Figure 2.
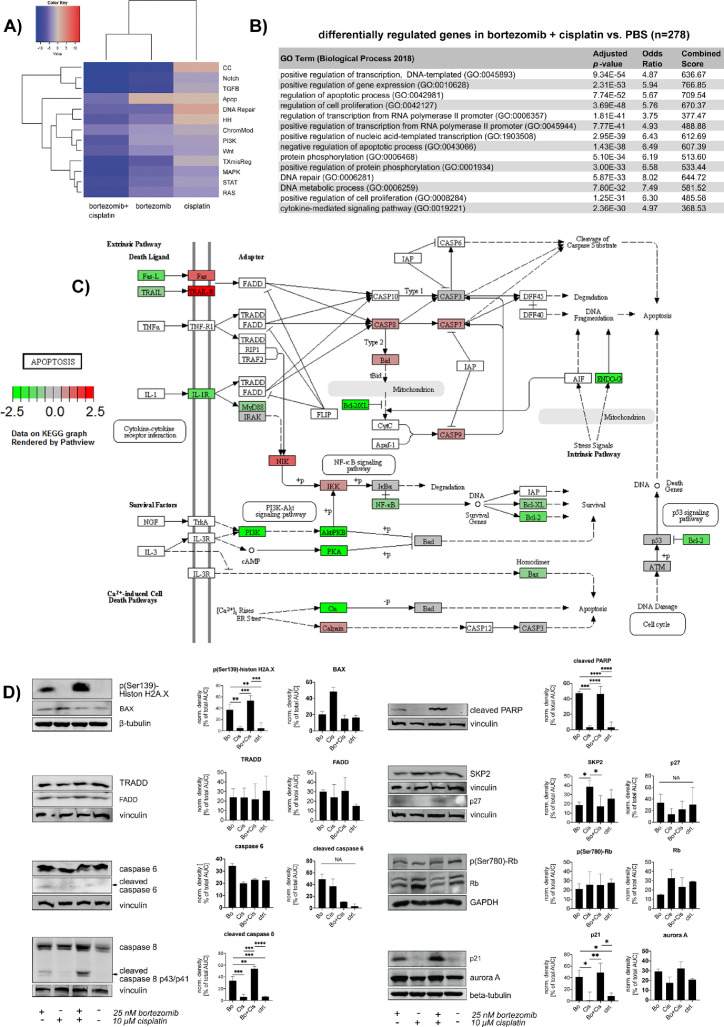
Gene expression after bortezomib, cisplatin and combinatory therapy demonstrated induction of apoptosis: BON cells were treated with 25 nM bortezomib, 10 µM cisplatin or both versus saline for 24 h and analyzed by nCounter gene expression array. (A) Gene set analyses of affected pathways after cisplatin, bortezomib and combination related to control. The directed analysis heatmap displays each treatment's directed global significance scores. Directed global significance statistics measure the extent to which a pathway's genes are up- or downregulated after treatment. Red denotes pathways whose genes exhibit extensive over-expression upon treatment, blue denotes pathways with extensive under-expression. Cisplatin upregulated genes associated with positive regulation of DNA repair and cell cycle regulation. After combined treatment, genes of all analyzed pathways were found predominantly downregulated. The detailed analysis of apoptosis-related gene expression, color-coded as upregulated in the bortezomib arm and downregulated in the combination arm, revealed that the bortezomib treatment affected three genes (ENOG, BCL2, and NFKB1) in a negative way and 5 genes (CASP7, BID, IKBK, CAPN2, and MAP3K14) in a positive manner. The combination of bortezomib and cisplatin changed the expression of eleven genes (ENDOG, PRKAR1B, BCL2, NFKB1, FASLG, PIK3CB, PPP3CB, PIK3R2, IL1RAP, PPP3CA and AKT2) negatively and upregulated nine genes (CASP8, CAPN2, CASP7, BID, IKBKG, TNFRSF10A, MAP3K14, TNFRSF10D, und FAS). Although the resulting score would lead to the assumption that bortezomib regulates apoptosis in a more positive way than the combined treatment, the combination affected more antiapoptotic genes, including BCL2, AKT2, subunits of NF-kappaB, PI3K, PKA and Bcl-2 (to a lower extent), in a negative way. Therefore, the signaling changes result in a proapoptotic signaling. Significantly differentially expressed genes have been filtered by minimum fold change ≥1.5-fold before detailed analysis. Gene expression raw data can be found in Supplementary Tables 1-3. (B) Pathway analysis of apoptosis-related genes after bortezomib plus cisplatin treatment. Visualization by KEGG ontology pathway system. Although the overall pathway score for apoptosis-related genes was determined negative, the differential analysis of the distinct transcripts demonstrated pro-apoptotic mechanisms: Genes of pro-apoptotic death receptor-mediated pathways, such as of Fas, TRAIL-R, caspases 7 and 8, BID and NIK were upregulated (red), whereas predominantly crucial antiapoptotic genes, including those of Bcl-2, NF-kappaB and genes of the PI3K pathway, were downregulated (green). This resulted in an overall negative pathway score. (C) GO enrichment analysis using the ENRICHR data analysis tool verified a strong modulation of gene expression affecting apoptotic processes. (D) For verification of the gene expression profiling, BON cells were treated with 25 nM bortezomib, 10 µM cisplatin, combination of both or control for 24 h and analyzed by western blot. Bortezomib and combined therapy induced massive DNA damage (DNA double stand breaks indicated by H2AX phosphorylation), but did not induce internal apoptosis via BAX. Both treatment arms presented death receptor-dependent extrinsic apoptotic signaling as detected by FADD upregulation and cleavage of caspase 8, caspase 6 and finally PARP. The relative effects were stronger in the cells that were treated with the combination of both, cisplatin and bortezomib. Expression of the p27 regulator and DNA repair associated protein SKP2 was reduced after bortezomib and combined therapy in association with an upregulation of the p27 cell cycle regulator. Independent from Rb protein abundance (which is repressed upon bortezomib and combined treatment), p21 is upregulated following bortezomib or combined treatment. CK2-alpha and aurora A were also upregulated upon bortezomib and the combination. Western Blot data was densitometrically quantified by use of ImageJ and statistically evaluated with Prism 8. Normal distribution of the data was assumed after passing Shapiro-Wilk test and according to the results, data was tested by Kruskal-Wallis or one-way ANOVA analysis. Graphs show mean with SD. Apop, apoptosis; CC, cell cycle; ChromMod, chromatin modifications; HH, hedgehog; TXmisReg, transcriptional misregulation; Bo, bortezomib; Cis, cisplatin, ctrl, control; NA, not applicable (due to too little contrast of the signal and error-prone densitometric measurements); *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. (Color version of figure is available online.)