Abstract
It is known that at least some fluorophores can act as ‘surrogate’ substrates for solute carriers (SLCs) involved in pharmaceutical drug uptake, and this promiscuity is taken to reflect at least a certain structural similarity. As part of a comprehensive study seeking the ‘natural’ substrates of ‘orphan’ transporters that also serve to take up pharmaceutical drugs into cells, we have noted that many drugs bear structural similarities to natural products. A cursory inspection of common fluorophores indicates that they too are surprisingly ‘drug-like’, and they also enter at least some cells. Some are also known to be substrates of efflux transporters. Consequently, we sought to assess the structural similarity of common fluorophores to marketed drugs, endogenous mammalian metabolites, and natural products. We used a set of some 150 fluorophores along with standard fingerprinting methods and the Tanimoto similarity metric. Results: The great majority of fluorophores tested exhibited significant similarity (Tanimoto similarity > 0.75) to at least one drug, as judged via descriptor properties (especially their aromaticity, for identifiable reasons that we explain), by molecular fingerprints, by visual inspection, and via the “quantitative estimate of drug likeness” technique. It is concluded that this set of fluorophores does overlap with a significant part of both the drug space and natural products space. Consequently, fluorophores do indeed offer a much wider opportunity than had possibly been realised to be used as surrogate uptake molecules in the competitive or trans-stimulation assay of membrane transporter activities.
Keywords: drugs, natural products, fluorophores, fingerprinting, similarity, cheminformatics, rdkit, Tanimoto distance
1. Introduction
Fluorescence methods have been used in biological research for decades, and their utility remains unabated (e.g., [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]). Our specific interest here is in the transporter-mediated means by which small fluorescent molecules enter living cells, and our interest has been stimulated by the recognition that a given probe may be a substrate for a large variety of both influx and efflux transporters [23]. Efflux transporters are often fairly promiscuous, since their job is largely to rid cells of unwanted molecules that may have entered, although they can and do have other, important physiological roles (e.g., [24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34]), and are capable of effluxing a variety of fluorescent probes (e.g., [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42]). However, given that most of these probes are contemporary, synthetic molecules, the uptake transporters for which they are substrates are nonetheless often ancient [43,44], and must have evolved in nature for other purposes. These purposes may reasonably be expected to include the uptake of endogenous metabolites in multicellular organisms [45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53], as well as exogenous natural products whose uptake can enhance biological fitness (e.g., [54,55]). This explanation does seems to hold well for synthetic, marketed pharmaceutical drugs [55].
Consequently, it seemed reasonable that existing fluorescent molecules, that are not specifically designed for the purpose but are taken up by biological cells, might also bear structural similarities to endogenous substrates (metabolites) and to natural products (including those from the marine environment), and potentially also to marketed drugs. Of course, some marketed pharmaceutical drugs that are transported into cells are, in fact, naturally fluorescent, including molecules such as anthracyclines [56,57,58], mepacrine (atebrin, quinacrine) [59], obatoclax [60,61], tetracycline derivatives [57,62] and topotecan [63], The same is true of certain vitamins such as riboflavin [64,65] (that necessarily have transporters, as cells cannot synthesise them), as well as certain bioactive natural products (e.g., [66,67,68]). As per this Special Issue, and in an era of increasing antimicrobial resistance [69,70,71,72], this is very much the case for novel antimicrobials, which classically come from natural products (e.g., [73,74,75,76,77,78]). If so, they might then serve as surrogate transporter substrates for them. Indeed, there are examples—so-called fluorescent false neurotransmitters—where such fluorescent analogues of natural substrates have been designed precisely for this purpose (e.g., [79,80]). The aim of the present work was to assess the extent to which this kind of structural similarity between (i) common fluorophores used in biology and (ii) other molecular classes (endogenous mammalian metabolites, marketed pharmaceutical drugs, and known natural products) might be true. It is concluded that in structural terms, common fluorophores do indeed overlap drug space significantly, and we offer an explanation based on the consonance between aromaticity, conjugated π-bonds, and fluorescence. Such fluorophores might then lend themselves readily to high-throughput assays in which their uptake and/or efflux are studied in the presence and absence of ‘competing’ drugs. A preprint is available [81].
2. Results
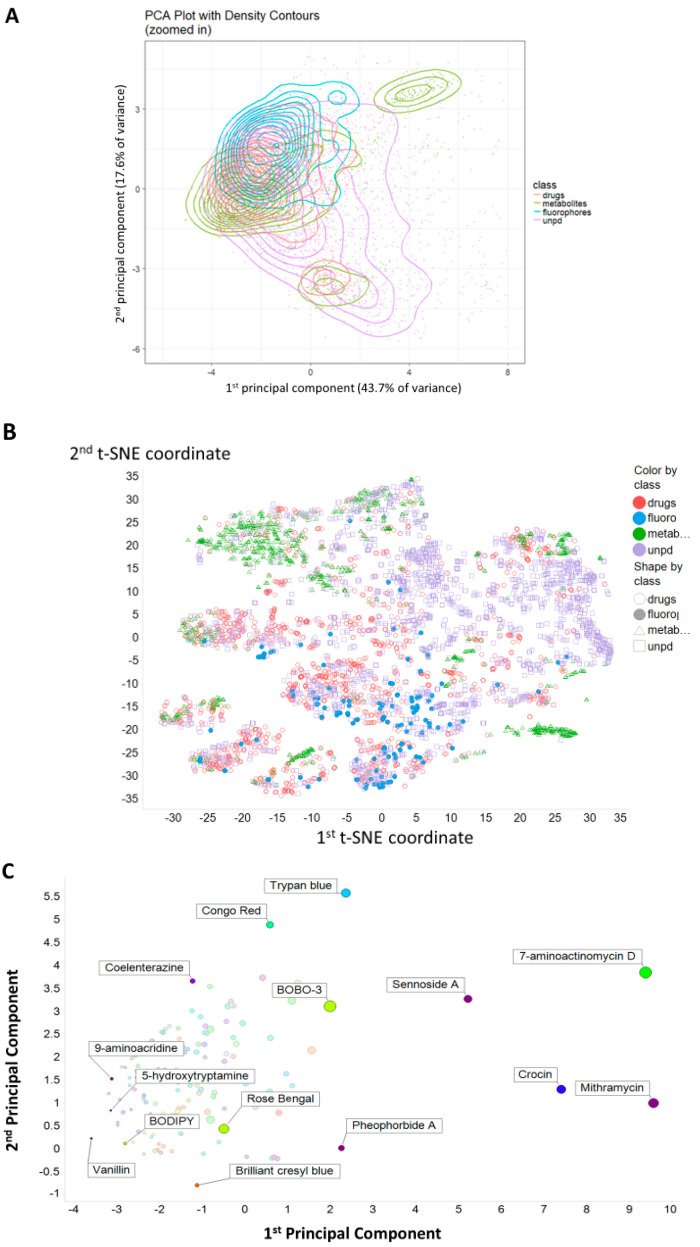
Figure 1A shows a Principal Components Analysis (PCA) plot of the distribution of the four classes based on a series of descriptors in RDKit (www.rdkit.org/), while Figure 1B shows a t-SNE [82] plot of the same data. These clearly show a strong overlap between the rather limited set of fluorophores used and quite significant parts of the drug space. Figure 1C gives just the fluorophores, with the nominal excitation maximum encoded in its colour. This suggests that even with just ~150 molecules, we have achieved a reasonable coverage of the relevant ‘fluorophore space’, with no obvious bias or trend in excitation wavelengths.
Figure 1.
Principal components and t-SNE plots of the principal components of the variance in calculated properties of the molecules used. (A) The first two principal components of the variance in calculated properties of the four classes fluorophores, drugs, metabolites and natural products. Molecules are as in Supplementary Fluorophores SI.xlsx, with the drugs and metabolites those given in [45]. A sampling of 2000 natural products from our download [55] of UNPD was used. Descriptors were z-scores normalised and correlation filtered (threshold 0.98). (B) t-SNE plot of the data in (A), using the same colour-coding. (C). Plot of the first two principal components of the variance in the fluorophores alone. The excitation wavelength is encoded in the colour of the markers. The size of the symbol encodes the molecular weight, indicating that much of the first PC is due to this (plus any other covarying properties).
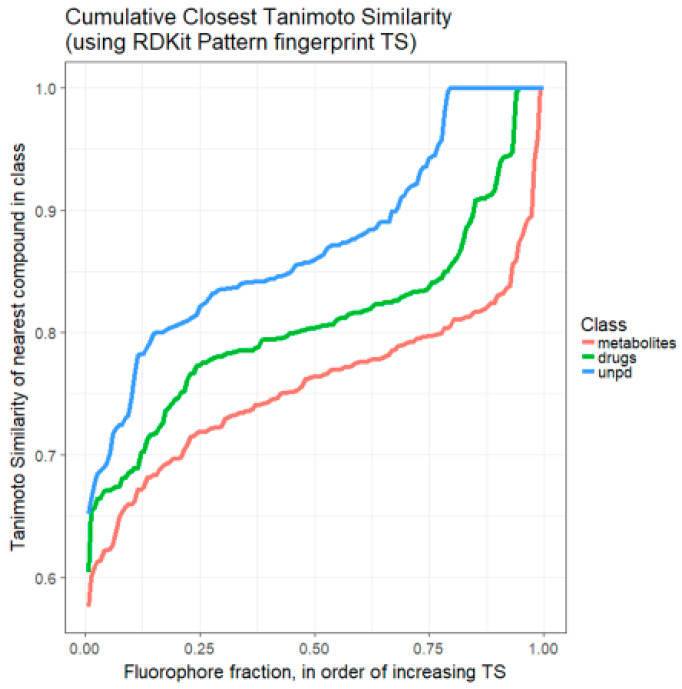
We previously developed the use of rank order plots for summarising the relationships (in terms of Tanimoto similarities) between a candidate molecule or set of molecules and a set of targets in a library [45]. Figure 2 shows such a rank order plot, ranking, for each fluorophore, the most similar molecule in the set of endogenous Recon2 [45,83] metabolites, the set of marketed drugs [45], and a random subset of 2000 of some 150,000 molecules taken [55,84] from the Unified Natural Products Database (UNPD) [85]. This again shows very clearly that the majority of fluorophores chosen do look moderately similar (TS > 0.75) to at least one drug (and even more so to representatives of the natural products database).
Figure 2.
Ranked order of Tanimoto similarity for fluorophores vs. marketed drugs (green line/—), fluorophores vs. Recon2 metabolites (red line/—), and fluorophores vs. a 2000-member sampling of UNPD (blue line/—). Each fluorophore was encoded using the RDKit ‘Patterned’ encoding, then the Tanimoto similarity for it was calculated against each drug, metabolite or natural product sample. The highest value of TS for each fluorophore was recorded and those values ranked. Read from right to left.
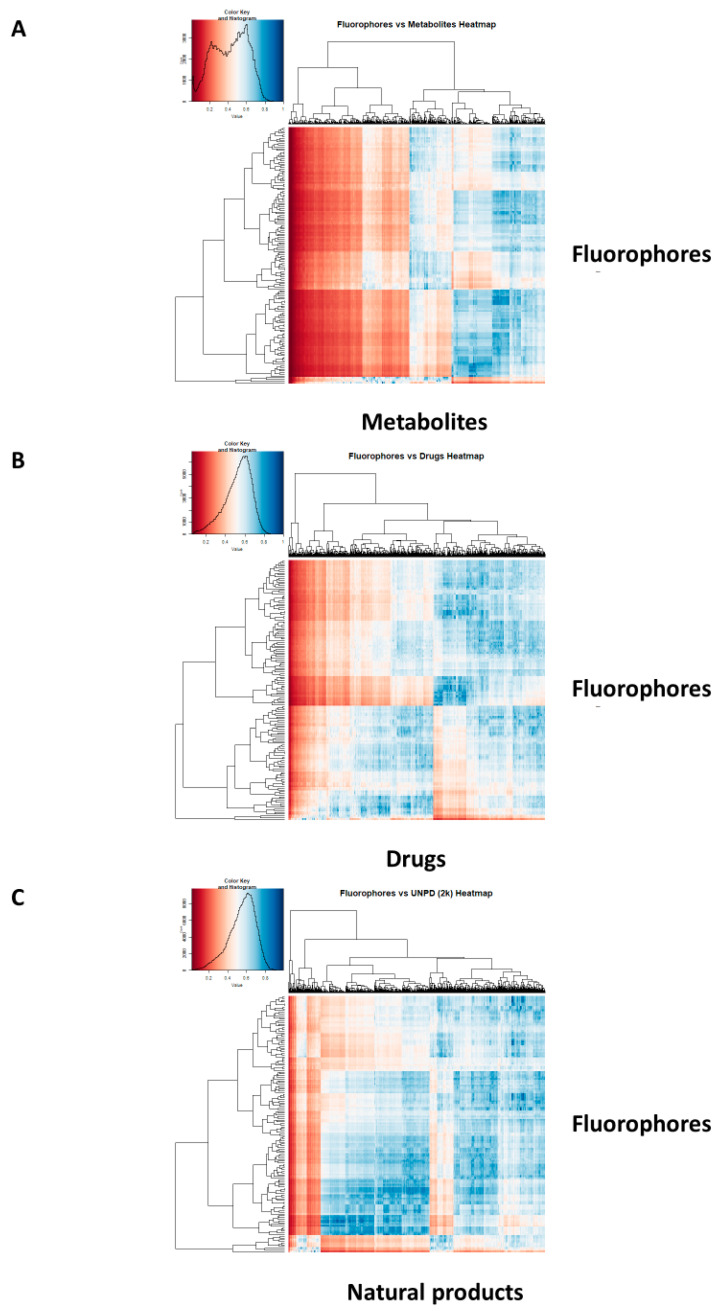
It is also convenient [45] to display such data as a heat map [86], where a bicluster is used to cluster similar structures and the colour of the cell at the intersection encodes their Tanimoto similarity. Figure 3 shows such heatmaps for fluorophores vs. (A) endogenous (Recon2 [87]) metabolites, (B) drugs, and (C) 2000 sampled natural products from UNPD. The data reflect those of Figure 2, and it is again clear that for each fluorophore there is almost always a drug or a natural product for which the average Tanimoto similarity is significantly greater than 0.7.
Figure 3.
Heat maps illustrating the Tanimoto similarities (using the RDKit patterned encoding) between our selected fluorophores and (A) Recon2 metabolites, (B) Drugs, and (C) a subset of 2000 natural products from UNPD.
While it is rather arbitrary, to say the least (given how the Tanimoto similarity varies with the encoding used), as to whether a particular chemical structure is seen by humans as ‘similar’ to another, we provide some illustrations that give a feeling of the kinds of similarity that may be observed.
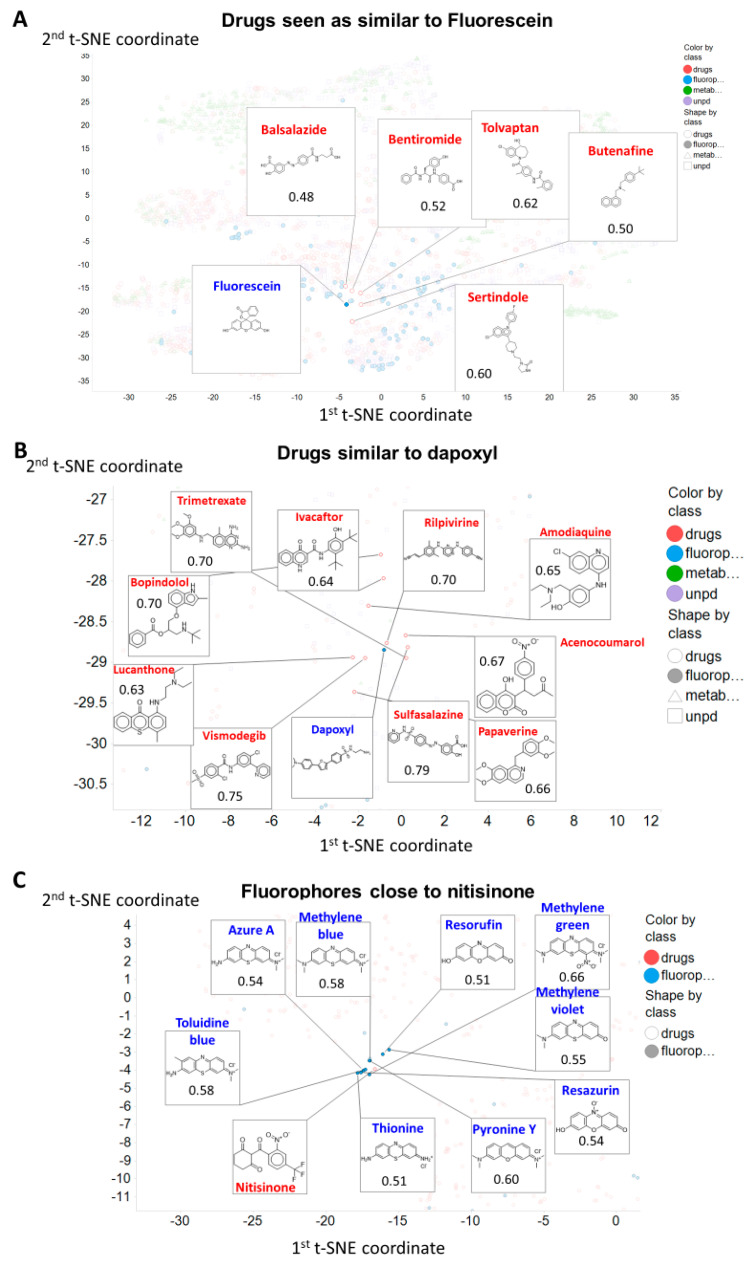
Thus (Figure 4A) we illustrate the drugs closest to fluorescein in the t-SNE space (as per Figure 1B), since fluorescein is a very common fluorophore, is also widely used in ophthalmology (e.g., [88,89]), and can enter cells via a variety of transporters [90] such as monocarboxylate transporters (SLC16A1, SLC16A4) [91], SLCO1B1/3B1 [92,93] and SLC 22A20 [94] (see also Table 1).
Figure 4.
Observable structural similarities between selected fluorophores and drugs. The chosen molecules are (A) fluorescein, (B) dapoxyl (both fluorophores) and (C) nitisinone (a drug). Data are annotated and/or zoomed from those in Figure 1B.
Fluorescein is similar in t-SNE space (Figure 4A) to a variety of drugs. This similarity is not at all related to the class of drug, however, as close ones include balsalazide (an anti-inflammatory used in inflammatory bowel disease [95]), bentiromide (a peptide used for assessing pancreatic function [96]), butenafine (a topical antifungal [97]), sertindole (an atypical antipsychotic), and tolvaptan (used in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease [98]). Similar remarks may be made of dapoxyl (Figure 4B). Note, of course, that the t-SNE plots are based on property descriptors, while the Tanimoto distances are based on a particular form of molecular fingerprint, so, a priori, we do not necessarily expect the closest molecules to be the same in the two cases. In addition, we note that molecules with different scaffolds may be quite similar; in the cheminformatics literature, this is known as ‘scaffold hopping’ (e.g., [99,100,101,102,103,104]).
For a drug, we picked nitisinone, a drug active against hereditary tyrosinaemia type I [105] and alkaptonuria [106,107], as it is surrounded in t-SNE space (Figure 4C) by several tricyclic fluorophores, that do indeed share similar structures (Figure 4C).
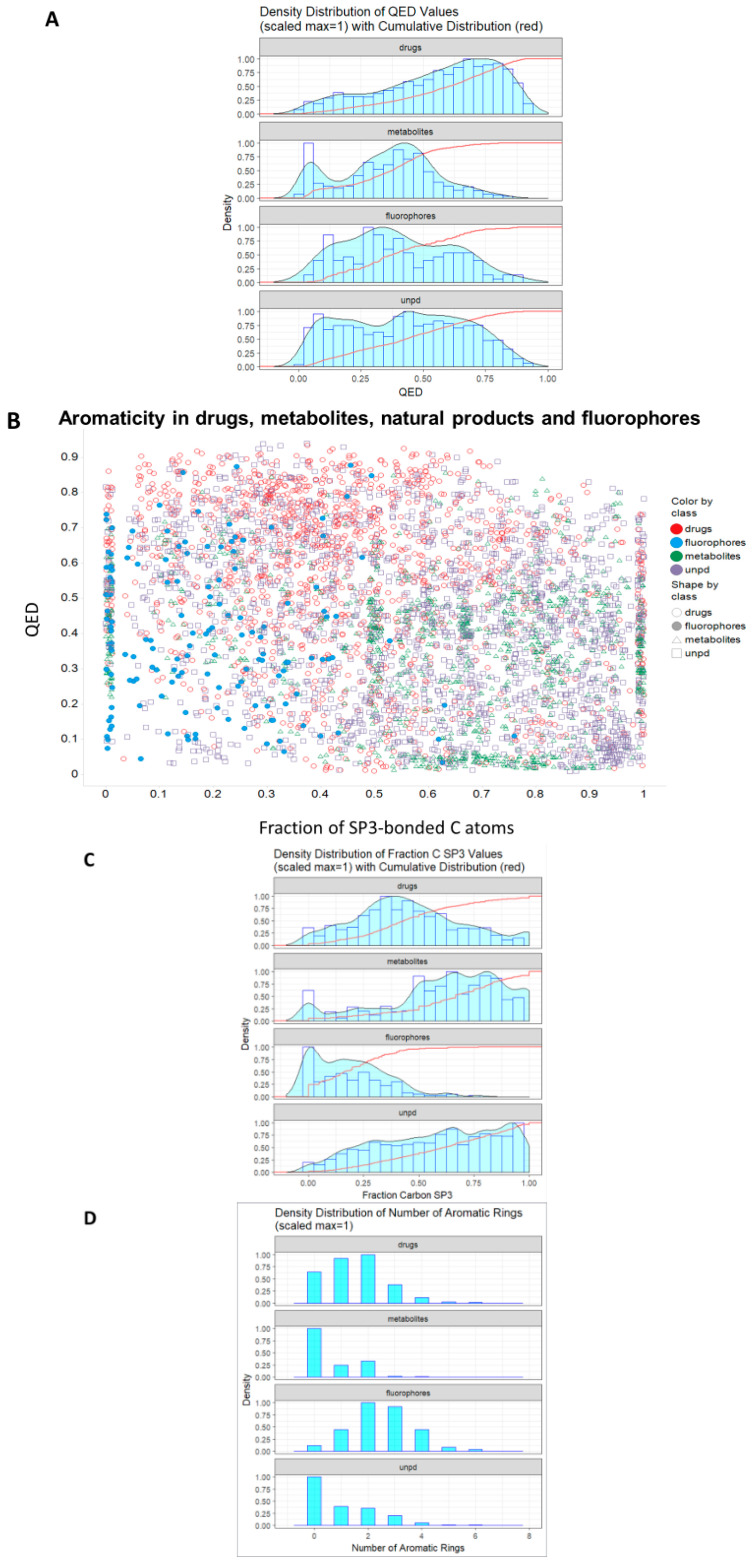
Bickerton and colleagues [108] introduced the concept of the quantitative estimate of drug-likeness (QED) (however, see [109]), and it is of interest to see how ‘drug-like’ our four classes of molecule are based on their criteria. Figure 5A shows the distribution of QED drug-likenesses for marketed drugs, for Recon2 metabolites, for our selected fluorophores, and for a sample of 2000 molecules from UNPD. Our fluorophores are noticeably more similar to drugs than are endogenous metabolites, and roughly as similar to drugs as are natural products (Figure 5A).
Figure 5.
Distribution of quantitative estimate of drug-likeness (QED) values in different classes of molecule. (A). Cumulative distributions for the four classes. (B). Relationship between QED and aromaticity for the four classes as encoded by the fraction of C atoms exhibiting sp3 bonding. QED values were calculated using the RDKit Python code as described in Methods and plotted in (A) using ggplot2 and in (B) using Spotfire. (C). Density distribution of fraction of C atoms with sp3 bonding. (D). Histogram of distributions of numbers of aromatic rings in the four given classes.
Given that essentially all drugs are similar to at least one natural product [55], this is entirely consistent with our thesis that most fluorophores do look rather like one or more of the marketed drugs. One aspect in which (a) drugs and fluorophores differ noticeably from (b) metabolites and natural products is the extent to which they exhibit aromaticity, encoded here (Figure 5B, on the abscissa) via the fraction of carbon atoms showing sp3 hybridisation (i.e., non-aromatic). This is shown as a distribution in Figure 5C. There is clearly a significant tendency for drugs to include (planar) aromatic rings, and although this is changing somewhat [110,111,112,113,114], there are strong thermodynamic reasons as to why this should be so (see Discussion). The modal number of aromatic rings for both drugs and fluorophores is two, significantly greater than that (zero) for metabolites and for natural products (Figure 5D). One reason for fluorophores to exhibit aromaticity is simple, as reasonable visible-wavelength fluorescence in organic molecules relies greatly on conjugation (e.g., [115]), to which aromatic rings can contribute strongly. This argument alone probably accounts in large measure for the drug-likeness of fluorophores.
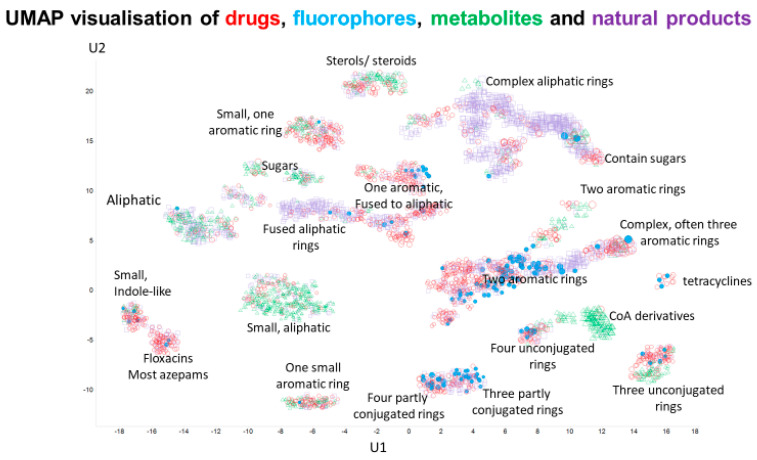
Finally, a very recent, principled, and effective clustering method [116,117], representing the state of the art, is that based on the Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) algorithm. In a similar vein, and based on the same descriptors as used in the t-SNE plots, we show the clustering of our four classes of molecule in UMAP space, where most clusters containing drugs also contain fluorophores. Despite being based on property descriptors, the UMAP algorithm is clearly very effective at clustering molecules into structurally related classes.
3. Discussion
Most drugs can act (often deeply) within the target organism or tissue, and thus the means by which they get to their sites of action is significant. This is considered especially true for natural products which (as with many drugs) normally do not adhere to the ‘rule of 5’ [76,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127]. The chief answer to the question of how drugs do get through biomembranes is ‘by using SLCs’, and so it would be desirable to have high-throughput methods to assesses the activities of these transporters. Among the commoner approaches are methods that assess the uptake of fluorophores, but these are likely to ‘work’ only if drugs and natural products, including marine drugs, do in fact structurally resemble fluorophores.
The basis of the main idea presented and tested here is that the structures of common fluorophores are in fact sufficiently similar to those of many drugs (including natural products) as to provide suitable surrogates for assessing their uptake via solute carriers of the SLC (and, indeed, their efflux via ABC) families. While the latter transporters are well known to be rather promiscuous, and to transport a variety of fluorophores [40,42,128,129,130], considerably less attention has been paid to the former. As mentioned in the Introduction, some marketed pharmaceutical drugs that are transported into cells are in fact naturally fluorescent, including anthracyclines [56,57,58], mepacrine (atebrin, quinacrine) [59], obatoclax [60,61], tetracycline derivatives [57,62] and topotecan [63], while the same is true of certain vitamins riboflavin [64,65] and certain bioactive natural products (e.g., [66,67,68]). As an illustration, and as a complement to our detailed gene knockout studies [23], Table 1 gives an indication of dyes whose interaction with specific transporters has been demonstrated directly. In some cases, their surrogacy as a substrate for a transporter with a known non-fluorescent substrate is clear, and as mentioned in the introduction, they are sometimes referred to as ‘false fluorescent substrates’. Overall, while not intended to be remotely exhaustive, this Table does serve to indicate the potentially widespread activity of transporters as mediators of fluorophore uptake, and indeed, a number of such transporters are known to be rather promiscuous.
Table 1.
Some examples in which fluorescent dyes have been found to interact with uptake transporters directly as substrates or inhibitors. We do not include known non-fluorescent substrates to which a fluorescent tag has been added (see, e.g., [131,132,133]).
| Dye | Transporter | Comments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amiloride | OCT2 (SLC22A2) | A drug. Rhodamine 123 and 6G also served as substrates. | [134] |
| 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindol (DAPI) | OCT1 (SLC22A1) | Potently inhibited by desipramine and also by various organophosphate pesticides. | [135,136] |
| DiBAC(4)3 | Na+/HCO3− NBCe1-A SLC4A4 | Competes with 4,4′-Diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid | [137] |
| 5-carboxyfluorescein | OAT3 (SLC22A8 | Very high Vmax | [94] |
| 6-carboxyfluorescein | OAT1 (SLC22A6) | [94,138] | |
| 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein | OATP1B1 (SLCO1B1) | Good substrate | [139] |
| 4-(4-(Dimethylamino) styryl)-N-methylpyridinium (ASP+) | Dopamine transporter (SLC6A3) | [140,141] | |
| Noradrenaline transporter (SLC6A2) | [140,142,143] | ||
| Serotonin transporter SLC6A4 | [140,144] | ||
| Various monoamine transporters | [145] | ||
| OCT1/OCT2 (SLC22A1/2); | Seen as a model substrate | [146] | |
| Various OCT transporters | [147] | ||
| Other, unknown (non-OCT1/2) transporters with low affinity | [148] | ||
| Ethidium | OCT1/2/3 (SLC22A1/2/3) | Substrate | [149] |
| FFN511 | VMAT2 (SLC18A2) | ‘False fluorescent neurotransmitter’ (i.e., surrogate substrates) concept | [79] |
| FFN54/246 | SLC6A4, SLC18 | ‘False’ fluorescent substrates for serotonin and VMAT transporters. Potent inhibition by imipramine and citalopram | [80] |
| FFN270 | SLC6A4, SLC18 | Another example of a fluorescent false neurotransmitter | [150] |
| Fluorescein | SLCO1B1/3B1 | Effective substrate; analysis of inhibitors | [92,93] |
| OAT6 (SLC22A20) | [94] | ||
| SLC16A1, SLC16A4 | [91] | ||
| Many OATPs (SLCO family) expressed in insect cells | [90] | ||
| Lucifer yellow | Sodium-dependent anion transporters | Inhibited by probenecid | [151,152] |
| Rhodamine 123 | OCT1/OCT2 (SLC22A1/2) | Potent substrate | [153] |
| Stilbazolium dyes | Norepinephrine transporter (SLC6) | Dyes related to ASP+ | [154] |
| Zombie Violet, Live/Dead Green, Cascade Blue, Alexa Fluor 405 | OATP (SLCO) 1B1/1B3 and 2B1 | All shown to be direct substrates, and uptake inhibited by known transporter inhibitors | [155] |
Structural similarity (or the assessment of properties based simply on analyzing structures) is an elusive concept (e.g., [156,157]), but as judged by a standard encoding (RDKit Patterned), there is considerable similarity in structure between almost all of our chosen fluorophores and at least one drug, whether this is judged by their descriptor- or fingerprint-based properties (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3), by observation (Figure 4 and Figure 6), or (Figure 5) via the QED [108] measure.
Figure 6.
UMAP projection into two dimensions of the four classes of molecules, annotated by the type of molecular structure in the various clusters.
Although there is a move towards phenotypic screening [158,159,160,161], many drugs were developed on the basis of their ability to bind potently in vitro to a target of interest. If the unbound molecule is conformationally very flexible, and the bound version is not, binding necessarily involves a significant loss of entropy. Potent binding (involving a significant loss in free energy) of such a molecule would thus require a very large enthalpic term. Consequently, it is much easier to find potent binders if the binding can involve flat (which implies aromatic), conformationally inflexible planar structures. Such reasoning presumably reflects the observation (Figure 5B) that drugs tend to have a low sp3 character, typically with a number of aromatic rings. Conjugated aromatic rings are also a major (physical and electronic) structure that allow fluorescence from organic molecules [162,163,164,165], with greater π-bond conjugation moving both absorbance and fluorescence toward the red end of the spectrum. Overall, these two separate roles for aromatic residues, in low entropy of binding and in electronic structure, provide a plausible explanation for much of the drug-likeness of common fluorophores.
While this study used a comparatively small set of fluorophores, increasing their number can only increase the likelihood of finding a drug (or natural product) to which they are seen to be similar. This said, this set of molecules provides an excellent starting point for the development of competitive high-throughput assays of drug transporter activity.
4. Materials and Methods
Fluorophores were selected from the literature and by scanning various catalogues of fluorophores, and included well known cytochemical stains, food dyes, laser dyes and other fluorophores, including just a few marketed drugs plus fluorescent natural products. We chose only those whose structures were known publicly. The final set included 150 molecules. Supplementary Fluorophores SI.xlsx gives a spreadsheet of all the relevant data that we discuss, including the marketed drugs, Recon2 metabolites [87] (both given also in Reference 37) and a subset of 2000 natural products from UNPD (see [55,85]).
Although there are a great many possible molecular encodings (whether using molecular fingerprints or vectors of calculated properties), each of which can give a different Tanimoto similarity, for our present purpose we chose to use only the Patterned encoding within RDKit (www.rdkit.org/). We also used the RDKit version of QED (https://www.rdkit.org/docs/source/rdkit.Chem.QED.html). Workflows were written in KNIME as per our standard methods [45,46,47,48,55,84,166,167]. t-SNE plots used the first 10 PCs (95.3% explained variance) as inputs based on 27 RDKit descriptors, and were otherwise as previously described [168].
5. Conclusions
An analysis of some 150 fluorophores in common usage in biological research has shown that a great many of them bear significant structural similarities to marketed drugs (and to natural products). This similarity holds true whether the analysis is done using structures encoded as fingerprints or via physico-chemical descriptors, by visual inspection, or via the quantitative estimate of drug likeness measure. For any given drug, there is thus likely to be a fluorophore or set of fluorophores that is best suited to competing with it for uptake, and thus for determining, by fluorimetric methods, the QSAR for the relevant transporters. This should provide the means for rapid and convenient competitive and trans-stimulation assays for screening the ability of drugs to enter cells via SLCs.
Abbreviations
| PCA | Principal Components Analysis |
| QED | Quantitative Estimate of Drug-likeness |
| QSAR | Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship |
| SLC | solute carrier |
| TS | Tanimoto similarity |
| UNPD | Universal Natural Products Database |
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/18/11/582/s1. Fluorophores SI.xlsx: The list of all the molecules and properties illustrated in the present analysis. The descriptors are taken from rdkit, and each of them is explained in detail, with relevant literature references, at https://www.rdkit.org/docs/GettingStartedInPython.html#list-of-available-descriptors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.O. and D.B.K.; methodology, S.O. and D.B.K.; software, S.O.; validation, S.O. and D.B.K.; resources, D.B.K.; data curation, S.O. and D.B.K.; writing—original draft preparation, S.O. and D.B.K.; writing—review and editing S.O. and D.B.K.; visualization, S.O. and D.B.K.; funding acquisition, D.B.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the UK BBSRC (grant BB/P009042/1) and the Novo Nordisk Foundation (grant NNF10CC1016517).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Chalfie M., Kain S. Green Fluorescent Protein: Properties, Applications, and Protocols. Wiley-Liss; New York, NY, USA: 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hemmilä I.A. Applications of Fluorescence in Immunoassays. Wiley; New York, NY, USA: 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Waggoner A.S. Fluorescent probes for cytometry. In: Melamed M.R., Lindmo T., Mendelsohn M.L., editors. Flow Cytometry and Sorting. 2nd ed. Wiley-Liss Inc.; New York, NY, USA: 1990. pp. 209–225. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kyrychenko A. Using fluorescence for studies of biological membranes: A review. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2015;3:042003. doi: 10.1088/2050-6120/3/4/042003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lagorio M.G., Cordon G.B., Iriel A. Reviewing the relevance of fluorescence in biological systems. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015;14:1538–1559. doi: 10.1039/c5pp00122f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Specht E.A., Braselmann E., Palmer A.E. A critical and comparative review of fluorescent tools for live-cell imaging. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017;79:93–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sahl S.J., Hell S.W., Jakobs S. Fluorescence nanoscopy in cell biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017;18:685–701. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mavrakis M., Pourquie O., Lecuit T. Lighting up developmental mechanisms: How fluorescence imaging heralded a new era. Development. 2010;137:373–387. doi: 10.1242/dev.031690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Johnson I. Fluorescent probes for living cells. Histochem. J. 1998;30:123–140. doi: 10.1023/a:1003287101868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kolanowski J.L., Liu F., New E.J. Fluorescent probes for the simultaneous detection of multiple analytes in biology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018;47:195–208. doi: 10.1039/c7cs00528h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhang J., Campbell R.E., Ting A.Y., Tsien R.Y. Creating new fluorescent probes for cell biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002;3:906–918. doi: 10.1038/nrm976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jiang X., Wang L., Carroll S.L., Chen J., Wang M.C., Wang J. Challenges and opportunities for small-molecule fluorescent probes in redox biology applications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018;29:518–540. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Winterbourn C.C. The challenges of using fluorescent probes to detect and quantify specific reactive oxygen species in living cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014;1840:730–738. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Davey H.M., Kell D.B. Flow cytometry and cell sorting of heterogeneous microbial populations: The importance of single-cell analysis. Microbiol. Rev. 1996;60:641–696. doi: 10.1128/mr.60.4.641-696.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shapiro H.M. Practical Flow Cytometry. 3rd ed. John Wiley; New York, NY, USA: 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lavis L.D., Raines R.T. Bright ideas for chemical biology. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008;3:142–155. doi: 10.1021/cb700248m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kell D.B. A Protet-Based, Protonic Charge Transfer Model of Energy Coupling in Oxidative and Photosynthetic Phosphorylation. OSF Preprint. [(accessed on 23 November 2020)];2020 doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2021.01.001. Available online: http://osf.io/2xsz8. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 18.Salcedo-Sora J.E., Jindal S., O’Hagan S., Kell D.B. A palette of fluorophores that are differentially accumulated by wild-type and mutant strains of Escherichia coli: Surrogate ligands for bacterial membrane transporters. bioRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.06.15.152629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Karasev M.M., Stepanenko O.V., Rumyantsev K.A., Turoverov K.K., Verkhusha V.V. Near-infrared fluorescent proteins and their applications. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2019;84:S32–S50. doi: 10.1134/S0006297919140037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Liu W.F., Deng M.Y., Yang C.M., Liu F., Guan X.M., Du Y.C., Wang L., Chu J. Genetically encoded single circularly permuted fluorescent protein-based intensity indicators. J. Phys. D. 2020;53:113001. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pedelacq J.D., Cabantous S. Development and applications of superfolder and split fluorescent protein detection systems in biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:3479. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shcherbakova D.M., Stepanenko O.V., Turoverov K.K., Verkhusha V.V. Near-infrared fluorescent proteins: Multiplexing and optogenetics across scales. Trends Biotechnol. 2018;36:1230–1243. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.06.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jindal S., Yang L., Day P.J., Kell D.B. Involvement of multiple influx and efflux transporters in the accumulation of cationic fluorescent dyes by Escherichia coli. BMC Microbiol. 2019;19:195. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1561-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kell D.B. Control of metabolite efflux in microbial cell factories: Current advances and future prospects. In: El-Mansi E.M.T., Nielsen J., Mousdale D., Allman T., Carlson R., editors. Fermentation Microbiology and Biotechnology. 4th ed. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2019. pp. 117–138. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Szakács G., Váradi A., Özvegy-Laczka C., Sarkadi B. The role of ABC transporters in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity (ADME-Tox) Drug Discov. Today. 2008;13:379–393. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2007.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schinkel A.H., Jonker J.W. Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family: An overview. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012;64:138–153. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(02)00169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tarling E.J., de Aguiar Vallim T.Q., Edwards P.A. Role of ABC transporters in lipid transport and human disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013;24:342–350. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2013.01.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Andreoletti P., Raas Q., Gondcaille C., Cherkaoui-Malki M., Trompier D., Savary S. Predictive structure and topology of peroxisomal ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017;18:1593. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sharom F.J. ABC multidrug transporters: Structure, function and role in chemoresistance. Pharmacogenomics. 2008;9:105–127. doi: 10.2217/14622416.9.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pahnke J., Fröhlich C., Paarmann K., Krohn M., Bogdanovic N., Årsland D., Winblad B. Cerebral ABC transporter-common mechanisms may modulate neurodegenerative diseases and depression in elderly subjects. Arch. Med. Res. 2014;45:738–743. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2014.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Abuznait A.H., Kaddoumi A. Role of ABC transporters in the pathogenesis of alzheimer’s disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012;3:820–831. doi: 10.1021/cn300077c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lam F.C., Liu R., Lu P., Shapiro A.B., Renoir J.M., Sharom F.J., Reiner P.B. Beta-amyloid efflux mediated by P-glycoprotein. J. Neurochem. 2001;76:1121–1128. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Molnar J., Ocsovszki I., Pusztai R. Amyloid-beta interactions with ABC transporters and resistance modifiers. Anticancer Res. 2018;38:3407–3410. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wijnholds J., Evers R., van Leusden M.R., Mol C.A.A.M., Zaman G.J.R., Mayer U., Beijnen J.H., van der Valk M., Krimpenfort P., Borst P. Increased sensitivity to anticancer drugs and decreased inflammatory response in mice lacking the multidrug resistance-associated protein. Nat. Med. 1997;3:1275–1279. doi: 10.1038/nm1197-1275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Prates R.A., Kato I.T., Ribeiro M.S., Tegos G.P., Hamblin M.R. Influence of multidrug efflux systems on methylene blue-mediated photodynamic inactivation of Candida albicans. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011;66:1525–1532. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Forster S., Thumser A.E., Hood S.R., Plant N. Characterization of rhodamine-123 as a tracer dye for use in in vitro drug transport assays. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e33253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ivnitski-Steele I., Holmes A.R., Lamping E., Monk B.C., Cannon R.D., Sklar L.A. Identification of nile red as a fluorescent substrate of the Candida albicans ATP-binding cassette transporters cdr1p and cdr2p and the major facilitator superfamily transporter mdr1p. Anal. Biochem. 2009;394:87–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2009.07.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Strouse J.J., Ivnitski-Steele I., Waller A., Young S.M., Perez D., Evangelisti A.M., Ursu O., Bologa C.G., Carter M.B., Salas V.M., et al. Fluorescent substrates for flow cytometric evaluation of efflux inhibition in ABCB1, ABCC1, and ABCG2 transporters. Anal. Biochem. 2013;437:77–87. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2013.02.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kell D.B. Control of Metabolite Efflux in Microbial Cell Factories: Current Advances and Future Prospects. [(accessed on 8 November 2020)]; Available online: https://osf.io/xg9jh/download?format=pdf.
- 40.Szabó E., Türk D., Telbisz Á., Kucsma N., Horváth T., Szakács G., Homolya L., Sarkadi B., Várady G. A new fluorescent dye accumulation assay for parallel measurements of the ABCG2, ABCB1 and ABCC1 multidrug transporter functions. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0190629. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gökirmak T., Shipp L.E., Campanale J.P., Nicklisch S.C.T., Hamdoun A. Transport in technicolor: Mapping ATP-binding cassette transporters in sea urchin embryos. Mol. Reprod Dev. 2014;81:778–793. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fardel O., Le Vee M., Jouan E., Denizot C., Parmentier Y. Nature and uses of fluorescent dyes for drug transporter studies. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2015;11:1233–1251. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2015.1053462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fredriksson R., Nordström K.J., Stephansson O., Hägglund M.G., Schiöth H.B. The solute carrier (SLC) complement of the human genome: Phylogenetic classification reveals four major families. FEBS Lett. 2008;582:3811–3816. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.10.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Darbani B., Kell D.B., Borodina I. Energetic evolution of cellular transportomes. BMC Genom. 2018;19:418. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4816-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.O’Hagan S., Swainston N., Handl J., Kell D.B. A ‘rule of 0.5’ for the metabolite-likeness of approved pharmaceutical drugs. Metabolomics. 2015;11:323–339. doi: 10.1007/s11306-014-0733-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.O’Hagan S., Kell D.B. Understanding the foundations of the structural similarities between marketed drugs and endogenous human metabolites. Front. Pharmacol. 2015;6:105. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.O’Hagan S., Kell D.B. Metmaxstruct: A Tversky-similarity-based strategy for analysing the (sub)structural similarities of drugs and endogenous metabolites. Front. Pharmacol. 2016;7:266. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.O’Hagan S., Kell D.B. Analysis of drug-endogenous human metabolite similarities in terms of their maximum common substructures. J. Cheminform. 2017;9:18. doi: 10.1186/s13321-017-0198-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nigam S.K. What do drug transporters really do? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015;14:29–44. doi: 10.1038/nrd4461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Girardi E., César-Razquin A., Lindinger S., Papakostas K., Lindinger S., Konecka J., Hemmerich J., Kickinger S., Kartnig F., Gürtl B., et al. A widespread role for SLC transmembrane transporters in resistance to cytotoxic drugs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020;16:469–478. doi: 10.1038/s41589-020-0483-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pizzagalli M.D., Bensimon A., Superti-Furga G. A guide to plasma membrane solute carrier proteins. FEBS J. 2020 doi: 10.1111/febs.15531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Superti-Furga G., Lackner D., Wiedmer T., Ingles-Prieto A., Barbosa B., Girardi E., Goldman U., Gürtl B., Klavins K., Klimek C. The RESOLUTE consortium: Unlocking SLC transporters for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020;19:429–430. doi: 10.1038/d41573-020-00056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kell D.B. Hitchhiking into the cell. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020;16:367–368. doi: 10.1038/s41589-020-0489-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gründemann D., Harlfinger S., Golz S., Geerts A., Lazar A., Berkels R., Jung N., Rubbert A., Schömig E. Discovery of the ergothioneine transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:5256–5261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408624102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.O’Hagan S., Kell D.B. Consensus rank orderings of molecular fingerprints illustrate the ‘most genuine’ similarities between marketed drugs and small endogenous human metabolites, but highlight exogenous natural products as the most important ‘natural’ drug transporter substrates. ADMET DMPK. 2017;5:85–125. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gautier J., Munnier E., Souce M., Chourpa I., Douziech Eyrolles L. Analysis of doxorubicin distribution in mcf-7 cells treated with drug-loaded nanoparticles by combination of two fluorescence-based techniques, confocal spectral imaging and capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015;407:3425–3435. doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-8566-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Khader H., Solodushko V., Al-Mehdi A.B., Audia J., Fouty B. Overlap of doxycycline fluorescence with that of the redox-sensitive intracellular reporter roGFP. J. Fluoresc. 2014;24:305–311. doi: 10.1007/s10895-013-1331-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Motlagh N.S.H., Parvin P., Ghasemi F., Atyabi F. Fluorescence properties of several chemotherapy drugs: Doxorubicin, paclitaxel and bleomycin. Biomed. Opt. Express. 2016;7:2400–2406. doi: 10.1364/BOE.7.002400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Baldini G., Doglia S., Dolci S., Sassi G. Fluorescence-determined preferential binding of quinacrine to DNA. Biophys. J. 1981;36:465–477. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84746-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Nguyen M., Marcellus R.C., Roulston A., Watson M., Serfass L., Murthy Madiraju S.R., Goulet D., Viallet J., Belec L., Billot X., et al. Small molecule obatoclax (GX15-070) antagonizes MCL-1 and overcomes MCL-1-mediated resistance to apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:19512–19517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709443104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Stamelos V.A., Fisher N., Bamrah H., Voisey C., Price J.C., Farrell W.E., Redman C.W., Richardson A. The bh3 mimetic obatoclax accumulates in lysosomes and causes their alkalinization. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0150696. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Pautke C., Vogt S., Kreutzer K., Haczek C., Wexel G., Kolk A., Imhoff A.B., Zitzelsberger H., Milz S., Tischer T. Characterization of eight different tetracyclines: Advances in fluorescence bone labeling. J. Anat. 2010;217:76–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2010.01237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Burke T.G., Malak H., Gryczynski I., Mi Z., Lakowicz J.R. Fluorescence detection of the anticancer drug topotecan in plasma and whole blood by two-photon excitation. Anal. Biochem. 1996;242:266–270. doi: 10.1006/abio.1996.0463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Yonezawa A., Inui K. Novel riboflavin transporter family rfvt/slc52: Identification, nomenclature, functional characterization and genetic diseases of rfvt/slc52. Mol. Aspects Med. 2013;34:693–701. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zhang S., Sakuma M., Deora G.S., Levy C.W., Klausing A., Breda C., Read K.D., Edlin C.D., Ross B.P., Wright Muelas M., et al. A brain-permeable inhibitor of the neurodegenerative disease target kynurenine 3-monooxygenase prevents accumulation of neurotoxic metabolites. Commun. Biol. 2019;2:271. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0520-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Liu Q., Liu Y., Guo M., Luo X., Yao S. A simple and sensitive method of nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced native fluorescence detection for the analysis of chelerythrine and sanguinarine in chinese herbal medicines. Talanta. 2006;70:202–207. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2006.02.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Duval R., Duplais C. Fluorescent natural products as probes and tracers in biology. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017;34:161–193. doi: 10.1039/c6np00111d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Taniguchi M., Lindsey J.S. Database of absorption and fluorescence spectra of >300 common compounds for use in photochemcad. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018;94:290–327. doi: 10.1111/php.12860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Li X.Z., Plésiat P., Nikaido H. The challenge of efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015;28:337–418. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00117-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Holmes A.H., Moore L.S.P., Sundsfjord A., Steinbakk M., Regmi S., Karkey A., Guerin P.J., Piddock L.J.V. Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet. 2016;387:176–187. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Salcedo-Sora J.E., Kell D.B. A quantitative survey of bacterial persistence in the presence of antibiotics: Towards antipersister antimicrobial discovery. Antibiotics. 2020;9:508. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9080508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Munita J.M., Arias C.A. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Spectrum. 2016;4:VMBF-0016-2015. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.VMBF-0016-2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Saleem M., Nazir M., Ali M.S., Hussain H., Lee Y.S., Riaz N., Jabbar A. Antimicrobial natural products: An update on future antibiotic drug candidates. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010;27:238–254. doi: 10.1039/b916096e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Roemer T., Davies J., Giaever G., Nislow C. Bugs, drugs and chemical genomics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012;8:46–56. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Gyawali R., Ibrahim S.A. Natural products as antimicrobial agents. Food Control. 2014;46:412–429. [Google Scholar]
- 76.Harvey A.L., Edrada-Ebel R., Quinn R.J. The re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015;14:111–129. doi: 10.1038/nrd4510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Moloney M.G. Natural products as a source for novel antibiotics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016;37:689–701. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2016.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Wright G.D. Opportunities for natural products in 21st century antibiotic discovery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017;34:694–701. doi: 10.1039/c7np00019g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Gubernator N.G., Zhang H., Staal R.G., Mosharov E.V., Pereira D.B., Yue M., Balsanek V., Vadola P.A., Mukherjee B., Edwards R.H., et al. Fluorescent false neurotransmitters visualize dopamine release from individual presynaptic terminals. Science. 2009;324:1441–1444. doi: 10.1126/science.1172278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Henke A., Kovalyova Y., Dunn M., Dreier D., Gubernator N.G., Dincheva I., Hwu C., Sebej P., Ansorge M.S., Sulzer D., et al. Toward serotonin fluorescent false neurotransmitters: Development of fluorescent dual serotonin and vesicular monoamine transporter substrates for visualizing serotonin neurons. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018;9:925–934. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.O’Hagan S., Kell D.B. Structural similarities between some common fluorophores used in biology and marketed drugs, endogenous metabolites, and natural products. bioRxiv. 2019;2019:834325. doi: 10.3390/md18110582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.van der Maaten L., Hinton G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008;9:2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Thiele I., Heinken A., Fleming R.M. A systems biology approach to studying the role of microbes in human health. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013;24:4–12. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2012.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.O’Hagan S., Kell D.B. Analysing and navigating natural products space for generating small, diverse, but representative chemical libraries. Biotechnol. J. 2018;13:1700503. doi: 10.1002/biot.201700503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Gu J.Y., Gui Y.S., Chen L.R., Yuan G., Lu H.Z., Xu X.J. Use of natural products as chemical library for drug discovery and network pharmacology. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e62839. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Eisen M.B., Spellman P.T., Brown P.O., Botstein D. Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1998;95:14863–14868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.25.14863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Thiele I., Swainston N., Fleming R.M.T., Hoppe A., Sahoo S., Aurich M.K., Haraldsdottír H., Mo M.L., Rolfsson O., Stobbe M.D., et al. A community-driven global reconstruction of human metabolism. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013;31:419–425. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Bakkar M.M., Hardaker L., March P., Morgan P.B., Maldonado-Codina C., Dobson C.B. The cellular basis for biocide-induced fluorescein hyperfluorescence in mammalian cell culture. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e84427. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Khan T.F., Price B.L., Morgan P.B., Maldonado-Codina C., Dobson C.B. Cellular fluorescein hyperfluorescence is dynamin-dependent and increased by tetronic 1107 treatment. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018;101:54–63. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Patik I., Kovacsics D., Német O., Gera M., Várady G., Stieger B., Hagenbuch B., Szakács G., Özvegy-Laczka C. Functional expression of the 11 human organic anion transporting polypeptides in insect cells reveals that sodium fluorescein is a general OATP substrate. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015;98:649–658. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.09.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Sun Y.C., Liou H.M., Yeh P.T., Chen W.L., Hu F.R. Monocarboxylate transporters mediate fluorescein uptake in corneal epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017;58:3716–3722. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-20998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.De Bruyn T., Fattah S., Stieger B., Augustijns P., Annaert P. Sodium fluorescein is a probe substrate for hepatic drug transport mediated by OATP1B1 and OATP1B3. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011;100:5018–5030. doi: 10.1002/jps.22694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.De Bruyn T., van Westen G.J., Ijzerman A.P., Stieger B., de Witte P., Augustijns P.F., Annaert P.P. Structure-based identification of OATP1B1/3 inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013;83:1257–1267. doi: 10.1124/mol.112.084152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Truong D.M., Kaler G., Khandelwal A., Swaan P.W., Nigam S.K. Multi-level analysis of organic anion transporters 1, 3, and 6 reveals major differences in structural determinants of antiviral discrimination. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:8654–8663. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708615200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Patil S.A., Moss A.C. Balsalazide disodium for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008;2:177–184. doi: 10.1586/17474124.2.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Egesel T., Ünsal I., Dikmen G., Bayraktar Y. The assessment of pancreatic exocrine function by bentiromide test in patients with chronic portal vein thrombosis. Pancreas. 2002;25:355–359. doi: 10.1097/00006676-200211000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Singal A. Butenafine and superficial mycoses: Current status. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008;4:999–1005. doi: 10.1517/17425255.4.7.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Blair H.A. Tolvaptan: A review in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Drugs. 2019;79:303–313. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Brown N., Jacoby E. On scaffolds and hopping in medicinal chemistry. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2006;6:1217–1229. doi: 10.2174/138955706778742768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Geppert H., Bajorath J. Advances in 2d fingerprint similarity searching. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010;5:529–542. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2010.486830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Lamberth C. Agrochemical lead optimization by scaffold hopping. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018;74:282–292. doi: 10.1002/ps.4755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Mauser H., Guba W. Recent developments in de novo design and scaffold hopping. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2008;11:365–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Sun H., Tawa G., Wallqvist A. Classification of scaffold-hopping approaches. Drug Discov. Today. 2012;17:310–324. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2011.10.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Zhao H. Scaffold selection and scaffold hopping in lead generation: A medicinal chemistry perspective. Drug Disc. Today. 2007;12:149–155. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2006.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Das A.M. Clinical utility of nitisinone for the treatment of hereditary tyrosinemia type-1 (ht-1) Appl. Clin. Genet. 2017;10:43–48. doi: 10.2147/TACG.S113310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Lock E., Ranganath L.R., Timmis O. The role of nitisinone in tyrosine pathway disorders. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2014;16:457. doi: 10.1007/s11926-014-0457-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Ranganath L.R., Khedr M., Milan A.M., Davison A.S., Hughes A.T., Usher J.L., Taylor S., Loftus N., Daroszewska A., West E., et al. Nitisinone arrests ochronosis and decreases rate of progression of alkaptonuria: Evaluation of the effect of nitisinone in the United Kingdom national alkaptonuria centre. Mol. Genet Metab. 2018;125:127–134. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2018.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Bickerton G.R., Paolini G.V., Besnard J., Muresan S., Hopkins A.L. Quantifying the chemical beauty of drugs. Nat. Chem. 2012;4:90–98. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Shultz M.D. Two decades under the influence of the rule of five and the changing properties of approved oral drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2019;62:1701–1714. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Lovering F., Bikker J., Humblet C. Escape from flatland: Increasing saturation as an approach to improving clinical success. J. Med. Chem. 2009;52:6752–6756. doi: 10.1021/jm901241e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Meyers J., Carter M., Mok N.Y., Brown N. On the origins of three-dimensionality in drug-like molecules. Future Med. Chem. 2016;8:1753–1767. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2016-0095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Campbell P.S., Jamieson C., Simpson I., Watson A.J.B. Practical synthesis of pharmaceutically relevant molecules enriched in sp(3) character. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2017;54:46–49. doi: 10.1039/c7cc08670a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Blakemore D.C., Castro L., Churcher I., Rees D.C., Thomas A.W., Wilson D.M., Wood A. Organic synthesis provides opportunities to transform drug discovery. Nat. Chem. 2018;10:383–394. doi: 10.1038/s41557-018-0021-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Boström J., Brown D.G., Young R.J., Keserü G.M. Expanding the medicinal chemistry synthetic toolbox. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018;17:709–727. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2018.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Yuan L., Lin W., Zheng K., He L., Huang W. Far-red to near infrared analyte-responsive fluorescent probes based on organic fluorophore platforms for fluorescence imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013;42:622–661. doi: 10.1039/c2cs35313j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.McInnes L., Healy J., Melville J. UMAP: Uniform manifold approximation and projection for dimension reduction. arXiv. 20181802.03426 [Google Scholar]
- 117.McInnes L., Healy J., Saul N., Großberger L. Umap: Uniform manifold approximation and projection. J. Open Source Softw. 2018 doi: 10.21105/joss.00861. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Koehn F.E., Carter G.T. The evolving role of natural products in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005;4:206–220. doi: 10.1038/nrd1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Dobson P.D., Patel Y., Kell D.B. “Metabolite-likeness” as a criterion in the design and selection of pharmaceutical drug libraries. Drug Disc. Today. 2009;14:31–40. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2008.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Doak B.C., Over B., Giordanetto F., Kihlberg J. Oral druggable space beyond the rule of 5: Insights from drugs and clinical candidates. Chem. Biol. 2014;21:1115–1142. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Quinn R.J., Carroll A.R., Pham N.B., Baron P., Palframan M.E., Suraweera L., Pierens G.K., Muresan S. Developing a drug-like natural product library. J. Nat. Prod. 2008;71:464–468. doi: 10.1021/np070526y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Krämer S.D., Aschmann H.E., Hatibovic M., Hermann K.F., Neuhaus C.S., Brunner C., Belli S. When barriers ignore the “rule-of-five”. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016;101:62–74. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Guimarães C.R.W., Mathiowetz A.M., Shalaeva M., Goetz G., Liras S. Use of 3d properties to characterize beyond rule-of-5 property space for passive permeation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012;52:882–890. doi: 10.1021/ci300010y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Leeson P.D. Molecular inflation, attrition and the rule of five. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016;101:22–33. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.01.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.DeGoey D.A., Chen H.J., Cox P.B., Wendt M.D. Beyond the rule of 5: Lessons learned from abbvie’s drugs and compound collection. J. Med. Chem. 2018;61:2636–2651. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Chen Y., Garcia de Lomana M., Friedrich N.O., Kirchmair J. Characterization of the chemical space of known and readily obtainable natural products. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018;58:1518–1532. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Newman D.J., Cragg G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020;83:770–803. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Ivnitski-Steele I., Larson R.S., Lovato D.M., Khawaja H.M., Winter S.S., Oprea T.I., Sklar L.A., Edwards B.S. High-throughput flow cytometry to detect selective inhibitors of ABCB1, ABCC1, and ABCG2 transporters. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2008;6:263–276. doi: 10.1089/adt.2007.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Tegos G.P., Evangelisti A.M., Strouse J.J., Ursu O., Bologa C., Sklar L.A. A high throughput flow cytometric assay platform targeting transporter inhibition. Drug Disc. Today Technol. 2014;12:e95–e103. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2014.03.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Windt T., Tóth S., Patik I., Sessler J., Kucsma N., Szepesi A., Zdrazil B., Özvegy-Laczka C., Szakács G. Identification of anticancer OATP2B1 substrates by an in vitro triple-fluorescence-based cytotoxicity screen. Arch. Toxicol. 2019;93:953–964. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02417-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Bednarczyk D., Mash E.A., Aavula B.R., Wright S.H. Nbd-tma: A novel fluorescent substrate of the peritubular organic cation transporter of renal proximal tubules. Pflügers Arch. 2000;440:184–192. doi: 10.1007/s004240000283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Stone M.R.L., Butler M.S., Phetsang W., Cooper M.A., Blaskovich M.A.T. Fluorescent antibiotics: New research tools to fight antibiotic resistance. Trends Biotechnol. 2018;36:523–536. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Jiang M., Li H., Johnson A., Karasawa T., Zhang Y., Meier W.B., Taghizadeh F., Kachelmeier A., Steyger P.S. Inflammation up-regulates cochlear expression of TRPV1 to potentiate drug-induced hearing loss. Sci. Adv. 2019;5:eaaw1836. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw1836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Ugwu M.C., Pelis R., Esimone C.O., Agu R.U. Fluorescent organic cations for human OCT2 transporters screening: Uptake in CHO cells stably expressing hoct2. ADMET DMPK. 2017;5:135–145. [Google Scholar]
- 135.Yasujima T., Ohta K., Inoue K., Yuasa H. Characterization of human OCT1-mediated transport of dapi as a fluorescent probe substrate. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011;100:4006–4012. doi: 10.1002/jps.22548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Chedik L., Bruyere A., Fardel O. Interactions of organophosphorus pesticides with solute carrier (SLC) drug transporters. Xenobiotica. 2018;49:363–374. doi: 10.1080/00498254.2018.1442030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Liu X., Williams J.B., Sumpter B.R., Bevensee M.O. Inhibition of the Na/bicarbonate cotransporter NBCE1-A by DIBAC oxonol dyes relative to niflumic acid and a stilbene. J. Membr. Biol. 2007;215:195–204. doi: 10.1007/s00232-007-9018-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Zou L., Stecula A., Gupta A., Prasad B., Chien H.C., Yee S.W., Wang L., Unadkat J.D., Stahl S.H., Fenner K.S., et al. Molecular mechanisms for species differences in organic anion transporter 1, oat1: Implications for renal drug toxicity. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018;94:689–699. doi: 10.1124/mol.117.111153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Izumi S., Nozaki Y., Komori T., Takenaka O., Maeda K., Kusuhara H., Sugiyama Y. Investigation of fluorescein derivatives as substrates of organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) 1B1 to develop sensitive fluorescence-based OATP1B1 inhibition assays. Mol. Pharm. 2016;13:438–448. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Schwartz J.W., Blakely R.D., DeFelice L.J. Binding and transport in norepinephrine transporters. Real-time, spatially resolved analysis in single cells using a fluorescent substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:9768–9777. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209824200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Inyushin M.U., Arencibia-Albite F., de la Cruz A., Vazquez-Torres R., Colon K., Sanabria P., Jimenez-Rivera C.A. New method to visualize neurons with dat in slices of rat vta using fluorescent substrate for DAT, ASP+ J. Neurosci. Neuroeng. 2013;2:98–103. doi: 10.1166/jnsne.2013.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Schwartz J.W., Novarino G., Piston D.W., DeFelice L.J. Substrate binding stoichiometry and kinetics of the norepinephrine transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:19177–19184. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M412923200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Haunsø A., Buchanan D. Pharmacological characterization of a fluorescent uptake assay for the noradrenaline transporter. J. Biomol. Screen. 2007;12:378–384. doi: 10.1177/1087057107299524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Oz M., Libby T., Kivell B., Jaligam V., Ramamoorthy S., Shippenberg T.S. Real-time, spatially resolved analysis of serotonin transporter activity and regulation using the fluorescent substrate, ASP+ J. Neurochem. 2010;114:1019–1029. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06828.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Zwartsen A., Verboven A.H.A., van Kleef R., Wijnolts F.M.J., Westerink R.H.S., Hondebrink L. Measuring inhibition of monoamine reuptake transporters by new psychoactive substances (NPS) in real-time using a high-throughput, fluorescence-based assay. Toxicol In Vitro. 2017;45:60–71. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2017.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Kido Y., Matsson P., Giacomini K.M. Profiling of a prescription drug library for potential renal drug-drug interactions mediated by the organic cation transporter 2. J. Med. Chem. 2011;54:4548–4558. doi: 10.1021/jm2001629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Salomon J.J., Endter S., Tachon G., Falson F., Buckley S.T., Ehrhardt C. Transport of the fluorescent organic cation 4-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-n-methylpyridinium iodide (ASP+) in human respiratory epithelial cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012;81:351–359. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2012.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Rytting E., Bryan J., Southard M., Audus K.L. Low-affinity uptake of the fluorescent organic cation 4-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-n-methylpyridinium iodide (4-di-1-ASP) in BeWo cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007;73:891–900. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.11.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Lee W.K., Reichold M., Edemir B., Ciarimboli G., Warth R., Koepsell H., Thévenod F. Organic cation transporters OCT1, 2, and 3 mediate high-affinity transport of the mutagenic vital dye ethidium in the kidney proximal tubule. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2009;296:F1504–F1513. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90754.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Dunn M., Henke A., Clark S., Kovalyova Y., Kempadoo K.A., Karpowicz R.J., Jr., Kandel E.R., Sulzer D., Sames D. Designing a norepinephrine optical tracer for imaging individual noradrenergic synapses and their activity in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:2838. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05075-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Masereeuw R., Moons M.M., Toomey B.H., Russel F.G.M., Miller D.S. Active lucifer yellow secretion in renal proximal tubule: Evidence for organic anion transport system crossover. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999;289:1104–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.de Gier R.P.E., Feitz W.F.J., Masereeuw R., Wouterse A.C., Smits D., Russel F.G.M. Anionic and cationic drug secretion in the isolated perfused rat kidney after neonatal surgical induction of ureteric obstruction. BJU Int. 2003;92:452–458. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2003.04352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Jouan E., Le Vee M., Denizot C., Da Violante G., Fardel O. The mitochondrial fluorescent dye rhodamine 123 is a high-affinity substrate for organic cation transporters (OCTs) 1 and 2. Fundam Clin. Pharmacol. 2014;28:65–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2012.01071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Wilson J.N., Brown A.S., Babinchak W.M., Ridge C.D., Walls J.D. Fluorescent stilbazolium dyes as probes of the norepinephrine transporter: Structural insights into substrate binding. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012;10:8710–8719. doi: 10.1039/c2ob26633d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Patik I., Székely V., Német O., Szepesi Á., Kucsma N., Várady G., Szakács G., Bakos É., Özvegy-Laczka C. Identification of novel cell-impermeant fluorescent substrates for testing the function and drug interaction of organic anion-transporting polypeptides, OATP1B1/1B3 and 2B1. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:2630. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20815-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Lajiness M.S., Maggiora G.M., Shanmugasundaram V. Assessment of the consistency of medicinal chemists in reviewing sets of compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2004;47:4891–4896. doi: 10.1021/jm049740z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Samanta S., O’Hagan S., Swainston N., Roberts T.J., Kell D.B. Vae-sim: A novel molecular similarity measure based on a variational autoencoder. Molecules. 2020;25:3446. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Kell D.B. Finding novel pharmaceuticals in the systems biology era using multiple effective drug targets, phenotypic screening, and knowledge of transporters: Where drug discovery went wrong and how to fix it. FEBS J. 2013;280:5957–5980. doi: 10.1111/febs.12268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Kell D.B., Wright Muelas M., O’Hagan S., Day P.J. The role of drug transporters in phenotypic screening. Drug Target Rev. 2018;4:16–19. [Google Scholar]
- 160.Prior M., Chiruta C., Currais A., Goldberg J., Ramsey J., Dargusch R., Maher P.A., Schubert D. Back to the future with phenotypic screening. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014;5:503–513. doi: 10.1021/cn500051h. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Swinney D.C. Opportunities for phenotypic screening in drug discovery. Drug Disc. World. 2014;15:33–42. [Google Scholar]
- 162.Yamaguchi Y., Matsubara Y., Ochi T., Wakamiya T., Yoshida Z. How the π conjugation length affects the fluorescence emission efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:13867–13869. doi: 10.1021/ja8040493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Lavis L.D., Raines R.T. Bright building blocks for chemical biology. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014;9:855–866. doi: 10.1021/cb500078u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Zambianchi M., Di Maria F., Cazzato A., Gigli G., Piacenza M., Della Sala F., Barbarella G. Microwave-assisted synthesis of thiophene fluorophores, labeling and multilabeling of monoclonal antibodies, and long lasting staining of fixed cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:10892–10900. doi: 10.1021/ja902416s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Di Maria F., Palamà I.E., Baroncini M., Barbieri A., Bongini A., Bizzarri R., Gigli G., Barbarella G. Live cell cytoplasm staining and selective labeling of intracellular proteins by non-toxic cell-permeant thiophene fluorophores. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014;12:1603–1610. doi: 10.1039/c3ob41982g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.O’Hagan S., Kell D.B. The KNIME workflow environment and its applications in genetic programming and machine learning. Genet. Progr. Evol. Mach. 2015;16:387–391. [Google Scholar]
- 167.O’Hagan S., Kell D.B. The apparent permeabilities of caco-2 cells to marketed drugs: Magnitude, and independence from both biophysical properties and endogenite similarities. PeerJ. 2015;3:e1405. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.O’Hagan S., Kell D.B. Generation of a small library of natural products designed to cover chemical space inexpensively. Pharm. Front. 2019;1:e190005. doi: 10.20900/pf20190005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.