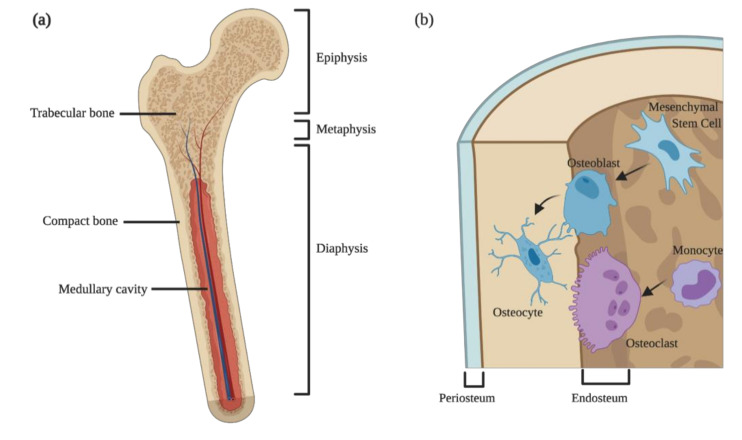
Figure 1.
Bone structure and cellular components. (a) Anatomical division and types of bone present in long bones; (b) cellular components of bone and their cellular precursors. Osteoblasts are derived from mesenchymal stem cells and form new bones by the deposition of extracellular and mineral matrix. When osteoblasts become entrapped in the newly formed bone, they mature into osteocytes. Bone degradation is accomplished by large multinucleated cells, the osteoclasts, which have a myeloid origin.