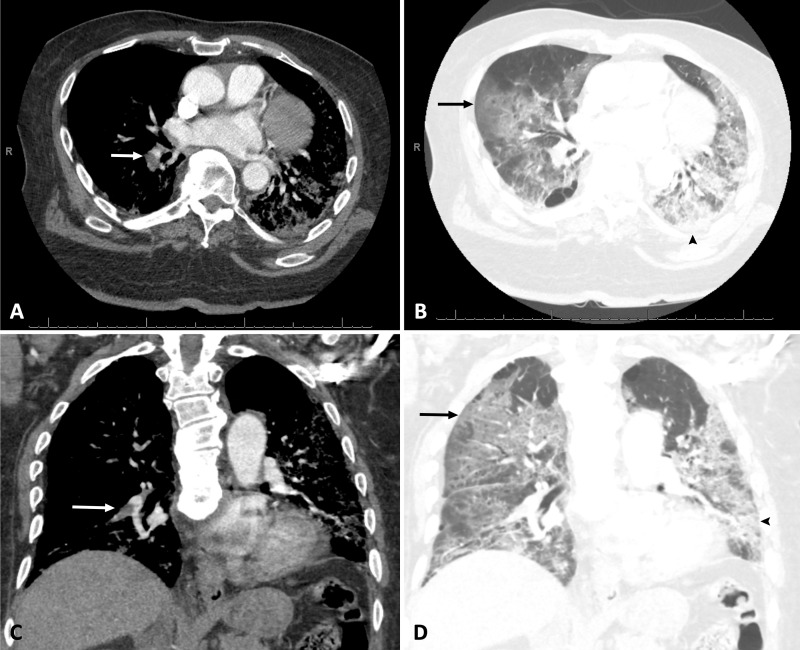
Figure 2:
A, B, Axial and, C, D, coronal pulmonary CT angiography images in a 76-year-old African American man with body mass index of 37 kg/m2 who required admission to medical intensive care unit for acute respiratory failure secondary to coronavirus disease 2019 confirmed with reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. Pulmonary CT angiography was obtained 4 days after admission and demonstrates acute pulmonary embolism in right lower lobar pulmonary artery (white arrows), bilateral ground glass opacities (black arrows), and consolidation (arrowheads).