate of renal function recovery over time was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method, and the difference between groups was examined using the log-rank test. We considered P<0.05 as statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 24 (IBM, United States).
Results
Basic patient demographics
The basic patient demographics are shown in Table 1. The proportion of AKI in the whole study group was 71.4%. Among them, 10 patients (66.7%) underwent RRT during the peri-transplant period. Emergent HT was the most common transplantation type; there was no statistically significant difference in HT type between the non-RRT and RRT groups. In the whole study group, the most common cause of HT was dilated cardiomyopathy (n=11, [52.4%]), followed by ischemic cardiomyopathy (n=9, [42.9%]). The mean pre-transplant LVEF of the AKI group was lower than that of the non-AKI group (p=0.009). However, there were no statistically significant differences in pre-transplant cardiac function or baseline renal function between the RRT and non-RRT groups.
Table 1.
Patients’ basic demographics.
| Variable | Non-AKI (n=6) | AKI | P value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (N=15) | Non-RRT (n=5) | RRT (n=10) | |||
| Age (years), mean±SD | 40.3±10.9 | 44.6±16.0 | 43.4±17.8 | 45.2±16.0 | 0.499 |
| Sex, Male, n (%) | 6 (100) | 12 (75.0) | 4 (80.0) | 8 (80.0) | 0.497 |
| Type of heart transplantation, n (%) | 0.504 | ||||
| Emergent | 4 (66.7) | 6 (40.0) | 2 (40.0) | 4 (40.0) | |
| Urgent | 2 (33.3) | 7 (46.7) | 3 (60.0) | 4 (40.0) | |
| Elective | 0 | 2 (13.3) | 0 | 2 (20.0) | |
| Follow-up duration (months), median (IQR) | 104.5 (4.7, 117.7) | 11.5 (5.9, 35.7) | 16.0 (6.6, 47.6) | 10.4 (3.3, 36.9) | 0.263 |
| Comorbidity | 0.433 | ||||
| HTN, n (%) | 1 (16.7) | 3 (20.0) | 1 (20.0) | 2 (20.0) | |
| DM, n (%) | 2 (33.3) | 6 (40.0) | 1 (20.0) | 5 (50.0) | |
| CAD, n (%) | 2 (33.3) | 8 (53.3) | 4 (80.0) | 4 (40.0) | |
| MI, n (%) | 2 (33.3) | 6 (40.0) | 3 (60.0) | 3 (30.0) | |
| Underlying cardiac disease, n (%) | 0.335 | ||||
| DCMP | 4 (66.7) | 7 (46.7) | 1 (20.0) | 6 (60.0) | |
| ICMP | 2 (33.3) | 7 (46.7) | 4 (80.0) | 3 (30.0) | |
| Other | 0 | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (10.0) | |
| Cardiac ischemic time (min), median (IQR) | 114.0 (83.0, 145.0) | 133.0 (110.5, 193.0) | 145.0 (126.0, 284.0) | 111.0 (87.0, 240.0) | 0.373 |
| LVEF at time of admission (%), mean±SD | 29.3±10.1 | 18.6±7.1 | 19.5±5.0 | 18.2±8.2 | 0.009** |
| Baseline serum Cr (mg/dL), mean±SD | 0.8±0.2 | 1.2±0.6 | 0.9±0.3 | 1.4±0.6 | 0.050** |
| Baseline CKD-EPI eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2), mean±SD | 113.1±17.3 | 78.2±32.5 | 96.3±30.0 | 69.1±31.2 | 0.024** |
| Serum Cr on 1 day before HT (mg/dL), median (IQR) | 0.8 (0.4,0.9) | 1.7* (1.3,2.0) | 1.6 (1.3,2.3) | 1.9* (1.3,2.1) | <0.001**, 0.040*** |
| CKD-EPI eGFR on 1 day before HT (mL/min/1.73 m2), median (IQR) | 113.8 (99.7,142.4) | 43.6* (36.1,59.7) | 56.5 (33.8,65.3) | 41.1* (33.7,61.9) | <0.001**, 0.036*** |
| Induction IST, n (%) | 0.186 | ||||
| Basiliximab | 6 (100) | 9 (60.0) | 3 (60.0) | 6 (60.0) | |
| ATG | 0 | 6 (40.0) | 2 (40.0) | 4 (40.0) | |
| Maintenance IST, n (%) | 0.856 | ||||
| Tacrolimus | 5 (83.3) | 13 (86.7) | 4 (80.0) | 9 (90.0) | |
| Cyclosporine | 1 (16.7) | 2 (13.3) | 1 (20.0) | 1 (10.0) | |
| Steroid | 2 (33.3) | 9 (60.0) | 4 (80.0) | 5 (50.0) | |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | 6 (100.0) | 15 (100.0) | 5 (100.0) | 10 (100.0) | |
| Everolimus | 1 (16.7) | 1 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (10.0) | |
ATG – anti-thymoglobulin; CAD – coronary artery disease; CKD-EPI eGFR – chronic kidney disease epidemiology collaboration estimated glomerular filtration rate; Cr – creatinine; DCMP – delayed cardiomyopathy; DM – diabetes mellitus; HTN – hypertension; ICMP – ischemic cardiomyopathy; IQR – interquartile range; IST – immunosuppressant; LVEF – left ventricular ejection fraction; MI – myocardial infarction; RRT – renal replacement therapy, SD – standard deviation.
If the patient required RRT, serum Cr and CKD-EPI eGFR were assessed immediately prior to RRT initiation;
p<0.05, non-AKI versus AKI group;
p<0.05; non-RRT versus RRT group.
Baseline renal function of the AKI group, which was accessed as CKD-EPI eGFR, was worse than that of the non-AKI group (SCr and CKD-EPI eGFR; p=0.050 and 0.024, respectively). However, in the AKI group, baseline renal function did not significantly differ between the RRT and non-RRT groups. The difference in renal function between the AKI group and non-AKI groups was observed again at 1 day before transplantation (SCr and CKD-EPI eGFR; p<0.001 for both). Even in the AKI group, the renal function of the RRT group was significantly worse than that of the non-RRT group (SCr and CKD-EPI eGFR; p=0.040 and 0.036, respectively) at 1 day before transplantation. Basiliximab and calcineurin inhibitors were the major induction and maintenance immunosuppressants in HTRs (71.4% and 100%, respectively). There were no significant differences in induction or maintenance immunosuppressant types between the non-AKI and AKI groups.
Comparison of clinical features and outcomes between RRT and non-RRT groups
A comparison of clinical outcomes between the RRT and non-RRT groups is shown in Table 2. Most patients (86.7%) developed AKI before transplantation. In the whole AKI group, 26.7% of patients were in AKI stage 1, 33.3% were in stage 2, and 40.0% were in stage 3. In the whole study group, 13 of 21 patients (61.9%) required ECMO support before transplantation; these patients all belonged to the AKI group. The average ECMO duration of the whole study group was 10.5 days. There were no significant differences in ECMO duration between the non-RRT and RRT groups. The change in LVEF over time after HT is shown in Figure 1. LVEF at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after HT was maintained at above 45% in both groups; no significant intergroup difference was noted except at 3 months after HT.
Table 2.
Comparison of clinical outcomes between non-RRT and RRT groups.
| Variable | Non-RRT (n=5) | RRT (n=10) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time of AKI, n (%) | 1.000 | ||
| Pre-transplantation | 4 (80.0) | 9 (90.0) | |
| Post-transplantation | 1 (20.0) | 1 (10.0) | |
| AKI stage, n (%) | 0.661 | ||
| Stage I | 2 (40.0) | 2 (20.0) | |
| Stage II | 1 (20.0) | 4 (40.0) | |
| Stage III | 2 (40.0) | 4 (40.0) | |
| ECMO during pre-transplant period, n (%) | 4 (80.0) | 9 (90.0) | 1.000 |
| Duration of ECMO (days), mean±SD | 11.3±12.7 | 10.2±6.8 | 0.796 |
| Urine volume during AKI period, ml/kg/hr, mean±SD | 1.6±1.2 | 1.4±1.2 | 0.660 |
| Interval from AKI to RRT start (days), mean±SD | NA | 1.3±1.3 | |
| Duration of RRT (days), median (IQR) | NA | 19.0 (5.0, 27.0) | |
| Type of RRT, n (%) | |||
| CRRT | NA | 9 (90.0) | |
| Intermittent HD | NA | 1 (10.0) | |
| Recovery from AKI, n (%) | 5 (100) | 7 (70.0) | 0.505 |
| Full recovery | 4 (80.0) | 4 (40.0) | 0.576 |
| Partial recovery | 1 (20.0) | 3 (30.0) | 0.576 |
| Interval from AKI to renal function recovery after HT (days), median (IQR) | 6.0 (3.5, 15.5) | 22.0 (20.0, 64.0) | 0.088 |
AKI – acute kidney injury; CRRT – continuous renal replacement therapy; ECMO – extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; HD – hemodialysis; HT – heart transplantation; IQR – interquartile range; RRT – renal replacement therapy; SD – standard deviation.
Figure 1.
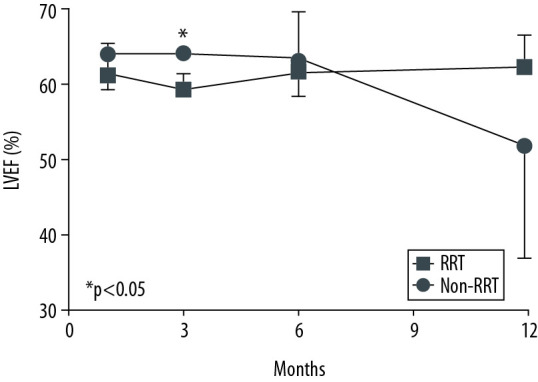
Cardiac function over time after heart transplantation. There were no statistically significantly differences in left ventricular ejection fraction at 1, 6, and 12 months after heart transplantation. At 3 months after heart transplantation, left ventricular ejection fraction of the RRT group (59.5±2.1%, mean±SD) was significantly lower than that of the non-RRT group (64.2±0.6%, mean±SD) (p=0.008). Left ventricular ejection fraction at 1 month was 61.5±3.9% (mean±SD) in the RRT group and 64.2±4.5% (mean±SD) in the non-RRT group. At 6 months, it was 61.8±3.2% (mean±SD) in the RRT group and 63.5±6.3% (mean±SD) in the non-RRT group. At 12 months, it was 62.5±4.2% (mean±SD) in the RRT group and 52.0±15.0% (mean±SD) in the non-RRT group. P values were calculated using the t test. * P<0.05 was considered statistical significance.
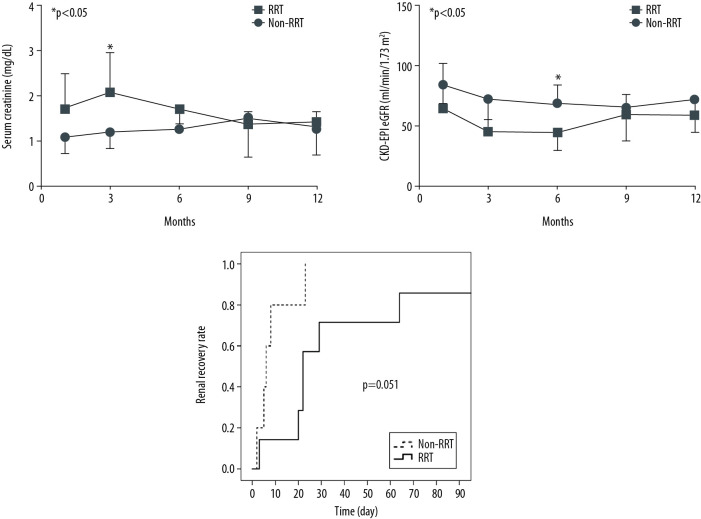
The entire RRT group underwent CRRT except for 1 patient who underwent IHD. The average time from AKI occurrence to RRT start was 1.3 days, while the median duration of RRT was 19 days. At 1 month after heart transplantation, SCr of the RRT group (1.7±0.8 mg/dL, mean±SD) was significantly higher than that of the non-RRT group (1.1±0.3 mg/dL, mean±SD) (p=0.039). At 6 months after heart transplantation, CKD-EPI eGFR of the RRT group (44.2±14.2 ml/min/1.73m2, mean±SD) was significantly lower than that of the non-RRT group (69.2±14.2 ml/min/1.73 m2, mean±SD) (p=0.015). However, at 9 and 12 months after HT, there were no significant intergroup differences in renal function (Figure 2A, 2B).
Figure 2.
Renal function over time after heart transplantation. (A) There were no statistically significant differences in serum creatinine at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months after heart transplantation. At 1 month after heart transplantation, serum creatinine of the RRT group (1.7±0.8 mg/dL, mean±SD) was significantly higher than that of the non-RRT group (1.1±0.3 mg/dL, mean±SD) (P=0.039). (B) There were no statistically significant differences in CKD-EPI eGFR at 1, 3, 9, and 12 months after heart transplantation. At 6 months after heart transplantation, CKD-EPI eGFR of the RRT group (44.2±14.2 ml/min/1.73 m2, mean±SD) was significantly lower than that of the non-RRT group (69.2±14.2 ml/min/1.73 m2, mean±SD) (P=0.015). (C) Renal recovery rate over time was not significantly different between the RRT and the non-RRT groups when calculated by the log-rank test (p=0.051). * p<0.05 was considered statistical significance.
All patients in the non-RRT group (100%) and 7 patients in the RRT group (70.0%) recovered renal function within 3 months after HT (Table 2, Figure 2C). Among 4 patients in whom renal function did not recover, 3 patients (non-RRT group, n=1; RRT group, n=2) died of HF or pneumonia as complications within 3 months after HT. One patient had CKD-EPI eGFR lower than 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 90 days after AKI, and even partial recovery was not reached, despite discontinuation of RRT. The rate of renal recovery over time from AKI to recovery after HT by group are shown in Figure 2C. The average time to recovery in the entire AKI group was 28 days. Renal recovery rate over time was not significantly different between the RRT and non-RRT groups (p=0.051). There were no statistically significant differences in the rate of renal recovery and time from AKI to renal recovery between the RRT and non-RRT groups, although the time from AKI to renal recovery in the non-RRT group was shorter than that in the RRT group (Table 2). All patients in the RRT group tolerated the treatment without requiring dialysis at discharge.
In the AKI group, 4 patients (26.7%) died, and 3 of them belonged to the RRT group. Two patients died of recurrent HF after HT and 1 patient died of acute respiratory distress syndrome due to pneumonia. The difference was not significant between the RRT group and non-RRT groups (p=0.675).
Discussion
This retrospective observational study reported the incidence of AKI during the peri-transplant period and renal outcomes over time according to RRT status in HTRs. Although renal function during hospitalization before HT was lower in the RRT group than in the non-RRT group, renal function recovery rates and interval time from AKI to renal function recovery did not differ significantly between groups. Therefore, this study may have identified the role of RRT in renal function deterioration following cardiac dysfunction.
In our study group, the incidence of AKI during the peri-transplant period was 71.4%. Our study showed a relatively high incidence of AKI associated with HT versus the range of 14–76% reported by previous studies [6,8,14–16,23,24]. It is noteworthy that 13 of 15 patients (86.7%) in the AKI group developed AKI before HT, whereas most previous studies reported AKI following HT [3,6–8,12–15,23,25–28]. We speculate there are several reasons for the high incidence of AKI in our study group. First, the AKI group had significantly lower cardiac function than the non-AKI group at the time of hospitalization for HT and renal function at 1 day before transplantation. Our study supports previous studies showing that baseline renal dysfunction was a risk factor for AKI associated with HT. AKI that occurred before HT can be presumed to be due to deteriorated cardiac function just prior to transplantation, as there is no difference in underlying comorbidities between groups. Second, there was a lack of deceased donors for HT in Korea compared to other countries. In Korea, transplant priority is determined according to the KONOS priority system. It is difficult for patients with acute HF to receive timely HT because of the relative lack of deceased donors compared to the number of patients waiting for transplantation. After hospitalization with decompensated acute HF, the waiting time for transplantation is relatively long. As a result, it is thought that the reduction of renal blood flow due to cardiac dysfunction continued, which influenced the increase in the incidence of AKI. Third, long-term durable mechanical circulatory support such as that provided by a ventricular assist device is unavailable because of the current reimbursement system in our country; rather, concurrent inotropic support is the most common treatment to maintain circulation for acute HF [29]. Due to this process, insufficient circulation and drug toxicities may be risk factors for AKI before transplantation.
In addition, the rate of RRT requirement was 47.6% in the whole study group and 66.7% in the AKI group. These rates are remarkably higher than the results of previous studies (3.8–28.8%) [6,8,12,14–16]. We speculate there are several reasons for the high rate of RRT requirement in our study group. First, Park et al. [30] reported that circulatory diseases such as coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, HF, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, and endocarditis were the second-leading indications of CRRT in Korea. Nephrologists in our center reported an association with continuous renal replacement therapy in 2020 [31]. In their study, the most common cause of indication for continuous renal replacement therapy was sepsis (52.6%) and cardiac disease was the second most common cause (37.5%). Second, due to the lack of clear guidelines for CRRT initiation, clinicians are asked to decide when to apply CRRT. Therefore, CRRT was applied not only to patients with oliguria or anuria, but also to those with pulmonary edema, pleural effusion, metabolic acidosis, electrolytes imbalances, and multi-organ failure. This may explain the high rate of CRRT application in our study group. In our study group, the average time from AKI occurrence to RRT start was 1.3±1.3 days. This means that RRT was applied as an early strategy for HTRs with AKI. This result appears to be consistent with previous studies. Several studies suggested that early RRT treatment in HTRs is associated with lower mortality and better improvement in renal dysfunction [32–36].
Renal function after HT tended to be lower in the RRT group than in the non-RRT group up to 6 months, but the gap gradually narrowed over time. As a result, similar renal functions were observed between the groups at 9 and 12 months after HT. Betuel et al. [33] reported similar results in a cohort of patients with AKI after HT. On the other hand, the difference in the interval time from AKI to renal function recovery between the groups was not statistically significant, although that in the RRT group was about 3 times longer than in the non-RRT group. As a result, most patients in both groups recovered renal function within 90 days and did not progress to CKD. Finally, according to the acute kidney disease and renal recovery consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative [20], there was good restoration of renal function. Patients who were admitted to the Intensive Care Unit for acute HF and underwent ECMO were compared to patients in our study with respect to renal function. The patients’ basic demographics, comparison of clinical outcomes, and cardiac function and renal function over time after acute HF are shown in the Supplementary Tables 1, 2 and Supplementary Figures 1, 2. None of the HF patients who underwent RRT without HT (the non-HT with RRT group in Supplementary Tables 1, 2) had full recovery of renal function. The interval from AKI to renal function recovery in the HF patients who underwent RRT without HT (the non-HT with RRT group in Supplementary Tables 1, 2) was significantly longer than that in the non-RRT of HT group with AKI (p=0.016) (Supplementary Table 2).
On the other hand, except for patients who died of HF, cardiac function was well maintained to an LVEF above of 40% during follow-up after HT in the RRT and non-RRT groups.
In our study group, patient survival rate was similar to previous studies, although the number of enrolled patients was small [1,2]. The 1-year survival rate in our study group was 81.0% and the cause of death in all patients who died was cardiac or pulmonary complication within 6 months after transplantation, which is consistent with previous studies [1,37].
Our study has several limitations. First, it was a retrospective, observational study and was performed in only 2 centers. Second, the number of enrolled patients was small. However, the results, such as AKI incidence, rate of renal recovery after HT, and cardiac outcomes, were similar to those of previous studies [3,6–8,12,23,26,38]. Therefore, renal function recovery in this study could help confirm the utility of RRT as bridge therapy in HT. Finally, some patients needed HT at the first visit to our center, so we could not accurately determine their baseline renal function. Fortunately, most of those patients had normal renal function at the time of the Emergency Department visit. Further clinical studies with larger numbers of patients are needed to confirm the value of RRT for AKI during the peri-transplant period of HT.
Conclusions
RRT during the peri-transplant period of HT could be a good bridge therapy for renal function recovery in patients with cardiorenal AKI and a low LVEF during the early post-transplant period.
Supplementary Data
Supplementary Table 1.
Basic demographics of patients in HF with HT and HF without HT.
| Variables | HF with HT (n=21) | HF without HT (n=35) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean±SD | 43.4±14.6 | 62.1±10.3 | <0.001 |
| Gender, Male, n (%) | 18 (85.7) | 29 (82.9) | 1.000 |
| Follow-up duration (months), median (IQR) | 16.0 (6.0, 77.1) | 12.4 (6.9, 27.9) | 0.234 |
| Comorbidity | 0.943 | ||
| HTN, n (%) | 4 (19.0) | 14 (40.0) | |
| DM, n (%) | 8 (38.1) | 15 (42.9) | |
| CAD, n (%) | 10 (47.6) | 9 (25.7) | |
| MI, n (%) | 8 (38.1) | 7 (20.0) | |
| Underlying cardiac disease, n (%) | 0.004 | ||
| DCMP | 11 (52.4) | 4 (11.4) | 0.001 |
| ICMP | 9 (42.9) | 29 (82.9) | 0.002 |
| Others | 1 (4.8) | 2 (5.7) | 1.000 |
| LVEF at time of admission (%), mean±SD | 21.7±9.2 | 28.7±12.4 | 0.029 |
| Baseline serum Cr (mg/dL), mean±SD | 1.1±0.5 | 1.1±0.4 | 0.905 |
| Baseline CKD-EPI eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m2), mean±SD | 88.2±32.8 | 78.1±25.5 | 0.207 |
| Serum Cr on 1 day before HT or ECMO (mg/dL), mean±SD | 1.9±1.1* | 1.7±0.8* | 0.735 |
| CKD-EPI eGFR on 1 day before HT or ECMO (ml/min/1.73 m2), mean±SD | 62.2±47.8* | 49.7±24.4* | 0.806 |
| AKI, n (%) | 15 (71.4) | 25 (71.4) | 1.000 |
| RRT, n (%) | 10 (47.6) | 8 (22.9) | 0.055 |
HF – heart failure; HT – heart transplantation; SD – standard deviation; IQR – interquartile range; HTN – hypertension; DM – diabetes mellitus; CAD – coronary artery disease; MI – myocardial infarction; DCMP – delated cardiomyopathy; ICMP – ischemic cardiomyopathy; LVEF – left ventricular ejection fraction; Cr – creatinine; CKD-EPI eGFR – chronic kidney disease epidemiology collaboration estimated glomerular filtration rate; ECMO – extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, AKI – acute kidney injury; RRT – renal replacement therapy.
If the patient required RRT, serum Cr and CKD-EPI eGFR were assessed immediately prior to RRT initiation.
Supplementary Table 2.
Comparison of clinical outcomes between the HT with AKI and non-HT with RRT groups.
| Variables | HT with AKI | Non-HT with RRT (n=8) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-RRT (n=5) | RRT (n=10) | |||
| ECMO during hospitalization, n (%) | 4 (80.0) | 9 (90.0) | 8 (100.0) | 0.218 |
| Duration of ECMO (days), median (IQR) | 8.5 (1.0, 24.3) | 8.0 (5.0, 17.0) | 2.0 (1.3, 5.8) | 0.305 |
| Interval from AKI to RRT start (days), mean±SD | NA | 1.3±1.3 | 0.6±0.7 | 0.994 |
| Duration of RRT (days), median (IQR) | NA | 19.0 (5.0, 27.0) | 23.5 (6.8, 57.5) | 0.819 |
| Type of RRT, n (%) | 1.000 | |||
| CRRT | NA | 9 (90.0) | 8 (100.0) | |
| Intermittent HD | NA | 1 (10.0) | 0 | |
| Recovery from AKI, n (%) | 5 (100.0) | 7 (70.0) | 5 (62.5) | 0.164 |
| Full recovery | 4 (80.0) | 4 (40.0) | 0 | 0.048* |
| Partial recovery | 1 (20.0) | 3 (30.0) | 5 (62.5) | |
| Interval from AKI to renal function recovery (days), median (IQR) | 6.0 (3.5, 15.5) | 22.0 (20.0, 64.0) | 61.0 (37.0, 200.5) | 0.016* |
HT – heart transplantation; AKI – acute kidney injury; RRT – renal replacement therapy; ECMO – extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; IQR – interquartile range; SD – standard deviation; CRRT – continuous renal replacement therapy; HD – kemodialysis.
p<0.05, HT-AKI without RRT group versus non-HT with RRT group.
Cardiac function over time after acute heart failure. * p<0.05, HT-AKI without RRT versus non-HT with RRT groups; # p<0.05; HT-AKI without RRT versus HT with RRT groups.
(A–C) Renal function over time after acute heart failure. * p<0.05, HT-AKI without RRT versus non-HT with RRT groups; # p<0.05; HT-AKI without RRT versus HT with RRT groups.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.co.kr) for English language editing.
Abbreviations
- HFrEF
HF due to reduced ejection fraction
- HTRs
heart transplant recipients
- KONOS
Korean Organ Network for Organ Sharing
- RRT
renal replacement therapy
- SCr
serum creatinine
Footnotes
Conflict of interest
None.
Source of support: Departmental sources
References
- 1.McCartney SL, Patel C, Del Rio JM. Long-term outcomes and management of the heart transplant recipient. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2017;31:237–48. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2017.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Stehlik J, Kobashigawa J, Hunt SA, et al. Honoring 50 years of clinical heart transplantation in circulation: In-depth state-of-the-art review. Circulation. 2018;137:71–87. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thongprayoon C, Lertjitbanjong P, Hansrivijit P, et al. Acute kidney injury in patients undergoing cardiac transplantation: A meta-analysis. Medicines (Basel) 2019;6:108. doi: 10.3390/medicines6040108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ronco C, Bellasi A, Di Lullo L. Cardiorenal syndrome: An overview. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018;25:382–90. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2018.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Duchnowski P, Hryniewiecki T, Kuśmierczyk M, Szymański P. Anisocytosis predicts postoperative renal replacement therapy in patients undergoing heart valve surgery. Cardiol J. 2019 doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2019.0020. [Online ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fortrie G, Manintveld OC, Caliskan K, et al. Acute kidney injury as a complication of cardiac transplantation: Incidence, risk factors, and impact on 1-year mortality and renal function. Transplantation. 2016;100:1740–49. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bastin AJ, Ostermann M, Slack AJ, et al. Acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery according to Risk/Injury/Failure/Loss/End-stage, Acute Kidney Injury Network, and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes classifications. J Crit Care. 2013;28:389–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2012.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gude E, Andreassen AK, Arora S, et al. Acute renal failure early after heart transplantation: Risk factors and clinical consequences. Clin Transplant. 2010;24:E207–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2010.01225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chertow GM, Levy EM, Hammermeister KE, et al. Independent association between acute renal failure and mortality following cardiac surgery. Am J Med. 1998;104:343–48. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(98)00058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hobson CE, Yavas S, Segal MS, et al. Acute kidney injury is associated with increased long-term mortality after cardiothoracic surgery. Circulation. 2009;119:2444–53. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.800011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ostermann ME, Rogers CA, Saeed I, et al. Pre-existing renal failure doubles 30-day mortality after heart transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2004;23:1231–37. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2003.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Boyle JM, Moualla S, Arrigain S, et al. Risks and outcomes of acute kidney injury requiring dialysis after cardiac transplantation. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;48:787–96. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2006.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Odim J, Wheat J, Laks H, et al. Peri-operative renal function and outcome after orthotopic heart transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2006;25:162–66. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2005.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Escoresca Ortega AM, Ruiz de Azua Lopez Z, Hinojosa Perez R, et al. Kidney failure after heart transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2010;42:3193–95. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2010.05.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.De Santo LS, Romano G, Amarelli C, et al. Implications of acute kidney injury after heart transplantation: What a surgeon should know. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;40:1355–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2011.02.068. ;discussion 1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wyatt CM, Arons RR. The burden of acute renal failure in nonrenal solid organ transplantation. Transplantation. 2004;78:1351–55. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000140848.05002.b8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cheung A, Bashir J, Davis M, et al. Clinical Guidelines for Adult Heart Transplantation British Columbia. 2017 [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ezekowitz JA, O’Meara E, McDonald MA, et al. 2017 comprehensive update of the canadian cardiovascular society guidelines for the management of heart failure. Can J Cardiol. 2017;33:1342–33. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2017.08.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Khwaja A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012;120:c179–84. doi: 10.1159/000339789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chawla LS, Bellomo R, Bihorac A, et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery: Consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13:241–57. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Forni LG, Darmon M, Ostermann M, et al. Renal recovery after acute kidney injury. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43:855–66. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4809-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Costanzo MR, Dipchand A, Starling R, et al. The International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation Guidelines for the care of heart transplant recipients. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2010;29:914–56. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2010.05.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Garcia-Gigorro R, Renes-Carreno E, Corres Peiretti MA, et al. Incidence, risk factors and outcomes of early acute kidney injury after heart transplantation: An 18-year experience. Transplantation. 2018;102:1901–8. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Turker M, Zeyneloglu P, Sezgin A, et al. RIFLE criteria for acute kidney dysfunction following heart transplantation: incidence and risk factors. Transplant Proc. 2013;45:3534–37. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.08.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fortrie G, Manintveld OC, Constantinescu AA, et al. Renal function at 1 year after cardiac transplantation rather than acute kidney injury is highly associated with long-term patient survival and loss of renal function – a retrospective cohort study. Transpl Int. 2017;30:788–98. doi: 10.1111/tri.12940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gultekin B, Beyazpinar DS, Ersoy O, et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute kidney injury after orthotopic cardiac transplant: A population-based cohort. Exp Clin Transplant. 2015;13(Suppl 3):26–29. doi: 10.6002/ect.tdtd2015.O15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yan X, Jia S, Meng X, et al. Acute kidney injury in adult postcardiotomy patients with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: Evaluation of the RIFLE classification and the Acute Kidney Injury Network criteria. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2010;37:334–38. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2009.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Crespo-Leiro MG, Delgado JF, Paniagua MJ, et al. Prevalence and severity of renal dysfunction among 1062 heart transplant patients according to criteria based on serum creatinine and estimated glomerular filtration rate: Results from the CAPRI study. Clin Transplant. 2010;24:E88–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2009.01178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kim IC, Youn JC, Kobashigawa JA. The past, present and future of heart transplantation. Korean Circ J. 2018;48:565–90. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2018.0189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Park S, Lee S, Jo HA, et al. Epidemiology of continuous renal replacement therapy in Korea: Results from the National Health Insurance Service claims database from 2005 to 2016. Kidney Research and Clinical Practice. 2018;37:119–29. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.2018.37.2.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Park Y, Ban TH, Kim HD, et al. Mortality prediction of serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in patients requiring continuous renal replacement therapy. Korean J Intern Med. 2020 doi: 10.3904/kjim.2019.446. [Online ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Luckraz H, Gravenor MB, George R, et al. Long and short-term outcomes in patients requiring continuous renal replacement therapy post cardiopulmonary bypass. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2005;27:906–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2005.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ivey-Miranda JB, Flores-Umanzor E, Farrero-Torres M, et al. Predictors of renal replacement therapy after heart transplantation and its impact on long-term survival. Clin Transplant. 2018;32:e13401. doi: 10.1111/ctr.13401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kolsrud O, Karason K, Holmberg E, et al. Renal function and outcome after heart transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;155:1593–604. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.11.087. e1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mirhosseini SM, Fakhri M, Asadollahi S, et al. Continuous renal replacement therapy versus furosemide for management of kidney impairment in heart transplant recipients with volume overload. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013;16:314–20. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivs492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Elahi MM, Lim MY, Joseph RN, et al. Early hemofiltration improves survival in post-cardiotomy patients with acute renal failure. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004;26:1027–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2004.07.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lund LH, Edwards LB, Dipchand AI, et al. The Registry of the International Society for heart and lung transplantation: Thirty-third adult heart transplantation report-2016; focus theme: Primary diagnostic indications for transplant. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2016;35:1158–69. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2016.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Peng YH, Yu XM, Yan C, et al. Recovery of renal function in a heart transplantation recipient with over 300 days of iatrogenic anuria: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e0451. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Table 1.
Basic demographics of patients in HF with HT and HF without HT.
| Variables | HF with HT (n=21) | HF without HT (n=35) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean±SD | 43.4±14.6 | 62.1±10.3 | <0.001 |
| Gender, Male, n (%) | 18 (85.7) | 29 (82.9) | 1.000 |
| Follow-up duration (months), median (IQR) | 16.0 (6.0, 77.1) | 12.4 (6.9, 27.9) | 0.234 |
| Comorbidity | 0.943 | ||
| HTN, n (%) | 4 (19.0) | 14 (40.0) | |
| DM, n (%) | 8 (38.1) | 15 (42.9) | |
| CAD, n (%) | 10 (47.6) | 9 (25.7) | |
| MI, n (%) | 8 (38.1) | 7 (20.0) | |
| Underlying cardiac disease, n (%) | 0.004 | ||
| DCMP | 11 (52.4) | 4 (11.4) | 0.001 |
| ICMP | 9 (42.9) | 29 (82.9) | 0.002 |
| Others | 1 (4.8) | 2 (5.7) | 1.000 |
| LVEF at time of admission (%), mean±SD | 21.7±9.2 | 28.7±12.4 | 0.029 |
| Baseline serum Cr (mg/dL), mean±SD | 1.1±0.5 | 1.1±0.4 | 0.905 |
| Baseline CKD-EPI eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m2), mean±SD | 88.2±32.8 | 78.1±25.5 | 0.207 |
| Serum Cr on 1 day before HT or ECMO (mg/dL), mean±SD | 1.9±1.1* | 1.7±0.8* | 0.735 |
| CKD-EPI eGFR on 1 day before HT or ECMO (ml/min/1.73 m2), mean±SD | 62.2±47.8* | 49.7±24.4* | 0.806 |
| AKI, n (%) | 15 (71.4) | 25 (71.4) | 1.000 |
| RRT, n (%) | 10 (47.6) | 8 (22.9) | 0.055 |
HF – heart failure; HT – heart transplantation; SD – standard deviation; IQR – interquartile range; HTN – hypertension; DM – diabetes mellitus; CAD – coronary artery disease; MI – myocardial infarction; DCMP – delated cardiomyopathy; ICMP – ischemic cardiomyopathy; LVEF – left ventricular ejection fraction; Cr – creatinine; CKD-EPI eGFR – chronic kidney disease epidemiology collaboration estimated glomerular filtration rate; ECMO – extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, AKI – acute kidney injury; RRT – renal replacement therapy.
If the patient required RRT, serum Cr and CKD-EPI eGFR were assessed immediately prior to RRT initiation.
Supplementary Table 2.
Comparison of clinical outcomes between the HT with AKI and non-HT with RRT groups.
| Variables | HT with AKI | Non-HT with RRT (n=8) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-RRT (n=5) | RRT (n=10) | |||
| ECMO during hospitalization, n (%) | 4 (80.0) | 9 (90.0) | 8 (100.0) | 0.218 |
| Duration of ECMO (days), median (IQR) | 8.5 (1.0, 24.3) | 8.0 (5.0, 17.0) | 2.0 (1.3, 5.8) | 0.305 |
| Interval from AKI to RRT start (days), mean±SD | NA | 1.3±1.3 | 0.6±0.7 | 0.994 |
| Duration of RRT (days), median (IQR) | NA | 19.0 (5.0, 27.0) | 23.5 (6.8, 57.5) | 0.819 |
| Type of RRT, n (%) | 1.000 | |||
| CRRT | NA | 9 (90.0) | 8 (100.0) | |
| Intermittent HD | NA | 1 (10.0) | 0 | |
| Recovery from AKI, n (%) | 5 (100.0) | 7 (70.0) | 5 (62.5) | 0.164 |
| Full recovery | 4 (80.0) | 4 (40.0) | 0 | 0.048* |
| Partial recovery | 1 (20.0) | 3 (30.0) | 5 (62.5) | |
| Interval from AKI to renal function recovery (days), median (IQR) | 6.0 (3.5, 15.5) | 22.0 (20.0, 64.0) | 61.0 (37.0, 200.5) | 0.016* |
HT – heart transplantation; AKI – acute kidney injury; RRT – renal replacement therapy; ECMO – extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; IQR – interquartile range; SD – standard deviation; CRRT – continuous renal replacement therapy; HD – kemodialysis.
p<0.05, HT-AKI without RRT group versus non-HT with RRT group.
Cardiac function over time after acute heart failure. * p<0.05, HT-AKI without RRT versus non-HT with RRT groups; # p<0.05; HT-AKI without RRT versus HT with RRT groups.
(A–C) Renal function over time after acute heart failure. * p<0.05, HT-AKI without RRT versus non-HT with RRT groups; # p<0.05; HT-AKI without RRT versus HT with RRT groups.